Hydrochemical Characteristics and Controlling Factors of Hengshui Lake Wetland During the Dry Season, North China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling and Measurement
- Accuracy control through standard solution spiking and spike recovery tests;
- Precision control via replicate analyses (relative deviations within acceptable thresholds);
- Blank monitoring with dual procedural blanks per batch (blank values ≤ 2/3 method detection limits);
- Charge balance verification for all samples, demonstrating 100% compliance with the 4% allowable ion balance error threshold.
2.3. Data Analysis Method
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Descriptive Statistics
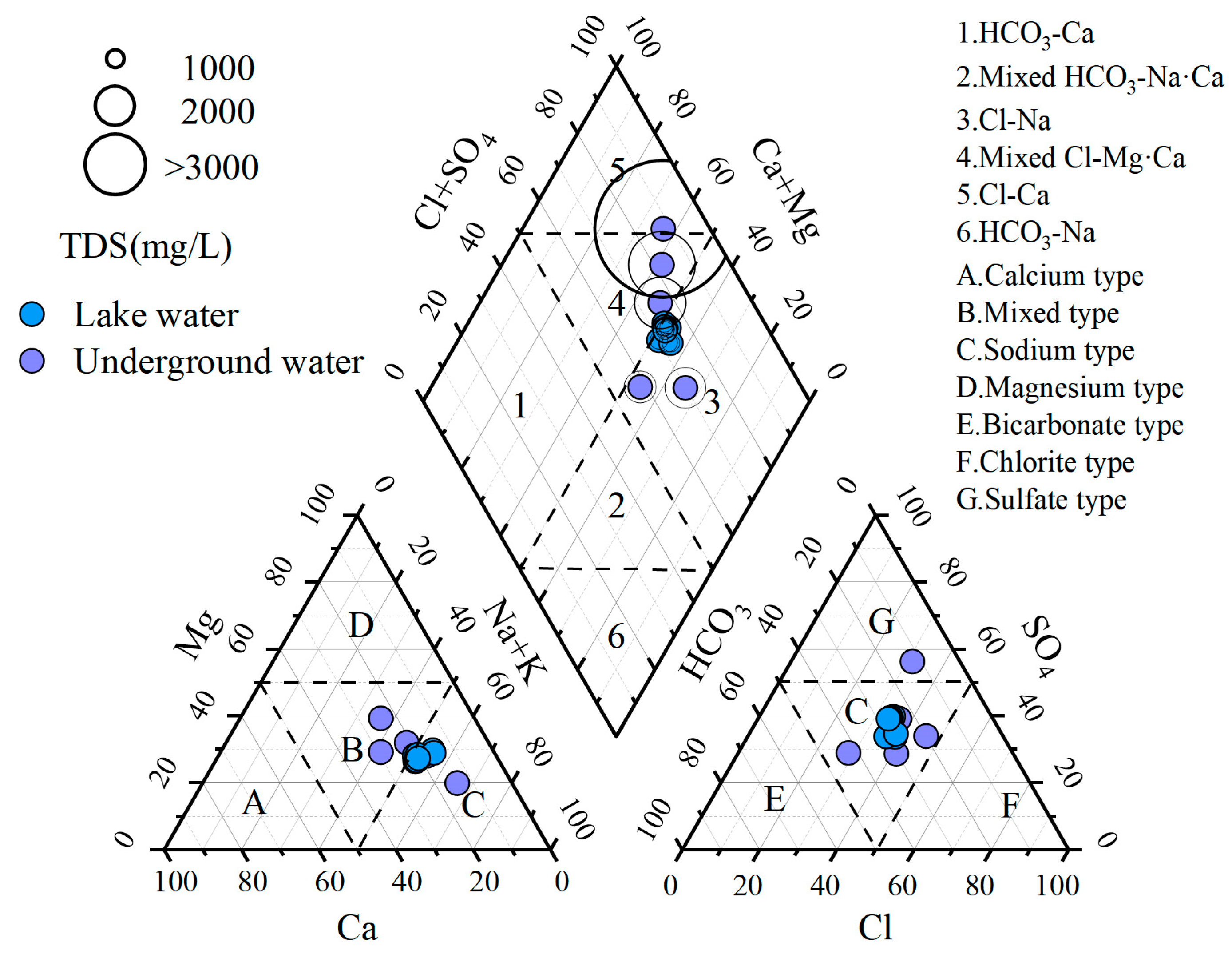
3.2. The Piper Diagram
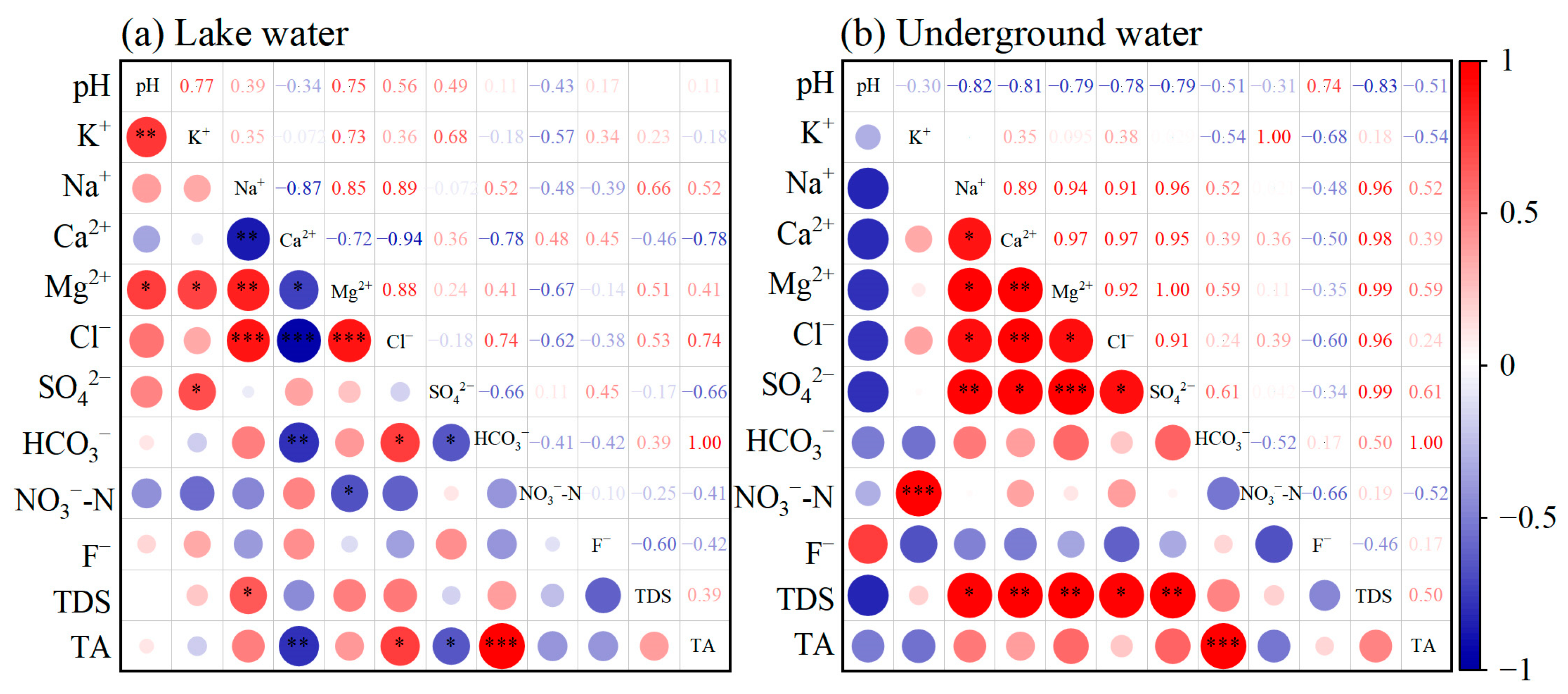
3.3. Correlation Analysis of Hydrochemical Indexes
4. Discussion
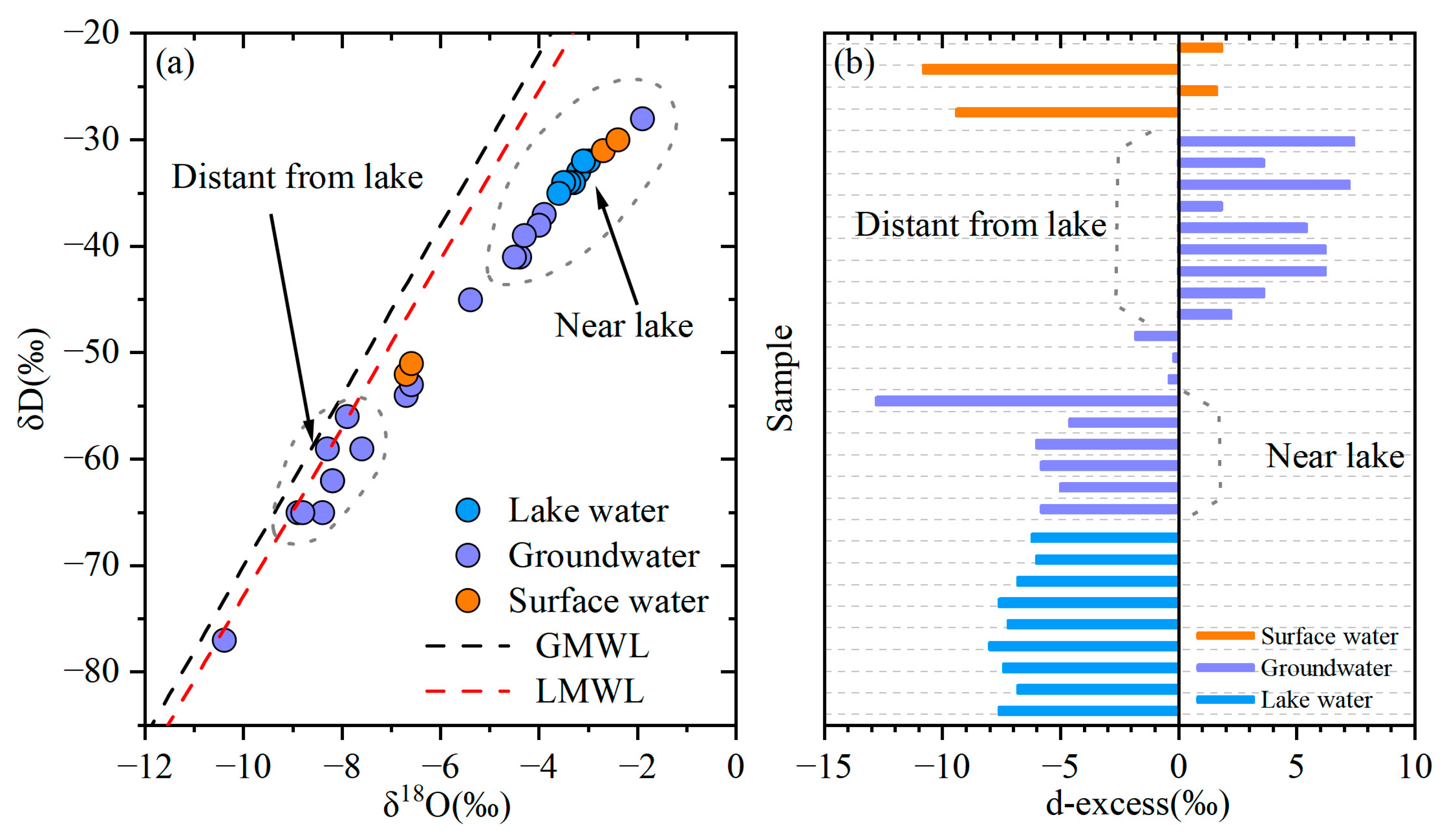
4.1. Interaction Between Lake Water and Groundwater
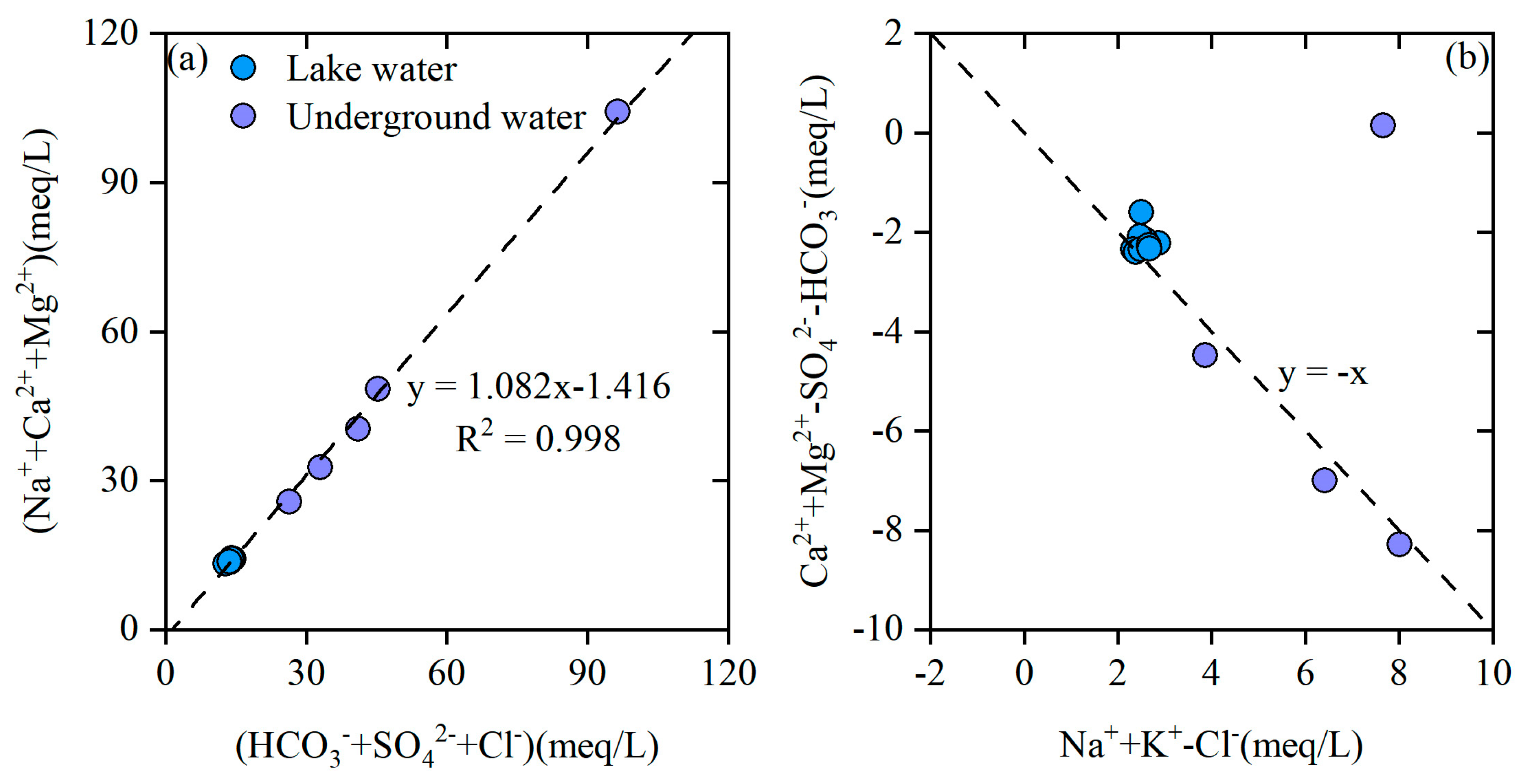
4.2. Ion Source Analysis
