Current Status of Groundwater Monitoring Networks in Korea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Laws and Regulations
3. Groundwater Monitoring
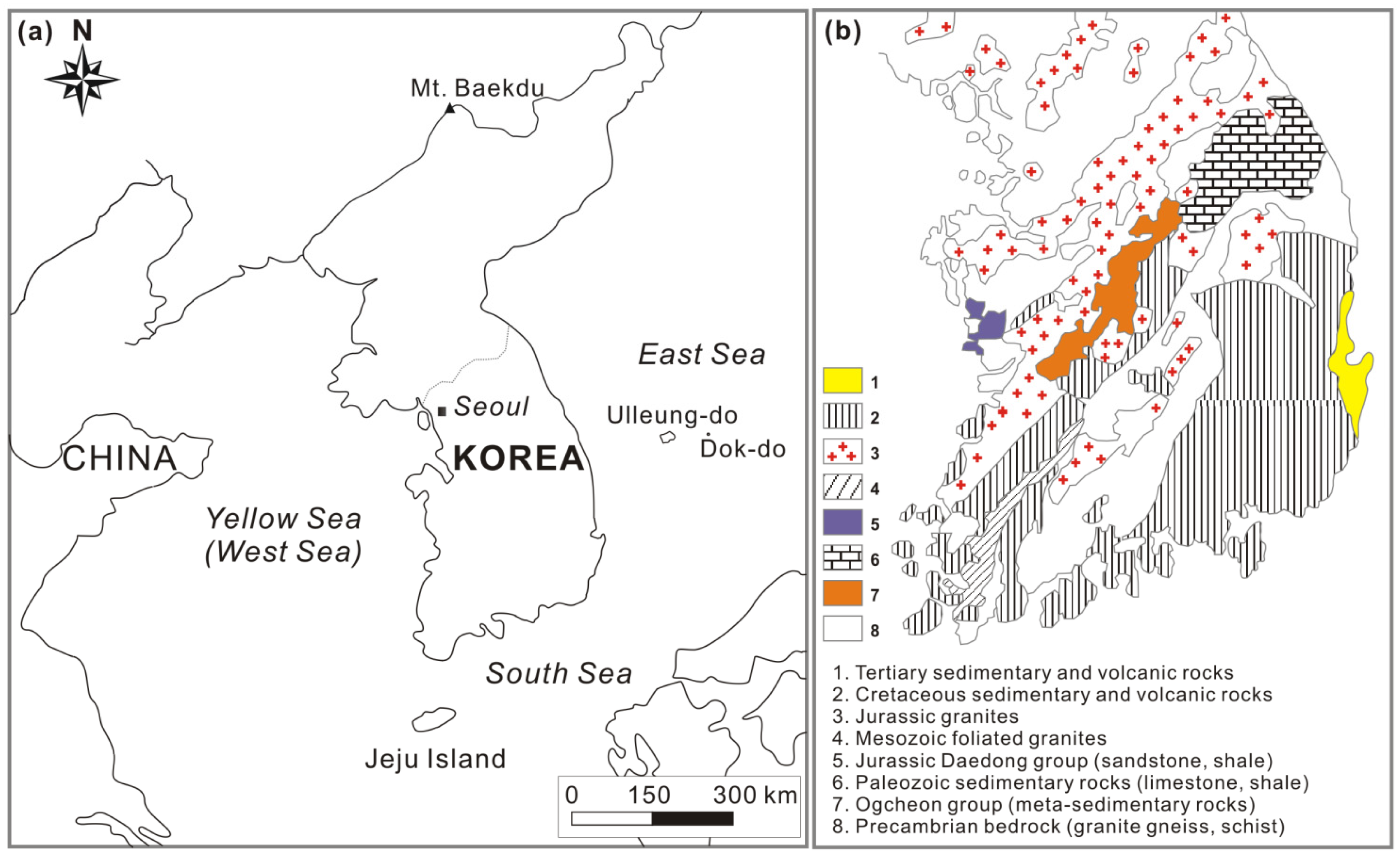
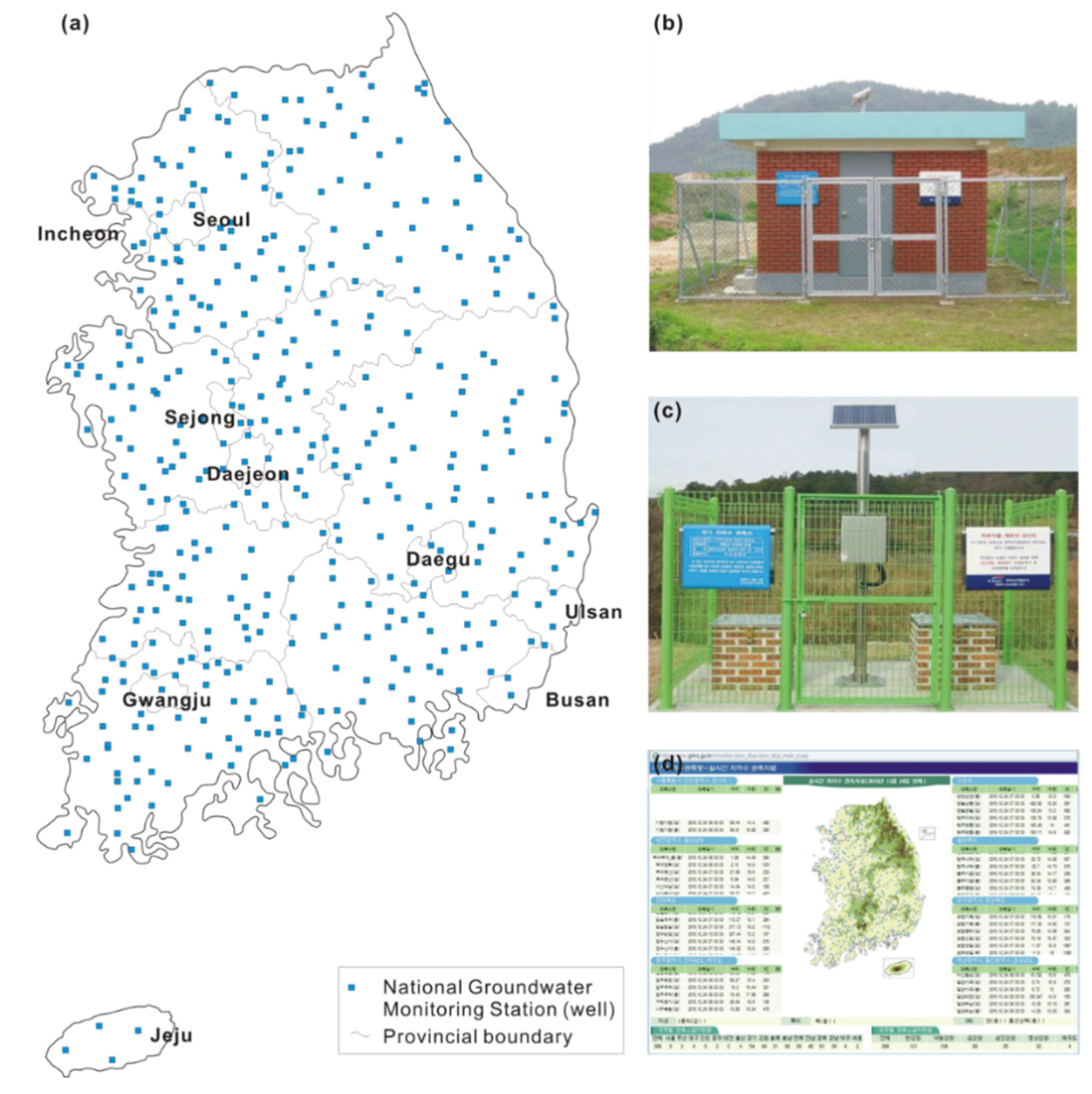
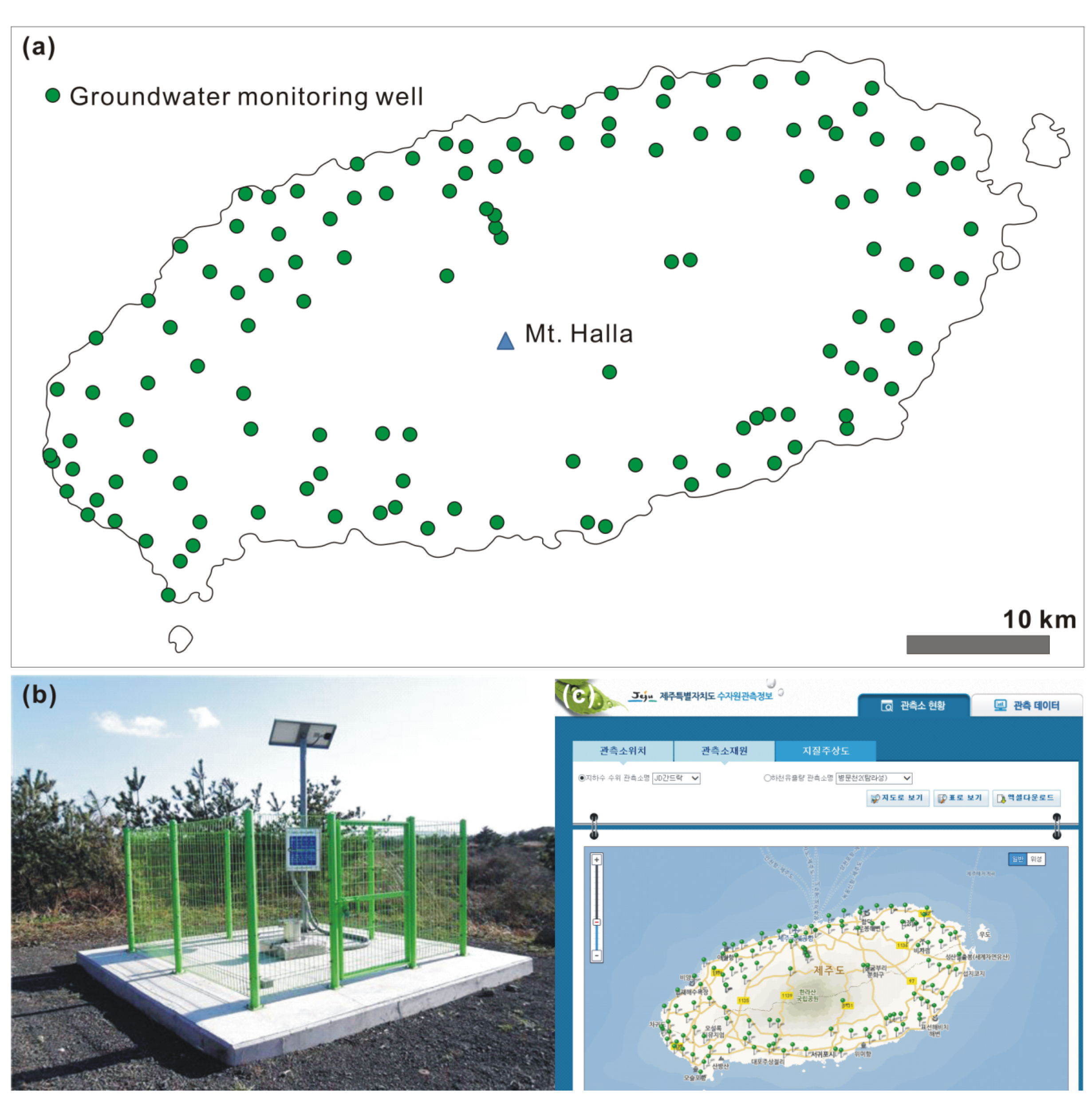
3.1. National Groundwater Monitoring Network (NGMN)
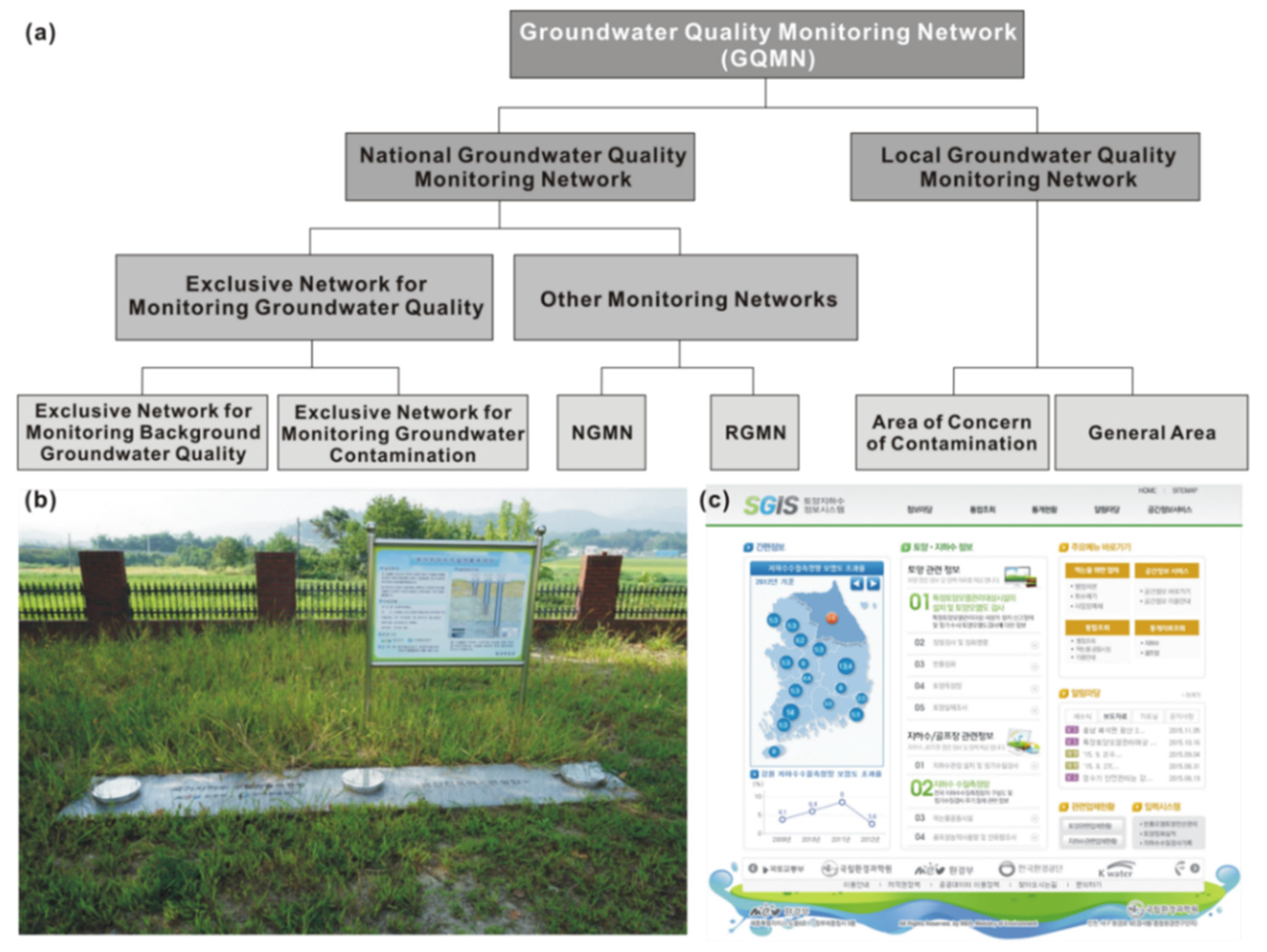
3.2. Groundwater Quality Monitoring Network (GQMN)
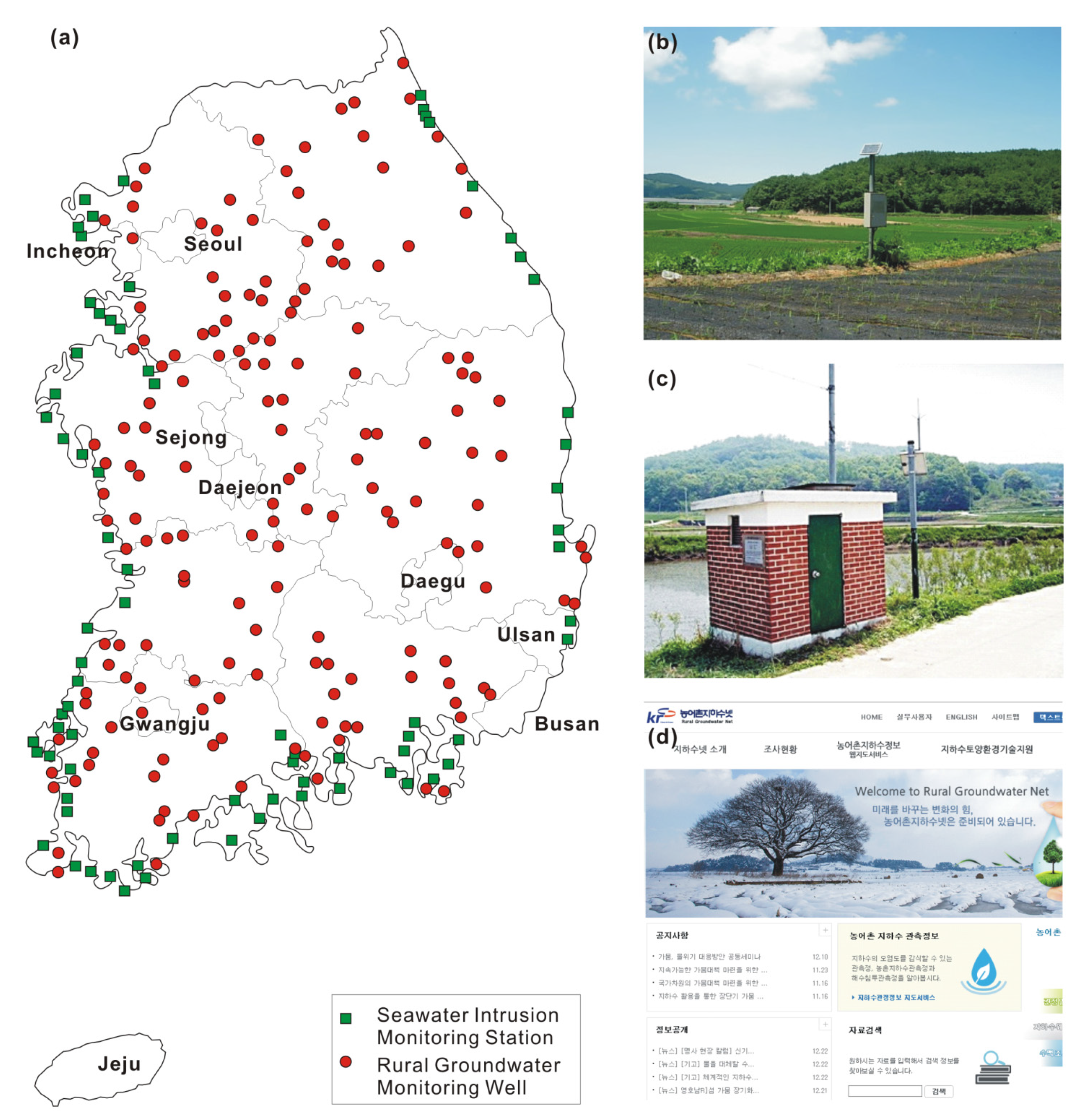
3.3. Seawater Intrusion Monitoring Network (SIMN)
3.4. Rural Groundwater Monitoring Network (RGMN)
3.5. Subsidiary or Local Groundwater Monitoring Network (SGMN or LGMN)
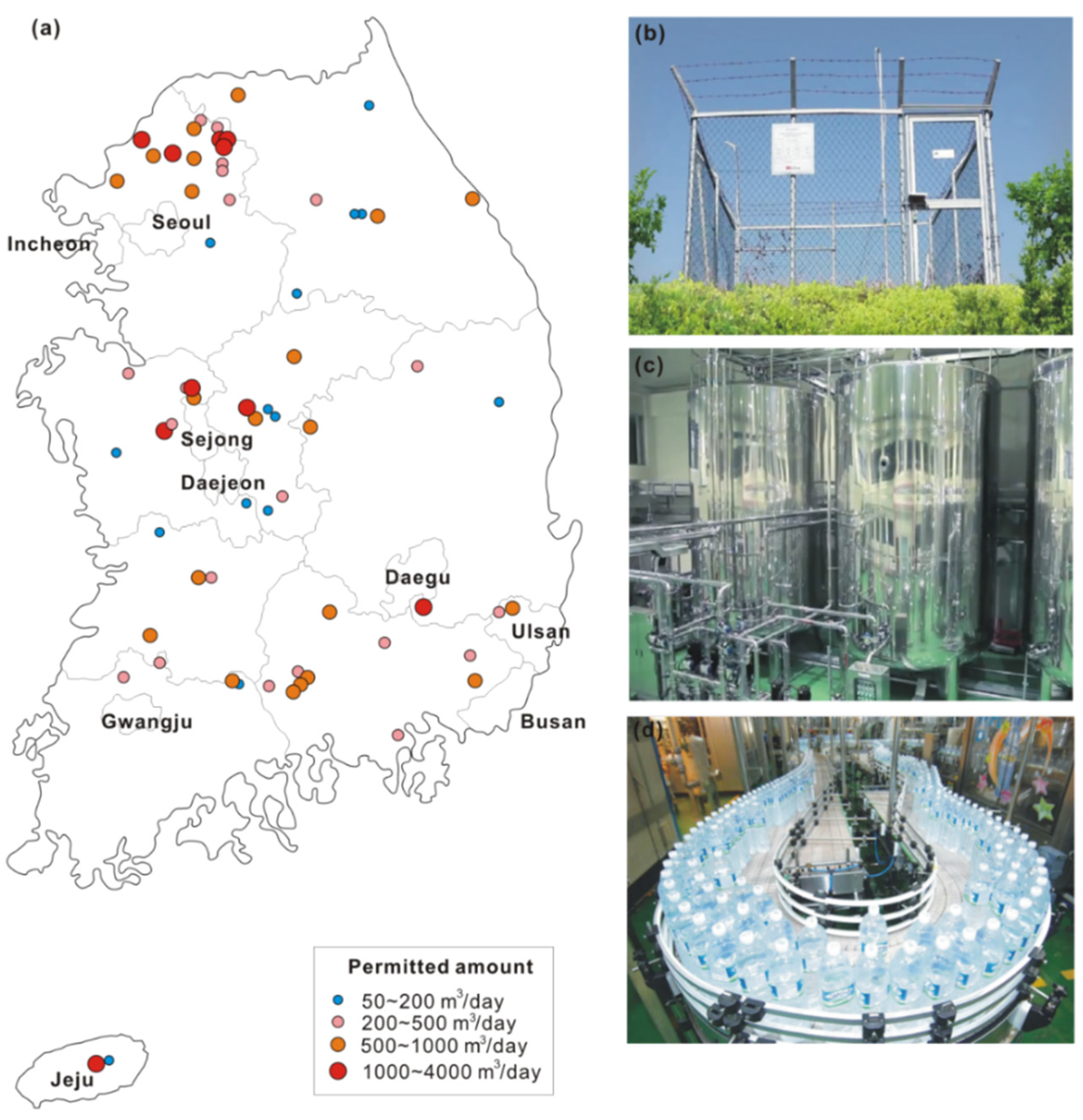
3.6. Drinking Water (Groundwater) Monitoring Network (DWMN)
4. Conclusions
- An integrated and comprehensive law is absent that can deal with overall groundwater affairs. At present, several laws and ministries are associated with the same groundwater resource but with their own distinct purposes and limited cooperation. When a groundwater quality issue is perceived by a ministry while conducting its inherent duties, it does not take appropriate measures if the ministry has only authority to deal with groundwater availability (i.e., water level decline or depletion). A comprehensive law is required to manage groundwater affairs in an integrated manner.
