Quantitative Detection and Attribution of Runoff Variations in the Aksu River Basin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
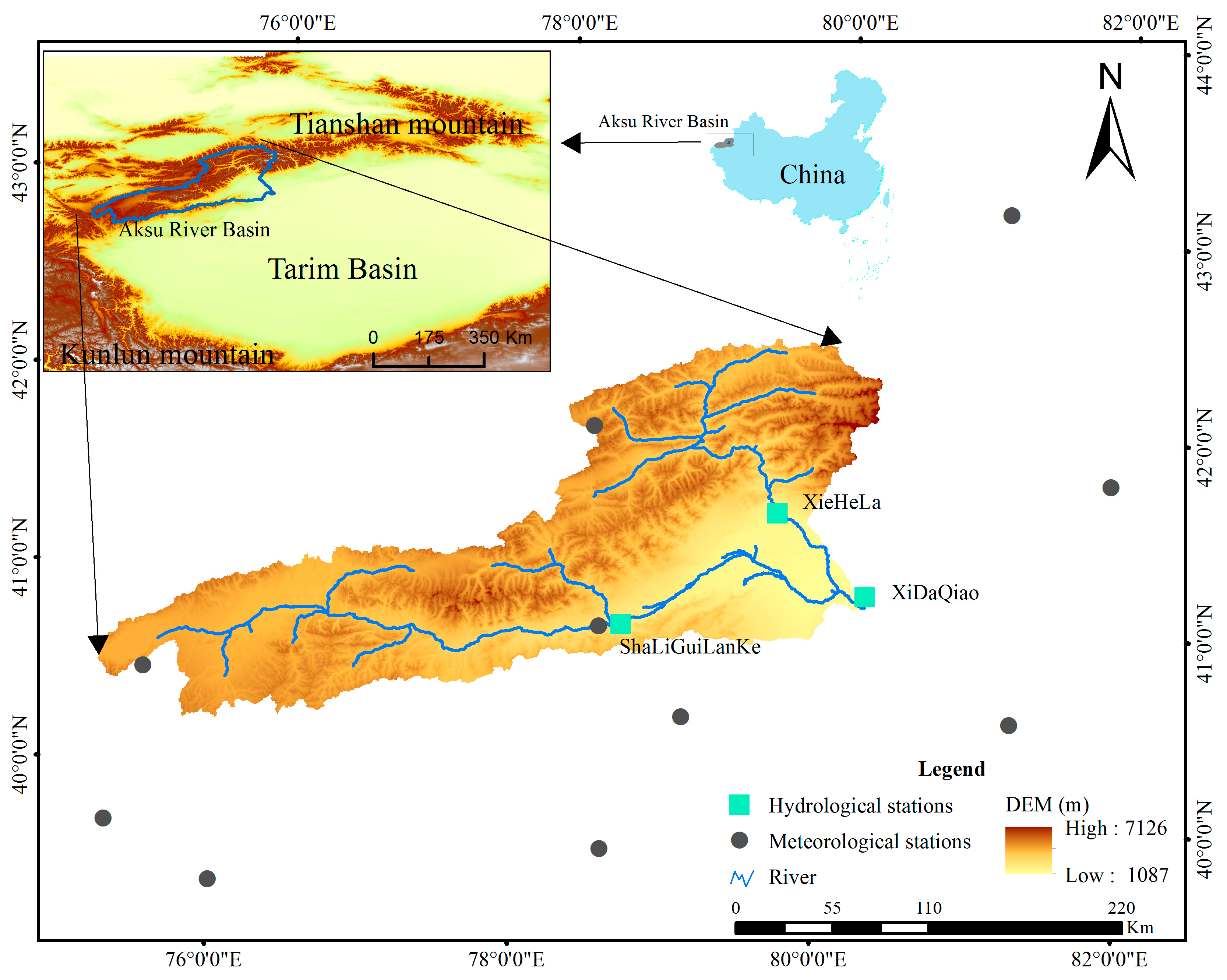
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Dataset
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Non-Parametric Mann-Kendall Test
2.3.2. Accumulative Anomaly Method
2.3.3. SCRCQ
2.3.4. Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT Model)
2.3.5. Pearson Correlation Analysis
2.3.6. Agricultural Water Footprint
3. Results and Discussion
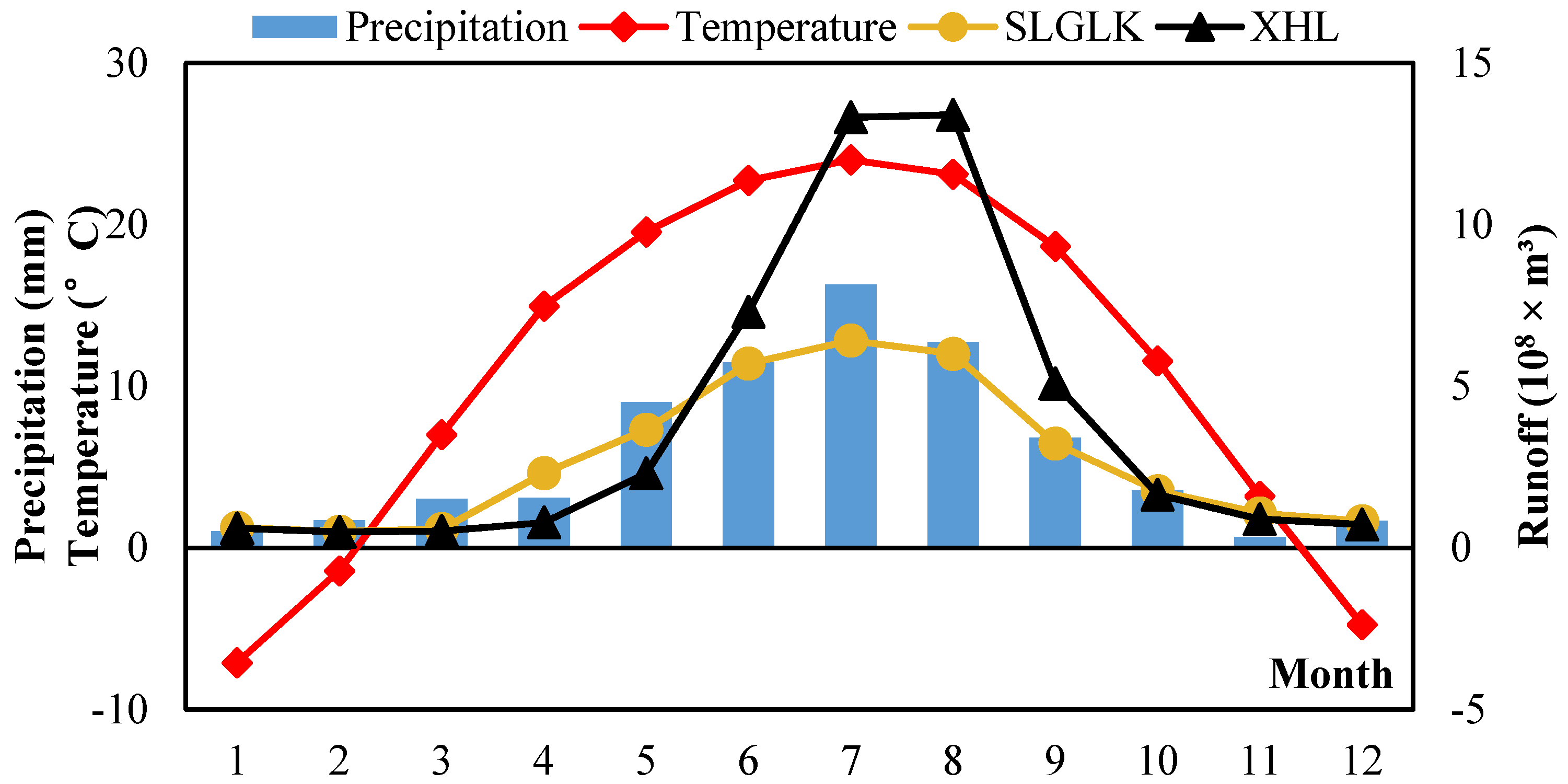
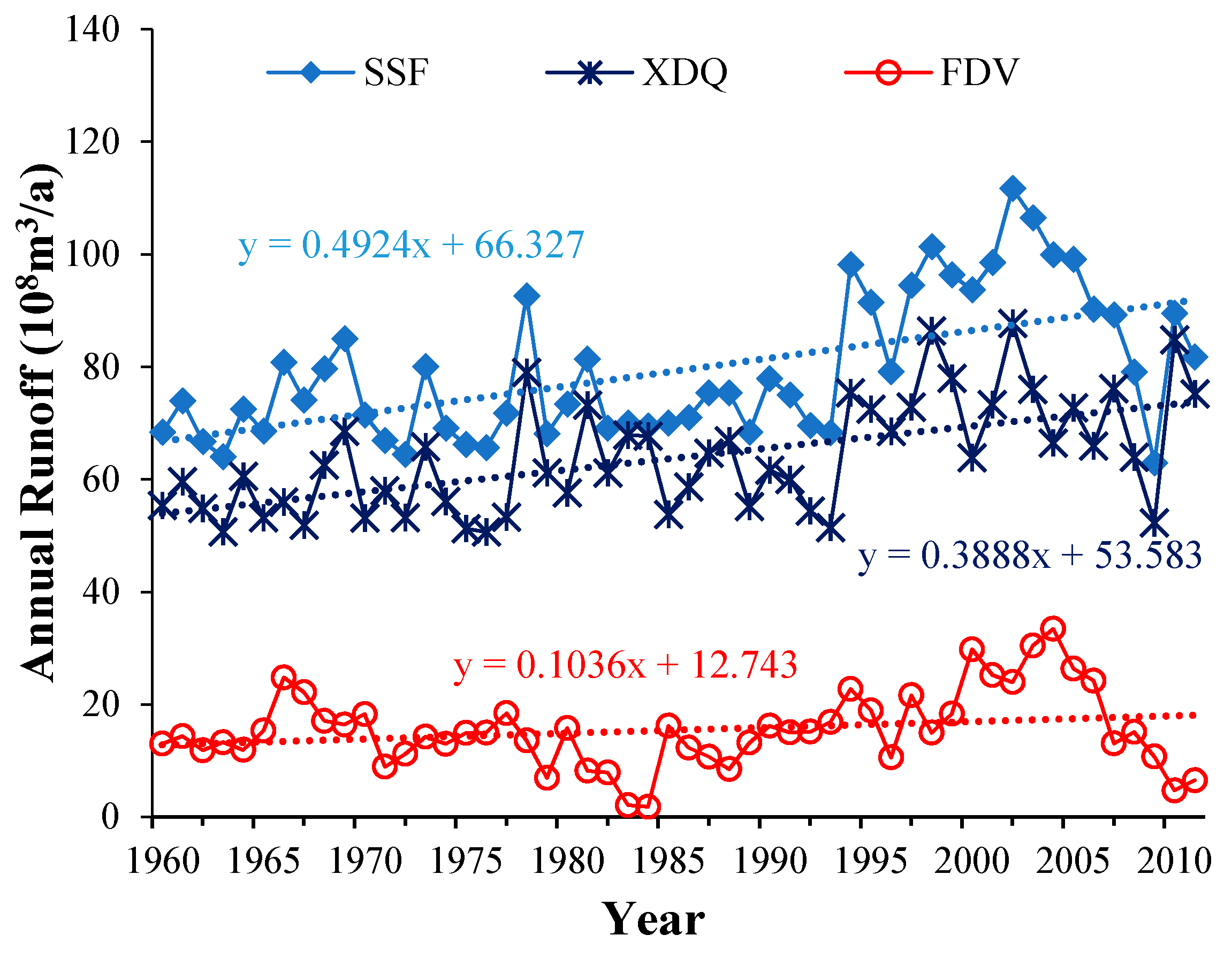
3.1. Changes and Trends in Annual Runoff
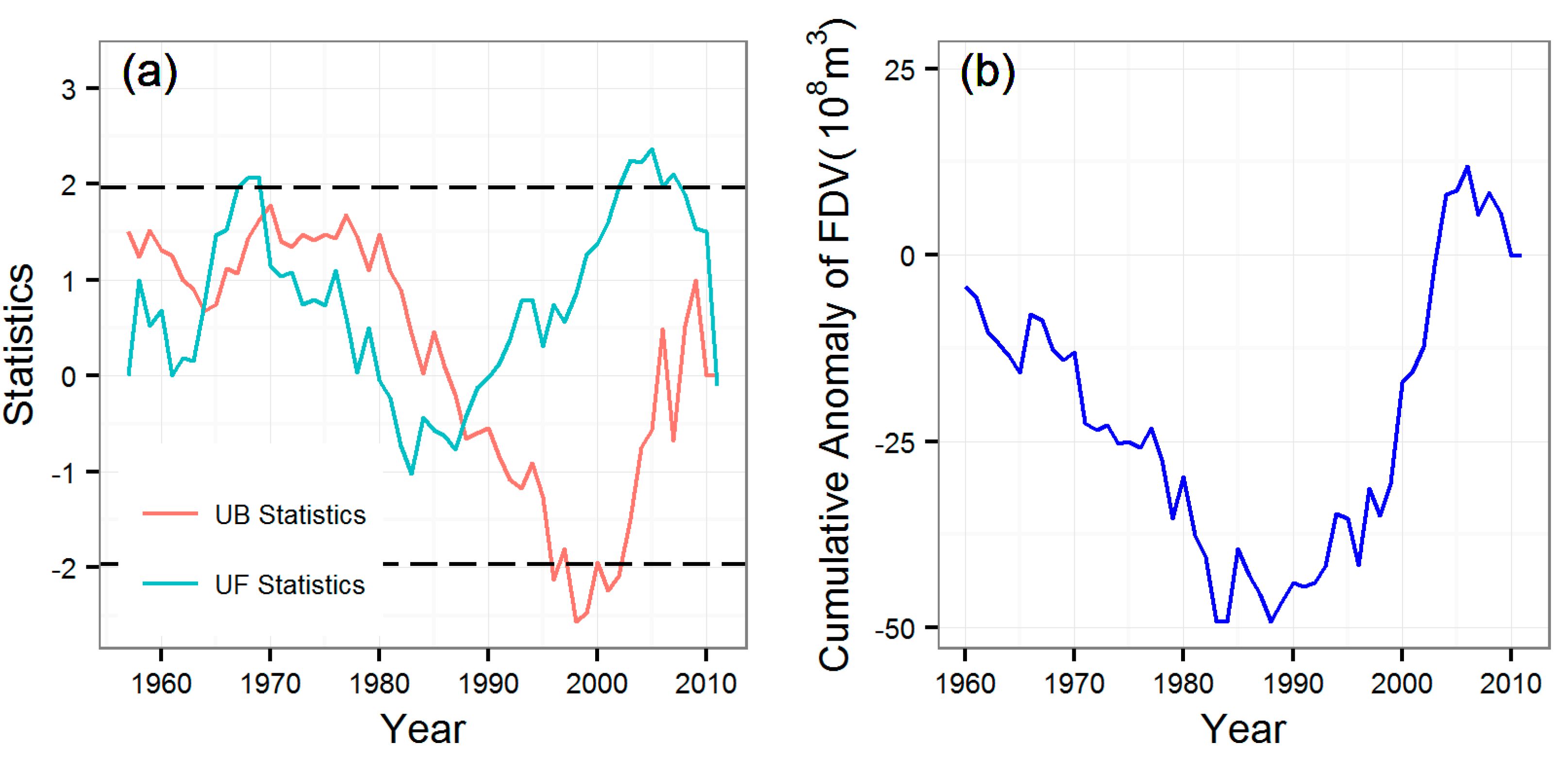
3.2. Mutation Analysis
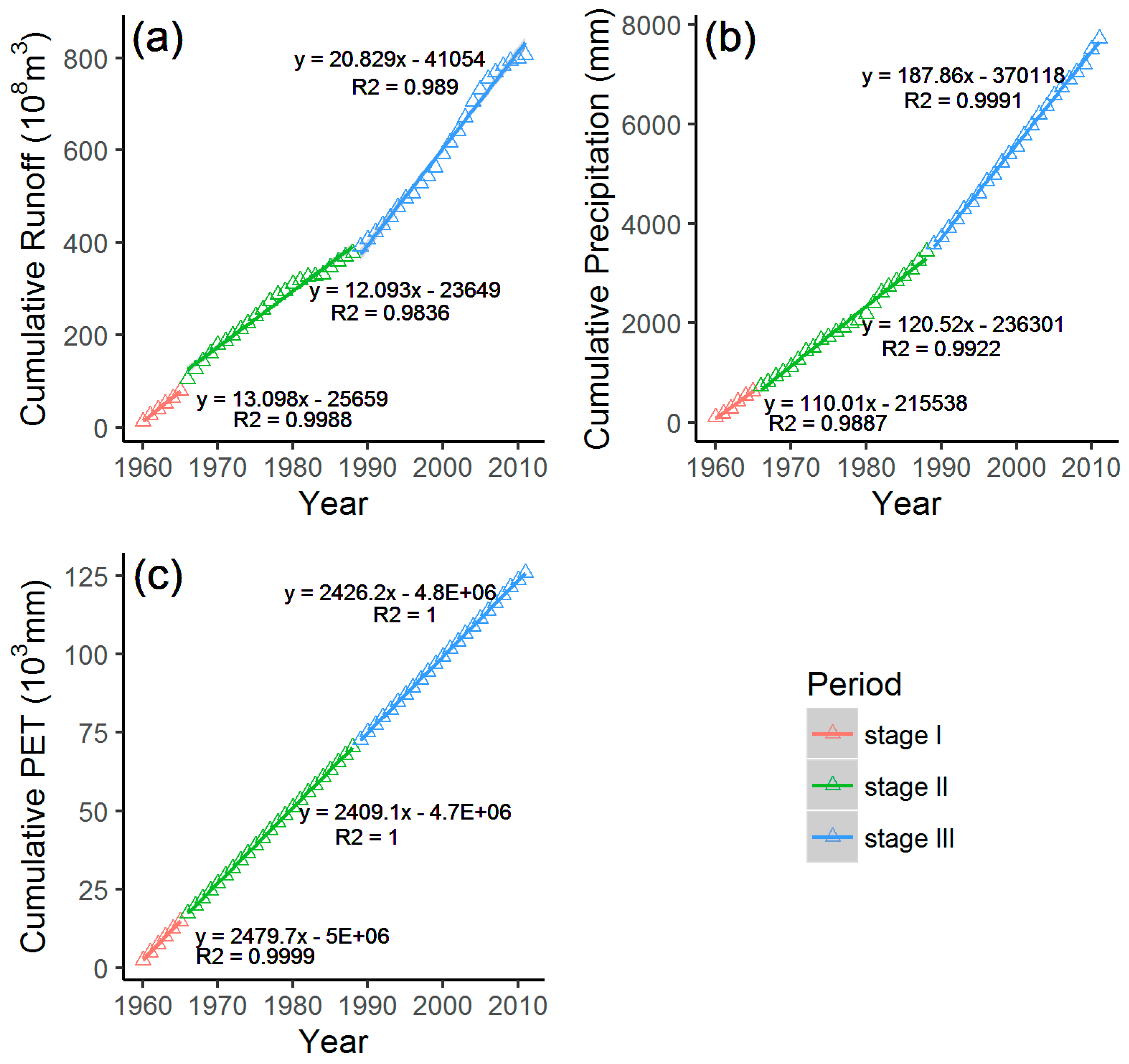
3.3. Contributions of Driving Factors to Changes in the FDV
3.3.1. SCRCQ Method
3.3.2. Model Simulation Method
3.4. Climate Change Factor
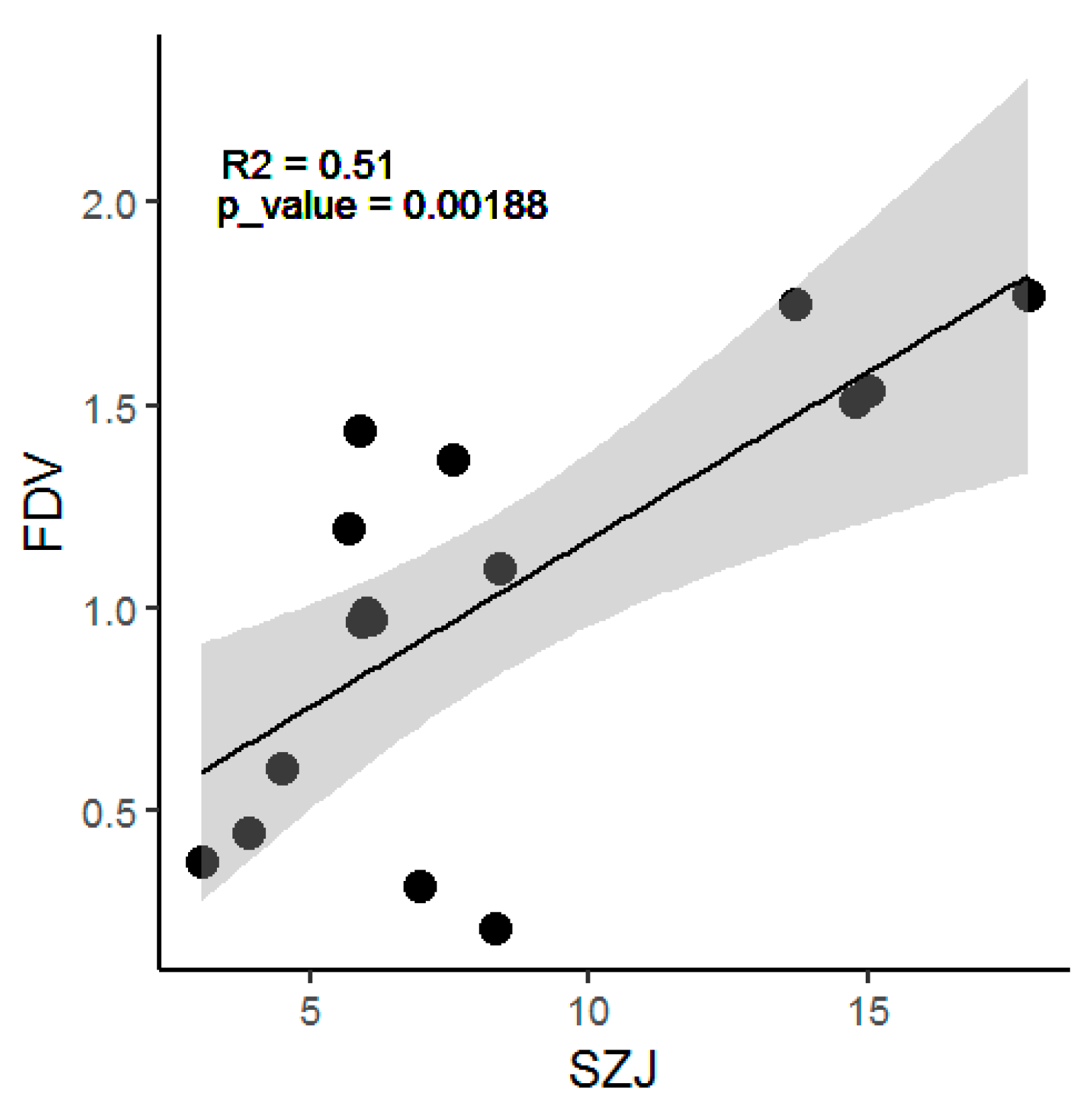
3.5. Human Activity Factor
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Törnqvist, R.; Jarsjö, J.; Pietroń, J.; Bring, A.; Rogberg, P.; Asokan, S.M.; Destouni, G. Evolution of the hydro-climate system in the lake baikal basin. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 1953–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohana-Levi, N.; Karnieli, A.; Egozi, R.; Givati, A.; Peeters, A. Modeling the effects of land-cover change on rainfall-runoff relationships in a semiarid, eastern mediterranean watershed. Adv. Meteorol. 2015, 2015, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljungqvist, F.C.; Krusic, P.J.; Sundqvist, H.S.; Zorita, E.; Brattstrom, G.; Frank, D. Northern hemisphere hydroclimate variability over the past twelve centuries. Nature 2016, 532, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, L.; Jiang, C.; Xue, B.; Liu, Q.; He, B.; Nath, R.; Cui, X. Vegetation dynamics and factor analysis in arid and semi-arid inner mongolia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 73, 2343–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, S.H.; Alazba, A.A. Hydrological response to land cover changes and human activities in arid regions using a geographic information system and remote sensing. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Allaban, M.; El-Naqa, A.; Jaber, M.; Hammouri, N. Water scarcity impact of climate change in semi-arid regions: A case study in mujib basin, jordan. Arab. J. Geosci. 2014, 8, 951–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Fang, H.; Willems, P.; Bao, A.M.; Chen, X.; Veroustraete, F.; Dong, Q.H. On the relationship between historical land-use change and water availability: The case of the lower tarim river region in northwestern china. Hydrol. Proc. 2013, 27, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Krysanova, V.; Zhai, J.; Su, B. Impact of intensive irrigation activities on river discharge under agricultural scenarios in the semi-arid aksu river basin, northwest china. Water Res. Manag. 