Treatment of Oily Wastewater with Membrane Bioreactor Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
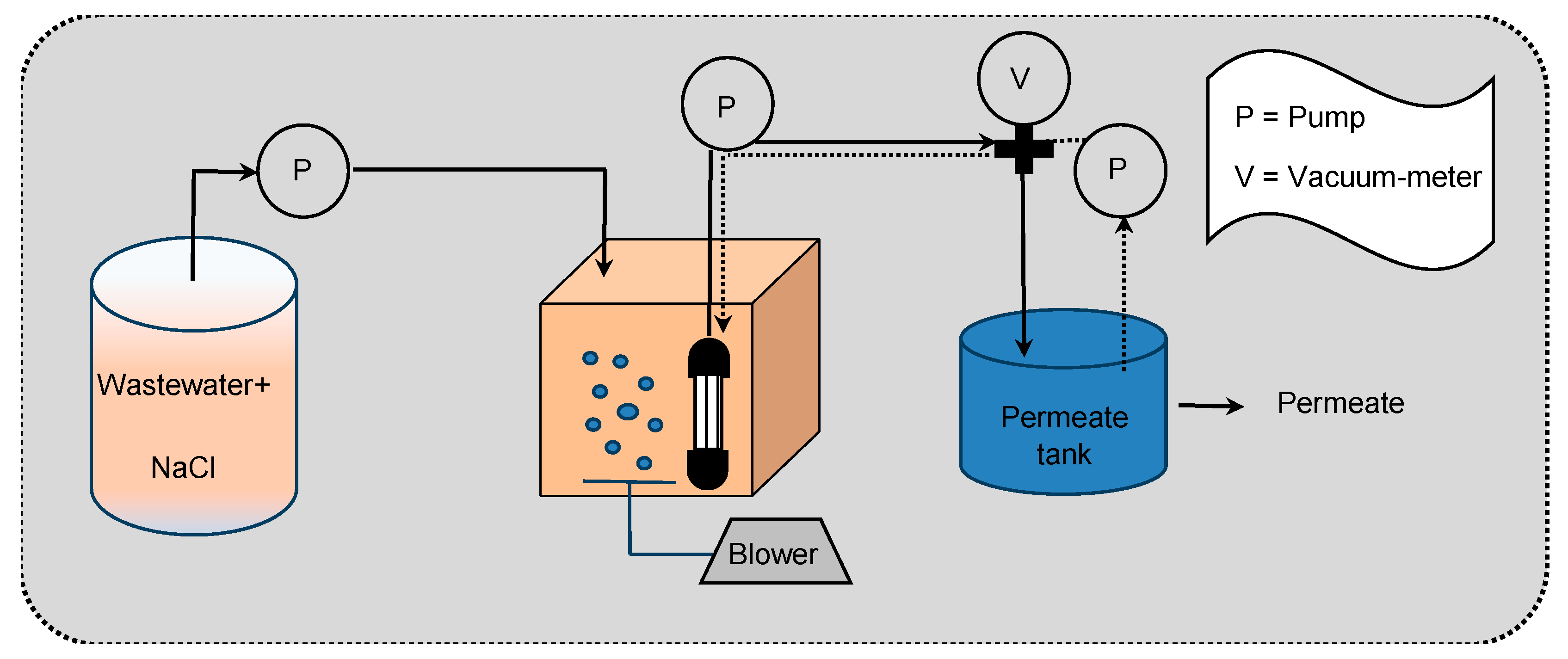
2.1. Pilot Plant Layout and Operative Conditions
2.2. Experimental Procedures
3. Results and Discussion
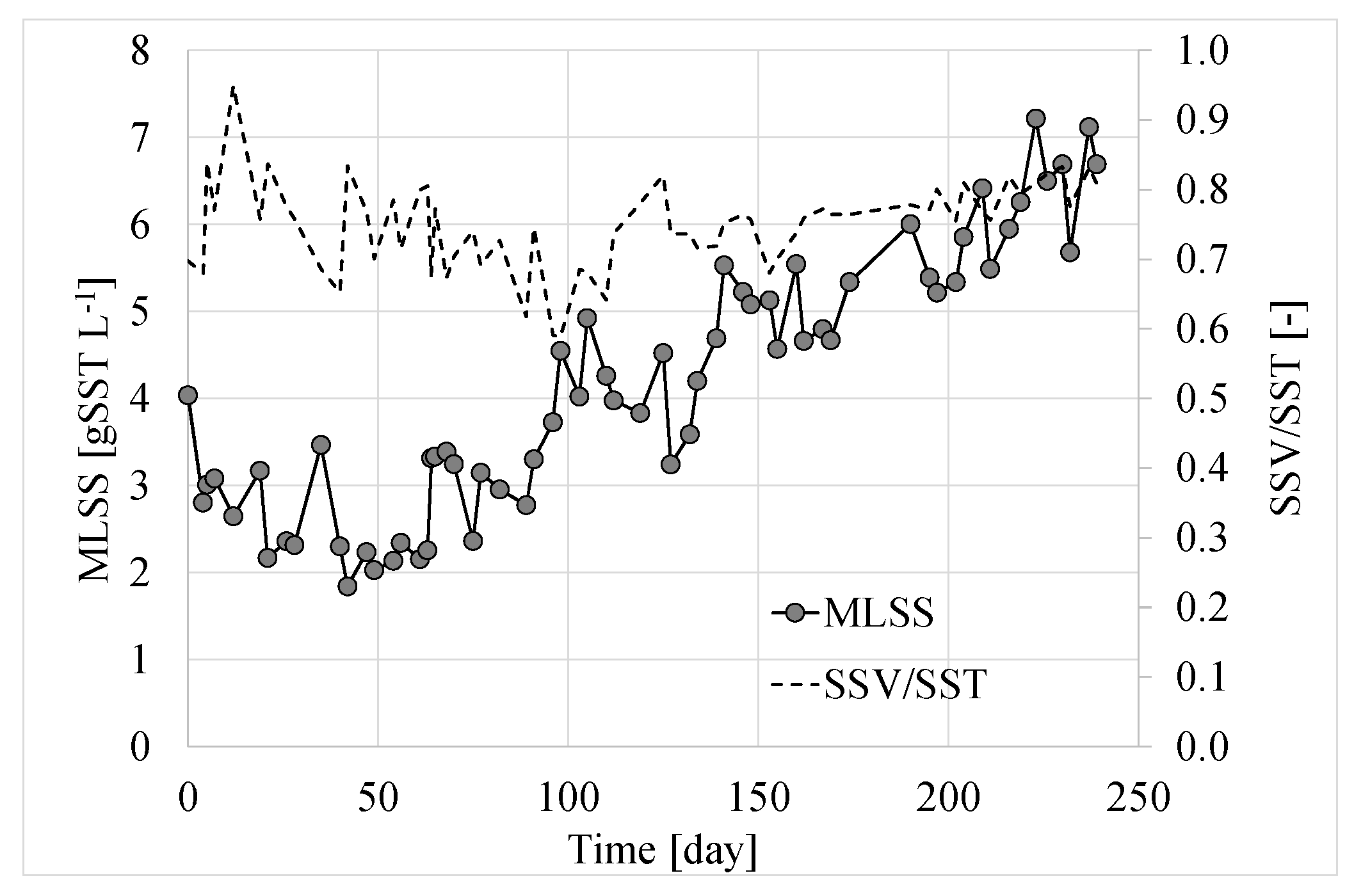
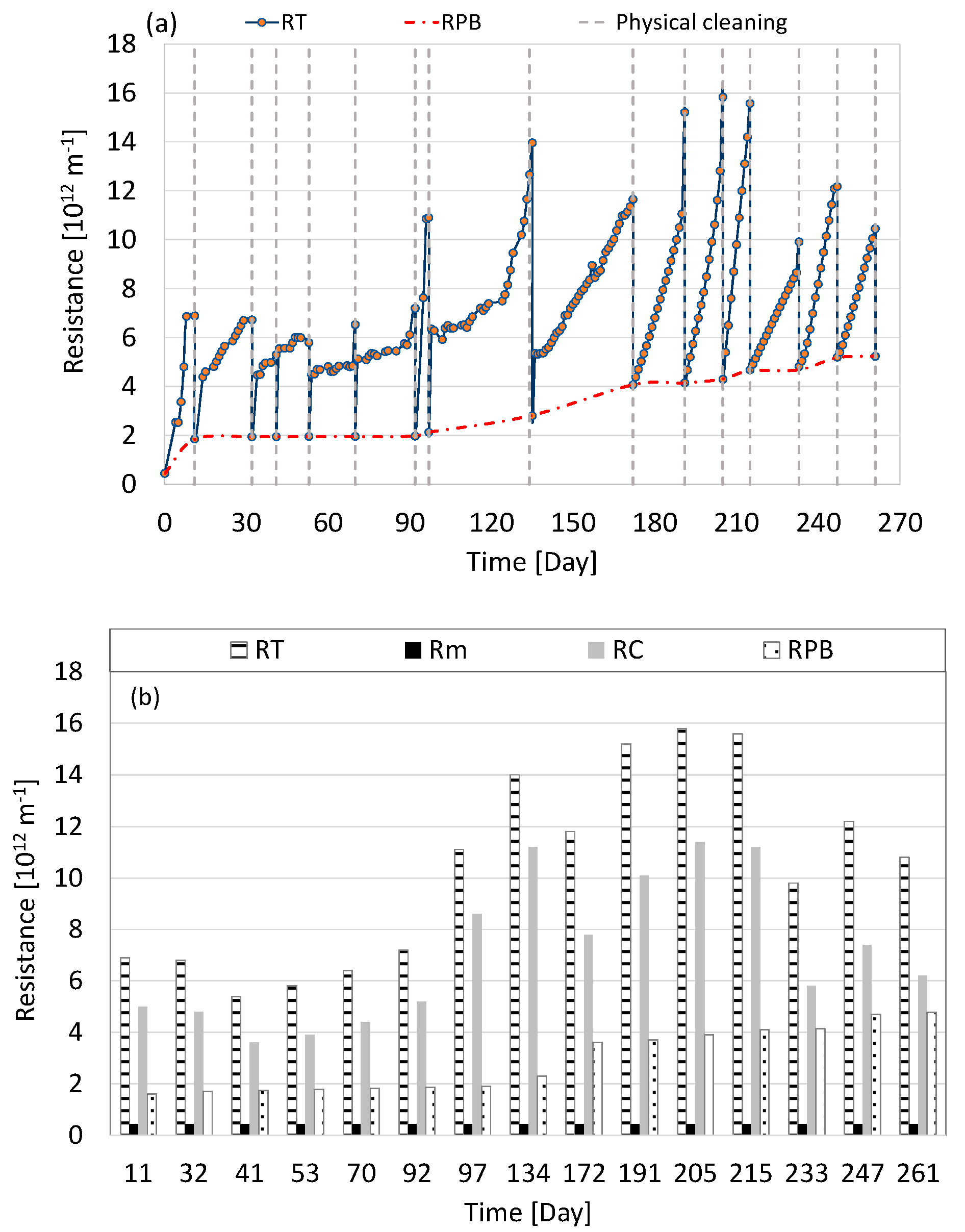
3.1. Suspended Biomass Growth
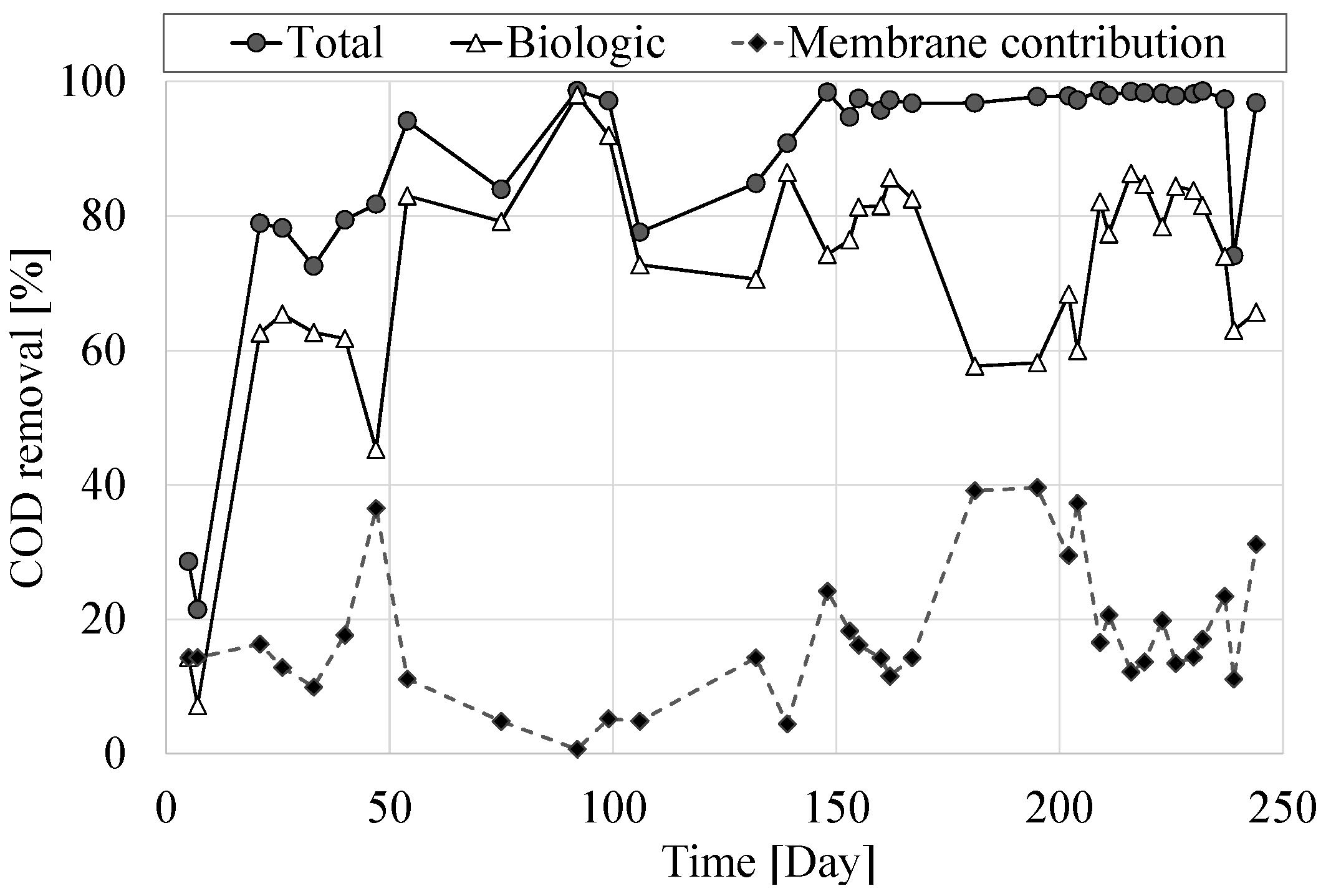
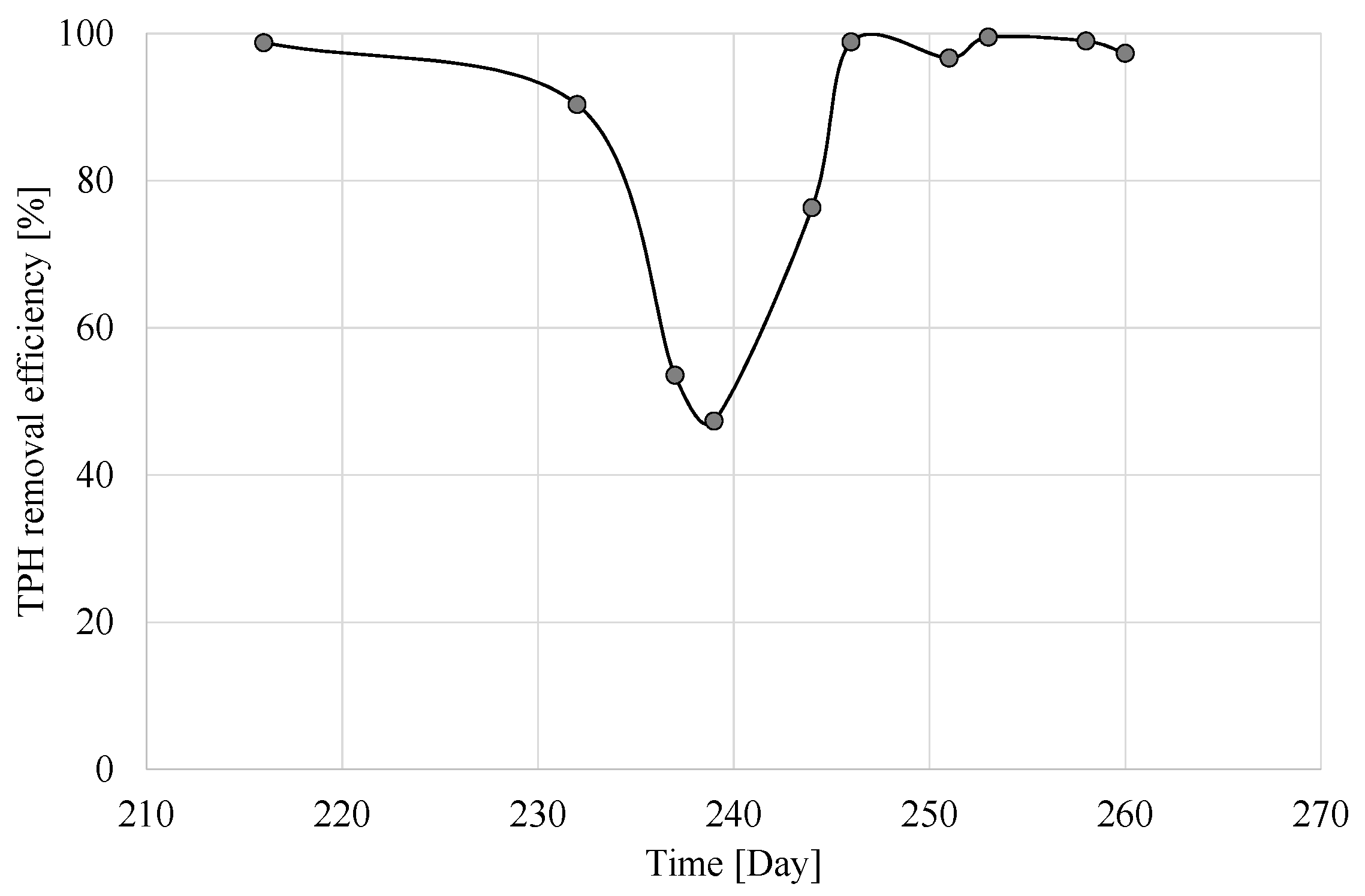
3.2. Organic Carbon and Hydrocarbons Removal
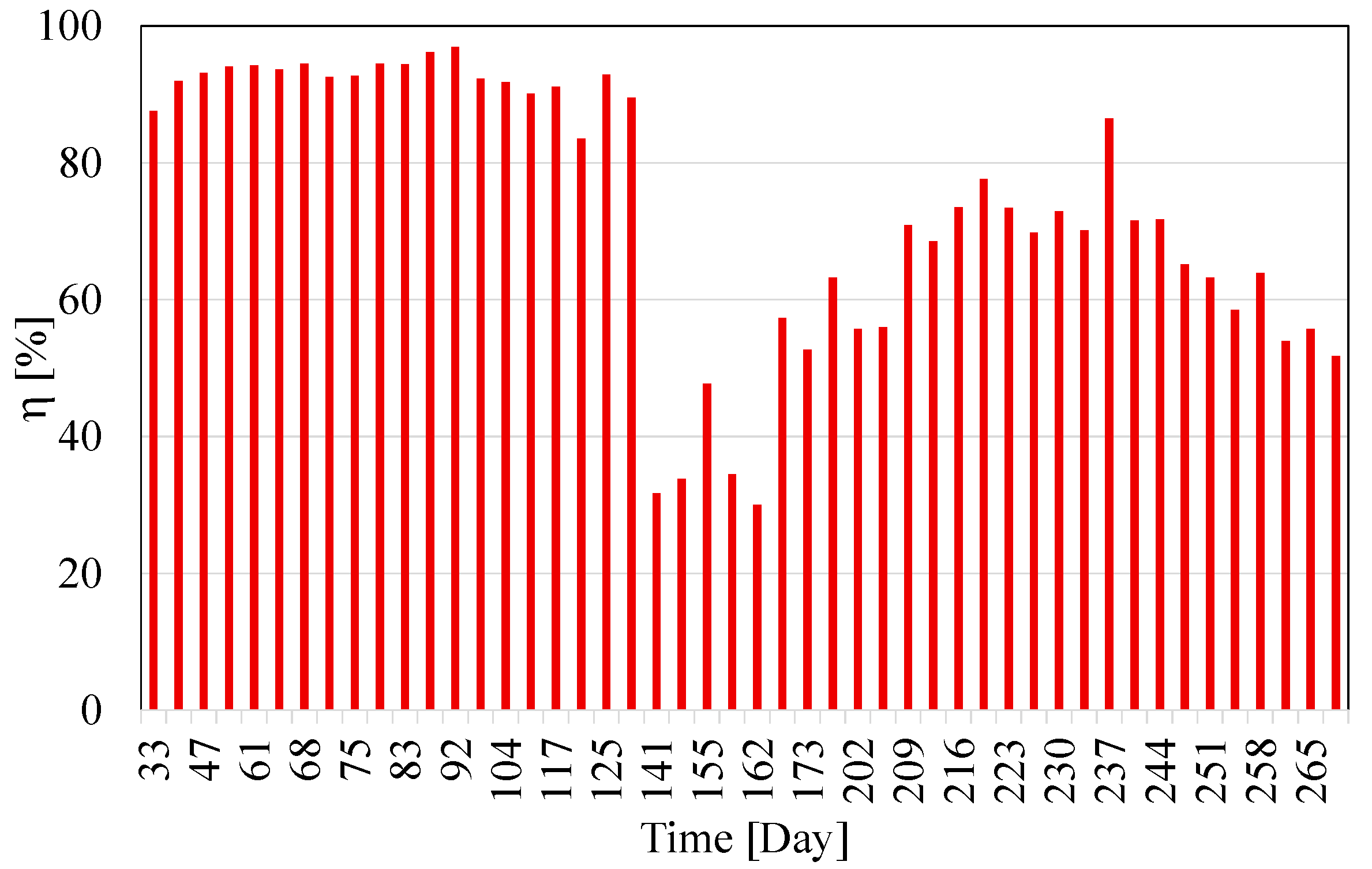
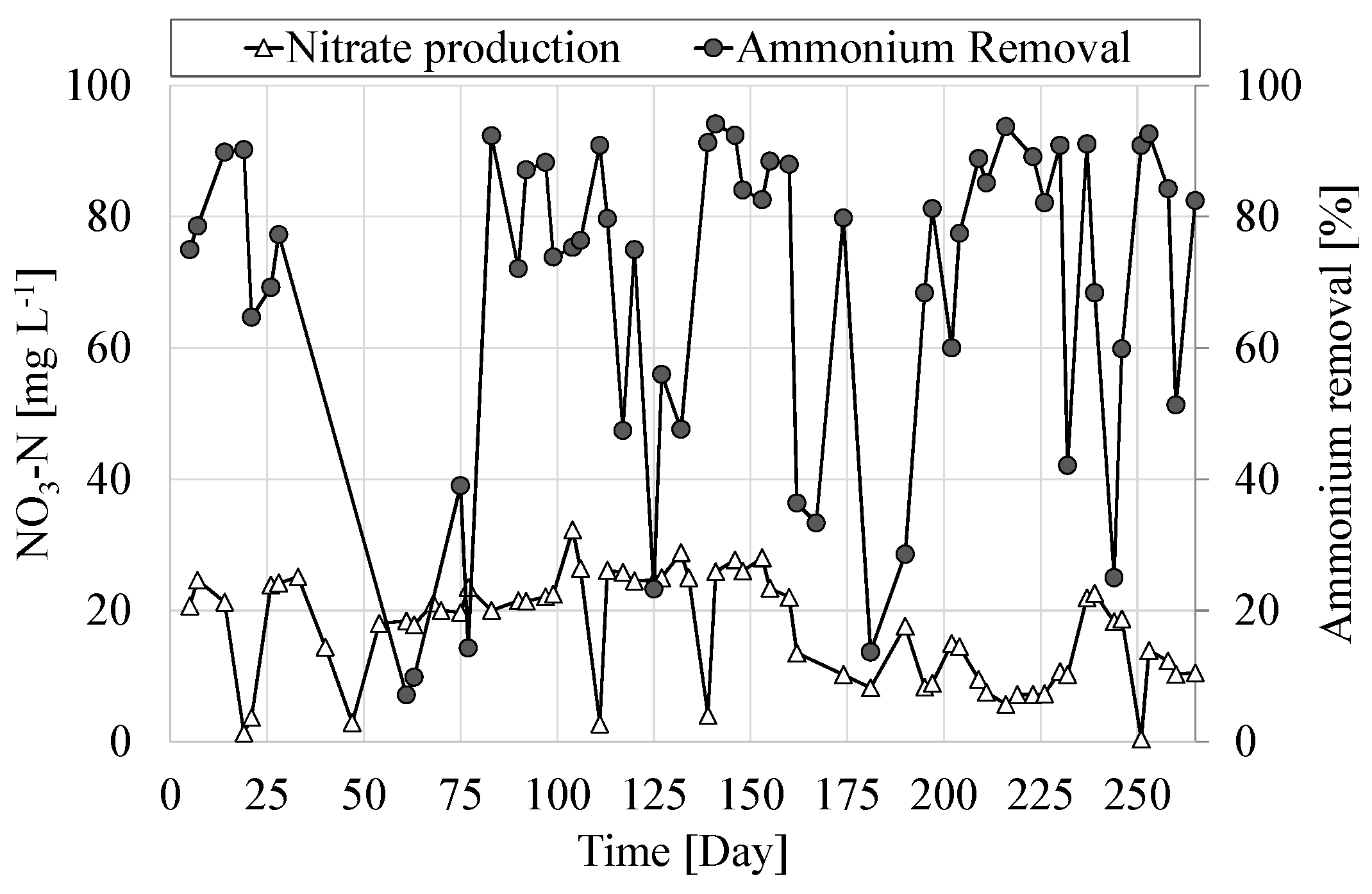
3.3. Nitrification Efficiency
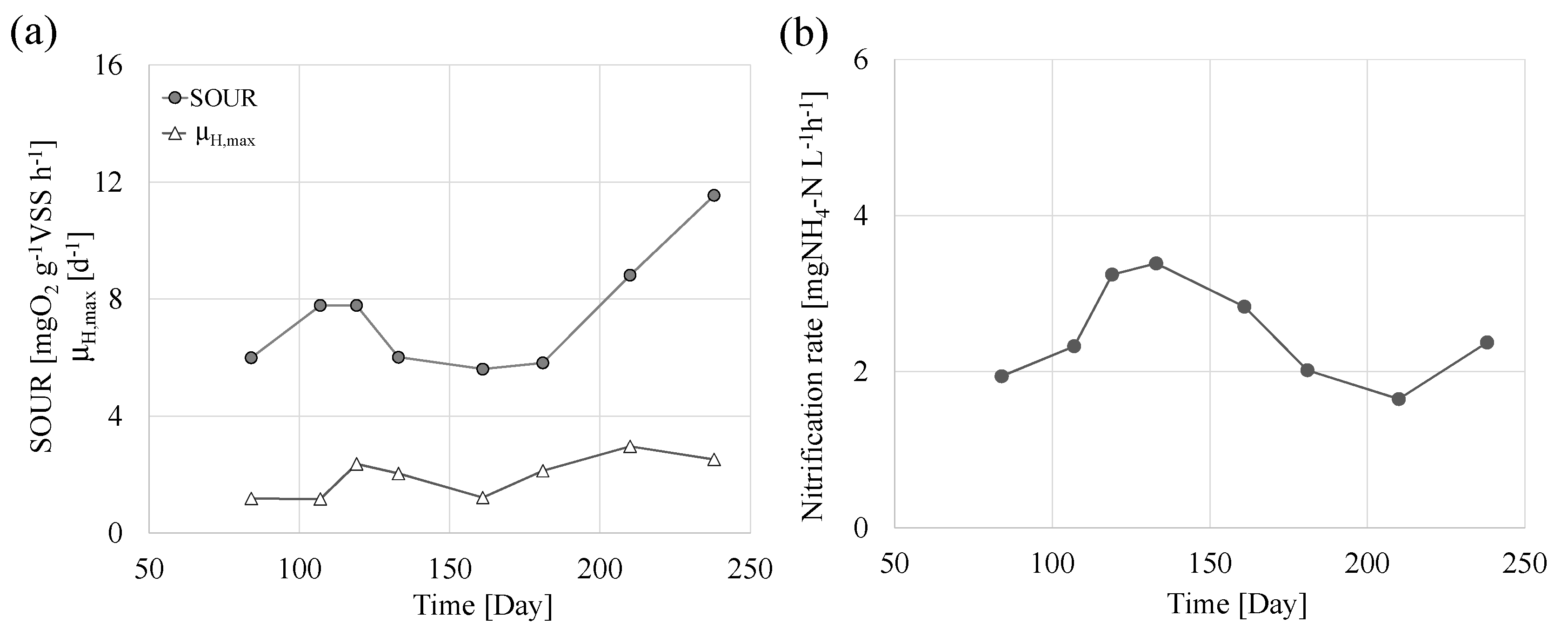
3.4. Biomass Biokinetic Parameters
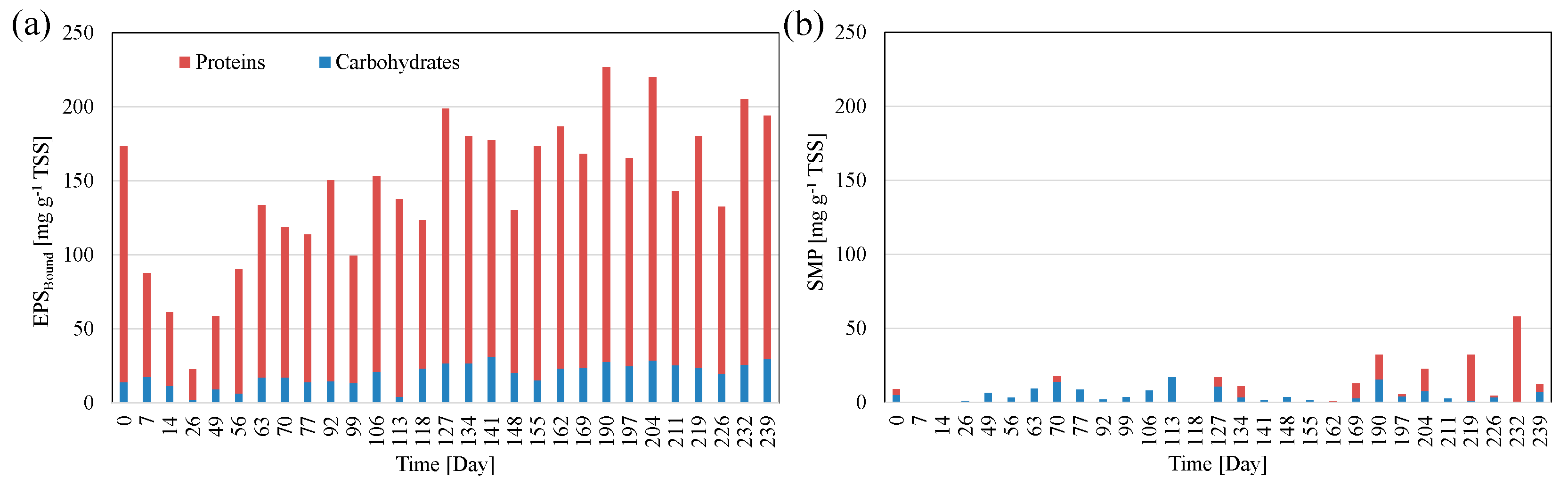
3.5. Extracellular Polymeric Substances Production
3.6. Membrane Fouling
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Di Bella, G.; Giustra, M.G.; Freni, G. Optimisation of coagulation/flocculation for pre-treatment of high strength and saline wastewater: Performance analysis with different coagulant doses. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 254, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, G.; Panzica, M.; Fino, D.; Cappello, S.; Yakimov, M.M.; Luciano, A. Feasibility of treating emulsified oily and salty wastewaters through coagulation and bio-regenerated GAC filtration. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, E.; Liu, X.; Judd, S.J. Effect of high salinity on activated sludge characteristics and membrane permeability in an immersed membrane bioreactor. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 283, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bella, G.; Di Prima, N.; Di Trapani, D.; Freni, G.; Giustra, M.G.; Torregrossa, M.; Viviani, G. Performance of membrane bioreactor (MBR) systems for the treatment of shipboard slops: Assessment of hydrocarbon biodegradation and biomass activity under salinity variation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 300, 765–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannina, G.; Cosenza, A.; Di Trapani, D.; Capodici, M.; Viviani, G. Membrane bioreactors for treatment of saline wastewater contaminated by hydrocarbons (diesel fuel): An experimental pilot plant case study. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 291, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannina, G.; Capodici, M.; Cosenza, A.; Di Trapani, D.; Viviani, G. Sequential batch membrane bio-reactor for wastewater treatment: The effect of increased salinity. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 209, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campo, R.; Di Prima, N.; Gabriella Giustra, M.; Freni, G.; Di Bella, G. Performance of a moving bed-membrane bioreactor treating saline wastewater contaminated by hydrocarbons from washing of oil tankers. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 22943–22952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, R.; Di Prima, N.; Freni, G.; Giustra, M.G.; Di Bella, G. Start-up of two moving bed membrane bioreactors treating saline wastewater contaminated by hydrocarbons. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 73, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cappello, S.; Volta, A.; Santisi, S.; Morici, C.; Mancini, G.; Quatrini, P.; Genovese, M.; Yakimov, M.M.; Torregrossa, M. Oil-degrading bacteria from a membrane bioreactor (BF-MBR) system for treatment of saline oily waste: Isolation, identification and characterization of the biotechnological potential. Int. Biodeter. Biodegrad. 2016, 110, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahzadeh Sharghi, E.; Bonakdarpour, B.; Pakzadeh, M. Treatment of hypersaline produced water employing a moderately halophilic bacterial consortium in a membrane bioreactor: Effect of salt concentration on organic removal performance, mixed liquor characteristics and membrane fouling. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 164, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Trapani, D.; Di Bella, G.; Mannina, G.; Torregrossa, M.; Viviani, G. Comparison between moving bed-membrane bioreactor (MB-MBR) and membrane bioreactor (MBR) systems: Influence of wastewater salinity variation. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 162, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Judd, S. The MBR Book: Principles and Applications of Membrane Bioreactors in Water and Treatment, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, V.; Purkait, M.K.; Das, C. Cross-flowmicrofiltration of industrial oilywastewater: Experimental and theoretical consideration. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2011, 46, 1213–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padaki, M.; Surya