Transport of Silica Colloid through Saturated Porous Media under Different Hydrogeochemical and Hydrodynamic Conditions Considering Managed Aquifer Recharge
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Procedure
2.1.1. Experimental Equipment
2.1.2. Experimental Methods
- (1)
- The effect of different pH values (pH = 5, 7, and 9);
- (2)
- The effect of variations in ionic strength (IS < 0.0005, 0.02, and 0.05 M);
- (3)
- The effect of cation valence (Na+, Ca2+), and
- (4)
- The effect of flow rate (0.1, 0.2, and 0.4 mL/min) on the transport of silica colloid in groundwater.
2.2. Colloidal Deposition Rate Coefficient
2.3. Simulating Colloid Migration in the Aquifer
3. Results and Discussion
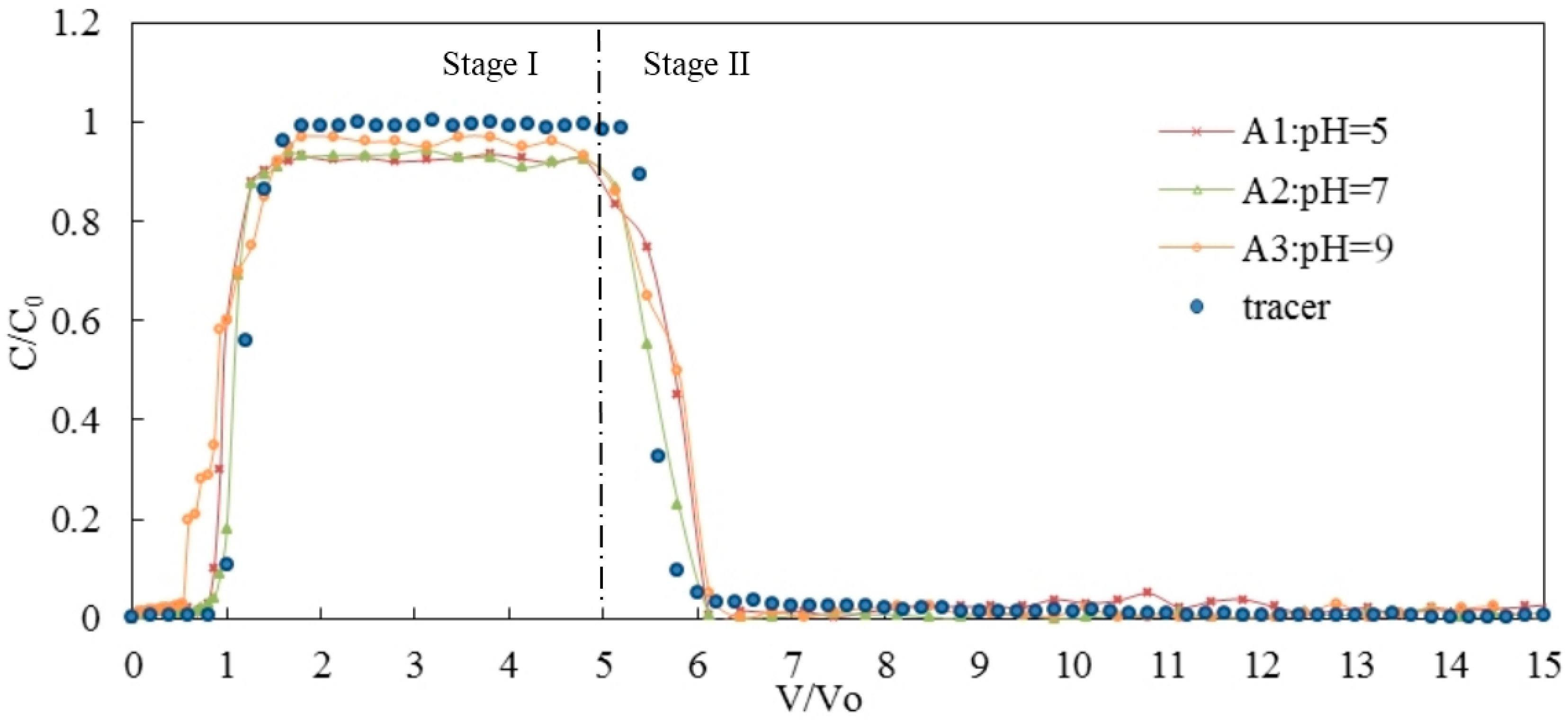
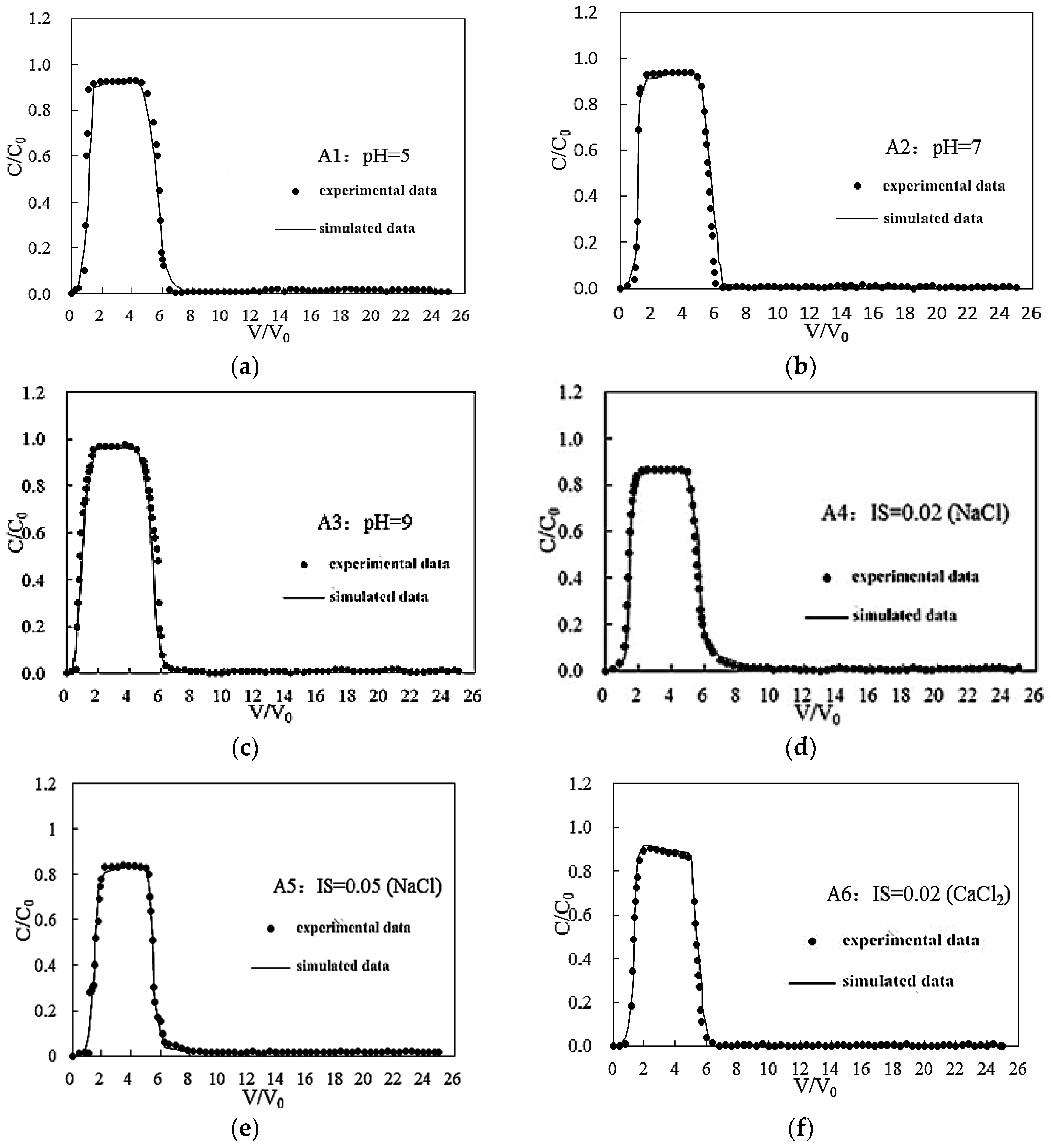
3.1. Effects of pH on the Transport of Silica Colloid
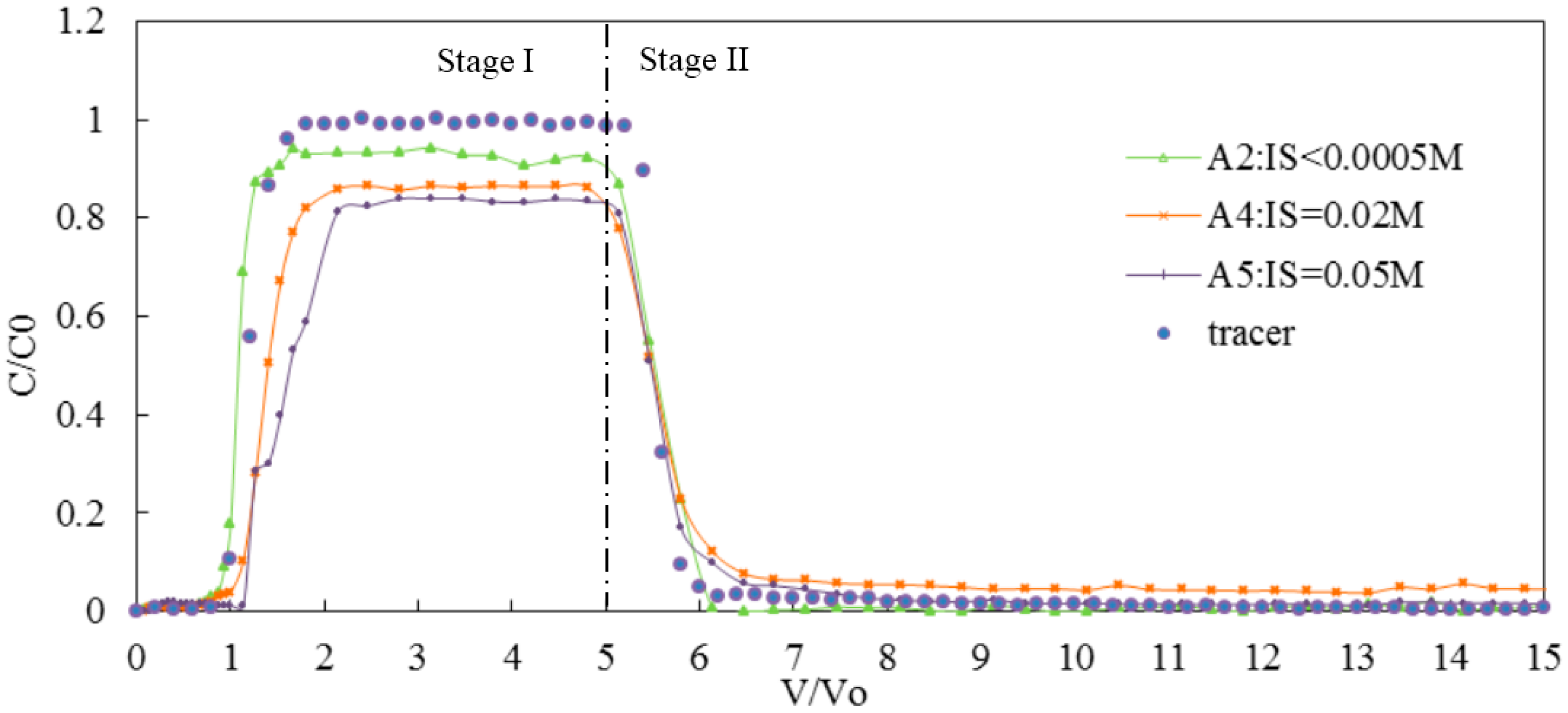
3.2. Effect of IS on Transport of Silica Colloid
3.2.1. Effect of Monovalent Cations on the Transport of Silica Colloid
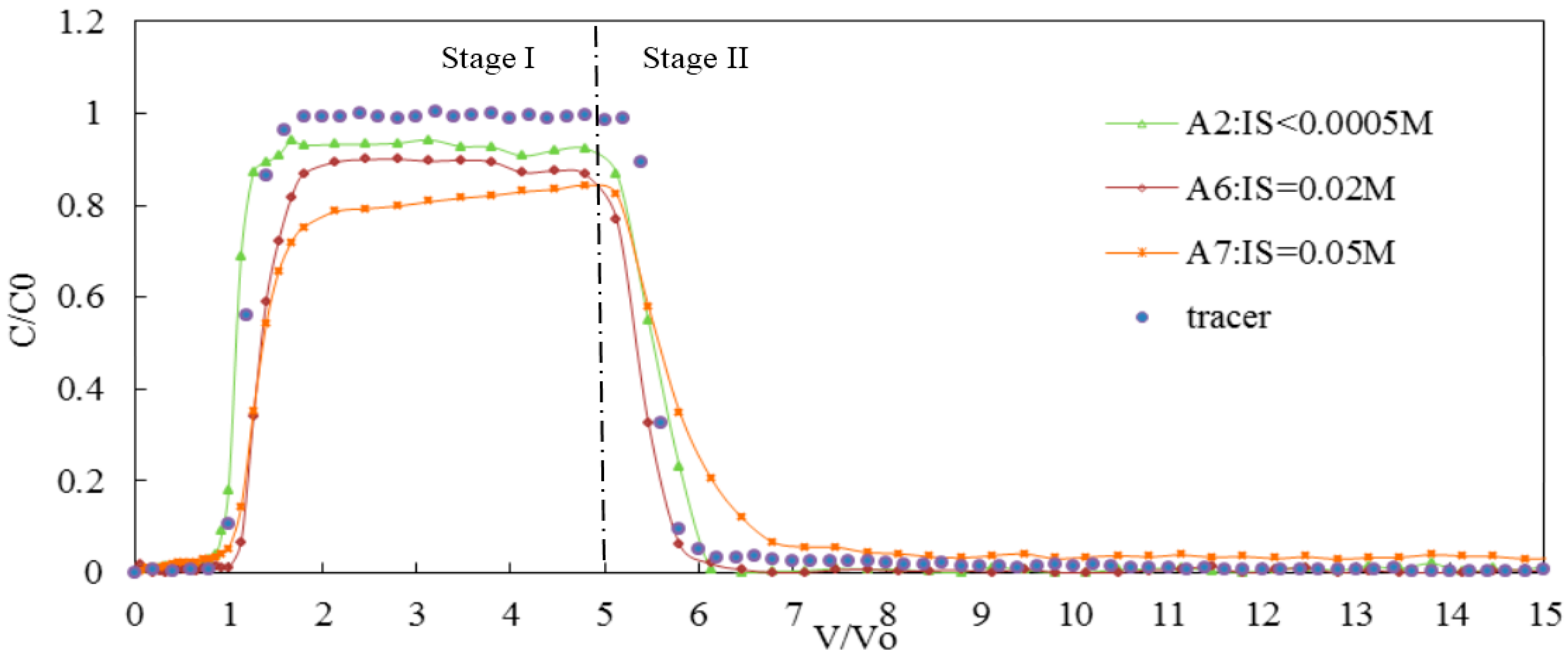
3.2.2. Effect of Bivalent Cations on the Transport of Silica Colloid
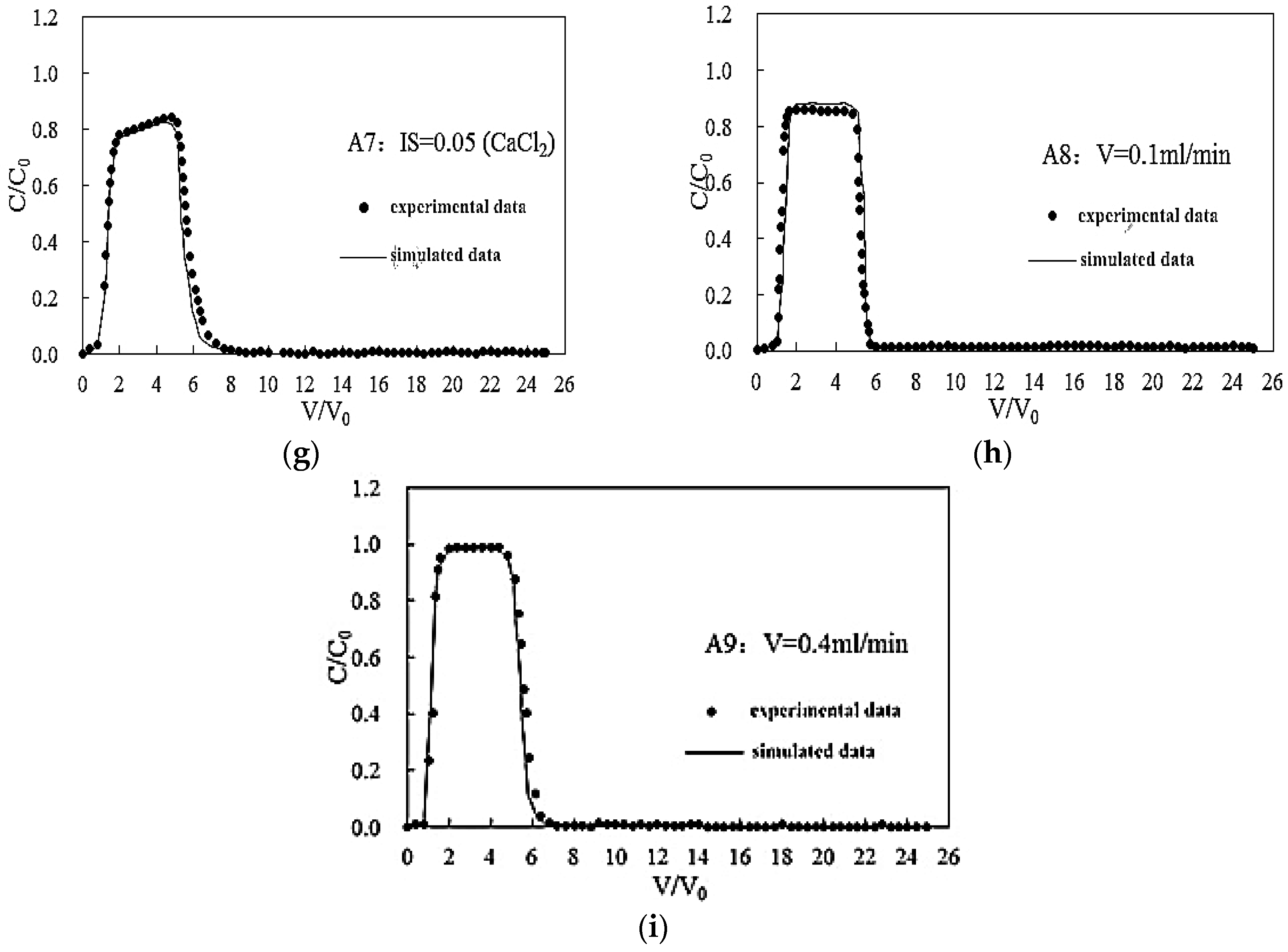
3.3. Effect of Flow Rate on the Transport of Silica Colloid
3.4. Simulation Results