- Unified manuals are necessary for the installation of monitoring wells. Each monitoring network has its own specifications for monitoring wells. Different probes are used with different resolutions; the monitoring data have different formats with different communication protocols, and thus it takes an unnecessarily long time to convert each network data to make them comparable with other network data.
- Ministries and affiliated agencies lack communication with each other. Each ministry develops a Monitoring Network for its own purposes almost independently, without sharing enough information with other ministries as to the well locations, well specifications, and monitoring devices. Often monitoring wells, each of which is operated by a different ministry, happen to be located very close to each other and annual reports published by different ministries contain redundant data. This current practice raises a sustainability issue for the overall monitoring system. Holistic approaches among different ministries and agencies are required to secure the groundwater resources of the country.
- Active participation and feedback from the public are missing in the current monitoring system. The data from the various Monitoring Networks are used mainly for administrative purposes and/or academic research, and in general, the public are not involved in planning the Networks. With growing concern regarding water resources and the effects of a changing climate on the public health and life style, the public should participate in the sustainable groundwater management system from the design step of Monitoring Networks to the operation step.
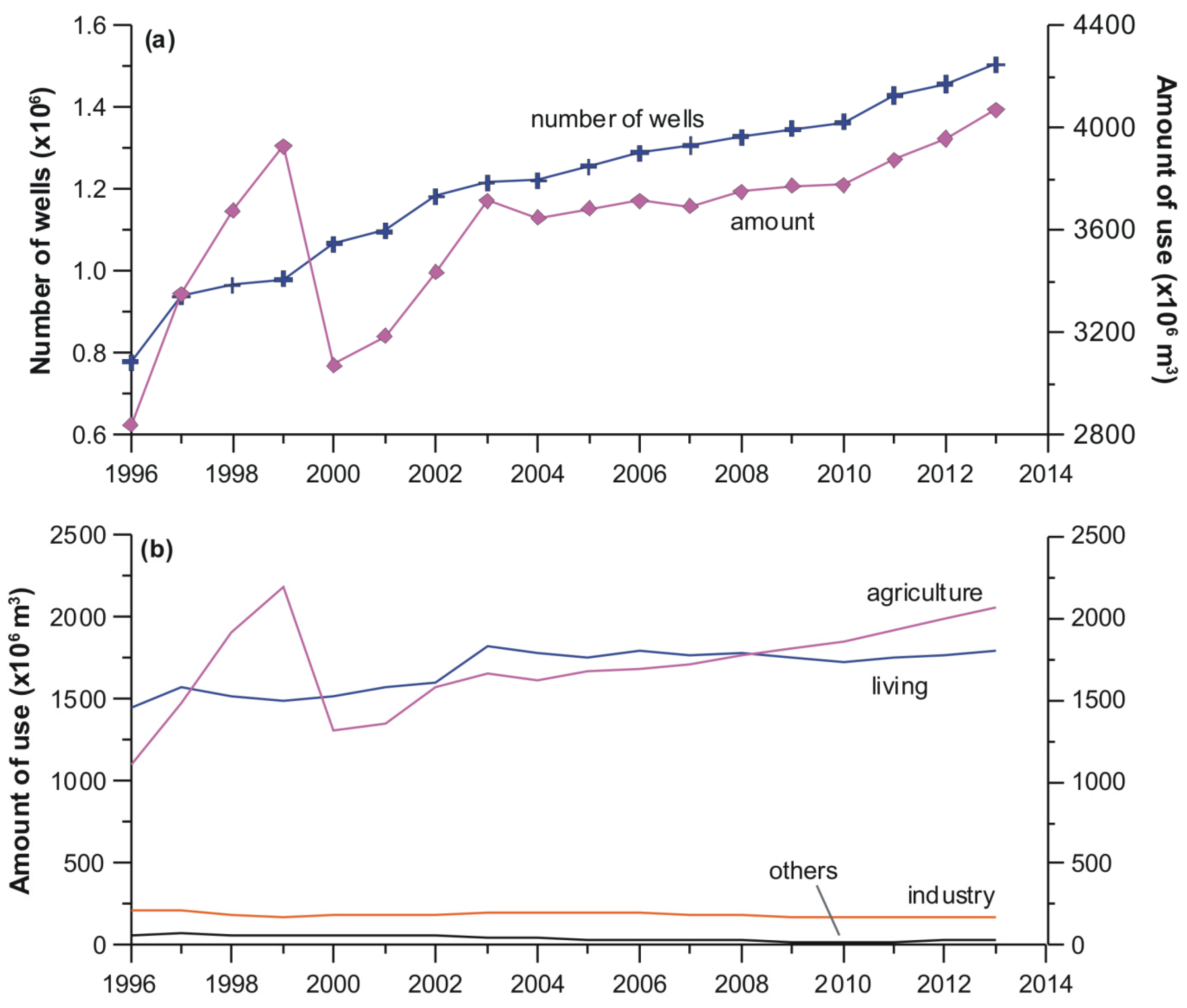
- Intensive and extensive reviews on the current number of monitoring wells, sampling frequency and position are immediately required. In addition, monitoring wells addressing other important issues including groundwater-surface water interaction [51], capture zone [52] and groundwater age [53,54] should be considered.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chung, I.M.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Chang, S.W. Status of exploitable groundwater estimation in Korea. J. Eng. Geol. 2015, 25, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Won, K.S.; Chung, S.Y.; Lee, C.S.; Jeong, J.H. Replacement of saline water through injecting fresh water into a confined saline aquifer at the Nakdong River delta area. J. Eng. Geol. 2015, 25, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y. Lessons learned from three groundwater disputes in Korea: Lack of comprehensive and integrated investigation. Int. J. Water 2016, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.Y.; Kwon, K. Groundwater resources in Gangwon Province: Tasks and perspectives responding to droughts. J. Geol. Soc. Korea 2015, 51, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.; Lee, T.; Choi, B.G.; Hong, S. Rainwater harvesting system for continuous water supply to the regions with high seasonal rainfall variations. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 961–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Amy, G.L.; Karanfil, T. Disinfection by-product formation during seawater desalination: A review. Water Res. 2015, 81, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, W.H.; Hayes, M.J.; Svoboda, M.D.; Tadesse, T.; Wilhite, D. Drought hazard assessment in the context of climate change for South Korea. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 160, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, H.R. Drought in 2016: Perspective and measures. In Proceedings of the Chuncheon International Water Forum, Chuncheon, Korea, 20 October 2015; pp. 9–21.
- Lee, J.Y.; Yi, M.J.; Yoo, Y.K.; Ahn, K.H.; Kim, G.B.; Won, J.H. A review of the National Groundwater Monitoring Network in Korea. Hydrol. Process. 2007, 21, 907–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y. Challenges of groundwater as resources in the near future. J. Soil Groundw. Environ. 2015, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, C.D.; Kim, Y.B.; Park, K.Y.; Park, S.J. Efficient management method of groundwater in farming and fishing villages. J. Soil Groundw. Environ. 2012, 17, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, J.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, J.W.; Koh, G.W. Groundwater occurrence on Jeju Island, Korea. Hydrogeol. J. 2006, 14, 532–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y. Environmental issues of groundwater in Korea: Implications for sustainable use. Environ. Conserv. 2011, 38, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, W.; Lee, J.Y. Source apportionment of trichloroethylene in groundwater of an industrial complex in Korea: A 15-year dispute and perspective. Water Environ. J. 2011, 25, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.M.; Lee, J.Y. Groundwater contamination and natural attenuation capacity at a petroleum spilled facility in Korea. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 1650–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Yi, M.J.; Moon, S.H.; Cho, M.; Lee, J.M.; Ahn, K.H.; Won, J.H. Causes of the changes in groundwater levels at Daegu, Korea: The effect of subway excavations. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2007, 66, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.J.; Cho, M.J.; Woo, N.C. Developing a national groundwater monitoring network in Korea. Hydrogeol. J. 1995, 3, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Land, Transport and Maritime Affairs. National Basic Plan for Groundwater Management (2012–2021); MLTMA: Sejong, Korea, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Shim, S.B.; Oh, S.G.; Chun, Y.J. The study of development skin improvement cosmetic by spring water of Onyang. J. Korea Acad. Ind. Coop. Soc. 2011, 12, 4257–4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.W.; Moon, S.H.; Kim, H.C. The evaluation of daily safe yield and influence of hot spring wells. J. Soil Groundw. Environ. 2006, 11, 41–47. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Interior. Hot Spring Management with Peoples. Available online: http://www.mogaha.go.kr/frt/sub/a06/b06/hotSpringMgr/screen.do (accessed on 20 April 2016).
