Using Salinity, Water Level, CFCs, and CCl4 to Assess Groundwater Flow Dynamics and Potential N2O Flux in the Intertidal Zone of Sanya, Hainan Province: Implications for Evaluating Freshwater Submarine Groundwater Discharge in Coastal Unconfined Aquifers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
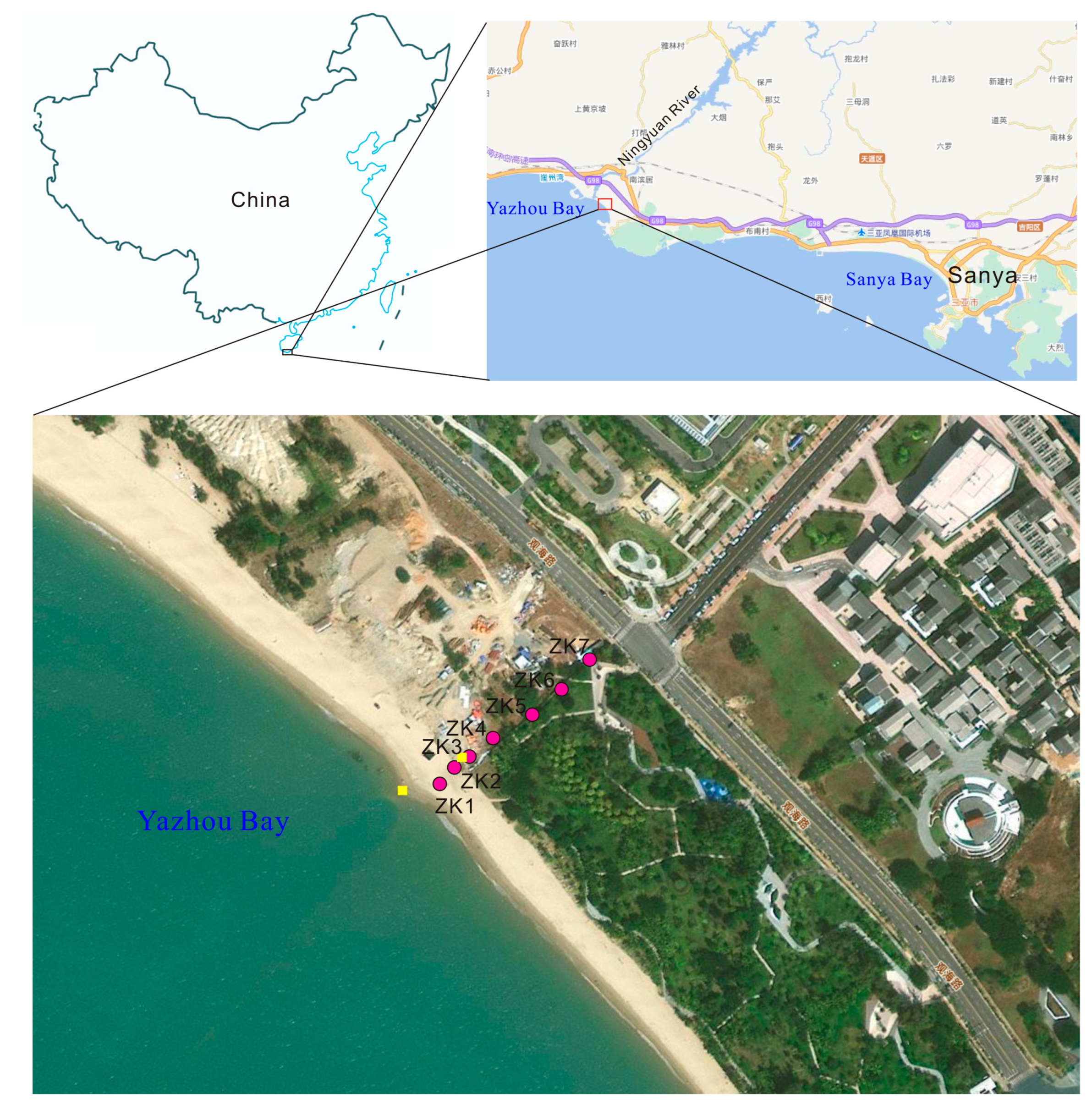
2.1. Site Description
- Geological Background of Yazhou District, Sanya
- 2.
