Sediment-Water Exchange, Spatial Variations, and Ecological Risk Assessment of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the Songhua River, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
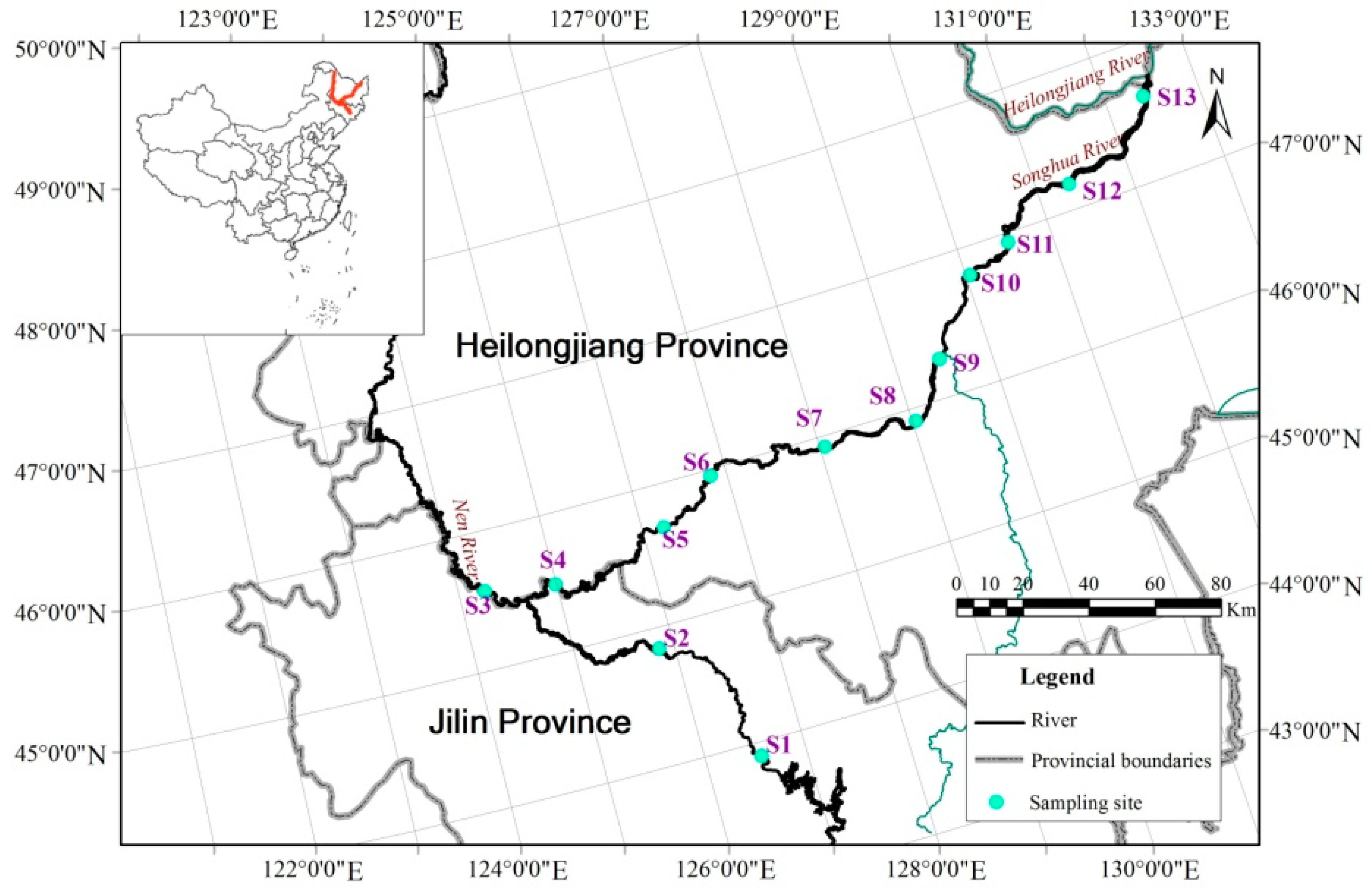
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources and Compilation
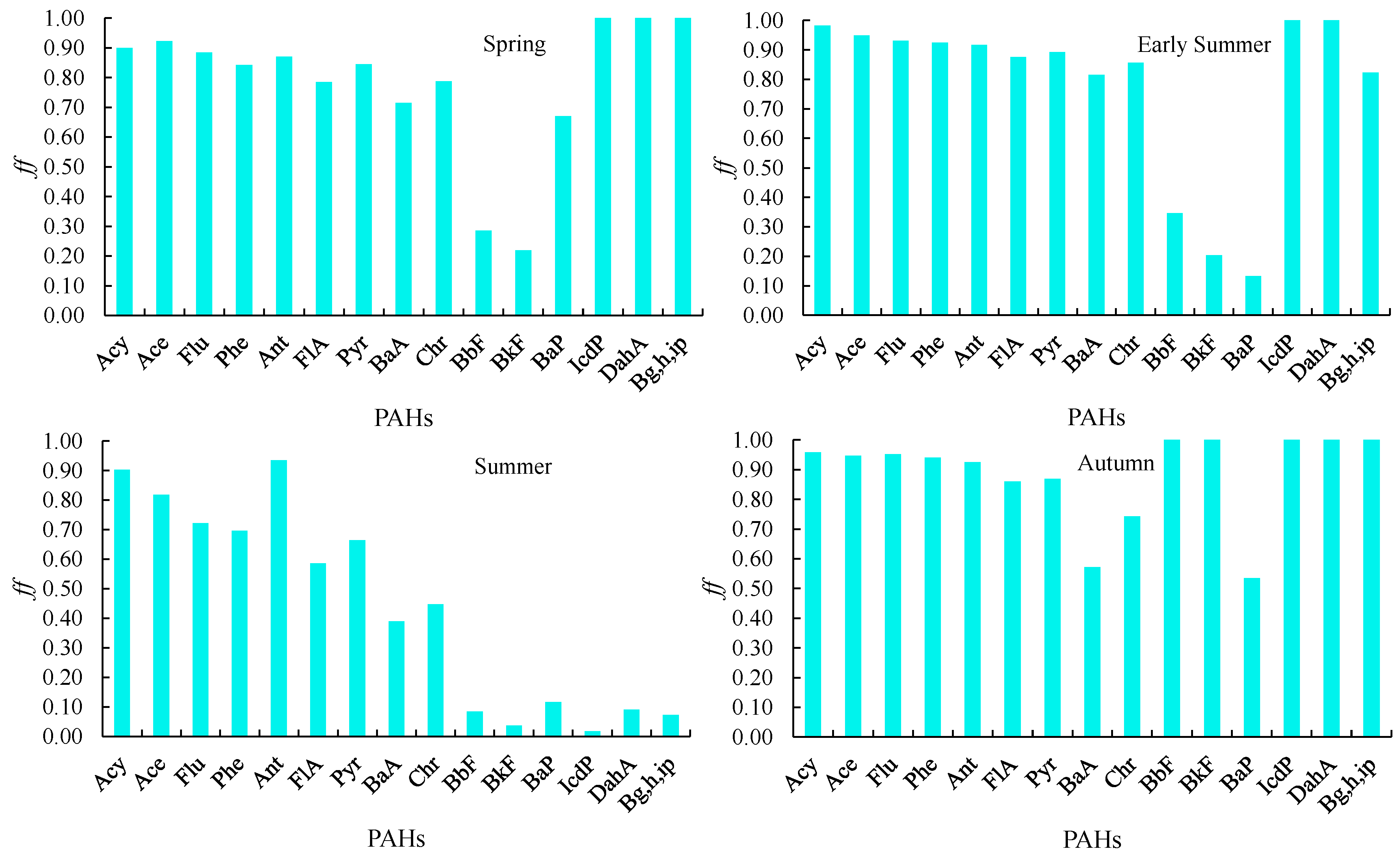
2.3. Fugacity Fraction Calculation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sediment–Water Exchange
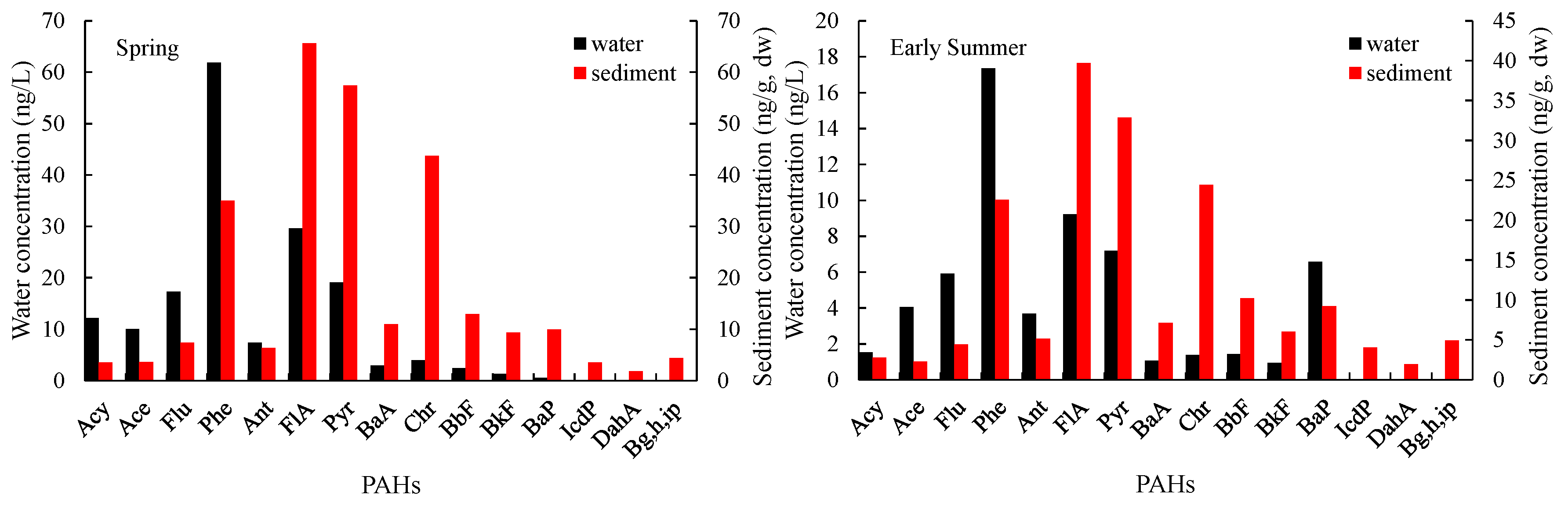
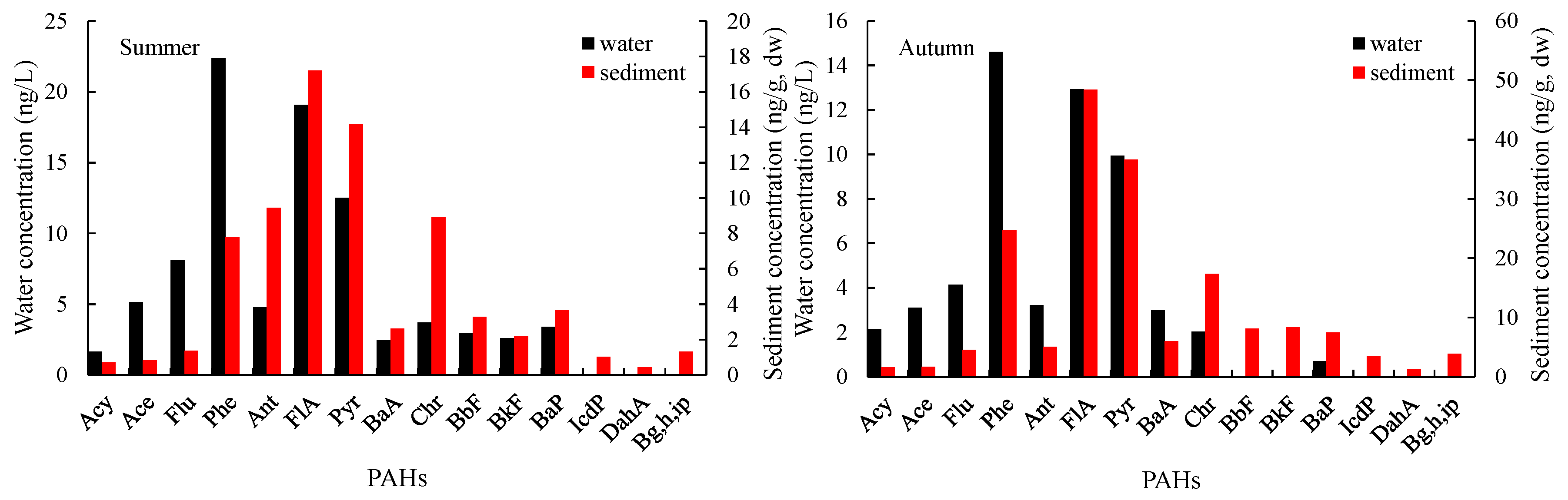
3.1.1. General Variations
3.1.2. Seasonal Variations in PAHs
3.1.3. Influence of Concentration on the Sediment–Water Exchange
3.1.4. ff Response to Variations in Organic Carbon
3.2. Spatial Variations of PAHs
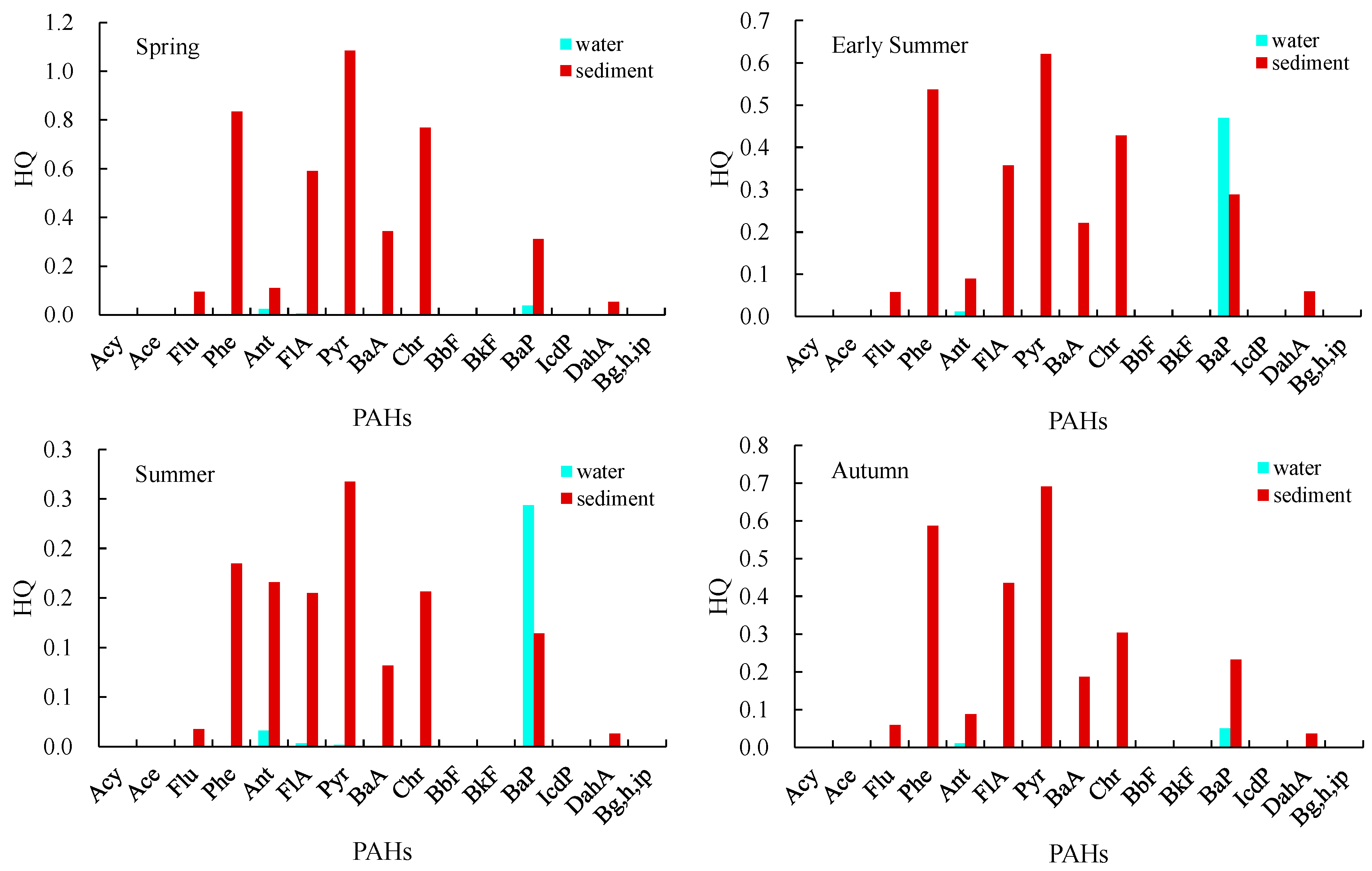
3.3. Ecological Risk Assessment
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, G.; Wu, F.; He, H.; Zhang, R.; Li, H.; Feng, C. Distribution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of PAHs in surface waters of China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2012, 55, 914–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.O.; Ko, F.C.; Lee, C.L.; Fang, M.D. Air–water exchange fluxes of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the tropical coast, Taiwan. Chemosphere 2013, 90, 2614–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, A.J.; Bradshaw, P.T.; Herring, A.H.; Teitelbaum, S.L.; Beyea, J.; Stellman, S.D.; Conway, K. Exposure to multiple sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and breast cancer incidence. Environ. Int. 2016, 89, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.L.; Li, Y.F.; Qi, H.; Sun, D.Z.; Liu, L.Y.; Wang, D.G. Seasonal variations of sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) to a northeastern urban city, China. Chemosphere 2010, 79, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esen, F.; Cindoruk, S.S.; Tasdemir, Y. Bulk deposition of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in an industrial site of Turkey. