Soil Moisture Variation in a Farmed Dry-Hot Valley Catchment Evaluated by a Redundancy Analysis Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
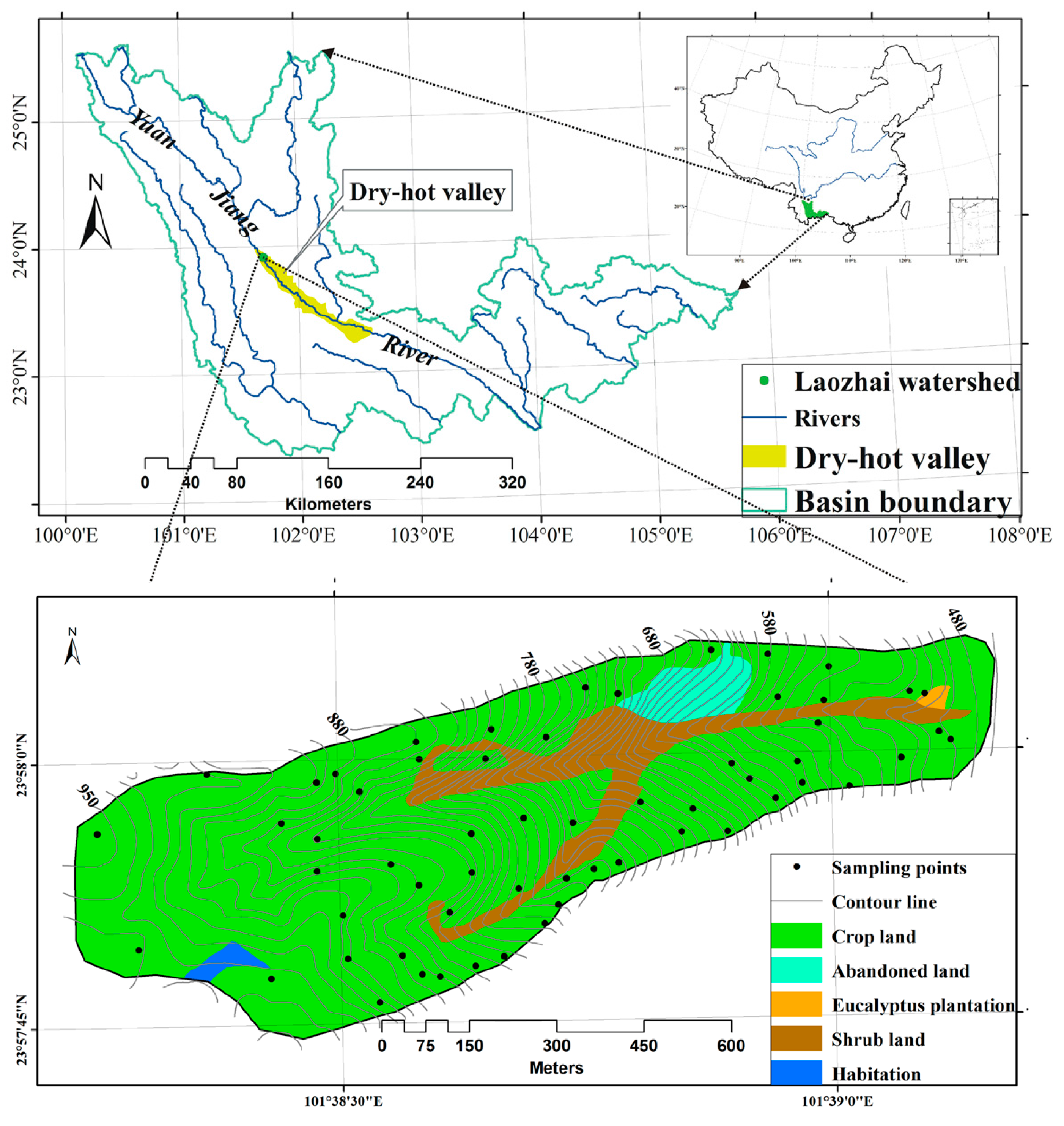
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Soil Moisture Monitoring
2.3. Environmental Variables
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
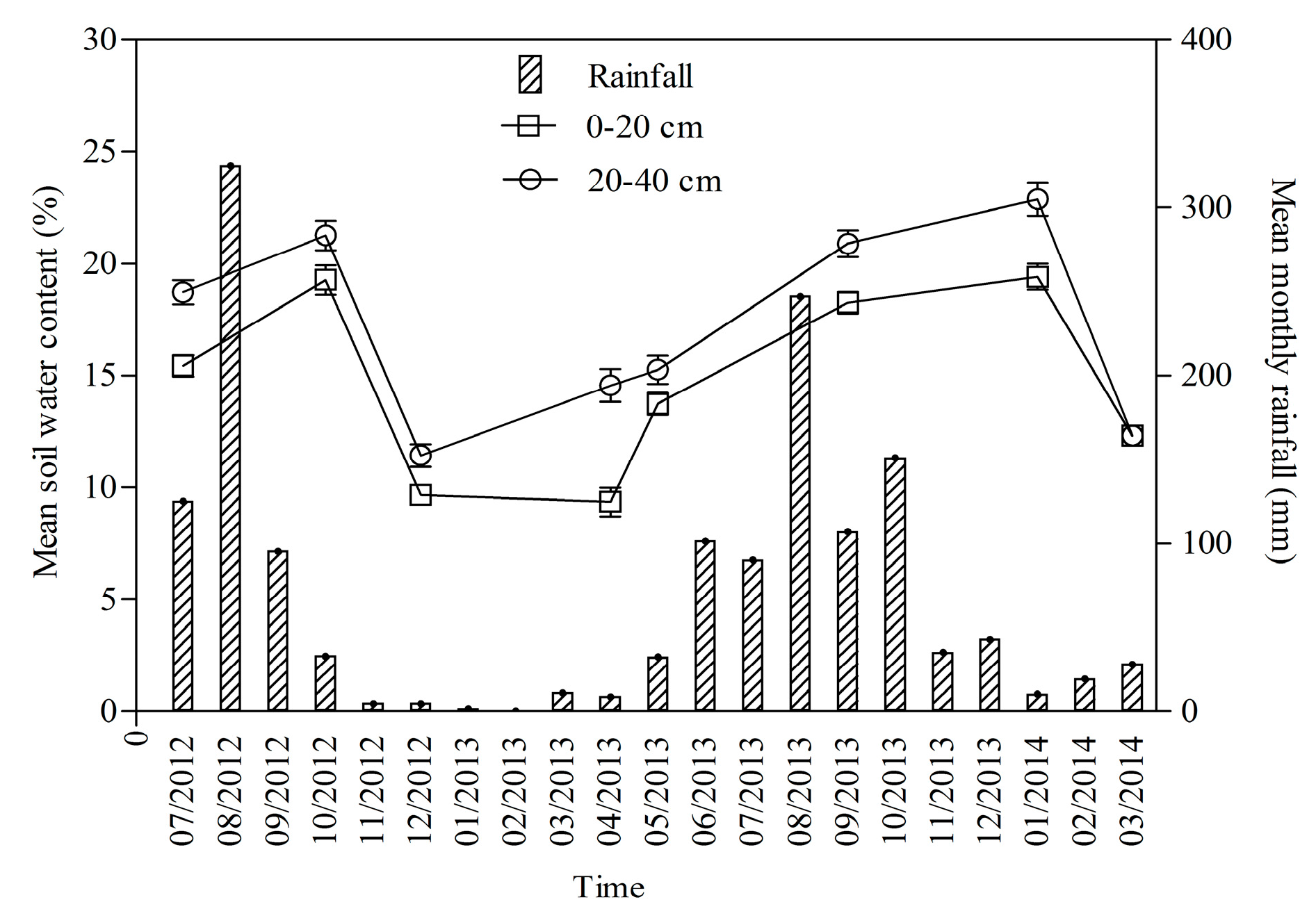
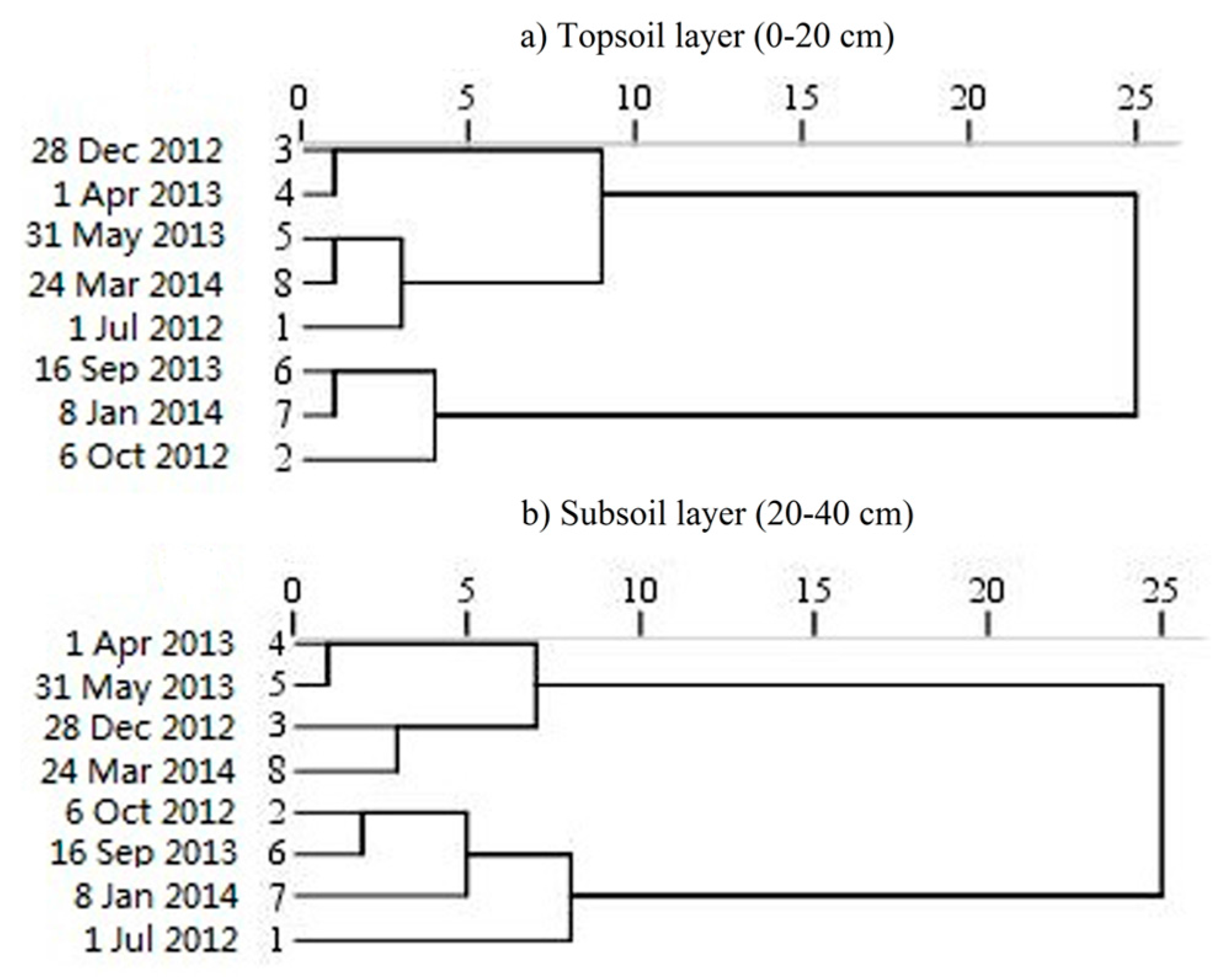
3.1. Temporal Variation of Soil Moisture
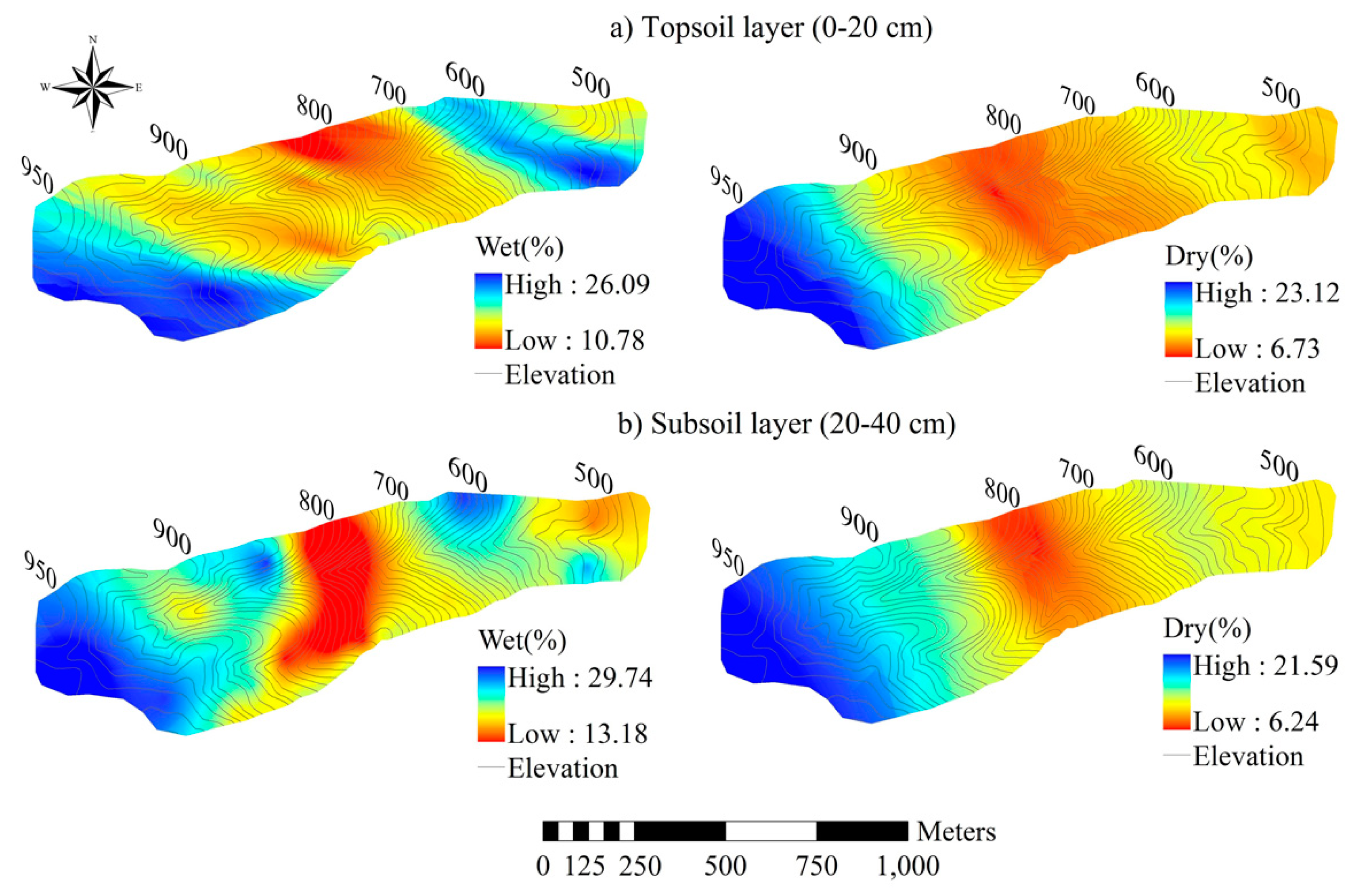
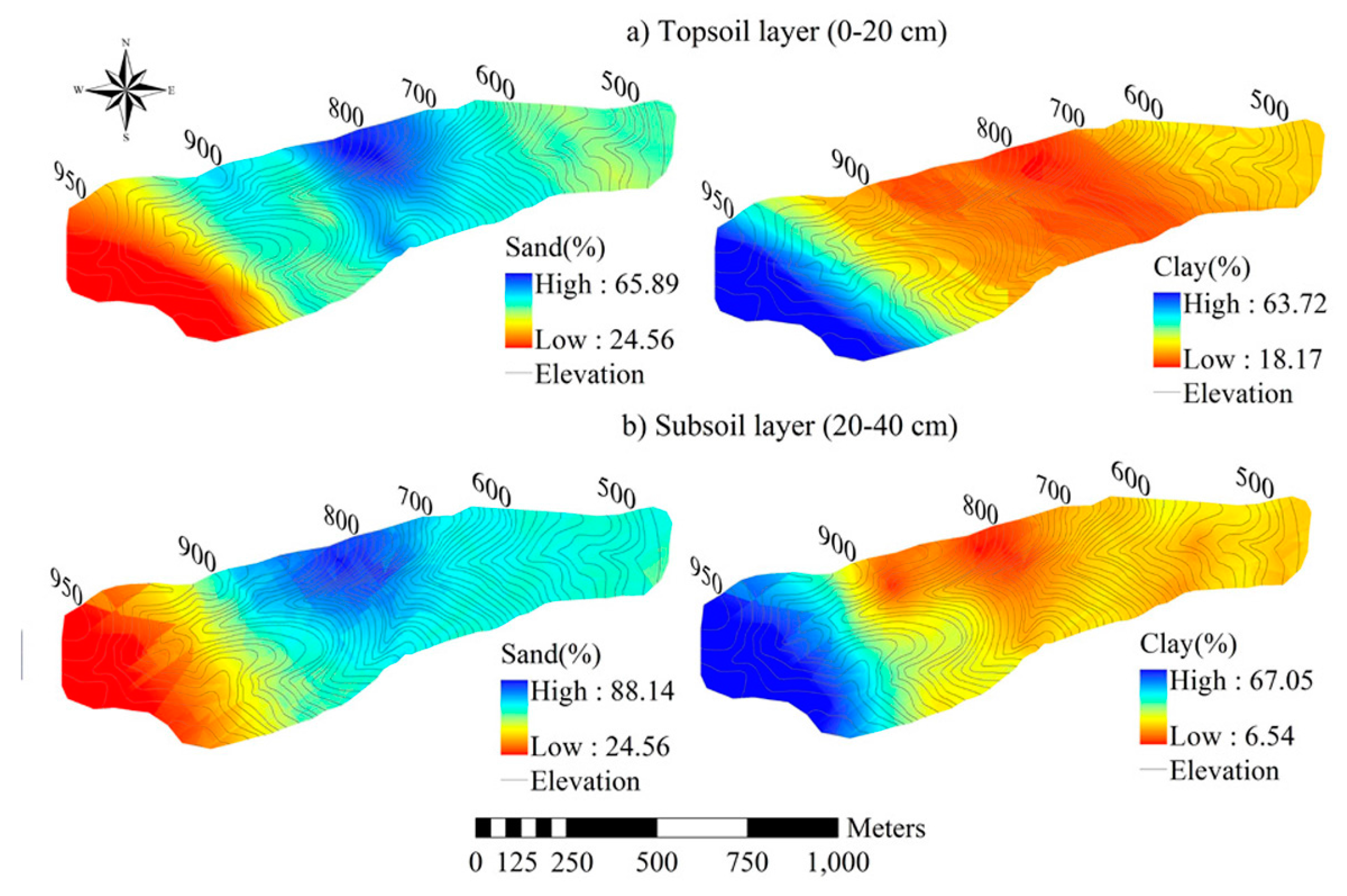
3.2. Spatial Distribution of Soil Moisture
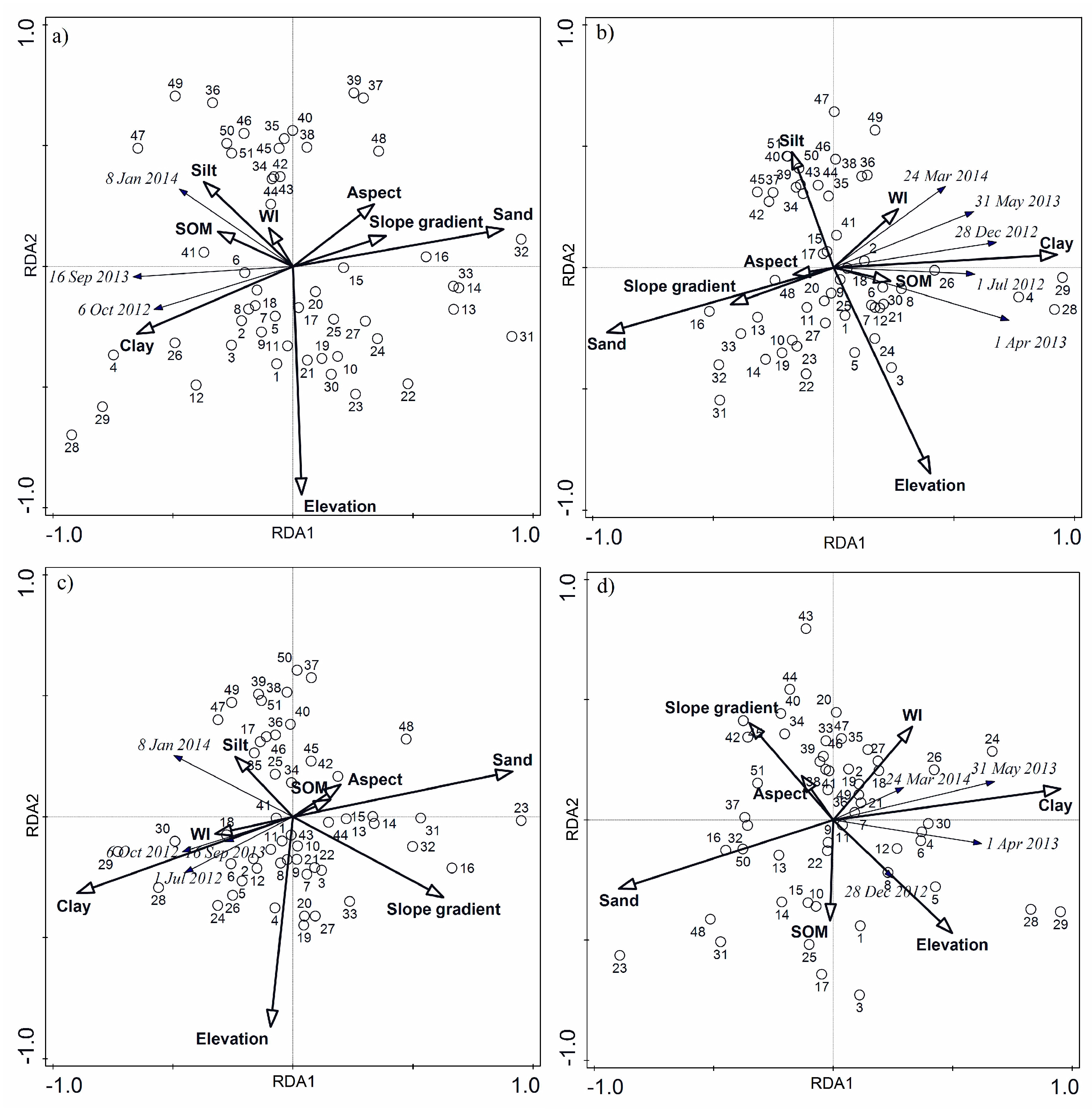
3.3. Correlations between Soil Moisture and Environmental Variables
3.4. The Dominant Controls on Soil Moisture
4. Summary and Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brocca, L.; Melone, F.; Moramarco, T.; Morbidelli, R. Spatial-temporal variability of soil moisture and its estimation across scales. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocca, L.; Tullo, T.; Melone, F.; Moramarco, T.; Morbidelli, R. Catchment scale soil moisture spatial–temporal variability. J. Hydrol. 2012, 422–423, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Western, A.W.; Grayson, R.B.; Blöschl, G.; Willgoose, G.R.; McMahon, T.A. Observed spatial organization of soil moisture and its relation to terrain indices. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 797–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mguidiche, A.; Provenzano, G.; Douh, B.; Khila, S.; Rallo, G.; Boujelben, A. Assessing hydrus-2D to simulate soil water content (SWC) and salt accumulation under an SDI system: Application to a potato crop in a semi-arid area of central Tunisia. Irrig. Drain. 2015, 64, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudena, M.; Andrea, F.D.; Provenzale, A. A model for soil-vegetation-atmosphere interactions in water-limited ecosystems. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Shao, M.G.; Han, F.P.; Reichardt, K.; Tan, J. Watershed scale temporal stability of soil water content. Geoderma 2010, 158, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantón, Y.; Solé-Benet, A.; Domingo, F. Temporal and spatial patterns of soil moisture in semiarid badlands of SE Spain. J. Hydrol. 2004, 285, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.J.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.D.; Qiu, Y. The effects of land use on soil moisture variation in the Danangou catchment of the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2003, 54, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korres, W.; Reichenau, T.G.; Fiener, P.; Koyama, C.N.; Bogena, H.R.; Cornelissen, T.; Baatz, R.; Herbast, M.; Deikkrüger, B.; Vereecken, H.; et al. Spatio-temporal soil moisture patterns—A meta-analysis using plot to catchment scale data. J. Hydrol. 2015, 520, 326–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Fu, B.J.; Gao, G.Y.; Zhou, J.; Jiao, L.; Liu, J.B. Liking the soil moisture distribution pattern to dynamic processes along slope transects in the Loess Plateau, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 777–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Chen, L.D.; Wei, W.