Influence of Seasonal Variation in Antibiotic Concentration on the Fate and Transport of Antibiotics Within an Artificial Pond System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Standards
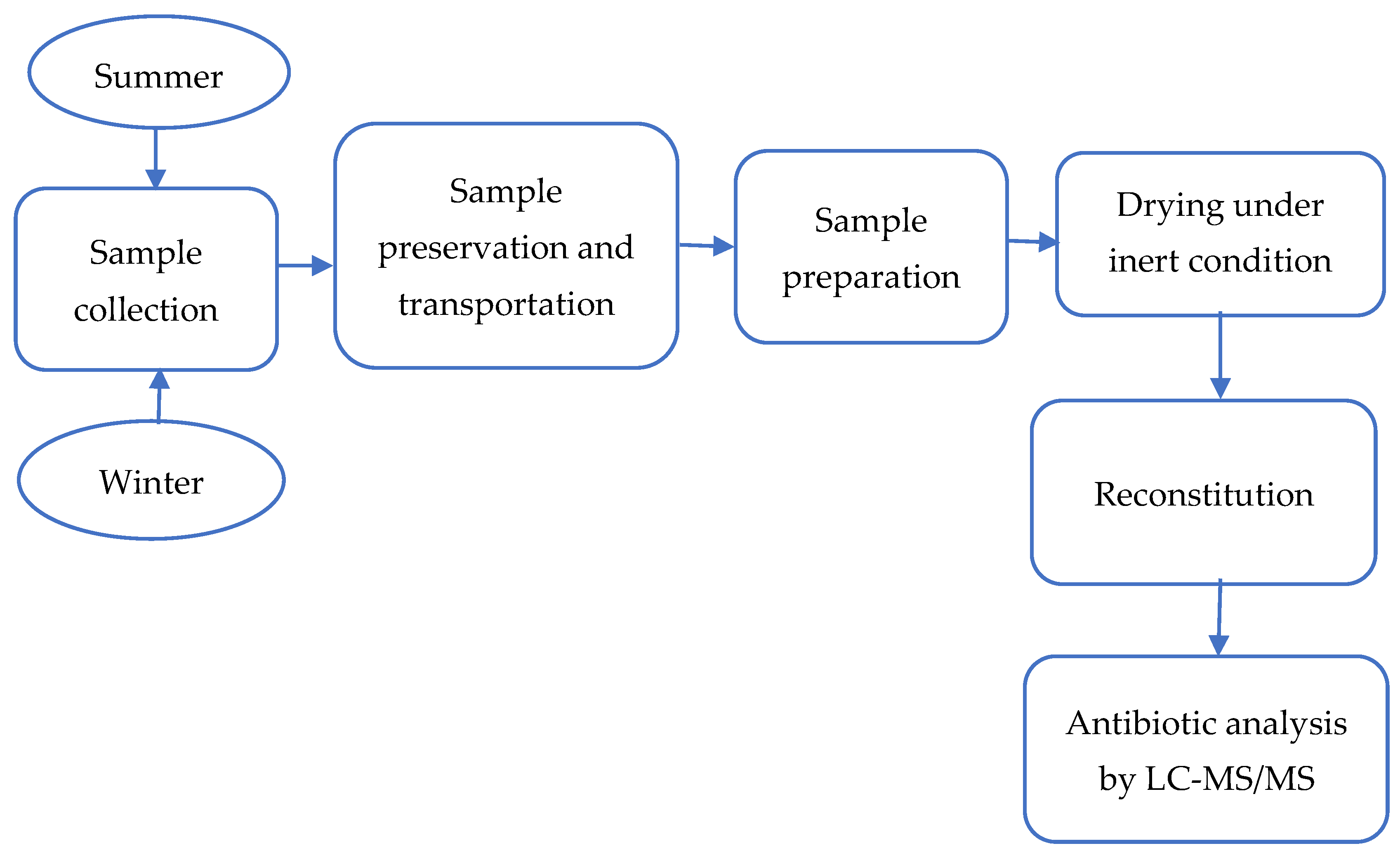
2.2. Study Site and Sample Collection
2.3. Sample Preparation and Extraction
2.4. Quantification of Antibiotics
2.5. Risk Assessment
3. Results
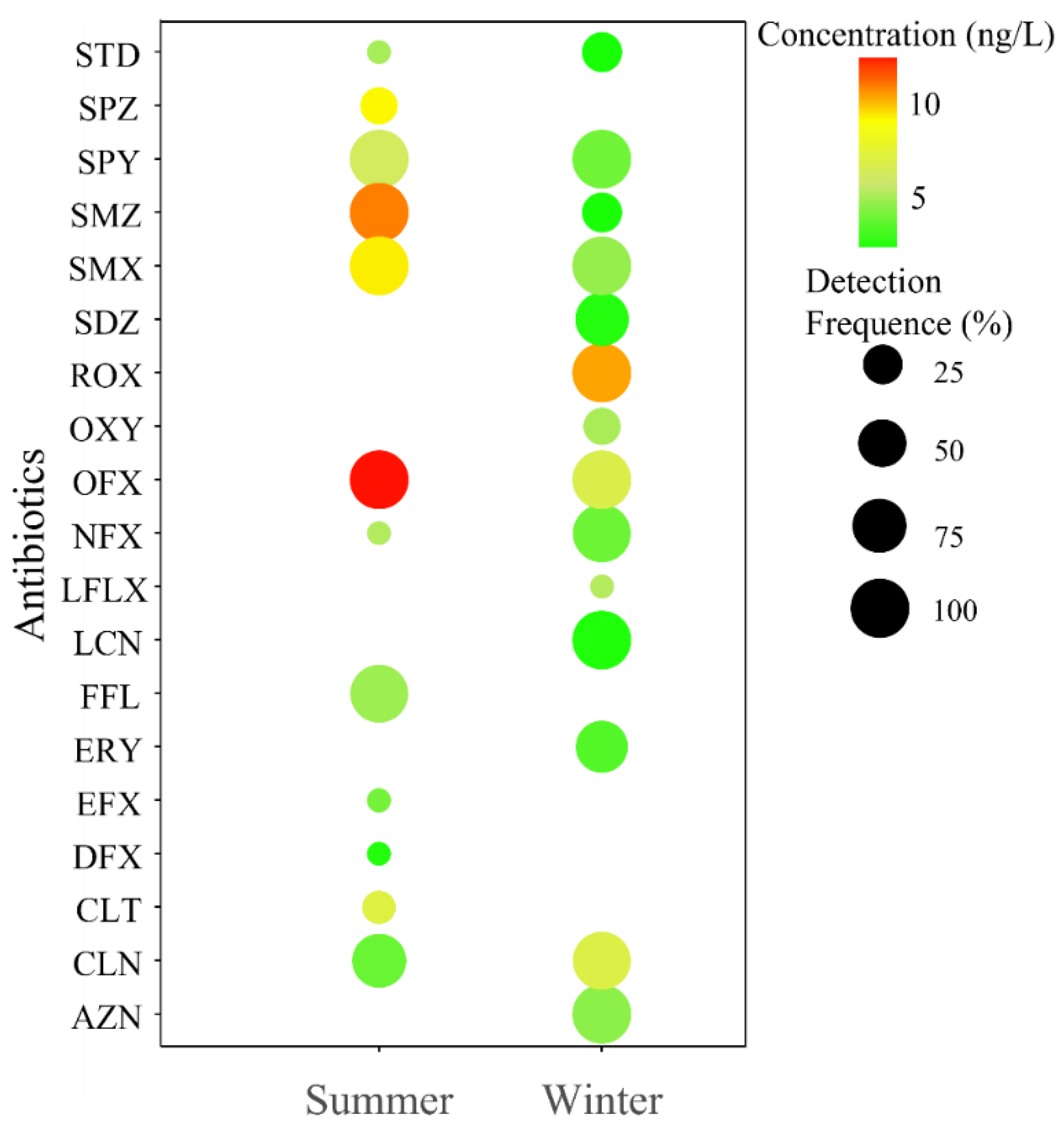
3.1. Occurrence of Antibiotics in the Artificial Stabilization Pond System (SPS)
3.2. Seasonal Variation in Antibiotics Within the SPS
3.2.1. Seasonal Variation of Sulfonamides Within the SPS
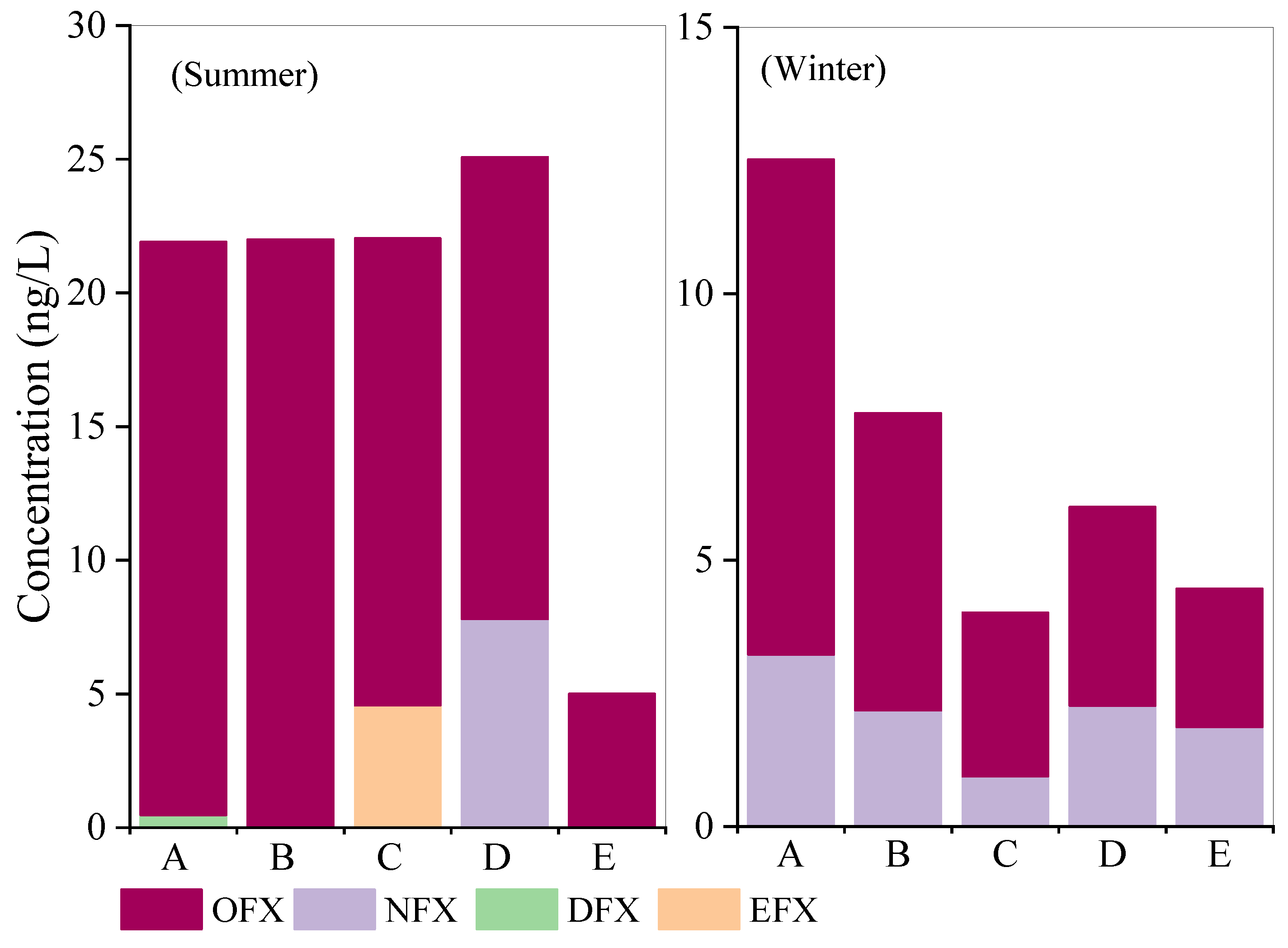
3.2.2. Seasonal Variation of Fluoroquinolones Within the SPS
3.2.3. Seasonal Variation of Macrolides Within the SPS
3.2.4. Seasonal Variation in Diaminopyrimidine Within the SPS
3.2.5. Seasonal Variation in Tetracyclines Within the SPS
3.2.6. Seasonal Variation in Antibiotics Classified as “Others” Within the SPS
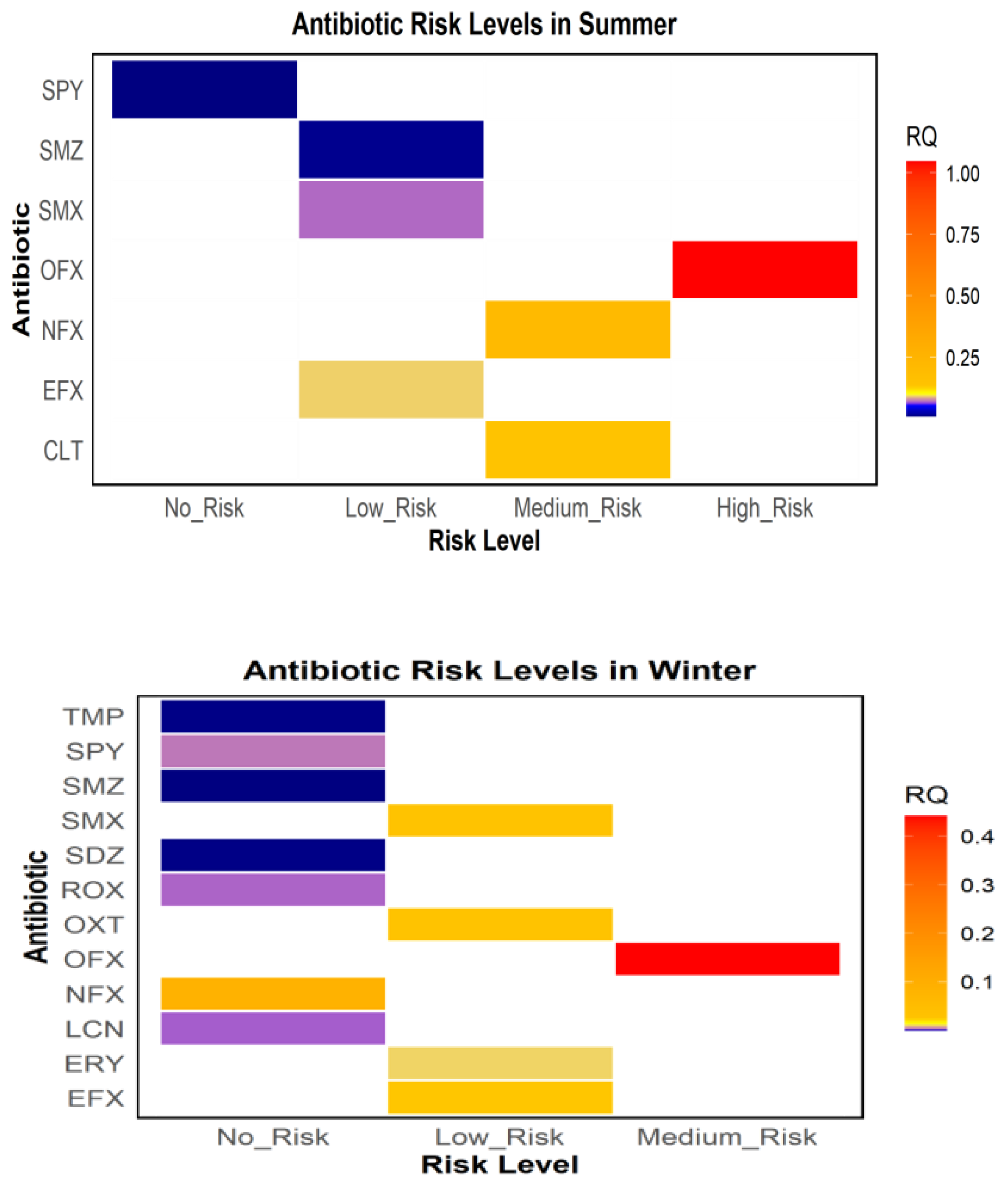
4. Environmental Risk Assessment of Antibiotics
| Antibiotic Compound | Taxonomic Group | Species | Toxicity Data (mg/L) | PNEC (ng/L) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sulfamethoxazole | Algae | C. meneghiniana | 0.00125 | 1250 | [72] |
| Algae | S. capricornutum | 0.0000146 | 146 | ||
| Invertebrate | D. magna | 0.0252 | 25,200 | ||
| Fish | D. rerio | 0.008 | 8000 | ||
| Sulfamethazine | Algae | L. gibba | 0.001277 | 1277 | [73] |
| Invertebrate | M. macrocopa | 0.001277 | 1277 | ||
| Fish | Danio rerio | 0.0326 | 32,600 | [74] | |
| Sulfapyridine | Algae | Freshwater algae | 0.02079 | 20,790 | |
| Invertebrate | D. magna | 0.0007 | 700 | ||
| Fish | Zebrafish embryos | 0.0454 | 45,400 | ||
| Sulfachloropyridazine | Algae | Freshwater algae | 0.02808 | 28,080 | |
| Invertebrate | D. magna | 0.0008 | 800 | ||
| Fish | Zebrafish embryos | 0.0789 | 78,900 | ||
| Sulfacetamide | Algae | N.O. | N.O. | N.O. | N.O. |
| Invertebrate | N.O. | N.O. | N.O. | N.O. | |
| Fish | N.O. | N.O. | N.O. | N.O. | |
| Sulfadiazine | Algae | S. capricornutum | 2.2 | 2200 | [75] |
| Invertebrate | N.O. | N.O. | N.O. | N.O. | |
| Fish | N.O. | N.O. | N.O. | N.O. | |
| Trimethoprim | Algae | R. saline | 0.016 | 16,000 | [72] |
| Algae | M. aeruginosa | 0.112 | 112,000 | ||
| Algae | S. capricornutum | 0.0255 | 25,500 | ||
| Invertebrate | D. magna | 0.06 | 6000 | ||
| Fish | B. rerio | 0.1 | 100,000 | ||
| Ofloxacin | Algae | M. aeruginosa | 0.021 | 21 | [76] |
| Invertebrate | C. dubia | 3.13 | 3130 | ||
| Fish | D. rerio | >1000 | 1,000,000 | ||
| Norfloxacin | Algae | M. wesenbergii | 0.038 | 38 | [77] |
| Invertebrate | D. magna | 0.88 | 880 | [78] | |
| Fish | N.O. | 20,081.355 | 20,081,355 | ECOSAR | |
| Enrofloxacin | Algae | M. aeruginosa | 0.000049 | 49 | [72] |
| Invertebrate | D. magna | 0.01 | 10,000 | ||
| Fish | O. mykiss | 0.01 | 10,000 | ||
| Difloxacin | Algae | N.O. | N.O. | N.O. | N.O. |
| Invertebrate | N.O. | N.O. | N.O. | ||
| Fish | N.O. | N.O. | N.O. | ||
| Clindamycin | Algae | N.O. | N.O. | N.O. | N.O. |
| Invertebrate | N.O. | N.O. | N.O. | ||
| Fish | N.O. | N.O. | N.O. | ||
| Lincomycin | Algae | P. subcapitata | 0.07 | 70 | ECOSAR |
| Invertebrate | Thamnocephalus platyurus | 33 | 33,000 | ECOSAR | |
| Fish | Danio rerio | 1000 | 10,000,000 | ECOSAR | |
| Roxithromycin | Algae | Freshwater algae | 0.00466 | 4660 | [74] |
| Invertebrate | D. magna | 0.006 | 6000 | ||
| Fish | D. magna | 0.023 | 23,000 | ||
| Erythromycin | Algae | Freshwater algae | 0.0023 | 2300 | |
| Invertebrate | D. magna | 0.0002 | 200 | [79] | |
| Fish | D. rerio | 0.0615 | 61,500 | [76,80] | |
| Azithromycin | Freshwater algae | N.O. | N.O. | N.O. | N.O. |
| Invertebrate | N.O. | N.O. | N.O. | ||
| Fish | N.O. | N.O. | N.O. | ||
| Oxytetracycline | Algae | M. aeruginosa | 0.23 | 230 | ECOSAR |
| Invertebrate | N.O. | 3.08 | 308,000 | ||
| Fish | Oryzias latipes | 50 | 500,000 | ||
| Chlortetracycline | Algae | P. subcapitata | 0.00017 | 170 | [81] |
| Invertebrate | M. macrocopa | 0.00005 | 50 | [73] | |
| Fish | M. saxatilis | 0.15 | 150,000 | ||
| Florfenicol | Algae | N.O. | N.O. | N.O. | N.O. |
| Invertebrate | N.O. | N.O. | N.O. | ||
| Fish | N.O. | N.O. | N.O. |
5. Discussion
5.1. Antibiotic Occurrence and Seasonal Variation Within the SPS
