Evaluating the Effects of Mulch and Irrigation Amount on Soil Water Distribution and Root Zone Water Balance Using HYDRUS-2D
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Experiment
2.1.1. Location
2.1.2. Design of Field Experiment
| Treatment Code | Total Irrigation Amount (m3) | Irrigation Times | Irrigation Interval (Day) | Amount of Each Irrigation (m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment (T1) | 166.5 | 10 | 7 | 16.65 |
| Treatment (T2) | 140.4 | 10 | 7 | 14.04 |
| Treatment (T3) | 115.4 | 10 | 7 | 11.54 |
| Treatment (T4) | 10.23 | 10 | 7 | 10.23 |
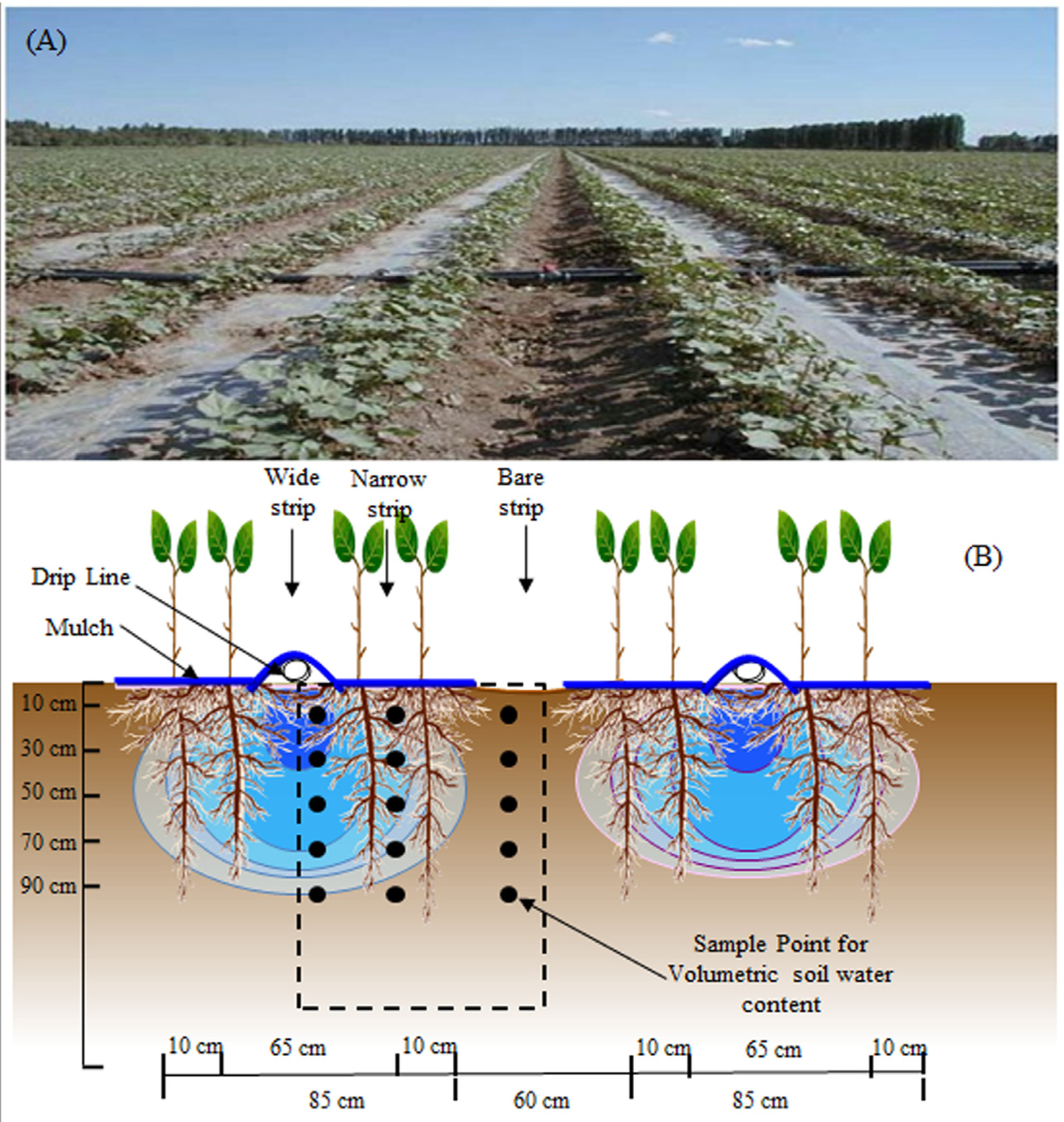
2.1.3. Measurement of Soil Physical Properties and Soil Moisture
| Depth | Bulk Density (g/cm3) | θr (cm3·cm−3) | θs (cm3·cm−3) | α | n | Ks (cm3/day) | l |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–10 | 1.52 | 0.040 | 0.453 | 0.012 | 2.00 | 27.3 | 0.5 |
| 10–20 | 1.58 | 0.040 | 0.483 | 0.011 | 1.70 | 12.5 | 0.5 |
| 20–30 | 1.59 | 0.040 | 0.482 | 0.010 | 1.50 | 8.90 | 0.5 |
| 30–40 | 1.58 | 0.039 | 0.453 | 0.004 | 1.80 | 11.4 | 0.5 |
| 40–60 | 1.56 | 0.039 | 0.482 | 0.009 | 1.37 | 9.30 | 0.5 |
| 60–80 | 1.56 | 0.039 | 0.474 | 0.005 | 1.35 | 4.70 | 0.5 |
| 80–100 | 1.54 | 0.043 | 0.486 | 0.006 | 1.35 | 4.50 | 0.5 |
| Depth (cm) | Soil Particle Size Distribution (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| <0.002 mm | 0.002–0.02 mm | >0.02 mm | |
| 0–10 | 5 | 46 | 49 |
| 10–20 | 5 | 48 | 47 |
| 20–30 | 5 | 49 | 46 |
| 30–40 | 11 | 74 | 15 |
| 40–60 | 16 | 80 | 4 |
| 60–80 | 6 | 48 | 46 |
| 80–100 | 4 | 39 | 57 |
2.1.4. Measurement of Leaf Area Index (LAI), Plant Height, and Root Length Density
2.2. Numerical Modeling
2.2.1. Water Flow Equations
2.2.2. Domain and Boundary Conditions
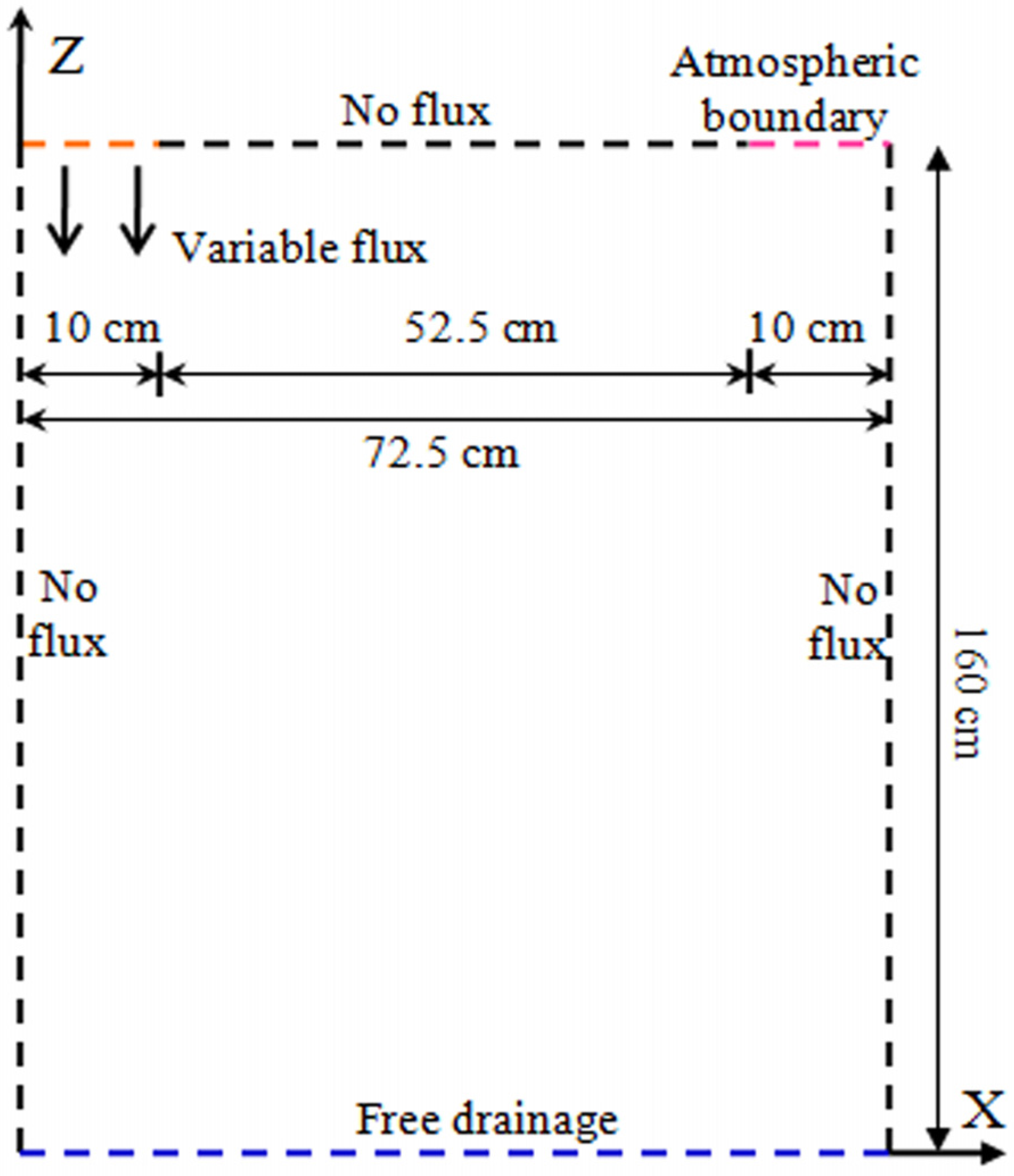
2.2.3. Initial Condition, and Temporal and Spatial Discretization
