Identification of Waters Incorporated in Laguna Lake, Republic of the Philippines, Based on Oxygen and Hydrogen Isotopic Ratios
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- The water resources of Laguna Lake are used for various competing purposes, including agriculture, industry, cultivation, drinking, transportation, and leisure. Therefore, it is increasingly important to develop water resource management policies.
- Rapid urbanization and development of industry and commerce from the northwestern to the western shores of Laguna Lake have led to land use changes that have resulted in water pollution and ecosystem degradation.
2. Materials and Methods
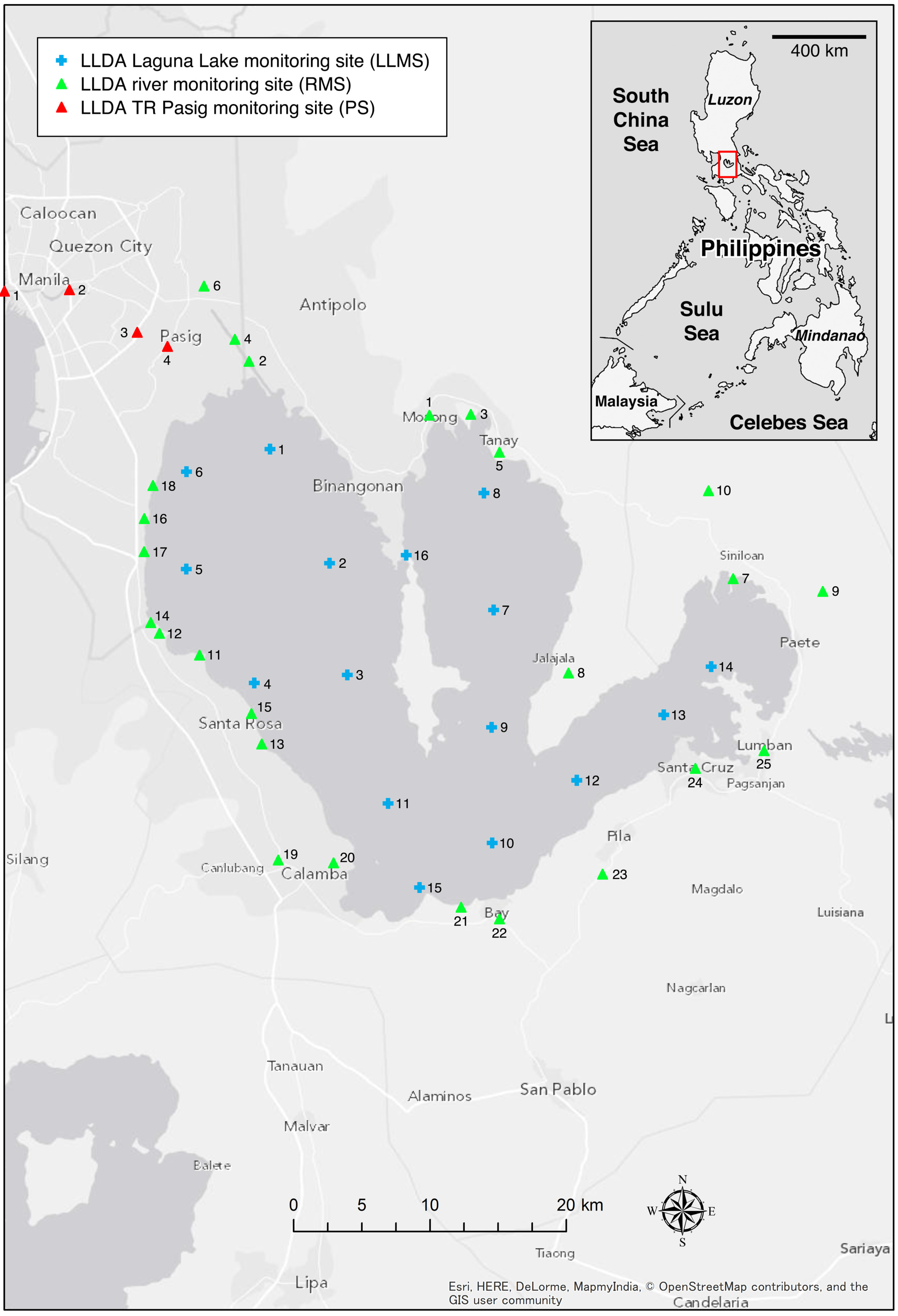
2.1. Water Samples
2.2. Analytical Procedures
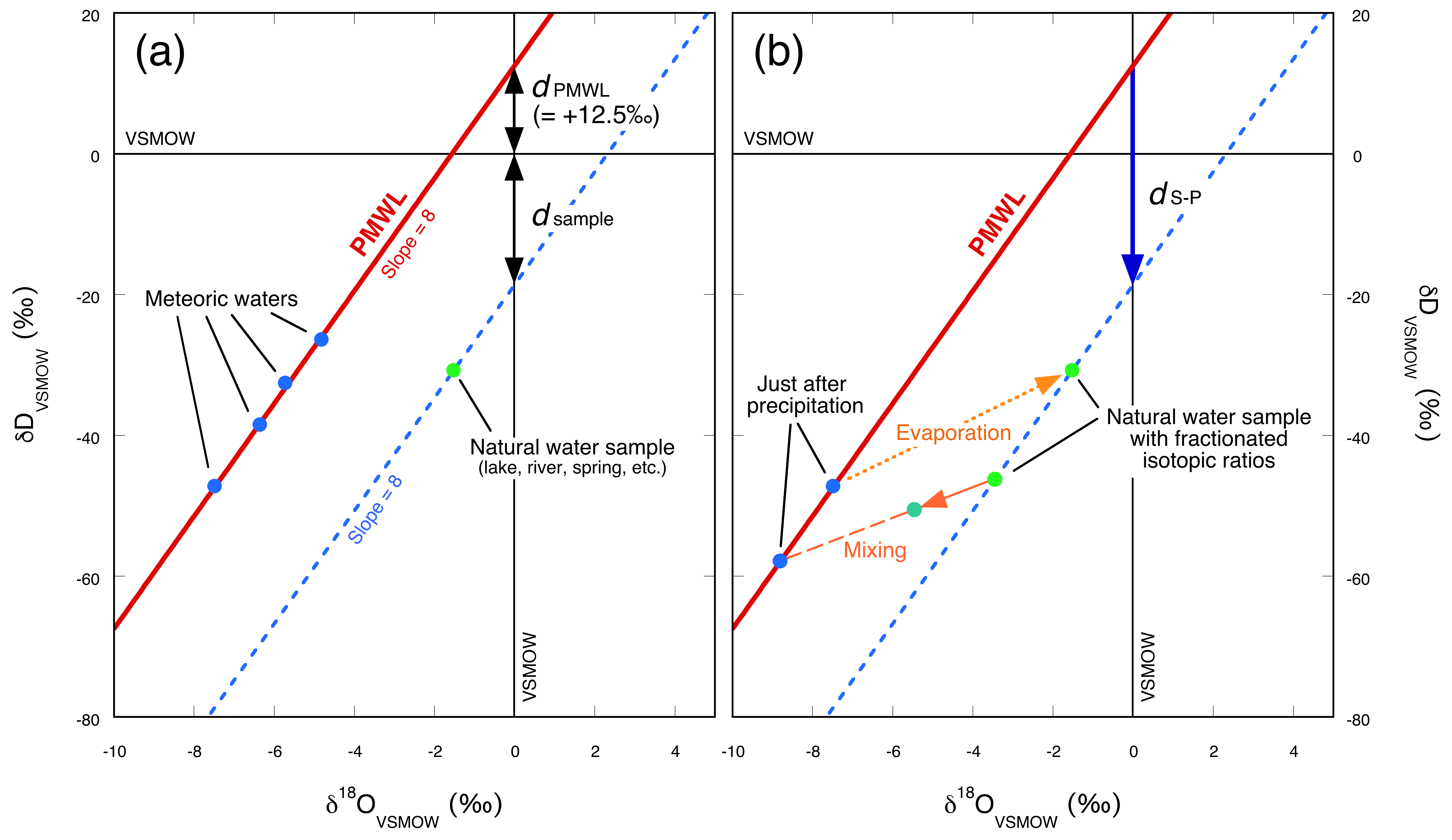
2.3. Meteoric Water Line and Deuterium Excess
3. Results
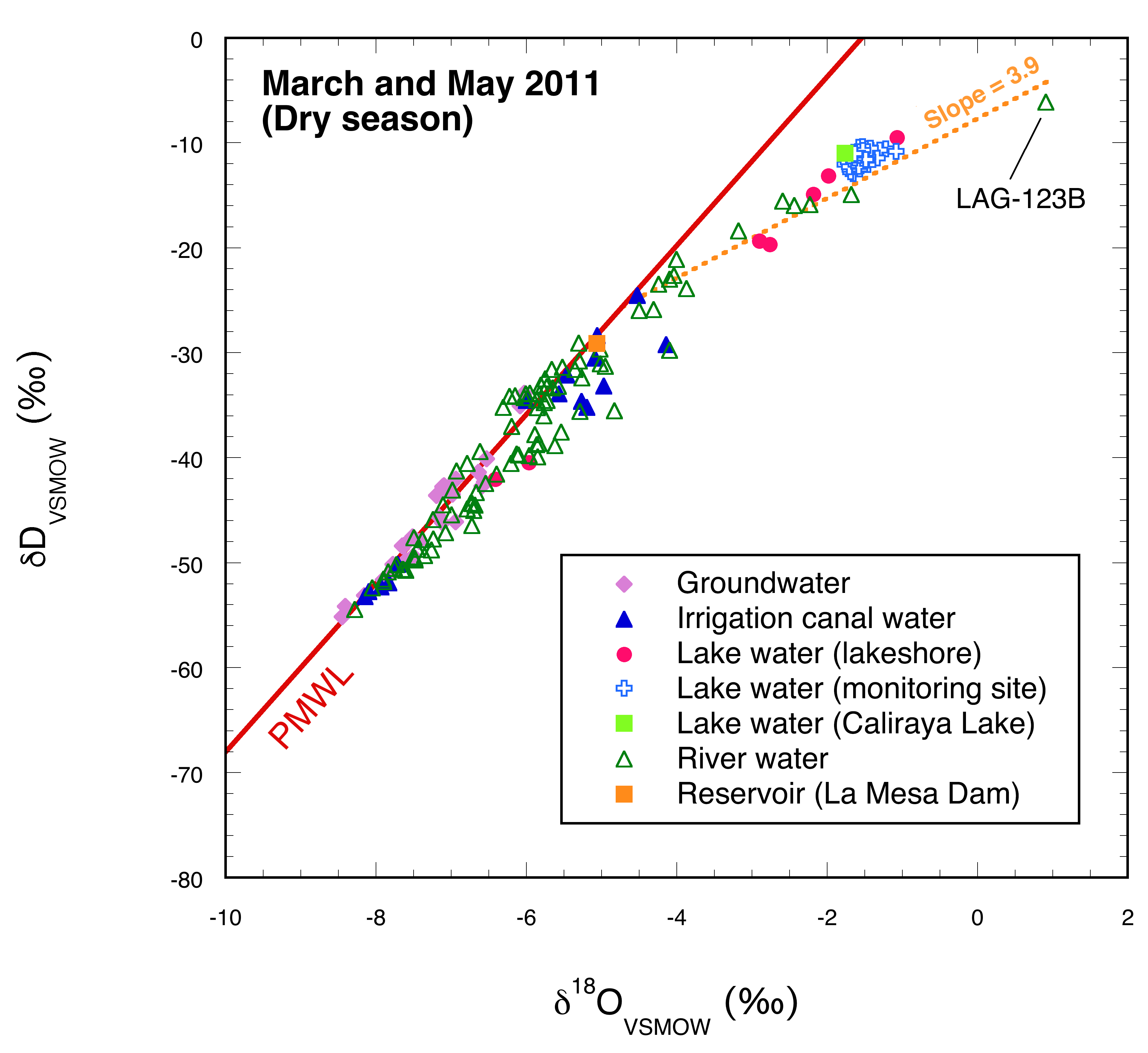
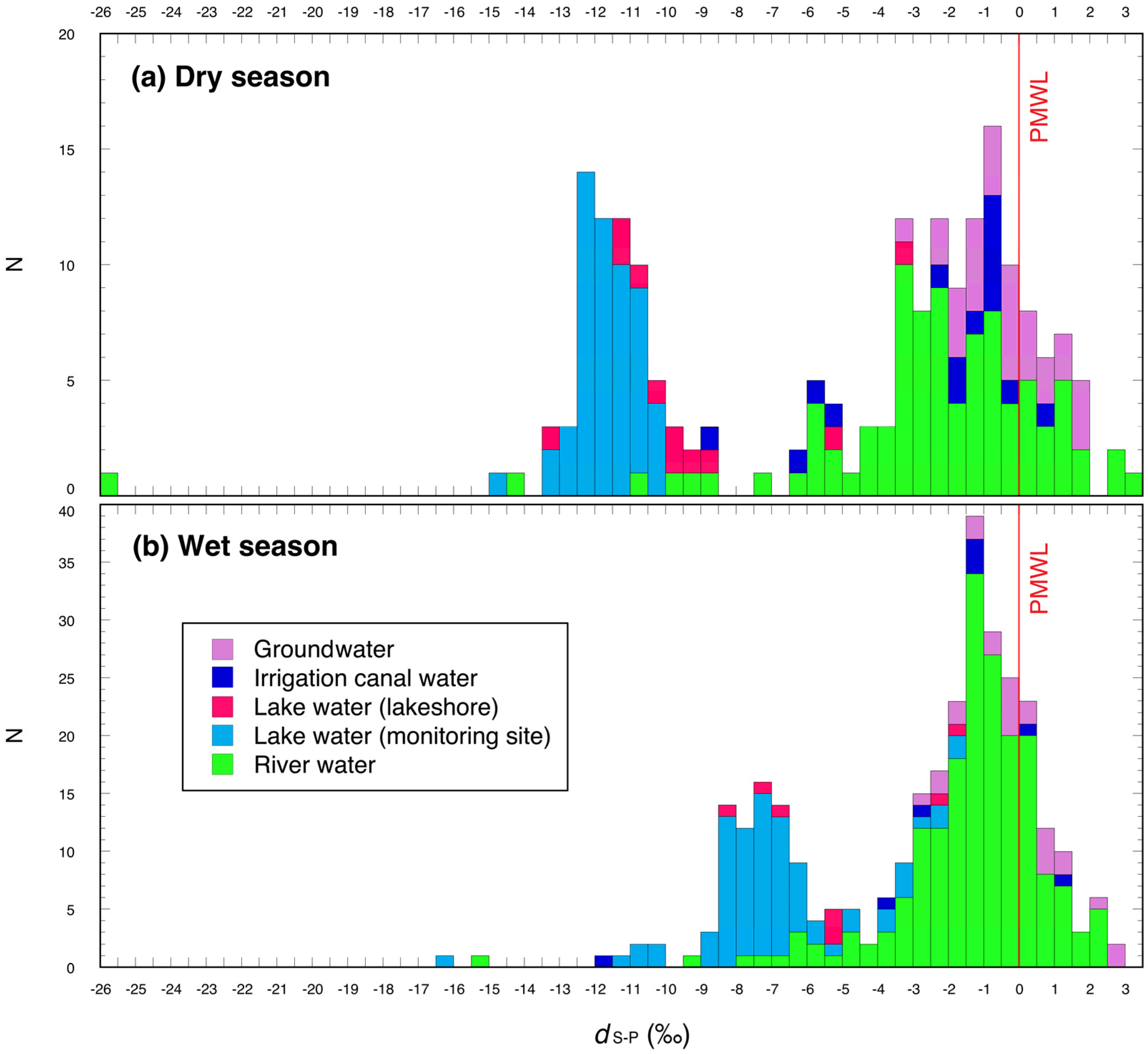
3.1. Dry Season
3.2. Wet Season
3.2.1. August 2011
