Abstract
Posidonia oceanica is an endemic seagrass of the Mediterranean Sea, forming extensive meadows and providing valuable ecosystem services underwater as well as on the shore. P. oceanica constantly generates new leaves while shedding the older ones. The latter may be deposited on the shoreline, forming “banquettes” that exhibit variable thickness, ranging from a few centimeters to several meters. These deposits act as natural barriers against coastal erosion, preventing sand loss and dissipating wave energy. Moreover, the degradation of the washed-up leaves releases large amounts of nutrients, relevant for the coastal food web. However, the presence of banquettes in touristic areas is often perceived as a nuisance, thus leading to their removal by local administrations. This study proposes a multidisciplinary approach for the assessment of P. oceanica banquettes along the coastline of the Campania region (Southern Italy), estimating their biomass and the associated concentrations of nutrients and other chemical elements, with the final aim to assess the potential loss of natural capital and ecosystem services due to their removal. Regional estimates show that approximately 40 tons of C are stored annually in the beached biomass, representing a potential carbon loss associated with their removal. The results highlight the crucial role that P. oceanica banquettes play in the blue carbon cycle and provide valuable insights to support their sustainable management.
1. Introduction
The Posidonia oceanica is an endemic seagrass in the Mediterranean Sea, forming extensive meadows from shallow waters up to greater depths of 40 m []. P. oceanica beds play a crucial role in providing a wide range of ecosystem services (ES) [,,] including their carbon sequestration and storage capacity, for which the species is also referred to as the “green lung” of the Mediterranean Sea. The meadows cover approximately 1–2% of the seabed, for a total of about 1,224,707 hectares [], mainly distributed along coastal areas, where they are essential for the entire littoral dynamics. In fact, the presence of the meadows is important for sediment retention, and they contribute to the attenuation of hydrodynamic forces, reducing the impact of waves and bottom currents by as much as 75% under the surface of their leaves []. Moreover, P. oceanica constantly produces new leaves, shedding the older ones, which, depending on weather conditions, hydrodynamic characteristics, and coastline conformation, may be deposited on the shoreline, locally and seasonally []. These deposits, often mixed with sediments, may vary from scattered layers to extensive piles with varying thicknesses from a few centimeters up to several meters. These formations, known as P. oceanica “banquettes”, act as natural barriers against coastal erosion, preventing sand loss and dissipating the wave energy. Furthermore, they provide food resources for local fauna and serve as a habitat for numerous animal species, including amphipods, isopods, crabs, beetles, spiders, and burrowing bivalves [,]. Moreover, the degradation of the leaves generates nutrients, which usually show a significant increase within the top 150 cm of the accumulation []. These nutrients play a crucial role in supporting the functioning and productivity of coastal food webs.
P. oceanica meadows are protected under various European directives [,] and are designated within Natura 2000 sites. Still, their occurrence in coastal areas makes them particularly susceptible to human activities (i.e., maritime infrastructures, water pollution, illegal fishing, and anchoring) []. Impacts arise both directly, through physical damage to the meadows, and indirectly, through effects on water and sediment quality [,,]. Indeed, a decline in P. oceanica meadows has been reported [,,] revealing an alarming situation due to the consequent loss of ES, among which is protection from coastal erosion.
Moreover, the occurrence of P. oceanica banquettes in touristic areas is often perceived as a nuisance, discouraging the presence of visitors and leading local administrations to seek their removal and/or displacement [,], often using particularly damaging means (e.g., excavators and heavy-wheeled vehicles). Therefore, given the strong connection to tourism-related activities, it is also essential to increase public awareness regarding the importance of these formations.
Under current regulations, there are no official laws concerning the specific management of banquettes. Only general indications are provided by the Italian Ministry for Environment, Land and Sea Protection (MATTM), outlining a list of different possible management options []. According to these guidelines, reintroducing the biomass into the marine environment may represent the optimal management approach, helping to restore its natural cycle; in fact, the introduction of manmade structures (e.g., ports and protective barriers) reduces the strength of sea currents actually necessary for naturally returning the biomass to the sea. On-site maintenance of P. oceanica banquettes is another option, particularly recommended for highly degraded beaches. Translocating the beached biomass to nearby areas is also suggested, with the additional opportunity to return it to the original site immediately after the tourist season. This approach could help to prevent coastal erosion while balancing ecological preservation with tourism needs.
Despite several ecological benefits of these above-mentioned practices, the most common management strategy remains the disposal of banquettes in landfills, since they are still considered as “municipal waste” under current regulations. Alternatively, on-site burials may be taken into account, but it requires careful planning to avoid altering the natural stratigraphy of the beach.