4.3. Analysis of the Formation Mechanism of Hydrochemistry
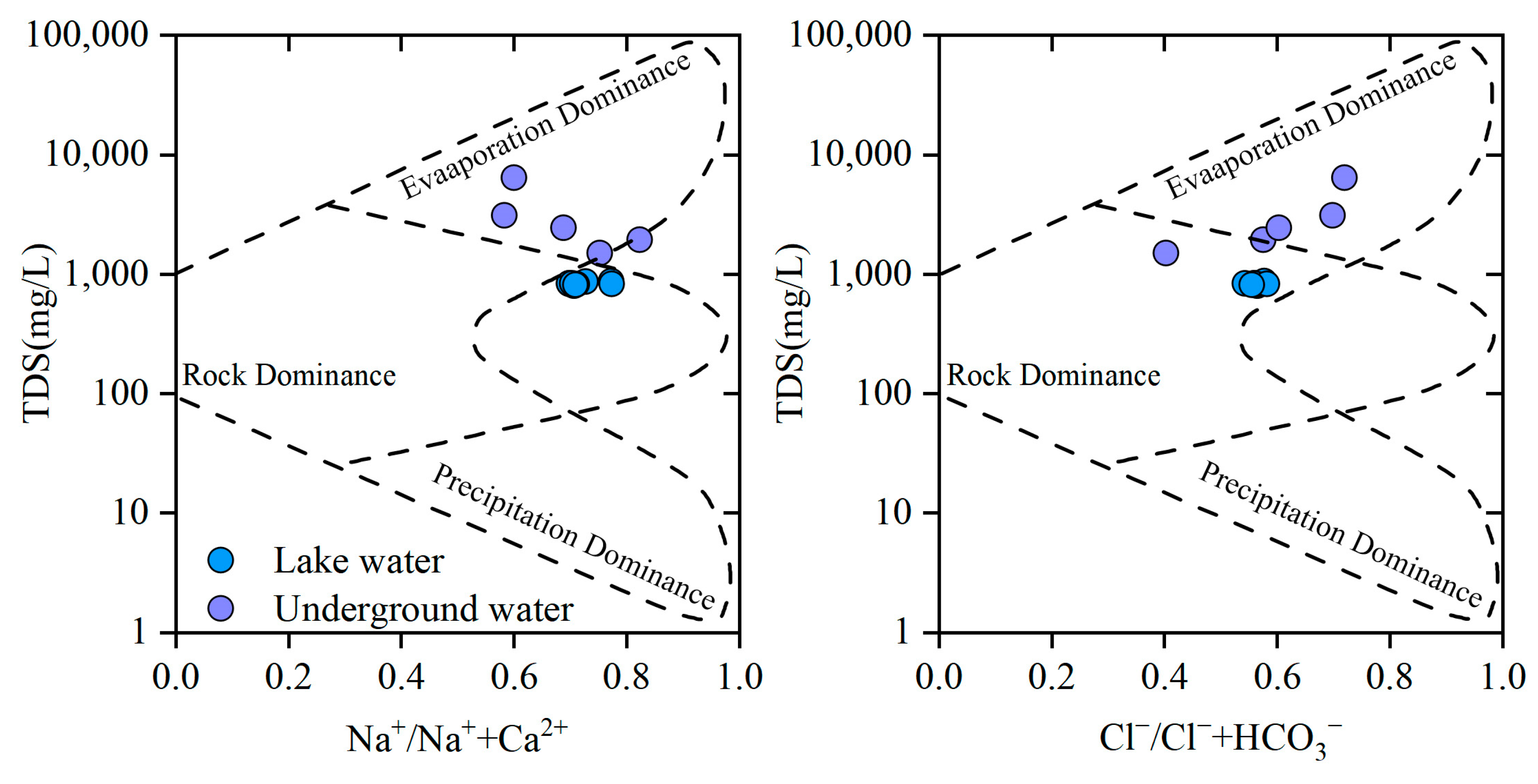
4.3.1. The Gibbs Diagram
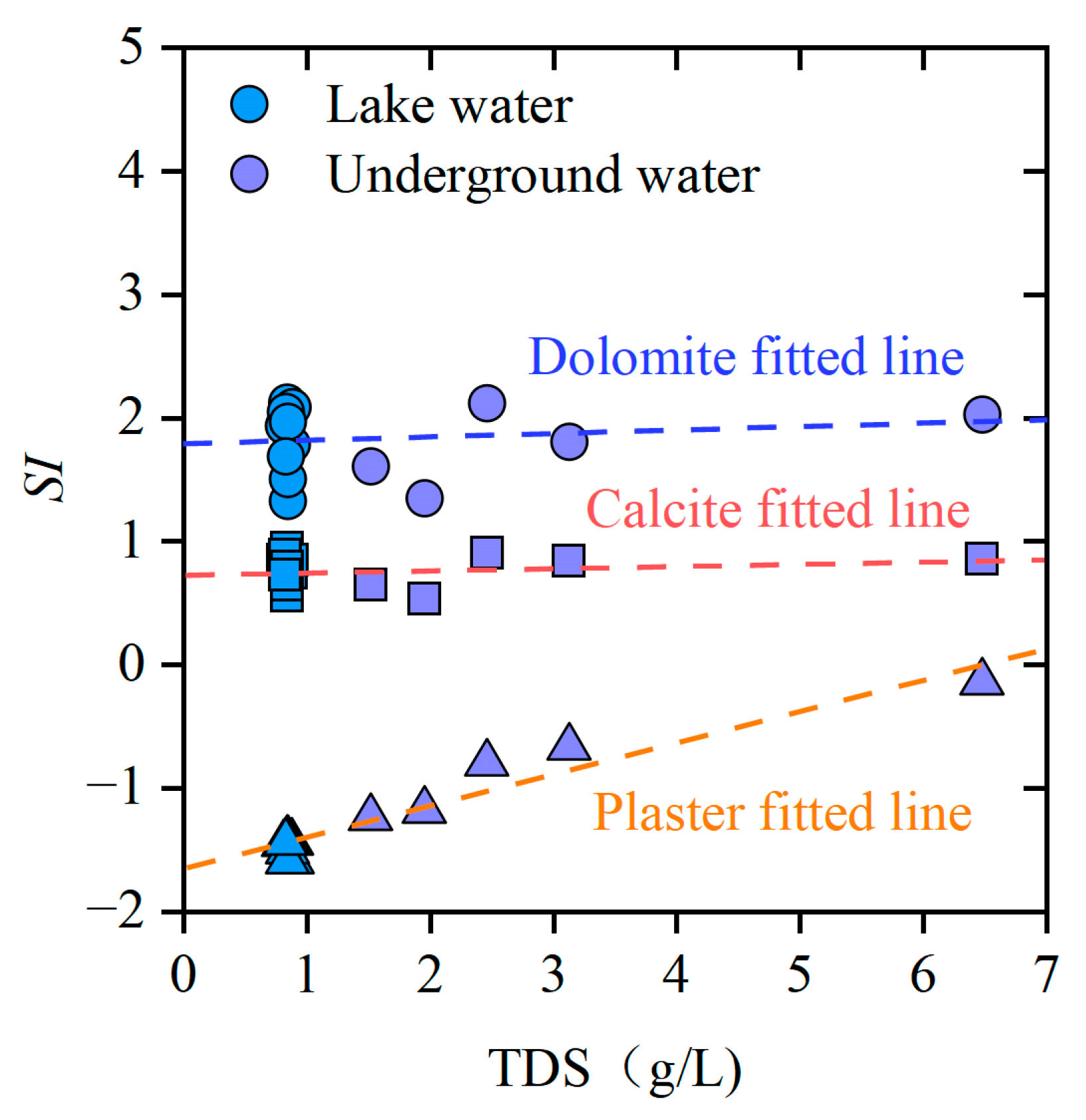
4.3.2. Mineral Saturation Index Analysis
4.3.3. Cation Exchange
4.3.4. Human Activities’ Impact
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Stratified differentiation of hydrochemical characteristics: Both lake water and shallow groundwater exhibit weakly alkaline systems, but show magnitude-level differences in Total Dissolved Solids (TDS)—the lake water represents low-mineralized freshwater while shallow groundwater constitutes high-mineralized saline water. Na+ and Mg2+ serve as dominant cations in both water types, with anion composition following the sequence SO42− > Cl− > HCO3−. The shallow groundwater system displays complex hydrochemical types reflecting multi-source recharge and intense water–rock interactions, whereas the lake system demonstrates homogenization features.
- (2)
- Multi-process coupled ion sources and formation mechanisms: Multivariate ratio analysis reveals that major cations originate from silicate mineral weathering and dissolution of evaporites (gypsum and mirabilite). Gibbs diagrams indicate evaporation-crystallization dominance, while mineral saturation indices show calcite and dolomite in supersaturated states. Continuous gypsum dissolution drives SO42− accumulation, a process coupled with the regional Quaternary geological background rich in evaporites. The intensity of cation exchange adsorption was more pronounced in groundwater than in lake water.