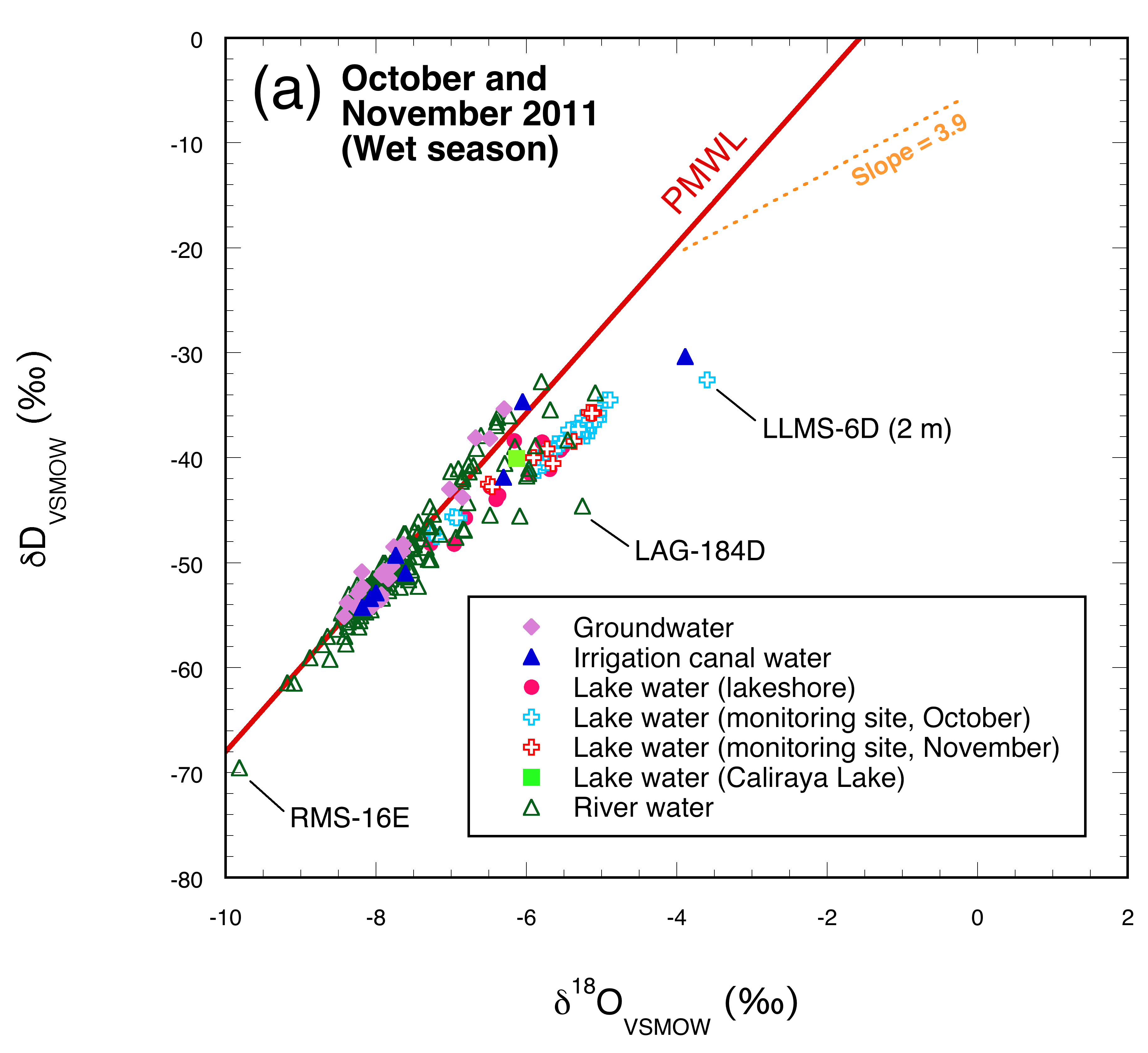
3.2.2. October and November 2011
4. Discussion
4.1. Dry Season
4.2. Wet season
4.3. Factors Controlling the Isotopic Properties of Laguna Lake
- Water from the original Laguna Lake system.
- Surface waters from rivers and irrigation canals.
- Groundwater incorporated into the rivers and that was directly incorporated into Laguna Lake.
- Rainwater falling directly onto Laguna Lake that was incorporated into the groundwater and surface water in the catchment area of the lake.
- Evaporative concentration of the water isotopes of Laguna Lake and of the groundwater and surface water in the water catchment area.