2014, 29, 945–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Guhathakurta, S.; Lee, S.; Moore, A.; Yan, L. Grid-based land-use composition and configuration optimization for watershed stormwater management. Water Res. Manag. 2014, 28, 2867–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Q.; Zhao, H.; Mao, C.; Ma, J.; Cui, G. Quantitative analysis of human-water relationships and harmony-based regulation in the tarim river basin. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2014, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, T.F.; Qin, D.; Plattner, G.-K.; Tignor, M.; Allen, S.K.; Boschung, J. IPCC 2013: Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kliment, Z.; Matoušková, M. Runoff changes in the šumava mountains (black forest) and the foothill regions: Extent of influence by human impact and climate change. Water Resour. Manag. 2008, 23, 1813–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Hejazi, M. Quantifying the relative contribution of the climate and direct human impacts on mean annual streamflow in the contiguous united states. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, W00J12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yang, Z.; Cui, B.; Sun, T. Temporal trends of hydro-climatic variables and runoff response to climatic variability and vegetation changes in the yiluo river basin, china. Hydrol. Proc. 2009, 23, 3030–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, I.; Mujumdar, P.P. Isolating the impacts of land use and climate change on streamflow. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2015, 12, 2201–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yan, M.; Yan, Y.; Shi, C.; He, L. Contributions of climate change and human activities to the changes in runoff increment in different sections of the yellow river. Quat. Int. 2012, 282, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Willems, P.; Feng, X.W.; Li, Q.; Huang, Y.; Bao, A.M.; Chen, X.; Veroustraete, F.; Dong, Q.H. On the usefulness of remote sensing input data for spatially distributed hydrological modelling: Case of the tarim river basin in china. Hydrol. Proc. 2012, 26, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stednick, J.D. Monitoring the effects of timber harvest on annual water yield. J. Hydrol. 1996, 176, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.F.; Zhu, Q.K.; Sun, Z.F.; Wei, T.X. Effects of different land uses and land mulching modes on runoff and silt generations on loess slopes. Agric. Res. Arid Areas 2005, 23, 137–141. [Google Scholar]
- Meginnis, H.G. Increasing Water Yields by Cutting Forest Vegetation. In Proceedings of the Symposium of Hannoversch-Munden, Gentbrugge, Germany, 8–14 September 1959; Publ. 48. International Association of Scientific Hydrology: Louvain, Belgium, 1959; pp. 59–68. [Google Scholar]