5.2. Summary of the Stabilization Pond Configuration and Mechanism
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhagat, C.; Kumar, M.; Tyagi, V.K.; Mohapatra, P.K. Proclivities for prevalence and treatment of antibiotics in the ambient water: A review. npj Clean Water 2020, 3, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavumiragira, J.P.; Ge, J.n.; Yin, H. Fate and transport of pharmaceuticals in water systems: A processes review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 823, 153635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Xu, C.; Wu, X.; Chen, Y.; Han, W.; Gin, K.Y.-H.; He, Y. Occurrence, Seasonal Variation and Risk Assessment of Antibiotics in Qingcaosha Reservoir. Water 2018, 10, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghsodian, Z.; Sanati, A.M.; Mashifana, T.; Sillanpää, M.; Feng, S.; Nhat, T.; Ramavandi, B. Occurrence and Distribution of Antibiotics in the Water, Sediment, and Biota of Freshwater and Marine Environments: A Review. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, L.; Wang, Y.; Tong, L.; Li, Y.; Deng, Y.; Guo, W.; Gan, Y. Seasonal variation of antibiotics concentration in the aquatic environment: A case study at Jianghan Plain, central China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 527–528, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kafaei, R.; Papari, F.; Seyedabadi, M.; Sahebi, S.; Tahmasebi, R.; Ahmadi, M.; Sorial, G.A.; Asgari, G.; Ramavandi, B. Occurrence, distribution, and potential sources of antibiotics pollution in the water-sediment of the northern coastline of the Persian Gulf. Iran. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Chen, L.; Chen, W.; Bao, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, B.; Mu, Q.; Wen, D.; Feng, C. Antibiotics in coastal water and sediments of the East China Sea: Distribution, ecological risk assessment and indicators screening. Mar. Pollut. Bullet. 2020, 151, 110810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhong, J.; Lou, Q.; Yang, P.; Fang, Y. Occurrence, distribution, and risk assessment of antibiotics in the surface water of Poyang Lake, the largest freshwater lake in China. Chemosphere 2017, 184, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Shi, T.; Wu, X.; Cao, H.; Li, X.; Hua, R.; Tang, F.; Yue, Y. The occurrence and distribution of antibiotics in Lake Chaohu, China: Seasonal variation, potential source and risk assessment. Chemosphere 2015, 122, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainab, S.M.; Junaid, M.; Xu, N.; Malik, R.N. Antibiotics and antibiotic resistant genes (ARGs) in groundwater: A global review on dissemination, sources, interactions, environmental and human health risks. Water Res. 2020, 187, 116455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, N.; Sun, P.; Sun, Q.; Li, X.; Yang, X.; Ji, X.; Zou, H.; Ottoson, J.; Nilsson, L.E.; Berglund, B.; et al. Presence of antibiotic residues in various environmental compartments of Shandong province in eastern China: Its potential for resistance development and ecological and human risk. Environ. Int. 2018, 114, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruchlik, Y.; Linge, K.; Joll, C. Removal of organic micropollutants in waste stabilisation ponds: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 206, 202–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Recio-Garrido, D.; Kleiner, Y.; Colombo, A.; Tartakovsky, B. Dynamic model of a municipal wastewater stabilization pond in the arctic. Water Res. 2018, 144, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahapatra, S.; Samal, K.; Dash, R.R. Waste Stabilization Pond (WSP) for wastewater treatment: A review on factors, modelling and cost analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 308, 114668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zou, H.; Zhao, L.; Li, X. Seasonal distribution and dynamic evolution of antibiotics and evaluation of their resistance selection potential and ecotoxicological risk at a wastewater treatment plant in Jinan, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 44505–44517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Xu, Z.; Dong, B. Occurrence, fate, and ecological risk of antibiotics in wastewater treatment plants in China: A review. J. Hazard. Mat. 2024, 469, 133925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Yau, P.C. Fate of Macrolide Antibiotics with Different Wastewater Treatment Technologies. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Suthar, S. Occurrence, seasonal variation, mass loading and fate of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in sewage treatment plants in cities of upper Ganges bank, India. J. Wat. Proc. Engin. 2021, 44, 102399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Hu, J.; Wang, P.; Han, G.; Jia, Z. Antibiotics in Wastewater Treatment Plants in Tangshan: Perspectives on Temporal Variation, Residents’ Use and Ecological Risk Assessment. Water 2024, 16, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Han, Q.; Jiang, L.; Ma, L.; Jin, L.; Zhang, D.; Lin, K.; Zhang, T. Occurrence, distribution, and seasonal variation of antibiotics in an artificial water source reservoir in the Yangtze River delta, East China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 19393–19402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Zhang, P.; Halsall, C.; Hou, Z.; Ge, L. Occurrence and seasonal variations of antibiotic micro-pollutants in the Wei River, China. Environ. Res. 2024, 252, 118863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Bao, Y.; Xu, B. Seasonal variation of antibiotics in surface water of Pudong New Area of Shanghai, China and the occurrence in typical wastewater sources. Chemosphere 2020, 239, 124816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salma, U.; Nishimura, Y.; Tokumura, M.; Hossain, A.; Watanabe, K.; Noro, K.; Raknuzzaman, M.; Amagai, T.; Makino, M. Occurrence, seasonal variation, and environmental risk of multiclass antibiotics in the urban surface water of the Buriganga River, Bangladesh. Chemosphere 2025, 370, 143956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wei, H.; Wang, C.; Cheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z. Distribution and ecological risk assessment of antibiotics in different freshwater aquaculture ponds in a typical agricultural plain, China. Chemosphere 2024, 361, 142498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, M.; Xing, L.; Yan, R.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, A.; Zhang, T. Spatiotemporal variations and ecological risks of typical antibiotics in rivers inflowing into Taihu Lake, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 309, 114699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, D.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Gong, W.; Liu, G.; Fu, W.; Cheng, M. Seasonal variation and sediment–water exchange of antibiotics in a shallower large lake in North China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 476–477, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Liu, D.; Wang, L.; Dong, D.; Guo, Z. Antibiotics in a seasonal ice-sealed reservoir: Occurrence, temporal variation, prioritization, and source apportionment. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dong, X.; Zang, J.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, F.; Jiang, L.; Xiong, C.; Wang, N.; Fu, C. Antibiotic residues of drinking-water and its human exposure risk assessment in rural Eastern China. Wat. Res. 2023, 236, 119940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karikari, A.Y.; Asmah, R.; Anku, W.W.; Amisah, S.; Agbo, N.W.; Telfer, T.C.; Ross, L.G. Heavy metal concentrations and sediment quality of a cage farm on Lake Volta, Ghana. Aquacult. Res. 2020, 51, 2041–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhang, G.; Li, X.; Zou, S.; Li, P.; Hu, Z.; Li, J. Occurrence and elimination of antibiotics at four sewage treatment plants in the Pearl River Delta (PRD), South China. Water Res. 2007, 41, 4526–4534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkinson, A.J.; Murby, E.J.; Kolpin, D.W.; Costanzo, S.D. The occurrence of antibiotics in an urban watershed: From wastewater to drinking water. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 2711–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mai, Z.; Xiong, X.; Hu, H.; Jia, J.; Wu, C.; Wang, G. Occurrence, distribution, and ecological risks of antibiotics in Honghu Lake and surrounding aquaculture ponds, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 50732–50742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayal, A.; Mandal, S. Microbial degradation of antibiotic: Future possibility of mitigating antibiotic pollution. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, W.; Zhao, X.; Teng, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhang, T. Review on Biogeochemical Characteristics of Typical Antibiotics in Groundwater in China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrower, J.; McNaughtan, M.; Hunter, C.; Hough, R.; Zhang, Z.; Helwig, K. Chemical Fate and Partitioning Behavior of Antibiotics in the Aquatic Environment-A Review. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 3275–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Zhao, H.; Liu, S.; Xie, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J. Antibiotics in the coastal water of the South Yellow Sea in China: Occurrence, distribution and ecological risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 595, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scaria, J.; Anupama, K.V.; Nidheesh, P.V. Tetracyclines in the environment: An overview on the occurrence, fate, toxicity, detection, removal methods, and sludge management. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 771, 145291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, X.; Lou, S.; Xu, Q.; Jin, Y.; Dorzhievna, R.L.; Elena, N.; Nikolavich, M.A.; Tavares, A.J.; Viktorovna, F.I. Occurrence of sulfonamides and tetracyclines in the coastal areas of the Yangtze River (China) Estuary. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 118567–118587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boleda, M.R.; Galceran, M.T.; Ventura, F. Validation and uncertainty estimation of a multiresidue method for pharmaceuticals in surface and treated waters by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1286, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Hu, X.; Yin, D.; Zhang, H.; Yu, Z. Occurrence, distribution and seasonal variation of antibiotics in the Huangpu River, Shanghai, China. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Xu, L.; Rysz, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Alvarez, P.J. Occurrence and transport of tetracycline, sulfonamide, quinolone, and macrolide antibiotics in the Haihe River Basin, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 1827–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conde-Cid, M.; Ferreira-Coelho, G.; Fernández-Calviño, D.; Núñez-Delgado, A.; Fernández-Sanjurjo, M.J.; Arias-Estévez, M.; Álvarez-Rodríguez, E. Single and simultaneous adsorption of three sulfonamides in agricultural soils: Effects of pH and organic matter content. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 744, 140872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Kroeze, C.; van de Schans, M.G.M.; Baartman, J.; Yang, J.; Li, S.; Xu, W.; Wang, M.; Ma, L.; et al. More inputs of antibiotics into groundwater but less into rivers as a result of manure management in China. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2025, 23, 100513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Du, M.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, D.; Lin, L.; Ye, H.; Zhang, X. Occurrence, seasonal variation and removal efficiency of antibiotics and their metabolites in wastewater treatment plants, Jiulongjiang River Basin, South China. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2015, 17, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, J.; Wei, X.Q.; Xiao, Y.Q.; Li, Q.S.; Fan, H.Y.; Liu, X.J.; Zhuang, M.Z.; Liu, C.X. [Pollution Characteristics and Risk Assessment of Antibiotics in Lianhua Reservoir]. Huan Jing Ke Xue = Huanjing Kexue 2020, 41, 4081–4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Liu, X.; Cheng, D.; Liu, G.; Liang, B.; Cui, B.; Bai, J. Temporal–spatial variation and partitioning prediction of antibiotics in surface water and sediments from the intertidal zones of the Yellow River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569–570, 1350–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diwan, V.; Hanna, N.; Purohit, M.; Chandran, S.; Riggi, E.; Parashar, V.; Tamhankar, A.J.; Stålsby Lundborg, C. Seasonal Variations in Water-Quality, Antibiotic Residues, Resistant Bacteria and Antibiotic Resistance Genes of Escherichia coli Isolates from Water and Sediments of the Kshipra River in Central India. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, K.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, W.; Pan, H.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Bobo, G.; Sweetman, A.; Lin, C.; Ouyang, W.; et al. Spatial and seasonal variations of antibiotics in river waters in the Haihe River Catchment in China and ecotoxicological risk assessment. Environ. Int. 2019, 130, 104919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maris, A.S.; Mody, P.; Brewer, D.J.; Humphries, R.M. The Fluoroquinolones: An Update for the Clinical Microbiologist. Clin. Microbiol. Newsl. 2021, 43, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Yang, Y.; Geng, C.; Tang, Z.; Wang, C.; Li, X. Norfloxacin versus alternative antibiotics for prophylaxis of spontaneous bacteria peritonitis in cirrhosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Inf. Dis. 2023, 23, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göbel, A.; McArdell, C.S.; Joss, A.; Siegrist, H.; Giger, W. Fate of sulfonamides, macrolides, and trimethoprim in different wastewater treatment technologies. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 372, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castiglioni, S.; Bagnati, R.; Fanelli, R.; Pomati, F.; Calamari, D.; Zuccato, E. Removal of pharmaceuticals in sewage treatment plants in Italy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, Q.; Huang, J.; Deng, S.; Chen, W.; Yu, G. Seasonal variation in the occurrence and removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in different biological wastewater treatment processes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 3341–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Xu, J.; Zhang, G.; Lu, S.; Liu, X.; Li, L.; Li, M. Occurrence of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in the Fuxian Lake and antibiotic source analysis based on principal component analysis-multiple linear regression model. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 127741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; You, E.; Zhong, Q.; Huang, F. Trends and seasonal variation of antibiotic consumption by community residents in Hefei, China, 2012–2016. Public Health 2023, 220, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, I.T.; Santos, L. Antibiotics in the aquatic environments: A review of the European scenario. Environ. Int. 2016, 94, 736–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, C.C.; Tan, D.T.; Arnold, W.A. Direct and indirect photolysis of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim in wastewater treatment plant effluent. Water Res. 2011, 45, 1280–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathon, B.; Coquery, M.; Miège, C.; Vandycke, A.; Choubert, J.M. Influence of water depth and season on the photodegradation of micropollutants in a free-water surface constructed wetland receiving treated wastewater. Chemosphere 2019, 235, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felis, E.; Kalka, J.; Sochacki, A.; Kowalska, K.; Bajkacz, S.; Harnisz, M.; Korzeniewska, E. Antimicrobial pharmaceuticals in the aquatic environment—Occurrence and environmental implications. Europ. J. pharmacol. 2020, 866, 172813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabilan, A.; Ledesma, D.G.B.; Horn, H.; Borowska, E. Mesocosm experiment to determine the contribution of adsorption, biodegradation, hydrolysis and photodegradation in the attenuation of antibiotics at the water sediment interface. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 866, 161385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smieja, M. Current indications for the use of clindamycin: A critical review. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 1998, 9, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spížek, J.; Řezanka, T. Lincosamides: Chemical structure, biosynthesis, mechanism of action, resistance, and applications. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 133, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B.; Chen, C.; Cheng, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, B.; Li, J. Antibiotic resistance genes in Chishui River, a tributary of the Yangtze River, China: Occurrence, seasonal variation and its relationships with antibiotics, heavy metals and microbial communities. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 846, 157472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hena, S.; Gutierrez, L.; Croué, J.-P. Removal of pharmaceutical and personal care products (PPCPs) from wastewater using microalgae: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 124041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, A.; Habibullah-Al-Mamun, M.; Nagano, I.; Masunaga, S.; Kitazawa, D.; Matsuda, H. Antibiotics, antibiotic-resistant bacteria, and resistance genes in aquaculture: Risks, current concern, and future thinking. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 11054–11075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhao, G.; Zhao, H.; Zhai, G.; Chen, J.; Zhao, H. Antibiotics in a general population: Relations with gender, body mass index (BMI) and age and their human health risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599–600, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, N.; Wang, B.; Zhao, Q.; Fang, H.; Fu, C.; Tang, C.; Jiang, F.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. Antibiotics in Drinking Water in Shanghai and Their Contribution to Antibiotic Exposure of School Children. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 2692–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Qiu, X.; Chen, B.; Yu, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhong, G.; Li, H.; Chen, M.; Sun, G.; Huang, H.; et al. Antibiotics pollution in Jiulong River estuary: Source, distribution and bacterial resistance. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 1677–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Li, J.; Yang, F.; Yang, J.; Yin, D. Prevalence of sulfonamide and tetracycline resistance genes in drinking water treatment plants in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 493, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Xu, Y.; Wang, H.; Guo, C.; Qiu, H.; He, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Meng, W. Occurrence of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in a sewage treatment plant and its effluent-receiving river. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 1379–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, Z.; Zeng, L.; Xu, T.; Sun, S.; Yan, S.; Yang, L.; Huang, Y.; Jia, J.; Dou, T. Antibiotic resistance genes in bacteria: Occurrence, spread, and control. J. Basic Microbiol. 2021, 61, 1049–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutiyar, P.K.; Mittal, A.K. Risk assessment of antibiotic residues in different water matrices in India: Key issues and challenges. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2014, 21, 7723–7736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Choi, K.; Park, S.; Choi, K. Hazard assessment of commonly used agricultural antibiotics on aquatic ecosystems. Ecotoxicology (London, England), 2008. Ecotoxicology 2008, 17, 526–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhuang, T.; Su, Z.; Chi, M.; Wang, H. Antibiotic residues in wastewaters from sewage treatment plants and pharmaceutical industries: Occurrence, removal and environmental impacts. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eguchi, K.; Nagase, H.; Ozawa, M.; Endoh, Y.S.; Goto, K.; Hirata, K.; Miyamoto, K.; Yoshimura, H. Evaluation of antimicrobial agents for veterinary use in the ecotoxicity test using microalgae. Chemosphere 2004, 57, 1733–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isidori, M.; Lavorgna, M.; Nardelli, A.; Pascarella, L.; Parrella, A. Toxic and genotoxic evaluation of six antibiotics on non-target organisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 346, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, T.; Nagase, H.; Eguchi, K.; Hirooka, T.; Nakamura, T.; Miyamoto, K.; Hirata, K. A novel method using cyanobacteria for ecotoxicity test of veterinary antimicrobial agents. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2007, 26, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, S.M.; Vasconcelos, E.C.; Dziedzic, M.; de Oliveira, C.M. Environmental risk assessment of antibiotics: An intensive care unit analysis. Chemosphere 2009, 77, 962–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, H.; Brain, R.A.; Johnson, D.J.; Wilson, C.J.; Solomon, K.R. Toxicity classification and evaluation of four pharmaceuticals classes: Antibiotics, antineoplastics, cardiovascular, and sex hormones. Toxicology 2004, 203, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Lee, S.E.; Lee, D.S.; Kim, Y.H. Risk assessment of human antibiotics in Korean aquatic environment. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2008, 26, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, B.; Carvalho, F.; Guilhermino, L. Acute toxicity of widely used pharmaceuticals in aquatic species: Gambusia holbrooki, Artemia parthenogenetica and Tetraselmis chuii. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2005, 61, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohedano, R.A.; Tonon, G.; Costa, R.H.R.; Pelissari, C.; Belli Filho, P. Does duckweed ponds used for wastewater treatment emit or sequester greenhouse gases? Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 691, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Delanka-Pedige, H.M.; Munasinghe-Arachchige, S.P.; Abeysiriwardana-Arachchige, I.S.; Smith, G.B.; Nirmalakhandan, N.; Zhang, Y. Removal of antibiotic resistance genes in an algal-based wastewater treatment system employing Galdieria sulphuraria: A comparative study. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 134435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raikova, S.; Smith-Baedorf, H.; Bransgrove, R.; Barlow, O.; Santomauro, F.; Wagner, J.L.; Allen, M.J.; Bryan, C.G.; Sapsford, D.; Chuck, C.J. Assessing hydrothermal liquefaction for the production of bio-oil and enhanced metal recovery from microalgae cultivated on acid mine drainage. Fuel Proces. Technol. 2016, 142, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, C.; Weisser, J.; Msigala, S.; Mdegela, R.; Jørgensen, S.E. Modelling antibiotics transport in a waste stabilization pond system in Tanzania. Ecol. Mod. 2015, 319, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Huang, L.; Wang, Q.; Zeng, H.; Xu, J.; Chen, Z. Antibiotics in aquaculture ponds from Guilin, South of China: Occurrence, distribution, and health risk assessment. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 112084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azanu, D.; Styrishave, B.; Darko, G.; Weisser, J.J.; Abaidoo, R.C. Occurrence and risk assessment of antibiotics in water and lettuce in Ghana. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622–623, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z. Antibiotic and antibiotic resistance genes in freshwater aquaculture ponds in China: A meta-analysis and assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 329, 129719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargenti, M.; Bartolacci, S.; Luciani, A.; Di Biagio, K.; Baldini, M.; Galarini, R.; Giusepponi, D.; Capuccella, M. Investigation of the Correlation between the Use of Antibiotics in Aquaculture Systems and Their Detection in Aquatic Environments: A Case Study of the Nera River Aquafarms in Italy. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Antibiotic Class | Antibiotic Compounds | CAS Number | Molecular Formula | Log Kow | pKa | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11 Sulfonamides | Sulfamethoxazole (SMX) | 723–46–6 | 253.28 | 0.89 a | 1.85, 5.60 b | Veterinary/Human |
| Sulfamethazine (SMZ) | 57–68–1 | 278.32 | 0.89 a | 2.65, 7.65 b | Veterinary | |
| Sulfapyridine (SPY) | 144–83–2 | 249.27 | n.a | 1.98, 5.96 b | Human | |
| Sulfamethizole (SML) | 144–82–1 | 260.29 | n.a | n.a | Human | |
| Sulfathiazole (STL) | 72–14–0 | 255.28 | n.a | n.a | Veterinary/Human | |
| Sulfacetamide (STD) | 144–80–9 | 254.26 | n.a | n.a b | Veterinary/Human | |
| Sulfadiazine (SDZ) | 68–35–9 | 250.27 | −0.09 a | 2.00, 6.48 b | Veterinary/Human | |
| Sulfamonomethoxine (SMM) | 1220–83–3 | 311.33 | 0.7 a | n.a | Veterinary | |
| Sulfadimethoxine (SDM) | 1220–87–7 | 310.33 | n.a | n.a | Veterinary | |
| Sulfaquinoxaline (SQL) | 59–40–5 | 314.32 | n.a | n.a | Veterinary | |
| 1 Diaminopyrimidine | Trimethoprim (TMP) | 738–70–5 | 290.31 | 0.91 a | 3.23, 6.76 b | Veterinary/Human |
| 8 Fluoroquinolones | Ofloxacin (OFX) | 82419–36–1 | 361.38 | −0.39 a | 5.97, 8.28 b | Veterinary/Human |
| Norfloxacin (NFX) | 70458–96–7 | 319.34 | −1.03 a | 3.11, 6.10, 8.60, 10.5 b | Veterinary/Human | |
