Using δ15N and δ18O Signatures to Evaluate Nitrate Sources and Transformations in Four Inflowing Rivers, North of Taihu Lake
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area
3. Sample Collection and Measurement
4. Results and Discussion
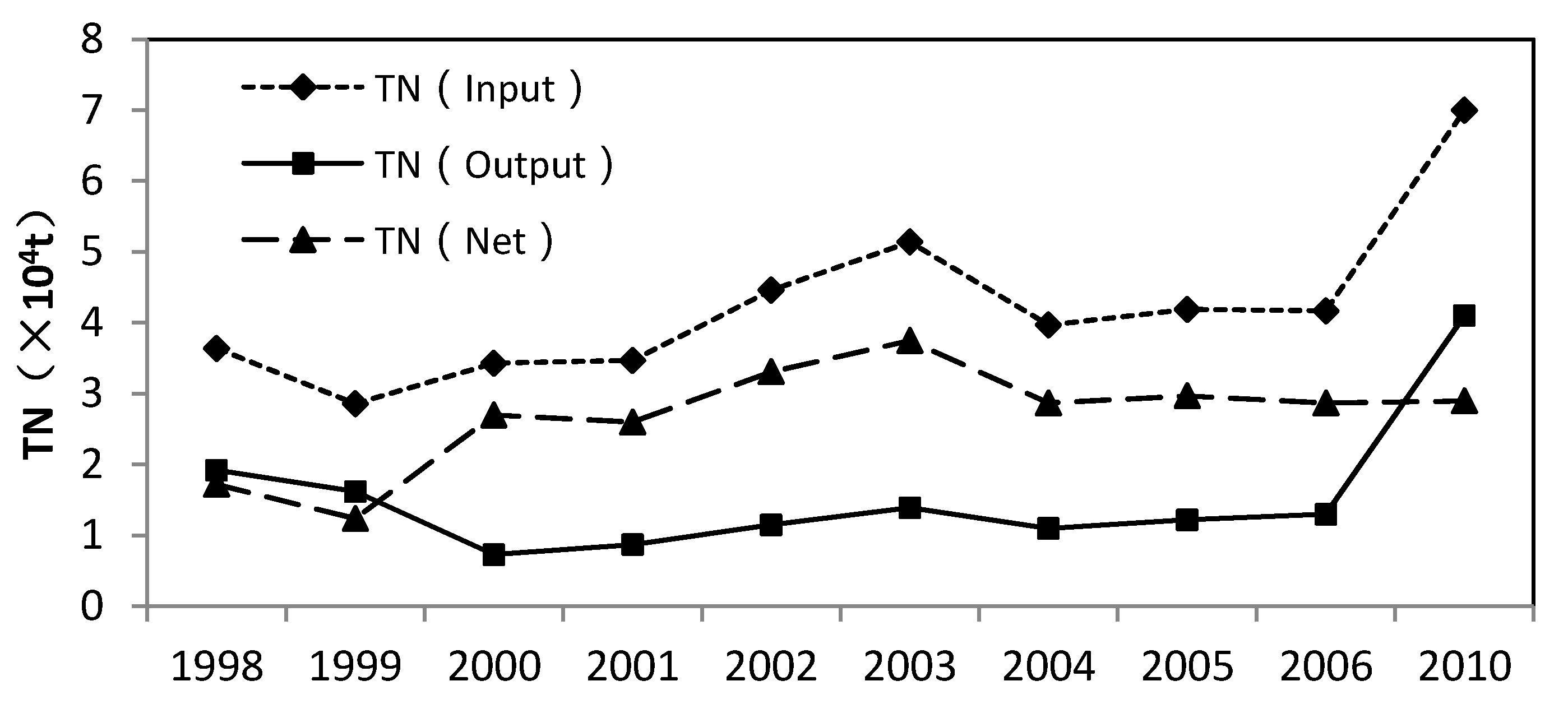
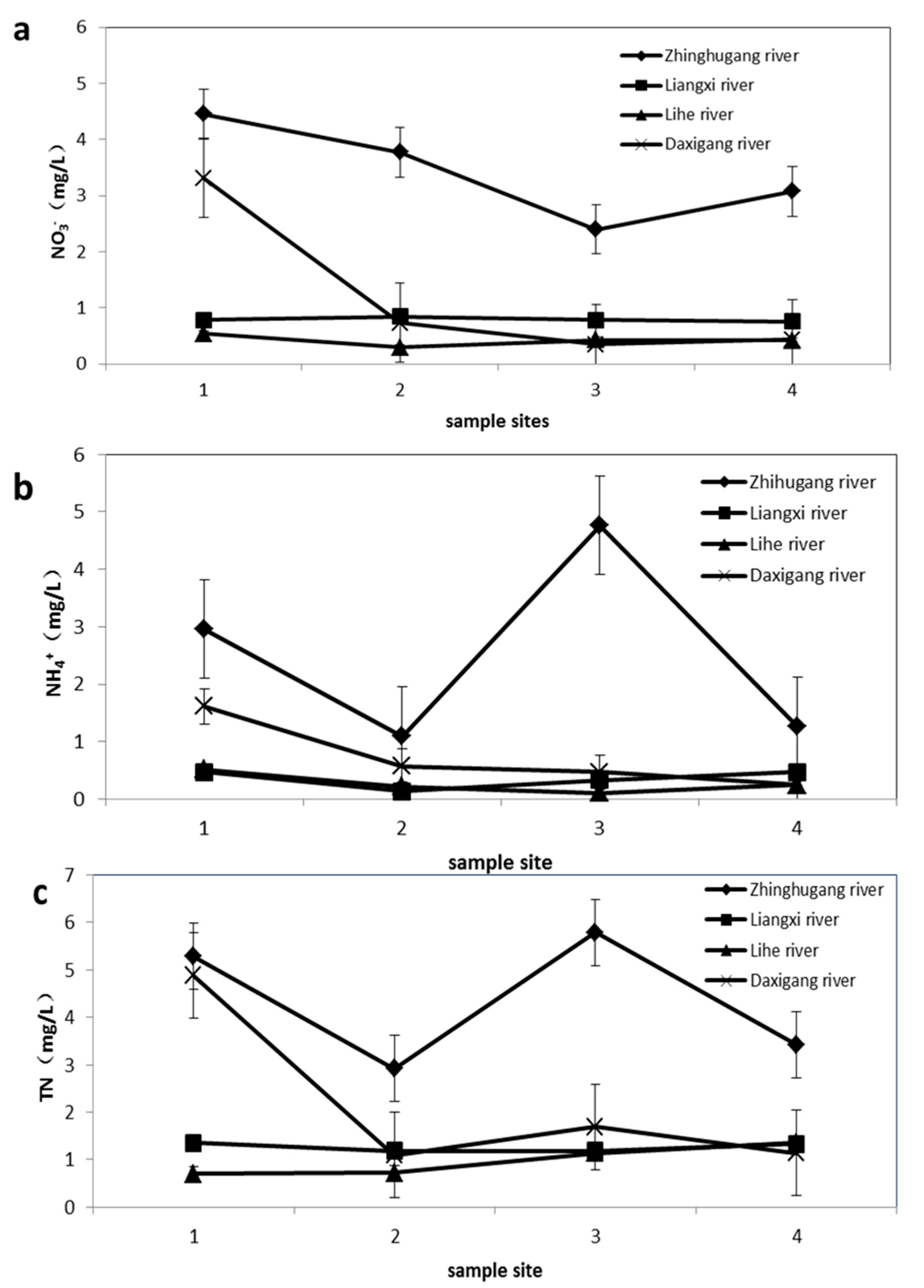
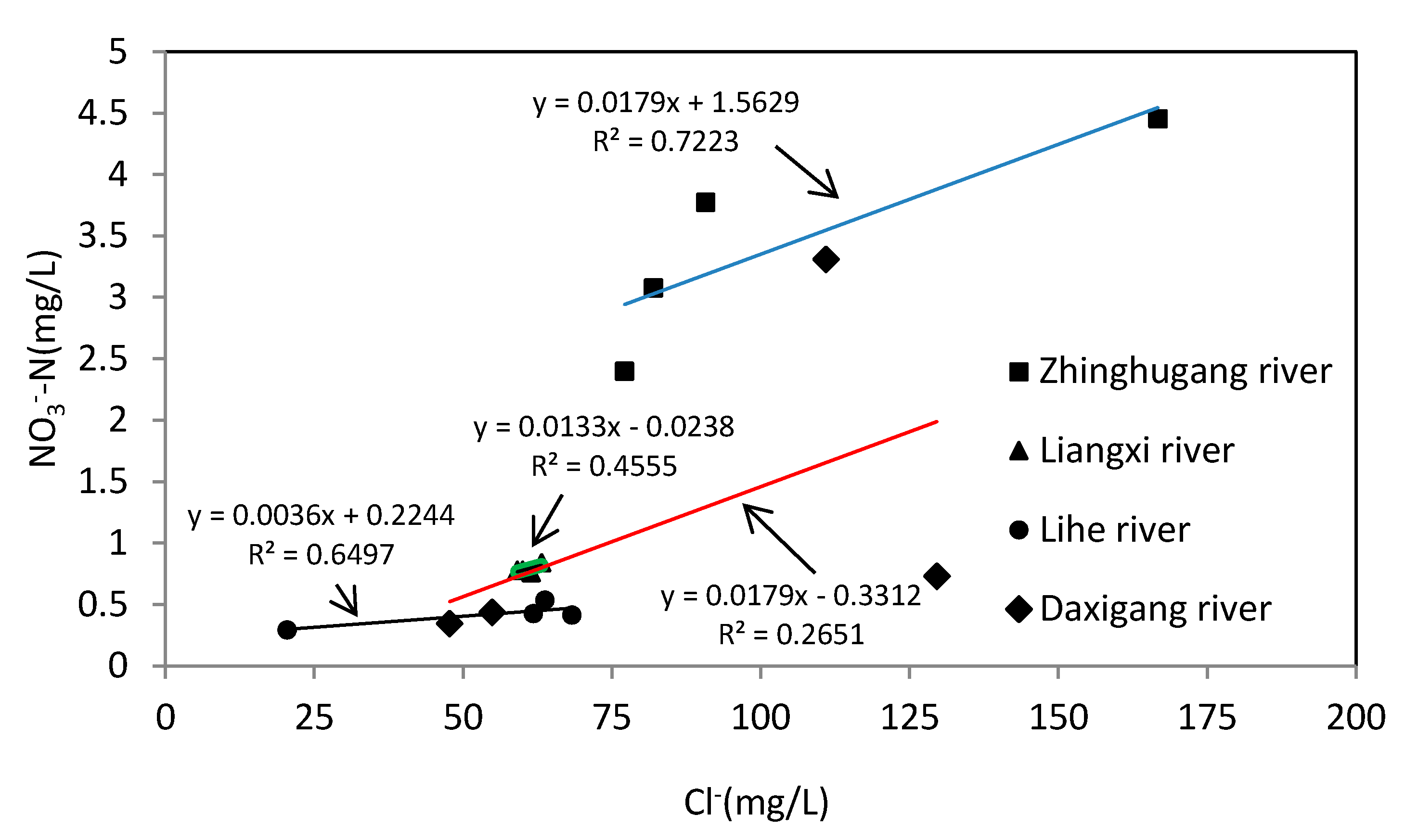
4.1. Physicochemical Characteristic of Water Samples
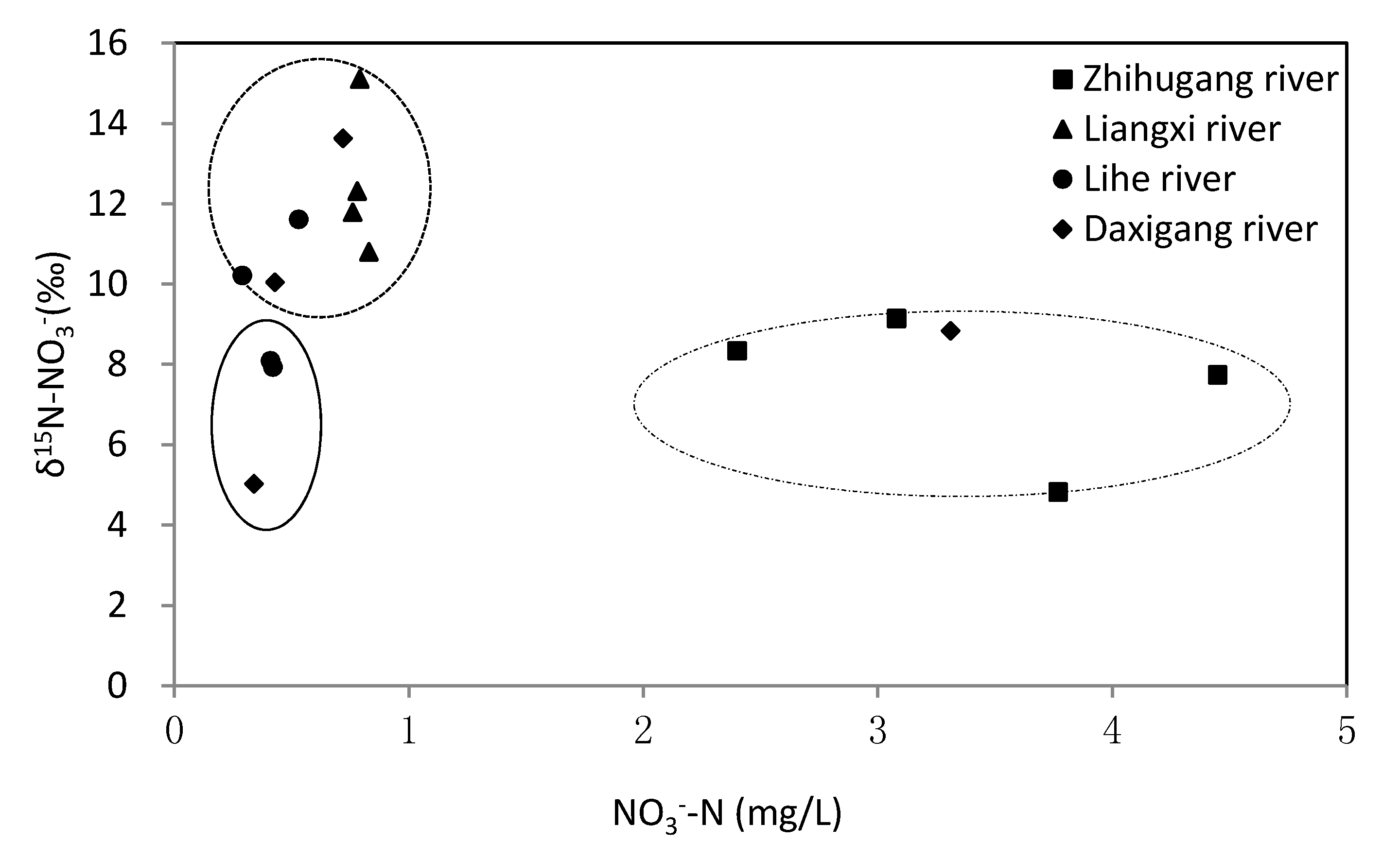
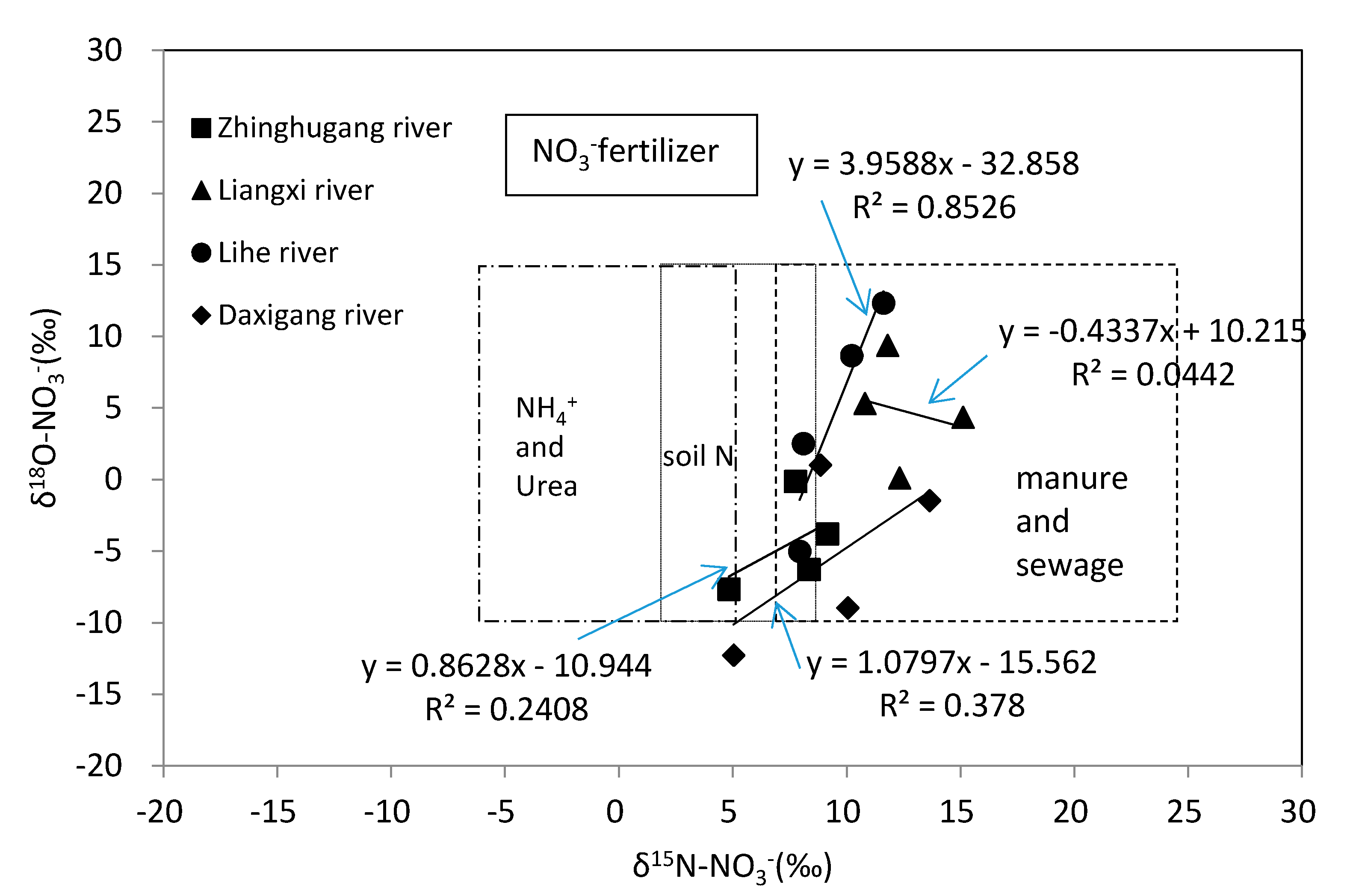
4.2. Nitrate Sources and Nitrogen Transformation
4.3. Quantification of Nitrate Sources in Rivers
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Ethical Statement
Appendix A
| Zhihugang River | |||||||
| pH | DO | TOC | Cl− | NH4+-N | NO3−-N | TN | |
| pH | 1 | 0.013 | 0.992 ** | −0.783 | −0.993 ** | −0.993 ** | −0.023 |
| DO | 1 | 0.136 | −0.391 | −0.060 | −0.060 | −0.933 * | |
| TOC | 1 | −0.806 | −0.986 ** | −0.986 ** | −0.124 | ||
| Cl− | 1 | 0.850 | 0.850 | 0.550 | |||
| NH4+ | 1 | 1.000 ** | 0.106 | ||||
| NO3− | 1 | 0.106 | |||||
| TN | 1 | ||||||
| Liangxi River | |||||||
| pH | DO | TOC | Cl- | NH4+-N | NO3−-N | TN | |
| pH | 1 | 0.196 | 0.349 | −0.073 | −0.591 | −0.591 | 0.075 |
| DO | 1 | 0.704 | 0.057 | 0.418 | 0.418 | −0.959 * | |
| TOC | 1 | −0.652 | −0.256 | −0.256 | −0.553 | ||
| Cl- | 1 | 0.675 | 0.675 | −0.172 | |||
| NH4+ | 1 | 1.000 ** | −0.642 | ||||
| NO3− | 1 | −0.642 | |||||
| TN | 1 | ||||||
| Lihe River | |||||||
| pH | DO | TOC | Cl- | NH4+-N | NO3−-N | TN | |
| pH | 1 | −0.077 | −0.275 | 0.358 | 0.257 | 0.257 | 0.479 |
| DO | 1 | 0.212 | −0.047 | −0.625 | −0.625 | 0.297 | |
| TOC | 1 | −0.982 * | −0.895 | −0.895 | −0.832 | ||
| Cl− | 1 | 0.806 | 0.806 | 0.922 | |||
| NH4+ | 1 | 1.000 ** | 0.530 | ||||
| NO3− | 1 | 0.530 | |||||
| TN | 1 | ||||||
| Daxigang River | |||||||
| pH | DO | TOC | Cl- | NH4+-N | NO3−-N | TN | |
| pH | 1 | 0.993 ** | −0.963 * | −0.713 | −0.533 | −0.533 | −0.362 |
| DO | 1 | −0.632 | −0.971 * | −0.620 | −0.620 | −0.463 | |
| TOC | 1 | 0.532 | 0.035 | 0.035 | −0.169 | ||
| Cl− | 1 | 0.515 | 0.515 | 0.373 | |||
| NH4+ | 1 | 1.000 ** | 0.978 * | ||||
| NO3− | 1 | 0.978 * | |||||
| TN | 1 | ||||||
References
