Effects of Rainfall Intensity and Duration on the First Flush from Parking Lots
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Rainfall Simulations
2.3. Analytical Chemistry
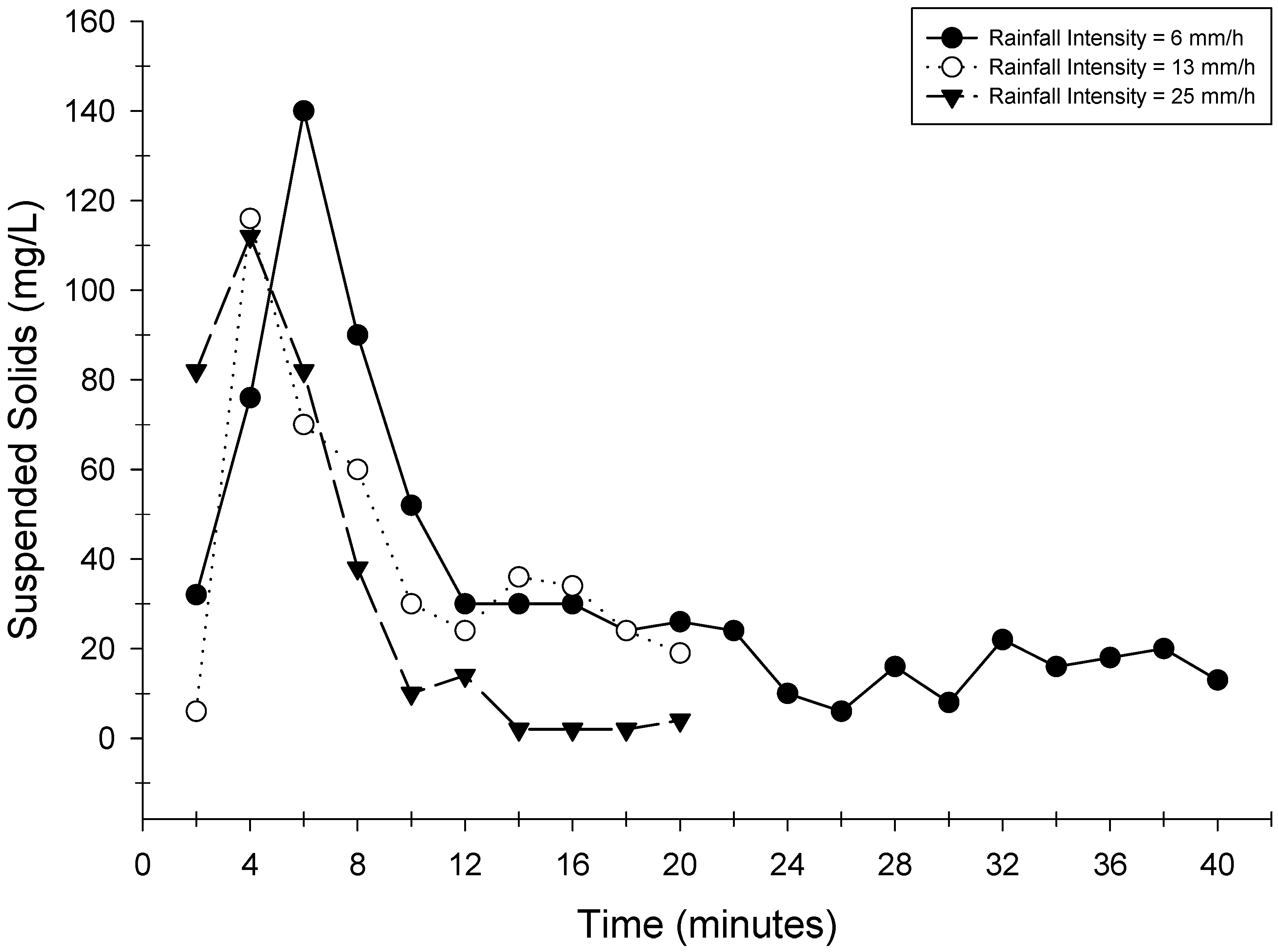
2.3.1. Suspended Solids
2.3.2. Trace Metal Analysis
2.3.3. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Al | Aluminum |
| ANOVA | Analysis of Variance |
| BMP | Best Management Practice |
| Cd | Cadmium |
| Cfs | cubic feet per second |
| Cr | Chromium |
| Cu | Copper |
| EPA | Environmental Protection Agency |
| GC | Gas chromotography |
| Km | kilometer |
| km2 | square kilometers |
| L/min | Liters per minute |
| Min | minutes |
| mL | milliliter |
| mm/hr | millimeters per hour |
| MS | Mass spectrometry |
| Ni | Nickel |
| PAH | Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons |
| ∑PAH | Total PAH |
| Pb | Lead |
| Psi | pounds per square inch |
| PVC | Polyvinyl chloride |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| TSS | Total Suspended Solids |
| μg/L | micrograms per liter |
| Zn | Zinc |
References
- Cole, R.H.; Frederick, R.E.; Healy, R.P.; Rolan, R.G. Preliminary findings of the priority pollutant monitoring project of the nationwide urban runoff program. J. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1984, 56, 898–908. [Google Scholar]
- Smullen, J.T.; Shallcross, A.L.; Cave, K.A. Updating the US nationwide urban runoff quality data base. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 39, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revitt, D.M.; Lundy, L.; Coulon, F.; Fairley, M. The sources, impact and management of car park runoff pollution: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 146, 552–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiefenthaler, L.L.; Stein, E.D.; Schiff, K.C. Watershed and land use–based sources of trace metals in urban storm water. Environ. Chem. 2008, 27, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenstrom, M.K.; Silverman, G.S.; Bursztynsky, T.A. Oil and grease in urban stormwater. J. Environ. Eng. 1984, 110, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schueler, T.R.; Kumble, P.A.; Hearty, M.A. A Current Assessment of Urban Best Management Practices: Techniques for Reducing Nonpoint Source Pollution in the Coastal Zone; Anacostia Restoration Team, Department of Environmental Programs, Metropolitan Washington Council of Governments: Washington, DC, USA, 1992.
- Barrett, M.E.; Walsh, P.M.; Malina, J.F., Jr.; Charbeneau, R.J. Performance of vegetative controls for treating highway runoff. J. Environ. Eng. 1998, 124, 1121–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannerman, R.T.; Owens, D.W.; Dodds, R.B.; Hornewer, N.J. Sources of pollutants in Wisconsin stormwater. Water Sci. Technol. 1993, 28, 241–259. [Google Scholar]
