Understanding the Role of Groundwater in a Remote Transboundary Lake (Hulun Lake, China)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
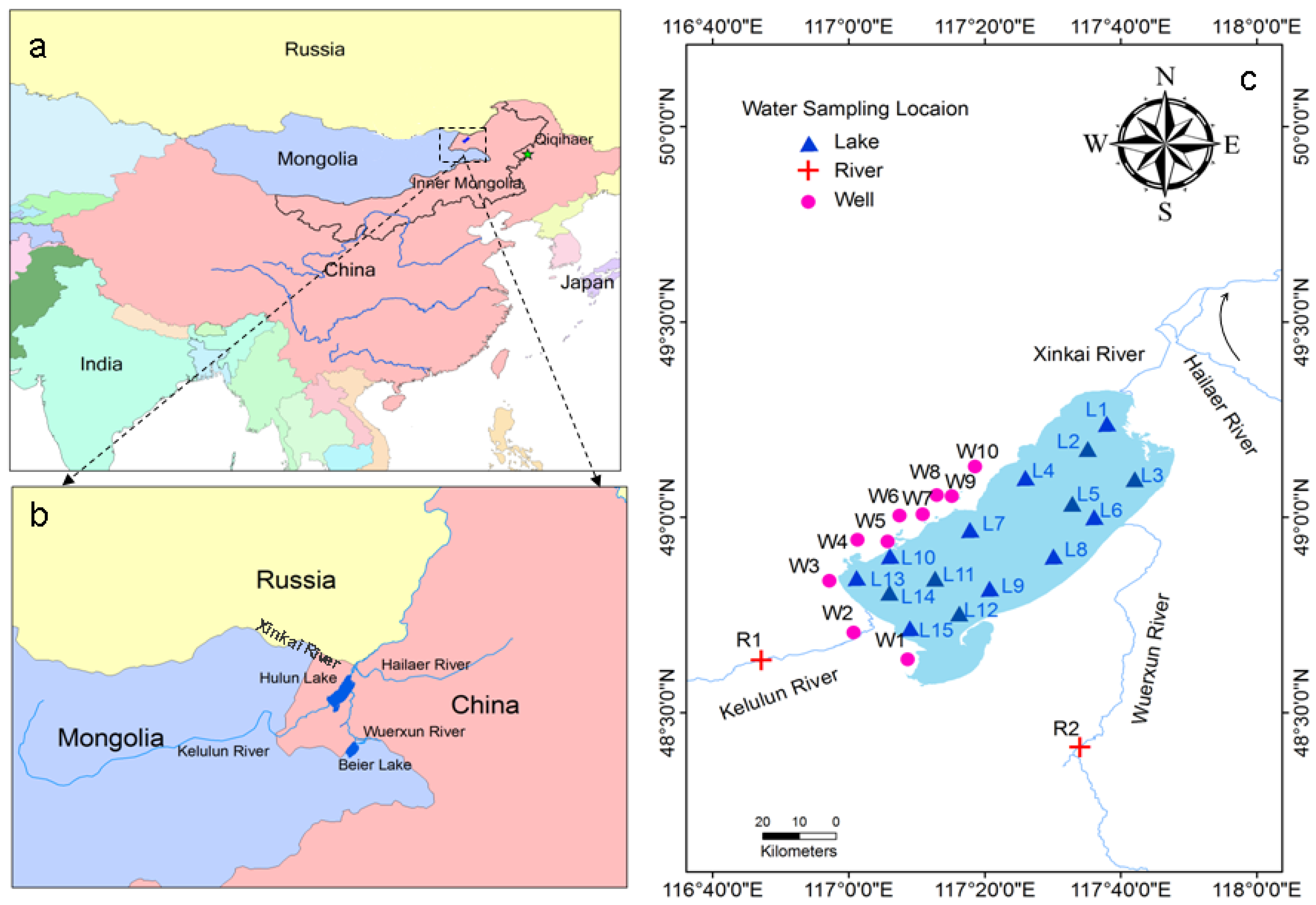
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Field Sampling and Analytical Methods
2.3. Average Annual Lake Water Balance
2.4. Estimation of Evaporative Loss Based on the Stable Isotope Composition
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Changes in Hydrological Budget and Net Groundwater
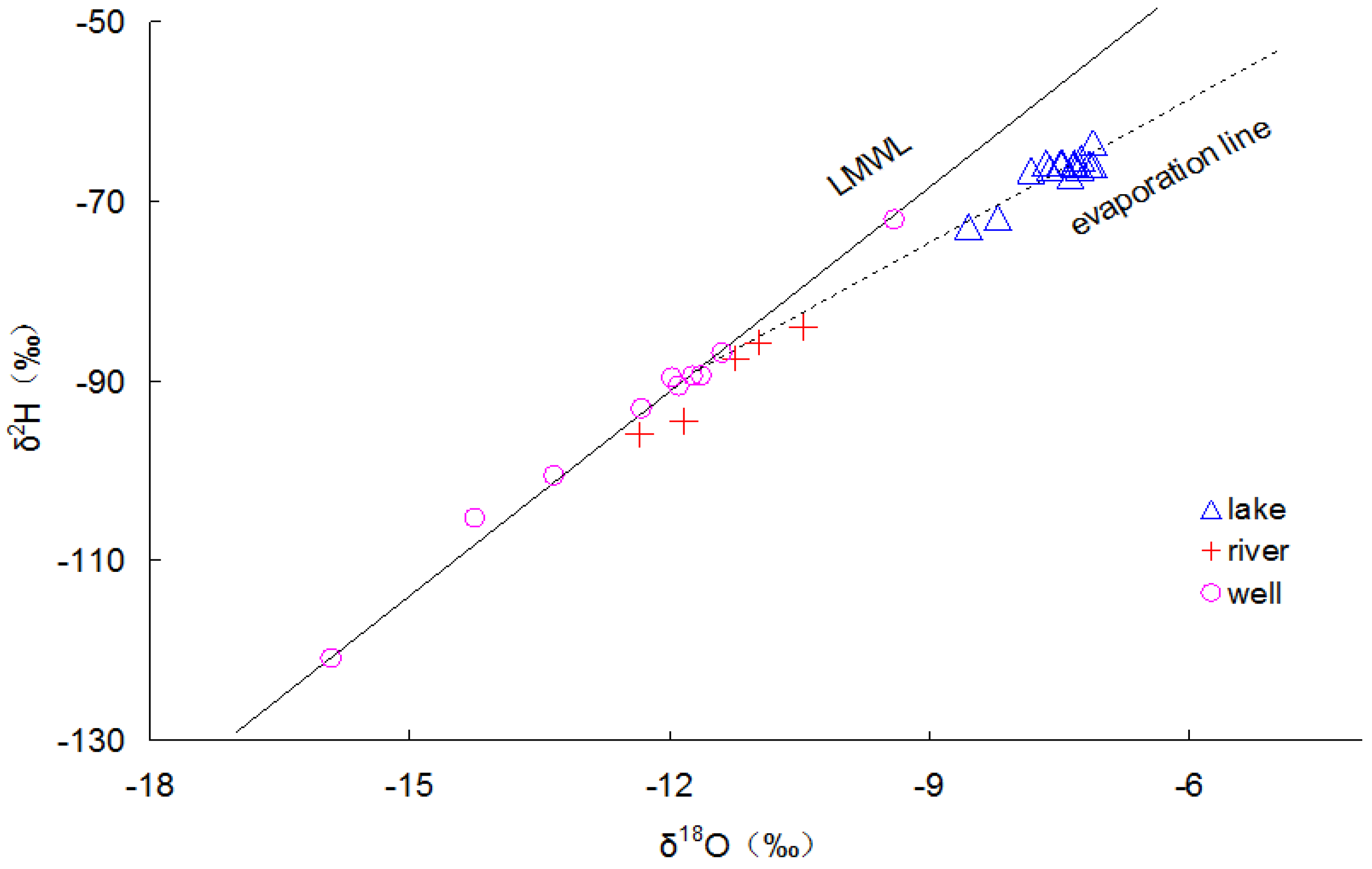
3.2. Isotopic Composition and Chloride Concentrations in Present Day Hulun Lake and Its Water Sources
3.3. Evaporative Loss Calculations as an Indication of Saline Groundwater Discharge to Hulun Lake
3.3.1. Evaporative Loss Calculations and Their Uncertainty
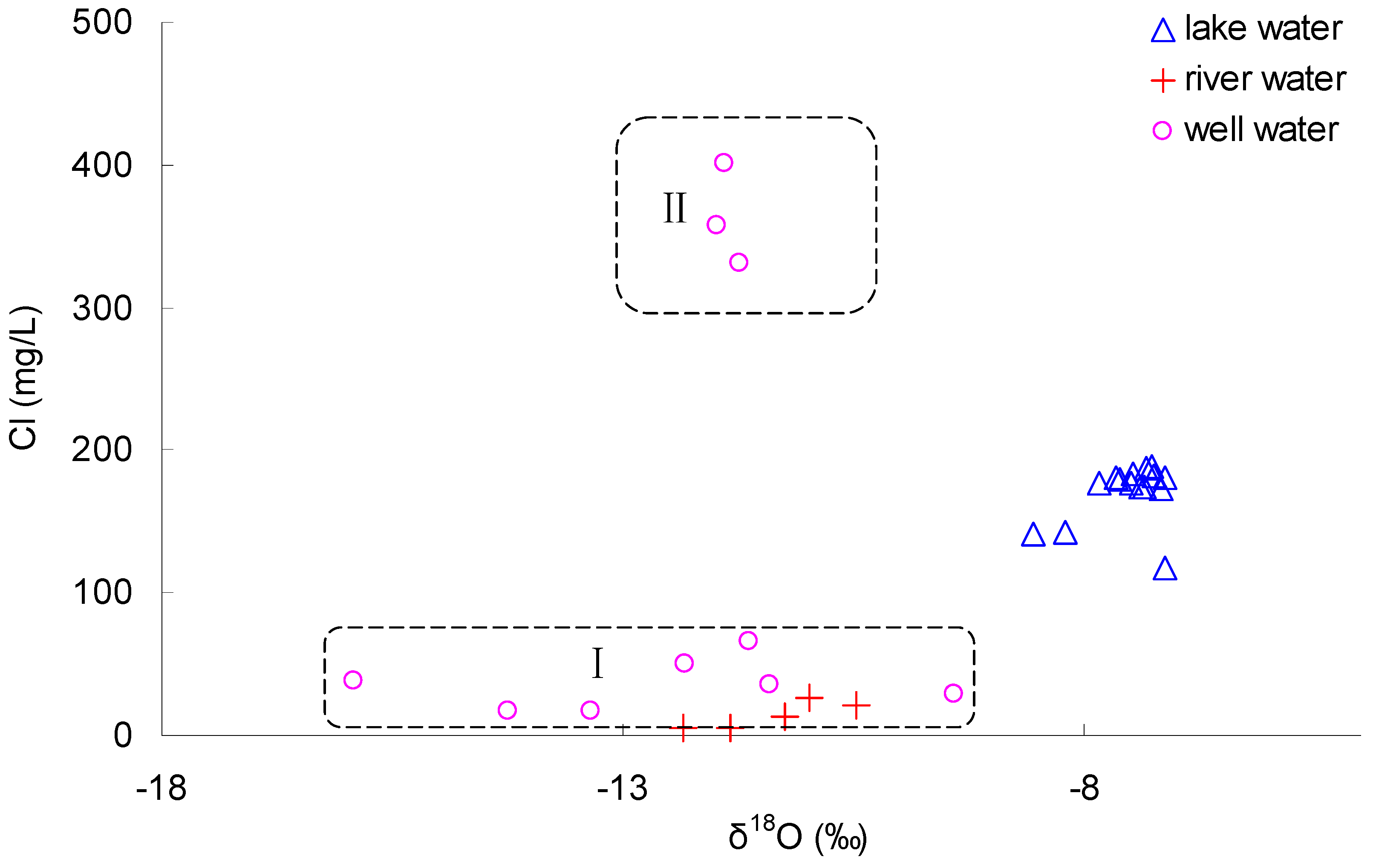
3.3.2. Evidence of Groundwater Discharge with High Salinity to Hulun Lake
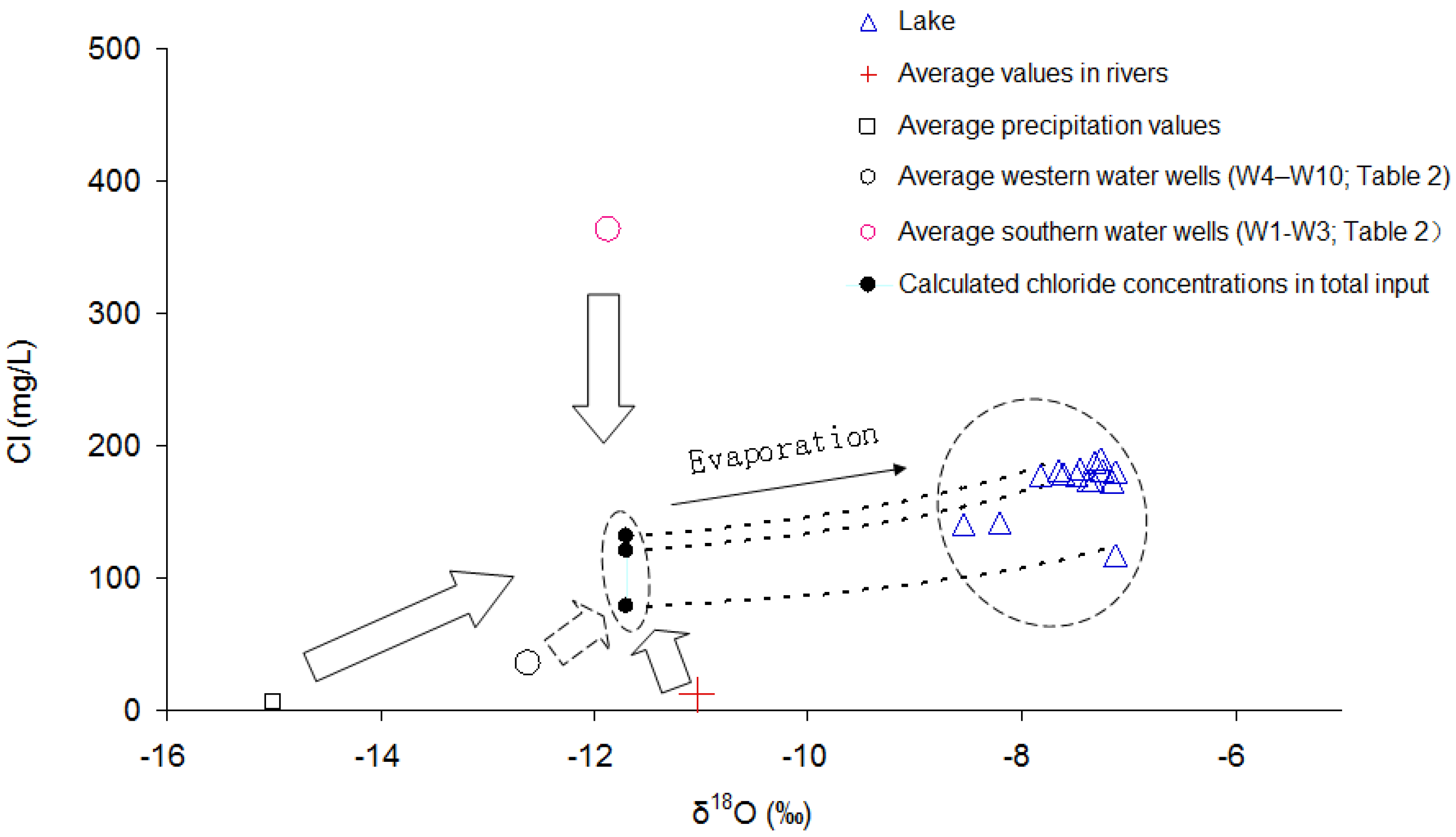
3.4. The Chloride Mass Balance on Hulun Lake Inflow
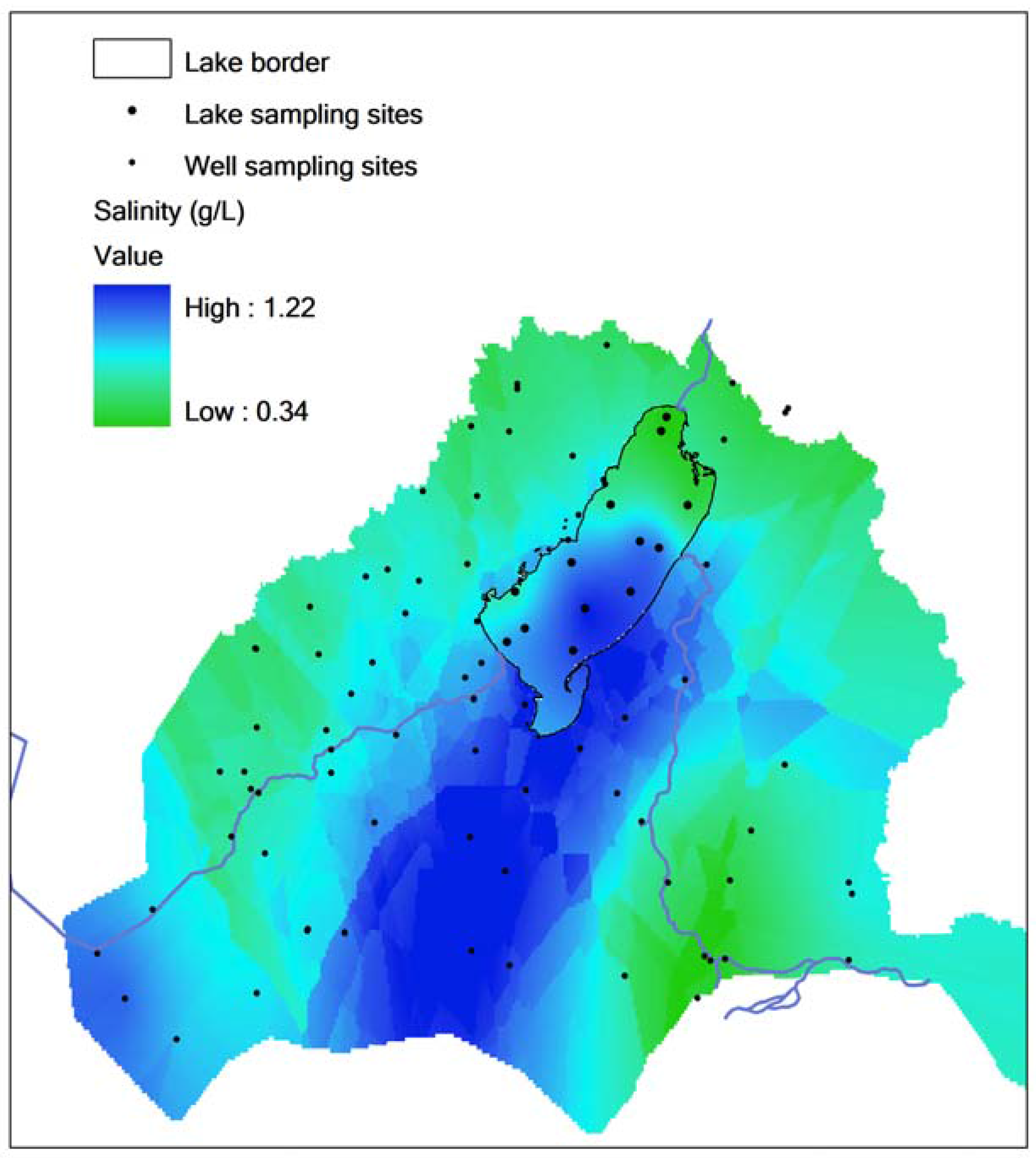
3.5. Additional Evidence for High Chloride in Groundwater Supplies South of Hulun Lake
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Helfer, F.; Lemckert, C.; Zhang, H. Impacts of climate change on temperature and evaporation from a large reservoir in Australia. J. Hydrol. 2012, 475, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.Q.; Huang, B.; Ke, L.H.; Richards, K.S. Remote sensing of alpine lake water environment changes on the Tibetan Plateau and surroundings: A review. ISPRS. J. Photogramm. 2014, 92, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Jin, T.; Li, C.; Ofterdinger, U.; Zhang, S.; Ding, Aizhong.; Li, J. Is China’s fifth-largest inland lake to dry-up? Incorporated hydrological and satellite-based methods for forecasting Hulun lake water levels. Adv. Water Resour. 