Effect of Geogenic Factors on Water Quality and Its Relation to Human Health around Mount Ida, Turkey
Abstract
:1. Introduction
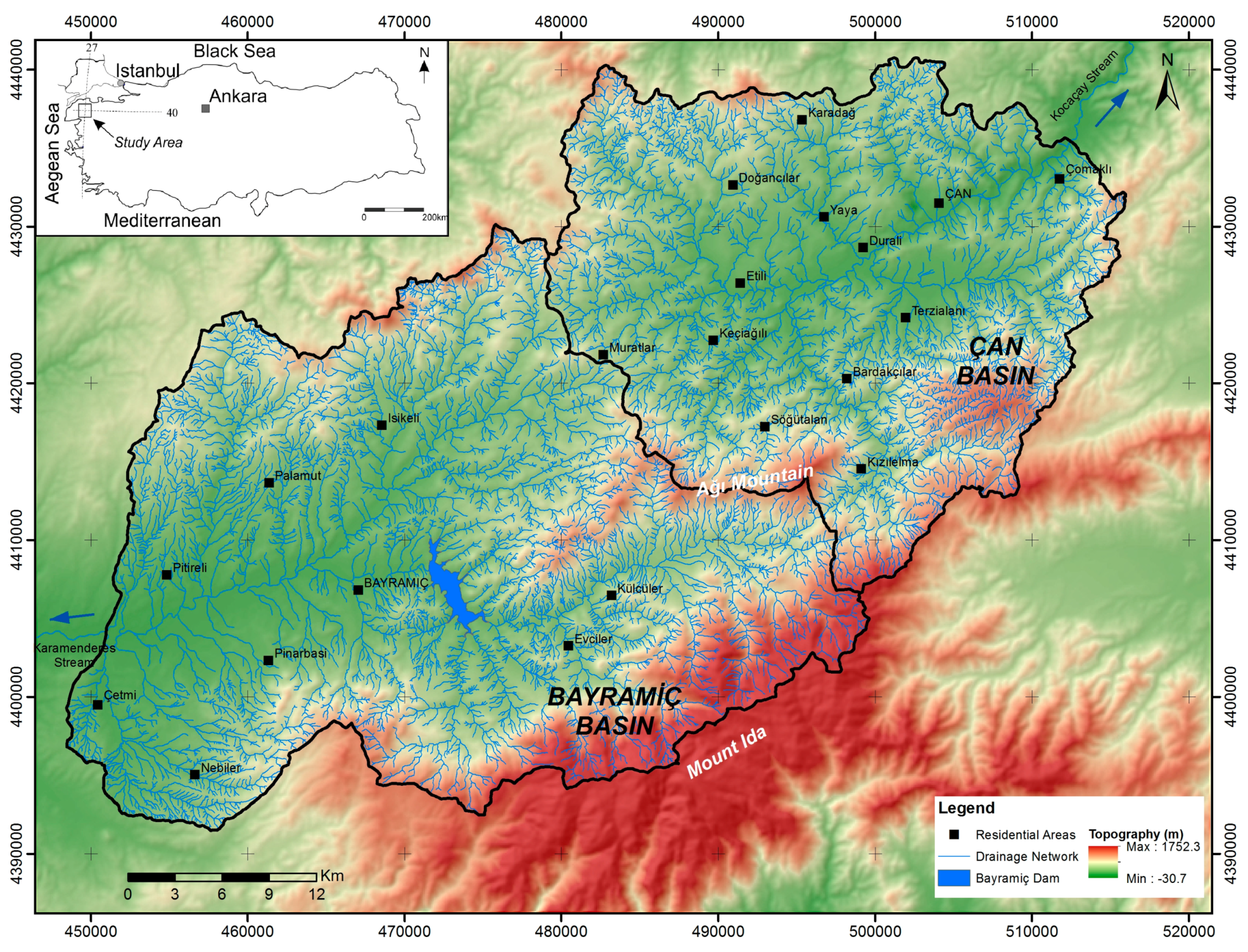
2. Characteristics of the Study Area
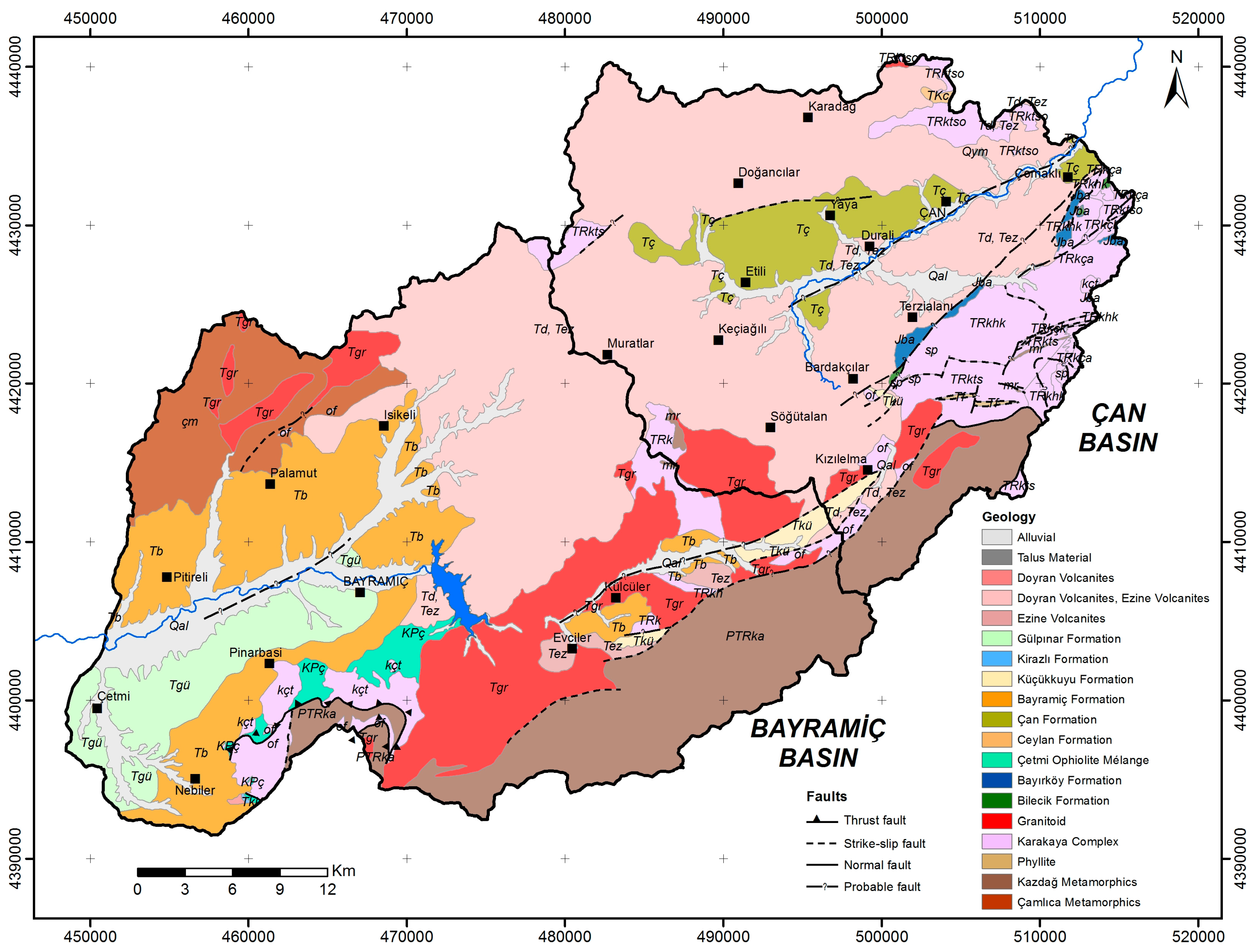
2.1. Geology of the Study Area
2.2. Hydrology of the Study Area
2.3. Hydrogeology of the Study Area
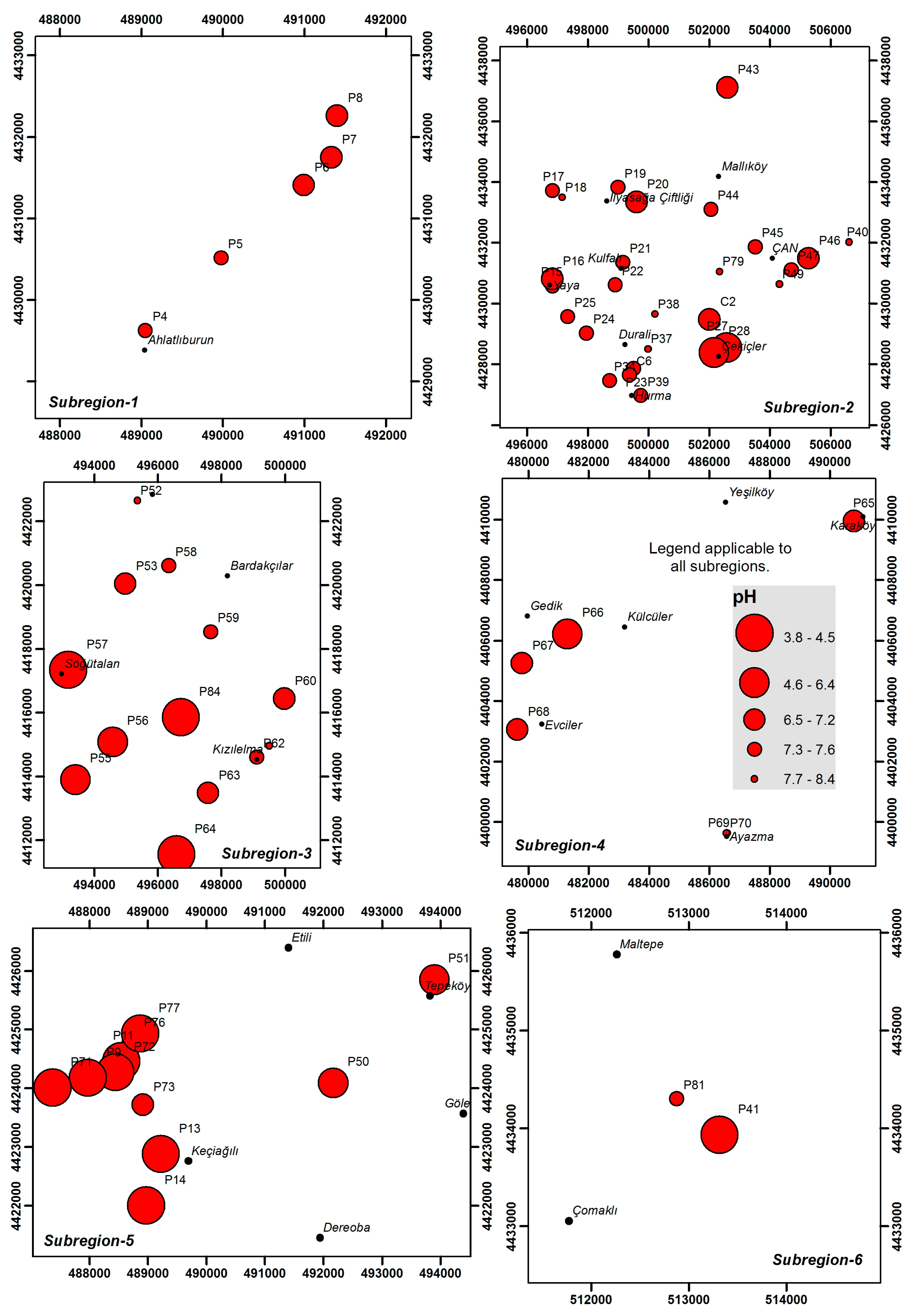
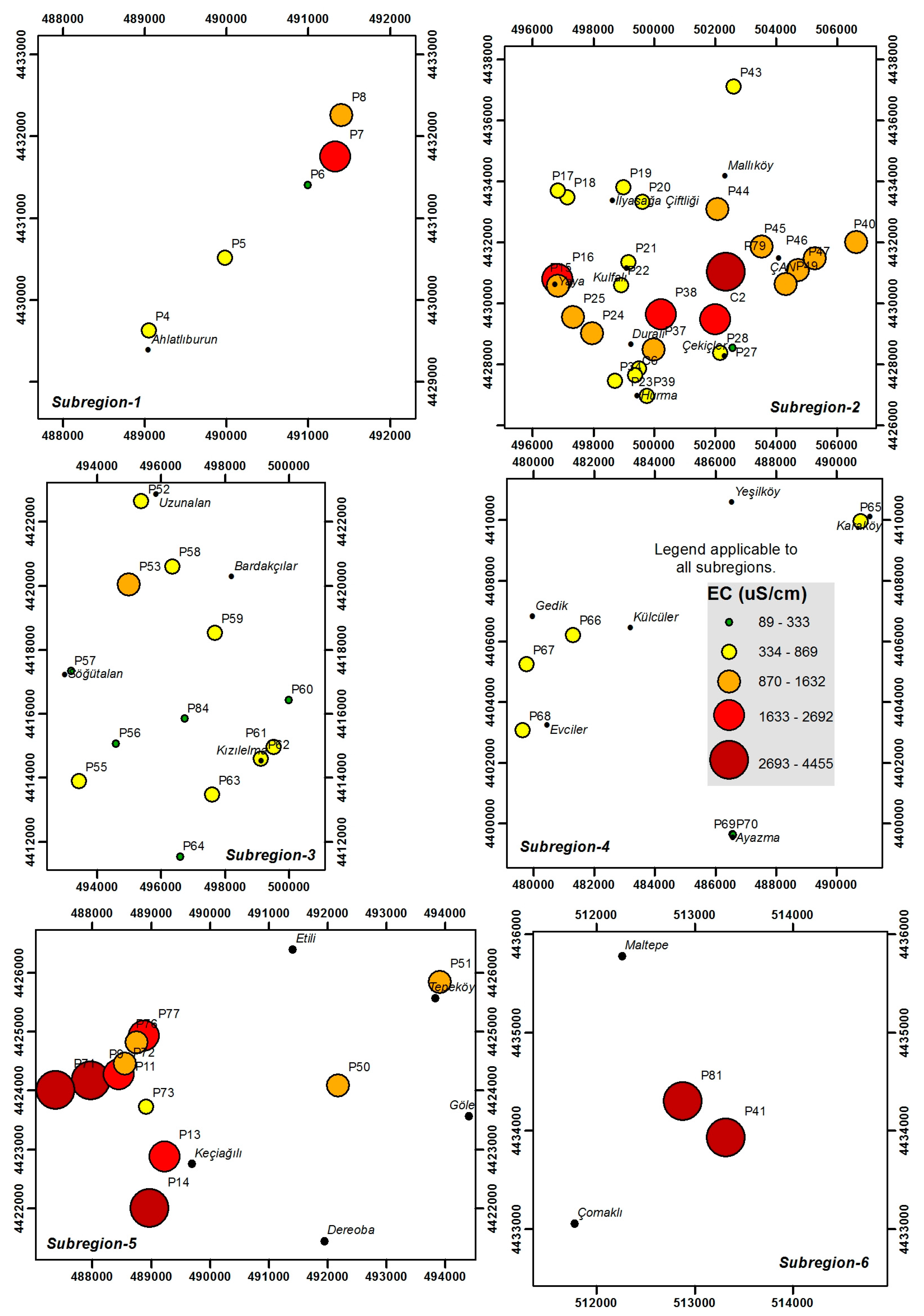
3. Materials and Methods
- (1)
- Ahlatlıburun sub-region
- (2)
- Çan sub-region
- (3)
- Ağı Mountain sub-region
- (4)
- Evciler sub-region
- (5)
- Acidic mining lakes sub-region-1
- (6)
- Acidic mining lakes sub-region-2
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Physical Properties
4.2. Major Ions
4.3. Heavy Metals and Trace Elements
4.4. Human Health Consequences
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martin, C.W. Heavy Metal trends in floodplain sediments and valley fill, River Lahn, Germany. Catena 2000, 39, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwalteney-Brant, S.M. Heavy metals. In Handbook of Toxicologic Pathology; Haschek, W.M., Rosseaux, C.G., Wallig, A.M., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 701–732. [Google Scholar]
- Jarup, L.J. Hazards of heavy metal contamination. Br. Med. Bull. 2003, 68, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakkar, P.; Jaffery, F. Biological markers for metal toxicity. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2005, 19, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nouri, J.; Mahvi, A.H.; Jahed, G.R.; Babaei, A.A. Regional distribution pattern of groundwater heavy metals resulting from agricultural activities. Environ. Geol. 2008, 55, 1337–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaaden, G. Geology and Ore Deposit Report around Çanakkale-Biga-Edremit Peninsula; MTA Report Number 2661; General Directorate of Mineral Research and Exploration (MTA): Ankara, Turkey, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- Ketin, I. Geological Report of Kapıdağ Peninsula, Marmara Island and Bandırma Region; MTA Report Number 1931; General Directorate of Mineral Research and exploration (MTA): İstanbul, Turkey, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Okay, I.A.; Siyako, M.; Bürkan, K.A. Geology and tectonic evaluation of Biga Peninsula, Northwest Turkey. Bull. Tech. Univ. Istanb. 1991, 44, 191–256. [Google Scholar]
- Okay, I.A.; Satır, M.; Maluski, H.; Siyako, M.; Metzger, R.; Akyüz, S. Paleo and Neo—Tethyan Events in Northwest Turkey: Geological and Geochrological constraints. In Tectonics of Asia; An, Y., Harrison, M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1996; pp. 420–441. [Google Scholar]
- Okay, A.I.; Satir, M. Coeval plutonism and metamorphism in a latest Oligocene metamorphic core complex in Northwest Turkey. Geol. Mag. 2000, 137, 495–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, Y. Comparisons of the young volcanic associations of western and eastern Anatolia under the compressional regime: A review. J. Volcanol. Geother. Res. 1990, 44, 69–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, H. Exploration at the Kuscayiri Au (Cu) prospect and its implications for porphyry-related mineralization in western Turkey. J. Geochem. Explor. 