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 152, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.X.; Cheng, S.P. Health risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the source water and drinking water of China: Quantitative analysis based on published monitoring data. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 410, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, W.J.; Jia, H.; Li, Y.F.; Sun, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, L. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and alkylated PAHs in the coastal seawater, surface sediment and oyster from Dalian, Northeast China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 128, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, L.J.; Maruya, K.A.; Snyder, S.A.; Zeng, E.Y. China’s water pollution by persistent organic pollutants. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 163, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Shang, J.; Zhao, J.; Guo, H. Factor analysis and dynamics of water quality of the Songhua River, Northeast China. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2003, 144, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; He, M.; Yang, Z.; Lin, C.; Quan, X. Characteristics of petroleum hydrocarbons in surficial sediments from the Songhuajiang River (China): Spatial and temporal trends. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 179, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.L.; Liu, L.Y.; Qi, H.; Zhang, Z.F.; Song, W.W.; Shen, J.M.; Li, Y.F. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water, sediment and soil of the Songhua River Basin, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 8399–8409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, S.; Sun, K.; Dong, S.; Wang, Y.M.; Wang, S.; Jia, L. Assessment of Organochlorine Pesticide Residues in Water, Sediment, and Fish of the Songhua River, China. Environ. Forensics 2014, 15, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Fu, Q.; Guo, L.; Li, Y.F.; Li, T.X.; Ma, W.L.; Li, W.L. Spatial–temporal variation, possible source and ecological risk of PCBs in sediments from Songhua River, China: Effects of PCB elimination policy and reverse management framework. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 106, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; He, M.; Yang, Z.; Lin, C.; Quan, X.; Wang, H. Comparison of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments from the Songhuajiang River (China) during different sampling seasons. J. Environ. Sci. Health A 2007, 42, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Yan, B.; Cao, H.; Wang, L. Risk assessment for methylmercury in fish from the Songhua River, China: 30 years after mercury-containing wastewater outfalls were eliminated. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harner, T.; Mackay, D.; Jones, K.C. Model of the long-term exchange of PCBs between soil and the atmosphere in the southern UK. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1995, 29, 1200–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.F.; Harner, T.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, N.Q.; Jia, H.; Sverko, E. Polychlorinated Biphenyls in Global Air and Surface Soil: Distributions, Air-Soil Exchange, and Fractionation Effect. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 2784–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, F.; Alegria, H.A.; Bidleman, T.F. Organochlorine pesticides in soils of Mexico and the potential for soil-air exchange. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 749–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrerizo, A.; Dachs, J.; Jones, K.C.; Barceló, D. Soil-Air exchange controls on background atmospheric concentrations of organochlorine pesticides. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 12799–12811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jantunen, L.M.; Bidleman, T. Air-water gas exchange of hexachlorocyclohexanes (HCHs) and the enantiomers of α-HCH in Arctic regions. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1996, 101, 28837–28846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelmans, A.A.; Poot, A.; Lange, H.J.D.; Velzeboer, I.; Harmsen, J.; Noort, P.C.V. Estimation of in situ sediment-to-water fluxes of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, polychlorobiphenyls and polybrominated diphenylethers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 3014–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, D.M.; Liu, X.X.; Hua, X.Y.; Guo, Z.Y.; Li, L.F.; Zhang, L.W.; Xie, Y.J. Sedimentary record of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Songhua River, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Cyterski, M.; Feng, Y.J.; Gao, P.; Sun, Q.F. Spatiotemporal characteristics of organic contaminant concentrations and ecological risk assessment in the Songhua River, China. Environ. Sci.-Proc. Impacts 2015, 17, 1967–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.J.; Sun, Q.F.; Gao, P.; Ren, N.Q.; Zhang, Z.H. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface water from the Songhua River of China. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2009, 18, 2388–2395. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Ding, J.; You, H. Spatial distribution and temporal trends of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in water and sediment from Songhua River, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2014, 36, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabin, L.D.; Maruya, K.A.; Lao, W.; Diehl, D.; Tsukada, D.; Stolzenbach, K.D.; Schiff, K.C. Exchange of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons among the atmosphere, water, and sediment in coastal embayments of southern California, USA. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2010, 29, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackay, D. Multimedia Environmental Models: The Fugacity Approach, 2nd ed.; CRC Press LLC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Mackay, D.; Shiu, W.Y.; Lee, S.C.; Ma, K.C. Handbook of Physical-Chemical Properties and Environmental Fate for Organic Chemicals, 2nd ed.; CRC Press LLC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Estimation Programs Interface Suite™; US EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2012.