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, W.; Ying, H.; Yu, X.; Dan, L.; Zhou, J. Multi-component transport and transformation in deep confined aquifer during groundwater artificial recharge. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 152C, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Wang, Y.; Guo, H. Mobilization Mechanism and the Effection on Contamination Movement of Colloids in Groundwater; China University of Geosciences: Wuhan, China, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Jie, M.; Guo, H.; Mei, L.; Wan, X.; Zhang, H.; Feng, X.; Wei, R.; Tian, L.; Han, X. Blocking effect of colloids on arsenate adsorption during co-transport through saturated sand columns. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 213, 638–647. [Google Scholar]
- Syngouna, V.I.; Chrysikopoulos, C.V. Experimental investigation of virus and clay particles cotransport in partially saturated columns packed with glass beads. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 440, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgo, J.J.W.; Williams, G.M.; Harrison, I.; Warwick, P.; Gardiner, M.P.; Longworth, G. Colloid transport in a glacial sand aquifer laboratory and field studies. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1993, 73, 179–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, B.J. Manufactured Nanoparticles: Assessing the Mobility of a Future Class of Containment in Groundwaters. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Birmingham, Birmingham, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Xu, S.; Liu, J. Comparition between Kaolinite and SiO2 Colloid in Transport Beheavir in Suturated Porous Media; Instituteof Soil Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences: Nanjing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Séquaris, J.M.; Klumpp, E.; Vereecken, H. Colloidal properties and potential release of water-dispersible colloids in an agricultural soil depth profile. Geoderma 2013, 193–194, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, S.A.; Simunek, J.; Bettahar, M.; Genuchten, M.T.V.; Yates, S.R. Significance of straining in colloid deposition: Evidence and implications. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42, 3660–3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Muñoz-Carpena, R.; Gao, B.; Perez-Ovilla, O. Effects of ionic strength, particle size, flow rate, and vegetation type on colloid transport through a dense vegetation saturated soil system: Experiments and modeling. J. Hydrol. 2013, 499, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, W.; Ying, H.; Yu, X.; Li, F.; Chen, X. Column experiments to investigate transport of colloidal humic acid through porous media during managed aquifer recharge. Hydrogeol. J. 2016, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elimelech, M.; Nagai, M.; Chunhan Ko, A.; Ryan, J.N. Relative insignificance of mineral grain zeta potential to colloid transport in geochemically heterogeneous porous media. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 2143–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syngouna, V.I.; Chrysikopoulos, C.V. Transport of biocolloids in water saturated columns packed with sand: Effect of grain size and pore water velocity. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2011, 126, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, L.; Goltz, M.; Close, M. Application of the method of temporal moments to interpret solute transport with sorption and degradation. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2003, 60, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruben, K.; Kurt, B.; Daniel, G.; Yan, Y.; Michal, B.; Hans, S. Experimental determination of colloid deposition rates and collision efficiencies in natural porous media. Water Resour. Res. 1997, 33, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar]
- Sojitra, I.; Valsaraj, K.T.; Reible, D.D.; Thibodeaux, L.J. Transport of hydrophobic organics by colloids through porous media 1 experimental results. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1995, 94, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.B.; Dzombak, D.A. Chemical factors influencing colloid-facilitated transport of contaminants in porous media. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torkzaban, S.; Bradford, S.A.; Genuchten, M.T.V.; Walker, S.L. Colloid transport in unsaturated porous media: The role of water content and ionic strength on particle straining. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2008, 96, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.Q.; Sun, H.M.; Lei, Y.I.; Yi-Qing, L.U.; Wang, G.D.; Zhang, X.C. Effect of flowrate of pore water on the transport of colloid in saturated porous media. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2010, 24, 101–104. [Google Scholar]
- Lahav, N.; Tropp, D. Movement of synthetic microspheres in saturated soil columns. Soil Sci. 1980, 130, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puls, R.W.; Paul, C.J.; Clark, D.A. Surface chemical effects on colloid stability and transport through natural porous media. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1993, 73, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, B. The Mobility of Colloids in Red Sandstone: The Effect of Flow Rate and Ionic Strength. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Birmingham, Birmingham, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Sätmark, B.; Albinsson, Y.; Liang, L. Chemical effects of goethite colloid on the transport of radionuclides through a quartz-packed column. J. Contam. Hydrol. 1996, 21, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretzschmar, R.; Sticher, H. Colloid transport in natural porous media: Influence of surface chemistry and flow velocity. Phys. Chem. Earth 1998, 23, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
