Quantifying Apparent Groundwater Ages near Managed Aquifer Recharge Operations Using Radio-Sulfur (35S) as an Intrinsic Tracer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Geochemistry of 35S
1.2. Field Locations
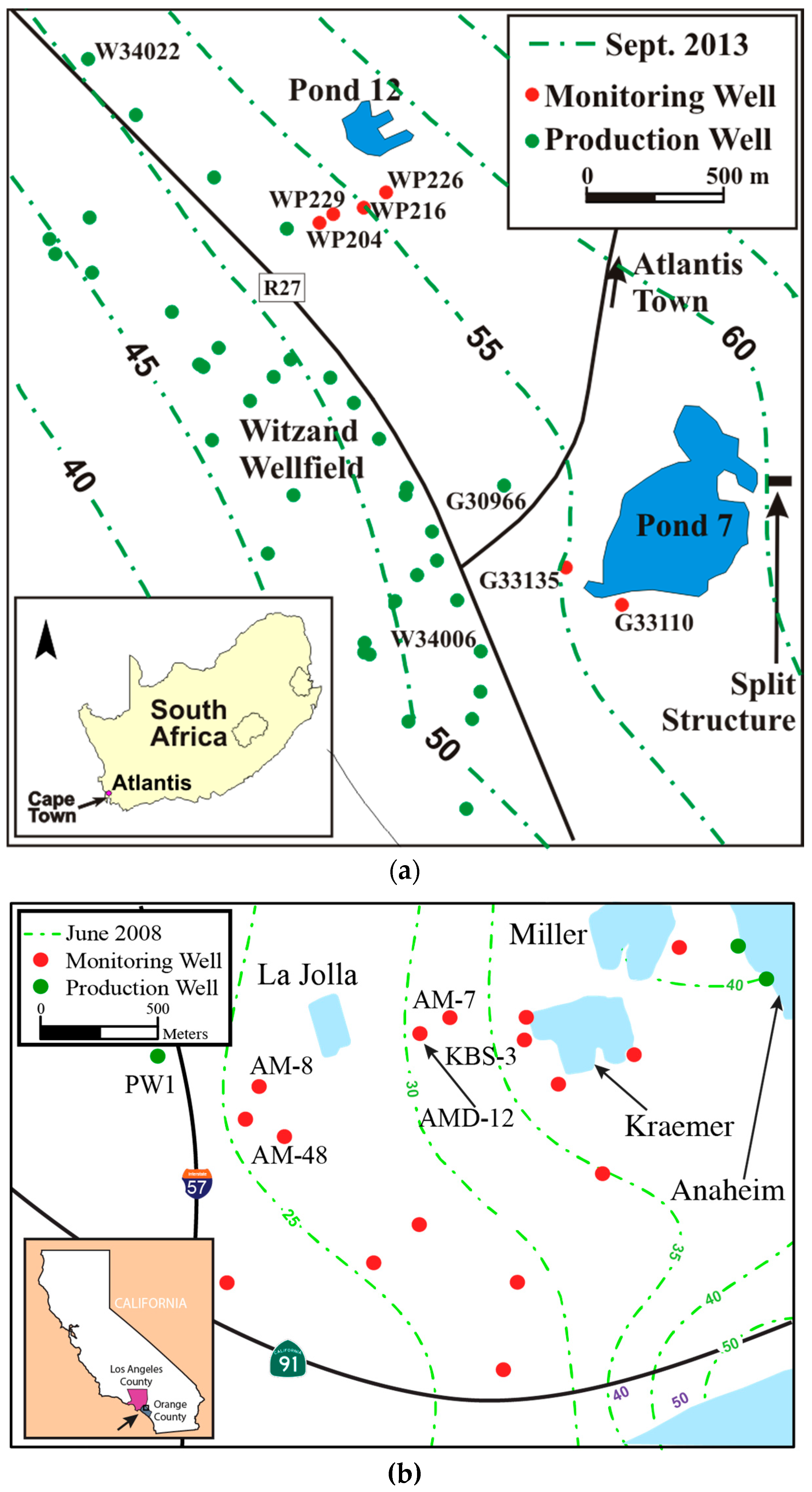
1.2.1. The Atlantis MAR System
1.2.2. The OCWD MAR System
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. The Atlantis MAR System
3.2. The Kraemer Spreading Basin
4. Discussion
4.1. The Atlantis MAR System
4.2. The OCWD MAR System
5. Conclusions and Implications
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stuyfzand, P.J. Hydrology and water quality aspects of Rhine bank groundwater in the Netherlands. J. Hydrol. 1989, 106, 341–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jonge, H.G.; Kortleve, M.W.; Frapporti, G. Sustainable use of aquifers for artificial recharge in South Holland. In Management of Aquifer Recharge for Sustainability; Dillon, P.J., Ed.; Balkema Publishers: Exton, PA, USA, 2002; pp. 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Olsthoorn, T.N.; Mosch, M.J.M. Fifty years artificial recharge in the Amsterdam dune area. In Management of Aquifer Recharge for Sustainability; Dillon, P.J., Ed.; Balkema Publishers: Exton, PA, USA, 2002; pp. 29–33. [Google Scholar]
- Eckert, P.; Rohms, H.P.; Irmscher, R. Dynamic processes during bank filtration and their impact on raw water quality. In Proceeding of the 5th International Symposium on Management of Aquifer Recharge (ISMAR5), Berlin, Germany, 11–16 June 2005; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2006; pp. 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, T.; Day, K.; Grischeck, T. Sustainability of riverbank filtration in Dresden, Germany. In Proceeding of the 5th International Symposium on Management of Aquifer Recharge (ISMAR5), Berlin, Germany, 11–16 June 2005; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2006; pp. 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Krüger, M.; Ende, K.; Grischeck, T. Management of river bank filtration in the Elbe River Basin near Torgau, Germany. In Proceeding of the 5th International Symposium on Management of Aquifer Recharge (ISMAR5), Berlin, Germany, 11–16 June 2005; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2006; pp. 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, T.A. Ground water recharge using recycled municipal waste water in Los Angeles County and the California Department of Public Health’s draft regulations on aquifer retention time. Groundwater 2009, 47, 496–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, W.R. The quest for water through artificial recharge and wastewater recycling. In Management of Aquifer Recharge for Sustainability; Dillon, P.J., Ed.; Balkema Publishers: Exton, PA, USA, 2002; pp. 