- Burgy, R.H.; Papazafiriou, Z.G. Vegetative management and water yield relationships. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Seminar for Hydrology Professors, Purdue University, Lafayette, IN, USA, 18–31 July 1971.
- Bosch, J.M.V.; Hewlett, J. A review of catchment experiments to determine the effect of vegetation changes on water yield and evapotranspiration. J. Hydrol. 1982, 55, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Ran, L.; Su, T. Climatic and anthropogenic impacts on runoff changes in the songhua river basin over the last 56 years (1955–2010), Northeastern China. Catena 2015, 127, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Wang, S.; Strauss, P. Decoupling streamflow responses to climate variability and land use/cover changes in a watershed in Northern China. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2014, 50, 1425–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, X. The impact of forest change on watershed hydrology—Discussing some controversies on forest hydrology. J. Nat. Res. 2000, 16, 474–480. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, J.; Rustomji, P.; Hairsine, P. Responses of streamflow to changes in climate and land use/cover in the Loess Plateau, China. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, W00A07. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, B.; Li, W.; Liu, M. Response of streamflow to climate change and human activity in xitiaoxi river basin in China. Hydrol. Proc. 2014, 28, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rust, W.; Corstanje, R.; Holman, I.P.; Milne, A.E. Detecting land use and land management influences on catchment hydrology by modelling and wavelets. J. Hydrol. 2014, 517, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.-Y.; Bosilovich, M.G. Planetary boundary layer and surface layer sensitivity to land surface parameters. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1996, 77, 353–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.L.; Lv, X.G.; Wang, L. A review on study methods of effect of land use and land cover change on watershed hydrology. Wetl. Sci. 2009, 7, 83–88. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Wei, X.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Fan, H.; Zhang, M.; Yin, J.; Zhan, M. How do climate and forest changes affect long-term streamflow dynamics? A case study in the upper reach of poyang river basin ecohydrology early view. Ecohydrology 2014, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, T.J.; Miller, S.N. Using the soil and water assessment tool (swat) to assess land use impact on water resources in an east African watershed. J. Hydrol. 