- Lee, J.I.; Yang, H.S. A study on the prosperity of hot spring industry using healthy hot spring. J. Korea Acad. Ind. Coop. Soc. 2008, 9, 1467–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korea Hotspring Association. Investigation and Analysis on Status of Hot Spring Resources in Unplanned Development Areas; MPAS: Seoul, Korea, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hagedorn, B.; El-Kadi, A.I.; Mair, A.; Whittier, R.B.; Ha, K. Estimating recharge in fractured aquifers of a temperate humid to semiarid volcanic island (Jeju, Korea) from water table fluctuations, and Cl, CFC-12 and 3H chemistry. J. Hydrol. 2011, 409, 650–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y. Comment on “Groundwater monitoring in Denmark: Characteristics, perspectives and comparison with other countries”. Hydrogeol. J. 2010, 18, 803–804. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, G.B. Optimal distribution of groundwater monitoring wells near the river barrages of the 4MRRP using a numerical model and topographic analysis. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 5497–5511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.C.; Jo, Y.J.; Lee, J.Y. Trends of groundwater data from the Korean National Groundwater Monitoring Stations: indication of any change? Geosci. J. 2011, 15, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Hamm, S.Y.; Jang, S.; Cheong, J.Y.; Kim, G.B. Relationship between groundwater and climate change in South Korea. Geosci. J. 2014, 18, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.K.; Kim, R.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Choi, D.H.; Kim, T.D. Evaluation of status of groundwater quality monitoring network of Korea: Implications for improvement. J. Soil Groundw. Environ. 2007, 12, 92–99. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Environment (ME). 2012 Operation Results of Groundwater Quality Monitoring Network; ME: Sejong, Korea, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, S.W.; Choi, H.M.; Lee, J.Y. Comparison of groundwater levels and groundwater qualities in six megacities of Korea. J. Geol. Soc. Korea 2014, 50, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Song, S.H. Evaluation of groundwater quality in coastal areas: Implications for sustainable agriculture. Environ. Geol. 2007, 52, 1231–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.C.; Yun, S.T.; Chae, G.T.; Yoo, I.S.; Shin, K.S.; Heo, C.H.; Lee, S.K. Regional hydrochemical study on salinization of coastal aquifers, western coastal area of South Korea. J. Hydrol. 2005, 313, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 2014 Seawater Intrusion Survey Report; Korea Rural Community Corporation (KRC): Uiwang, Korea, 2014.
- Song, S.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Yi, M.J. Evaluation of long-term data obtained from seawater intrusion monitoring network using variation type analysis. J. Korea Earth Sci. Soc. 2007, 28, 478–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, N.S. Use of vertical electrical soundings to delineate seawater intrusion in a coastal area of Byunsan, Korea. Environ. Geol. 2007, 52, 1207–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Song, S.H. National scale evaluation of groundwater chemistry in Korea coastal aquifers: Evidences of seawater intrusion. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 66, 707–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Shin, J.Y.; Koh, E.H.; Koh, G.W.; Lee, K.K. Sea level rise around Jeju Island due to global warming and movement of groundwater/seawater interface in the eastern part of Jeju Island. J. Soil Groundw. Environ. 2009, 14, 68–79. [Google Scholar]
- 2014 Report on Rural Groundwater Management Monitoring Network; Korea Rural Community Corporation (KRC): Uiwang, Korea, 2014.
- Lee, B.S.; Kim, Y.I.; Choi, K.J.; Song, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Woo, D.K.; Seol, M.K.; Park, K.Y. Rural groundwater monitoring network in Korea. J. Soil Groundw. Environ. 2014, 19, 1–11. (In Korean) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Song, S.H. Groundwater chemistry and ionic ratios in a western coastal aquifer of Buan, Korea. Geosci. J. 2007, 11, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Method of Reporting Operation Result of Subsidiary Groundwater Monitoring Network and Voluntary Declaration on Illegal Groundwater Facilities; Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport (MOLIT): Sejong, Korea, 2015.
- Kim, J.W.; Lee, J.Y.; Yi, M.J.; Kim, G.B.; Won, J.H.; Lee, K.K. Allocating local groundwater monitoring stations for South Korea using an analytic hierarchy process. Hydrogeol. J. 2007, 15, 615–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Lee, G.S.; Song, S.H. An interpretation of changes in groundwater level and electrical conductivity in monitoring wells in Jeju Island. J. KoreaEarth Sci. Soc. 2007, 28, 925–935. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, H.M.; Lee, J.Y. Parametric and non-parametric trend analyses for water levels of groundwater monitoring wells in Jeju Island. J. Soil Groundw. Environ. 2009, 14, 41–50. [Google Scholar]
- Unno, T.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.; Nguyen, S.G.; Guevarra, R.B.; Kim, G.P.; Lee, J.H.; Sadowsky, M.J. Influence of seawater intrusion on microbial communities in groundwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 532, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Study on Plan for Characterizing Drinking Groundwater; Korea Institute of Geoscience and Mineral Resources (KIGAM): Sejong, Korea, 2011.
- National Institute of Environmental Research (NIER). Soil and Groundwater Information System. Available online: http://sgis.nier.go.kr (accessed on 17 February 2016).
- Lee, J.Y.; Park, Y.; Kim, N.J.; Jeon, W.H. Status of community drinking water in Korea and implications for appropriate management. J. Soil Groundw. Environ. 2013, 18, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plan of Installation of Groundwater Quality Monitoring Network and Measurement of Groundwater Pollution Status; Ministry of Environment (ME): Sejong, Korea, 2014.