2003, 77, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, Y.; Genç, Ş.C.; Gürer, F.Ö.; Bozcu, M.; Yılmaz, K.; Karacık, Z.; Altunkaynak, Ş.; Elmas, A. When did the western Anatolian grabens begin to develop? Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2000, 173, 353–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houssa, C.E. Talking Turkey—An update on the Turkish minerals industry. Ind. Miner. 1999, 379, 21–47. [Google Scholar]
- Erdogan, E. Geothermal Energy Possibility of Survey and Tectonic Mapping of Tuzla Hot Springs and Surrounding; MTA Report; General Directorate of Mineral Research and Exploration (MTA): Ankara, Turkey, 1966; Unpublished. [Google Scholar]
- General Directorate of Mineral Research and Exploration (MTA). Hot and Mineral Water Inventory; MTA Report; General Directorate of Mineral Research and Exploration (MTA): Ankara, Turkey, 1980; Unpublished. [Google Scholar]
- General Directorate of Mineral Research and Exploration (MTA). Gold and Silver Deposit in Turkey; General Directorate of Mineral Research and Exploration (MTA): Ankara, Turkey, 1993; p. 46. [Google Scholar]
- Erler, A.; Larson, L.T. Genetic classification of gold occurrences for the Aegean region of Turkey. In Proceedings of the International Earth Science Colloquium on the Aegean Region, Izmir, Turkey, 1–6 October 1990.