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, J.F.; Hudson, G.B.; Davisson, M.L.; Woodside, G.; Herndon, R. Geochemical imaging of flow near an artificial recharge facility, Orange County, California. Groundwater 2004, 42, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, P.K.; Makam, R. Surface area and travel time relationships in aquifer treatment systems. Water Environ. Res. 2009, 81, 2337–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laws, B.V.; Dickensen, E.R.V.; Johnson, T.A.; Snyder, S.A.; Drewes, J.E. Attenuation of contaminants of emerging concern during surface-spreading aquifer recharge. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 1087–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yates, M.V.; Gerba, C.P.; Kelley, L.M. Virus persistence in groundwater. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1985, 49, 778–781. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yates, M.V.; Yates, S.R. A comparison of geostatistical methods for estimating virus inactivation rates in ground water. Water Res. 1987, 21, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, P.K.; Narayanaswamy, A.; Genz, A.; Drewes, J.E. Water quality transformations during soil aquifer treatment at the Mesa Northwest Water Reclamation Plant, USA. Water Sci. Technol. 2001, 43, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Drewes, J.E.; Heberer, T.; Rauch, T.; Reddersen, K. Fate of pharmaceuticals during groundwater recharge. Ground Water Monit. Remedit. 2002, 23, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiscock, K.M.; Grischeck, T. Attenuation of groundwater pollution by bank filtration. J. Hydrol. 2002, 266, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, P. Future management of aquifer recharge. Hydrogeol. J. 2005, 13, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, C. The Big Thirst; Free Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011; p. 370. [Google Scholar]
- Sedlak, D. Water 4.0; Yale University Press: New Haven, CT, USA, 2014; p. 332. [Google Scholar]
- Asano, T.; Levine, A.D. Wastewater reclamation, recycling, and reuse: Past, present, and future. Water Sci. Technol. 1996, 33, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Water Quality Management Strategy. Australian Guidelines for Water Recycling, Managed Aquifer Recharge; National Water Quality Strategy Document No 24; Biotext: Canberra, Australia, 2009; p. 237.
- National Research Council. Water Reuse; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; p. 262. [Google Scholar]
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). 2012 Guidelines for Water Reuse; U.S. EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; p. 643.
- McDermott, J.A.; Avisar, D.; Johnson, T.; Clark, J.F. Groundwater travel times near spreading ponds: Inferences from geochemical and physical approaches. J. Hydrol. Eng.-ASCE 2008, 13, 1021–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- California Division of Drinking Water. Groundwater Replenishment Using Recycled Water; California State Water Resources Control Board, Division of Drinking Water: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2014. Available online: http://www.cdph.ca.gov/services/DPOPP/regs/Pages/DPH14003EGroundwaterReplenishmentUsingRecycledWater.aspx (accessed on 1 September 2015).
