Impacts of Climate Change on the Water Quality of a Regulated Prairie River
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Water Quality Model
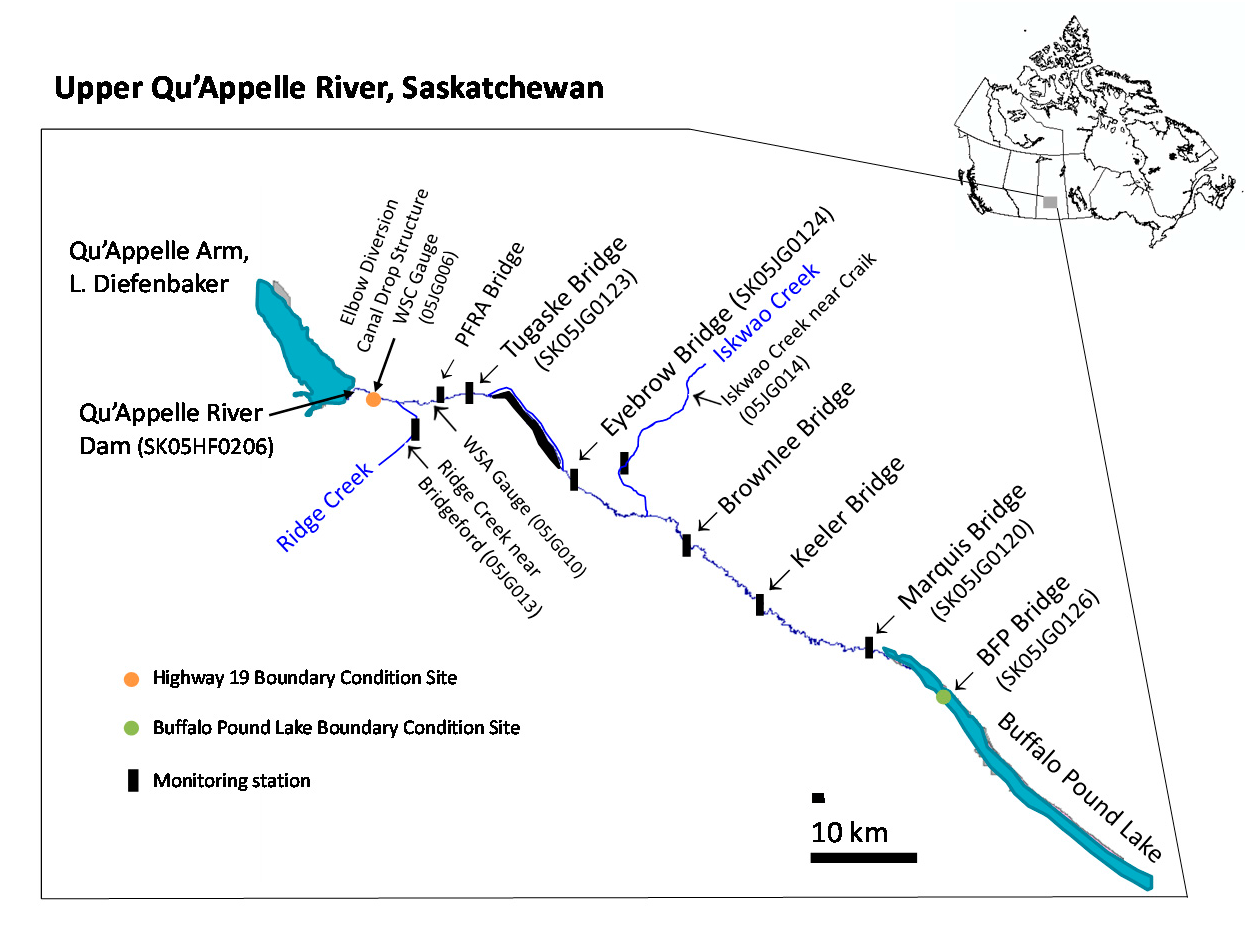
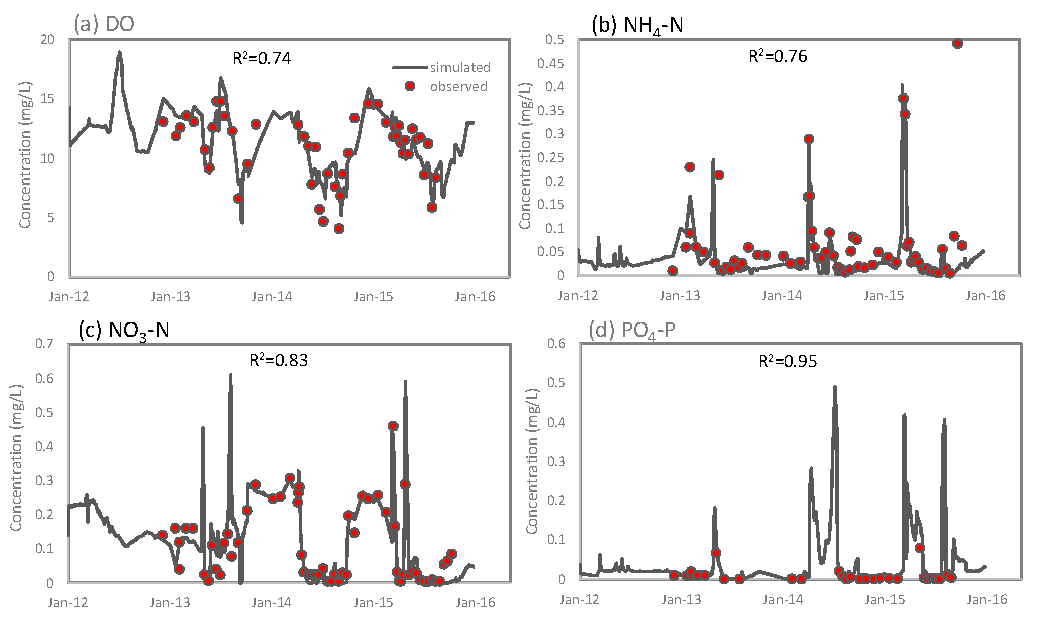
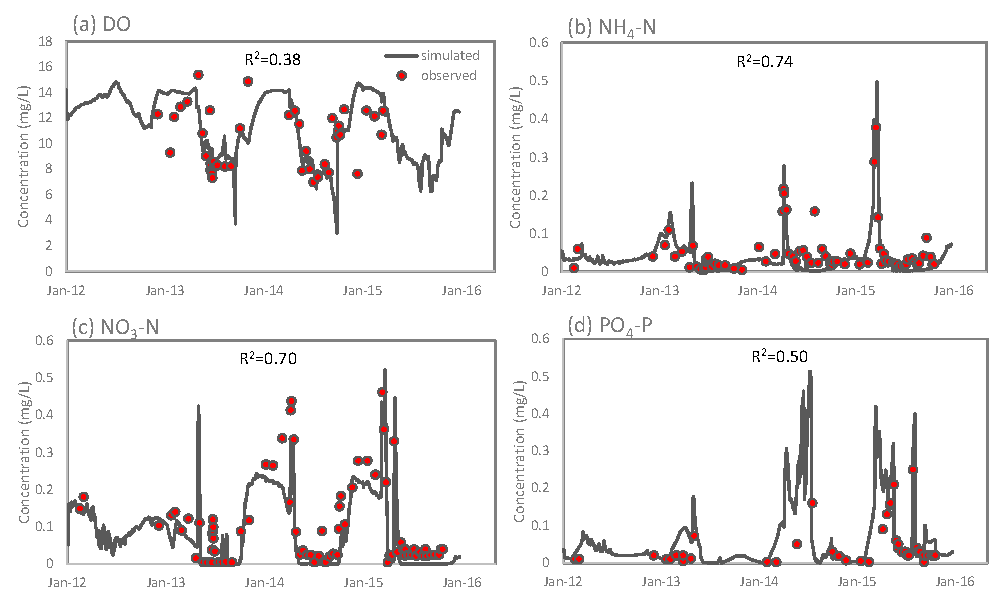
2.2. Model Set-Up
2.3. Climate Change Scenarios
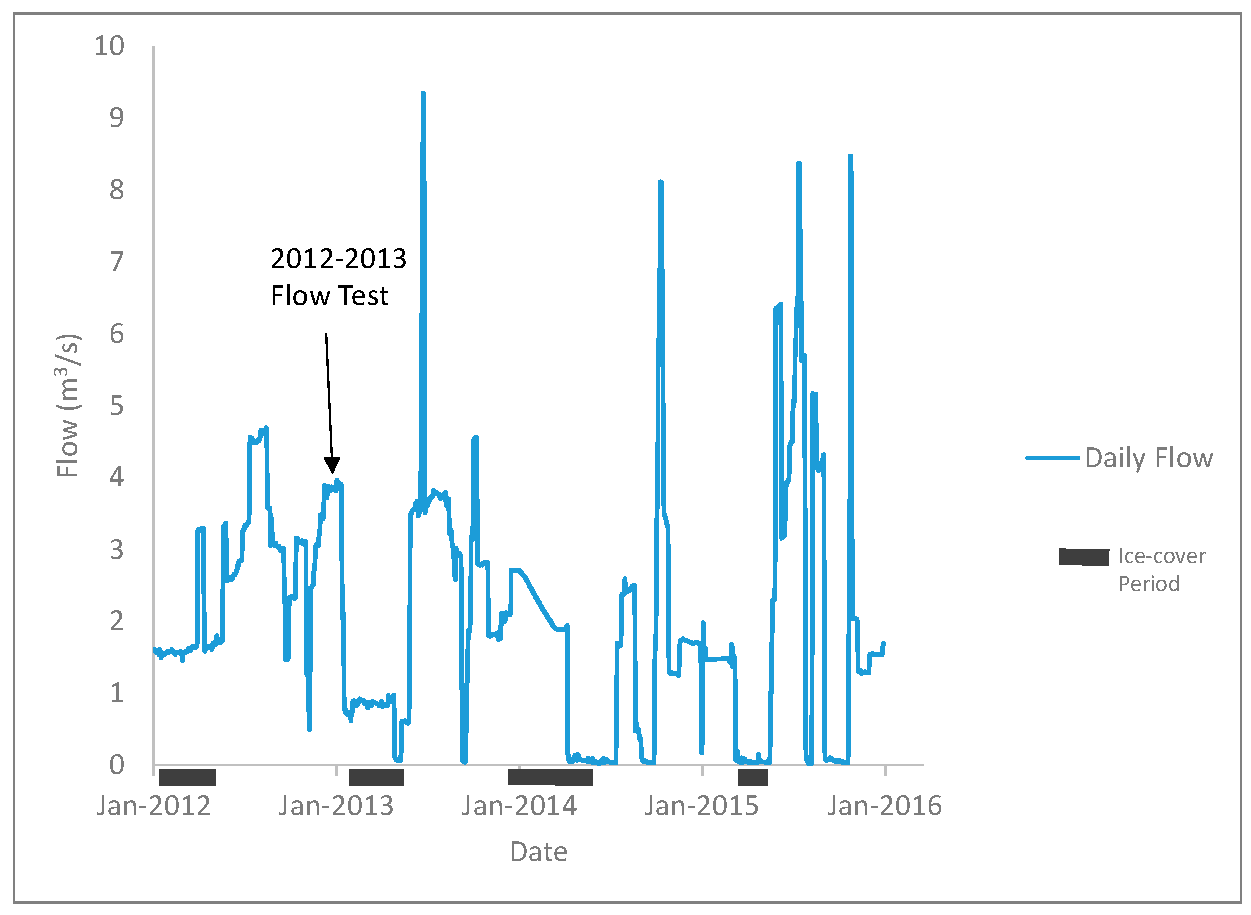
2.4. Water Managment
3. Results
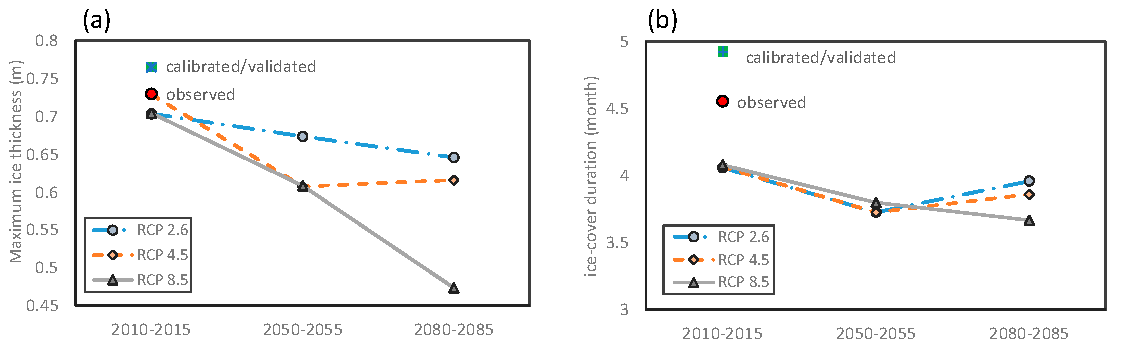
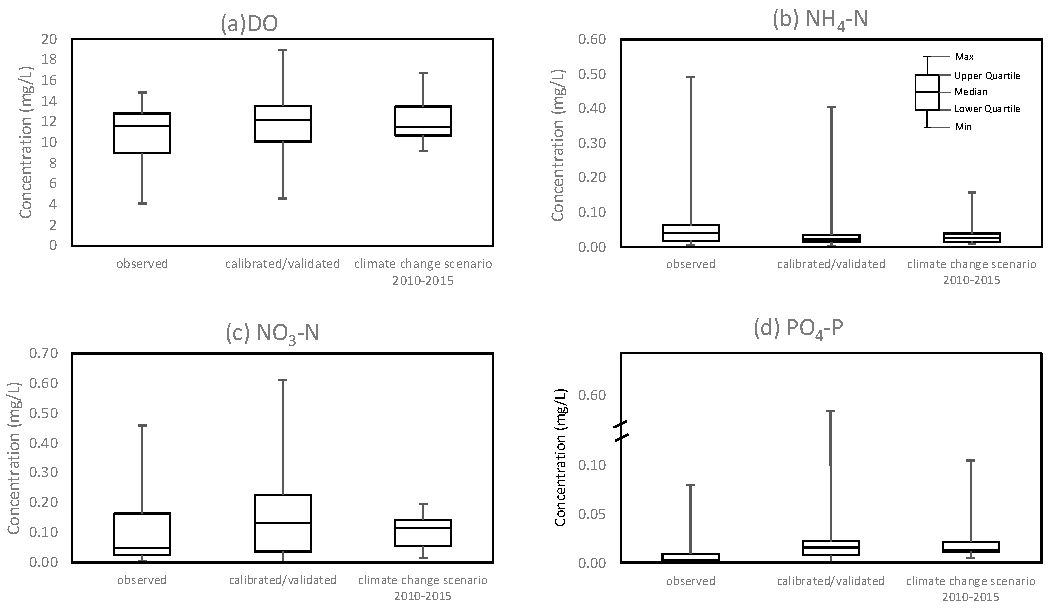
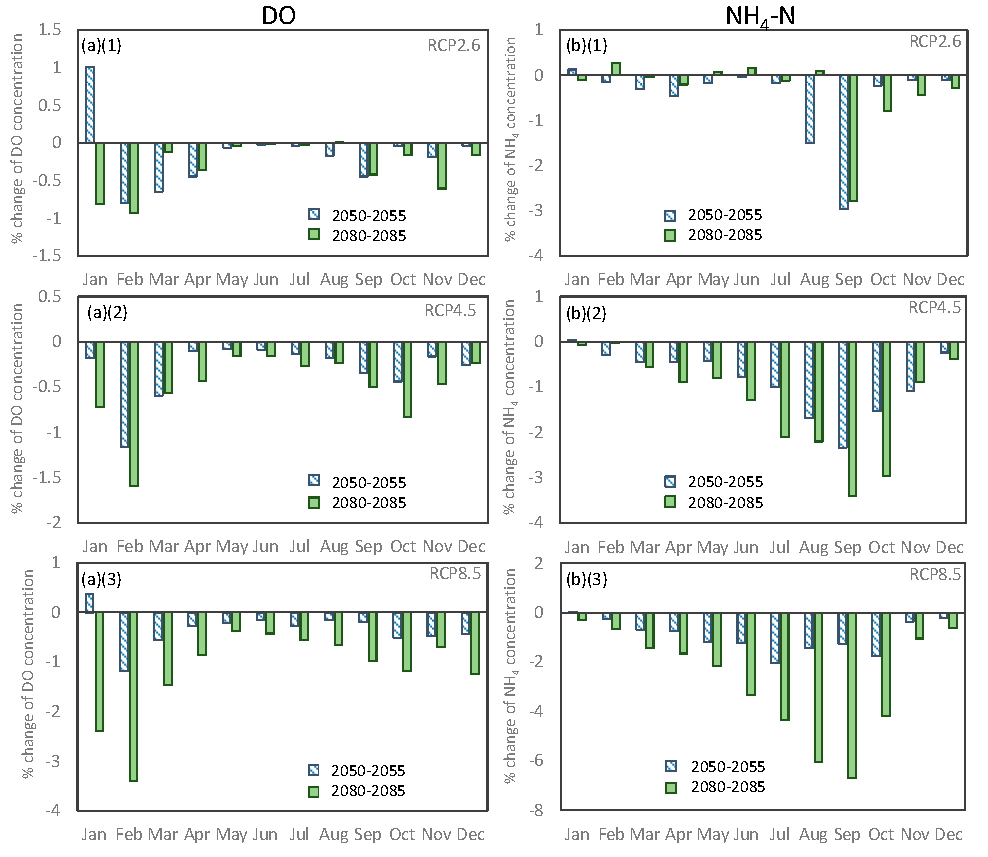
3.1. Climate Change
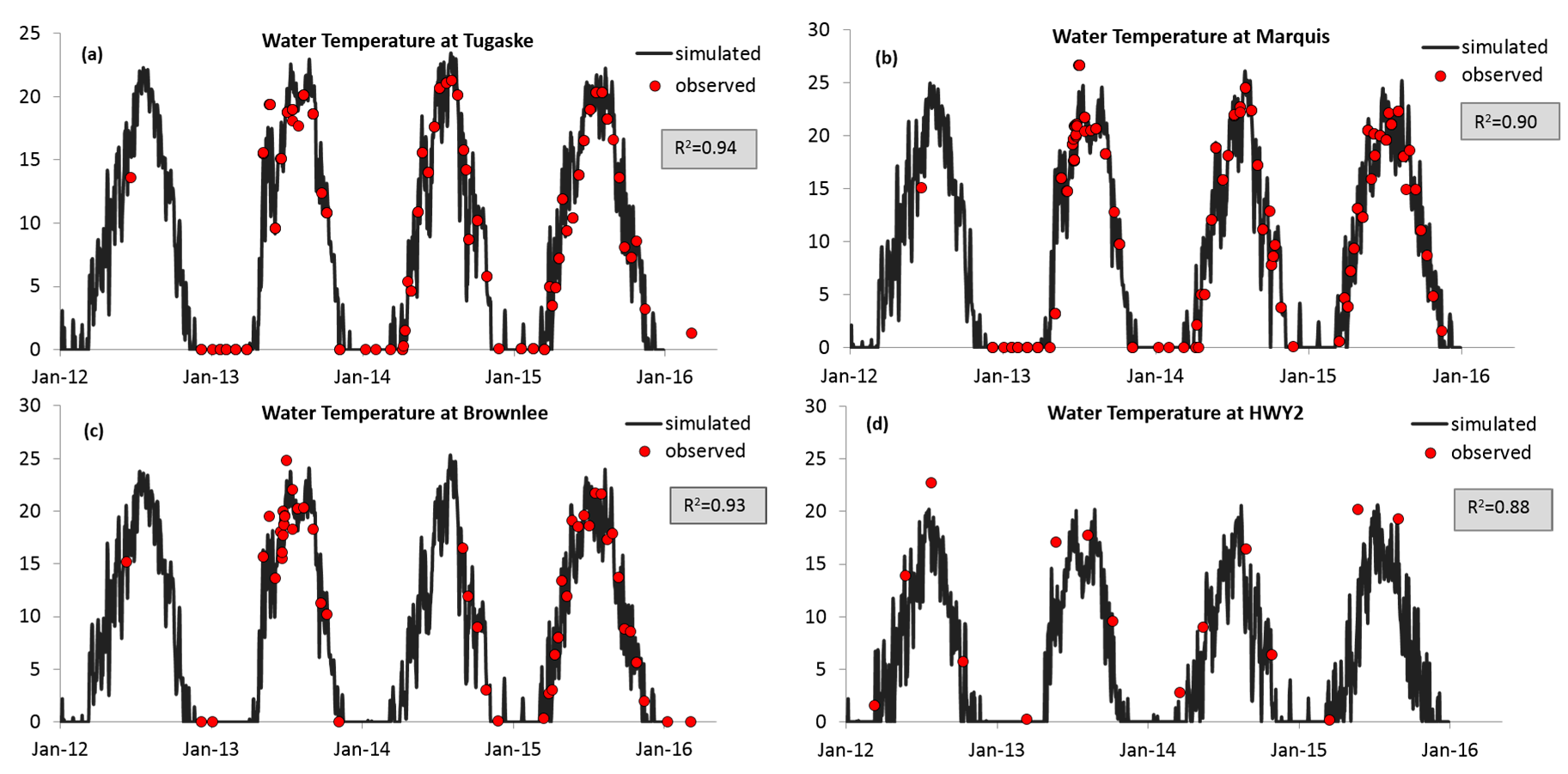