- Agdemir, N.; Kirikoglu, M.S.; Lehmann, B.; Tietze, J. Petrology and alteration geochemistry of the epithermal Balya Pb-Zn-Ag deposit, NW Turkey. Miner. Depos. 1994, 29, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirajno, F. Volcanic-hosted epithermal systems in Northwest Turkey. S. Afr. J. Geol. 1995, 98, 13–24. [Google Scholar]
- Oygur, V. Anatomy of an epithermal mineralization: Mumcu (Balikesir-Sindirgi), inner-western Anatolia, Turkey. Miner. Res. Explor. Bull. 1997, 119, 29–39. [Google Scholar]
- Jankovic, S. The Carpatho-Balkanides and adjacent area: A sector of the Tethyan Eurasian metallogenic belt. Miner. Depos. 1997, 32, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, Y.; Tüysüz, O.; Yiğitbaş, E.; Genç, Ş.; Şengör, A.M.C. Geology and tectonic evolution of the Pontides. In Regional and Petroleum Geology of the Black Sea and Surrounding Region; Robinson, A.G., Ed.; American Association of Petroleum Geologists (AAPG): Tulsa, OK, USA, 1997; Volume 68, pp. 183–226. [Google Scholar]
- Baba, A.; Save, D.; Gündüz, O.; Gürdal, G.; Bozcu, M.; Sülün, S.; Özcan, H.; Hayran, O.; İkiışık, H.; Bakırcı, L. The Assessment of the Mining Activities in Çan Coal Basin from a Medical Geology Perspective; Final Report; Project No. ÇAYDAG-106Y041; The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TÜBİTAK): Ankara, Turkey, 2009. (In Turkish)
- World Health Organization (WHO). World Health Organization Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Environmental Protection Agency Office of Water National Primary Drinking Water Standards; EPA 816-F-03-016; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2003.
- Regulation on Waters Intended for Human Consumption (ITASHY), Official Gazette, Number 25730, 2005. Available online: http://www.ecolex.org/details/legislation/regulation-on-water-intended-for-human-consumption-lex-faoc151039/? (accessed on 20 January 2017).
- Sanliyuksel, Y.D.; Balci, N.; Baba, A. Generation of Acid Mine Lakes Associated with Abandoned Coal Mines in Northwest Turkey. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2016, 70, 757–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanliyuksel, Y.D.; Baba, A. Geochemical characterization of acid mine lakes and their effect on the environment, NW of Turkey. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2013, 64, 357–376. [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann, T.M.; Friese, K.; Zachmann, D.W. Redox and pH conditions in the water column and in the sediments of an acidic mining lake. J. Geochem. Explor. 