- Syracuse Research Corporation (SRC). PHYSPROP Database; Syracuse Research Corporation: North Syracuse, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, L.K.; Honkanen, J.O.; Jæger, I.; Carroll, J. Bioaccumulation of phenanthrene and benzo [a] pyrene in Calanus finmarchicus. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 78, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harner, T.; Bidleman, T.F.; Mackay, D. Soil-air exchange model of persistent pesticides in the United States Cotton Belt. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2001, 20, 1612–1621. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meijer, S.N.; Shoeib, M.; Jantunen, L.M.; Jones, K.C.; Harner, T. Air-soil exchange of organochlorine pesticides in agricultural soils. 1. Field measurements using a novel in situ sampling device. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 33, 1292–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidleman, T.F.; Leone, A.D. Soil–air exchange of organochlorine pesticides in the Southern United States. Environ. Pollut. 2004, 128, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, C.; Tao, S.; Wang, X.J.; Zhang, G.; Li, J.; Fu, J.M. Seasonal variation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Pearl River Delta region, China. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 8370–8379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.G.; Alaee, M.; Byer, J.; Liu, Y.J.; Tian, C.G. Fugacity approach to evaluate the sediment-water diffusion of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13, 1589–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Huang, J.; Yu, G.; Hong, H. Occurrence of PAHs, PCBs and organochlorine pesticides in the Tonghui River of Beijing, China. Environ. Pollut. 2004, 130, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mai, B.X.; Zeng, E.Y.; Luo, X.J.; Yang, Q.S.; Zhang, G.; Li, X.D.; Sheng, G.Y.; Fu, J.M. Abundances, depositional fluxes, and homologue patterns of polychlorinated biphenyls in dated sediment cores from the Pearl River Delta, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Hou, H.