| Enrofloxacin (EFX) | 93106–60–6 | 359.39 | 0.7 a | 3.86, 6.19, 7.59, 9.86 b | Veterinary | |
| Ciprofloxacin (CPX) | 85721–33–1 | 331.34 | 0.28 a | 3.10, 6.14, 8.70, 10.5b | Veterinary/Human | |
| Fleroxacin (FLX) | 79583–68–1 | 346.33 | 1.12 a | n.a | Veterinary | |
| Difloxacin (DFX) | 98105–99–8 | 349.35 | 2.36 a | n.a | Human | |
| Lomefloxacin (LFLX) | 98079–51–7 | 362.36 | -0.3 a | 5.00, 5.87, 9.23 b | Human | |
| Sarafloxacin (SFX) | 98105–99–8 | 362.36 | n.a | n.a | Human | |
| 5 Macrolides | Roxithromycin (ROX) | 80214–83–1 | 837.94 | 2.75 a | 9.17 b | Veterinary/Human |
| Erythromycin (ERY) | 114–07–8 | 733–749 | 3.06 a | 8.9 b | Veterinary/Human | |
| Azithromycin (AZT) | 83905–01–5 | 749–767 | 4.02 a | 8.74, 9.45 b | Veterinary/Human | |
| Rifampicin (RFN) | 13292–46–1 | 822–823 | n.a | n.a | Veterinary/Human | |
| Tylosin (TYL) | n.a | 916–918 | 1.63 a | n.a | Veterinary | |
| 2 Tetracyclines | Oxytetracycline (OXY) | n.a | 460–475 | −0.9 a | 3.27, 7.32, 9.11 b | Veterinary/Human |
| Chlortetracycline (CLT) | n.a | 479–480 | −0.62 a | 3.30, 7.55, 9.15 b | Veterinary/Human | |
| others | Lincomycin (LIN) | 154–21–2 | 406–407 | 0.56 a | 7.60 b | Veterinary/Human |
| Clindamycin (CLN) | 18,323–44–9 | 714–716 | n.a | n.a | Veterinary/Human | |
| Chloramphenicol (CPL) | n.a | 323–325 | 1.14 a | 5.5 b | Veterinary/Human | |
| Thiamphenicol (TPL) | n.a | 356–358 | n.a | n.a | Veterinary | |
| Florfenicol (FFL) | n.a | 358–359 | n.a | n.a | Veterinary |
| Antibiotic Compounds | SPS | Waste Stabilization Pond | Waste Stabilization Pond | Aquaculture Pond | Waste Stabilization Pond | Aquaculture Pond | Aquaculture Pond |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| China | Tanzania | India | China | Ghana | China | Italy | |
| SMX | 10.51 | 336 | 0–2000 | 121.34 | 103–320 | 0.02–30,792 | 0.74 |
| SMZ | 19.37 | – | 20–120 | – | – | 0.02–162.5 | 0.1 |
| SPY | 6.93 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| SPZ | 12.2 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| STD | 7.19 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| SDZ | 0.42 | – | – | 138.75 | 0.02–984 | 145.06 | |
| TMP | 1.27 | 8480 | 3–710 | – | 31–255 | 0.02–106.7 | 34.5 |
| OFX | 22 | – | – | 189.57 | – | 0.38–2208 | – |
| NFX | 7.8 | – | 30–251,000 | 185.70 | – | 0.1–160.95 | 0.02 |
| EFX | 4.57 | – | 0–488 | 218.12 | – | 0.07–4863 | – |
| DFX | 0.47 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| LFXL | 0.94 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| ROX | 13.87 | – | – | – | – | 0.02–40.33 | – |
| ERY | 2.28 | – | 1.41–15.9 | – | 47–882 | – | 1.1 |
| AZT | 4.81 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| OXT | 6.29 | – | 110–4200 | – | 2.4–24 | 0.31–1015 | 18.2 |
| CLT | 6.82 | – | 0–600 | – | 6.0–19 | 0.1–670.04 | – |
| CLN | 8.78 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| LCN | 0.2 | – | 3.13–248.9 | – | – | – | – |
| FFL | 3.5 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Reference | This study | [85] | [1] | [86] | [87] | [88] | [89] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bavumiragira, J.P.; Yin, H.; Jin, W.; Fangninou, F.F.; Eheneden, I. Influence of Seasonal Variation in Antibiotic Concentration on the Fate and Transport of Antibiotics Within an Artificial Pond System. Water 2025, 17, 1363. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091363
Bavumiragira JP, Yin H, Jin W, Fangninou FF, Eheneden I. Influence of Seasonal Variation in Antibiotic Concentration on the Fate and Transport of Antibiotics Within an Artificial Pond System. Water. 2025; 17(9):1363. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091363
Chicago/Turabian StyleBavumiragira, Jean Pierre, Hailong Yin, Wei Jin, Fangnon Firmin Fangninou, and Iyobosa Eheneden. 2025. "Influence of Seasonal Variation in Antibiotic Concentration on the Fate and Transport of Antibiotics Within an Artificial Pond System" Water 17, no. 9: 1363. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091363
APA StyleBavumiragira, J. P., Yin, H., Jin, W., Fangninou, F. F., & Eheneden, I. (2025). Influence of Seasonal Variation in Antibiotic Concentration on the Fate and Transport of Antibiotics Within an Artificial Pond System. Water, 17(9), 1363. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091363