Other sustainable options listed in the MATTM guidelines include the so-called “alternative uses” (e.g., bioenergy production, composting, and recycling), designed to convert the banquettes biomass into renewable energy, nutrient-rich material, and many other products. In this way, it may be possible to reduce landfill reliance and to contribute to circular economy initiatives.
However, each of these management strategies requires specific authorization from the MATTM itself and/or from local administrations, often difficult to obtain. Additionally, most of these procedures demand careful attention to ensure the biomass is properly separated from the trapped sediment and from any other anthropogenic waste often found within it. Lastly, each method incurs environmental impacts and economic costs that must be properly assessed for a more comprehensive understanding of potential environmental and economic benefits.
Although P. oceanica is protected by different European Directives, its dead leaves are not specifically mentioned, despite being part of its natural life cycle []. The latter also includes decomposition processes, which play a key role in the carbon cycle and in the release of other essential nutrients. Consequently, the common practice of removing banquettes from the beaches significantly alters these biogeochemical cycles [], reducing the associated natural capital stocks and their ability to provide essential ES.
With reference to the scientific interest in the topic, a review of the literature on P. oceanica banquettes was conducted using bibliometric network analysis [,], revealing recent research attention to the theme. The research, through the Scopus web search engine, produced only 74 published articles in the last twenty years. Figure 1 shows the temporal distribution of keywords in the scientific literature related to P. oceanica banquette. It shows a more recent focus (yellow cluster) on the concepts of “Ecosystem Services” and “Climate Change”, highlighting the current relevance of our study.
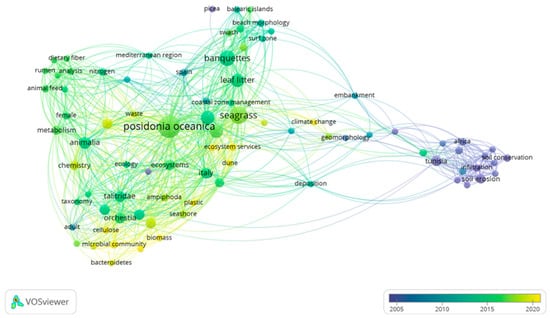
Figure 1.
Temporal distribution of keywords related to P. oceanica banquettes in the scientific literature, based on a color gradient, from blue (older publications) to yellow (more recent publications). Moreover, the larger the size of the items and the smaller the distance between them, the greater is the strength of correlation.
Given this premise, the goal of this study was to assess the biomass stocks and the associated concentrations of nutrients and other chemical elements in Posidonia oceanica banquettes along the coastline of the Campania region (Southern Italy), with the final aim to assess the potential loss of natural capital and ES due to their removal. Assessing and preserving banquettes is essential for raising awareness of their importance. These natural accumulations play a crucial role in maintaining coastal stability, supporting biodiversity, and regulating nutrient cycles. Monitoring banquettes contributes to the long-term resilience of coastal environments, helping them withstand climate change and human-induced disturbances.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The sites selected for the purpose of the present study are located along the Mediterranean coastline of the Campania region (SW Italy). This coastal area that extends approximately 500 km along the Tyrrhenian Sea hosts vigorous and widely distributed meadows of Posidonia oceanica. The study sites are distributed in 12 municipalities in the provinces of Napoli and Salerno, including Agropoli, Casal Velino, Castellabate, Forio, Ischia, Massa Lubrense, Montecorice, Pisciotta, Pollica, Santa Marina, San Giovanni a Piro, and Vibonati (Figure 2). The sampling site coordinates range from 40.7307° N, 15.8608° E in the northeast to 40.0516° S, 13.8608° W in the southwest. For each municipality, P. oceanica banquettes were detected, resulting in a total of 22 beaches of interest. Site selection was based on visual surveys conducted from a research vessel along the Campania coastline, aiming to identify areas with significant P. oceanica strandings and accumulations. Detected deposits were georeferenced for accurate mapping, followed by in situ samplings at these locations.
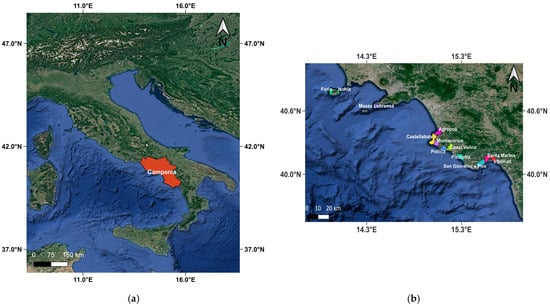
Figure 2.
(a) Campania region; (b) Municipalities where the deposition of banquettes was recorded.