2016, 94, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chuai, X.; Yang, L.; Zhao, H. Climatic warming and overgrazing induced the high concentration of organic matter in Lake Hulun, a large shallow eutrophic steppe lake in northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 431, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuai, X.; Chen, X.; Yang, L.; Zeng, J.; Miao, A.; Zhao, H. Effects of climatic changes and anthropogenic activities on lake eutrophication in different ecoregions. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 9, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Feng, W.; Zhang, L.; Zong, Z.; Meng, H.; Peng, B.; Li, Z. Monitoring and evaluation on water quality and biology resource quantity in Hulun lake. J. Hydroecology 2011, 32, 64–68. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, F.; Wang, S.; Wang, F. Annals of Hulun Lake (Ⅱ); Inner Mongolia Culture: Inner Mongolia, China, 2008. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Ma, W.; Ye, B.; Liao, W. Estimation of water evaporation and water balance in ungauged Hulun lake. J. China Hydrol. 2006, 26, 41–44. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yan, D.; Yan, H.; Deng, W.; Wang, M. Influences of eco-hydrological process to water environmental system in Hulun Lake basin. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2001, 21, 1–5. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yu, G.; Shen, H. Lake water changes in response to climate change in northern China: Simulation and uncertainty analysis. Quatern. Int. 2010, 212, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xie, H.; Yao, T.; Kang, S. Water balance estimates of ten greatest lakes in China using ICESat and Landsat data. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 3815–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuber, A. On the environmental isotope method for determining the water balance of some lakes. J. Hydrol. 