- Li, Y.K. The Population and Regional Economies Development Collaborative Researeh about Taihu Lake Basin (1990-); College of Law and Political Seience, Zhejiang Normal University: Jinhua, China, 2011; pp. 22–40. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Y.C.; He, P. An Analysison the Changes in the Water Quality in Taihu Basin during 1998–2006. Acta Agric. Univ. Jiangxiensis 2009, 2, 371–374. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Yan, S.W.; Xu, J. Multivariate statistical analysis of river water quality around Taihu Lake. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2010, 19, 696–702. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.F.; Chuai, X.M.; Zheng, J.; Liu, T.; Yang, L.Y. Nitrogen Fluxes and Its Self-Purification Capacity in Lake Taihu. Environ. Sci. 2012, 33, 2309–2314. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Sum, H. A case study on Wuxi city: Relationship between economic growth and water environment. Resour. Ind. 2009, 11, 146–149. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.L.; Xu, H.; Yang, G.J.; Zhu, G.W.; Qin, B.Q. Progress in nitrogen pollution research in Lake Taihu. J. Lake Sci. 2014, 26, 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, S.H.; Zhang, H.J. Water quantity and waste load variation of rivers around Lake Taihu from 2000 to 2002. J. Lake Sci. 2006, 18, 225–230. [Google Scholar]
- Curt, M.D.; Aguado, P.; Sánchez, G.; Bigeriego, M.; Fernández, J. Nitrogen isotope ratios of synthetic and organic sources of nitrate water contamination in Spain. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2004, 151, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smil, V. Nitrogen in crop production: An account of global flows. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 1999, 13, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkovitz, C.M.; Scholtz, M.T.; Pacyna, J.; Tarrasón, L.; Dignon, J.; Voldner, E.C.; Spiro, P.A.; Logan, J.A.; Graedel, T.E. Global gridded inventories of anthropogenic emissions of sulfur and nitrogen. J. Geophys. Res. 1996, 101, 29239–29253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Xu, P.; Wu, Q.; Luo, L.; Zhang, Y. Environmental issues of Lake Taihu, China. Hydrobiologia 2007, 581, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, E.R.; Krothe, N.C. Seasonal fluctuation in δ15N of groundwater nitrate in a mantled karst aquifer due to macropore transport of fertilizer-derived nitrate. J. Hydrol. 