2.2. Sampling Methods
Field sampling was conducted at each beach four times throughout the year to monitor the full seasonal cycle, spanning from spring 2022 to spring 2023. The field campaigns took place in April 2022 (Spring 2022, referred to as S22), November 2022 (Fall 2022, referred to as F22), January 2023 (Winter 2023, referred to as W23), and April 2023 (Spring 2023, referred to as S23) (Table 1). The summer season was excluded from the analysis because the 22 beaches of interest are popular tourist destinations. During this period, Posidonia oceanica banquettes are typically removed or relocated before the bathing season, significantly reducing their presence and visibility.

Table 1.
Surface areas (S, expressed in m2) and volumes (V, expressed in m3) of banquette assessed for each municipality and for different sampling campaigns.
On each investigated beach, one or more accumulations may have been identified. For each, GPS coordinates were recorded at multiple locations along the banquettes (starting edge, midpoint, and ending edge). To ensure an accurate spatial assessment, the length and width were also recorded with a measuring tape in the same locations, together with its thickness using a manual penetrometer. The collected data were then integrated into a GIS environment using Quantum GIS Desktop version 3.16.1, which facilitated the delineation of banquettes in terms of surface occupied and their volume.
In order to estimate the concentration of nutrients and other chemical compounds during each season, fresh samples of P. oceanica banquettes were collected in 2 L jars on five reference beaches in different municipalities: Acciaroli (Pollica), Agnone (Montecorice), Ischia (Ischia), Scario (San Giovanni a Piro), and Marina (Agropoli).
2.3. The Determination of Carbon, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Ions
After sample collection, demineralized water was used for washing to remove any residual salts, minimizing potential seawater interference and ensuring the accuracy of the measurements. Collected samples of P. oceanica banquettes were then dried in an oven at 60 °C for about 48 h until they reached a constant dry weight (DW). Dry weights (g) were converted into grams of carbon (gC) using a conversion factor of 0.36 []. The amounts of N and P were then calculated according to the ratio C:N:P of 41:7:1 [].
In the absence of an established method for analyzing Posidonia oceanica banquette samples, a methodology from previous studies on terrestrial samples was adopted []. A small aliquot of dried samples was finely ground to uniform powder. For the characterization of the water-soluble fraction, we performed, as a first step, an extraction with 20 mL of ultrapure water for each ground aliquot in a glass beaker, then sonicated, with ultrasonic vibrations extracting soluble components. After extraction, solutions were filtered through 0.45 and 0.2 μm filters and directly analyzed for ionic determination [,].
Ultrapure water solutions were analyzed using a Dionex ICS1100 system (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Sunnyvale, CA, USA). For anion detection, we used an ASRS 300-4 mm suppressor (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Sunnyvale, CA, USA) with a current of 33 mA, an AS22 column working with a cell volume of 100 μL, and a buffer solution, with 3.5 mM of sodium carbonate/bicarbonate as an eluent, at a flow rate of 1.20 mL/min; calibration curves were calculated using certified multistandard solutions. The anions detectable with this method include Cl−, F−, Br−, NO2−, NO3−, PO43−, and SO42− as inorganic species and HCOO−, CH3COO− and C2O42− as organic species. For cations we used a CERS 500-4 mm suppressor (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Sunnyvale, CA, USA) with a current of 15 mA, a CS12A column working with a cell volume of 25 μL, and 20 mM methanesulfonic acid solution as an eluent, at a flow rate of 0.25 mL/min; as for anions, calibration curves were defined using certified multistandard solutions. Cations detectable with this method are Li+, Na+, K+, NH4+, Ca2+, and M2+ [].
2.4. Statistical Analysis
To assess differences in elemental concentrations of banquette samples across sampling sites, inferential statistical methods were conducted using R Studio (version 4.3.2). Data normality was evaluated through the Shapiro–Wilk test. Due to the non-normal distribution of data, the non-parametric Kruskal–Wallis test was applied. A p-value below 0.05 (p < 0.05) was considered indicative of statistically significant differences. Owing to data limitations, nitrites, nitrates, and acetates were excluded from the analysis.
3. Results
3.1. Banquettes Biomass
Table 1 shows the total surface areas (m2) and volumes (m3) of P. oceanica banquettes assessed for each municipality at the time of the survey during the different field campaigns. Empty cells mean that banquettes were not detected for the municipality in that specific field campaign. The municipality of Castellabate in Spring 2022 showed the highest surface and volume values (9250.20 m2 and 6493.49 m3). The total surface and volume values also resulted in higher values in Spring 2022 (24,637.90 m2 and 16,738.22 m3).