1983, 6, 409–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krabbenhoft, D.P.; Bowser, C.J.; Anderson, M.P.; Valley, J.W. Estimating groundwater exchange with lakes 1. The stable isotope mass balance method. Water Resour. Res. 1990, 26, 2445–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, J.J.; Prepas, E.E.; McEachern, P. Quantitative comparison of lake throughflow, residency, and catchment runoff using stable isotopes: Modelling and results from a survey of boreal lakes. J. Hydrol. 2002, 262, 128–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, K.E.; Gibson, J.J.; McEachern, P. Water yield estimates for critical loadings assessment: Comparisons of gauging methods vs. an isotopic approach. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2008, 65, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyamani, M.S. Isotopic composition of rainfall and groundwater recharge in the western province of Saudi Arabia. J. Arid Environ. 2001, 49, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, J.; Edwards, T.; Birks, S.; Amour, N.; Buhay, W.; McEachern, P.; Wolfe, B.; Peters, D. Progress in isotope tracer hydrology in Canada. Hydrol. Process. 2005, 19, 303–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carol, E.; Kruse, E.; Mas-Pla, J. Hydrochemical and isotopical evidence of ground water salinization processes on the coastal plain of Samborombo´n Bay, Argentina. J. Hydrol. 2009, 365, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassenaar, L.I.; Athanasopoulos, P.; Hendry, M.J. Isotope hydrology of precipitation, surface and ground waters in the Okanagan Valley, British Columbia. Can. J. Hydrol. 2011, 411, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanduc, T.; Mori, N.; Kocman, D.; Stibilj, V.; Grassa, F. Hydrogeochemistry of Alpine springs from North Slovenia: insights from stable isotopes. Chem. Geol. 2012, 300, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.; Li, X. Characteristics of stable isotope and hydrochemistry of the groundwater around Qinghai Lake, NE Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 