- Friedlander, G.; Kennedy, J.W.; Macias, E.S.; Miller, J.M. Nuclear and Radiochemistry, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1991; p. 684. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, N.; Turekian, K.K. Use of cosmogenic 35S to determine the rates of removal of atmospheric SO2. Nature 1991, 352, 226–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, N.; Turekian, K.K. Determination of the dry deposition flux of SO2 using cosmogenic 35S and 7Be measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 1995, 100, 2841–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, L.W.; Olsen, C.R.; Solomon, D.K.; Larsen, I.L.; Cook, R.B.; Grebmeier, J.M. Stable isotopes of oxygen and natural and fallout radionuclides used for tracing runoff during snowmelt in an Arctic watershed. Water Resour. Res. 1991, 27, 2171–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueker, J.K.; Turk, J.T.; Michel, R.L. Use of cosmogenic 35S for comparing ages of water from three alpine/subalpine basins in the Colorado Front Range. Geomorphology 1999, 27, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, R.L.; Campbell, D.; Clow, D.; Turk, J.T. Timescales for migration of atmospherically derived sulphate through an alpine/subalpine watershed, Loch Vale, Colorado. Water Resour. Res. 2000, 36, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanley, J.B.; Mayer, B.; Mitchell, M.J.; Michel, R.L.; Bailey, S.W.; Kendall, C. Tracing sources of streamwater sulfate during snowmelt using S and O isotope ratios of sulfate and 35S activity. Biogeochemistry 2005, 76, 161–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urióstegui, S.H.; Bibby, R.K.; Esser, B.K.; Clark, J.F. Analytical method for measuring 35S in natural waters. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 6064–6070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tredoux, G.; Cavé, L.C.; Bishop, R. Long-term stormwater and wastewater infiltration into a sandy aquifer, South Africa. In Management of Aquifer Recharge for Sustainability; Dillon, P.J., Ed.; Balkema Publishers: Exton, PA, USA, 2002; pp. 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, R.; Tredoux, G.; Ravenscroft, P.; Botha, F. Strategy Development: A National Approach to Implement Artificial Recharge as Part of Water Resources Planning; Department of Water Affairs and Forestry: Pretoria, South Africa, 2007; p. 194. [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson, A.S. 2011–2012 Report on Groundwater Recharge in the Orange County Groundwater Basin; Orange County Water District: Fountain Valley, CA, USA, 2013; p. 50. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, J.F.; Morrissey, S.; Dadakis, J.; Hutchinson, A.; Herndon, R. Investigation of groundwater flow variations near a spreading pond with repeat deliberate tracer experiments. Water 2014, 6, 1826–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urióstegui, S.H.; Bibby, R.K.; Esser, B.K.; Clark, J.F. Quantifying groundwater travel time near managed recharge operations using 35S as an intrinsic tracer. J. Hydrol. 2016, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample ID | Collection Date | SO4 (mg/L) | 35SO4 ± 1σ (mBq/L) a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | Field Duplicate | Reported b | |||