3.2. The Assessment of Carbon, Nitrogen, Phosphorous, and Ions
The concentrations of C, N, and P, along with other chemical elements, were estimated by analyzing a total of 17 samples, each representing a reference season. These samples were collected from the following locations: Acciaroli, Agnone, Ischia, Scario, and Marina. Their concentrations (Table 2) are presented in grams per unit volume (g m−3). Empty cells indicate the absence of banquettes in the respective municipality during specific field campaigns. For all potential nutrients, the concentrations per unit volume were highest during the spring season. However, an exception was observed at Agnone in Spring 2023 (Agnone S23), where carbon levels were lower than in Fall 2022 (Agnone F22), though still higher than in Winter 2023 (Agnone W23), which had the site’s lowest recorded concentration (Table 2). In contrast, concentrations at Scario in Spring 2022 (Scario S22) were notably higher than at other sites (Table 2). For Ischia, the lowest concentrations were recorded in Fall 2022 (Ischia F22) (Table 2).

Table 2.
Concentrations of C, N, and P per unit volume at the sampled sites (g m−3). A hyphen in the cells mean no banquette was detected.
Table 3 shows the concentrations of elements and chemical compounds of 17 samples collected. The concentrations of some compounds (i.e., CH2COO−, NO2−, and NO3−) were found to be so low as to be undetectable by the instrument. In this case, the wording “<LOD” is recorded, meaning “Limit of Detection”, defined as the minimum concentration of an analyte that can be reliably detected (<0.02 mg g−1).

Table 3.
Seasonal concentration of chemical elements and compounds (mg g−1) at the selected sites of the study area. LOD: limit of detection. A hyphen in the cells mean no banquette was detected.
The most represented anion was chloride (Cl−), while the major cation was sodium (Na+) (Table 3). As for C, N, and P (Table 2), also ionic concentrations tend to be higher during the spring season among most sites (Table 3). However, an exception was observed at Ischia, where ion concentrations were generally higher during fall, except for nitrate (NO3−) and potassium (K+). Additionally, isolated instances were noted at Acciaroli and Agnone, where K+ and Ca2+, respectively, reached their highest seasonal values during the fall (Table 3).
To evaluate seasonal fluctuations, we also analyzed temporal variation in ion concentrations across the four seasons (Figure 3). Spatial variation (Figure 4) was assessed by analyzing the samples collected from five distinct coastal sites along the Campania coast: Acciaroli, Agnone, Ischia, Scario, and Marina. This dual approach aimed to explore the influence of environmental factors on the chemical composition of P. oceanica banquettes of the region.
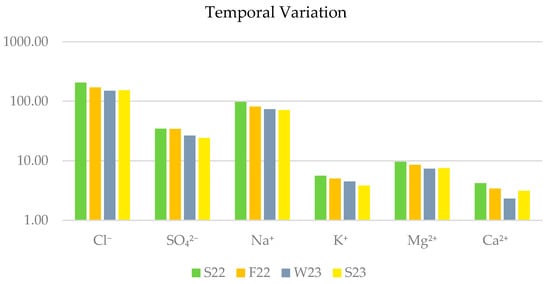
Figure 3.
Temporal variation of chemical elements concentration in Posidonia oceanica banquette.
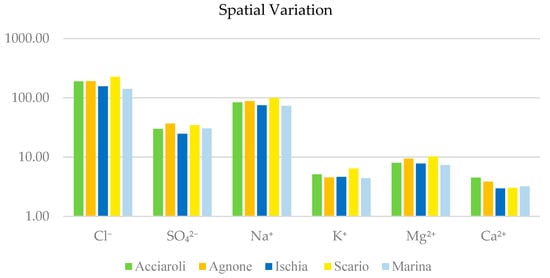
Figure 4.
Spatial variation of chemical elements concentration in Posidonia oceanica banquette.
Specifically, temporal variation was evaluated by averaging the concentrations of each anion across all sampling sites for each season. On the other hand, spatial variation was calculated by averaging the concentrations of each anion across all seasons for each sampling site. Figure 3 shows the temporal variation of the concentrations of six ions (Cl−, SO42−, Na+, K+, Mg2+, and Ca2+) measured across the four seasons. The concentrations are plotted on a logarithmic scale, facilitating the comparison of values across a wide dynamic range.
Among all ions, chloride consistently has the highest concentrations, reflecting its prevalence in coastal and semi-arid environments. Sodium maintained the second-highest concentration and showed seasonal variability. Sulfate decreased from S22 to S23. Potassium, magnesium, and calcium concentrations are relatively low and stable, with magnesium slightly exceeding both.
Figure 4 shows the spatial variation in the concentrations of six ions (Cl−, SO42−, Na+, K+, Mg2+, and Ca2+) across the five sampling sites along the Campania coast. As in the case of temporal variation, the concentrations are presented on a logarithmic scale.
Chloride concentrations are consistently the highest across all sites, with minor location variability. Sulfate levels remain relatively stable across sites, with a slight increase observed at Agnone and Scario. Sodium concentrations are consistently high and exhibit minimal spatial variation, mirroring the trends observed for chloride. Potassium and calcium exhibit lower concentrations than magnesium and significantly vary across sites.