- Hydrogeological Background of Yazhou District
2.2. Drilling Shallow Wells and On-Site Testing
2.3. Sampling and Measurement
2.4. Calculation of the Flux of Groundwater in the Shallow Aquifer
3. Results
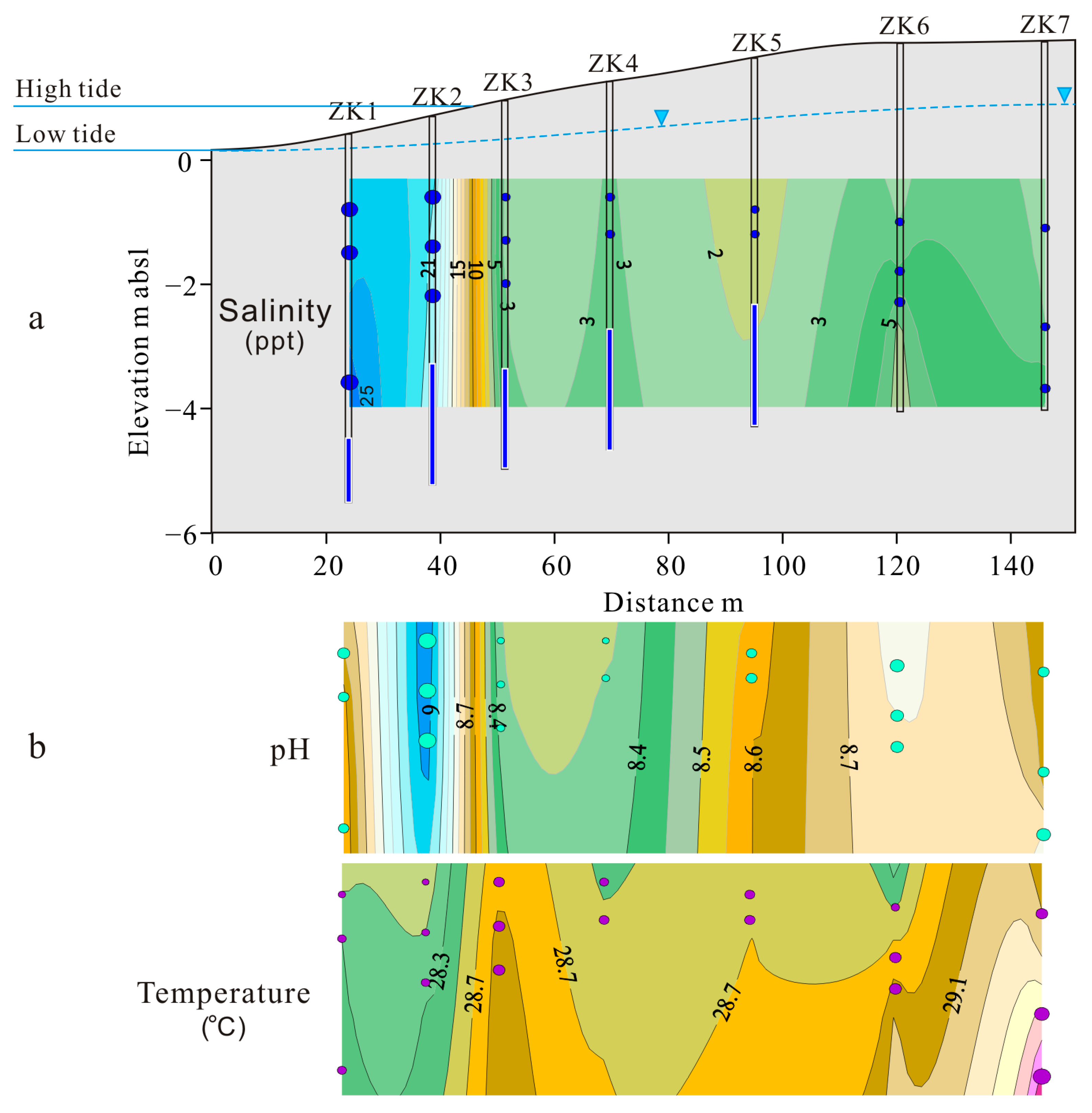
3.1. Variation in Salinity, pH and Temperature of Groundwater
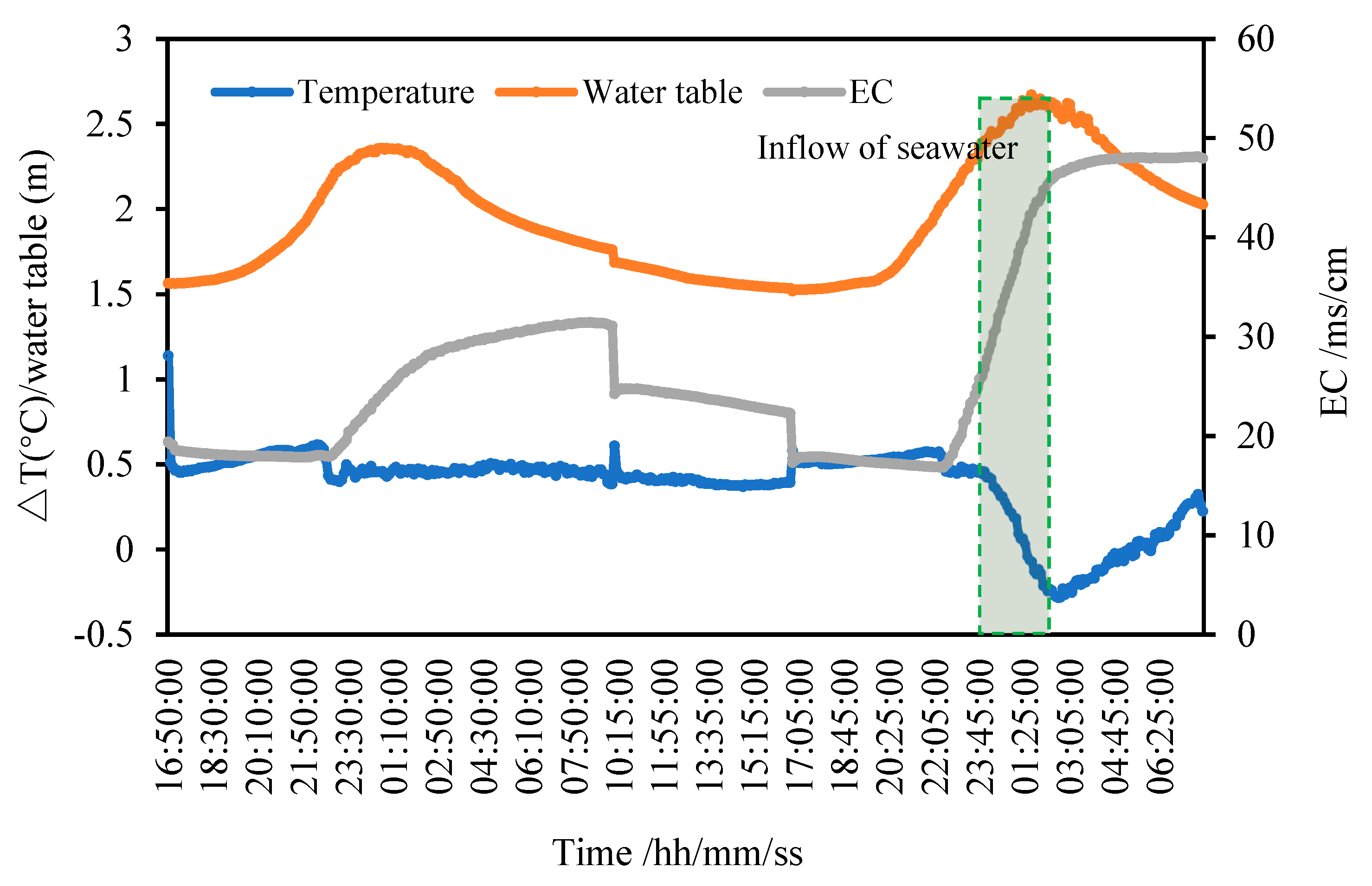
3.2. Groundwater Logging Data
3.3. Variation in Groundwater N2O
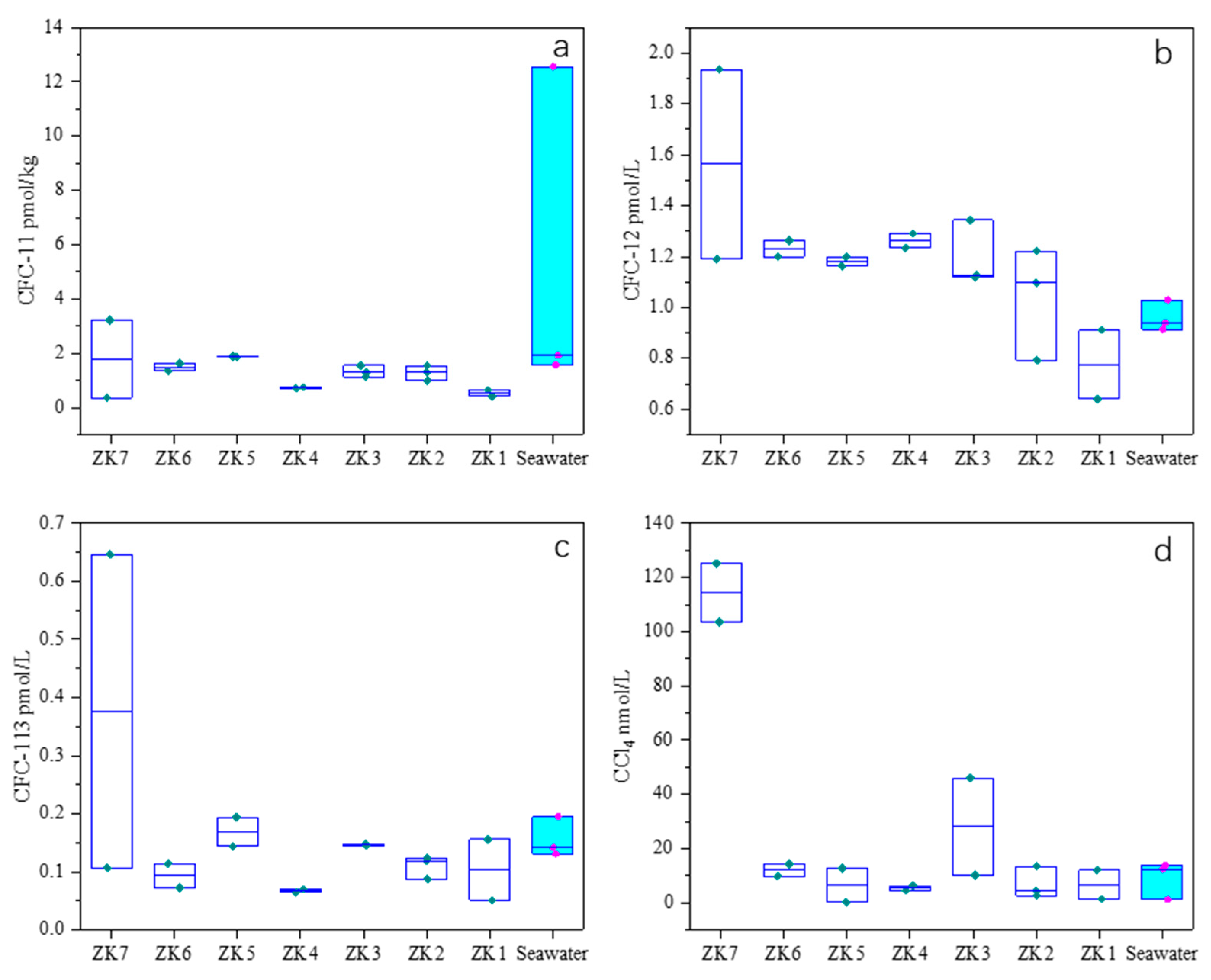
3.4. Concentrations of CFC-11, CFC-12, CFC-113, and CCl4 in Groundwater
3.4.1. CFC-11 Distribution (Figure 6a)
3.4.2. CFC-12 Distribution (Figure 6b)
3.4.3. CFC-113 and CCl4 Distribution (Figure 6c,d)
3.4.4. Boundary Identification
- Hydraulic Connectivity
- 2.
- Boundary Between Flow Systems
4. Discussion
4.1. Groundwater Flux in the Intertidal Zone
4.2. Potential N2O Flux During Groundwater Discharge in the Intertidal Zone
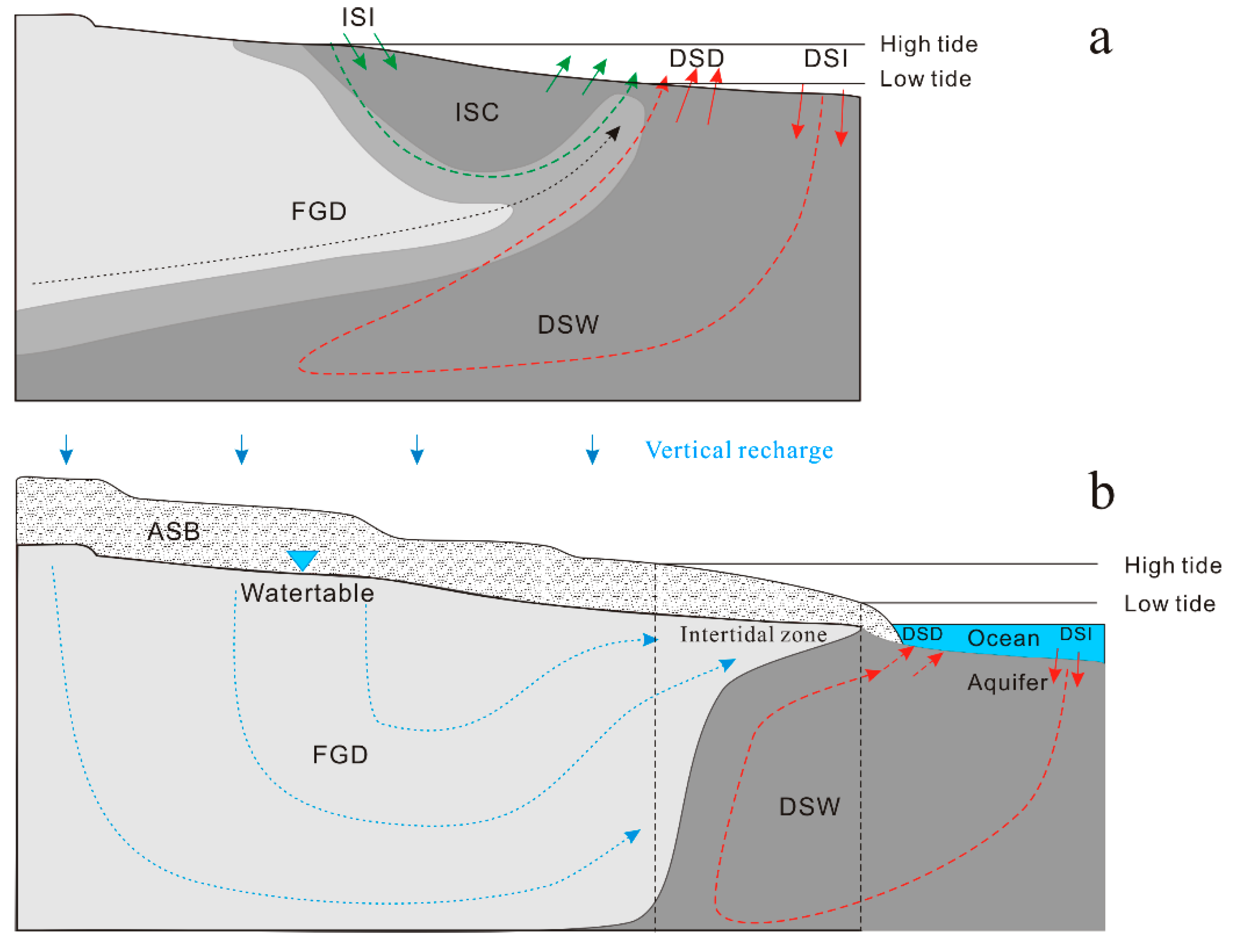
4.3. Model of Submarine Groundwater Discharge of Coastal Unconfined Aquifer
4.3.1. Dynamics of Coastal Groundwater Discharge and Controlling Factors
4.3.2. Construction of New Conceptual Model in the Intertidal Zone
- Kinetic Boundary Conditions in Intertidal Coastal Aquifers
- 2.
- The development of the upper saline plume (USP)
- 3.
- Impact of Beach Elevation and Slope on Flow Dynamics
- 4.
- Freshwater Wedge as a Direct Fast Pathway for Nutrient Transport
- 5.
- The Saltwater Wedge Mixing Zone
- 6.
- Implication for understanding seawater intrusion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Michael, H.A.; Post, V.E.A.; Wilson, A.M.; Werner, A.D. Science, society, and the coastal groundwater squeeze. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 2610–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, A.D.; Bakker, M.; Post, V.E.A.; Vandenbohede, A.; Lu, C.; Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Simmons, C.T.; Barry, D.A. Seawater intrusion processes, investigation and management: Recent advances and future challenges. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 51, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, R.H.; Erler, D.V.; Eyre, B.D. Nitrous oxide fluxes in estuarine environments: Response to global change. Glob. Change Biol. 2015, 21, 3219–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurado, A.; Borges, A.V.; Brouyère, S. Dynamics and emissions of N2O in groundwater: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584–585, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, W.C.; Bokuniewicz, H.; Huettel, M.; Moore, W.S.; Taniguchi, M. Groundwater and pore water inputs to the coastal zone. Biogeochemistry 2003, 66, 3–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, W.S.; Sarmiento, J.L.; Key, R.M. Submarine groundwater discharge revealed by 228Ra distribution in the upper Atlantic Ocean. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 309–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcallister, S.M.; Barnett, J.M.; Heiss, J.W.; Findlay, A.J.; Macdonald, D.J.; Dow, C.L.; Luther, G.W.; Michael, H.A.; Chan, C.S. Dynamic hydrologic and biogeochemical processes drive microbially enhanced iron and sulfur cycling within the intertidal mixing zone of a beach aquifer: Fe and S cycling in a beach aquifer. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2015, 60, 329–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, C.E.; Xin, P.; Santos, I.R.; Charette, M.A.; Li, L.; Barry, D.A. Groundwater dynamics in subterranean estuaries of coastal unconfined aquifers: Controls on submarine groundwater discharge and chemical inputs to the ocean. Adv. Water Resour. 2018, 115, 315–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, B.B. Nitrification and denitrification: Probing the nitrogen cycle in aquatic environments. Microb. Ecol. 1996, 32, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codispoti, L.A.; Brandes, J.; Christensen, J.P.; Devol, A.; Naqvi, S.W.A.; Paerl, H.; Yoshinari, T. The Oceanic Fixed Nitrogen and Nitrous Oxide Budgets: Moving Targets as We Enter the Anthropocene? Sci. Mar. 2001, 65, 85–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myrhe, G.; Shindell, D.; Breon, F.M.; Collins, W.; Al, E. Anthropogenic and natural radiative forcing. In Climate Change 2013 the Physical Science Basis: Working Group I Contribution to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Chapter 8: Anthropogenic and Natural Radiative Forcing; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013; pp. 659–740. [Google Scholar]