- (3)
- The impact of human activities presents an edge-permeation characteristic. The analysis results show that the overall area of the study region remains in a natural local state; however, shallow groundwater in the lakeshore zone exhibits anomalies in NO3−, indicating the potential risk of early-stage pollution in the wetland buffer zone. It is recommended to establish a long-term monitoring ecological early warning system with NO3− as the core indicator.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, M.; Li, J.; Luo, Z.; Sun, J.; Xu, F.; Jing, Q.; Deng, H. Impact of water–rock interaction on the pore structures of red-bed soft rock. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Dong, S.; Tang, S.; Ji, Y.; Luo, J.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Li, C.; Zeng, M. Molecular structure characterization of coal under the water–rock interaction in acid mine drainage (AMD). J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1251, 132043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slukovskii, Z.I.; Dauvalter, V.; Guzeva, A.; Denisov, D.; Cherepanov, A.; Siroezhko, E. The Hydrochemistry and Recent Sediment Geochemistry of Small Lakes of Murmansk, Arctic Zone of Russia. Water 2020, 12, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuchman, N.C.; Larkin, D.J.; Geddes, P.; Wildova, R.; Jankowski, K.; Goldberg, D.E. Patterns of Environmental Change Associated with Typha x glauca Invasion in a Great Lakes Coastal Wetland. Wetlands 2009, 29, 964–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheta, B.M.; Abdelhalim, A.A.; Elgyar, E.E.; Khalil, M.A.; Ageba, M.F. Wetland Habitat Suitability and Diversity for Migratory and Resident Birds in the Ramsar Site Lake Burllus, Egypt. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2023, 27, 253–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odero, D.O.; Odenyo, V.A.O. Optimizing community participation in the management of Yala Wetland Ecosystem, Lake Victoria Basin, Kenya: The Yala Hub Framework. Afr. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 16, 10–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munishi, S.J.G. Degradation of Kilombero Valley Ramsar wetlands in Tanzania. Phys. Chem. Earth 2019, 112, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olea-Olea, S.; Silva-Aguilera Raúl, A.; Alcocer, J.; Escolero, O.; Morales-Casique, E.; Florez-Peñaloza, J.; Almora-Fonseca, K.; Oseguera, L. Water–Rock Interaction Processes in Groundwater and Flows in a Maar Lake in Central Mexico. Water 2024, 16, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, Q.; Xie, C.; Lu, X. Source identification and health risks of nitrate contamination in shallow groundwater: A case study in Subei Lake basin. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 13660–13670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quenet, M.; Celle-Jeanton, H.; Voldoire, O.; Albaric, J.; Huneau, F.; Peiry, J.L.; Allain, E.; Garreau, A.; Beauger, A. Coupling hydrodynamic, geochemical and isotopic approaches to evaluate oxbow connection degree to the main stream and to adjunct alluvial aquifer. J. Hydrol. 2019, 577, 123936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigate, F.; Van Camp, M.; Yenehun, A.; Sewale Belay, A.; Walraevens, K. Recharge-discharge relations of groundwater in volcanic terrain of semi-humid tropical Highlands of Ethiopia:The case of infranz springs, in the Upper Blue Nile. Water 2020, 12, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Wang, S.; Chen, J.; Aghakouchak, A. Global assessment and hotspots of lake drought. Commun. Earth Environ. 2025, 6, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Wu, J.; Zhan, S.; Miao, J.; Saparov, A.S.; Abuduwaili, J. Spatial variations and controls on the hydrochemistry of surface waters across the Ili-Balkhash Basin, arid Central Asia. J. Hydrol. 2021, 600, 126565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Jiang, C.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Zheng, L. Combining hydrochemistry and hydrogen and oxygen stable isotopes to reveal the influence of human activities on surface water quality in Chaohu Lake Basin. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 312, 114933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Liu, Z.; Bao, Q.; Wei, Y.; Chen, C.; Sun, H.; Wang, Y. Lake metabolic processes and their effects on the carbonate weathering CO2 sink: Insights from diel variations in the hydrochemistry of a typical karst lake in SW China. Water Res. J. Int. Water Assoc. 2022, 222, 118907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, R.; Paudel, G.; Dahal, B.; Bishwakarma, K.; Sharma, S.; Shrestha, S.; Sharma, M.L.; Awasthi, M.P. Assessment of hydrochemical characteristics of the Taudaha lake, Kathmandu, Nepal. Sci. World 2022, 15, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J. A Characterization of the Hydrochemistry and Main Controlling Factors of Lakes in the Badain Jaran Desert, China. Water 2021, 13, 2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. Analysis of Ammonia Nitrogen Pollution in Hengshui Lake. J. Henan Water Conserv. South-North Water Divers 2021, 3, 34–35. Available online: https://www.nstl.gov.cn/paper_detail.html?id=0b7ec83c8fcdb5bae99d95b185eba61f (accessed on 14 January 2025). (In Chinese).