3.1.1. Water Temperature and Ice Cover
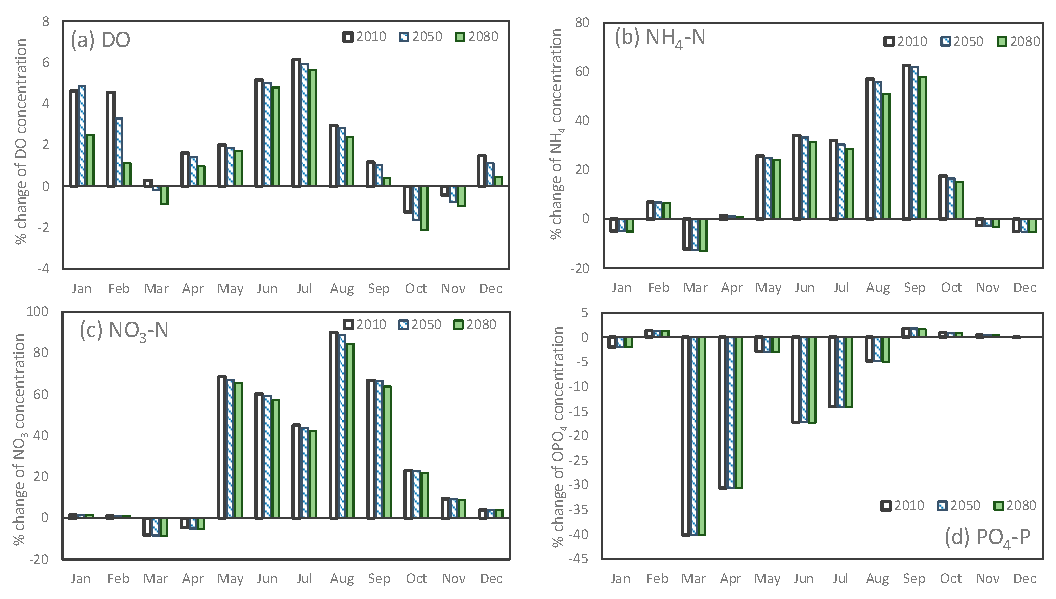
3.1.2. Water Quality
3.2. Water Management
4. Discussion
4.1. Impact of Increased Air Temperature on Water Quality
4.2. Impact of Increased Flow
4.3. Future Studies
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parsons, G.F.; Thorp, T.; Kulshreshtha, S.; Gates, C. Upper Qu’Appelle Water Supply Project: Economic Impact Sensitivity Analysis; Springer: Saskatchewan, SK, Canada, 2012; p. 113. [Google Scholar]
- Delpla, I.; Jung, A.V.; Baures, E.; Clement, M.; Thomas, O. Impacts of climate change on surface water quality in