- Prieto, C.; Destouni, G. Is submarine groundwater discharge predictable? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L01402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.R. A device for measuring seepage flux in lakes and estuaries. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1977, 22, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, W.S. The subterranean estuary: A reaction zone of ground water and sea water. Mar. Chem. 1999, 65, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlüter, M.; Sauter, E.J.; Andersen, C.E.; Dahlgaard, H.; Dando, P.R. Spatial Distribution and Budget for Submarine Groundwater Discharge in Eckernförde Bay (Western Baltic Sea). Limnol. Oceanogr. 2004, 49, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi Janetti, E.; Dror, I.; Riva, M.; Guadagnini, A.; Sanchez-Vila, X.; Berkowitz, B. Mobility and Interaction of Heavy Metals in a Natural Soil. Transp. Porous Media 2013, 97, 295–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabulut, S.; Cengiz, M.; Balkaya, Ç.; Aysal, N. Spatio-Temporal Variation of Seawater Intrusion (SWI) inferred from geophysical methods as an ecological indicator; A case study from Dikili, NW İzmir, Turkey. J. Appl. Geophys. 2021, 189, 104318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, W.C.; Dulaiova, H. Estimating the dynamics of groundwater input into the coastal zone via continuous radon-222 measurements. J. Environ. Radioact. 2003, 69, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, M. Tidal effects on submarine groundwater discharge into the ocean. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 2-1–2-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slomp, C.P.; Van Cappellen, P. Nutrient inputs to the coastal ocean through submarine groundwater discharge: Controls and potential impact. J. Hydrol. 