2.2.4. Estimating Evaporation and Transpiration

2.2.5. Root Water Uptake
| Zm (cm) | z* (cm) | Pz | Xm (cm) | x* (cm) | Px |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 70 | 45.22 | 0.107 | 67.5 | 37.63 | 2.89 |
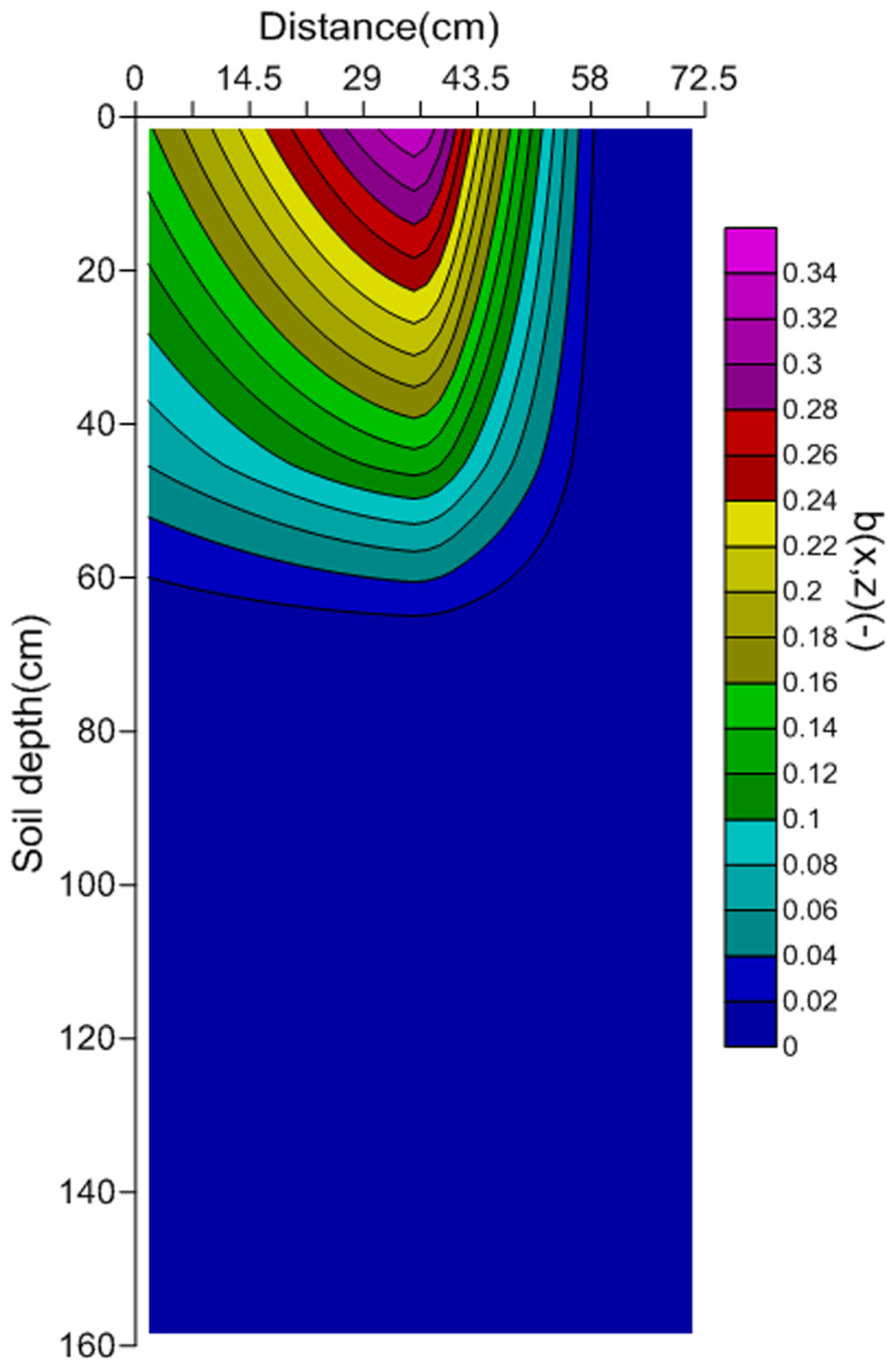
2.2.6. Variable Flux Boundary
2.2.7. Input Parameters
2.3. Effect of Mulch
2.4. Criteria of Model Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Model Evaluation
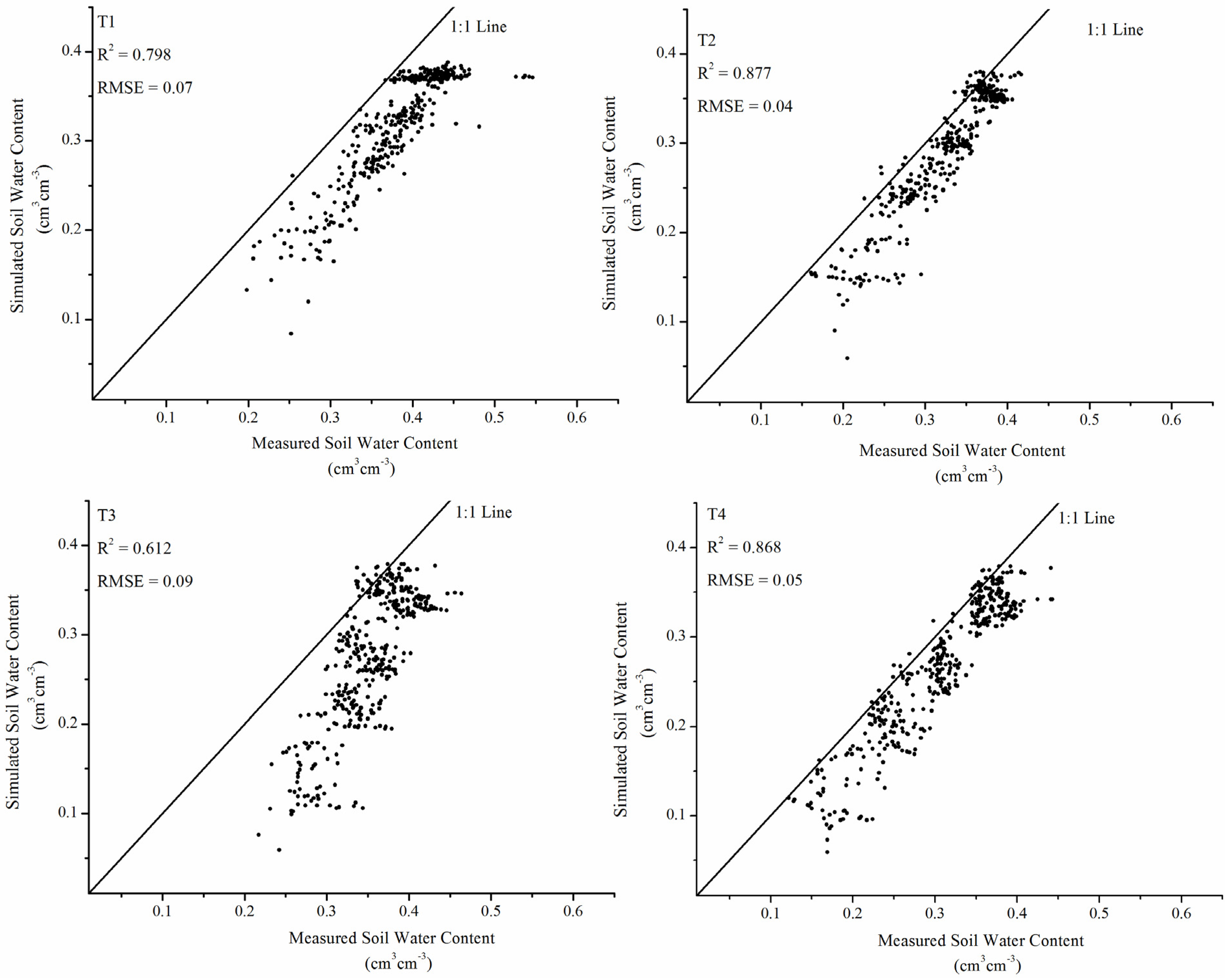
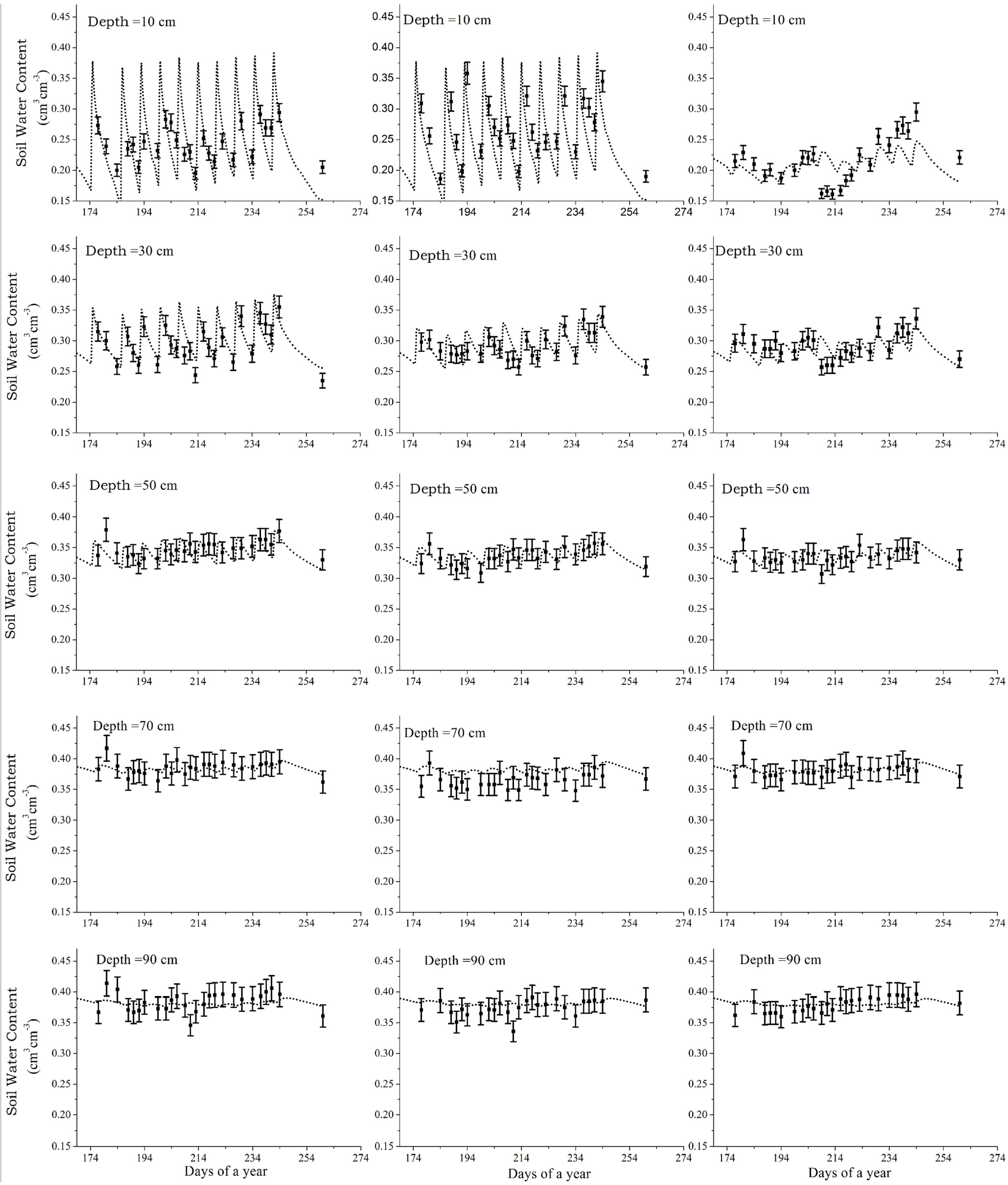
3.2. Comparison of Water Distribution Patterns among Treatments
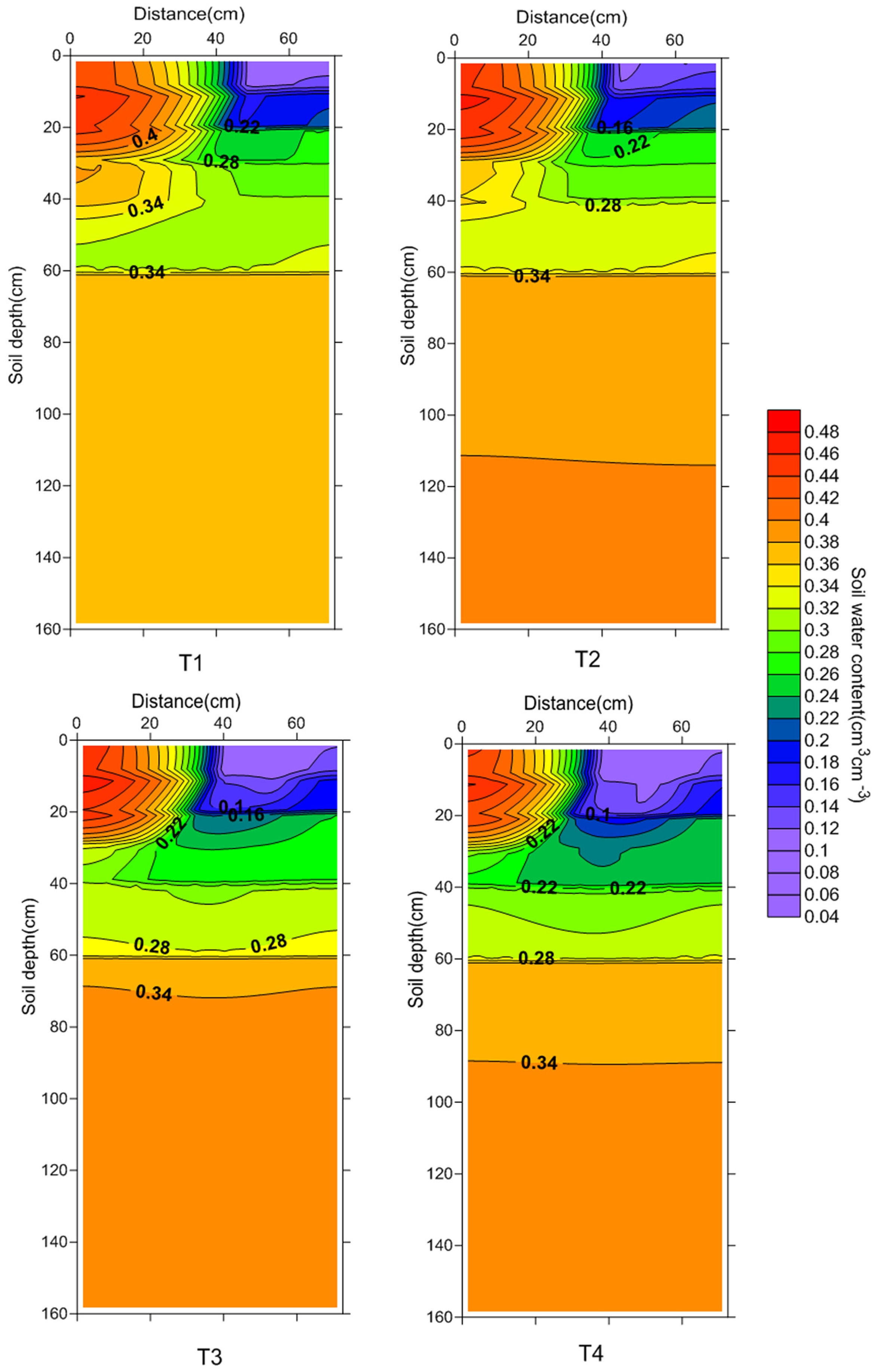
3.3. Comparison of Water Balance Components among Treatments
| Water Balance Component | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Root water uptake (mm) | 439.7 | 429.2 | 404.4 | 385.7 |
| Evaporation (mm) | 7.5 | 3.4 | 1.8 | 1.7 |
| Drainage (mm) | 14.9 | −13.6 | −31.9 | −38.1 |
| Storage Change (mm) | −30.6 | −53.5 | −79.6 | −81.7 |
| Irrigation (mm) | 426.5 | 359.7 | 294.7 | 261.9 |
3.4. Effect of Mulch on Soil Water Fluctuation Patterns
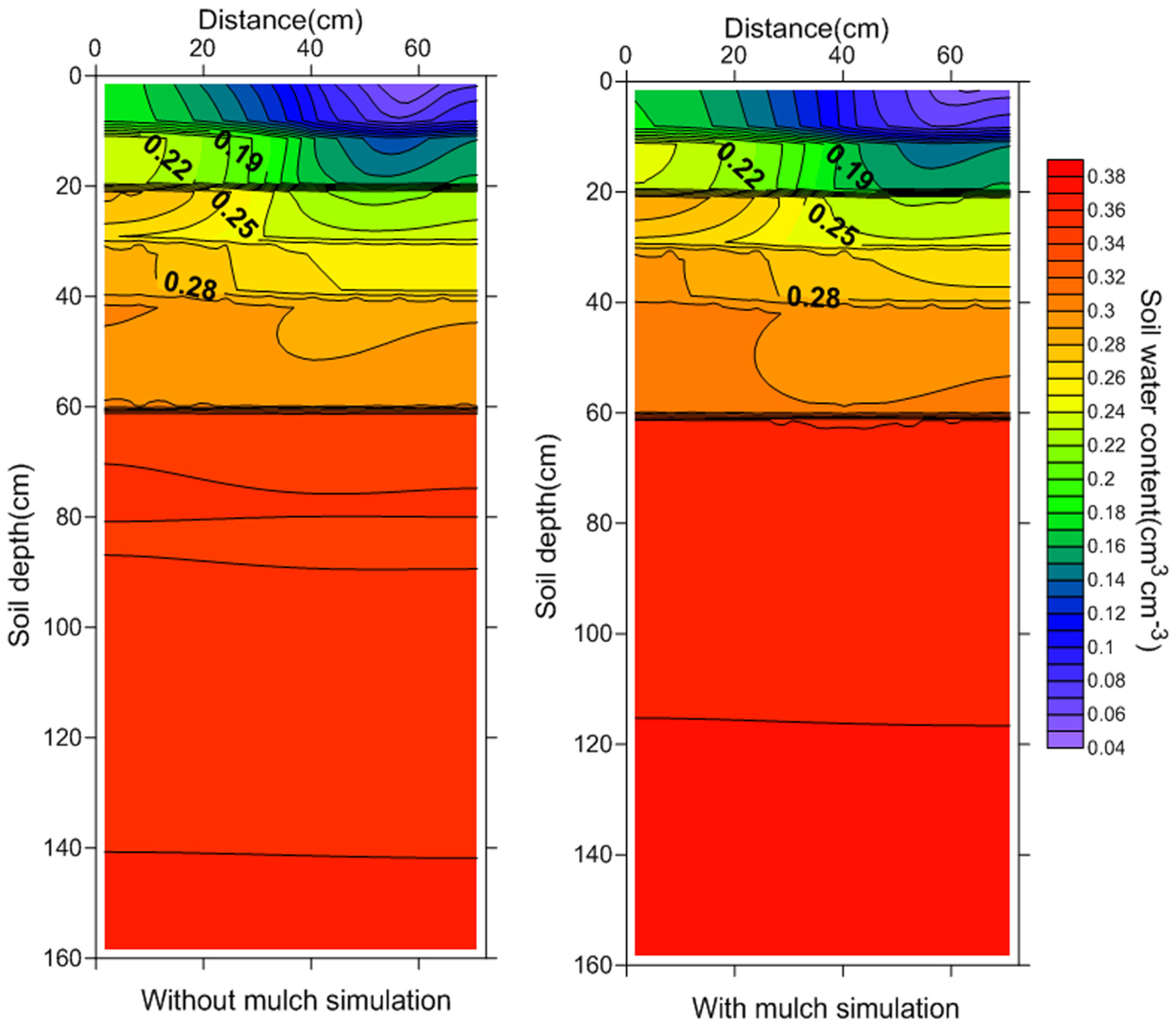
3.5. Effect of Mulch on Water Balance Components
| Water Balance Component | SWM | SM |
|---|---|---|
| Root water uptake (mm) | 418.0 | 429.2 |
| Evaporation (mm) | 25.1 | 3.4 |
| Drainage (mm) | −18.3 | −13.6 |
| Storage change (mm) | −57.8 | −53.5 |
| Irrigation (mm) | 359.7 | 359.7 |
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hou, Z.; Chen, W.; Li, X.; Xiu, L.; Wu, L. Effects of salinity and fertigation practice on cotton yield and 15n recovery. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 1483–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayars, J.; Phene, C.; Hutmacher, R.; Davis, K.; Schoneman, R.; Vail, S.; Mead, R. Subsurface drip irrigation of row crops: A review of 15 years of research at the water management research laboratory. Agric. Water Manag. 