Murali, R.; Abdullah, M.S.; Misdan, N.; Moslehyani, A.; Kassim, M.A.; Hilal, N.; Ismail, A.F. Membrane technology enhancement in oil–water separation. A review. Desalination 2015, 357, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.; Wilén, B.M.; Lant, P. Impacts of morphological, physical and chemical properties of sludge flocs on dewaterability of activated sludge. Chem. Eng. J. 2004, 98, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Ngo, H.H.; Li, J. A mini-review on membrane fouling. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 122, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Chae, S.R.; Drews, A.; Kraume, M.; Shin, H.S.; Yang, F. Recent advances in membrane bioreactors (MBRs): Membrane fouling and membrane material. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1489–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.J.; Han, M.N.; Qu, X.; Xu, C.; Liao, B.Q. Characteristics of wastewater and mixed liquor and their role in membrane fouling. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 128, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Tu, W.; Wee, K.H.; Bai, R. Effective and low fouling oil/water separation by a novel hollow fiber membrane with both hydrophilic and oleophobic surface properties. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 466, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvořák, L.; Svojitka, J.; Wanner, J.; Wintgens, T. Nitrification performance in a membrane bioreactor treating industrial wastewater. Water Res. 2013, 13, 4412–4421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannina, G.; Di Bella, G. Comparing two start-up strategies for MBRs: Experimental study and mathematical modelling. Biochem. Eng. J. 2012, 68, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Quality Assurance/Quality Control (QA/QC) for 301(h) Monitoring Programs: Guidance on Field and Laboratory Methods: Final Report; Tetra Tech Inc.: Bellevue, WA, USA, 1987.
