Variability of Bed Drag on Cohesive Beds under Wave Action
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
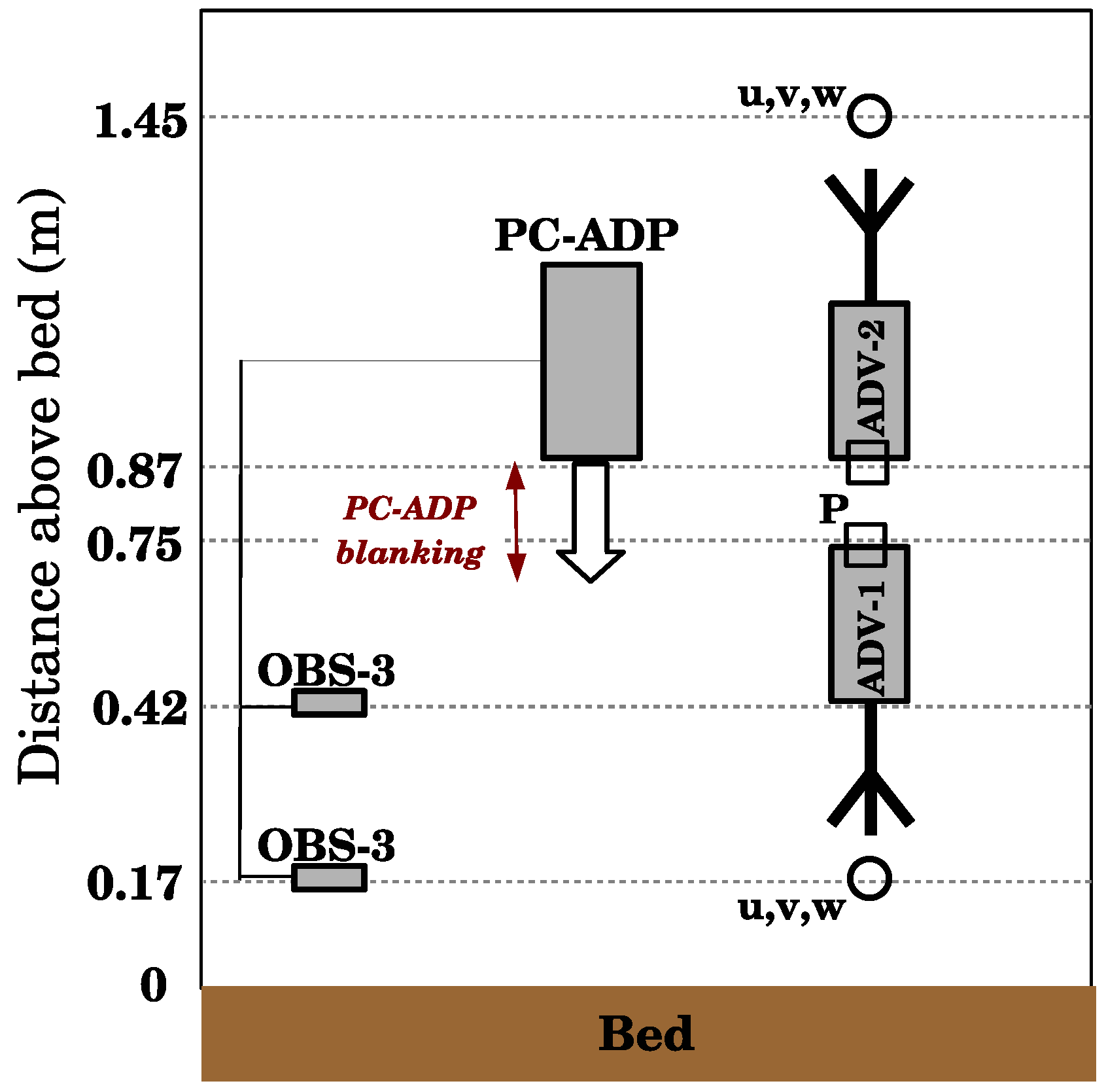
2.2. Field Experiment
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Logarithmic Law of the Wall
2.3.2. Bottom Boundary Layer Model
2.3.3. Dual-Sensor Method
2.3.4. Wind Stress
3. Results
3.1. Field Observations
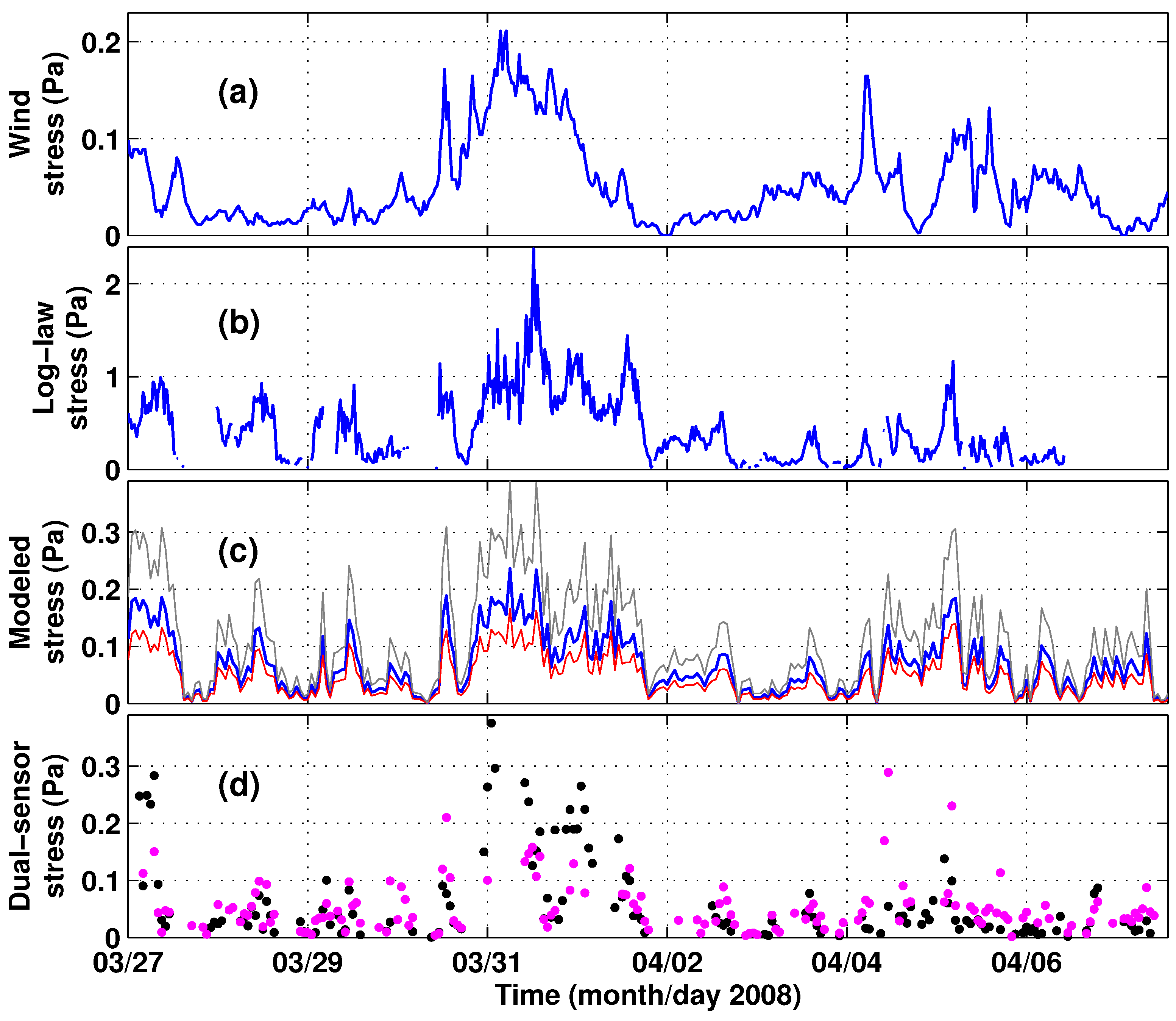
3.2. Stress Estimates
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADV | Acoustic Doppler Velocimeter |
| OBS | Optical Backscatterance Sensor |
| PC-ADP | Pulse Coherent Acoustic Doppler Profiler |
References
- Inoue, T.; Glud, R.N.; Stahl, H.; Hume, A. Comparison of three different methods for assessing in situ friction velocity: A case study from Loch Etive, Scotland. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2011, 9, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, J.C.; Butman, B.; Dalyander, P.S. Storm-driven sediment transport in Massachusetts Bay. Cont. Shelf Res. 2008, 28, 257–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennekes, H.; Lumley, J.L. A First Course in Turbulence; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1972; p. 300. [Google Scholar]
- Lueck, R.G.; Lu, Y. The logarithmic layer in a tidal channel. Cont. Shelf Res. 1997, 17, 1785–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, C.E.; Weatherly, G.L. Some effects of suspended sediment stratification on an oceanic bottom boundary layer. J. Geophys. Res. 1981, 86, 4161–4172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, H.O. Turbulence measurements in straified and well-mixed estuarine flows. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1983, 17, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenn, S.M.; Grant, W.D. A suspended sediment stratification correction for combined wave and current flows. J. Geophys. Res. 1987, 92, 8244–8264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.H. Tide-induced sediment resuspension and the bottom boundary layer in an idealized estuary with a muddy bed. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2002, 32, 3113–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntley, D.A.; Hazen, D.G. Seabed stresses in combined wave and steady flow conditions on the Nova Scotia continental shelf: Field measurements and predictions. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1988, 18, 347–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, W.D.; Madsen, O.S. Combined wave and current interaction with a rough bottom. J. Geophys. Res. 1979, 84, 1797–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, C.K.; Wiberg, P.L. A two-dimensional, time-dependent model of suspended sediment transport and bed reworking for continental shelves. Comput. Geosci. 2001, 27, 675–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, O.S. Spectral wave-current bottom boundary layer flows. Proc. Int. Conf. Coast. Eng. 1994, 24, 385–398. [Google Scholar]
- Benilov, A.Y.; Filyushkin, B.N. Application of methods of linear filtration to an analysis of fluctuations in the surface layer of the sea. Izv. Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 1970, 6, 810–819. [Google Scholar]
- Trowbridge, J.H. On a technique for measurement of turbulent shear stress in the presence of surface waves. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1998, 15, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternberg, R.W. Friction factors in tidal channels with differing bed roughness. Mar. Geol. 1968, 6, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntley, D.A.; Huthnance, J.M.; Collins, M.B.; Liu, C.-L.; Nicholls, R.J.; Hewitson, C. Hydrodynamics and sediment dynamics of North Sea sand waves and sand banks. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A 1993, 343, 461–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntley, D.A.; Nicholls, R.J.; Liu, C.; Dyer, K.R. Measurements of the semi-diurnal drag coefficient over sand waves. Cont. Shelf Res. 1994, 14, 437–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Signell, R.P.; List, J.H. Effect of wave-enhanced bottom friction on storm-driven circulation in Massachusetts Bay. J. Wtrwy. Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 1997, 123, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricker, J.D.; Inagaki, S.; Monismith, S.G. Bed drag coefficient variability under wind waves in a tidal estuary. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2005, 131, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwood, C.R.; Lacy, J.R.; Voulgaris, G. Shear velocity estimates on the inner shelf off Grays Harbor, Washington, USA. Cont. Shelf Res. 2006, 26, 1995–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neill, C.F.; Allison, M.A. Subaqueous deltaic formation on the Atchafalaya Shelf, Louisiana. Mar. Geol. 2005, 214, 411–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safak, I.; Allison, M.A.; Sheremet, A. Floc variability under changing turbulent stresses and sediment availability on a wave-energetic muddy shelf. Cont. Shelf Res. 2013, 53, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, W.J.; Trowbridge, J.H. The direct estimation of near-bottom turbulent fluxes in the presence of energetic wave motions. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2001, 18, 1540–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, P. Coastal bottom boundary layers and sediment transport. In Advanced Series on Ocean Engineering; World Scientific: Singapore, 1992; p. 324. [Google Scholar]
- Lacy, J.R.; Sherwood, C.R.; Wilson, D.J.; Chisholm, T.A.; Gelfenbaum, G.R. Estimating hydrodynamic roughness in a wave-dominated environment with a high-resolution acoustic Doppler profiler. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, C. Investigation of the variability of floc sizes on the Louisiana Shelf using acoustic estimates of cohesive sediment properties. Mar. Geol. 2014, 353, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamphuis, J.W. Friction factor under oscillatory waves. J. Wtrwy. Harb. Coast. Eng. Div. 1975, 101, 135–144. [Google Scholar]
- Feddersen, F.; Williams, A.J., III. Direct estimation of the Reynolds stress vertical structure in the nearshore. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2007, 24, 102–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priestley, M.B. Spectral Analysis and Time Series; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Haykin, S. Adaptive Filter Theory; Prentice Hall: New York, NY, USA, 1996; p. 989. [Google Scholar]
- Safak, I.; Sheremet, A.; Allison, M.A.; Hsu, T.-J. Bottom turbulence on the muddy Atchafalaya Shelf, Louisiana, USA. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Large, W.G.; Yeager, S.G. Diurnal to decadal global forcing for ocean and sea-ice models: The data sets and flux climatologies. In NCAR/TN-460+STR; NCAR: Boulder, CO, USA, 2004; p. 105. [Google Scholar]