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Xue, N.D.; Li, H.Y.; Li, F.S. Distribution and ecological risk of polychlorinated biphenyls and organochlorine pesticides in surficial sediments from Haihe River and Haihe Estuary Area, China. Chemosphere 2010, 78, 1285–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.S.; Shao, L.Y.; Yang, H.Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, W.P. Residues and sources recognition of polychlorinated biphenyls in surface sediments of Jiaojiang Estuary, East China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.F.; Shen, Z.Y.; Gao, F.; Tang, Z.W.; Niu, J.F. Occurrence and possible sources of polychlorinated biphenyls in surface sediments from the Wuhan reach of the Yangtze River, China. Chemosphere 2009, 74, 1522–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.Y.; Xue, B.; Jin, L.X.; Zhou, S.S.; Liu, W.P. Polychlorinated biphenyls in surface sediments of Yueqing Bay, Xiangshan Bay, and Sanmen Bay in East China Sea. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barhoumi, B.; LeMenach, K.; Dévier, M.H.; Hammami, B.; Ameur, W.B.; Hassine, S.B.; Cachot, J.; Budzinski, H.; Driss, M.R. Distribution and ecological risk of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in surface sediments from the Bizerte lagoon, Tunisia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 6290–6302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everitt, B.S. The Cambridge Dictionary of Statistics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Solomon, K.; Giesy, J.; Jones, P. Probabilistic risk assessment of agrochemicals in the environment. Crop Prot. 2000, 19, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brain, R.A.; Sanderson, H.; Sibley, P.K. Probabilistic ecological hazard assessment: Evaluating pharmaceutical effects on aquatic higher plants as an example. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2006, 64, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, C.; Luo, Q.; Wang, Z. Concentration levels and potential ecological risks of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Chinese rivers. Water Qual. Expo. Health 2009, 1, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