1159–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currell, M.J.; Dahlhaus, P.; Ii, H. Stable isotopes as indicators of water and salinity sources in a southeast Australian coastal wetland: Identifying relict marine water, and implications for future change. Hydrogeol. J. 2015, 23, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, I.D.; Frjtz, P. Environmental Isotopes in Hydrogeology; Lewis Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, J.J.; Edwards, T.W.D.; Bursey, G.G. Estimating evaporation using stable isotopes. Nord. Hydrol. 1993, 24, 79–94. [Google Scholar]
- Kirchner, J.; Tetzlaff, D.; Soulsby, C. Comparing chloride and water isotopes as hydrological tracers in two Scottish catchments. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 1631–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Jiang, F.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Z; Sun, L. Annals of Hulun Lake; Jilin Literature and History Publishing House Press: Jilin, China, 1989; pp. 691–692. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, B.; Li, C.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, S. Analysis of Hulun digital basin based on spatial information technology. Environ. Pollut. Control. 2010, 32, 5–19. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wen, R.; Xiao, J.; Chang, Z.; Zhai, D.; Xu, Q.; Li, Y.; Itoh, S.; Lomtatidze, Z. Holocene climate changes in the mid-high-latitude-monsoon margin reflected by the pollen record from Hulun Lake, northeastern Inner Mongolia. Quatern, Res. 2010, 73, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, H.; Gordon, L.I. Deuterium and oxygen 18 variations in the ocean and the marine atmosphere. In Stable Isotopes in Oceanographic Studies and Paleotemperatures; Ongiorgi, E., Ed.; Laboratorio di Geologia Nucleare: Pisa, Italy, 1965; pp. 9–130. [Google Scholar]