2004, 295, 64–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroeger, K.D.; Swarzenski, P.W.; Greenwood, W.J.; Reich, C. Submarine groundwater discharge to Tampa Bay: Nutrient fluxes and biogeochemistry of the coastal aquifer. Mar. Chem. 2007, 104, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Meteorological Organization (WMO). Scientific Assessment of Ozone Depletion: 2022, GAW Report No. 278. 509; World Meteorological Organization (WMO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Huang, J.; Hu, X.; Zhang, L.; Ma, M.; Hu, L.; Chen, D.; Du, Q.; Sun, Y.; Cai, Z.; et al. CCl4 emissions in eastern China during 2021–2022 and exploration of potential new sources. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigby, M.; Park, S.; Saito, T.; Western, L.M.; Redington, A.L.; Fang, X.; Henne, S.; Manning, A.J.; Prinn, R.G.; Dutton, G.S.; et al. Increase in CFC-11 emissions from eastern China based on atmospheric observations. Nature 2019, 569, 546–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benish, S.E.; Salawitch, R.J.; Ren, X.; He, H.; Dickerson, R.R. Airborne Observations of CFCs Over Hebei Province, China in Spring 2016. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2021JD035152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darling, W.G.; Gooddy, D.C.; MacDonald, A.M.; Morris, B.L. The practicalities of using CFCs and SF6 for groundwater dating and tracing. Appl. Geochem. 2012, 27, 1688–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, L.A.; Gooddy, D.C.; Binley, A.M. Use and application of CFC-11, CFC-12, CFC-113 and SF6 as environmental tracers of groundwater residence time: A review. Geosci. Front. 2018, 10, 1643–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darling, W.G.; Gooddy, D.C.; Riches, J.; Wallis, I. Using environmental tracers to assess the extent of river–groundwater interaction in a quarried area of the English Chalk. Appl. Geochem. 2010, 25, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.F.; Yu, S.W.; Fu, Y.L.; Wang, X.L.; Wu, D.Y.; Fu, G.J. Demonstration on Emergency Groundwater Field in Hongtang Bay, Sanya City of Hainan Province. S. China Geol. 2021, 37, 330–338. [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi, M.; Ishitobi, T.; Shimada, J. Dynamics of submarine groundwater discharge and freshwater-seawater interface. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2006, 111, C01008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Boufadel, M.C.; Weaver, J.W. Tide-induced seawater–groundwater circulation in shallow beach aquifers. J. Hydrol. 2008, 352, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, C.; Gibbes, B.; Carey, H.; Li, L. Salt-freshwater dynamics in a subterranean estuary over a spring-neap tidal cycle. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2007, 112, C09007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pool, M.; Post, V.E.A.; Simmons, C.T. Effects of tidal fluctuations on mixing and spreading in coastal aquifers: Homogeneous case. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 6910–6926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charette, M.A.; Sholkovitz, E.R. Oxidative precipitation of groundwater-derived ferrous iron in the subterranean estuary of a coastal bay. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 85-81–85-84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charbonnier, C.; Anschutz, P.; Poirier, D.; Bujan, S.; Lecroart, P. Aerobic respiration in a high-energy sandy beach. Mar. Chem. 2013, 155, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, I.R.; Eyre, B.D.; Huettel, M. The driving forces of porewater and groundwater flow in permeable coastal sediments: A review. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 98, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itugha, O.D.; Chen, D.; Guo, Y. Pollutant advective spreading in beach sand exposed to high-energy tides. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 181, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abarca, E.; Karam, H.; Hemond, H.F.; Harvey, C.F. Transient groundwater dynamics in a coastal aquifer: The effects of tides, the lunar cycle, and the beach profile. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 2473–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urish, D.W.; McKenna, T.E. Tidal Effects on Ground Water Discharge Through a Sandy Marine Beach. Groundwater 2004, 42, 971–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, H.A.; Mulligan, A.E.; Harvey, C.F. Seasonal oscillations in water exchange between aquifers and the coastal ocean. Nature 2005, 436, 1145–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiss, J.W.; Michael, H.A. Saltwater-freshwater mixing dynamics in a sandy beach aquifer over tidal, spring-neap, and seasonal cycles. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 6747–6766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Chen, D.; Guo, Y.; Hu, W. Saltwater-freshwater mixing fluctuation in shallow beach aquifers. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 207, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grünenbaum, N.; Günther, T.; Greskowiak, J.; Vienken, T.; Müller-Petke, M.; Massmann, G. Salinity distribution in the subterranean estuary of a meso-tidal high-energy beach characterized by Electrical Resistivity Tomography and direct push technology. J. Hydrol. 2023, 617, 129074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Volker, R.E.; Lockington, D.A. Tidal effects on sea water intrusion in unconfined aquifers. J. Hydrol. 1999, 216, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiori, A.; Jankovic, I. On Preferential Flow, Channeling and Connectivity in Heterogeneous Porous Formations. Math. Geosci. 2012, 44, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greskowiak, J.; Massmann, G. The impact of morphodynamics and storm floods on pore water flow and transport in the subterranean estuary. Hydrol. Process. 2021, 35, e14050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavo, M.; Colombani, N.; Mastrocicco, M. Modeling stochastic saline groundwater occurrence in coastal aquifers. Water Res. 2023, 235, 119885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavo, M.; Riva, M.; Guadagnini, L.; Zehe, E.; Guadagnini, A. Probabilistic identification of Preferential Groundwater Networks. J. Hydrol. 2022, 610, 127906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riva, M.; Guadagnini, A.; Dell’Oca, A. Probabilistic assessment of seawater intrusion under multiple sources of uncertainty. Adv. Water Resour. 2015, 75, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

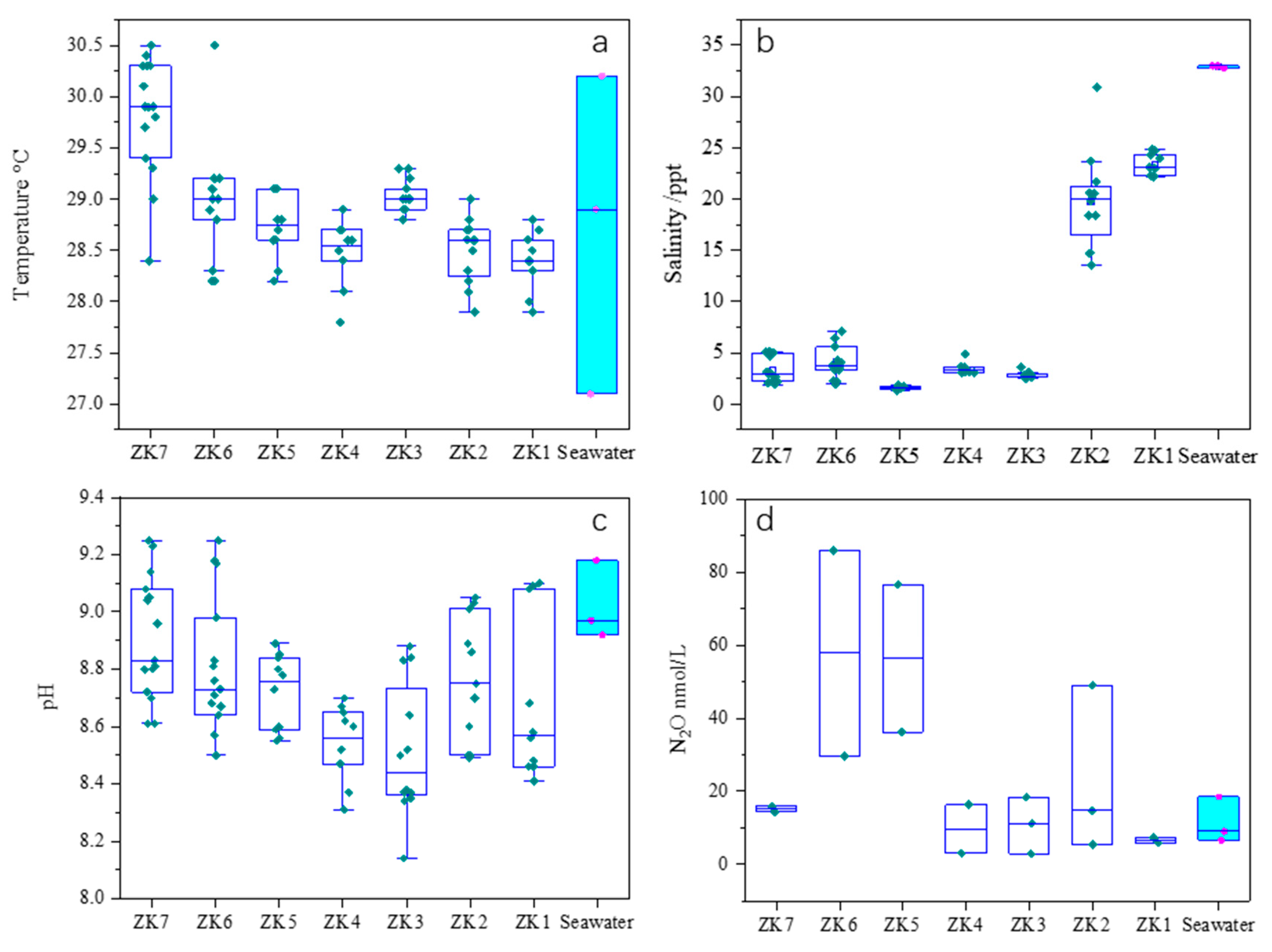