3.3. Statistical Analysis Results
The statistical analysis of nutrient and chemical element concentrations showed no significant differences among samples (p-values > 0.05) with respect to both sampling site and season.
Table 4 and Table 5 show the p-values (p) for the various nutrients and chemical elements and compounds detected. In both tables, the term “Sites” refers to all the sampled locations grouped for the comparison. The concentrations of CH3COO−, NO2−, and NO3− were found to be <LOD; thus, they were not included in the statistical analysis.

Table 4.
Kruskal–Wallis analysis of the main elements with p-value values (p) > 0.05.

Table 5.
Kruskal–Wallis analysis of chemical elements with p-value values (p) > 0.05.
3.4. Natural Capital Stock Accounting
The statistical analysis results allowed the upscale of data to the entire regional scale of the Campania region (Table 6). The regional upscaling was obtained for all nutrients by taking into account the total estimated volume of Posidonia oceanica banquettes along the Campania coastline. The total carbon stocks represent the overall element content present annually during the specific season, taking into account all the recorded banquettes along the investigated coastline. For the spring season (the only season sampled twice), the volume values of S22 and S23 were averaged. Since the respective samples were collected during the same period in subsequent years (April 2022 and April 2023), they also represent an estimate of the annual storage in the investigated area. The total carbon stock resulted in 39.68 t in spring, 29.82 t in fall, and 12.61 t in winter.

Table 6.
Upscale of nutrient stocks associated with Posidonia oceanica banquettes in the Campania region, in the investigated seasons. Each total stock refers to the overall element concentration during the specific season, considering the entire Campania coastline.
Concerning the potential loss of natural capital and potential ecosystem services, the spring season was selected for the estimation, as it immediately precedes the tourist season and thus effectively represents the biomass that is typically removed. Therefore, results show that about 40 t of C, 7 t of N, and 1 t of P (Table 6) are stored in the banquette biomass that is annually removed along the Campania coastline.
Figure 5 shows the values of banquette biomass in each municipality during the spring season. The highest biomass values correspond to the highest carbon concentrations in each municipality, using a color gradient to visually indicate these variations. The color variation indicates that the municipality of Castellabate, distinguished by the darkest shade, has a higher carbon concentration, whereas the municipality of Pisciotta, with the lightest shade, demonstrates a lower carbon concentration.
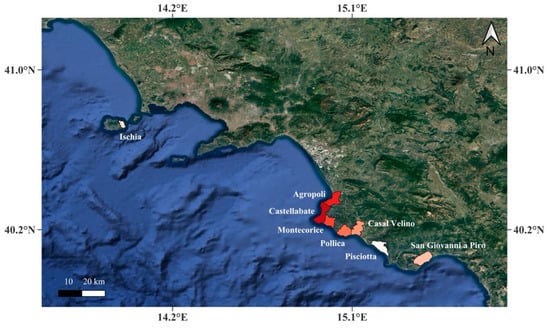
Figure 5.
Location of the municipalities where the depositions of banquettes were recorded along the coastline of the Campania region.
4. Discussion
The ecological significance of Posidonia oceanica extends beyond its living meadows to include its associated dead components, which contribute to temporary accumulations, such as banquettes [] and macerating bottoms []. These accumulations represent a substantial fraction of primary production exported by the wave and current action [], often overlooked in carbon budget assessments [].
Along the coast of the Campania region, as in other Mediterranean areas, banquettes primarily consist of the dead P. oceanica leaves and rhizome residues, along with a considerable portion of trapped sediments [,]. Despite their ecological importance, these seagrass deposits are often perceived negatively, particularly in the context of recreational beach use. Consequently, local administrators often authorize their removal [], leading to significant environmental implications, including the loss of carbon stocks that could be stored as blue carbon, as well as the loss of nutrients that could support primary production of coastal ecosystems []. Additionally, given the significant amount of trapped sediment, one direct consequence is increased coastal erosion []. Moreover, if the biomass is disposed of in landfills, biodegradation processes can release carbon into the atmosphere, further contributing to anthropogenic climate change [].
This study integrates chemical analyses with the assessment of natural capital stocks of P. oceanica banquette with the final aim to assess the potential loss of natural capital and ES due to their removal from beaches. Chemical analyses provide insights into the composition of P. oceanica banquettes along the Campania coast and reveal that chloride consistently has the highest concentrations (Table 3), reflecting its prevalence in coastal and semi-arid environments. The strong marine influence is also confirmed by the dominance of Cl- and Na+ across all sites.