- Gonfiantini, R. Environmental isotopes in lake studies. In Handbook of Environmental Isotope Geochemistry; Volume 2: The Terrestrial Environment; Fritz, P., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1986; pp. 113–163. [Google Scholar]
- Gat, J.R. Stable isotopes of fresh and saline lakes. In Physics and Chemistry of Lakes; Lerman, D.I., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1995; pp. 139–165. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, J.J. Short-term evaporation and water budget comparisons in shallow Arctic lakes using non-steady isotope mass balance. J. Hydrol. 2002, 264, 242–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horita, J.; Rozanski, K.; Cohen, S. Isotope effects in the evaporation of water: A status report of the Craig–Gordon model. Isot. Environ. Health Stud. 2008, 44, 23–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gat, J.R.; Levy, Y. Isotope hydrology of inland Sabkhas in the Bardawil area. Sinai. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1978, 23, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gat, J.R. Properties of the isotopic species of water: the ‘‘isotope effect’’. In Stable Isotope Hydrology, Deuterium and Oxygen-18 in the Water Cycle; Gat, J.R., Gonfiantini, R., Eds.; IAEA Tech. Rep. Ser. No. 210; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 1981; pp. 7–19. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, J.J.; Reid, R. Water balance a chain of tundra lakes: a 20-years isotopic perspective. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 2148–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welhan, J.A.; Fritz, P. Evaporation pan isotopic behaviour as an index of isotopic evaporation conditions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta. 1977, 41, 682–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, G.B.; Leaney, F.W. Estimation of isotopic exchange parameters using constant-feed pans. J. Hydrol. 1982, 55, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, J.J.; Reid, R. Stable isotope fingerprint of open-water evaporative losses and effective drainage area fluctuations in a subarctic shield watershed. J. Hydrol. 