1999, 42, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlberg, L.; Penning de Vries, F.W.T. Exploring potentials and constraints of low-cost drip irrigation with saline water in sub-saharan africa. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2004, 29, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfving, D. Crop response to trickle irrigation. Hortic. Rev. 1982, 4, 1–48. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, X.; Zhang, J.; Liy, Z.; Li, M.; Yang, G.; Sun, J. Effects of different water treatments on yield and water use efficiency of cotton with drip irrigation under film mulch. Agric. Res. Arid Areas 2012, 30, 118–124. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.T.; Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Meng, X.B.; Chen, F.H. Effects of soil water content on cotton root growth and distribution under mulched drip irrigation. Agric. Sci. China 2009, 8, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, Y.; Hu, S.; Li, Y. Effects of spatial variability on estimation of evapotranspiration in the continental river basin. J. Arid Environ. 2004, 56, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.X.; Zhao, C.Y.; Chuan, Z.Q.; Sheng, Y.; Lin, Q.H. Root distribution characteristics of cotton in different drip irrigation amounts irrigation under mulched. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2007, 21, 96–100. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.Y.; Zhao, C.Y.; Sheng, Y.; Li, J.Y.; Peng, D.M.; Li, Z.L.; Feng, S.L. Effects of drip irrigation under mulching on cotton root and shoot biomass and yield. J. Appl. Ecol. 2009, 20, 970–976. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.; Yan, Y.; Yimamu, Y.; Li, J.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, L. Effects of soil moisture on cotton root length density and yield under drip irrigation with plastic mulch in aksu oasis farmland. J. Arid Land 2010, 2, 243–249. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.Y.; Yan, Y.Y. Distributed characteristics of soil water-salt of cotton field under drip irrigation under mulching in tarim irrigated area. Arid Land Geogr. 2009, 32, 892–898. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.Y.; Wang, Y.C.; Li, Z.L.; Li, G.Z. Study on the spatial variability of soil moisture content and salt content in the field scale. Arid Zone Res. 2003, 20, 252–256. [Google Scholar]
- Zai, S.M.; Wu, F.; Wen, J.; Han, Q.B. Effect of drip fertigation on soil salinity of cotton field in northwest china. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2011, 42, 1496–1503. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.S.; Lei, X.Y.; Chen, D.C.; Zhou, S.J.; Liu, H.X.; Pan, T. Spatial variability of soil moisture on cotton field under mulched drip irrigation. J. Irrig. Drain. 2010, 28, 10–16. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Yang, J.; Li, X.; Yu, M.; Wang, J. Effects of irrigation water quality and drip tape arrangement on soil salinity, soil moisture distribution, and cotton yield (Gossypium hirsutum L.) under mulched drip irrigation in Xinjiang, China. J. Integr. Agric. 2012, 11, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Ren, J.; Xue, C.; Lin, E. Study on the relationship between soil selenium and plant selenium uptake. Plant Soil 2005, 277, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, Y.; Song, Y.; Li, B. Biological drainage characteristics of alakalized desert soils in north-western china. J. Arid Environ. 2004, 56, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zuo, H.; Xiao, X.; Wang, S.; Chen, B.; Chen, J. Modelling the effects of plastic mulch on water, heat and CO2 fluxes over cropland in an arid region. J. Hydrol. 