In addition, the assessment of C, N, and P (Table 6) stored in the banquette biomass that is annually removed along the Campania coastline provides a proxy measure of the natural capital loss resulting from banquette removal.
The carbon content found in this study (Table 2) aligns with data published in previous studies []. In fact, Tommasello et al. [] investigated the important role played by P. oceanica banquette in the blue carbon exchange across land–ocean boundaries, providing estimates of carbon content ranging from 2.3 to 17.9 Kg m−3.
Results suggest that the sustainable management of P. oceanica banquettes could have meaningful implications on carbon sequestration and storage, and therefore, on climate change, at both local and global scales.
Finally, the absence of significant differences among sites in terms of element concentrations shows that it would be possible to reduce the intense sampling effort required to obtain field data on P. oceanica banquettes while ensuring the robustness of upscaling natural capital values at higher spatial levels. This would save both time and resources while still ensuring reliable and representative data.
5. Conclusions
The essential ES provided by Posidonia oceanica banquettes is often underrated, as the natural deposition of these formations in coastal areas is considered a nuisance, leading local authorities to prioritize their removal from public beaches to foster tourism activities. This results in a significant loss of natural capital and ES, mainly caused by the alteration of nutrient cycling in the coastal trophic web and an increase in coastal erosion.
The present study quantifies the biomass of P. oceanica banquettes and the associated concentrations of nutrients and other chemical elements along the coastline of the Campania region (Southern Italy). Laboratory analyses were conducted to determine concentrations of potential nutrients such as C, N, and P and other major soluble chemical elements, providing a comprehensive profile of banquette composition.
In addition, by integrating field data into a Geographic Information System (GIS) environment, this study provides a detailed characterization of Posidonia oceanica banquettes in terms of their distribution, surface area (m2), and volumes (m3).
The assessment of the potential loss of natural capital and ES due to the removal of banquettes from the coast was based on ad hoc samplings in the spring, since the biomass deposited during this season, which immediately precedes the tourist period, represents the biomass that is typically lost.
This research also introduces an innovative approach that integrates both chemical and ecological perspectives that could serve as a reference for larger-scale assessments, supporting the development of sustainable management strategies crucial to the health and functionality of coastal ecosystems.
Among the various potential management strategies, the reintroduction of banquette biomass into the marine environment appears to be the most ecological solution. This practice aligns with the natural cycle, counteracting the disruption caused by human-made structures, which have diminished the strength of sea currents essential for the natural return of biomass to the water. Nevertheless, a thorough assessment is required to determine the practical feasibility of this approach, with particular attention to resource consumption and logistical considerations.
In conclusion, this study highlights the need to apply sustainable management practices that recognize the ecological value of P. oceanica banquettes and aim to protect them.
Although our results provide valuable insights, there are some limitations that could be overcome in future studies. These include conducting direct C:N:P measurements to increase the accuracy of content estimates and incorporating vertical sampling, which could potentially reveal spatial variations in carbon storage within different layers of Posidonia oceanica banquettes.
Future developments of this study could also focus on environmental accounting models to assess environmental costs and impacts and the potential ecosystem services and disservices associated with the different management strategies. This would broaden its applicability, providing a robust set of multicriteria indicators to underscore the significant role of P. oceanica banquettes in the ecological balance of coastal ecosystems. Lastly, there is the need to raise public awareness of their importance, to promote a deeper knowledge of these vital ecosystems in all their forms, ultimately supporting their conservation and sustainable management.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.F.R. and E.B.; methodology, I.D. and L.C.; software, U.G.; validation, E.C. and L.C.; formal analysis, E.C., U.G., L.C., and I.D.; investigation, L.C.; data curation, I.D., L.C., U.G., and R.C.; writing—original draft preparation, I.D. and L.C.; writing—review and editing, P.P.F., G.F.R., and E.B.; supervision, E.B., G.F.R., and P.P.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The dataset is available from the authors upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Borum, J.; Duarte, C.M.; Greve, T.M.; Krause-Jensen, D. European Seagrasses: An Introduction to Monitoring and Management. Monitoring and Managing of European Seagrasses (M&MS) EVK3-CT-2000-00044, 2004; ISBN 8789143213. [Google Scholar]
- Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (MA). Ecosystems and Human Well Being: Synthesis; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hein, L.; van Koppen, K.; de Groot, R.S.; van Ierland, E.C. Spatial scales, stakeholders and the valuation of ecosystem services. Ecol. Econ. 2006, 57, 209–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonocore, E.; Grande, U.; Franzese, P.P.; Russo, G.F. Trends and Evolution in the concept of Marine Ecosystem Services: An Overview. Water 2021, 13, 2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telesca, L.; Belluscio, A.; Criscoli, A.; Ardizzone, G.; Apostolaki, E.T.; Fraschetti, S.; Gristina, M.; Knittweis, L.; Martin, C.S.; Pergent, G.; et al. Seagrass meadows (Posidonia oceanica) distribution and trajectories of change. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capasso, L.; Buonocore, E.; Franzese, P.P.; Russo, G.F. The scientific literature on Posidonia oceanica meadows and related ecosystem services. Ecol. Quest. 2023, 35, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Mateo, M.A.; Sanchez-Lizaso, J.L.; Romero, J. Posidonia oceanica ‘banquettes’: A preliminary assessment of the relevance for meadow carbon and nutrients budget. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2003, 56, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudouresque, C.F.; Bernard, G.; Bonhomme, P.; Charbonnel, E.; Diviacco, G.; Meinesz, A.; Pergent, G.; Pergent-Martini, C.; Ruitton, S.; Tunesi, L. Préservation et Conservation Des Herbiers à Posidonia Oceanica; Ramoge Publisher: Monaco, Monaco, 2006; pp. 1–202. ISBN 2-905540-30-3. [Google Scholar]
- De Matthaeis, E.; Ronci, L.; Davolos, D.; Campanaro, A.; Zapparoli, M. Faunistic assemblage of the supralittoral zone in the Thyrrhenian coast (Central Italy): The invertebrates inhabiting the Posidonia oceanica banquette. In Proceedings of the Management and Protection of Coasts, XIX World Water Day, Accademia dei Lincei, Rome, Italy, 22 March 2019. [Google Scholar]
- European Communities, Council. Council Directive 92/43/EEC on the Conservation of Natural Habitats and of Wild Fauna and Flora. Off. J. Eur. Communities 1992, L206, 7–50. [Google Scholar]
- The European Parliament and the Council of the European Union. Council Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council. Off. J. Eur. Communities 2000, L327, 1–73. [Google Scholar]
- Duarte, C.M. The future of seagrass meadows. Environ. Conserv. 2002, 29, 192–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montefalcone, M.; Lasagna, R.; Bianchi, C.N.; Morri, C.; Albertelli, G. Anchoring damage on Posidonia oceanica meadow cover: A case study in Prelo cove (Ligurian Sea, NW Mediterranean). Chem. Ecol. 2007, 22, S207–S217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montefalcone, M.; Parravicini, V.; Vacchi, M.; Albertelli, G.; Ferrari, M.; Morri, C.; Bianchi, C.N. Human influence on seagrass habitat fragmentation in NW Mediterranean Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2010, 86, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montefalcone, M.; Albertelli, G.; Morri, C.; Bianchi, C.N. Urban seagrass: Status of Posidonia oceanica facing the Genoa city waterfront (Italy) and implications for management. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2006, 54, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudouresque, C.F.; Bernard, G.; Pergent, G.; Shili, A.; Verlaque, M. Regression of Mediterranean seagrasses caused by natural processes and anthropogenic disturbances and stress: A critical review. Bot. Mar. 2009, 52, 395–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waycott, M.; Duarte, C.M.; Carruthers, T.J.B.; Orth, R.J.; Dennison, W.C.; Olyarnik, S.; Calladine, A.; Fourqurean, J.W.; Heck, K.L., Jr; Randall Hughes, A.; et al. Accelerating loss of seagrasses across the globe threatens coastal ecosystems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12377–12381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, T.F.; Elrick-Barr, C.E.; Thomsen, D.C.; Celliers, L.; Tissier, M.L. Impacts of tourism on coastal areas. Camb. Prism. Coast. Futures 2022, 1, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trégarot, E.; Catry, T.; Pottier, A.; El-Hacen, E.M.; Cheikh, M.a.S.; Cornet, C.C.; Maréchal, J.; Failler, P. Coastal protection assessment: A tradeoff between ecological, social, and economic issues. Ecosphere 2021, 12, e03364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotini, A.; Chiesa, S.; Manfra, L.; Borrello, P.; Piermarini, R.; Silvestri, C.; Cappucci, S.; Parlagreco, L.; Devoti, S.; Pisapia, M.; et al. Effectiveness of the “Ecological Beach” model: Beneficial management of Posidonia Beach casts and banquettes. Water 2020, 12, 3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of the Environment and Protection of the Territory and the Sea (MATTM). Gestione degli accumuli di Posidonia oceanica spiaggiati; Ministero dell’Ambiente e della Sicurezza Energetica (MASE): Roma, Italia, 2019. Available online: https://www.mase.gov.it/sites/default/files/archivio/allegati/rifiuti/circolare_rin_posidonia_8838_20052019.pdf (accessed on 3 April 2025).