| Atlantis MAR | |||||
| Pond 7 | 02-Aug-2010 | 46.3 | 13.7 ± 0.8 | NA | 13.7 ± 0.8 |
| Pond 12 | 04-Aug-2010 | 57.1 | 16.2 ± 0.9 | NA | 16.2 ± 0.9 |
| Split Structure | 04-Aug-2010 | 58.2 | 12.8 ± 0.8 | NA | 12.8 ± 0.8 |
| OCWD MAR (Data from [38]) | |||||
| Kraemer Basin | 20-Mar-2012 | 2.3 | <2.7 c | NA | <2.7 c |
| Kraemer Basin | 05-Jun-2012 | <0.5 | 0.3 ± 0.6 d | 0.5 ± 0.6 d | 0.4 ± 0.4 |
| Kraemer Basin | 10-Dec-2012 | 72.7 | <1.4 c | NA | <1.4 c |
| Kraemer Basin | 05-Feb-2013 | 109 | 17.1 ± 1.7 | 19.4 ± 1.9 | 18.3±1.3 |
| La Jolla Basin | 10-Dec-2012 | 73.4 | ND | 0.3 ± 0.8 | 0.3 ± 0.8 |
| La Jolla Basin | 04-Feb-2013 | 117 | 13.6 ± 1.8 | 16.0 ± 2.0 | 14.8 ± 1.3 |
| La Jolla Basin | 01-Apr-2013 | 215 | 16.0 ± 2.3 | 15.0 ± 2.3 | 15.5 ± 1.6 |
| Precipitation e | 25-Feb-2011 | NA | 19.9 ± 1.1 | 21.4 ± 1.2 | 20.7 ± 0.8 |
| GWRS TF f | 06-Apr-2012 | 1.1 | 0.6 ± 0.1 d | NA | 0.6 ± 0.1 d |
| GWRS MB f | 06-Apr-2012 | 0.6 | 0.7 ± 0.1 d | NA | 0.7 ± 0.1 d |
| Well ID | Sample Date | Well Type a | Distance (m) | [SO4] (mg/L) | 35SO4 ± 1σ b (mBq/L) | Age ± σ c (wk) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G30966 | 01-Aug-2010 | PW | 420 | 34.3 | 15.5 ± 3.8 | −1 ± 4 |
| G33110 | 04-Aug-2010 | MW | 65 | 50.1 | 14.1 ± 0.8 | 1 ± 1 |
| G33135 | 04-Aug-2010 | MW | 140 | 42.4 | 9.6 ± 0.7 | 8 ± 1 |
| W34006 | 04-Aug-2010 | PW | 510 | 52.2 | 9.5 ± 0.8 | 8 ± 2 |
| W34022 | 04-Aug-2010 | PW | 1000 | 28.0 | 9.9 ± 0.8 | 7 ± 1 |
| WP204 | 02-Aug-2010 | MW | 265 | 29.3 | 6.3 ± 0.6 | 16 ± 2 |
| WP216 | 02-Aug-2010 | MW | 190 | 35.7 | 9.6 ± 0.7 | 8 ± 1 |
| WP226 | 02-Aug-2010 | MW | 130 | 38.0 | 5.9 ± 0.7 | 17 ± 2 |
| WP229 | 02-Aug-2010 | MW | 220 | 45.7 | 12.5 ± 0.8 | 3 ± 1 |
| Well ID and Collection Date | Well Type a | Dist. (m) b | [SO4] (mg/L) | 35SO4 ± 1 σ (mBq/L) c | 35SO4 ± 1σ (mBq/L) c | Reported d | Appt. Age Time ± 1 σ (wk) e |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KBS-3/1 | MW | 25 | |||||
| 13-Sep-2012 | 2.3 | 7.3 ± 0.7 f | NA | 7.3 ± 0.7 f | * | ||
| 10-Dec-2012 | 99.5 | ND | NA | ND | >53 g | ||
| 05-Feb-2013 | 112 | 15.9 ± 1.8 | 11.3 ± 1.8 | 13.6 ± 1.3 | 6 ± 2 | ||
| 02-Apr-2013 | 177 | 5.4 ± 1.8 | NA | 5.4 ± 1.8 | 30 ± 6 | ||
| AM-7/1 | MW | 350 | |||||
| 21-Mar-2012 | 6.4 | 4.2 ± 0.6 | NA | 4.2 ± 0.6 | * | ||
| 22-May-2012 | 3.1 | 2.0 ± 0.2 f | 2.2 ± 0.6 | 2.1 ± 0.3 | * | ||
| 25-Sep-2012 | 4.3 | 2.5 ± 0.3 | 2.3 ± 0.3 | 2.4 ± 0.2 | * | ||
| 19-Nov-2012 | 2.4 | 1.4 ± 0.2 f | 1.6 ± 0.2 f | 1.5 ± 0.1 | * | ||
| 27-Feb-2013 | 17.3 | 4.5 ± 0.4 | 3.4 ± 0.5 | 4.0 ± 0.3 | * | ||
| 16-Apr-2013 | 46.3 | 3.1 ± 0.4 | 2.4 ± 0.5 | 2.8 ± 0.3 | 20 ± 2 | ||