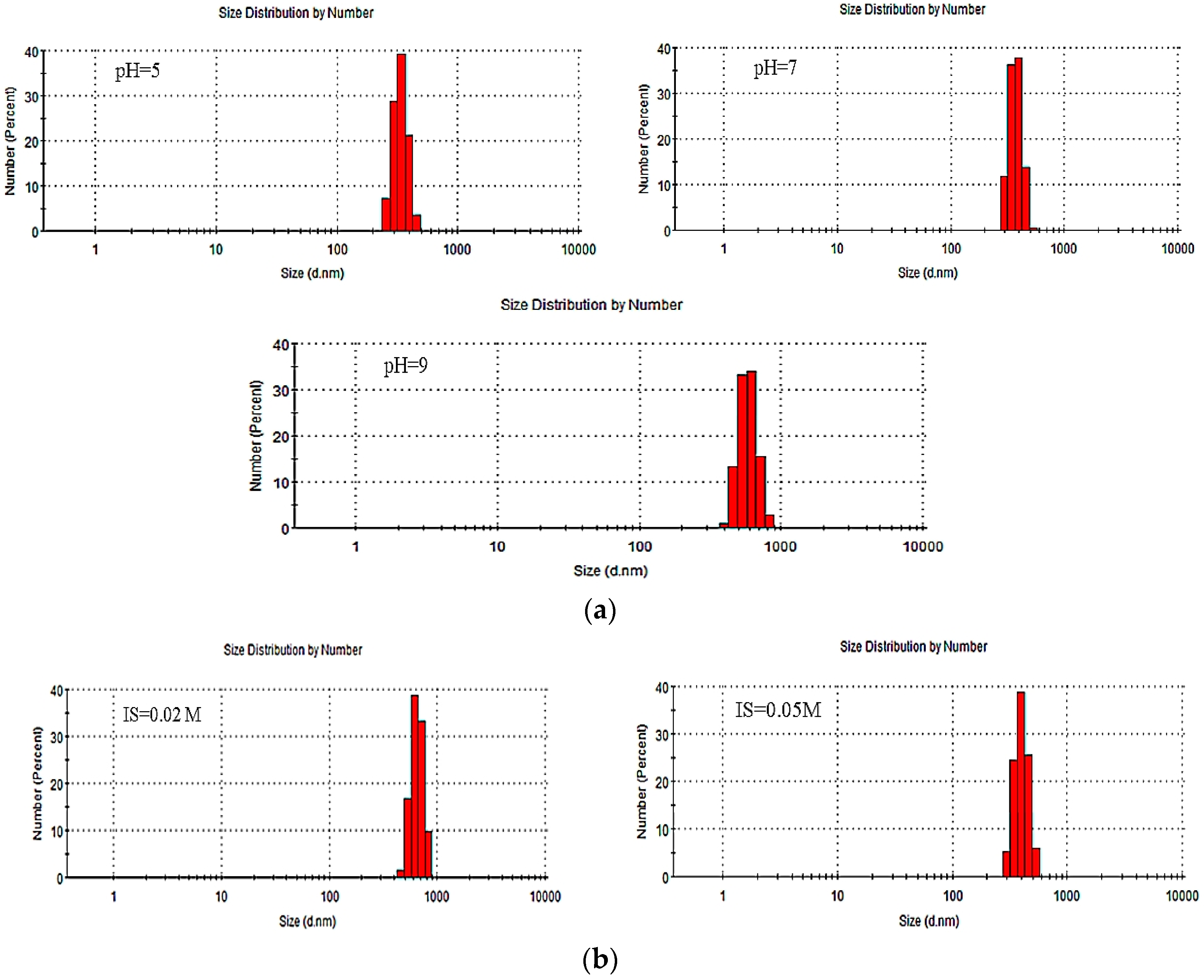


| Influence Factor | pH | IS | PdI | Pk 1 Mean Int (d.nm) | Pk 2 Mean Int (d.nm) | Pk 3 Mean Int (d.nm) | Pk 1 Area Int (Percent) | Pk 2 Area Int (Percent) | Pk 3 Area Int (Percent) | ZP (mV) (±0.3~1.8) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 5 | <0.0005 | 0.855 | 352.8 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | −20.2 |
| 7 | <0.0005 | 0.742 | 372.4 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | −27.4 | |
| 9 | <0.0005 | 0.792 | 409.9 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | −32.1 | |
| 7 | <0.0005 | 0.742 | 372.4 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | −27.4 | |
| IS | 7 | 0.02 | 0.714 | 406.2 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | −24.0 |
| (NaCl) | 7 | 0.05 | 0.840 | 653.4 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | −19.8 |
| 7 | <0.0005 | 0.742 | 372.4 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | −27.4 | |
| IS | 7 | 0.02 | 0.728 | 410.5 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | −22.6 |
| (CaCl2) | 7 | 0.05 | 0.547 | 738.0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | −12.7 |