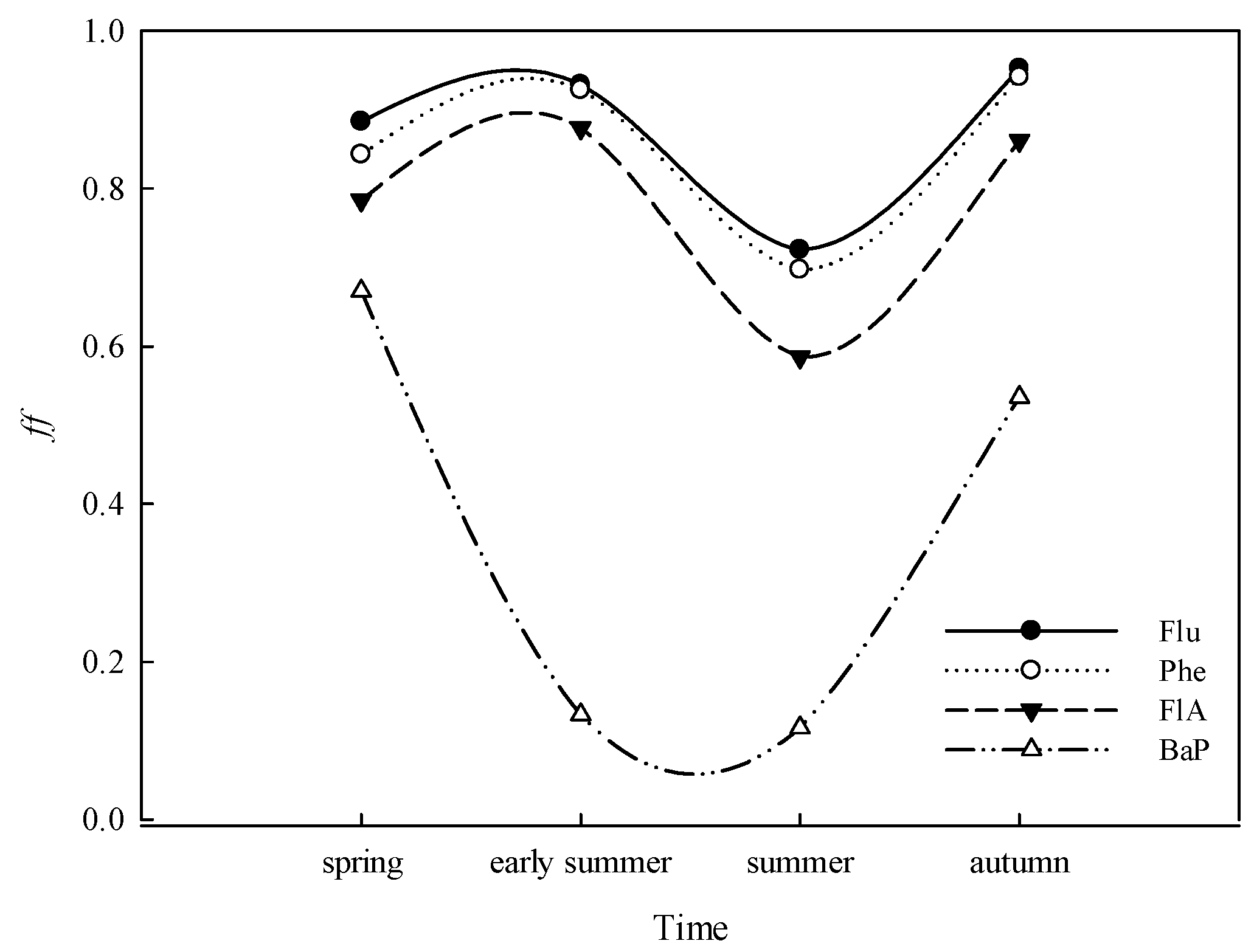
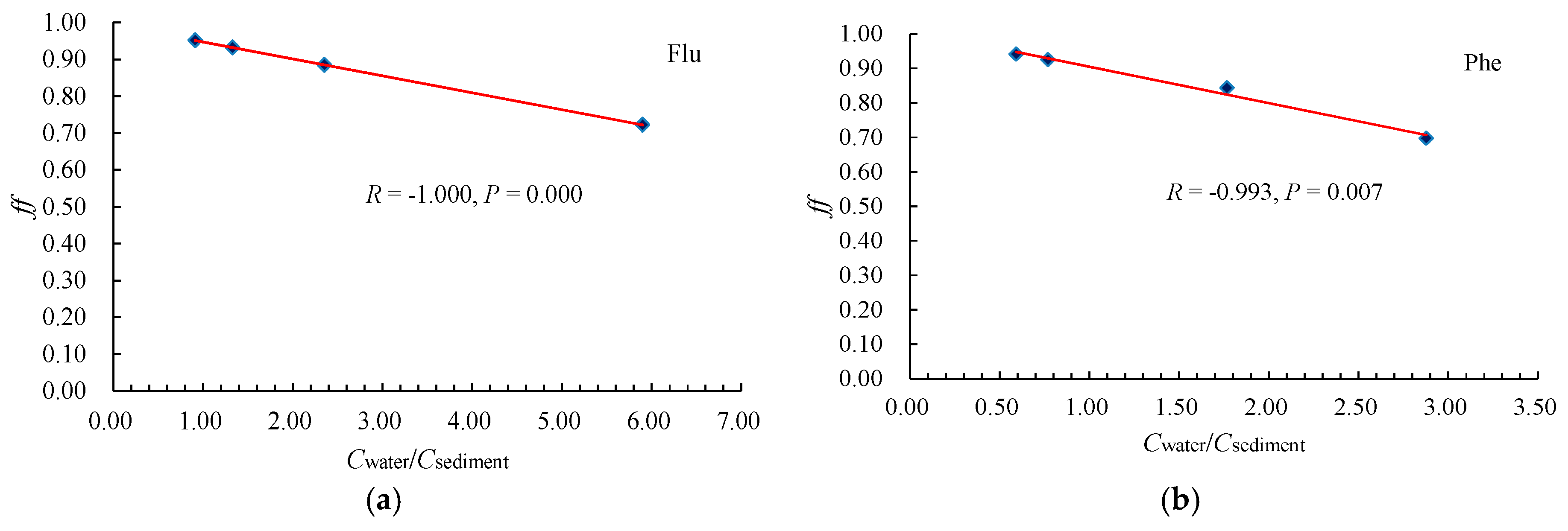

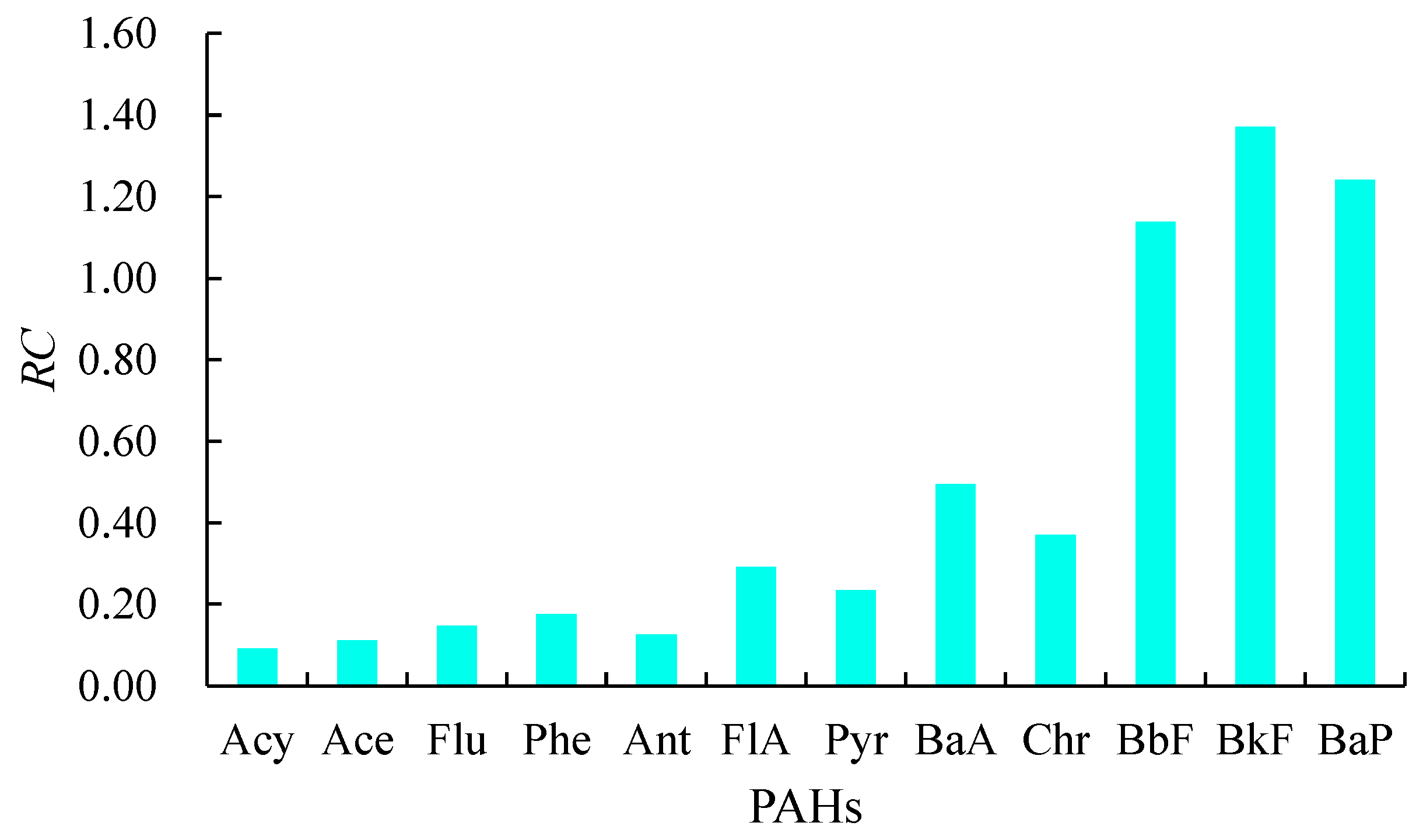
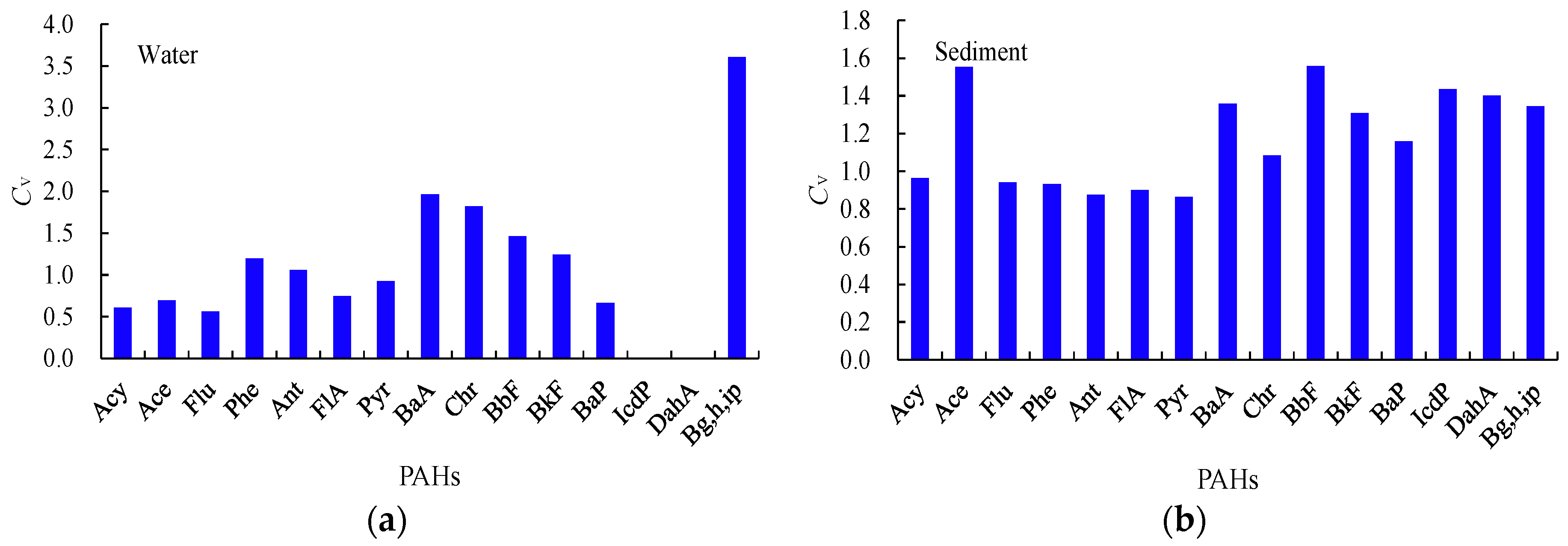
| PAHs | LogKow | Water | Sediment | ff | ff 0.32% OC mean | ff 1.68% OC mean | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| min | max | mean | Std. | min | max | mean | Std. | min | max | mean | ||||
| Acy | 3.94 | 1.53 | 12.18 | 4.37 | 5.21 | 0.70 | 3.48 | 2.15 | 1.23 | 0.83 | 0.98 | 0.95 | 0.98 | 0.89 |
| Ace | 3.92 | 3.10 | 10.07 | 5.58 | 3.10 | 0.83 | 3.64 | 2.11 | 1.18 | 0.86 | 0.96 | 0.94 | 0.97 | 0.87 |
| Flu | 4.18 | 4.15 | 17.32 | 8.86 | 5.86 | 1.37 | 7.36 | 4.43 | 2.45 | 0.80 | 0.94 | 0.91 | 0.96 | 0.83 |
| Phe | 4.46 | 14.60 | 61.86 | 29.04 | 22.11 | 7.77 | 35.00 | 22.49 | 11.22 | 0.74 | 0.93 | 0.89 | 0.95 | 0.80 |
| Ant | 4.54 | 3.23 | 7.37 | 4.76 | 1.86 | 5.02 | 9.45 | 6.48 | 2.07 | 0.84 | 0.97 | 0.93 | 0.97 | 0.85 |
| FlA | 5.22 | 9.22 | 29.62 | 17.70 | 8.92 | 17.21 | 65.60 | 42.70 | 20.13 | 0.66 | 0.90 | 0.82 | 0.92 | 0.68 |
| Pyr | 5.18 | 7.19 | 19.08 | 12.18 | 5.09 | 14.18 | 57.45 | 35.28 | 17.74 | 0.74 | 0.91 | 0.86 | 0.94 | 0.74 |
| BaA | 5.61 | 1.08 | 3.01 | 2.37 | 0.90 | 2.62 | 10.99 | 6.68 | 3.45 | 0.57 | 0.82 | 0.69 | 0.84 | 0.50 |
| Chr | 5.91 | 1.37 | 3.97 | 2.76 | 1.27 | 8.93 | 43.74 | 23.60 | 14.84 | 0.66 | 0.86 | 0.77 | 0.89 | 0.60 |
| BbF | 6.57 | 0.00 | 2.94 | 1.69 | 1.29 | 3.28 | 12.90 | 8.63 | 4.07 | 0.15 | 1.00 | 0.30 | 0.51 | 0.17 |
| BkF | 6.84 | 0.00 | 2.60 | 1.21 | 1.08 | 2.20 | 9.42 | 6.49 | 3.19 | 0.07 | 1.00 | 0.20 | 0.37 | 0.10 |
| BaP | 6.4 | 0.54 | 6.57 | 2.81 | 2.84 | 3.66 | 9.97 | 7.58 | 2.82 | 0.08 | 0.67 | 0.25 | 0.45 | 0.14 |