- Huber, M.; Welker, A.; Helmreich, B. Critical review of heavy metal pollution of traffic area runoff: Occurrence, influencing factors, and partitioning. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 895–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackerman, D.; Schiff, K.C.; Weisberg, S.B. Evaluating HSPF in an arid, urbanized watershed. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2005, 41, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culliton, T.; Warren, M.; Goodspeed, T.; Remer, D.; Blackwell, C.; McDonough, J., Jr. Fifty Years of Population Change along the Nation’s Coasts, 1960–2010; NOAA Coastal Trends Series; National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, U.S. Department of Commerce: Rockville, MD, USA, 1990.
- Tiefenthaler, L.L.; Schiff, K.; Leecaster, M.K. Temporal variability patterns of stormwater concentrations in urban stormwater runoff. Water Res. 2002, 36, 1556–1564. [Google Scholar]
- Egodawatta, P.; Thomas, E.; Goonetilleke, A. Mathematical interpretation of pollutant wash-off from urban road surfaces using simulated rainfall. Water Res. 2007, 41, 3025–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Economic Development Bureau. Demographic data provided by Claritas for the City of Long Beach. 1999. Available online: http://www.ci.long-beach.ca.us/bdc/demographics.htm (accessed on 11 July 2001). [Google Scholar]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Methods for the Determination of Metals in Environmental Samples; EPA/600/4-91/010; Office of Research and Development, United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1991.
- Athayde, D.N.; Shelley, P.E.; Driscoll, E.D.; Boyd, G. Results of the Nationwide Urban Runoff Program, Volume I; Final Report; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1983.
- Irish, L.B.; Lesso, W.G.; Barrart, M.E.; Malina, J.J.F.; Charbeneau, R.J.; Ward, G.H. An Evaluation of the Factors Affecting the Quality of Highway Runoff in the Austin, Texas Area; Interim Report. FHWA/TX-96/1943-5; U.S. Federal Highway Administration: San Francisco, CA, USA; Texas Department of Transportation: Austin, TX, USA, 1996.
- Sansalone, J.J.; Buchberger, S.G. Partitioning and first flush of metals in urban roadway storm water. J. Environ. Eng. 1997, 123, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodie, I.M.; Egodawatta, P. Relationships between rainfall intensity, duration and suspended particle washoff from an urban road surface. Hydrol. Res. 2011, 42, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorman, M.E.; Hartigan, J.; Johnson, F.; Maestri, B. Retention, Detention, and Overland Flow for Pollutant Removal from Highway Stormwater Runoff: Interim Guidelines for Management Measures; NTIS: Springfield, VA, USA, 1988.