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, H.D. Comparsion of deep soil moisture in two re–vegetation watershed in semi–arid regions. J. Hydrol. 2014, 513, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wei, W.; Chen, L.D.; Chen, W.L.; Wang, J.L. Response of temporal variation of soil moisture to vegetation restoration in semi–arid Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2014, 115, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucco, G.; Brocca, L.; Moramarco, T.; Morbidelli, R. Influence of land use on soil moisture spatial–temporal variability and moitoring. J. Hydrol. 2014, 516, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersahin, S.; Brohi, A.R. Spatial variation of soil water content in topsoil and subsoil of a Typic Ustifluvent. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 83, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famiglietti, J.S.; Rudnicki, J.W.; Rodell, M. Variability in surface moisture content along a hillslope transect, Ratttlesnake Hill, Texas. J. Hydrol. 1998, 210, 259–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Plaza, A.; Martínez-Mena, M.; Albaladejo, J.; Castillo, V.M. Factors regulating spatial distribution of soil water content in small semiarid catchments. J. Hydrol. 2001, 253, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hébrard, O.; Voltz, M.; Andrieux, P.; Moussa, R. Spatio-temporal distribution of soil surface moisture in a heterogeneously farmed Mediterranean catchment. J. Hydrol. 2006, 329, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Fu, B.J.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.D. Soil moisture variation in relation to topography and land use in a hillslope catchment of the Loess Plateau, China. J. Hydrol. 2001, 240, 243–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Fu, B.J.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.D. Spatial variability of soil moisture content and its relation to environmental indices in a semi-arid gully catchment of Loess Plateau, China. J. Arid Environ. 2001, 49, 723–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borcard, D.; Gillet, F.; Legendre, P. Numerical Ecology with R; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 154–194. [Google Scholar]
- Andrea, B.; Francesc, G.; Jérôme, L.; Eusebi, V.; Francesc, S. Cross-site comparison of variability of DOC and nitrate c-q hysteresis during the autumn-winter period in three Mediterranean headwater streams, a synthetic approach. Biogeochemistry 2006, 77, 327–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldeck, C.A.; Colgan, M.S.; Féret, J.B.; Levick, S.R.; Martin, R.E.; Asner, G.P. Landscape-scale variation in plant community composition of an African savanna from airborne species mapping. Ecol. Appl. 2014, 24, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madre, F.; Vergnes, A.; Machon, N.; Clergeau, P. Green roofs as habitats for wild plant species in urban landscapes, first insights from a large-scale sampling. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 122, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stibal, M.; Telling, J.; Cook, J.; Mark, K.M.; Anesio, A.M. Environmental controls on microbial abundance and activity on the Greenland ice sheet, a multivariate analysis approach. Microb. Ecol. 2012, 63, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.; Shi, X.; Wang, X.; Hao, H.H.; Zhang, X.M.; Zhang, L.P. Environmental Controls over Actinobacteria Communities in Ecological Sensitive Yanshan Mountains Zone. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, C.; Laverman, A.M.; Pallud, C.E. Environmental controls on nitrogen and sulfur cycles in surficial aquatic sediments. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.; McCormack, L.; Wang, J.Y.; Guo, D.L.; Wang, Q.F.; Zhang, X.X.; Yu, G.R.; Blagodatskaya, E.; Kuzyakov, Y. Linkages between the soil organic matter fractions and the microbial metabolic functional diversity within a broad-leaved Korean pine forest. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2015, 66, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Lu, Q.; Wei, Y.Q.; Cui, H.Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.Q.; Shan, S.; Wei, Z.M. Effect of actinobacteria agent inoculation methods on cellulose degradation during composting based on redundancy analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 219, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šmilauer, P.; Lepš, J. Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Data Using Canoco 5; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesh, B.; Lakshman, N.; Purandara, B.K.; Reddy, V.B. Analysis of observed soil moisture patterns under different land covers in Western Gahats, India. J. Hydrol. 2011, 397, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rallo, G.; Agnese, C.; Minacapilli, M.; Provenzano, G. Comparison of SWAP and FAO agro-hydrological models to schedule irrigation of wine grapes. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2012, 138, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motisi, A.; Consoli, S.; Papa, R.; Cammalleri, C.; Rossi, F.; Minacapilli, M.; Rallo, G. Eddy covariance and sap flow measurement of energy and mass exchanges of woody crops in a Mediterranean environment. Acta Hortic. 2012, 951, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawley, M.E.; Jackson, Y.J.; McCuen, R.H. Surface soil moisture variation on small agricultural watersheds. J. Hydrol. 1983, 62, 179–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.C.; McConchie, J.A. The dry-hot valleys and forestation in southwest China. J. For. Res. 2001, 12, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.; Xie, J.; Sun, H. Revisiting sustainable development of dry valleys in Hengduan Mountains Region. J. Mt. Sci. 2004, 1, 38–45. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.P.; Yang, Z.; Wang, D.J.; Zhang, X.B. Climate change and causes in the Yuanmou dry-hot valley of Yunnan, China. J. Arid Environ. 