- Liu, W.; Cui, L.; Guo, Z.; Wang, D.; Zhang, M. Wetland ecosystem health improvement from ecological conservation and restoration offset the decline from socio-economic development. Land Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Li, H.; Cao, J.; Lu, Q.; Wang, Z.; He, L.; Sun, H.; Han, K. Investigating the climatology of North China’s urban inland lake based on six years of observations. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 826, 154120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Zhang, M.; Cui, L.; Pan, X.; Liu, W.; Li, W.; Li, Y. Winter Decomposition of Emergent Macrophytes Affects Water Quality under Ice in a Temperate Shallow Lake. Water 2020, 12, 2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Yan, B.; Tuo, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xie, X. Chemical evolution characteristics and influencing factors of groundwater in the saline and fresh water funnel area in Hengshui City, North China. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Li, H.; Zheng, Y.; Guo, R.; Liu, Z. Study of water quality analysis and evaluation of Hengshui Lake. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Environmental Pollution and Governance (ICEPG 2021), Xiamen, China, 21–23 May 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wei, S.; Liu, J. Pollution Characteristics and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal Elements in Sediment in the West Lake of Hengshui Lake. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 2021, 178966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhang, M.; Cui, L.; Ma, M.; Yan, L.; Mu, Y.; Qin, P. Contamination and ecological risk assessment of mercury in Hengshuihu wetland, Hebei Province. Environ. Sci. 2016, 37, 1754–1762. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, M.; Cui, L.; Guo, Z.; Wang, D. Evaluation of Ecological Environment Quality of HengshuiLake Wetlands based on DPSlR Model. Wetl. Sci. 2019, 17, 193–198. Available online: https://www.nstl.gov.cn/paper_detail.html?id=bac60e1c452463514e4507d3d3834d28 (accessed on 14 January 2025). (In Chinese).
- Liu, W.; Guo, Z.; Wang, D.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y. Spatial-Temporal Variation of Water Environment Quality and Pollution Source Analysis in Hengshui Lake. Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 361–371. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Xie, P.; Sun, D.; Liu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Huang, F.; Qiao, F. Effects of aquatic plant growth on water quality in Hengshui Lake wetland. China Environ. Sci. 2024, 44, 2247–2255. Available online: https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZGHJ202404046.html (accessed on 14 January 2025). (In Chinese).
- Wang, H.; Zhang, M.; Guo, Z.; Wang, D.; Liu, W. Distribution of contents of 7 kinds of heavy metal elements in the sediments of Hengshui Lake and their ecological risk assessment. Wetl. Sci. 2020, 18, 191–199. Available online: https://www.nstl.gov.cn/paper_detail.html?id=81327899b15a34e8e113c3ae68ebf25f (accessed on 17 April 2025). (In Chinese).
- Yongliang, W. Mechanism analysis and prediction of water level influencing factors in Hengshui Lake. Water Sci. Eng. Technol. 2020, 3, 55–60. Available online: https://www.nstl.gov.cn/paper_detail.html?id=ae7297c42833ca4ae81ac7aa1ded1556 (accessed on 14 January 2025). (In Chinese).
- Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Wu, L.; Li, Z. Study on the interaction between lake water and groundwater in Hengshui Lake. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2019, 49, 60–63. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, A.M. A Graphic Procedure in the Geochemical Interpretation and Analysis of Water Samples; USGS, Water Supply 1953, Paper 1454; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1953.
- Omed, M.; Broder, M.; Stephan, W. Assessment of Hydrogeochemistry and Environmental Isotopes in Karst Springs of Makook Anticline, Kurdistan Region, Iraq. Hydrology 2015, 2, 48–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, U.; Dhar, A.; Panda, S.N.; Sena, D.R. Correction to: Spatiotemporal evaluation and assessment of shallow groundwater quality for irrigation of a tropical coastal groundwater basin. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 30, 116741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoud, A.M.; Abu El-Magd, S.A. Integration of hydrochemical and isotopic characteristics for identifying groundwater recharge sources of the Eocene carbonate aquifer, Western Desert, Egypt. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2022, 187, 104449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokadem, N.; Demdoum, A.; Hamed, Y.; Bouri, S.; Hadji, R.; Boyce, A.; Laouar, R.; Saad, A. Hydrogeochemical and stable isotope data of groundwater of a multi-aquifer system: Northern Gafsa basin—Central Tunisia. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2016, 114, 174–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordstrom, D.K.; Blowes, D.W.; Ptacek, C.J. Hydrogeochemistry and microbiology of mine drainage: An update. Appl. Geochem. 