1989, 112, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, B.; Boyer, E.W.; Goodale, C.; Jaworski, N.A.; Breemen, N.V.; Howarth, R.W.; Seitzinger, S.; Billen, G.; Lajtha, K.; Nadelhoffer, K.; et al. Sources of nitrate in rivers draining sixteen watersheds in the northeastern U.S.: Isotopic constraints. Biogeochemistry 2002, 57/58, 171–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, B.; Bollwerk, S.M.; Mansfeldt, T.; Hütter, B.; Veizer, J. The oxygen isotope composition of nitrate generated by nitrification in acid forest floors. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2001, 65, 2743–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.L.; Liu, C.Q.; Li, J.; Liu, X.L.; Chetelat, B.; Wang, B.L.; Wang, F.S. Assessment of the sources of nitrate in the Changjiang River, China using a nitrogen and oxygen isotopic approach. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1573–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kendall, C.; Elliott, E.M.; Wankel, S.D. Tracing anthropogenic inputs of nitrogen to ecosystems. In Stable Isotopes in Ecology and Environmental Science, 2nd ed.; Michener, R., Lajtha, K., Eds.; Blackwell Publishing: Oxfordshire, UK, 2007; pp. 375–449. [Google Scholar]
- Hales, H.C.; Ross, D.S.; Lini, A. Isotopic signature of nitrate in two contrasting watersheds of Brush Brook, Vermont, USA. Biogeochemistry 2007, 84, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellman, L.; Hillaire-Marcel, C. Nitrate cycling in streams: Using natural abundances of NO3-δ15N to measure in-situ denitrification. Biogeochemistry 1998, 43, 273–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delwiche, C.; Steyn, P. Nitrogen isotope fractionation in soils and microbial reactions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1970, 4, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macko, S.A.; Ostrom, N.E. Molecular and pollution studies using stable isotope. In Stable Isotopes in Ecology and Environmental Science; Lajtha, K., Michner, R., Eds.; Blackwell Scientific: Oxford, UK, 1994; pp. 45–62. [Google Scholar]
