A Systematic Review of Programs and Mechanisms for Industry Engagement in Flood Water Management: Global Challenges and Perspectives
Abstract
1. Introduction
- R.Q.1. What are the dominant strategies for industrial engagement in flood water management?
- R.Q.2. What are the main challenges in implementing these strategies, and how can they be overcome?
- R.Q.3. Who are the key researchers and what methodological approaches are most frequently applied in this field?
- R.Q.4. How do different types of infrastructure (blue-green, grey-blue) compare in terms of effectiveness in reducing flood risk?
- R.Q.5. What are the key research gaps and future opportunities for improving flood management through industrial cooperation?
2. Materials and Methods
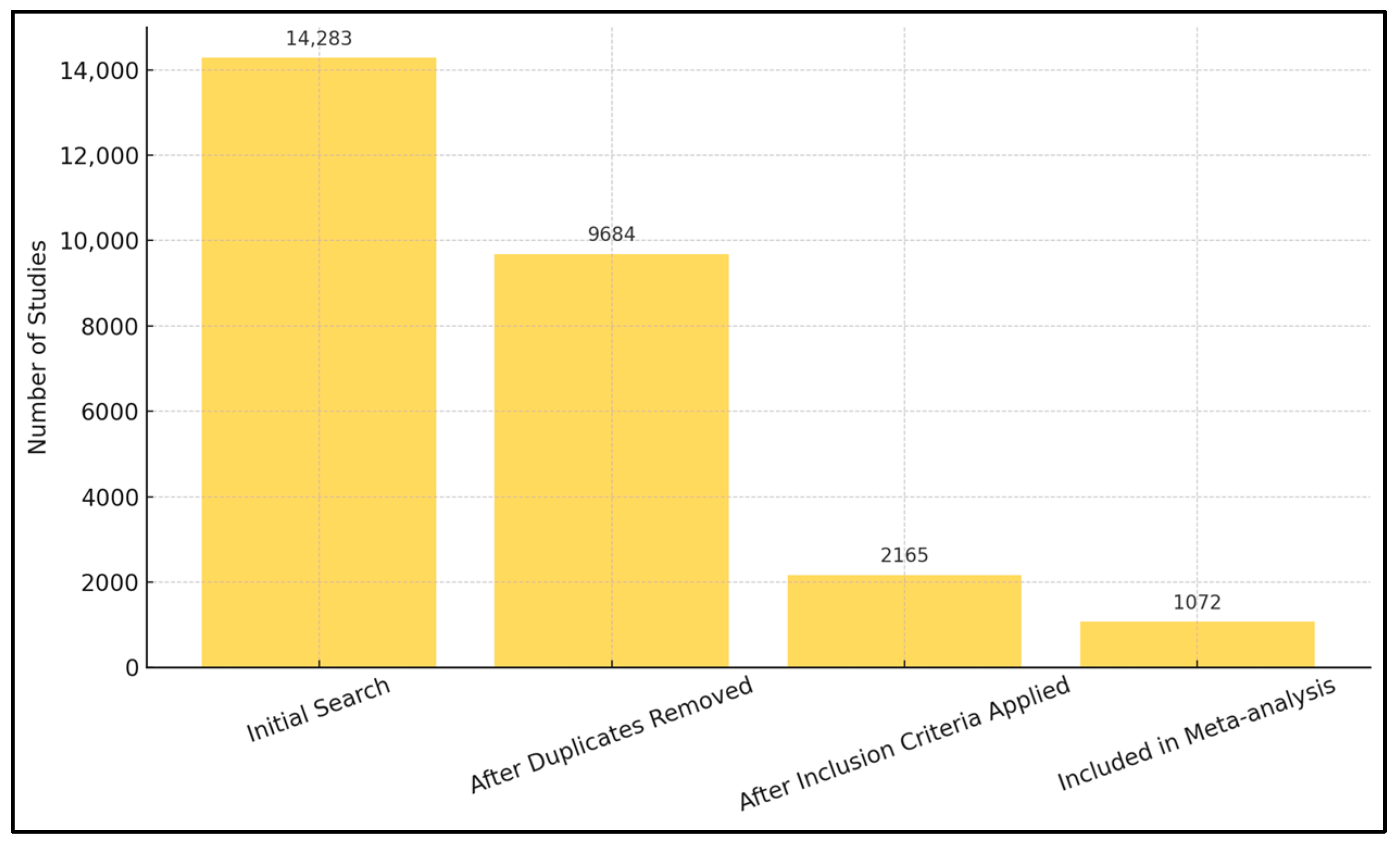
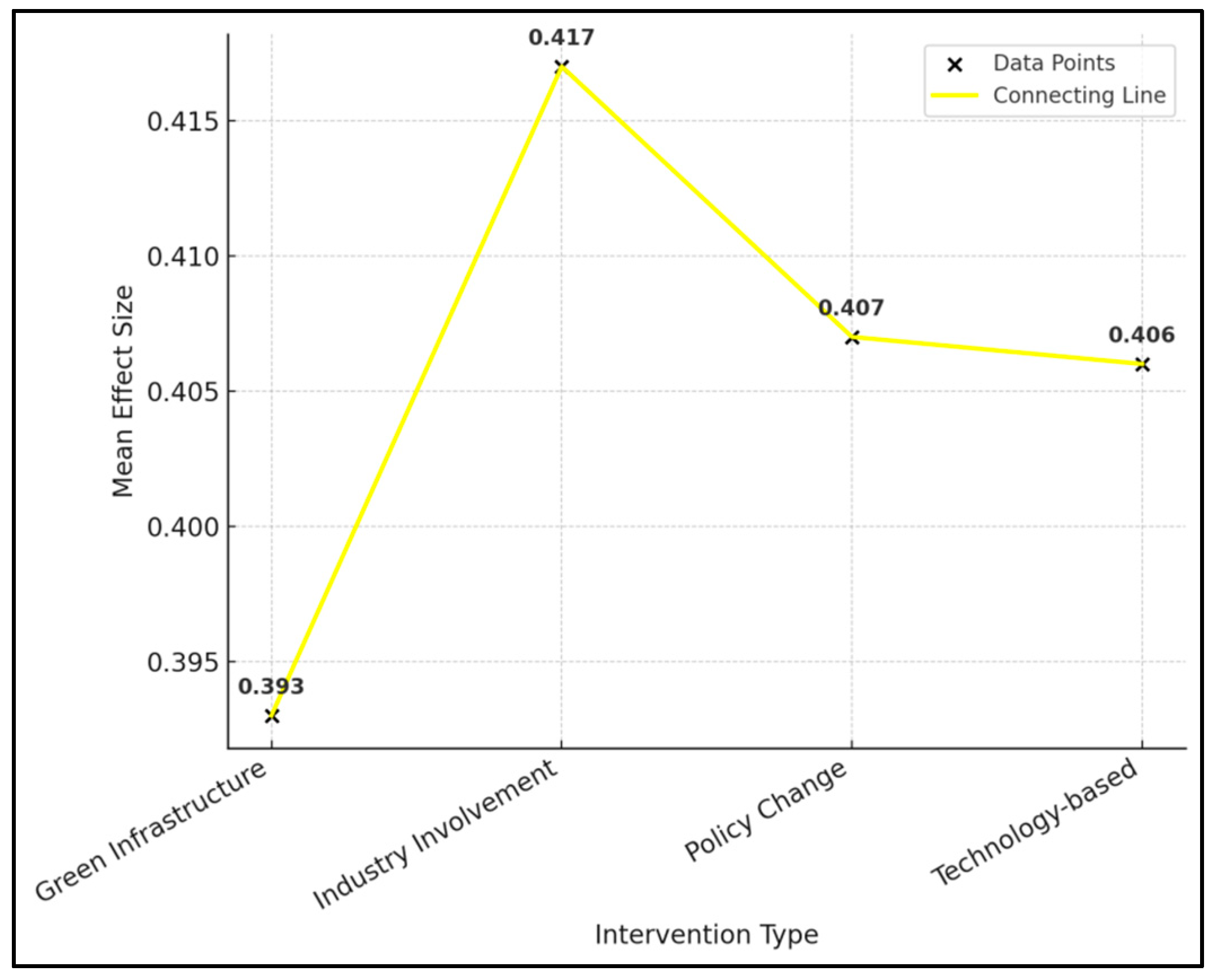
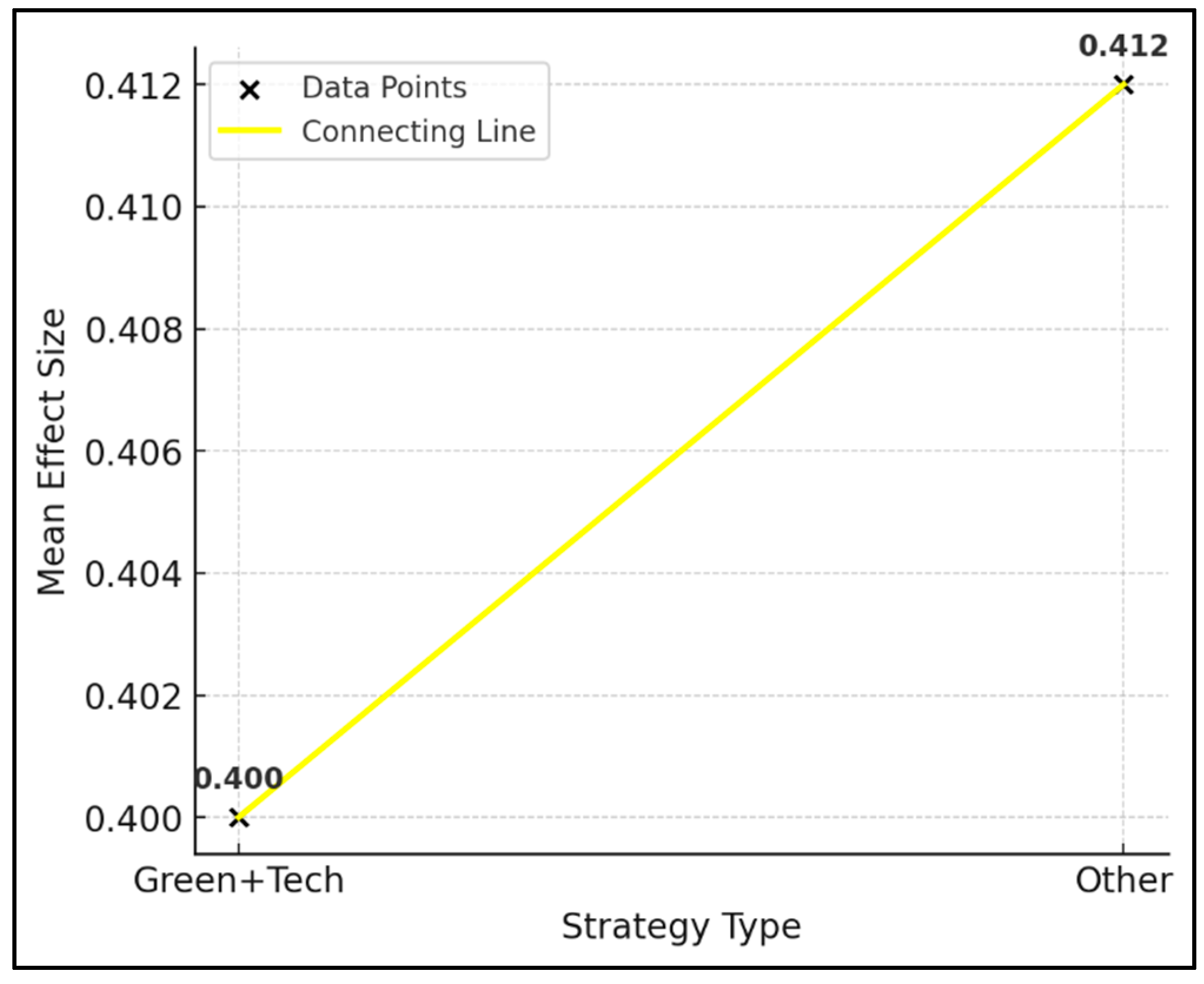
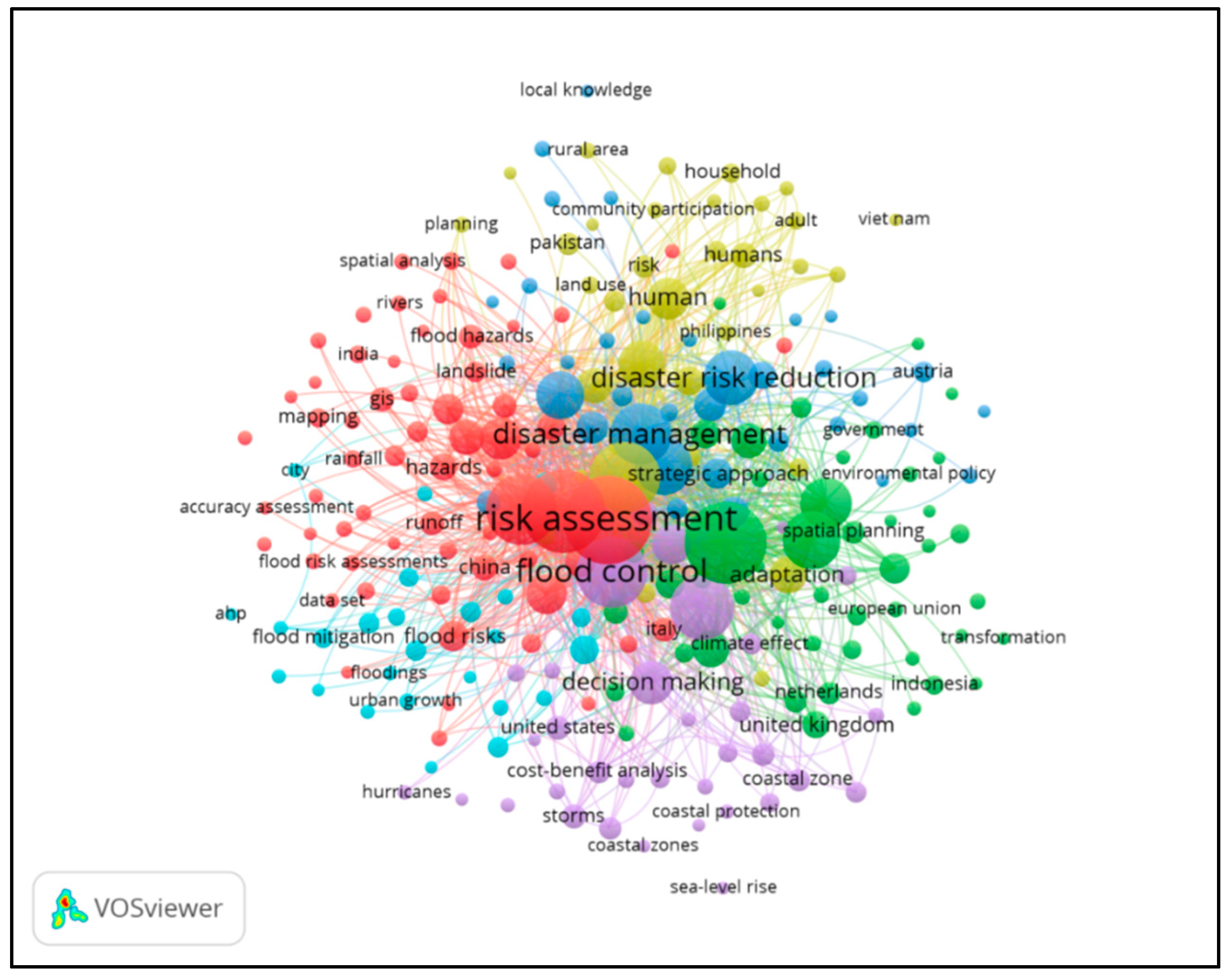
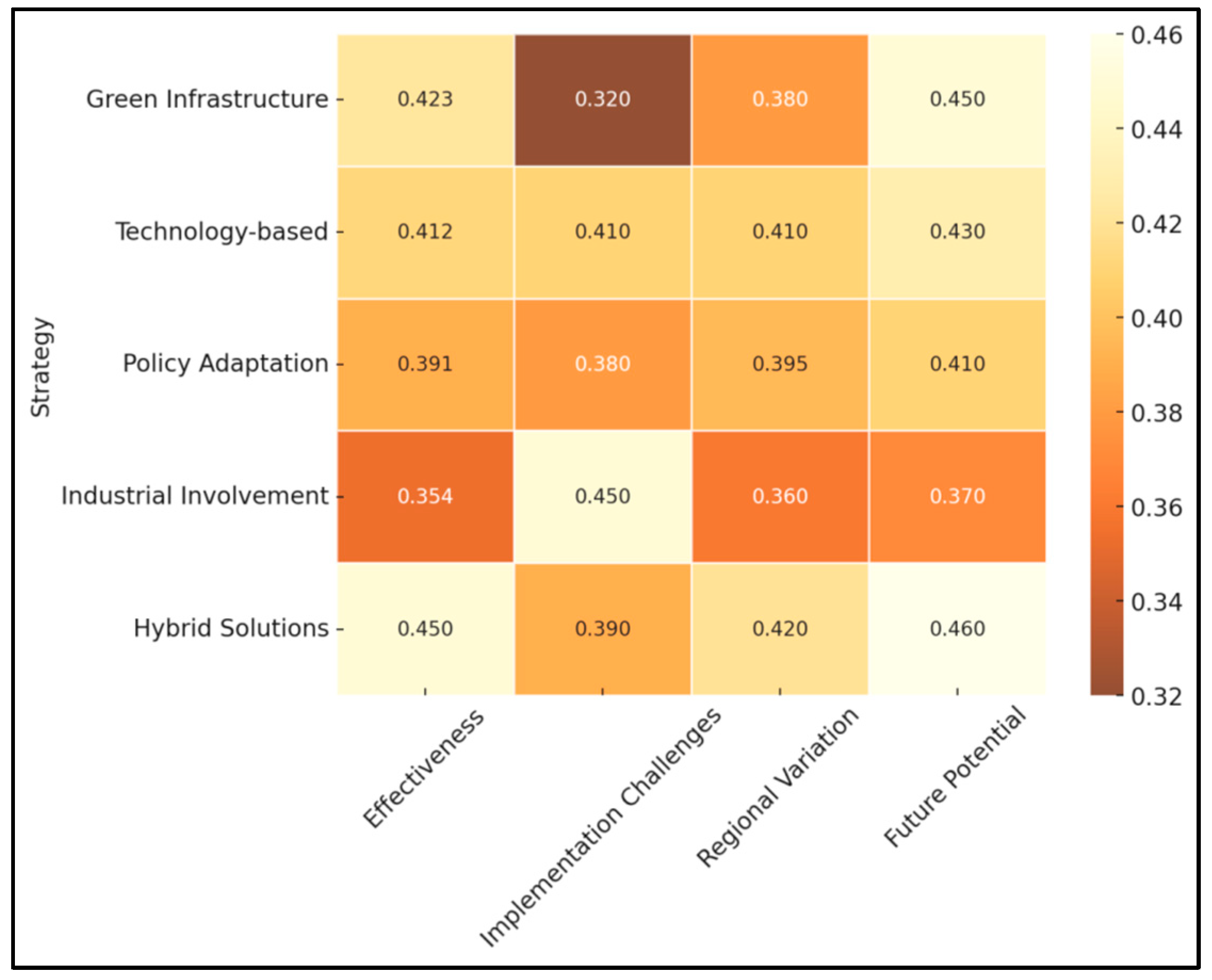
3. Results
Meta-Analysis
- -
- M1 and M2 represent the means of the experimental and control groups, respectively.
- -
- SDp is the pooled standard deviation.
- -
- N is the total sample size across all studies
- -
- Q represents the total amount of variation in effect estimates across studies.