2010, 381, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horita, J.; Wesolowski, D.J. Liquid-vapor fractionation of oxygen and hydrogen isotopes of water from the freezing to the critical temperature. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1994, 58, 3425–3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrzypek, G.; Mydłowski, A.; Dogramaci, S.; Hedley, P.; Gibson, J.J.; Grierson, P.F. Estimation of evaporative loss based on the stable isotope composition of water using Hydrocalculator. J. Hydrol. 2015, 523, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IAEA Global Network of isotopes in precipitation. The GNIP database, 2017. Available online: http://www.iaea.org/water (accessed on 16 May 2017).
- Mulligan, B.M.; Ryan, M.C.; Cámbara, T.P. Delineating volcanic aquifer recharge areas using geochemical and isotopic tools. Hydrogeol. J. 2011, 19, 1335–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, H. Isotope variations in meteoric waters. Science 1961, 133, 1702–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herczeg, A.L.; Dogramaci, S.S.; Leaney, F.W.J. Origin of dissolved salts in a large, semi-arid groundwater system: Murray Basin, Australia. Mar. Freshwatyer. Res. 2001, 52, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartwright, I.; Weaver, T.R.; Fifield, L.K. Cl/Br ratios and environmental isotopes as indicators of recharge variability and groundwater flow: An example from the southeast Murray Basin, Australia. Chem. Geol. 2006, 231, 38–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogramaci, S.; Firmani, G.; Hedley, P.; Skrzypek, G.; Grierson, P.F. Evaluating recharge to an ephemeral dryland stream using a hydraulic model and water, chloride and isotope mass balance. J. Hydrol. 