- Widory, D.; Kloppmann, W.; Chery, L.; Bonnin, J.; Rochdi, H.; Guinamant, J.L. Nitrate in groundwater, an isotope multi-tracer approach. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2004, 72, 165–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seiler, R.L. Combined use of 15N and 18O of nitrate and 11B to evaluate nitrate contamination in groundwater. Appl. Geochem. 2005, 20, 1626–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böttcher, J.; Strebel, O.; Voerkelius, S.; Schmidt, H.L. Using isotope fractionation of nitrate nitrogen and nitrate oxygen for evaluation of microbial denitrification in a sandy aquifer. J. Hydrol. 1990, 114, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengis, M.; Schiff, S.L.; Harris, M.; English, M.C.; Aravena, R.; Elgood, R.J.; Maclean, A. Multiple geochemical and isotopic approaches for assessing ground water NO3− elimination in a riparian zone. Ground Water 1999, 37, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukada, T.; Hiscock, K.M.; Dennis, P.F.; Grischek, T. A dual isotope approach to identify denitrification in ground water at a river bank infiltration site. Water Res. 2003, 37, 3070–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panno, S.V.; Hackley, K.C.; Kelly, W.R.; Hwang, H.-H. Isotopic evidence of nitrate sources and denitrification in the Mississippi River, Illinois. J. Environ. Qual. 2006, 35, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durka, W.; Schulze, E.D.; Gebauer, G.; Voerkelius, S. Effects of forest decline on uptake and leaching of deposited nitrate determined from 15N and 18O measurements. Nature 1994, 372, 765–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassenaar, L.I. Evaluation of the origin and fate of nitrate in the Abbotsford Aquifer using the isotopes of 15N and 18O in NO3−. Appl. Geochem. 1995, 10, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koba, K.; Tokuchi, N.; Wada, E.; Nakajima, T.; Iwatsubo, G. Intermittent denitrification: The application of δ15N natural abundance method to a forested ecosystem. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1997, 61, 5043–5050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Wu, J.L.; Zeng, H.-A.; Liu, W. Stable nitrogen isotope tracing anthropogenic influence on Lake Taihu. J. Lake Sci. 2012, 4, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend-Small, A.; McCarthy, M.J.; Brandes, J.A.; Yang, L.; Zhang, L.; Gardner, W.S. Stable isotopic composition of nitrate in Lake Taihu, China, and major inflow rivers. Hydrobiologia 2007, 581, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.X. Using Nitrogen and Oxygen Isotopic Composition in Dissolved Nitrate to Identify Nitrate Source in Taihu Lake and Chaohu Lake, China. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.X.; Xiong, Z.Q.; Xing, G.X.; Sun, G.Q.; Zhu, Z.L. Assessment of nitrogen pollutant sources in surface waters of Taihu Lake region. Pedosphere 2007, 17, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, S.; Zhu, W. Analysis of isotope tracing of domestic sewage sources in Taihu Lake—A case study of Meiliang Bay and Gonghu Bay. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 66, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.G.; Liu, G.; Han, Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Xing, G.X. Nitrate distribution and denitrification in the saturated zone of paddy field under rice/wheat rotation. Chemosphere 2003, 50, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.T.; Xi, B.D.; Rutai, G.B.; He, L.S.; Liu, H.L.; Dai, X.L.; Yu, Y.J. Identifying diffused nitrate sources in a stream in an agricultural field using a dual isotopic approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 484, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.Q.; Chen, Q.W. Spatial-temporal characteristic of water quality in Lake Taihu and its relationship with algal bloom. J. Lake Sci. 2011, 23, 339–347. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.P.; Huang, W.Y.; Yang, G.S.; Liu, X.M. Non-point pollutant concentrations for diferent land uses in Lihe River watershed of Taihu Region. China Environ. Sci. 2006, 26, 243–247. [Google Scholar]
- System Planning of Wuxi. Available online: https://wenku.baidu.com/view/5835764002d276a200292ec2.html?from=search (accessed on 18 December 2007).