| Number of Wells | Number of Samples | Mean | STD | Median | Sum | Minimum | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZK7 | 2 | 15.15 | 1.11 | 15.15 | 30.3 | 14.36 | 15.94 |
| ZK6 | 2 | 57.77 | 39.83 | 57.77 | 115.54 | 29.6 | 85.93 |
| ZK5 | 2 | 56.34 | 28.5 | 56.34 | 112.68 | 36.19 | 76.5 |
| ZK4 | 2 | 9.69 | 9.41 | 9.69 | 19.39 | 3.04 | 16.35 |
| ZK3 | 3 | 10.85 | 7.7 | 11.23 | 32.54 | 2.96 | 18.35 |
| ZK2 | 3 | 23.03 | 22.93 | 14.74 | 69.1 | 5.4 | 48.96 |
| ZK1 | 2 | 6.63 | 1.03 | 6.63 | 13.25 | 5.9 | 7.35 |
| Seawater | 3 | 11.4 | 6.25 | 9.09 | 34.21 | 6.64 | 18.48 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, D.; Geng, J.; Ren, B.; Yang, B. Using Salinity, Water Level, CFCs, and CCl4 to Assess Groundwater Flow Dynamics and Potential N2O Flux in the Intertidal Zone of Sanya, Hainan Province: Implications for Evaluating Freshwater Submarine Groundwater Discharge in Coastal Unconfined Aquifers. Water 2025, 17, 1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091371
Qin D, Geng J, Ren B, Yang B. Using Salinity, Water Level, CFCs, and CCl4 to Assess Groundwater Flow Dynamics and Potential N2O Flux in the Intertidal Zone of Sanya, Hainan Province: Implications for Evaluating Freshwater Submarine Groundwater Discharge in Coastal Unconfined Aquifers. Water. 2025; 17(9):1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091371
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Dajun, Jing Geng, Bingnan Ren, and Bo Yang. 2025. "Using Salinity, Water Level, CFCs, and CCl4 to Assess Groundwater Flow Dynamics and Potential N2O Flux in the Intertidal Zone of Sanya, Hainan Province: Implications for Evaluating Freshwater Submarine Groundwater Discharge in Coastal Unconfined Aquifers" Water 17, no. 9: 1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091371
APA StyleQin, D., Geng, J., Ren, B., & Yang, B. (2025). Using Salinity, Water Level, CFCs, and CCl4 to Assess Groundwater Flow Dynamics and Potential N2O Flux in the Intertidal Zone of Sanya, Hainan Province: Implications for Evaluating Freshwater Submarine Groundwater Discharge in Coastal Unconfined Aquifers. Water, 17(9), 1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091371