2015, 57, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekwere, A.S.; Kudamnya, E.A.; Oyonga, O.A. Hydrogeochemistry, ionic speciation, controlling processes and agricultural suitability of groundwaters in sections of the semi-arid basement complex of north-central Nigeria. Solid Earth Sci. 2023, 8, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Liang, X.; Li, J.; Ma, B.; Ge, Q. Paleoclimate indication of grain size and deuterium-oxygen isotope of saline sediments in Hengshui Area. Earth Sci. 2016, 41, 499–507. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, R.J. Mechanisms Controlling World Water Chemistry. Science 1970, 170, 1088–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Zhang, B.; Xia, W.; Cui, Z.; Wang, L. Analysis of water chemical composition and main ion sources in Tianjin Qilihai Wetland. Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 10. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Soulsby, C.; Chen, M.; Ferrier, R.C.; Helliwell, R.C.; Jenkins, A.; Harriman, R. Hydrogeochemistry of shallow groundwater in an upland Scottish catchment. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 12, 1111–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmoay, A.A.; Mousa, I.E.; Mabrouk, W.A. Simulation of Rock-Water Interaction in the Southwestern Part of El Minya Governorate of Egypt. J. Geol. Soc. India 2024, 100, 153–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, D.; Zhou, J. Hydrochemical evolution characteristics, controlling factors, and high nitrate hazards of shallow groundwater in a typical agricultural area of Nansi Lake Basin, North China. Environ. Research. Sect. A 2023, 223, 115430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, J.; Chen, Y.; Wei, X.; Zeng, Y.; Sun, Y. Identifying the factors controlling surface water and groundwater chemical characteristics and irrigation suitability in the Yarkant River Basin, northwest China. Environ. Res. 2023, 223, 115452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, R.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y. Hydrochemical variations and driving mechanisms in a large linked river-irrigation-lake system. Environ. Res. 2023, 225, 115596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Rishi, M.S.; Herojeet, R.; Kaur, L.; Sharma, K. Evaluation of groundwater quality and human health risks from fluoride and nitrate in semi-arid region of northern India. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 1833–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Index | Underground Water (N = 5) | Lake Water (N = 10) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIN | MAX | AVG | SD | CV | MIN | MAX | AVG | SD | CV | |
| Ca2+ | 92.20 | 507.98 | 230.13 | 174.33 | 75.75 | 45.33 | 60.63 | 55.89 | 5.64 | 10.09 |
| Mg2+ | 78.70 | 497.70 | 199.06 | 172.02 | 86.41 | 43.53 | 52.22 | 48.06 | 2.75 | 5.71 |
| Na+ | 319.74 | 871.92 | 515.35 | 209.67 | 40.69 | 155.97 | 178.12 | 164.33 | 7.94 | 4.83 |
| K+ | 1.11 | 13.41 | 4.21 | 5.24 | 124.38 | 9.91 | 10.93 | 10.48 | 0.33 | 3.13 |
| Cl− | 267.15 | 1076 | 619.31 | 306.05 | 49.42 | 160.85 | 196.15 | 172.05 | 11.91 | 6.92 |
| SO42− | 367.40 | 2606.50 | 988.02 | 921.80 | 93.30 | 206.05 | 268.65 | 250.06 | 19.33 | 7.73 |
| HCO3− | 551.62 | 724.92 | 634.85 | 68.99 | 10.87 | 219.06 | 247.74 | 228.15 | 8.86 | 3.88 |
| NO3-N | 10.66 | 343.90 | 95.33 | 141.92 | 148.86 | 4.04 | 5.37 | 4.59 | 0.49 | 10.73 |
| F− | 0.11 | 1.60 | 0.78 | 0.64 | 81.59 | 0.64 | 0.79 | 0.72 | 0.05 | 6.67 |
| pH | 7.30 | 7.69 | 7.51 | 0.14 | 1.89 | 8.02 | 8.45 | 8.31 | 0.14 | 1.66 |
| TDS | 1512 | 6475 | 3103.80 | 1978.17 | 63.73 | 807 | 881 | 840.10 | 22.05 | 2.63 |
| TA | 452.36 | 594.48 | 520.62 | 56.57 | 10.87 | 179.64 | 203.16 | 187.10 | 7.26 | 3.88 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
An, H.; Wang, T.; Meng, X.; Niu, X.; Song, D.; Wang, Y.; Gao, G.; Li, M.; Zhang, T.; Song, H.; et al. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Controlling Factors of Hengshui Lake Wetland During the Dry Season, North China. Water 2025, 17, 1468. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101468
An H, Wang T, Meng X, Niu X, Song D, Wang Y, Gao G, Li M, Zhang T, Song H, et al. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Controlling Factors of Hengshui Lake Wetland During the Dry Season, North China. Water. 2025; 17(10):1468. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101468
Chicago/Turabian StyleAn, Hongyan, Tianjiao Wang, Xianzhou Meng, Xueyao Niu, Dongyang Song, Yibing Wang, Ge Gao, Mingming Li, Tong Zhang, Hongliang Song, and et al. 2025. "Hydrochemical Characteristics and Controlling Factors of Hengshui Lake Wetland During the Dry Season, North China" Water 17, no. 10: 1468. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101468
APA StyleAn, H., Wang, T., Meng, X., Niu, X., Song, D., Wang, Y., Gao, G., Li, M., Zhang, T., Song, H., Wang, X., & Mao, K. (2025). Hydrochemical Characteristics and Controlling Factors of Hengshui Lake Wetland During the Dry Season, North China. Water, 17(10), 1468. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101468