2013, 486, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memarian, H.; Balasundram, S.K.; Talib, J.B.; Teh Boon Sung, C.; Mohd Sood, A.; Abbaspour, K.C. Kineros2 application for land use/cover change impact analysis at the Hulu Langat basin, Malaysia. Water Environ. J. 2013, 27, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.M.B.; Sanches Fernandes, L.F.; Moura, J.P.; Pereira, M.G.; Pacheco, F.A.L. The impact of climate change, human interference, scale and modeling uncertainties on the estimation of aquifer properties and river flow components. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 1297–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cibin, R.; Athira, P.; Sudheer, K.P.; Chaubey, I. Application of distributed hydrological models for predictions in ungauged basins: A method to quantify predictive uncertainty. Hydrol. Proc. 2014, 28, 2033–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Q. Attribution of runoff change for the xinshui river catchment on the Loess Plateau of China in a changing environment. Water 2016, 8, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.-J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Yang, J.-W.; Jiang, D.-J.; Li, J.-Y.; Qin, D.-Y. Assessing the impact of climate variability and human activities on streamflow from the wuding river basin in China. Hydrol. Proc. 2007, 21, 3485–3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Yang, D.; Tan, S.K.; Gao, B.; Hu, Q. Impact of climate variability and human activity on streamflow decrease in the Miyun reservoir catchment. J. Hydrol. 2010, 389, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Kang, S.; Zhang, L.; Tong, L.; Su, X. Analysis of impacts of climate variability and human activity on streamflow for a river basin in arid region of Northwest China. J. Hydrol. 2008, 352, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhang, G.; Xu, Y. Separating the impacts of climate variation and human activities on runoff in the Songhua river basin, Northeast China. Water 2014, 6, 3320–3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y. Assessing the impact of climate variability and human activities on streamflow variation. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 1547–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenegro, A.; Ragab, R. Hydrological response of a brazilian semi-arid catchment to different land use and climate change scenarios: A modelling study. Hydrol. Proc. 2010, 24, 2705–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Xia, J.; Chen, J. Quantification of effects of climate variations and human activities on runoff by a monthly water balance model: A case study of the chaobai river basin in Northern China. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Ye, B.