2012, 452, 102–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Hu, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, J. Effect of plastic mulch and winter catch crop on water availability and vegetable yield in a rain-fed vegetable cropping system at mid-yunnan plateau, china. Sci. Hortic. 2013, 164, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatfield, J.L.; Sauer, T.J.; Prueger, J.H. Managing soils to achieve greater water use efficiency. Agron. J. 2001, 93, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Tian, X.; Li, S. Effects of plastic sheet-mulching on ridge for rainwater-harvesting cultivation on wue and yield of winter wheat. Zhongguo Nongye Kexue 2003, 37, 208–214. [Google Scholar]
- Philip, J. Steady infiltration from buried point sources and spherical cavities. Water Resour. Res. 1968, 4, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrick, A. Time-dependent linearized infiltration. I. Point sources. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1974, 38, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartzman, M.; Zur, B. Emitter spacing and geometry of wetted soil volume. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 1986, 112, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelakis, A.N.; Rolston, D.E.; Kadir, T.N.; Scott, V.H. Soil-water distribution under trickle source. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 1993, 119, 484–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, S.T. Green-ampt analysis of wetting patterns for surface emitters. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 1994, 120, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncef, H.; Hedi, D.; Jelloul, B.; Mohamed, M. Approach for predicting the wetting front depth beneath a surface point source: Theory and numerical aspect. Irrig. Drain. 