2002, 51, 153–162. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.Q.; Shen, Y.X.; Chen, Q.B.; Wang, Z.H. Soil water environment of artificial vegetation in Jinshajiang dry-hot valley. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2004, 15, 809–813. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, D.H.; Zhou, H.Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, X.B. Slope lithologic property; soil moisture condition and revegetation in dry-hot valley of Jinsha river. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2005, 15, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.F.; Xiong, D.H.; Su, Z.A.; Li, J.J.; Yang, D.; Shi, L.T.; Liu, G.C. The distribution of and factors influencing the vegetation in a gully in the dry-hot valley of southwest China. Catena 2014, 116, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.M.; Cui, P.; Ge, Y.G.; Chen, C.; Wang, D.J.; Wu, C.Z.; Li, J.; Yu, W.; Zhang, G.S.; Lin, H. The succession characteristics of soil erosion during different vegetation succession stages in dry-hot river valley of Jinsha River, upper reaches of Yangtze River. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 62, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.G.; Xiong, D.H.; Dong, Y.F.; Li, J.J.; Yang, D.; Zhang, J.H.; He, G.X. Simulated headward erosion of bank gullies in the dry-hot valley region of southwest China. Geomorphology 2014, 204, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.Z. Dry Valleys in the Hengduan Mountains; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1992. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- National Soil Survey Office. Soils in China; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 1998; pp. 274–275. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.S. Soil Physics and Chemistry Analysis and Description of Soil Profiles; China Standard Press: Beijing, China, 1996. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Beven, K.J.; Kirkby, M. A physical based variable contributing area model of basin hydrology. Hydrol. Sci. Bull. 1979, 24, 43–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, I.D.; Burch, G.J.; Mackenzie, D.H. Topographic effects on the distribution of surface soil water and the location of ephemeral gullies. Trans. Am. Soc. Agric. Eng. 1988, 31, 1098–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cressie, N. Spatial prediction and ordinary kriging. Math. Geol. 1988, 20, 405–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, J.A.; Snepvangers, J.J.J.C.; Bouten, W.; Heuvelink, G.B.M. Mapping spatial variation in surface soil water content: Comparison of ground penetrating radar and time domain reflectometry. J. Hdrol. 2002, 269, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, H.X.; Li, X.Y.; Liu, X.; Guo, M.X.; Li, J. A case study of spatial heterogeneity of soil moisture in the Loess Plateau, western China: A geostatistical approach. Intern. J. Sediments Res. 2009, 1, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.D.