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yi, S.; Wang, J.; Shangguan, D.; Zhao, C.; Han, H. Coupling a glacier melt model to the variable infiltration capacity (vic) model for hydrological modeling in North-Western China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 68, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wortmann, M.; Krysanova, V.; Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Su, B.; Li, X. Assessing the influence of the merzbacher lake outburst floods on discharge using the hydrological model swim in the Aksu headwaters, kyrgyzstan/nw China. Hydrol. Proc. 2014, 28, 6337–6350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, X.; Xu, H.; Ling, H.; Yu, P. Influences of climate change and human activities on tarim river runoffs in China over the past half century. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 67, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duethmann, D.; Bolch, T.; Farinotti, D.; Kriegel, D. Attribution of streamflow trends in snow and glacier melt-dominated catchments of the Tarim river, central Asia. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 4727–4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Y.; Shen, Y.P.; Chao, H.; Wang, J.; Mao, W.Y.; Gao, Q.Z.; Wang, S.D. Runoff changes in aksu river basin during 1956–2006 and their impacts on water availability for Tarim river. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2008, 30, 562–568. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhou, C.H.; Cheng, W.M. Analysis on runoff supply and viriation characteristics of Aksu drainage basin. J. Nat. Res. 2005, 20, 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Mao, W. The effects of human activities on oasis climate and hydrologic environment in the Aksu river basin, Xinjiang, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 59, 1759–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, W. Increasing precipitation and baseflow in Aksu river since the 1950s. Quat. Int. 2014, 336, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, D.; Xiang, X.; Huang, X. Impact of agricultural development on variation in surface runoff in arid regions: A case of the Aksu river basin. J. Arid Land 2012, 4, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Jiang, Z.; Yang, Q. Association of north atlantic oscillations with Aksu river runoff in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2009, 19, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.C.; Luo, G.P.; Yin, C.Y.; Xu, W.Q.; Feng, Y.X. Land use/cover change of the Aksu river watershed in the period of 1960–2008. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2010, 32, 275–284. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, R.; Ding, H. Responses of surface runoff to climate change and human activities in the arid region of central Asia: A case study in the Tarim river basin, China. Environ. Manag. 2013, 51, 926–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabiti, M.; Hu, J.L. Land use change in aksu river basin in 1957–2007 and its hydrological effects analysis. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2011, 33, 182–189. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Sun, G.; McNulty, S.G.; Amatya, D.M. A comparison of six potential evapotranspiration methods for regional use in the Southeastern United States1. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2005, 41, 621–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, G.H.; Samani, Z.A. Reference crop evapotranspiration from temperature. Appl. Eng. Agric. 1985, 1, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration—Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements—FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Erhan, B. Fifty Years in Xinjiang; Historical Accounts Press: Beijing, China, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Bureau of Statistics of Xinjiang Autonomous Region. Xinjiang Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 1965–2012.
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Methods; C. Griffin: London, UK, 1948. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, F.Y. Modern Climatic Statistical Diagnosis and Prediction Technology; China Meteorological Press: Beijing, China, 1999.
- Arnold, J.G.; Moriasi, D.N.; Gassman, P.W.; Abbaspour, K.C.; White, M.J.; Srinivasan, R.; Santhi, C.; Harmel, R.D.; van Griensven, A.; van Liew, M.W. Swat: Model use, calibration, and validation. Trans. ASABE 2012, 55, 1491–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Su, X.; Singh, V.; Jin, J. Impacts of climate and land use/cover change on streamflow using swat and a separation method for the xiying river basin in Northwestern China. Water 2016, 8, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Chen, H.; Ju, W.; Hua, W.; Yu, M.; Yin, Y. Assessing the future hydrological cycle in the Xinjiang basin, China, using a multi-model ensemble and swat model. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 2972–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, K. Mathematical Contributions to the Theory of Evolution; Dulau and Co.: London, UK, 1904. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, S.; Wang, C.Y. Applicability of prewhitening to eliminate the influence of serial correlation on the mann-kendall test. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.G.; Srinivasan, R.; Muttiah, R.S.; Williams, J.R. Large area hydrologic modeling and assessment part i: Model development. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1998, 34, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Griensven, A.; Meixner, T.; Grunwald, S.; Bishop, T.; Diluzio, M.; Srinivasan, R. A global sensitivity analysis tool for the parameters of multi-variable catchment models. J. Hydrol. 2006, 324, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaspour, K.C.; Vejdani, M.; Haghighat, S. SWAT-CUP calibration and uncertainty programs for SWAT. In MODSIM 2007 International Congress on Modelling and Simulation; Modelling and Simulation Society of Australia and New Zealand: Perth, Australia, 2007; pp. 1596–1602. [Google Scholar]