| 11-Jun-2013 | 53 | 1.7 ± 1.4 | 1.5 ± 1.4 | 1.6 ± 1.0 | 23 ± 13 | ||
| AM-8/1 | MW | 1220 | |||||
| 22-May-2012 | 58.9 | 1.7 ± 0.6 | 1.0 ± 0.6 | 1.4 ± 0.4 | 36 ± 5 | ||
| 13-Sep-2012 | 34.2 | 7.0 ± 0.7 | NA | 7.0 ± 0.7 | * | ||
| 19-Nov-2012 | 26.1 | ND | ND | ND | >36 g | ||
| 27-Feb-2013 | 15.7 | 3.0 ± 0.4 | 2.8 ± 0.3 | 2.9 ± 0.3 | 4 ± 2 | ||
| 16-Apr-2013 | 20.7 | 2.4 ± 0.3 | 2.1 ± 0.3 | 2.3 ± 0.2 | 15 ± 2 | ||
| 11-Jun-2013 | 21 | 2.6 ± 0.8 | 2.5 ± 0.8 | 2.6 ± 0.6 | 7 ± 4 | ||
| AM-48/1 | MW | 1200 | |||||
| 21-Mar-2012 | 86.3 | ND | NA | ND | >26 g | ||
| 03-Oct-2012 | 36.8 | ND | ND | ND | >31 g | ||
| 05-Feb-2013 | 25.2 | 3.9 ± 0.5 | 4.2 ± 0.6 | 4.1 ± 0.4 | 4 ± 2 | ||
| 04-Apr-2013 | 44.3 | 2.7 ± 0.4 | 4.3 ± 0.6 | 3.5 ± 0.4 | 13 ± 4 | ||
| AMD-12/1 | MW | 470 | |||||
| 21-Mar-2012 | 36.7 | ND | ND | ND | >24 g | ||
| 22-May-2012 | 51.4 | 2.6 ± 0.6 | NA | 2.6 ± 0.6 | 19 ± 4 | ||
| 19-Nov-2012 | 52.5 | ND | ND | ND | >37 f | ||
| 05-Feb-2013 | 17.9 | 2.9 ± 0.3 | 3.8 ± 0.5 | 3.4 ± 0.3 | 1 ± 2 | ||
| 16-Apr-2013 | 9.1 | 1.7 ± 0.2 | 2.6 ± 0.3 | 2.2 ± 0.2 | 0 ± 2 | ||
| 11-Jun-2013 | 4 | 1.6 ± 0.5 | 1.9 ± 0.6 | 1.8 ± 0.4 | * | ||
| AMD-12/2 | MW | 500 | |||||
| 21-Mar-2012 | 74 | 2.5 ± 2.1 | 1.2 ± 1.6 | 1.9 ± 1.3 | 34 ± 15 | ||
| 26-Feb-2013 | 136 | 4.8 ± 1.6 | 10.3 ± 1.8 | 7.6 ± 1.2 | 20 ± 3 | ||
| 16-Apr-2013 | 142 | ND | NA | ND | >41 g | ||
| 11-Jun-2013 | 108 | 3.2 ± 2.7 | 10.1 ± 3.2 | 6.7 ± 2.1 | 18 ± 6 | ||
| PW1 | PW | 1650 | |||||
| 04-Jun-2012 | 83.7 | ND | NA | ND | >35 g | ||
| 10-Dec-2012 | 29.9 | ND | ND | ND | >38 g | ||
| 04-Feb-2013 | 27.8 | 4.3 ± 0.5 | 4.4 ± 0.6 | 4.4 ± 0.4 | 4 ± 2 | ||
| 03-Jun-2013 | 26 | 2.7 ± 0.9 | NA | 2.7 ± 0.9 | 11 ± 4 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Clark, J.F.; Urióstegui, S.H.; Bibby, R.K.; Esser, B.K.; Tredoux, G. Quantifying Apparent Groundwater Ages near Managed Aquifer Recharge Operations Using Radio-Sulfur (35S) as an Intrinsic Tracer. Water 2016, 8, 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8110474
Clark JF, Urióstegui SH, Bibby RK, Esser BK, Tredoux G. Quantifying Apparent Groundwater Ages near Managed Aquifer Recharge Operations Using Radio-Sulfur (35S) as an Intrinsic Tracer. Water. 2016; 8(11):474. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8110474
Chicago/Turabian StyleClark, Jordan F., Stephanie H. Urióstegui, Richard K. Bibby, Bradley K. Esser, and Gideon Tredoux. 2016. "Quantifying Apparent Groundwater Ages near Managed Aquifer Recharge Operations Using Radio-Sulfur (35S) as an Intrinsic Tracer" Water 8, no. 11: 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8110474
APA StyleClark, J. F., Urióstegui, S. H., Bibby, R. K., Esser, B. K., & Tredoux, G. (2016). Quantifying Apparent Groundwater Ages near Managed Aquifer Recharge Operations Using Radio-Sulfur (35S) as an Intrinsic Tracer. Water, 8(11), 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8110474