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CRDS | Cavity Ring-Down Spectrometer |
| GMWL | Global Meteoric Water Line |
| IRMS | Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometer |
| IAEA | International Atomic Energy Agency |
| JICA | Japan International Cooperation Agency |
| LLDA | Laguna Lake Development Authority |
| PMWL | Philippines Meteoric Water Line |
| RIHN | Research Institute for Humanity and Nature |
| OA-ICOS | Off-Axis Integrated Cavity Output Spectrometer |
| VSMOW | Vienna Standard Mean Ocean Water |
References
- Shikiomanov, I.A. Chapter 2 World fresh water resources. In Water in Crisis: A Guide to the World’s Fresh Water Resources; Gleick, P.H., Ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1993; pp. 13–24. [Google Scholar]
- Nakagami, K.; Kubota, J.; Setiawan, B.I. (Eds.) Sustainable Water Management; Springer: Singapore, 2016; p. 189. [Google Scholar]
- Kashiwagi, S.; Abe, M. International contribution to restore ecosystem services at inland waters environment: In the case of Laguna Lake in the Philippines. Jpn. Riverfront Res. Cent. Rep. 2012, 23, 127–128. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Laguna Lake Development Authority (LLDA). Available online: http://www.llda.gov.ph/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=74&Itemid=475 (accessed on 27 March 2017).
- Duyanen, J.P.; Siringan, F.P.; Santos, M.G.D.; Jaraula, C.M.B. Data Base and Methodology. In Sedimentation Patterns, Sediment Quality and Bathymetry of Laguna de Bay: Establishing Environmental Baselines for Lake Management Using the Sediment Record, Final Report; National Institute of Geological Sciences University of the Philippines Diliman and U. P. Science Research Foundation: Quezon City, Philippines, 2000; pp. 2–22. [Google Scholar]
- National Water Resources Council. Philippine Water Resources, First Assessment; Report No. 19; National Water Resources Council: Quezon City, Philippines, 1976.
- National Statistical Coordination Board. Philippine Water Resources. In Philippine Asset Accounts: Forest, Land/Soil, Fishery, Mineral, and Water Resources; Bartelmus, P., Alfieri, A., Eds.; ENRA Report No., 2; National Statistical Coordination Board: Manila, Philippines, 1998; pp. 171–227. [Google Scholar]
- Greenpeace. The State of Water Resources in the Philippines; Greenpeace Southeast Asia: Quezon City, Philippines, 2007; p. 49. [Google Scholar]
- Santos-Borja, A.; Nepomuceno, D.N. Laguna de Bay: Institutional development and charge for lake basin management. Lakes Reserv. Res. Manag. 2006, 11, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Public Works and Highways (DPWH) of JICA. Manual on flood control planning. Project for the Enhancement of Capabilities in Flood Control and Sabo Engineering of the DPWH. 2003, p. 123. Available online: https://www.jica.go.jp/project/philippines/0600933/04/pdf/Manual_on_FC_Planning.pdf (accessed on 27 March 2017).
- Nakagiri, T.; Kato, H.; Maruyama, S.; Hashimoto, S. Hydrogeochemical Assessment of the Contribution of Caldera Lake and Paddy Irrigation to River Water Stability. In Sustainable Water Management: New Perspectives, Design, and Practices; Nakagami, K., Kubota, J., Setiawan, B.I., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2016; pp. 81–95. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, M.S., Jr.; Rabanal, H.R. The Napindan hydraulic control structure and its effects on fish production on Laguna Lake Philippines. J. Aquacult. Trop. 1988, 3, 47–62. [Google Scholar]
- Barril, C.R.; Tumlos, E.T.; Moraga, W.C. Seasonal variations in water quality of Laguna de Bay, Philippines: Trends and implications. Philipp. Agric. Sci. 2001, 84, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Barril, C.R.; Tumlos, E.T. Water quality trends and trophic state assessment of Laguna de Bay, Philippines. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2002, 5, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varca, L.M. Pesticide residues in surface waters of Pagsanjan-Lumban catchment of Laguna de Bay, Philippines. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 106, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manila, Luzon Climate Manila, Luzon Temperatures Manila, Luzon Weather Averages. Available online: http://www.manila.climatemps.com/ (accessed on 27 March 2017).