- Wang, P.; Wang, C. Water Quality in Taihu Lake and the Effects of the Water Transfer from the Yangtze River to Taihu Lake Project. Compr. Water Qual. Purif. 2014, 4, 136–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigman, D.M.; Casciotti, K.L.; Andreani, M.; Barford, C.; Galanter, M.; Böhlke, J.K. A bacterial method for the nitrogen isotopic analysis of nitrate in seawater and freshwater. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 4145–4153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casciotti, K.L.; Sigman, D.M.; Hastings, M.G.; Bohlke, J.K.; Hilkert, A. Measurement of the oxygen isotopic composition of nitrate in seawater and freshwater using the denitrifier method. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 4905–4912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wankel, S.D.; Kendall, C.; Francis, C.A.; Paytan, A. Nitrogen sources and cycling in the San Francisco Bay Estuary: A nitrate dual isotopic composition approach. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 1654–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Han, J.Y.; Xu, L.G.; Zhang, Q. Spatial and seasonal variations of the contamination within water body of the The Grand Canal, China. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 1513–1520. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, T.; Wang, S.N.; Cao, H.Y.; Zhang, C.S.; Li, H.T.; Li, H.P.; Song, W.C.; Chong, Z.Y. Estimation of ammonia nitrogen load from nonpoint sources in the Xitiao River catchment, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 1195–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francois, P.; Tangomo, M.; Hibbs, J.; Bonetti, E.J.; Boehme, C.C.; Notomi, T.; Perkins, M.D.; Schrenzel, J. Robustness of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification reaction for diagnostic applications. Fems Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 62, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zheng, F.; Du, S. Assessment and analysis of non-point source nitrogen and phosphorus loads in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area of Hubei Province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 412–413, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Hu, W.; Zhai, S.; Wu, H. Effects on water quality following water transfer in Lake Taihu, China. Ecological Engineering 2010, 36, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xie, P.; Man, Z.M.; Niu, Y.; Tao, M.; Deng, X.W.; Wang, Q. A systematic study on spatial and seasonal patterns of eight taste and odor compounds with relation to various biotic and abiotic parameters in Gonghu Bay of Lake Taihu, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 409, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kendall, C. Tracing sources and cycling of nitrate in catchments. In Isotope Tracers in Catchmenthydrology; Kendall, C., Mcdonnell, J.J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998; pp. 519–576. [Google Scholar]
- Fogel, M.L.; Cifuentes, L.A. Isotope fractionation during primary production. In Organic Geochemistry; Engel, M.H., Macko, S.A., Eds.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1993; pp. 73–98. [Google Scholar]
- Hollocher, T.C. Source of the oxygen atoms of nitrate in the oxidation of nitrite by Nitrobacter agilis and evidence against a P-O-N anhydride mechanism in oxidative phosphorylation. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1984, 233, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, D.M.; Botte, J.; De Baets, B.; Accoe, F.; Nestler, A.; Taylor, P.; Van Cleemput, O.; Berglund, M.; Boeckx, P. Present limitations and future prospects of stable isotope methods for nitrate source identification in surface- and groundwater. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1159–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singleton, M.J.; Esser, B.K.; Moran, J.E.; Hudson, G.B.; McNab, W.W.; Harter, T. Saturated zone denitrification: Potentialfor natural attenuation of nitrate contamination in shallow groundwater under dairy operations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 759–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.S.; Bong, Y.S.; Lee, D.; Kim, Y.; Kim, K. Tracing the sources of nitrate in the Han River watersheds in Korea, using δ15N-NO3− and δ18O-NO3− values. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 395, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umezawa, Y.; Hosono, T.; Onodera, S.; Siringan, F.; Buapeng, S.; Delinom, R.; Yoshimizu, C.; Tayasu, I.; Nagata, T.; Taniguchi, M. Sources of nitrate and ammonium contamination in ground water under developing Asianmegacities. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 404, 361–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aravena, R.; Robertson, W.D. Use of multiple isotope tracers to evaluate denitrification in ground water: Study of nitrate from a large-flux septic system plume. Ground Water 1998, 36, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.R.; Wang, Y.S.; Yin, J.P.; Wang, Q.J.; Zhang, F.Q.; He, L.; Sun, C.C. Transformation of dissolved inorganic nitrogen species and nitrigication and denitrification processes in the near sea section of Zhujiang river. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2005, 25, 686–692. [Google Scholar]
- Kendall, C.; Grim, E. Combustion tube method for measurement of nitrogen isotope ratios using calcium oxide for total removal of carbon dioxide and water. Anal. Chem. 1990, 62, 526–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebilo, M.; Billen, G.; Grably, M.; Mariotti, A. Isotopic composition of nitrate-nitrogen as a marker of riparian and benthic denitrification at the scale of the whole Seine river system. Biogeochemistry 2003, 63, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, M.F.; Reichert, P.; Bernasconi, S.M.; Barbieri, A.; McKenzie, A. Modelling nitrogen and oxygen isotope fractionation during denitrification in a lacustrine redoxtransition zone. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2003, 67, 2529–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglin, W.A.; Kendall, C.; Chang, C.C.; Silva, S.R.; Campbell, D. Chemical and isotopic evidence of nitrogen transformationin the Mississippi River, 1997−98. Hydrol. Process. 2001, 15, 1285–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannsen, A.; Dähnke, K.; Emeis, K. Isotopic composition of nitrate in five German rivers discharging into the North Sea. Org. Geochem. 2008, 39, 1678–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, F.D.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Li, J.; Liu, Q. Tracing nitrate pollution sources and transformation in surface- and ground-waters using environmental isotopes. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 490, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, F.J.; Li, S.L.; Liu, C.Q.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Hu, J. Using dual isotopes to evaluate sources and transformation of nitrogen in the Liao River, northeast China. Appl. Geochem. 2013, 36, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granger, J.; Sigman, D.M.; Needoba, J.A.; Harrison, P.J. Coupled nitrogen and oxygen isotope fractionation of nitrate during assimilation by cultures of marine phytoplankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2004, 49, 1763–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widory, D.; Petelet-Giraud, E.; Brenot, A.; Bronders, J.; Tirez, K.; Boeckx, P. Improving the management of nitrate pollution in water by the use of isotope monitoring: The δ15N, δ18O and δ11B triptych. Isot. Environ. Health Stud. 2013, 49, 29–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.L.; Lu, Y.L.; Han, J.Y.; He, G.Z.; Wang, T.Y. Identification of anthropogenic influences on water quality of rivers in Taihu watershed. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 19, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amberger, A.; Schmidt, H.L. Naturliche isotopengehalte von nitrat als indikatoren fur dessen Herkunft. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1987, 51, 2699–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.W.; Fan, C.X.; Katrin, T.; Dokulil, M. Changes of nutrients and phytoplankton chlorophyll-a in a large shallow lake Taihu, China: An 8-year investigation. Hydrobiologia 2003, 506, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.H.; Yin, B.; Yang, L.Z.; Yin, S.X.; Zhu, Z.L. Nitrogen runoff and leaching losses during rice-wheat rotations in Taihu Lake region, China. Pedosphere 2007, 4, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.Z. The Water Environment Synthetically Regulation Planning and Research of Daxigang River and Xiaoxigang River; Nanjing Agricultural University: Nanjing, China, 2005; pp. 12–47. [Google Scholar]
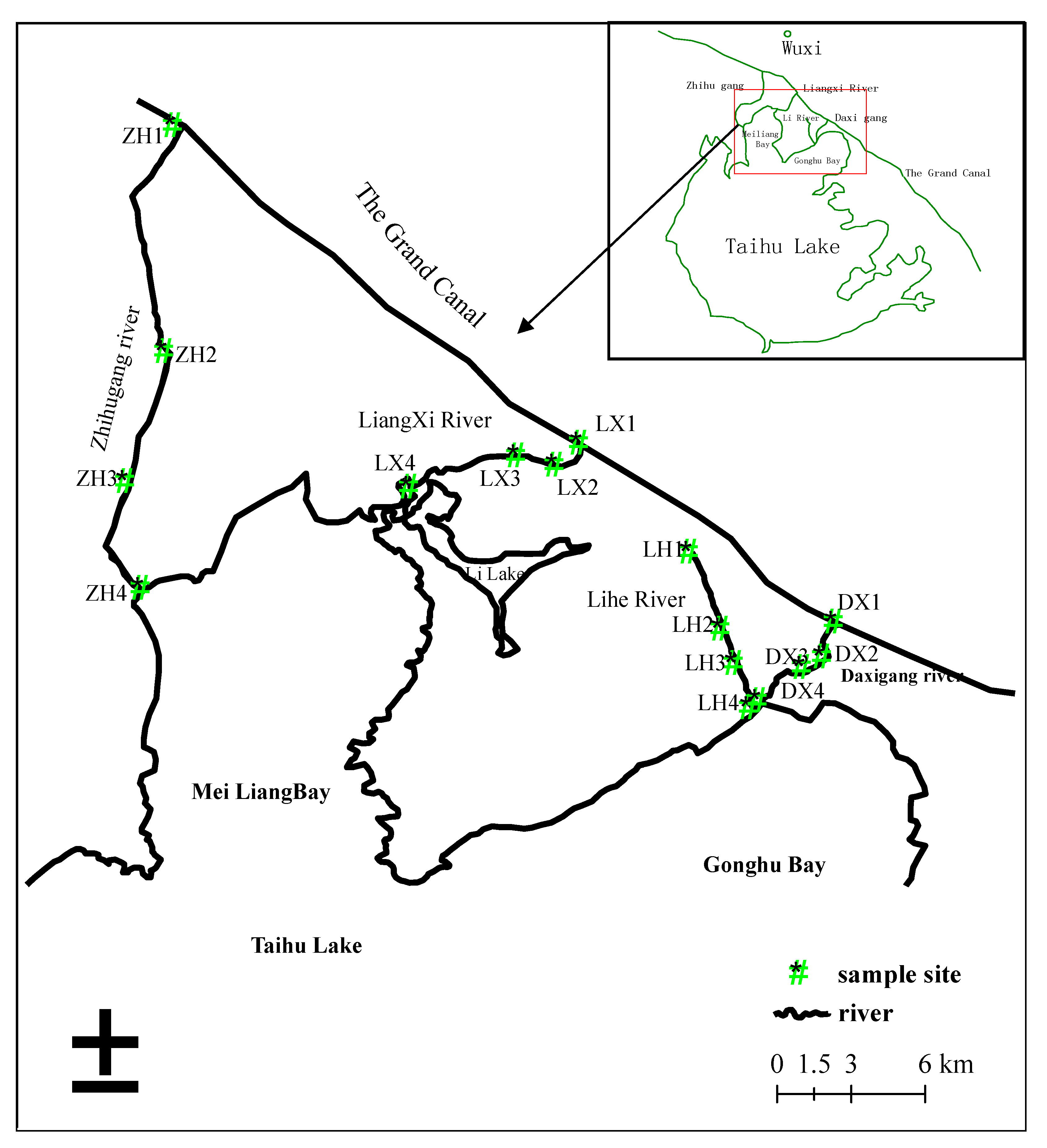
| River Name | Connected Lake Area | Length (km) | Bottom Width (m) | Annual Runoff (×108 m3) | Annual Amounts of Contaminants Imported (ton) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TN | TP | |||||
| Zhihugang river a,b | Meiliang Bay | 20.51 | 20–40 | 3.15 | 930.15 | 33.33 |
| Liangxi river a,b | Meiliang Bay | 7.97 | 15–60 | 0.42 | 280.80 | 11.36 |