| IcdP | 7.66 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.03 | 4.03 | 3.02 | 1.35 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| DahA | 6.5 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.43 | 1.96 | 1.35 | 0.69 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Bg,h,ip | 7.1 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 1.32 | 4.94 | 3.64 | 1.60 | 0.71 | 1.00 | 0.94 | 0.97 | 0.88 |
| PAHs | Water (μg/L) | Sediments (μg/g) |
|---|---|---|
| Acy | NA | NA |
| Ace | 23 | NA |
| Flu | 11 | 0.077 |
| Phe | 30 | 0.042 |
| Ant | 0.3 | 0.057 |
| FlA | 6.16 | 0.111 |
| Pyr | 7 | 0.053 |
| BaA | 34.6 | 0.032 |
| Chr | 7 | 0.057 |
| BbF | NA | NA |
| BkF | NA | NA |
| BaP | 0.014 | 0.032 |
| IcdP | NA | NA |
| DahA | 5 | 0.033 |
| BghiP | NA | NA |
| ∑PAHs | NA | 4 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, S.; Fu, Q.; Li, T.-x.; Ma, W.-l.; Liu, D.; Wang, M. Sediment-Water Exchange, Spatial Variations, and Ecological Risk Assessment of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the Songhua River, China. Water 2016, 8, 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8080334
Cui S, Fu Q, Li T-x, Ma W-l, Liu D, Wang M. Sediment-Water Exchange, Spatial Variations, and Ecological Risk Assessment of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the Songhua River, China. Water. 2016; 8(8):334. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8080334
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Song, Qiang Fu, Tian-xiao Li, Wan-li Ma, Dong Liu, and Min Wang. 2016. "Sediment-Water Exchange, Spatial Variations, and Ecological Risk Assessment of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the Songhua River, China" Water 8, no. 8: 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8080334
APA StyleCui, S., Fu, Q., Li, T.-x., Ma, W.-l., Liu, D., & Wang, M. (2016). Sediment-Water Exchange, Spatial Variations, and Ecological Risk Assessment of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the Songhua River, China. Water, 8(8), 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8080334