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, X.W.; Zhang, J.G.; Li, C.J. Spatiotemporal distribution of soil moisture and salinity in the Taklimakan desert highway shelterbelt. Water 2015, 7, 4343–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.X.; Han, X.Z.; Wang, S.Y.; Li, L.H.; Wang, F.J. A study on dynamics of soil moisture of soil profile in black soil. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2009, 3, 130–134. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Choi, M.; Jacobs, J.M. Soil moisture variability of root zone profiles within SME02 remote sensing footprints. Adv. Water Resour. 2007, 30, 883–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penna, D.; Borga, M.; Norbiato, D.; Fontana, G.D. Hillslope scale soil moisture variability in a steep alpine terrain. J. Hydrol. 2009, 364, 311–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grayson, R.B.; Western, A.W.; Chiew, F.H.S. Preferred states in spatial soil moisture patterns, local and nonlocal controls. Water Resour. Res. 1997, 33, 2897–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.Z. A phytosociological stuy on the semi-savanna vegetation in the dry-hot valleys of Yuanjiang River, Yunnan. Guihaia 1999, 19, 289–302. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tanner, C.B.; Jury, W.A. Estimating evaporation and transpiration from a row crop during incomplete cover. Agron. J. 1976, 68, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagley, J.E.; Desai, A.R.; Dirmeyer, P.A.; Foley, J.A. Effects of land cover change on moisture availability and potential crop yield in the world’s breadbaskets. Environ. Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 014009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Wu, P.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J.; Shi, Y. Effects of land use on soil moisture variations in a semi–arid catchment, implications for land and agricultural water management. Land Degrad. Dev. 2014, 25, 163–172. [Google Scholar]
- Baroni, G.; Ortuani, B.; Facchi, A.; Gandolfi, C. The role of vegetation and soil properties on the spatio-temporal variability of the surface soil moisture in a maize-cropped field. J. Hydrol. 2013, 489, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teuling, A.J.; Uijlenhoet, R.; Hupet, F.; van Loonm, E.; Troch, P.A. Estimating spatial mean root-zone soil mositure from point-scale observations. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2006, 10, 755–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.D.; Shen, W.S.; Zou, C.X.; Jiang, J.; Fu, L.D.; She, G.H. Spatio-temporal variability of soil moisture and its effect on vegetation in a desertified aeolian riparian ecotone on the Tibetan Plateau, China. J. Hydrol. 2013, 479, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdà, A. The influence of geomorphological position and vegetation cover on the erosional and hydrological processes on a Mediterranean hillslope. Hydrol. Process. 