2002, 51, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, F.J.; Thorburn, P.J.; Fitch, P.; Bristow, K.L. Wetup: A software tool to display approximate wetting patterns from drippers. Irrig. Sci. 2003, 22, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandelous, M.M.; Šimůnek, J. Numerical simulations of water movement in a subsurface drip irrigation system under field and laboratory conditions using hydrus-2d. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 1070–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandelous, M.M.; Šimůnek, J.; van Genuchten, M.T.; Malek, K. Soil water content distributions between two emitters of a subsurface drip irrigation system. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2011, 75, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajdary, K.; Singh, D.K.; Singh, A.K.; Khanna, M. Modelling of nitrogen leaching from experimental onion field under drip fertigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 89, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, T.L.; White, S.A.; Warrick, A.W.; Thompson, T.L. Tape depth and germination method influence patterns of salt accumulation with subsurface drip irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2008, 95, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravikumar, V.; Vijayakumar, G.; Šimůnek, J.; Chellamuthu, S.; Santhi, R.; Appavu, K. Evaluation of fertigation scheduling for sugarcane using a vadose zone flow and transport model. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 98, 1431–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beggs, R.A.; Hills, D.J.; Tchobanoglous, G.; Hopmans, J.W. Fate of nitrogen for subsurface drip dispersal of effluent from small wastewater systems. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2011, 126, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanson, B.R.; Šimůnek, J.; Hopmans, J.W. Evaluation of urea-ammonium-nitrate fertigation with drip irrigation using numerical modeling. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 86, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmaloglou, S.; Diamantopoulos, E. Simulation of soil water dynamics under subsurface drip irrigation from line sources. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 1587–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandelous, M.M.; Kamai, T.; Vrugt, J.A.; Šimůnek, J.; Hanson, B.; Hopmans, J.W. Evaluation of subsurface drip irrigation design and management parameters for alfalfa. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 109, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.; Rajput, T.B.S. Dynamics and modeling of soil water under subsurface drip irrigated onion. Agric. Water Manag. 2008, 95, 1335–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaggs, T.; Trout, T.; Šimunek, J.; Shouse, P. Comparison of hydrus-2d simulations of drip irrigation with experimental observations. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2004, 130, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provenzano, G. Using hydrus-2d simulation model to evaluate wetted soil volume in subsurface drip irrigation systems. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2007, 133, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, L.A. Capillary conduction of liquids through porous mediums. Physics 1931, 1, 318–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Genuchten, M.T. A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1980, 44, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimůnek, J.; van Genuchten, M.T.; Šejna, M. The Hydrus Software Package for Simulating Two- and Three-Dimensional Movement of Water, Heat, and Multiple Solutes in Variably-Saturated Media; PC Progress: Prague, Czech Republic, 2006; p. 241. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Smith, M.; Raes, D.; Wright, J.L. Fao-56 dual crop coefficient method for estimating evaporation from soil and application extensions. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2005, 131, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feddes, R.A.; Kowalik, P.J.; Zaradny, H. Simulation of Field Water Use and Crop Yield; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Vrugt, J.; Hopmans, J.; Šimunek, J. Calibration of a two-dimensional root water uptake model. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2001, 65, 1027–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmott, C.J. Some comments on the evaluation of model performance. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1982, 63, 1309–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, M.; Zhao, C.; Feng, G.; Yan, Y.; Sheng, Y. Evaluating the Effects of Mulch and Irrigation Amount on Soil Water Distribution and Root Zone Water Balance Using HYDRUS-2D. Water 2015, 7, 2622-2640. https://doi.org/10.3390/w7062622
Han M, Zhao C, Feng G, Yan Y, Sheng Y. Evaluating the Effects of Mulch and Irrigation Amount on Soil Water Distribution and Root Zone Water Balance Using HYDRUS-2D. Water. 2015; 7(6):2622-2640. https://doi.org/10.3390/w7062622
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Ming, Chengyi Zhao, Gary Feng, Yingyu Yan, and Yu Sheng. 2015. "Evaluating the Effects of Mulch and Irrigation Amount on Soil Water Distribution and Root Zone Water Balance Using HYDRUS-2D" Water 7, no. 6: 2622-2640. https://doi.org/10.3390/w7062622
APA StyleHan, M., Zhao, C., Feng, G., Yan, Y., & Sheng, Y. (2015). Evaluating the Effects of Mulch and Irrigation Amount on Soil Water Distribution and Root Zone Water Balance Using HYDRUS-2D. Water, 7(6), 2622-2640. https://doi.org/10.3390/w7062622