2015, 521, 520–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Jin, M.; Liang, X.; Zhan, H. Estimating groundwater recharge beneath irrigated farmland using environmental tracers fluoride, chloride and sulfate. Hydrogeol. J. 2013, 21, 1469–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Li, C.; Sun, B.; Shi, X.; Fan, C. Solutes transport between lake water and sediment pore water during the lake water level fluctuation. J. Lake Sci. 2017, (unpublished; accepted). [Google Scholar]
| Year | Δ S | Qin | Qout | P | E | Δ V (GW) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1981–2013 | Water budget (108 m3) | −0.6 | 10.8 | 0.3 | 4.8 | 21.1 | 5.2 |
| % of total lake input | -- * | 52.2 | -- | 23.0 | -- | 24.8 | |
| 1981–2000 | Water budget (108 m3) | 1.8 | 14.5 | 0.6 | 5.7 | 20.4 | 24.8 |
| % of total lake input | -- | 63.6 | -- | 24.9 | -- | 11.4 | |
| 2001–2013 | Water budget (108 m3) | −4.3 | 5.4 | -- | 3.5 | 22.0 | 8.9 |
| % of total lake input | -- | 30.7 | -- | 19.4 | -- | 49.9 |
| Sample Type (and Date) | δ18O (‰) | δ2H (‰) | Cl (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lake water | |||
| L1 | −72.83 | −8.55 | 140.6 |
| L2 | −71.87 | −8.21 | 141.9 |
| L3 | −66.23 | −7.27 | 189.3 |
| L4 | −66.59 | −7.83 | 177.3 |
| L5 | −65.88 | −7.16 | 172.6 |
| L6 | −65.71 | −7.66 | 181.1 |
| L7 | −66.36 | −7.61 | 179.1 |
| L8 | −65.97 | −7.34 | 173.7 |
| L9 | −65.71 | −7.33 | 187.2 |
| L10 | −65.7 | −7.47 | 182.9 |
| L11 | −65.91 | −7.12 | 180.3 |
| L12 | −67.24 | −7.38 | 173.5 |
| L13 | −65.75 | −7.49 | 176.8 |
| L14 | −63.44 | −7.12 | 116.9 |
| L15 | −65.21 | −7.25 | 181.6 |
| Kelulun River | |||
| R1 (25 June 2014) | −11.84 | −94.48 | 5.0 |
| R1 (26 June 2014) | −12.35 | −95.99 | 5.7 |
| R1 (4 July 2014) | −10.98 | −85.72 | 25.8 |
| R1 (3 August 2014) | −10.46 | −84.00 | 21.0 |
| Wuerxun River | |||
| R2 (4 July 2014) | −11.24 | −87.56 | 12.6 |
| Domestic well water (south of Hulun Lake) | |||
| W1 | −11.74 | −89.43 | 330.7 |
| W2 | −11.90 | −90.52 | 400.7 |
| W3 | −11.98 | −89.61 | 357.8 |