- Capodici, M.; Corsino, S.F.; Di Pippo, F.; Di Trapani, D.; Torregrossa, M. An innovative respirometric method to assess the autotrophic active fraction: Application to an alternate oxic-anoxic MBR pilot plant. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 300, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Trapani, D.; Di Bella, G.; Mannina, G.; Torregrossa, M.; Viviani, G. Effect of C/N shock variation on the performances of a moving bed membrane bioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 189, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Zhang, H.M.; Li, Y.S.; Zhang, X.W.; Yang, F.L.; Xiao, J.N. Cake layer morphology in microfiltration of activated sludge wastewater based on fractal analysis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2005, 44, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Yang, F. Fouling mechanisms of deflocculated sludge, normal sludge, and bulking sludge in membrane bioreactor. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 305, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bella, G.; Durante, F.; Torregrossa, M.; Viviani, G.; Mercurio, P.; Cicala, A. The role of fouling mechanisms in a membrane bioreactor. Water Sci. Technol. 2007, 55, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosenza, A.; Di Bella, G.; Mannina, G.; Torregrossa, M. The role of EPS in fouling and foaming phenomena for a membrane bioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 147, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin-Phenol Reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dubois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric Method for Determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza Razavi, S.M.; Miri, T. A real petroleum refinery wastewater treatment using hollow fiber membrane bioreactor (HF-MBR). J. Water Proc. Eng. 2015, 8, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Units | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical oxygen demand (COD) | [mg·L−1] | 500 |
| Total petroleum hydrocarbon (TPH) | [ppm] | 20 |
| Ammonium nitrogen (NH4–N) | [mg·L−1] | 20 |
| Conductivity | [mS·cm−1] | 1.6 |
| Parameter | Units | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Permeate Flux | [L·m−2·h−1] | 15 |
| Flow rate | [L·h−1] | 0.8 |
| HRT | [h] | 27 |
| Heterotrophic | YH | µH max | KS | OURmax | SOUR |
| mg VSS∙mg COD−1 | d−1 | mg COD∙L−1 | mg O2∙L−1∙h−1 | mg O2∙g VSS−1∙h−1 | |
| average | 0.64 | 1.97 | 10.88 | 17.20 | 7.28 |
| St. deviation | 0.05 | 0.65 | 10.88 | 5.23 | 1.95 |
| Autotrophic | YA | µA max | KN | OURmax | Nitrification rate |
| mg VSS∙mg N−1 | d−1 | mg N∙L−1 | mg O2∙L−1∙h−1 | mg N∙L−1∙h−1 | |
| average | 0.20 | 0.23 | 0.16 | 13.73 | 2.37 |
| St. deviation | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.11 | 3.32 | 0.66 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Capodici, M.; Cosenza, A.; Di Trapani, D.; Mannina, G.; Torregrossa, M.; Viviani, G. Treatment of Oily Wastewater with Membrane Bioreactor Systems. Water 2017, 9, 412. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9060412
Capodici M, Cosenza A, Di Trapani D, Mannina G, Torregrossa M, Viviani G. Treatment of Oily Wastewater with Membrane Bioreactor Systems. Water. 2017; 9(6):412. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9060412
Chicago/Turabian StyleCapodici, Marco, Alida Cosenza, Daniele Di Trapani, Giorgio Mannina, Michele Torregrossa, and Gaspare Viviani. 2017. "Treatment of Oily Wastewater with Membrane Bioreactor Systems" Water 9, no. 6: 412. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9060412
APA StyleCapodici, M., Cosenza, A., Di Trapani, D., Mannina, G., Torregrossa, M., & Viviani, G. (2017). Treatment of Oily Wastewater with Membrane Bioreactor Systems. Water, 9(6), 412. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9060412