- Dowdy, S.; Wearden, S.; Chilko, D. Statistics for Research; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra, A.Y.; Chapagain, A.K. Water footprints of nations: Water use by people as a function of their consumption pattern. Water Res. Manag. 2006, 21, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.H.; Xu, Z.M.; Li, Y.H. A rough estimate of water footprint of Gansu province in 2003. J. Nat. Res. 2005, 20, 909–915. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Singh, V.P.; Li, J.; Jiang, F.; Bai, Y. Spatio-temporal variations of precipitation extremes in Xinjiang, China. J. Hydrol. 2012, 434, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, Z.; Tang, J.; Wei, C. Understanding temporal and spatial complexity of precipitation distribution in Xinjiang, China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2016, 123, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorg, A.; Bolch, T.; Stoffel, M.; Solomina, O.; Beniston, M. Climate change impacts on glaciers and runoff in Tien Shan (Central Asia). Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Yang, D.; Huang, M. Impacts of climate change and vegetation dynamics on runoff in the mountainous region of the haihe river basin in the past five decades. J. Hydrol. 2014, 511, 786–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Chen, Y.; Lu, F.; Li, W.; Zhang, L.; Hong, Y. The nonlinear trend of runoff and its response to climate change in the Aksu river, Western China. Int. J. Climatol. 2011, 31, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, H.; Xu, H.; Fu, J. Temporal and spatial variation in regional climate and its impact on runoff in Xinjiang, China. Water Res. Manag. 2012, 27, 381–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taye, G.; Poesen, J.; Wesemael, B.V.; Vanmaercke, M.; Teka, D.; Deckers, J.; Goosse, T.; Maetens, W.; Nyssen, J.; Hallet, V. Effects of land use, slope gradient, and soil and water conservation structures on runoff and soil loss in semi-arid northern Ethiopia. Phys. Geogr. 2013, 34, 236–259. [Google Scholar]
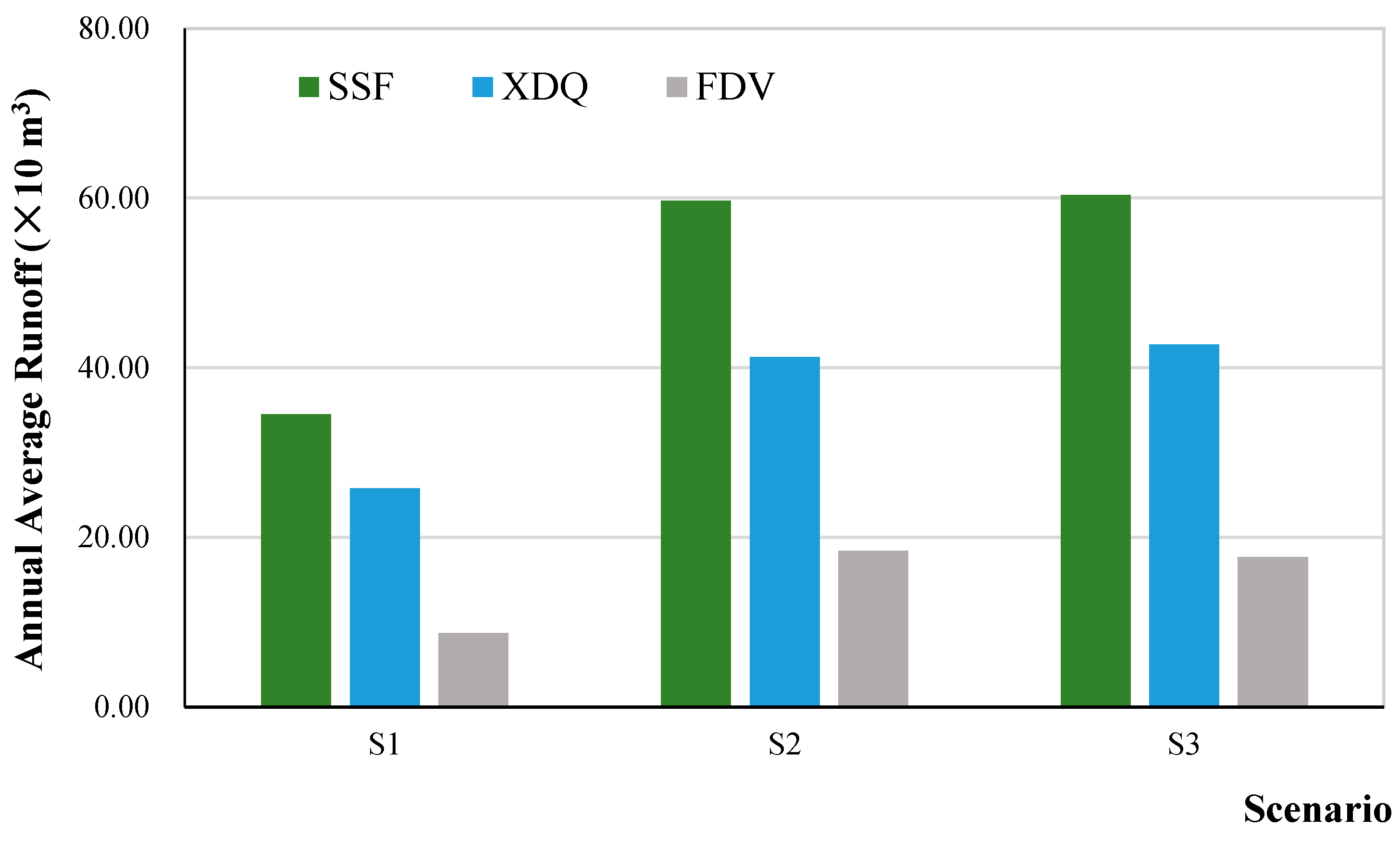
| Data | Application | Data Description and Configuration Details | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digital Elevation Model (DEM) | Sub-basin delineation and stream network extraction | Data at 90 m resolution; used to define four slope classes: 0%–25%, 25%–45%, 45%–65% and >65%. | Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) |
| Land use/cover | HRU definition | Vector data; 12 basic land use/cover categories. | Key Laboratory of Remote Sensing and Geographic Information System, Xinjiang Institute of Ecology and Geography, Chinese Academy of Sciences |
| Soil characteristics | HRU definition | 1 km resolution, 15 soil types. | Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), Harmonized World Soil Database version 1.1 (HWSD) |
| Meteorological data | Meteorological forcing | Daily maximum and minimum temperature, daily precipitation. | China Meteorological Data Sharing Service System |