- Deletic, A.; Maksimovic, C. Evaluation of water quality factors in storm runoff from paved areas. J. Environ. Eng 1998, 124, 869–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desta, M.B.; Bruen, M.; Higgins, N.; Johnston, P. Highway runoff quality in Ireland. J. Environ. Monit. 2007, 9, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Hou, P.; Wan, W.; Ren, Y.; Ouyang, Z.; Yang, L. The temporal changes in road stormwater runoff quality and the implications to first flush control in Chongqing, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 9763–9775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.H.; Lau, S.L.; Kayhanian, M.; Stenstrom, M.K. Correlation analysis among highway stormwater pollutants and characteristics. Water Sci. Technol. 2006, 53, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jirik, A.; Bay, S.M.; Greenstein, D.J.; Zellers, A.; Lau, S.L. Application of TIEs in studies of urban stormwater impacts on marine organisms. In Environmental Toxicology and Risk Assessment: ASTM STP 1333; Little, E.E., DeLonay, A.J., Greenberg, B.M., Eds.; American Technical Publishers: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1998; Volume 302, pp. 284–298. [Google Scholar]
- Greenstein, D.; Tiefenthaler, L.; Bay, S. Toxicity of parking lot runoff after application of simulated rainfall. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2004, 47, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiff, K.; Bay, S.M.; Diehl, D. Stormwater toxicity in Chollas Creek and San Diego Bay. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2003, 81, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, M.E.; Zuber, R.D.; Collins, E.R., III; Malina, J.F.; Charbeneau, R.J., Jr.; Ward, G.H. A Review and Evaluation of Literature Pertaining to the Quality and Control of Pollution from Highway Runoff and Construction; Technical Report CRWR 239; Center for Research in Water Resources, Bureau of Engineering Research, The University of Texas, Balcones Research Center: Austin, TX, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll, E.D.; Shelley, P.E.; Strecker, E.W. Pollutant Loadings and Impacts from Highway Stormwater Runoff. Volume I: Design Procedure; Final Report, FHWA-RD-88-006; U.S. Federal Highway Administration: Anchorage, AK, USA, 1990.
- Pitt, R. Characterizing and Controlling Urban Runoff through Street and Sewerage Cleaning; EPA/600/S2-85/038, PB 85-186500; United States Environmental Protection Agency (U.S. EPA), Storm and Combined Sewer Program, Risk Reduction Engineering Laboratory: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1985.
- Pitt, R.; McLean, J. Toronto Area Watershed Managment Strategy Study, Humber River Pilot Watershed Project; Ontario Ministry of the Environment: Toronto, ON, Canada, 1986; p. 483. [Google Scholar]
| Parameter | 6.3 mm/h | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0–10 min | 10–20 min | 20–40 min | |
| Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | |
| Suspended Solids (mg/L) | 72.7 (18.1) | 20.3 (6.5) | 11.7 (5.2) |
| Metals (Total) | |||
| Aluminum (μg/L) | 1036.7 (172.7) | 233.3 (177.5) | 180 (55.9) |
| Cadmium (μg/L) | 2.4 (0.6) | 1.0 (0.8) | 0 (0) |
| Chromium (μg/L) | 7.7 (0.7) | 4.1 (0.3) | 2.2 (0.2) |
| Copper (μg/L) | 54.3 (6.4) | 27.3 (4.2) | 10.3 (0.5) |
| Iron (μg/L) | 556.7 (56.8) | 446.7 (27.4) | 216.7 (71.5) |
| Lead (μg/L) | 168.7 (84.2) | 93 (58) | 27.7 (14.5) |
| Nickel (μg/L) | 44.7 (7.4) | 21.3 (4.7) | 6.8 (0.9) |
| Zinc (μg/L) | 430 (47.5) | 213.3 (35.5) | 76.7 (3.2) |
| Metals (Dissolved) | |||