| Domestic well water (west of Hulun Lake) | |||
| W4 | −11.40 | −86.86 | 35.6 |
| W5 | −9.41 | −72.02 | 28.7 |
| W6 | −12.33 | −93.05 | 49.8 |
| W7 | −13.34 | −100.54 | 17.0 |
| W8 | −11.64 | −89.38 | 65.6 |
| W9 | −14.25 | −105.24 | 17.2 |
| W10 | −15.91 | −120.87 | 38.4 |
| Site Name | E/I | Calculated Total Inflow [Cl] (mg/L) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calculated using δ2H | Calculated using δ18O | Mean | ||
| L1 | 0.33 | 0.20 | 0.27 | 112.5 |
| L2 | 0.36 | 0.23 | 0.30 | 109.3 |
| L3 | 0.56 | 0.32 | 0.44 | 128.7 |
| L4 | 0.55 | 0.26 | 0.41 | 131.2 |
| L5 | 0.58 | 0.33 | 0.46 | 115.6 |
| L6 | 0.59 | 0.28 | 0.44 | 130.4 |
| L7 | 0.56 | 0.28 | 0.42 | 129.0 |
| L8 | 0.57 | 0.31 | 0.44 | 119.8 |
| L9 | 0.59 | 0.31 | 0.45 | 129.2 |
| L10 | 0.59 | 0.3 | 0.45 | 128.0 |
| L11 | 0.58 | 0.33 | 0.46 | 120.8 |
| L12 | 0.52 | 0.31 | 0.42 | 119.7 |
| L13 | 0.58 | 0.29 | 0.44 | 125.5 |
| L14 | 0.69 | 0.33 | 0.51 | 78.4 |
| L15 | 0.61 | 0.32 | 0.47 | 123.5 |
| Average | 0.55 | 0.29 | 0.42 | 120.1 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, H.; Ryan, M.C.; Li, C.; Sun, B. Understanding the Role of Groundwater in a Remote Transboundary Lake (Hulun Lake, China). Water 2017, 9, 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9050363
Gao H, Ryan MC, Li C, Sun B. Understanding the Role of Groundwater in a Remote Transboundary Lake (Hulun Lake, China). Water. 2017; 9(5):363. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9050363
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Hongbin, M. Cathryn Ryan, Changyou Li, and Biao Sun. 2017. "Understanding the Role of Groundwater in a Remote Transboundary Lake (Hulun Lake, China)" Water 9, no. 5: 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9050363
APA StyleGao, H., Ryan, M. C., Li, C., & Sun, B. (2017). Understanding the Role of Groundwater in a Remote Transboundary Lake (Hulun Lake, China). Water, 9(5), 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9050363