| Hydrological observation data | Calibration and validation | Daily observation runoff data of SLGLK and XHL. | Tarim River Basin Management Bureau |
| Component | Parameter Name | Sensitivity Rate | Calibration Range | Subbasin | Final Estimate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basin/snow | SFTMP | 4 | −5~5 | Share | −0.552 |
| SMTMP | 1 | −5~5 | Share | −0.2478 | |
| SMFMX | 7 | 0~10 | Share | 6.8002 | |
| SMFMN | 10 | 0~10 | Share | 1.5104 | |
| TIMP | 8 | 0.01~1 | Share | 0.0873 | |
| PLAPS | 2 | 0~500 | SLGLK | 70 | |
| XHL | 280 | ||||
| TLAPS | 3 | −10~10 | SLGLK | −6.5 | |
| XHL | −4.5 | ||||
| Surface runoff | LAT_TTIME | 5 | 0~180 | SLGLK | 7 |
| XHL | 3 | ||||
| CH_K2 | 9 | 0~500 | SLGLK | 0.006 | |
| XHL | 0.65 | ||||
| Ground water | ALPHA_BF | 6 | 0~1 | SLGLK | 0.5 |
| XHL | 1 |
| Agricultural Products | Food Crops | Commercial Crops | Animal Products | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cotton | Oil Plants | Beet | Vegetable | Fruits | Meat | ||
| Unit Factor/(m3/kg) | 1.532 | 3.871 | 2.74 | 0.171 | 1.152 | 1.152 | 5.91 |
| Time Period | (108 m3/a) | (mm/a) | (mm/a) | (%) | (%) | (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| II | 12.09 | 120.52 | 2409.1 | - | - | - |
| III | 20.83 | 187.86 | 2426.2 | 77.35 | −0.98 | 23.63 |
| Climate Factors | Stage II | Stage III | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annual Mean Temperature | Annual Precipitation | Annual Mean Temperature | Annual Precipitation | |
| Annual FDV | 0.024 | –0.272 | 0.082 | –0.472 |
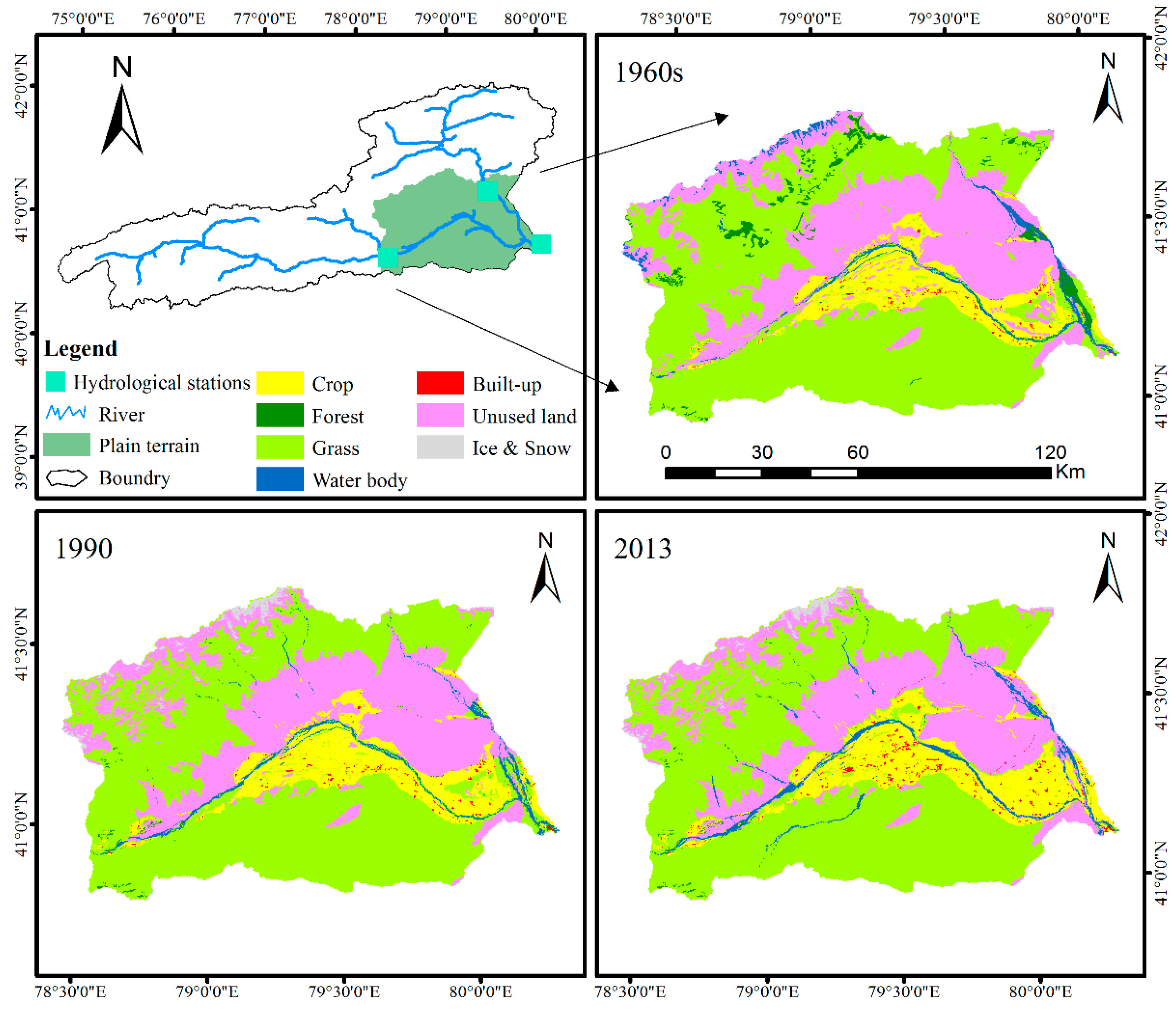
| Year | Area (km2) | Increment (km2) | Increased Proportion (%) | Increased Speed (km2/a) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1960s | 965.87 | - | - | - |
| 1990 | 1113.16 | 147.29 | 15.25 | 4.91 |
| 2013 | 1347.67 | 234.51 | 21.07 | 10.20 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, F.; Liu, T.; Huang, Y.; Luo, M.; Bao, A.; Hou, D. Quantitative Detection and Attribution of Runoff Variations in the Aksu River Basin. Water 2016, 8, 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8080338
Meng F, Liu T, Huang Y, Luo M, Bao A, Hou D. Quantitative Detection and Attribution of Runoff Variations in the Aksu River Basin. Water. 2016; 8(8):338. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8080338
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Fanhao, Tie Liu, Yue Huang, Min Luo, Anming Bao, and Dawei Hou. 2016. "Quantitative Detection and Attribution of Runoff Variations in the Aksu River Basin" Water 8, no. 8: 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8080338
APA StyleMeng, F., Liu, T., Huang, Y., Luo, M., Bao, A., & Hou, D. (2016). Quantitative Detection and Attribution of Runoff Variations in the Aksu River Basin. Water, 8(8), 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8080338