| Influence Factors | Test No. | pH | IS (mol/L) | Flow Rate (mL/min) | Medium | Stage I (%) | Stage II (%) | Retention (%) | Peak C/C0 | R | K (s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | A1 | 5 | <0.0005 | 0.20 | GB | 75 | 21 | 4 | 0.93 | 1.05 | 2.79 × 10−6 |
| A2 | 7 | <0.0005 | 0.20 | GB | 84 | 10 | 6 | 0.95 | 1.05 | 2.03 × 10−6 | |
| A3 | 9 | <0.0005 | 0.20 | GB | 86 | 11 | 3 | 0.97 | 1.12 | 1.21 × 10−6 | |
| IS (NaCl) | A2 | 7 | <0.0005 | 0.20 | GB | 84 | 10 | 6 | 0.95 | 1.05 | 2.03 × 10−6 |
| A4 | 7 | 0.02 | 0.20 | GB | 68 | 18 | 14 | 0.89 | 1.31 | 3.47 × 10−6 | |
| A5 | 7 | 0.05 | 0.20 | GB | 64 | 15 | 21 | 0.85 | 1.50 | 4.37 × 10−5 | |
| A2 | 7 | <0.0005 | 0.20 | GB | 84 | 10 | 6 | 0.95 | 1.05 | 2.03 × 10−6 | |
| IS (CaCl2) | A6 | 7 | 0.02 | 0.20 | GB | 65 | 13 | 22 | 0.90 | 1.25 | 4.19 × 10−6 |
| A7 | 7 | 0.05 | 0.20 | GB | 56 | 18 | 26 | 0.82 | 1.81 | 6.43 × 10−5 | |
| Flow rate | A8 | 7 | <0.0005 | 0.1 | GB | 67 | 9 | 24 | 0.85 | 1.03 | 6.83 × 10−5 |
| A2 | 7 | <0.0005 | 0.2 | GB | 84 | 10 | 6 | 0.95 | 1.05 | 2.03 × 10−6 | |
| A9 | 7 | <0.0005 | 0.4 | GB | 87 | 10 | 3 | 0.98 | 1.05 | 4.32 × 10−7 |
| Variable No. | A1 | A2 | A3 | A4 | A5 | A6 | A7 | A8 | A9 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Katt | [1/s] | 2.79 × 10−6 | 2.03 × 10−6 | 1.21 × 10−6 | 3.47 × 10−6 | 4.37 × 10−5 | 4.19 × 10−6 | 6.43 × 10−5 | 6.83 × 10−5 | 4.32 × 10−7 |
| Kre | [1/s] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.6 × 10−4 | 0 | 0 |
| λs | [1/s] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0016 | 0 | 0 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Li, S.; Zhou, J.; Liu, D. Transport of Silica Colloid through Saturated Porous Media under Different Hydrogeochemical and Hydrodynamic Conditions Considering Managed Aquifer Recharge. Water 2016, 8, 555. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8120555
Wang Z, Zhang W, Li S, Zhou J, Liu D. Transport of Silica Colloid through Saturated Porous Media under Different Hydrogeochemical and Hydrodynamic Conditions Considering Managed Aquifer Recharge. Water. 2016; 8(12):555. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8120555
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhuo, Wenjing Zhang, Shuo Li, Jingjing Zhou, and Dan Liu. 2016. "Transport of Silica Colloid through Saturated Porous Media under Different Hydrogeochemical and Hydrodynamic Conditions Considering Managed Aquifer Recharge" Water 8, no. 12: 555. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8120555
APA StyleWang, Z., Zhang, W., Li, S., Zhou, J., & Liu, D. (2016). Transport of Silica Colloid through Saturated Porous Media under Different Hydrogeochemical and Hydrodynamic Conditions Considering Managed Aquifer Recharge. Water, 8(12), 555. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8120555