- Boudouresque, C.F.; Pergent, G.; Pergent-Martini, C.; Ruitton, S.; Thibaut, T.; Verlaque, M. The necromass of the Posidonia oceanica seagrass meadow: Fate, role, ecosystem services and vulnerability. Hydrobiologia 2016, 781, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeone, S.; De Falco, G. Posidonia oceanica banquettes removal: Sedimentological, geomorphological and ecological implications. J. Coast. Res. 2013, 65, 1045–1050. [Google Scholar]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Manual for VOSviewer Version 1.6.8. CWTS Meaningful Metrics; Universiteit Leiden: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrigno, F.; Rendina, F.; Sandulli, R.; Russo, G. Coralligenous assemblages: Research status and trends of a key Mediterranean biodiversity hotspot through bibliometric analysis. Ecol. Quest. 2024, 35, 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Duarte, C.M. Seagrass nutrient content. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1990, 67, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redfield, A.C. The influence of organisms on the composition of seawater. In The Sea; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1963; Volume 2, pp. 26–77. ISBN 10: 0674017285. [Google Scholar]
- Frankowski, M. Simultaneous determination of inorganic and organic ions in plant parts of Betula pendula from two different types of ecosystems (Wielkopolski National Park and Chemical Plant in Luboń, Poland). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 11046–11057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Aquino, L.; Lanza, B.; Gambale, E.; Sighicelli, M.; Menegoni, P.; Modarelli, G.; Rimauro, J.; Chianese, E.; Nenna, G.; Fasolino, T.; et al. Growth and metabolism of basil grown in a new-concept microcosm under different lighting conditions. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 299, 111035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Aquino, L.; Cozzolino, R.; Nardone, G.; Borelli, G.; Gambale, E.; Sighicelli, M.; Menegoni, P.; Modarelli, G.C.; Rimauro, J.; Chianese, E.; et al. Effects of White and Blue-Red Light on Growth and Metabolism of Basil Grown under Microcosm Conditions. Plants 2023, 12, 1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudouresque, C.; Ponel, P.; Astruch, P.; Barcelo, A.; Blanfunè, A.; Geoffroy, D.; Thibaut, T. The high heritage value of the Mediterranean sandy beaches, with a particular focus on the Posidonia oceanica “banquettes”: A review. Sci. Rep. Port Cros Natl. Park 2017, 31, 23–70. [Google Scholar]
- Cocozza di Montanara, A.; Semprucci, F.; Rendina, F.; Russo, G.F.; Sandulli, R. Re-discovering macerating Posidonia oceanica bottoms: Characterization of meiofaunal community inhabiting a peculiar Mediterranean habitat. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2024, 309, 108956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, M.A.; Cebrián, J.; Dunton, K.H.; Mutchler, T. Carbon flux in seagrass ecosystems. In Seagrasses: Biology, Ecology and Conservation; Springer eBooks; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 159–192. [Google Scholar]
- Istituto Superiore per la Protezione e la Ricerca Ambientale (ISPRA). Formazione e gestione delle banquettes di Posidonia oceanica sugli arenili. Manuali Linee Guida ISPRA 2010, 55. Available online: https://www.isprambiente.gov.it/it/pubblicazioni/manuali-e-linee-guida/formazione-e-gestione-delle-banquettes-di (accessed on 3 April 2025).
- Chessa, L.A.; Fustier, V.; Fernandez, C.; Mura, F.; Pais, A.; Pergent, G.; Serra, S.; Vitale, L. Contribution to the knowledge of ‘banquettes’ of Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile in Sardinia Island. Biol. Mar. Mediterr. 2000, 7, 35–38. [Google Scholar]
- Manfra, L.; Chiesa, S.; Simeone, S.; Borrello, P.; Piermarini, R.; Agaoglou, C.; Elbour, M.; Zaaboub, N.; Vandarakis, D.; Kourliaftis, I.; et al. Towards Sustainable Management of Beach-Cast Seagrass in Mediterranean Coastal Areas. Sustainability 2024, 16, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roig-Munar, F.X.; Rodriguez-Perea, A.; Martin-Prieto, J.A.; Ferrer, B.G. Quantification of sediment loss due to the mechanical removal of berms of on the beaches of the Balearic Islands: Geomorphological consequences. Rev. Soc. Geol. Esp. 2019, 32, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Xu, T.; Feng, H.; Chen, S. Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Landfills: A Review and Bibliometric Analysis. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasello, A.; Bosman, A.; Signa, G.; Rende, S.F.; Andolina, C.; Cilluffo, G.; Cassetti, F.P.; Mazzola, A.; Calvo, S.; Randazzo, G.; et al. 3D-Reconstruction of a Giant Posidonia oceanica Beach Wrack (Banquette): Sizing Biomass, Carbon and Nutrient Stocks by Combining Field Data With High-Resolution UAV Photogrammetry. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 903138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).