1998, 12, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanasyk, D.S.; Mapfumo, E.; Willms, W. Quantification and simulation of surface runoff from fescue grassland watersheds. Agric. Water Manag. 2003, 59, 137–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.L.; Fu, B.J.; Lü, Y.H.; Chang, R.Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.F.; Su, C.H. The multi-scale spatial variance of soil moisture in the semi-arid Loess Plateau of China. J. Soils Sediment 2012, 12, 694–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brutsaert, W. Evaporation into the Atmosphere, Theory; History and Application; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, J.S.; Milchunas, D.G.; Lauenroth, W.K. Soil water dynamics and vegetation patterns in a semiarid grassland. Plant Ecol. 1998, 134, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, V.Y.; Fatichi, S.; Jenerette, G.D.; Espeleta, J.F.; Tronch, P.A.; Huxman, T.E. Hysteresis of soil moisture spatial heterogeneity and the “homogenizing” effect of vegetation. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, W09521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppens, F.; Gamier, P.; DeGryze, S.; Merckx, R.; Recous, S. Soil moisture, carbon and nitrogen dynamics following incorporation and surface application of labeled crop residues in soil columns. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2006, 57, 894–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, A.; Beaugrand, J.; Garnier, P.; Recous, S. Tissue density determines the water storage characteristics of crop residues. Plant Soil 2013, 367, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, K.T. Soil Degradation; Conservation and Remediation; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands; Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA; London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- De Vita, P.; Di Paolo, E.; Fecondo, G.; Di Fonzo, N.; Pisante, M. No-tillage and conventional tillage effects on durum wheat yield; grain quality and soil moisture content in southern Italy. Soil Till. Res. 2007, 92, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, K.; Lin, H.S. Changing controls of soil moisture spatial organization in the Shale Hills Catchment. Geoderma 2012, 173–174, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Soil erosion impact on agronomic productivity and environment quality. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 1998, 17, 319–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| EF 1 | SL 2 | M 3 | Min. 4 | Max. 5 | S.D 6 | C.V 7 | K 8 | S 9 | P 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silt (%) | Topsoil | 16.15 | 7.39 | 26.44 | 3.74 | 0.23 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.97 |
| Subsoil | 15.54 | 5.32 | 21.66 | 3.46 | 0.22 | 0.34 | −0.48 | 0.98 | |
| Clay (%) | Topsoil | 34.12 | 18.17 | 63.72 | 9.42 | 0.28 | 2.80 | 1.34 | 0.42 |
| Subsoil | 37.40 | 6.54 | 67.05 | 10.48 | 0.28 | 1.91 | 0.33 | 0.67 | |
| Sand (%) | Topsoil | 49.73 | 24.56 | 65.89 | 8.59 | 0.17 | 1.92 | −0.85 | 0.44 |