relation to drinking water production. Environ. Int. 2009, 35, 1225–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitehead, P.G.; Wilby, R.L.; Battarbee, R.W.; Kernan, M.; Wade, A.J. A review of the potential impacts of climate change on surface water quality. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2009, 54, 101–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, E.; Fukushima, T.; Harasawa, H. A modeling approach to forecast the effect of long-term climate change on lake water quality. Ecol. Model. 2007, 209, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, P.G.; Barbour, E.; Futter, M.N.; Sarkar, S.; Rodda, H.; Caesar, J.; Butterfield, D.; Jin, L.; Sinha, R.; Nicholls, R.; et al. Impacts of climate change and socio-economic scenarios on flow and water quality of the Ganges, Brahmaputra and Meghna (GBM) river systems: Low flow and flood statistics. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2015, 17, 1057–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mimikou, M.A.; Baltas, E.; Varanou, E.; Pantazis, K. Regional impacts of climate change on water resources quantity and quality indicators. J. Hydrol. 2000, 234, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vliet, M.T.H.; Franssen, W.H.P.; Yearsley, J.R.; Ludwig, F.; Haddeland, I.; Lettenmaier, D.P.; Kabat, P. Global river discharge and water temperature under climate change. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2013, 23, 450–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kienzle, S.W.; Nemeth, M.W.; Byrne, J.M.; MacDonald, R.J. Simulating the hydrological impacts of climate change in the upper North Saskatchewan River basin, Alberta, Canada. J. Hydrol. 2012, 412, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasper, K.; Calanca, P.; Gyalistras, D.; Fuhrer, J. Differential imapcts of climate change on the hydrology of two alpine river basins. Clim. Res. 2004, 26, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mote, P.W. Climate-driven variability and trends in mountain snowpack in western North America. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 6209–6220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wool, T.A.; Ambrose, R.B.; Martin, J.L.; Comer, E.A. Water Quality Analysis Simulation Program (WASP) Version 6.0 Manual. Draft User’s Manual; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2006.