| Aluminum (μg/L) | 78.7 (12.4) | 92.7 (97.2) | 0 (0) |
| Cadmium (μg/L) | 2.1 (0.6) | 0.9 (0.7) | 0 (0) |
| Chromium (μg/L) | 4.1 (0.4) | 2.5 (0.2) | 0.8 (0.7) |
| Copper (μg/L) | 47.3 (5.2) | 24.7 (4.8) | 8.5 (0.9) |
| Iron (μg/L) | 360 (64.4) | 203.3 (40.3) | 46.7 (35.5) |
| Lead (μg/L) | 133.3 (77.4) | 85.3 (63.1) | 23.9 (16.4) |
| Nickel (μg/L) | 41.3 (6.9) | 19.3 (4.7) | 6.4 (1.1) |
| Zinc (μg/L) | 336.7 (52.1) | 170.0 (47.5) | 56.0 (11.2) |
| Total PAHs (μg/L) | 8.5 (6.2) | 4.3 (2.8) | 2.7 (2.1) |
| Parameter | 6.3 mm/h | 12.7 mm/h | 25.4 mm/h | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 min | 20 min | 40 min | 20 min | 10 min | 20 min | |
| Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | |
| Suspended Solids (mg/L) | 72.7 (18.1) | 46.5 (29.8) | 34.9 (29.5) | 28.7 (14.6) | 41 (13.3) | 26.5 (17.6) |
| Metals (Total) | ||||||
| Aluminum (μg/L) | 1036.7 (172.7) | 635 (444.6) | 483.3 (422.2) | 316.7 (73.5) | 540 (114.7) | 341.7 (218.3) |
| Cadmium (μg/L) | 2.4 (0.6) | 1.7 (1) | 1.1 (1.1) | 0.8 (0.6) | 0.5 (0.8) | 0.3 (0.6) |
| Chromium (μg/L) | 7.7 (0.7) | 5.9 (1.9) | 4.7 (2.4) | 2.6 (0.4) | 4 (1.2) | 2.9 (1.4) |
| Copper (μg/L) | 54.3 (6.4) | 40.8 (14.8) | 30.7 (18.9) | 19.7 (1.3) | 29.7 (7.6) | 20 (11.3) |
| Iron (μg/L) | 556.7 (56.8) | 501.7 (71.1) | 406.7 (153.3) | 560 (115.4) | 610 (195.4) | 438.3 (222.7) |
| Lead (μg/L) | 168.7 (84.2) | 130.8 (80.6) | 96.4 (82.3) | 61.7 (28.6) | 48.7 (18.4) | 33.7 (20.4) |
| Nickel (μg/L) | 44.7 (7.4) | 33 (13.4) | 24.3 (16.6) | 14 (2.3) | 23.7 (6.9) | 15.1 (10) |
| Zinc (μg/L) | 430 (47.5) | 321.7 (118) | 240 (151.2) | 160 (8.5) | 216.7 (26.1) | 143 (77.7) |
| Metals (Dissolved) | ||||||
| Aluminum (μg/L) | 78.7 (12.4) | 85.7 (68.2) | 57.1 (68.8) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 12.8 (29.3) |
| Cadmium (μg/L) | 2.1 (0.6) | 1.5 (0.9) | 1 (1) | 0 (0) | 0.5 (0.7) | 0.3 (0.6) |
| Chromium (μg/L) | 4.1 (0.4) | 3.3 (0.9) | 2.5 (1.4) | 1.6 (0) | 1.9 (0.6) | 1.1 (1) |
| Copper (μg/L) | 47.3 (5.2) | 36 (12.6) | 26.8 (16.6) | 15.3 (1.8) | 24.3 (9.4) | 16.2 (10.7) |
| Iron (μg/L) | 360 (64.4) | 281.7 (95.7) | 203.3 (138) | 133.3 (26.1) | 190 (30.7) | 121.7 (77.9) |
| Lead (μg/L) | 133.3 (77.4) | 109.3 (73.3) | 80.8 (72.7) | 45.1 (28.7) | 34 (12.6) | 24 (14.3) |
| Nickel (μg/L) | 41.3 (6.9) | 30.3 (12.6) | 22.3 (15.4) | 12 (1.5) | 21 (7.4) | 13.4 (9.4) |
| Zinc (μg/L) | 336.7 (52.1) | 253.3 (98.1) | 187.6 (123.5) | 104.7 (22.6) | 156.7 (34.5) | 103.7 (59.9) |
| Total PAHs (μg/L) | 8.5 (6.2) | 6.4 (5.2) | 5.2 (4.7) | 5.5 (2.9) | 3.3 (1) | 2.4 (1.2) |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schiff, K.C.; Tiefenthaler, L.L.; Bay, S.M.; Greenstein, D.J. Effects of Rainfall Intensity and Duration on the First Flush from Parking Lots. Water 2016, 8, 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8080320
Schiff KC, Tiefenthaler LL, Bay SM, Greenstein DJ. Effects of Rainfall Intensity and Duration on the First Flush from Parking Lots. Water. 2016; 8(8):320. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8080320
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchiff, Kenneth C., Liesl L. Tiefenthaler, Steven M. Bay, and Darrin J. Greenstein. 2016. "Effects of Rainfall Intensity and Duration on the First Flush from Parking Lots" Water 8, no. 8: 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8080320
APA StyleSchiff, K. C., Tiefenthaler, L. L., Bay, S. M., & Greenstein, D. J. (2016). Effects of Rainfall Intensity and Duration on the First Flush from Parking Lots. Water, 8(8), 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8080320