| Subsoil | 47.06 | 24.56 | 88.14 | 10.70 | 0.23 | 3.62 | 0.98 | 0.50 | |
| SOM (g·kg−1) | Topsoil | 23.37 | 12.28 | 41.63 | 6.06 | 0.26 | 1.33 | 0.80 | 0.29 |
| Subsoil | 18.18 | 7.41 | 34.95 | 6.05 | 0.33 | 0.27 | 0.80 | 0.12 | |
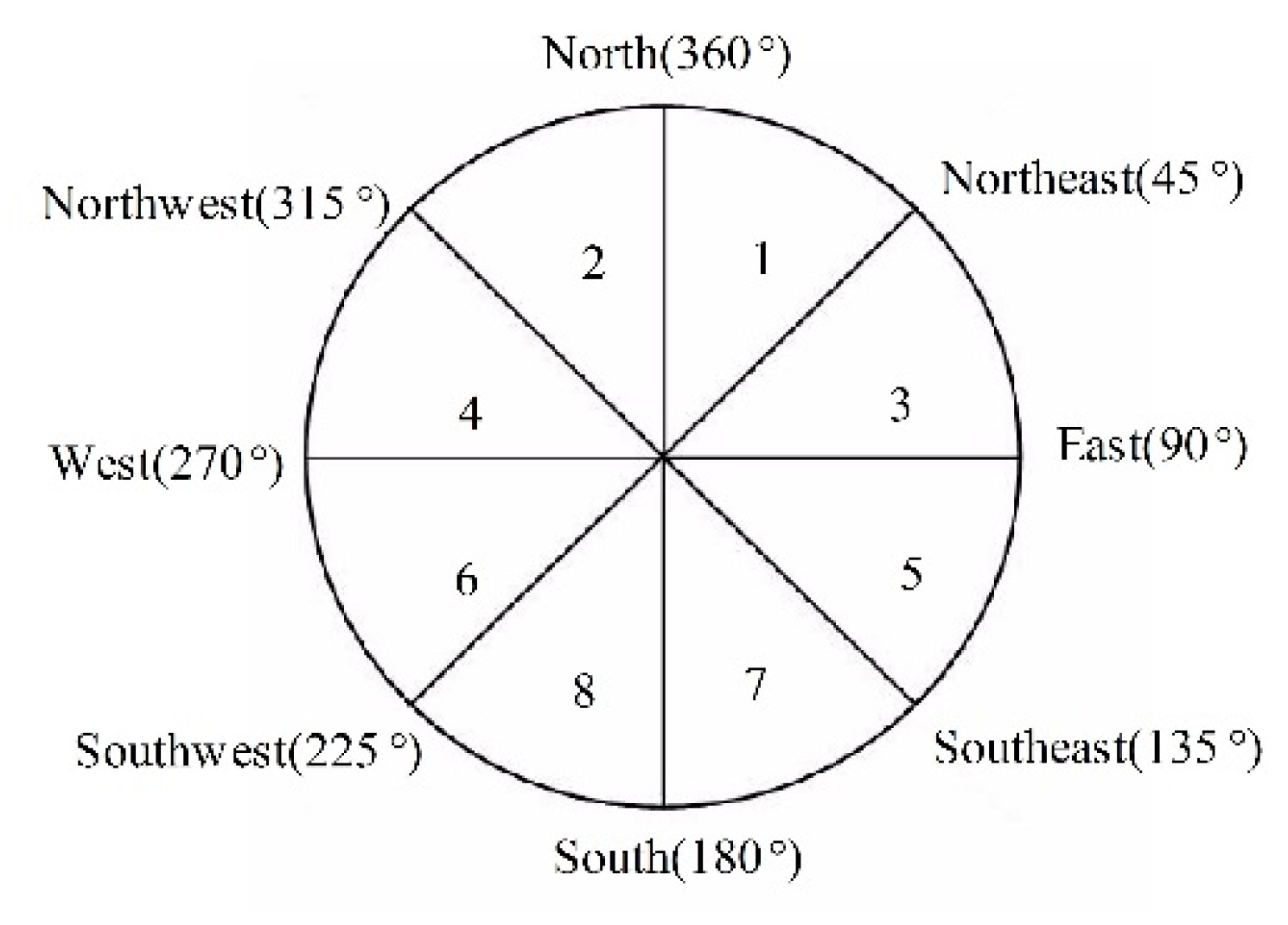
| Aspect | — | 3.29 | 1 | 7 | 2.10 | 0.64 | −1.00 | 0.46 | 0.03 |
| Elevation (m) | — | 740.29 | 490.34 | 940.00 | 144.99 | 0.20 | −1.33 | −0.45 | 0.19 |
| Slope gradient (°) | — | 24.99 | 0.00 | 50.44 | 11.54 | 0.46 | 0.47 | −0.16 | 0.85 |
| WI | — | 15.83 | 11.98 | 18.89 | 1.61 | 0.10 | −0.25 | −0.57 | 0.34 |
| Soil moisture (%) | Topsoil | 14.67 | 8.99 | 23.35 | 2.59 | 0.18 | 1.92 | 0.77 | 0.31 |
| Subsoil | 17.16 | 10.00 | 25.66 | 3.19 | 0.19 | 0.33 | −0.00 | 0.95 |
| SC 1 | SL 2 | M 3 | Min. 4 | Max. 5 | S.D 6 | C.V 7 | K 8 | S 9 | P 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wet | Topsoil | 18.97 | 10.78 | 26.09 | 3.35 | 0.18 | −0.02 | 0.01 | 0.46 |
| subsoil | 20.93 | 13.18 | 29.74 | 3.62 | 0.17 | 0.25 | 0.03 | 0.67 | |
| dry | Topsoil | 12.09 | 6.73 | 23.12 | 2.68 | 0.22 | 4.98 | 1.64 | 0.09 |
| subsoil | 13.38 | 6.24 | 21.59 | 3.18 | 0.24 | 0.36 | 0.28 | 0.64 |
| Environmental Factors | Topsoil | Subsoil | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wet Condition | Dry Condition | Wet Condition | Dry Condition | |||||
| R 1 | P 2 | R 1 | P 2 | R 1 | P 2 | R 1 | P 2 | |
| Silt | 0.26 | 0.06 | −0.09 | 0.52 | 0.12 | 0.39 | −0.12 | 0.39 |
| Clay | 0.44 ** | 0.00 | 0.74 ** | 0.00 | 0.47 ** | 0.00 | 0.59 ** | 0.00 |
| Sand | −0.60 ** | 0.00 | −0.78 ** | 0.00 | −0.50 ** | 0.00 | −0.54 ** | 0.00 |
| SOM | 0.22 | 0.12 | 0.18 | 0.20 | −0.09 | 0.52 | −0.04 | 0.76 |
| Aspect | −0.20 | 0.15 | −0.02 | 0.91 | −0.07 | 0.63 | −0.02 | 0.88 |
| Elevation | −0.06 | 0.69 | 0.26 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.56 | 0.33 * | 0.02 |
| Slope gradient | −0.26 | 0.06 | −0.35 * | 0.01 | −0.31 * | 0.03 | −0.23 | 0.10 |
| WI | 0.08 | 0.60 | 0.22 | 0.11 | 0.18 | 0.21 | 0.19 | 0.17 |
| SL 1 | Wet Condition | Dry Condition | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Statistic | E 2 | EV 3 (%) | EFV 4 (%) | Statistic | E 2 | EV 3 (%) | EFV 4 (%) | |
| Topsoil | Axis 1 | 0.32 | 32.23 | 84.13 | Axis 1 | 0.40 | 40.37 | 84.67 |
| Axis 2 | 0.05 | 37.12 | 96.90 | Axis 2 | 0.04 | 44.73 | 93.81 | |
| Axis 3 | 0.01 | 38.30 | 100.00 | Axis 3 | 0.02 | 46.49 | 97.50 | |
| Axis 4 | — | — | — | Axis 4 | 0.01 | 47.41 | 99.43 | |
| Subsoil | Axis 1 | 0.19 | 19.33 | 74.05 | Axis 1 | 0.31 | 30.96 | 88.66 |
| Axis 2 | 0.04 | 23.26 | 89.11 | Axis 2 | 0.02 | 33.45 | 95.79 | |
| Axis 3 | 0.02 | 25.45 | 97.52 | Axis 3 | 0.01 | 34.66 | 99.25 | |
| Axis 4 | 0.01 | 26.10 | 100.00 | Axis 4 | 0.00 | 34.92 | 100.00 | |
| SL 1 | V 2 | Wet Condition (Correlation Coefficient) | Dry Condition (Correlation Coefficient) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Axis1 | Axis2 | Axis3 | Axis4 | Axis1 | Axis2 | Axis3 | Axis4 | ||
| Top 3 | Silt | 0.26 | 0.18 | 0.21 | 0.00 | −0.14 | 0.32 | 0.21 | −0.17 |
| Clay | 0.45 | −0.14 | −0.13 | −0.00 | 0.75 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 0.08 | |