- Maruyama, S.; Tada, Y. Comparison of cavity ring-down spectroscopy with isotope ratio mass spectrometry for measurements of water isotopes. Geochem. J. 2014, 48, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Hirayama, S.; Kusakabe, M.; Zhang, J.; Nakano, T. High-precision measurements of water isotopes using laser absorption spectroscopy. Geochem. J. 2013, 47, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, H. Isotopic variations in meteoric waters. Science 1961, 133, 1702–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozanski, K.; Araguás-Araguás, L.; Gonfiantini, R. Isotopic patterns in modern global precipitation. In Climate Change in Continental Isotopic Records; Swart, P.K., Lohmann, K.C., McKenzie, J., Savin, S., Eds.; Geophysical Monograph No. 78; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 1993; pp. 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Salonga, N.D. Estimating the Isotopic Composition of Meteoric Water Index in Geothermal Fields in the Philippines. In Proceedings of the World Geothermal Congress 2015, Melbourne, Australia, 19–25 April 2015; p. 7. [Google Scholar]
- Dansgaard, W. Stable isotopes in precipitation. Tellus 1964, 16, 436–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IAEA Global Network for Isotopes in Precipitation (GNIP). Available online: https://nucleus.iaea.org/Pages/GNIPR.aspx (accessed on 27 March 2017).
- Gerardo-Abaya, J. Determination of recharge from stable isotope data to the hydrological systems in the southern Negros geothermal field and its environs, Philippines. In Proceedings of the World Geothermal Congress 2005, Antalya, Turkey, 24–29 April 2005; p. 8. [Google Scholar]
- Gat, J.R. The stable isotope composition of Dead Sea waters. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1984, 71, 361–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, G.B.; Brown, R.M.; Fritz, P. Estimation of the isotopic composition of lake evaporate. J. Hydrol. 1979, 42, 109–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyahara, S.; Hiroyuki, II; Dahlhaus, P. Proposal of measurement method for evaporation rate for surface water using oxygen isotope in dry area. J. Jpn. Soc. Civ. Eng. Ser. B1 2014, 70, I_1603–I_1608. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Cunanan, A.M.; Salvacion, J.W.L. Analysis of water temperature of Laguna Lake using EFDC model. Int. J. Sci. Technol. Res. 2014, 3, 68–76. [Google Scholar]


| Season/Month | Groundwater | River Water | Irrigation Canal Water | Lake Water (Monitoring Site) | Lake Water (Lakeshore) | Lake Water (Caliraya Lake) | Reservoir (La Mesa Dam) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry season | |||||||
| March | 7 | 20 | 4 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| May | 21 | 69 | 11 | 54 | 7 | 1 | 1 |
| Wet season | |||||||
| August | 0 | 26 | 0 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| October | 18 | 87 | 4 | 54 | 12 | 1 | 0 |
| November | 7 | 77 | 4 | 9 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Total (Dry) | 28 | 89 | 15 | 54 | 10 | 1 | 1 |
| Total (Wet) | 25 | 190 | 8 | 75 | 13 | 1 | 0 |
| Total | 53 | 279 | 23 | 129 | 23 | 2 | 1 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maruyama, S.; Kato, H. Identification of Waters Incorporated in Laguna Lake, Republic of the Philippines, Based on Oxygen and Hydrogen Isotopic Ratios. Water 2017, 9, 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9050328
Maruyama S, Kato H. Identification of Waters Incorporated in Laguna Lake, Republic of the Philippines, Based on Oxygen and Hydrogen Isotopic Ratios. Water. 2017; 9(5):328. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9050328
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaruyama, Seiji, and Hisaaki Kato. 2017. "Identification of Waters Incorporated in Laguna Lake, Republic of the Philippines, Based on Oxygen and Hydrogen Isotopic Ratios" Water 9, no. 5: 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9050328
APA StyleMaruyama, S., & Kato, H. (2017). Identification of Waters Incorporated in Laguna Lake, Republic of the Philippines, Based on Oxygen and Hydrogen Isotopic Ratios. Water, 9(5), 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9050328