2001, 73, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessmann, D.; Deneke, R.; Ender, R.; Hemm, M.; Kapfer, M.; Krumbeck, H. Lake Plessa 107 (Lusatia, Germany)—An extremely acidic shallow mining lake. Hydrobiologia 1999, 408, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espana, J.S.; Pamo, E.L.; Pastor, E.S.; Ercilla, M.D. The acidic mine pit lakes of the Iberian Pyrite Belt: An approach to their physical limnology and hydrogeochemistry. Appl. Geochem. 2008, 23, 1260–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordstrom, D.K. Aqueous pyrite oxidation and the consequent formation of secondary iron minerals. In Acid Sulfate Weathering; Kittrick, J.A., Fanning, D.S., Hossner, L.R., Eds.; Soil Science Society of America Special Publication 10; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1982; pp. 37–55. [Google Scholar]
- Bigham, J.M.; Nordstrom, D.K. Iron and aluminum hydroxysulfates from acid sulfate water. In Review in Mineralogy and Geochemistry: Sulfate Minerals: Crystallography, Geochemistry, and Environmental Significance, 40th ed.; Alpers, C.N., Jambor, J.L., Nordstrom, D.K., Eds.; The Mineralogical Society of America: Washington, DC, USA, 2000; pp. 351–403. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, G.; Bigham, J.M.; Faure, G. Removal of trace metals by coprecipitation with Fe, Al and Mn from natural waters contaminated with acid mine drainage in the Ducktown Mining District, Tennessee. Appl. Geochem. 2002, 17, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Chon, H.T. Hydrogeochemical characteristics of acid mine drainage in the vicinity of an abandoned mine, Daduk Creek, Korea. J. Geochem. Explor. 2006, 88, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Equeenuddin, S.M.; Tripathy, S.; Sahoo, P.K.; Panigrahi, M.K. Hydrogeochemical characteristics of acid mine drainage and water pollution at Makum Coalfield, India. J. Geochem. Explor. 2010, 105, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, J.C.; Storandt, M.; Miller, P.; McKeel, D.W.; Price, J.L.; Rubin, E.H.; Berg, L.M. Cognitive impairment represents early-stage Alzheimer disease. Arch. Neurol. 