| Sand | −0.61 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.00 | −0.76 | −0.18 | −0.00 | −0.01 | |
| SOM | 0.22 | 0.07 | −0.03 | 0.00 | 0.19 | −0.04 | 0.02 | 0.08 | |
| Aspect | −0.23 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.00 | −0.14 | −0.02 | −0.31 | 0.05 | |
| El 4 | −0.02 | −0.48 | −0.00 | −0.00 | 0.33 | −0.50 | −0.03 | −0.09 | |
| Slope 5 | −0.27 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.00 | −0.35 | −0.10 | 0.16 | −0.06 | |
| WI | 0.07 | 0.08 | −0.03 | 0.00 | 0.22 | 0.08 | 0.06 | −0.05 | |
| Sub 6 | Silt | −0.13 | 0.13 | −0.24 | 0.06 | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Clay | −0.47 | −0.14 | 0.07 | −0.03 | 0.63 | 0.06 | 0.01 | −0.03 | |
| Sand | 0.51 | 0.10 | 0.08 | −0.02 | −0.60 | −0.14 | 0.07 | 0.04 | |
| SOM | 0.09 | 0.04 | −0.30 | −0.10 | −0.01 | −0.21 | −0.25 | −0.01 | |
| Aspect | 0.11 | 0.07 | 0.04 | −0.09 | −0.09 | −0.09 | −0.04 | 0.12 | |
| El 4 | −0.05 | −0.48 | 0.07 | −0.09 | 0.33 | −0.23 | 0.07 | 0.06 | |
| Slope 5 | 0.35 | −0.18 | −0.11 | 0.12 | −0.24 | 0.20 | −0.01 | 0.03 | |
| WI | −0.18 | −0.04 | −0.02 | 0.05 | 0.22 | 0.19 | 0.00 | 0.09 | |
| SL 1 | Effects | Wet Condition | Dry Condition | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ExV 2 | Explained (%) | F 3 | P 4 | ExV 2 | Explained (%) | F 3 | P 4 | ||
| Top 5 | Simple effects | Sand | 24.9 | 16.2 | 0.002 | Sand | 36.1 | 27.6 | 0.002 |
| Clay | 14.3 | 8.2 | 0.002 | Clay | 34.7 | 26.0 | 0.002 | ||
| - | - | - | - | elevation | 9.6 | 5.2 | 0.01 | ||
| - | - | - | Slope gradient | 7.7 | 4.1 | 0.01 | |||
| Conditional effects | Sand | 24.9 | 16.2 | 0.002 | Sand | 36.1 | 27.6 | 0.002 | |
| Clay | 6.1 | 4.2 | 0.02 | elevation | 7.1 | 6.0 | 0.002 | ||
| Sub 6 | Simple effects | Sand | 16.4 | 9.6 | 0.002 | Clay | 28.0 | 19.0 | 0.002 |
| Clay | 14.4 | 8.2 | 0.004 | Sand | 25.2 | 16.5 | 0.002 | ||
| Slope gradient | 8.3 | 4.4 | 0.008 | Elevation | 8.3 | 4.4 | 0.03 | ||
| Conditional effects | Sand | 16.4 | 9.6 | 0.002 | Clay | 28.0 | 19.0 | 0.002 | |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rong, L.; Duan, X.; Feng, D.; Zhang, G. Soil Moisture Variation in a Farmed Dry-Hot Valley Catchment Evaluated by a Redundancy Analysis Approach. Water 2017, 9, 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9020092
Rong L, Duan X, Feng D, Zhang G. Soil Moisture Variation in a Farmed Dry-Hot Valley Catchment Evaluated by a Redundancy Analysis Approach. Water. 2017; 9(2):92. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9020092
Chicago/Turabian StyleRong, Li, Xingwu Duan, Detai Feng, and Guangli Zhang. 2017. "Soil Moisture Variation in a Farmed Dry-Hot Valley Catchment Evaluated by a Redundancy Analysis Approach" Water 9, no. 2: 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9020092
APA StyleRong, L., Duan, X., Feng, D., & Zhang, G. (2017). Soil Moisture Variation in a Farmed Dry-Hot Valley Catchment Evaluated by a Redundancy Analysis Approach. Water, 9(2), 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9020092