| Lihe river a | GongHu Bay | 6.87 | 10 | 1.07 | 910.60 | 37.61 |
| Daxigang river a,b | GongHu Bay | 5.04 | 8 | 1.31 | 105.40 | 29.10 |
| Sample | pH | DO | Cl− | TOC | NH4+-N | NO3−-N | TN | δ15N-NO3− | δ18O-NO3− |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mg/L) | (mg/L) | (mg/L) | (mg/L) | (mg/L) | (mg/L) | (‰) | (‰) | ||
| ZH1 | 7.66 ± 0.23 | 6.24 ± 0.33 | 166.7 ± 2.4 | 28.9 ± 2.2 | 2.95 ± 0.43 | 4.45 ± 0.73 | 7.50 ± 1.03 | 7.75 ± 0.2 | −0.12 ± 0.1 |
| ZH2 | 7.72 ± 0.33 | 7.55 ± 0.44 | 90.7 ± 4.3 | 33.4 ± 2.1 | 1.09 ± 0.23 | 3.77 ± 0.43 | 5.12 ± 0.63 | 4.83 ± 0.1 | −7.65 ± 0.2 |
| ZH3 | 7.94 ± 0.23 | 5.9 ± 0.23 | 77.1 ± 3.2 | 48.4 ± 4.2 | 4.75 ± 0.37 | 2.40 ± 0.12 | 7.34 ± 1.31 | 8.35 ± 0.2 | −6.28 ± 0.2 |
| ZH4 | 7.84 ± 0.34 | 9.24 ± 0.46 | 81.9 ± 2.3 | 43.9 ± 2.2 | 1.25 ± 0.22 | 3.08 ± 0.27 | 4.55 ± 0.68 | 9.15 ± 0.1 | −3.78 ± 0.2 |
| LX1 | 8.46 ± 0.31 | 10.49 ± 0.13 | 59.9 ± 3.1 | 28.4 ± 2.7 | 0.46 ± 0.24 | 0.79 ± 0.22 | 1.35 ± 0.23 | 15.11 ± 0.2 | 4.35 ± 0.1 |
| LX2 | 8.48 ± 0.13 | 10.68 ± 0.23 | 63.1 ± 2.7 | 29.2 ± 4.2 | 0.13 ± 0.04 | 0.83 ± 0.21 | 1.18 ± 0.33 | 10.81 ± 0.2 | 5.32 ± 0.1 |
| LX3 | 8.53 ± 0.32 | 10.73 ± 0.51 | 59.1 ± 2.1 | 45.5 ± 1.7 | 0.32 ± 0.11 | 0.78 ± 0.14 | 1.18 ± 0.32 | 12.32 ± 0.1 | 0.11 ± 0.2 |
| LX4 | 8.58 ± 0.31 | 10.57 ± 0.23 | 61.4 ± 3.3 | 31.1 ± 1.9 | 0.46 ± 0.13 | 0.76 ± 0.17 | 1.33 ± 0.28 | 11.80 ± 0.2 | 9.38 ± 0.1 |
| LH1 | 8.37 ± 0.36 | 8.37 ± 0.38 | 63.7 ± 5.1 | 24.6 ± 2.3 | 0.51 ± 0.13 | 0.53 ± 0.31 | 1.14 ± 0.21 | 11.62 ± 0.2 | 12.35 ± 0.2 |
| LH2 | 8.23 ± 0.43 | 9.57 ± 0.53 | 20.4 ± 4.2 | 31.8 ± 2.9 | 0.21 ± 0.03 | 0.29 ± 0.03 | 0.71 ± 0.53 | 10.22 ± 0.2 | 8.67 ± 0.1 |
| LH3 | 8.08 ± 0.53 | 9.87 ± 0.37 | 61.8 ± 1.1 | 25.5 ± 3.3 | 0.10 ± 0.03 | 0.42 ± 0.11 | 1.14 ± 0.13 | 7.94 ± 0.2 | −5.00 ± 0.1 |
| LH4 | 8.53 ± 0.38 | 10.07 ± 0.49 | 68.2 ± 1.6 | 25.4 ± 2.5 | 0.24 ± 0.11 | 0.41 ± 0.15 | 1.35 ± 0.23 | 8.10 ± 0.1 | 2.52 ± 0.1 |
| DX1 | 8.20 ± 0.31 | 8.79 ± 0.33 | 110.9 ± 2.1 | 30.2 ± 1.6 | 1.61 ± 0.55 | 3.31 ± 0.41 | 5.12 ± 0.53 | 8.84 ± 0.2 | 1.01 ± 0.2 |
| DX2 | 8.09 ± 0.45 | 8.66 ± 0.53 | 129.5 ± 3.6 | 33.1 ± 1.7 | 0.57 ± 0.11 | 0.72 ± 0.23 | 1.30 ± 0.39 | 13.64 ± 0.2 | −1.47 ± 0.1 |
| DX3 | 8.84 ± 0.34 | 11.38 ± 0.56 | 47.7 ± 1.8 | 25.9 ± 2.2 | 0.46 ± 0.18 | 0.34 ± 0.02 | 1.68 ± 0.32 | 5.04 ± 0.2 | −12.26 ± 0.1 |
| DX4 | 8.56 ± 0.53 | 10.53 ± 0.43 | 54.8 ± 1.9 | 32.7 ± 2.2 | 0.24 ± 0.02 | 0.43 ± 0.11 | 1.14 ± 0.13 | 10.05 ± 0.2 | −8.96 ± 0.1 |
| River Name | NM (‰) | OM (‰) | Contributions of the Respective Sources | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Fertilizer (%) | Soil Organic N (%) | Sewage (%) | |||
| Zhihugang river | 7.51 | −4.46 | 5.43–19.45 | 75.06–79.47 | 1.44–17.04 |
| Liangxi river | 12.51 | 4.49 | 7.68–9.85 | 27.89–35.63 | 56.70–71.13 |
| Lihe river | 9.47 | 4.63 | 15.50–26.97 | 33.24–41.20 | 35.43–48.51 |
| Daxigang river | 9.39 | 5.42 | 17.79–29.01 | 30.09–38.48 | 35.06–49.36 |
| Value of different NO3−-N sources | |||||
| chemical fertilizer a | 0–0.8 | 17 c–19 | |||
| soil organic N a | 6.6–9 | −10–−9 | |||
| Sewage b | 15–16.3 | 10–11 | |||
| River Name | Annual Amounts of NO3−-N (ton) | Respective Sources Imported (ton) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Fertilizer | Soil Organic N | Sewage | ||
| Zhihugang river | 1078.8 | 58.5–209.8 | 809.8–857.3 | 15.5–183.8 |
| Liangxi river | 33.5 | 2.5–3.3 | 9.3–11.9 | 19..3–23.8 |
| Lihe river | 44.13 | 6.8–11.9 | 14.6–15.7 | 15.6–21.4 |
| Daxigang river | 157.2 | 27.9–45.6 | 47.3–60.4 | 55.1–77.5 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, D.; Jiang, X.; Zheng, B. Using δ15N and δ18O Signatures to Evaluate Nitrate Sources and Transformations in Four Inflowing Rivers, North of Taihu Lake. Water 2017, 9, 345. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9050345
Li D, Jiang X, Zheng B. Using δ15N and δ18O Signatures to Evaluate Nitrate Sources and Transformations in Four Inflowing Rivers, North of Taihu Lake. Water. 2017; 9(5):345. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9050345
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Da, Xia Jiang, and Binghui Zheng. 2017. "Using δ15N and δ18O Signatures to Evaluate Nitrate Sources and Transformations in Four Inflowing Rivers, North of Taihu Lake" Water 9, no. 5: 345. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9050345
APA StyleLi, D., Jiang, X., & Zheng, B. (2017). Using δ15N and δ18O Signatures to Evaluate Nitrate Sources and Transformations in Four Inflowing Rivers, North of Taihu Lake. Water, 9(5), 345. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9050345