- Cerucci, M.; Jaligama, G.; Amidon, T.; Cosgrove, A. The simulation of dissolved oxygen and orthophosphate for large scale watersheds using WASP7.1 with nutrient luxury uptake. Water Environ. Fed. 2007, 12, 5765–5776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Liu, N.; Wang, M.; Yan, K. Application WASP Model on Validation of Reservoir-Drinking Water Source Protection Areas Delineation. In Proceedings of the 2010 3rd International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Informatics (BMEI), Yantai, China, 16–18 October 2010.
- Alam, A.; Badruzzaman, A.B.M.; Ali, M.A. Assessing effect of climate change on the water quality of the Sitalakhya river using WASP model. J. Civ. Eng. 2013, 41, 21–30. [Google Scholar]
- Akomeah, E.; Chun, K.P.; Lindenschmidt, K.E. Dynamic water quality modelling and uncertainty analysis of phytoplankton and nutrient cycles for the upper South Saskatchewan River. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 18239–18251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Toro, D.M.; Fitzpatrick, J.J.; Thomann, R.V. Documentation for Water Quality Analysis Simulation Program (WASP) and Model Verification Program (MVP); United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1983.
- Ambrose, R.B.; Wool, T.A.; Connolly, J.P.; Schanz, R.W. WASP4, a Hydrodynamic and Water Quality Model—Model Theory, User’s Manual, and Programmer’s Guide; EPA-600/3-87/039; Office of Research and Development, United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1988.
- Connolly, J.; Winfield, R. A User’s Guide for WASTOX, a Framework for Moeling the Fate of Toxic Chemicals in Aquatic Environments. Part 1: Exposure Concentration; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Athens, GA, USA, 1984.
- Ambrose, R.B.; Wool, T. WASP7 Stream Transport-Model Theory and User’s Guide: Supplement to Water Quality Analysis Simulation Program (WASP) User Documentation; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2009.
- Cole, T.M.; Buchak, E.M. CE-QUAL-W2: A Two-Dimensional, Laterally Averaged, Hydrodynamic and Water Quality Model, Version 2; Instruction Report EL-95-1; Waterways Experiment Station, US Army Corps of Engineers: Vicksburg, MS, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Tufford, D.L.; McKellar, H.N. Spatial and temporal hydrodynamic and water quality modeling analysis of a large reservoir on the South Carolina (USA) coastal plain. Ecol. Model. 1999, 114, 137–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindenschmidt, K.-E. Winter Flow Testing of the Upper Qu’Appelle River; Lambert Academic Publishing: Saarbrücken, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lindenschmidt, K.-E.; Sereda, J. The impact of macrophytes on winter flows along the Upper Qu’Appelle River. Can. Water Resour. J. 2014, 39, 342–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, S.R.; Lodge, D.M. Effects of submersed macrophytes on ecosystem processes. Aquat. Bot. 1986, 26, 341–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sand-jensen, K.; Prahl, C.; Stokholm, H. Oxygen release from roots of submerged aquatic macrophytes. Wiley Behalf Nord. Soc. Oikos 2016, 38, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sereda, J. Assessment of Macrophyte Control Options in the Upper Qu’Appelle Conveyance Channel: Nutrient Amendments and Harvesting; Unpublished Report; Saskatchewan Water Security Agancy: Moose Jaw, SK, Canada, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Tolson, B.A.; Shoemaker, C.A. Dynamically dimensioned search algorithm for computationally efficient watershed model calibration. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matott, L.S. OSTRICH: An Optimization Software Tool; Documentation and User’s Guide; Univisity of Buffalo: Buffalo, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Murdock, T.Q.; Spittlehouse, D.L. Selecting and Using Climate Change Scenarios for British Columbia; Pacific Climate Impacts Consortium: Univisity of Victoria, Victoria, BC, Canada, 2011; Volume 39, p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, K.E.; Stouffer, R.J.; Meehl, G.A. An overview of CMIP5 and the experiment design. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2012, 93, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenney, D.W.; Hutchiinson, M.F.; Papadopol, P.; Lawrence, K.; Pedlar, J.; Campbell, K.; Milewska, E.; Hopkinson, R.F.; Price, D.; Owen, T. Customized spatial climate models for North America. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 92, 1611–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkinson, R.F.; Mckenney, D.W.; Milewska, E.J.; Hutchinson, M.F.; Papadopol, P.; Vincent, A.L.A. Impact of aligning climatological day on gridding daily maximum-minimum temperature and precipitation over Canada. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2011, 50, 1654–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Reed, P.; Wagener, T.; van Werkhoven, K. Comparing sensitivity analysis methods to advance lumped watershed model identification and evaluation. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2007, 11, 793–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, S.; Gupta, H.V. What do we mean by sensitivity analysis? The need for comprehensive characterization of “global” sensitivity in earth and environmental systems models. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 3070–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltelli, A.; Ratto, M.; Tarantola, S.; Campolongo, F. Sensitivity analysis for chemical models. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 2811–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.Y.; Park, G.A.; Kim, S.J. Assessment of future climate change impact on water quality of Chungju Lake, South Korea, Using WASP Coupled with SWAT. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2013, 49, 1225–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnuson, J.J.; Robertson, D.M.; Benson, B.J.; Wynne, R.H.; Livingstone, D.M.; Arai, T.; Assel, R.A.; Barry, R.G.; Card, V.; Kuuisisto, E.; et al. Historical trends in lake and river ice cover in the Northern Hemisphere. Science 2000, 289, 1743–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Lai, S.; Gao, X.; Xu, L. Potential impacts of climate change on water quality in a shallow reservoir in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 14971–14982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettersson, K.; Grust, K.; Weyhenmeyer, G.; Blenckner, T. Seasonality of chlorophyll and nutrients in Lake Erken—Effects of weather conditions. Hydrobiologia 2003, 506–509, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, B.A.; Whitehead, P.G. Impacts of climate change scenarios on dissolved oxygen in the River Thames, UK. Hydrol. Res. 2009, 40, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murdoch, P.S.; Baron, J.S.; Miller, T.L. Potential effects of climate change on surface-water quality in North America. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2000, 36, 347–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilby, R.L.; Whitehead, P.G.; Wade, A.J.; Butterfield, D.; Davis, R.J.; Watts, G. Integrated modelling of climate change impacts on water resources and quality in a lowland catchment: River Kennet, UK. J. Hydrol. 2006, 330, 204–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodson, S.I. Introduction to Limnology. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2004, 23, 661–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J. Combined impact of climate and land use changes on streamflow and water quality in eastern Massachusetts, USA. J. Hydrol. 2009, 379, 268–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arheimer, B.; Andreasson, J.; Fogelberg, S.; Johnsson, H.; Pers, C.B.; Persson, K. Climate change impact on water quality: Model results from southern Sweden. AMBIO 2005, 34, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, S.T.Y.; Chen, W.L. Modeling the relationship between land use and surface water quality. J. Environ. Manag. 2002, 66, 377–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Station Names | Number of Observations from January 2012 to December 2015 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DO | NH4-N | NO3-N | PO4-P | Chl a | |
| Qu’Appelle River at Marquis Bridge | 79 | 80 | 80 | 39 | 7 |
| Qu’Appelle River at Keeler | 5 * | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Qu’Appelle River at Brownlee | 53 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Qu’Appelle River below Eyebrown Bridge | 4 | 6 | 6 | 2 | 0 |
| Qu’Appelle River at Tugaske Bridge | 64 | 64 | 64 | 31 | 1 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hosseini, N.; Johnston, J.; Lindenschmidt, K.-E. Impacts of Climate Change on the Water Quality of a Regulated Prairie River. Water 2017, 9, 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9030199
Hosseini N, Johnston J, Lindenschmidt K-E. Impacts of Climate Change on the Water Quality of a Regulated Prairie River. Water. 2017; 9(3):199. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9030199
Chicago/Turabian StyleHosseini, Nasim, Jacinda Johnston, and Karl-Erich Lindenschmidt. 2017. "Impacts of Climate Change on the Water Quality of a Regulated Prairie River" Water 9, no. 3: 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9030199
APA StyleHosseini, N., Johnston, J., & Lindenschmidt, K.-E. (2017). Impacts of Climate Change on the Water Quality of a Regulated Prairie River. Water, 9(3), 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9030199