- -
- df is the degrees of freedom.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wehn, U.; Rusca, M.; Evers, J.; Lanfranchi, V. Participation in flood risk management and the potential of citizen observatories: A governance analysis. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 48, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, A.; Gersonius, B.; Kapelan, Z.; Vojinovic, Z.; Sanchez, A. Assessing the Co-Benefits of green-blue-grey infrastructure for sustainable urban flood risk management. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 239, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fotovatikhah, F.; Herrera, M.; Shamshirband, S.; Chau, K.W.; Faizollahzadeh Ardabili, S.; Piran, M.J. Survey of computational intelligence as basis to big flood management: Challenges, research directions and future work. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 2018, 12, 411–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, A.; Vojinovic, Z.; Kapelan, Z.; Sanchez, A.; Gersonius, B. Exploring trade-offs among the multiple benefits of green-blue-grey infrastructure for urban flood mitigation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 134980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klijn, F.; Kreibich, H.; De Moel, H.; Penning-Rowsell, E. Adaptive flood risk management planning based on a comprehensive flood risk conceptualisation. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Chang. 2015, 20, 845–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechowska, E. What determines flood risk perception? A review of factors of flood risk perception and relations between its basic elements. Nat. Hazards 2018, 94, 1341–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, F.K.S.; Griffiths, J.A.; Higgitt, D.; Xu, S.; Zhu, F.; Tang, Y.T.; Thorne, C.R. “Sponge City” in China—A breakthrough of planning and flood risk management in the urban context. Land Use Policy 2018, 76, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zevenbergen, C.; Ma, Y. Urban pluvial flooding and stormwater management: A contemporary review of China’s challenges and “sponge cities” strategy. Environ. Sci. Policy 2018, 80, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josipovic, N.; Viergutz, K. Smart solutions for municipal flood management: Overview of literature, trends, and applications in German cities. Smart Cities 2023, 6, 944–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xiong, L.; He, S.; Wang, L.; Yu, Z. Opportunities and challenges of the Sponge City construction related to urban water issues in China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2017, 60, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, B.; Liang, Q.; Bosher, L.; Chen, H.; Nicholson, A. A systematic review of natural flood management modelling: Approaches, limitations, and potential solutions. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2023, 16, e12899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahiablame, L.; Shakya, R. Modeling flood reduction effects of low impact development at a watershed scale. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 171, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pour, S.H.; Abd Wahab, A.K.; Shahid, S.; Asaduzzaman, M.; Dewan, A. Low impact development techniques to mitigate the impacts of climate-change-induced urban floods: Current trends, issues and challenges. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 62, 102373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barasa, E.; Mbau, R.; Gilson, L. What is resilience and how can it be nurtured? A systematic review of empirical literature on organizational resilience. Int. J. Health Policy Manag. 2018, 7, 491–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenzweig, B.R.; McPhillips, L.; Chang, H.; Cheng, C.; Welty, C.; Matsler, M.; Davidson, C.I. Pluvial flood risk and opportunities for resilience. WIREs Water 2018, 5, e1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Brito, M.M.; Evers, M. Multi-criteria decision-making for flood risk management: A survey of the current state of the art. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 16, 1019–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebre, S.L.; Cattrysse, D.; Van Orshoven, J. Multi-criteria decision-making methods to address water allocation problems: A systematic review. Water 2021, 13, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloscious, A.A.; Artuso, M.; Torabi Moghadam, S. Nature-Based Solutions for Flood Mitigation: The Case Study of Kochi. Sustainability 2025, 17, 1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permanasari, E.; Wijaya, M.; Feliren, V.; Khikmah, F.; Lechner, A.; Virani, A.; Saputra, R. Enhancing urban resilience through integrated flood policy and planning: A mixed-methods evaluation of retention ponds for flood mitigation in South Bandung. AQUA—Water Infrastruct. Ecosyst. Soc. 2025, 74, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Liu, X.; Narayanasamydamodaran, S.; Pandey, K.K. A systematic review comparing urban flood management practices in India to China’s sponge city program. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adem Esmail, B.; Suleiman, L. Analyzing evidence of sustainable urban water management systems: A review through the lenses of sociotechnical transitions. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, T.; Mushtaq, S.; Reardon-Smith, K.; Webb, P.; Stone, R.; Kath, J.; An-Vo, D.A. Defining flood risk management strategies: A systems approach. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2020, 47, 101550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiwatari, M. Flood risk governance: Establishing collaborative mechanism for integrated approach. Prog. Disaster Sci. 2019, 2, 100014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, S.; Gonela, V. Rainwater harvesting for domestic use: A systematic review and outlook from the utility policy and management perspectives. Util. Policy 2022, 77, 101383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.; Scholten, L.; Kapelan, Z. A review of serious games for urban water management decisions: Current gaps and future research directions. Water Res. 2022, 215, 118217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dziekański, P.; Popławski, Ł.; Popławska, J. Interaction Between Pro-Environmental Spending and Environmental Conditions and Development. J. Geogr. Inst. Jovan Cvijić SASA 2024, 74, 329–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajić, T.; Vukolić, D.; Spasojević, A.; Blešić, I.; Petrović, M.D.; Bugarčić, J.; Bugarčić, M.; Drašković, B.D.; Milivojević, M. Exploring Attitudes on the Sustainable Balance Between Nature Conservation and Economic Development Through Ecotourism—Lessons from EU and Non-EU Countries. Land 2025, 14, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.K.; Mani, P.; Jain, S.K.; Prakash, P.; Singh, V.P.; Tullos, D.; Dimri, A.P. A Brief review of flood forecasting techniques and their applications. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2018, 16, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, Q.; Wang, H.; Deng, M. A machine learning ensemble approach based on random forest and radial basis function neural network for risk evaluation of regional flood disaster: A case study of the Yangtze River Delta, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, M.I.; Slater, L.; Tallaksen, L.M.; Clark, M. Challenges in modeling and predicting floods and droughts: A review. WIREs Water 2021, 8, e1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, S.N. Natural flood management. WIREs Water 2017, 4, e1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madani, K.; AghaKouchak, A.; Mirchi, A. Iran’s socio-economic drought: Challenges of a water-bankrupt nation. Iran. Stud. 2016, 49, 997–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadson, S.J.; Hall, J.W.; Murgatroyd, A.; Acreman, M.; Bates, P.; Beven, K.; Wilby, R. A restatement of the natural science evidence concerning catchment-based ‘natural’ flood management in the UK. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2017, 473, 20160706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvez, V.; Rojas, R. Collaboration and integrated water resources management: A literature review. World Water Policy 2019, 5, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Vaio, A.; Trujillo, L.; D’Amore, G.; Palladino, R. Water governance models for meeting sustainable development Goals: A structured literature review. Util. Policy 2021, 72, 101255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raikes, J.; Smith, T.F.; Jacobson, C.; Baldwin, C. Pre-disaster planning and preparedness for floods and droughts: A systematic review. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2019, 38, 101207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernyshev, K.A.; Alov, I.N.; Li, Y.; Gajić, T. How Real Is Migration’s Contribution to the Population Change in Major Urban Agglomerations? J. Geogr. Inst. Jovan Cvijić SASA 2023, 73, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorne, C.R.; Lawson, E.C.; Ozawa, C.; Hamlin, S.L.; Smith, L.A. Overcoming uncertainty and barriers to adoption of Blue-Green Infrastructure for urban flood risk management. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2018, 11, S960–S972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosmadi, H.S.; Ahmed, M.F.; Mokhtar, M.B.; Lim, C.K. Reviewing challenges of flood risk management in Malaysia. Water 2023, 15, 2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguez, M.G.; Mascarenhas, F.C.B.; Magalhães, L.D. Multifunctional landscapes for urban flood control in developing countries. WIT Trans. Ecol. Environ. 2025, 84, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weichselgartner, J.; Pigeon, P. The role of knowledge in disaster risk reduction. Int. J. Disaster Risk Sci. 2015, 6, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babcicky, P.; Seebauer, S. The two faces of social capital in private flood mitigation: Opposing effects on risk perception, self-efficacy and coping capacity. J. Risk Res. 2017, 20, 1017–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flood, S.; Cradock-Henry, N.A.; Blackett, P.; Edwards, P. Adaptive and interactive climate futures: Systematic review of ‘serious games’ for engagement and decision-making. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 063005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabortty, R.; Pal, S.C.; Ruidas, D.; Roy, P.; Saha, A.; Chowdhuri, I. Living with floods using state-of-the-art and geospatial techniques: Flood mitigation alternatives, management measures, and policy recommendations. Water 2023, 15, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Wang, X.C.; Ren, N.; Li, G.; Liang, H. Implementation of a specific urban water management—Sponge City. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Fonseca, M.N.; da Silva, L.P.; Tedim, F.M.S. Challenges and Opportunities Regarding Flood Risk Communication in Brazil. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2025, 119, 105292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekarwangi, P.A.; Cahyaningtyas, M.S.; Fakhriyah, F.; Ismaya, E.A. Systematic Literature Review (SLR): Model Pembelajaran Problem Based Learning (PBL) Terhadap Minat Belajar. J. Ilm. Profesi Guru 2024, 5, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gałdyn, F.; Sośnica, K. Impact of the combination and replacement of SLR-based low-degree gravity field coefficients in GRACE solutions. Prog. Earth Planet Sci. 2024, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Li, C. SLR-YOLO: An improved YOLOv8 network for real-time sign language recognition. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2024, 46, 1663–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simamora, S.C.; Gaffar, V.; Arief, M. Systematic literature review dengan metode PRISMA: Dampak teknologi blockchain terhadap periklanan digital. J. Ilm. M-Prog. 2024, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mewafarosh, R.; Naeem, F.; Malhan, S.; Agnihotri, S. Exploring the linkage between sustainability and well-being at the workplace: The PRISMA approach. Sustain. Dev. Green Econ. 2024, 114, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirani, Y.; Eitiveni, I.; Sucahyo, Y.G. Framework of Smart and Integrated Household Waste Management System: A Systematic Literature Review Using PRISMA. Sustainability 2024, 16, 4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blut, M.; Chaney, D.; Lunardo, R.; Mencarelli, R.; Grewal, D. Customer perceived value: A comprehensive meta-analysis. J. Serv. Res. 2024, 27, 501–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarmohammadi, F.; Wallace Hayes, A.; Karimi, G. Molecular mechanisms involved in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity: A bibliometrics analysis by VOSviewer. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2024, 397, 1971–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gersonius, B.; Ashley, R.; Pathirana, A.; Zevenbergen, C. Climate change uncertainty: Building flexibility into water and flood risk infrastructure. Clim. Chang. 2016, 133, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojinović, Z.; Abbott, M.B. Flood Risk and Social Justice: From Quantitative to Qualitative Flood Risk Assessment and Mitigation; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Tullos, D. How to achieve better flood-risk governance in the United States. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 3731–3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabisch, N.; Qureshi, S.; Haase, D. Human–environment interactions in urban green spaces—A systematic review of contemporary issues and prospects for future research. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2016, 50, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zevenbergen, C.; Veerbeek, W.; Gersonius, B.; Van Herk, S. Challenges in urban flood management: Travelling across spatial and temporal scales. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2018, 11, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, C.M.; Frantzeskaki, N.; Kabisch, N.; Berry, P.; Breil, M.; Nita, M.R.; Geneletti, D.; Calfapietra, C. A framework for assessing and implementing the co-benefits of nature-based solutions in urban areas. Environ. Sci. Policy 2017, 77, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisbois, M.C.; Morris, M.; de Loë, R.C. Augmenting the capabilities of impact assessments to enable learning for sustainability: Insights from resilience, transitions, and vulnerability frameworks. Environ. Sci. Policy 2019, 94, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Variable | Coefficient | Std. Error | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 0.399055 | 0.197013 | 0.042814 |
| South America | 0.009598 | 0.278148 | 0.972474 |
| Europe | −0.01038 | 0.27816 | 0.970232 |
| Africa | - | - | - |
| Asia | −0.01715 | 0.278138 | 0.950833 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Issakov, Y.; Shynbergenova, K.; Qasenuly, M.; Gajić, T.; Skakova, A. A Systematic Review of Programs and Mechanisms for Industry Engagement in Flood Water Management: Global Challenges and Perspectives. Water 2025, 17, 1155. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081155
Issakov Y, Shynbergenova K, Qasenuly M, Gajić T, Skakova A. A Systematic Review of Programs and Mechanisms for Industry Engagement in Flood Water Management: Global Challenges and Perspectives. Water. 2025; 17(8):1155. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081155
Chicago/Turabian StyleIssakov, Yerlan, Karlygash Shynbergenova, Murat Qasenuly, Tamara Gajić, and Aizhan Skakova. 2025. "A Systematic Review of Programs and Mechanisms for Industry Engagement in Flood Water Management: Global Challenges and Perspectives" Water 17, no. 8: 1155. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081155
APA StyleIssakov, Y., Shynbergenova, K., Qasenuly, M., Gajić, T., & Skakova, A. (2025). A Systematic Review of Programs and Mechanisms for Industry Engagement in Flood Water Management: Global Challenges and Perspectives. Water, 17(8), 1155. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081155