2001, 58, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaten, T.P. Aluminum as a risk factor in Alzheimer’s disease, with emphasis on drinking water. Brain Res. Bull. 2001, 55, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solfrizzi, V.; Panza, F.; Capurso, A. The role of diet in cognitive decline. J. Neural. Transm. 2003, 110, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Molloy, D.W.; Standish, T.I.; Nieboer, E.; Turnbull, J.D.; Smith, S.D.; Dubois, S. Effects of acute exposure to aluminum on cognition in humans. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2007, 70, 2011–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer-Baron, M.; Schaper, M.; Knapp, G.; van Thriel, C. Occupational aluminum exposure: Evidence in support of its neurobehavioral impact. Neurotoxicology 2007, 28, 1068–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakar, C.; Karaman, H.I.Ö.; Baba, A.; Sengünalp, F. Effect of high aluminum concentration in water resources on human health, case study: Biga Peninsula, Northwest part of Turkey. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 58, 935–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, A.; Gunduz, O. Effect of alteration zones on water quality: A case study from Biga Peninsula, Turkey. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 58, 499–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

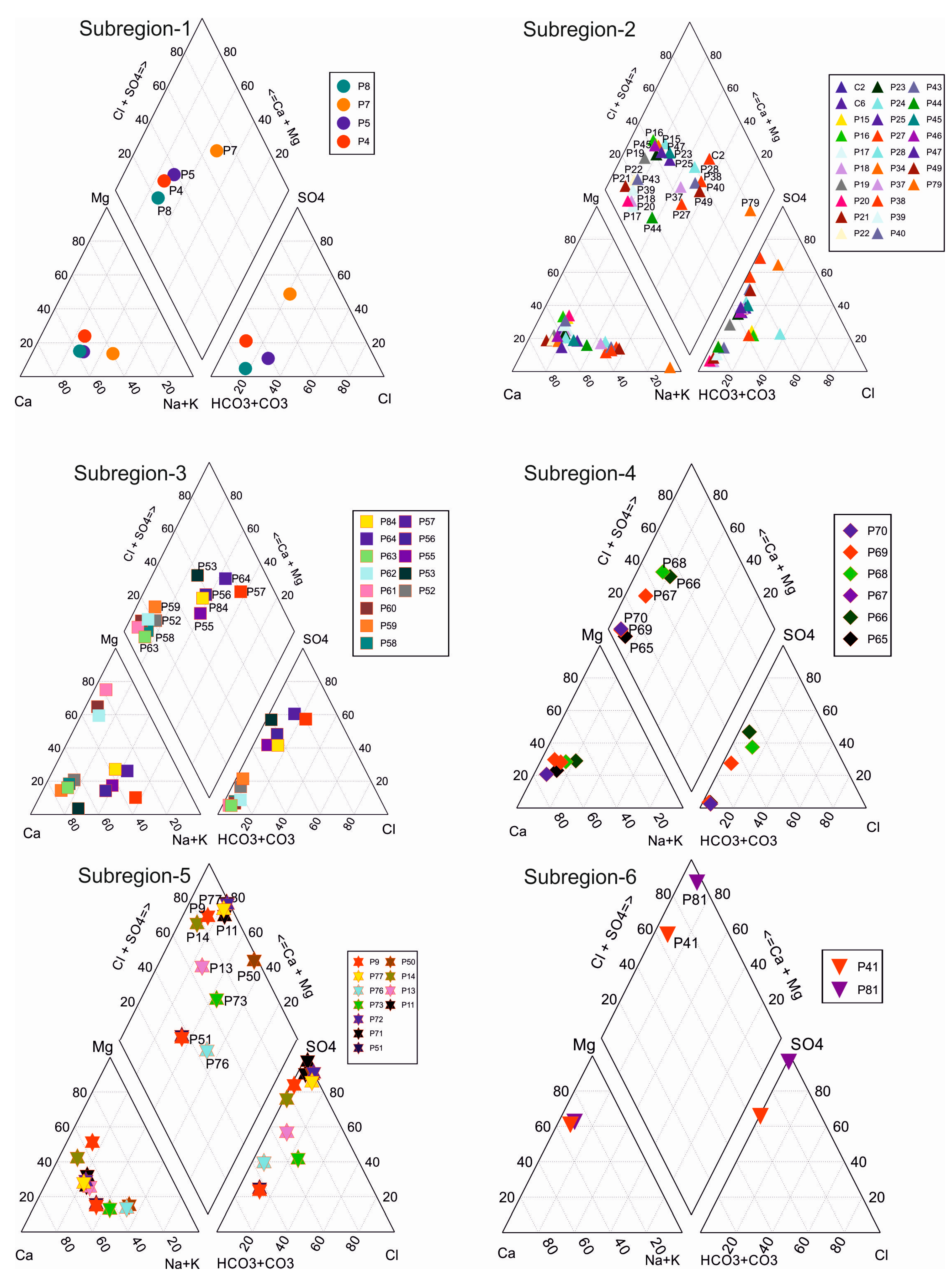
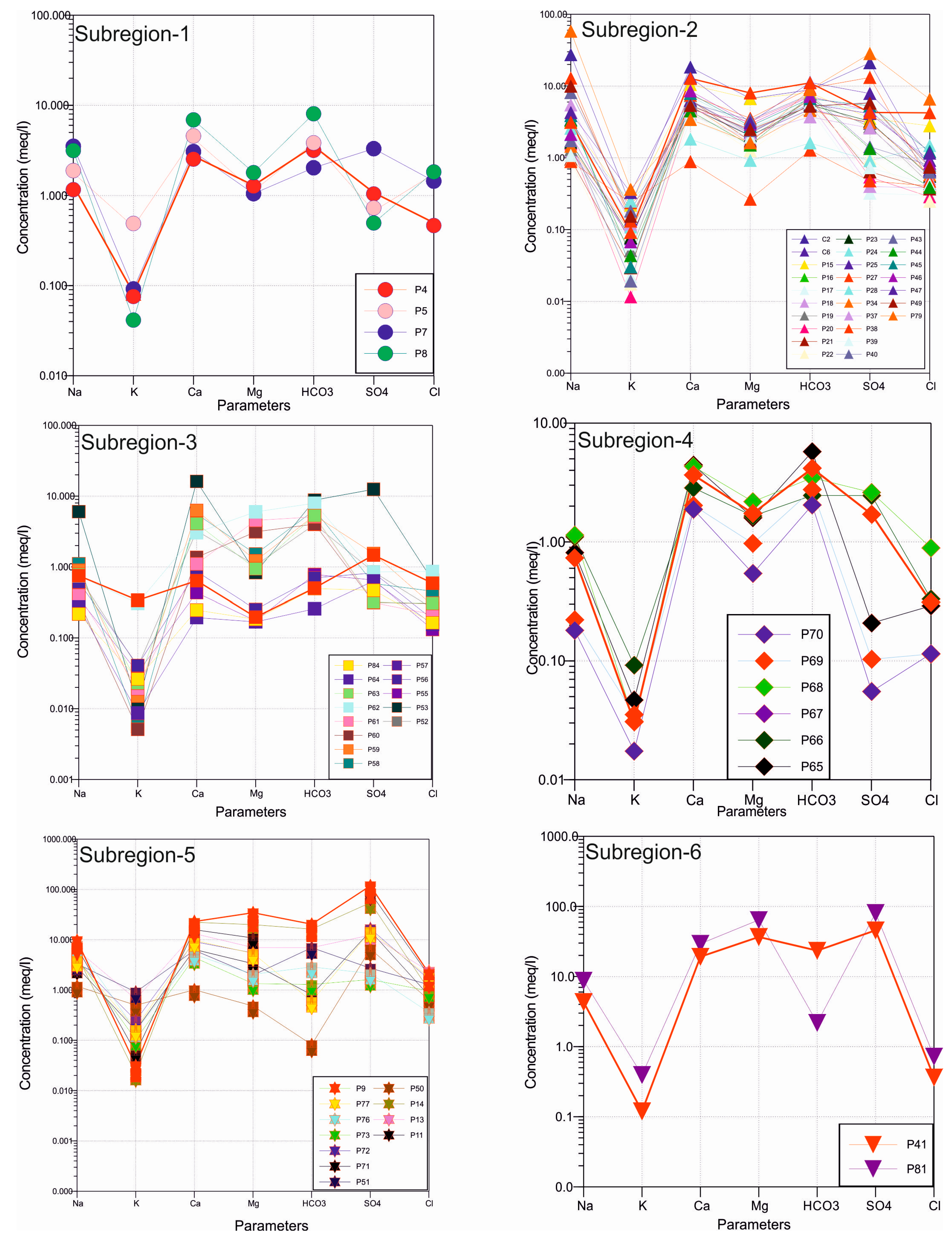

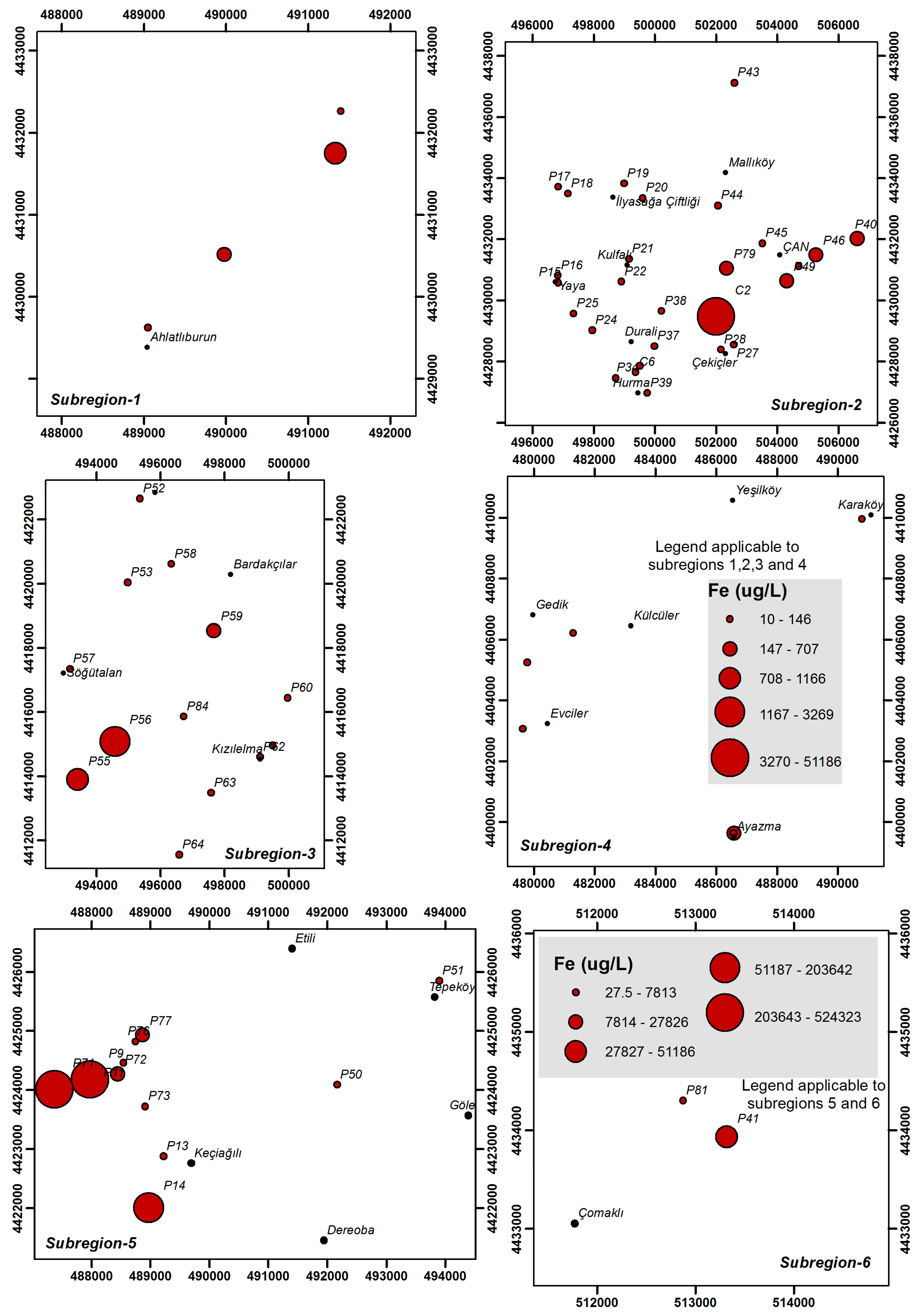
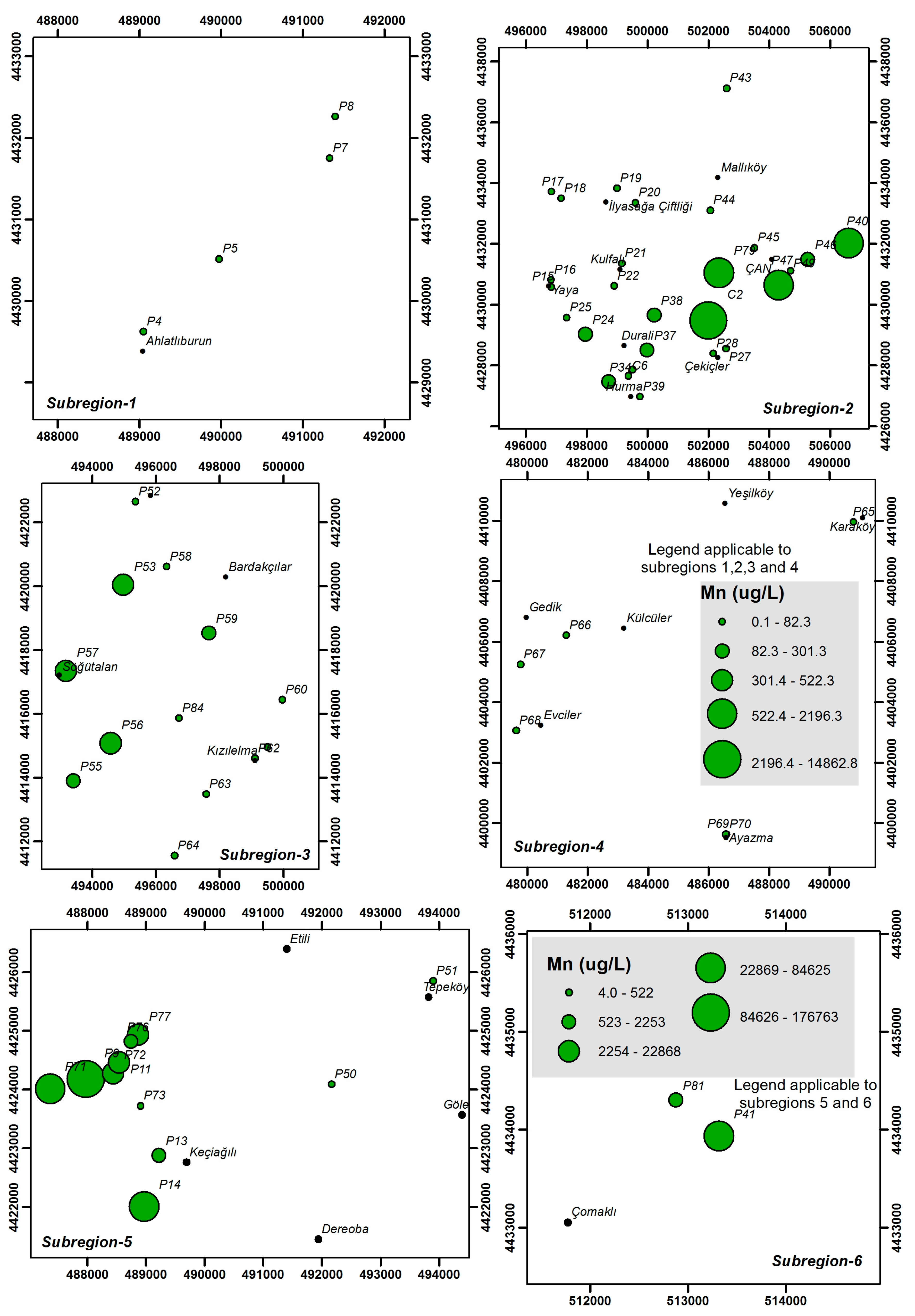
| Parameter | Unit | Min | Max | Average | Std. Dev. | WHO [25] | EPA [26] | ITASHY [27] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temp | °C | 9.9 | 24.2 | 16.7 | 2.8 | - | - | 25 |
| pH | - | 2.6 | 8.4 | 6.6 | 1.6 | 6.5–8.5 | 6.5–8.5 | 6.5–9.5 |
| EC | μS/cm | 89.3 | 7040.0 | 1248.2 | 1293.7 | - | - | 2500 |
| Na+ | mg/L | 4.2 | 1333.2 | 94.9 | 183.3 | 200 | - | 200 |
| Ca2+ | mg/L | 3.9 | 587.0 | 132.6 | 118.5 | - | - | 200 |
| Mg2+ | mg/L | 2.1 | 778.7 | 57.8 | 120.7 | - | - | 50 |
| K+ | mg/L | 0.2 | 35.6 | 5.3 | 6.5 | - | - | - |
| SO42− | mg/L | 2.7 | 5669.3 | 473.0 | 1040.0 | 250 | 250 | 250 |
| Cl− | mg/L | 4.1 | 232.4 | 32.0 | 36.4 | 250 | 250 | 250 |
| F− | mg/L | 0.03 | 3.7 | 0.56 | 0.60 | 1.5 | 2 | 1.5 |
| HCO3− | mg/L | b.d.l. | 1425.0 | 329.5 | 266.1 | - | - | - |
| Al | μg/L | 1.3 | 982,056 | 29,321 | 131,668 | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| As | μg/L | 0.5 | 58.0 | 5.4 | 10.9 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| B | μg/L | 5.0 | 5621.5 | 505.7 | 1135.4 | 500 | - | 1000 |