- Lentz, S.; Guza, R.T.; Elgar, S.; Feddersen, F.; Herbers, T.H.C. Momentum balances on the North Carolina inner shelf. J. Geophys. Res. 1999, 104, 18205–18226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulsby, R.L.; Wainwright, B.L.S.A. A criterion for the effect of suspended sediment on near-bottom velocity profiles. J. Hydraul. Res. 1987, 25, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacchione, D.A.; Drake, D.E.; Kayen, R.W.; Sternberg, R.W.; Kineke, G.C.; Tate, G.B. Measurements in the bottom boundary layer on the Amazon subaqueous delta. Mar. Geol. 1995, 125, 235–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacey, M.T.; Monismith, S.G.; Burau, J.R. Observations of turbulence in a partially stratified estuary. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1999, 29, 1950–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.O.; McCave, I.N. Seabed drag coefficient under tidal currents in the eastern Irish Sea. Wind-enhanced resuspension in the shallow waters of South San Francisco Bay: Mechanisms and potential implications for cohesive sediment transport. J. Geophys. Res. 1995, 100, 16057–16069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, A.; Lacy, J.R.; Hsu, K.; Hoover, D.; Gladding, S.; Stacey, M.T. Wind-enhanced resuspension in the shallow waters of South San Francisco Bay: Mechanisms and potential implications for cohesive sediment transport. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safak, I.; Sahin, C.; Kaihatu, J.M.; Sheremet, A. Modeling wave-mud interaction on the central-chenier plain coast, western Louisiana Shelf, USA. Ocean Model. 2013, 70, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.O.; Black, K.P.; Amos, C.L. Control of estuarine sediment dynamics by interactions between currents and waves at several scales. Mar. Geol. 1997, 144, 97–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








© 2016 by the author; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Safak, I. Variability of Bed Drag on Cohesive Beds under Wave Action. Water 2016, 8, 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8040131
Safak I. Variability of Bed Drag on Cohesive Beds under Wave Action. Water. 2016; 8(4):131. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8040131
Chicago/Turabian StyleSafak, Ilgar. 2016. "Variability of Bed Drag on Cohesive Beds under Wave Action" Water 8, no. 4: 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8040131
APA StyleSafak, I. (2016). Variability of Bed Drag on Cohesive Beds under Wave Action. Water, 8(4), 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8040131