- Donath, F.M.; Daughney, C.J.; Morgenstern, U.; Cameron, S.G.; Toews, M.W. Hydrochemical interpretation of groundwater-surface water interactions at catchment and local scales, Lake Rotorua catchment, New Zealand. J. Hydrol. N. Z. 2015, 54, 11–32. [Google Scholar]
- Moreau, M.; Cameron, S.G.; Daughney, C.J.; Gusyev, M.A.; Tschritter, C. Envirolink Tools Project: Capture Zone Delineation; GNS Science: Lower Hutt, New Zealand, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Moreau, M.; Daughney, C.J.; Morgenstern, U.; van der Raaij, R.; Reeves, R.R. Discriminant analysis for estimation of groundwater age from hydrochemistry and well construction: Application to New Zealand aquifers. Hydrogeol. J. 2010, 18, 417–428. [Google Scholar]
- Morgenstern, U.; Daughney, C.J. Groundwater age for identification of baseline groundwater quality and the impacts of land-use intensification-The National Groundwater Monitoring Programme of New Zealand. J. Hydrol. 2012, 456, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Laws | Objects | Enactments | Jurisdictions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Groundwater Act | All except the groundwater that the other Acts control | 10 December 1993 | Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport (MOLIT); Ministry of Environment (ME) |
| Hot Spring Act | Hot spring water (groundwater over 25 °C) | 2 Mary 1981 | Ministry of The Interior (MOI) |
| Drinking Water Management Act | Drinking groundwater (spring water) | 5 January 1995 | ME |
| Rearrangement of Agricultural and Fishing Villages Act | Groundwater used for agriculture | 22 December 1994 | Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs (MAFRA) |
| Act on National Defense and Military Installations Projects | Groundwater facilities for military affairs | 14 January 1991 | Ministry of National Defense (MND) |
| Framework Act on Civil Defense | Groundwater facilities for national emergency (e.g., war, disasters) | 25 July 1975 | Ministry of Public Safety and Security (MPSS) |
| Special Act on The Establishment of Jeju Special Self-Governing Province and The Development of Free International City | All groundwater on Jeju Island (Province) | 21 February 2006 | MOI; MOLIT |
| Networks | Parameters | No. of Wells | Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| National Groundwater Monitoring Network (NGMN) | water level, water temperature, EC | 552 (386 deep + 166 shallow, as of December 2015) | MOLIT and K-water |
| Groundwater Quality Monitoring Network (GQMN) | ~0 parameters including pH, EC, NO3−, Cl−, As | 3141 (as of December 2014) | ME and Korea Environment Corporation |
| Seawater Intrusion Monitoring Network (SIMN) | water level, water temperature, EC, and major ions | 145 (as of December 2014) | MAFRA and KRC |
| Rural Groundwater Monitoring Network (RGMN) | water level, water temperature, EC | 176 (as of December 2014) | MAFRA and KRC |
| Subsidiary or Local Groundwater Monitoring Network (SGMN or LGMN) | water level | 1803 (as of September 2015) | Local governments (city and county) |
| Drinking Water (groundwater) Monitoring Network (DWMN) | water level, water temperature, EC, Water quality | 189 (as of February 2013) | ME and commercial bottled groundwater companies |
| Constituting Networks | Monitoring Parameters | No. of Wells | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| exclusive network for monitoring groundwater quality | 67 parameters including basic parameters and drinking water standards parameters | 508 | 4 times per year |
| NGMN | 19 groundwater quality standards parameters for living use and EC | 552 (386 deep + 166 shallow) | 2 times per year |
| RGMN | 19 groundwater quality standards parameters for living use and EC | 60 | 2 times per year |
| local groundwater quality monitoring network | 19 groundwater quality standards parameters for living use and EC | 2021 | 2 times per year |
| City/Province | Total | Type of Wells | Monitoring Methods | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monitoring Only | Using Well | Automatic (with RTU) | Semi-Auto (No RTU) | Manual | ||
| Seoul | 214 | 18 | 196 | 114 | 56 | 44 |
| Busan | 189 | 18 | 171 | 132 | 48 | 9 |
| Daegu | 136 | – | 136 | – | – | 136 |
| Incheon | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Gwangju | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Daejeon | 39 | – | 39 | 15 | 24 | – |
| Ulsan | 36 | – | 36 | 9 | – | 27 |
| Sejong | 3 | 3 | – | 3 | – | – |
| Gyeonggi | 144 | 66 | 78 | 61 | 26 | 57 |
| Gangwon | 46 | 28 | 18 | 37 | – | 9 |
| Chungbuk | 308 | 240 | 68 | 308 | – | – |
| Chungnam | 167 | 155 | 12 | 40 | 21 | 106 |
| Jeonbuk | 6 | 6 | – | – | – | 6 |
| Jeonnam | 10 | 4 | 6 | 5 | – | 5 |
| Gyeongbuk | 12 | 2 | 10 | 2 | – | 10 |
| Gyeongnam | 493 | 111 | 382 | 370 | 91 | 32 |
| Subtotal | 1803 | 651 | 1152 | 1096 | 266 | 441 |
| Jeju | 132 | 132 | – | 132 | – | – |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.-Y.; Kwon, K.D. Current Status of Groundwater Monitoring Networks in Korea. Water 2016, 8, 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8040168
Lee J-Y, Kwon KD. Current Status of Groundwater Monitoring Networks in Korea. Water. 2016; 8(4):168. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8040168
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jin-Yong, and Kideok D. Kwon. 2016. "Current Status of Groundwater Monitoring Networks in Korea" Water 8, no. 4: 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8040168
APA StyleLee, J.-Y., & Kwon, K. D. (2016). Current Status of Groundwater Monitoring Networks in Korea. Water, 8(4), 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8040168