| Fe | μg/L | 10.0 | 524,323 | 20,687 | 85,354 | 200 | 300 | 200 |
| Mn | μg/L | 0.1 | 176,763 | 7077 | 25,694 | 400 | 50 | 50 |
| Ni | μg/L | 0.2 | 2615.8 | 103.8 | 388.1 | 20 | - | 20 |
| Zn | μg/L | 0.9 | 20,831 | 657 | 2881 | 5000 | 5000 | 5000 |
| Parameter | Unit | Sub-Region 1 (N = 4) | Sub-Region 2 (N = 27) | Sub-Region 3 (N = 13) | Sub-Region 4 (N = 6) | Sub-Region 5 (N = 11) | Sub-Region 6 (N = 2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temp | °C | 15.2–19.7 | 12.2–24.2 | 10.8–17.3 | 9.9–20.6 | 15.4–20.4 | 19.8–21.6 |
| (17.1 ± 1.8) | (17.4 ± 2.3) | (14.3 ± 2.1) | (14.7 ± 3.8) | (18.3 ± 1.5) | (20.7 ± 0.9) | ||
| pH | - | 7.0–7.4 | 5.8–8.4 | 3.8–8.0 | 6.4–8.4 | 2.6–7.0 | 3.1–7.4 |
| (7.2 ± 0.2) | (7.4 ± 0.6) | (6.4 ± 1.4) | (7.2 ± 0.7) | (4.3 ± 1.6) | (5.2 ± 2.1) | ||
| EC | μS/cm | 455–2692 | 209–4455 | 89–1568 | 193–563 | 813–7040 | 3817–4395 |
| (1210.5 ± 875.1) | (1105.6 ± 826.2) | (513.2 ± 368.4) | (409.5 ± 137.0) | (2418.7 ± 1876.0) | (4105.8 ± 289.2) | ||
| Na+ | mg/L | 29.5–80.9 | 20.4–1333.2 | 5.0–139.0 | 4.2–26.2 | 27.4–221.0 | 99.1–201.0 |
| (56.0 ± 21.3) | (140.3 ± 264.3) | (23.5 ± 33.9) | (16.1 ± 8.8) | (114.7 ± 53.6) | (150.1 ± 50.9) | ||
| Ca2+ | mg/L | 54.9–138.3 | 17.7–366.9 | 3.9–324.1 | 37.6–89.0 | 20.2–461.2 | 383.0–587.0 |
| (85.1 ± 32.8) | (128.4 ± 72.8) | (66.7 ± 84.2) | (64.1 ± 20.5) | (211.7 ± 138.3) | (485.0 ± 102.0) | ||
| Mg2+ | mg/L | 12.7–21.8 | 3.2–97.4 | 2.1–73.1 | 6.6–26.5 | 5.8–418.2 | 444.7–778.6 |
| (16.0 ± 3.5) | (32.6 ± 21.2) | (18.9 ± 21.8) | (17.6 ± 6.5) | (101.8 ± 119.0) | (611.6 ± 167.0) | ||
| K+ | mg/L | 1.6–17.7 | 0.5–14.2 | 0.2–13.3 | 0.7–3.6 | 0.8–35.6 | 4.7–15.4 |
| (6.5 ± 6.5) | (4.7 ± 3.7) | (2.6 ± 4.3) | (1.7 ± 0.9) | (10.7 ± 10.8) | (10.0 ± 5.4) | ||
| SO42− | mg/L | 23.8–158.8 | 15.4–1356.4 | 15.1–600.3 | 2.7–125.2 | 77.4–5669.3 | 2183.1–3865.3 |
| (66.6 ± 54.2) | (232.6 ± 303.4) | (78.8 ± 151.6) | (57.1 ± 53.0) | (1439.6 ± 1791.0) | (3024.2 ± 841.1) | ||
| Cl− | mg/L | 17.7–64.7 | 8.7–232.4 | 4.7–30.6 | 4.1–31.6 | 12.7–83.6 | 12.9–25.6 |
| (48.7 ± 18.6) | (37.9 ± 48.2) | (12.4 ± 7.6) | (12.1 ± 9.2) | (47.8 ± 22.3) | (19.2 ± 6.3) | ||
| F− | mg/L | 0.2–0.7 | 0.2–1.0 | 0.03–0.9 | 0.2–0.3 | 0.2–3.7 | 1.1–1.6 |
| (0.4 ± 0.2) | (0.5 ± 0.2) | (0.3 ± 0.2) | (0.3 ± 0.1) | (1.2 ± 1.1) | (1.4 ± 0.3) | ||
| HCO3− | mg/L | 123.9–492.1 | 77.8–683.8 | 15.8–537.8 | 124.8–350.5 | b.d.l.–1240.0 | 133.0–1425.0 |
| (266.3 ± 136.8) | (386.0 ± 141.6) | (233.0 ± 176.2) | (209.9 ± 75.6) | (311.3 ± 410.7) | (779.0 ± 646.0) | ||
| Al | μg/L | 2.3–463 | 1.7–377.0 | 1.3–4851.7 | 2.0–73.7 | 7.0–982,056 | 110.0–113,248 |
| (127.9 ± 193.7) | (51.1 ± 92.0) | (841.4 ± 1429.2) | (16.1 ± 25.8) | (156,449 ± 280,302) | (56,679 ± 56,569) | ||
| As | μg/L | 2.0–54.5 | 0.5–58.0 | 0.5–5.4 | 0.5–4.5 | 0.7–36.9 | 0.5–4.7 |
| (20.3 ± 20.6) | (5.2 ± 10.8) | (1.5 ± 1.5) | (1.3 ± 1.5) | (7.7 ± 10.8) | (2.6 ± 2.1) | ||
| B | μg/L | 40.3–68.0 | 8.0–5063.5 | 5.3–1222.0 | 5.0–10.0 | 80.5–4029.3 | 2529.7–5621.5 |
| (48.5–11.4) | (478.6 ± 1057.0) | (111.6 ± 320.8) | (7.1 ± 1.9) | (827.3 ± 1125.9) | (4075.6 ± 1545.9) | ||
| Fe | μg/L | 10.0–937.0 | 10.0–51,186 | 10.0–3269 | 10.0–518.0 | 27.5–524,323 | 317.0–48,499 |
| (369.9 ± 378.3) | (1997.5 ± 9647.8) | (420.5 ± 888.3) | (99.1 ± 187.5) | (108,455 ± 178,774) | (24,408 ± 24,091) | ||
| Mn | μg/L | 0.4–9.9 | 0.1–14,862.8 | 0.8–522.3 | 0.4–25.7 | 4.0–176,763 | 2253–50,896 |
| (5.1 ± 4.2) | (719.3 ± 2795.4) | (139.5 ± 183.1) | (7.0 ± 8.9) | (33,764 ± 51,686) | (26,575 ± 24,321) | ||
| Ni | μg/L | 0.2–0.9 | 0.2–20.7 | 0.2–26.2 | 0.2–31.1 | 0.2–2615.8 | 19.0–1205.6 |
| (0.6 ± 0.3) | (2.6 ± 4.2) | (5.3 ± 8.1) | (8.4 ± 11.4) | (465.6 ± 758.5) | (612.3 ± 593.3) | ||
| Zn | μg/L | 1.4–47.4 | 1.1–113.4 | 0.9–116 | 0.9–10.8 | 25.9–20,831 | 81.4–2052.5 |
| (19.2 ± 17.3) | (14.2 ± 21.9) | (21.6 ± 32.4) | (3.9 ± 3.7) | (3498.4 ± 6114.3) | (1067.0 ± 985.6) |
© 2017 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baba, A.; Gündüz, O. Effect of Geogenic Factors on Water Quality and Its Relation to Human Health around Mount Ida, Turkey. Water 2017, 9, 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9010066
Baba A, Gündüz O. Effect of Geogenic Factors on Water Quality and Its Relation to Human Health around Mount Ida, Turkey. Water. 2017; 9(1):66. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9010066
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaba, Alper, and Orhan Gündüz. 2017. "Effect of Geogenic Factors on Water Quality and Its Relation to Human Health around Mount Ida, Turkey" Water 9, no. 1: 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9010066
APA StyleBaba, A., & Gündüz, O. (2017). Effect of Geogenic Factors on Water Quality and Its Relation to Human Health around Mount Ida, Turkey. Water, 9(1), 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9010066






