Identification of Nitrate Sources in the Upper Reaches of Xin’an River Basin Based on the MixSIAR Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
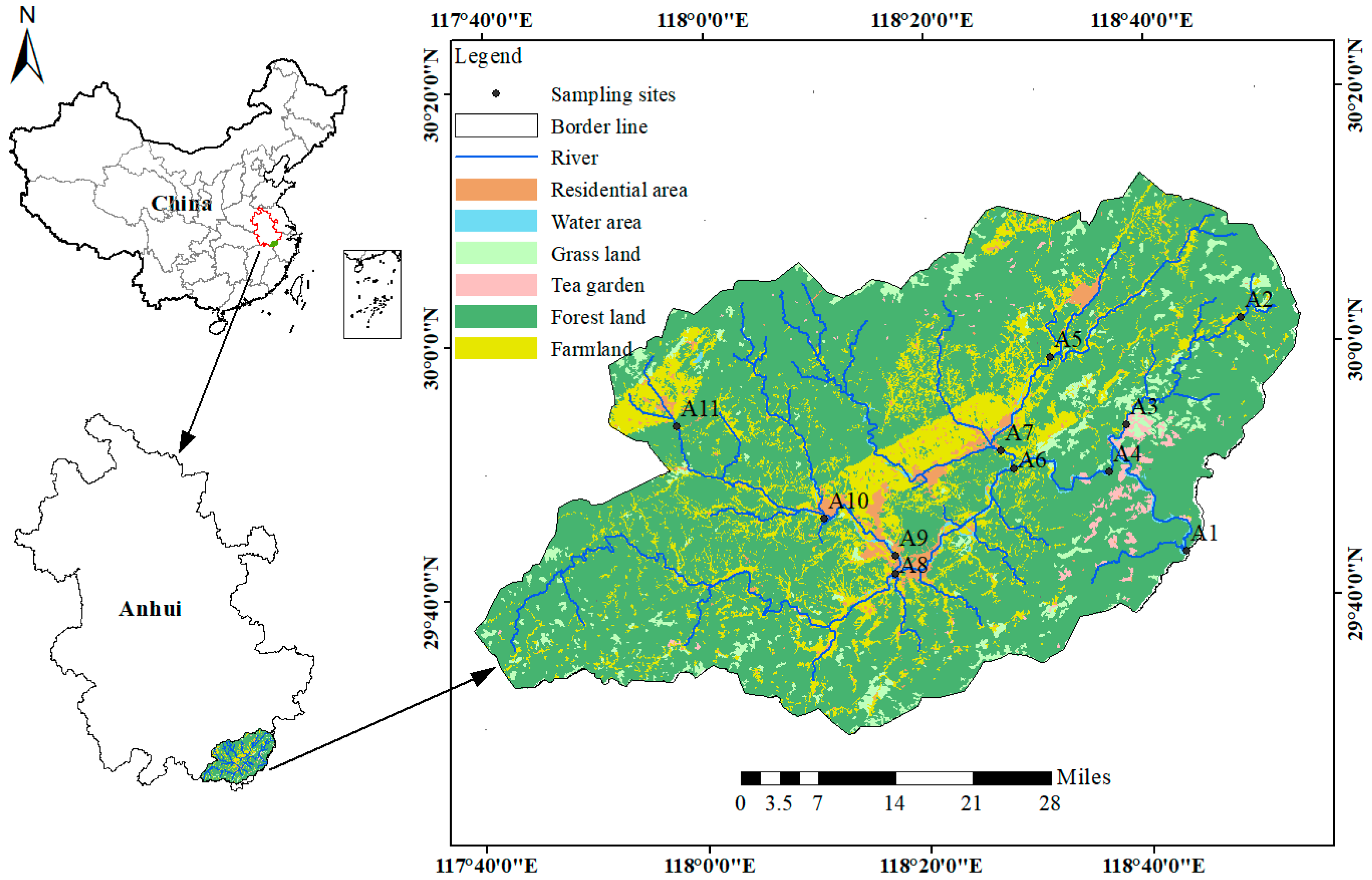
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Sample Collection and Method
2.3. MixSIAR Model
3. Results
3.1. Seasonal Variation in Nitrate Concentrations
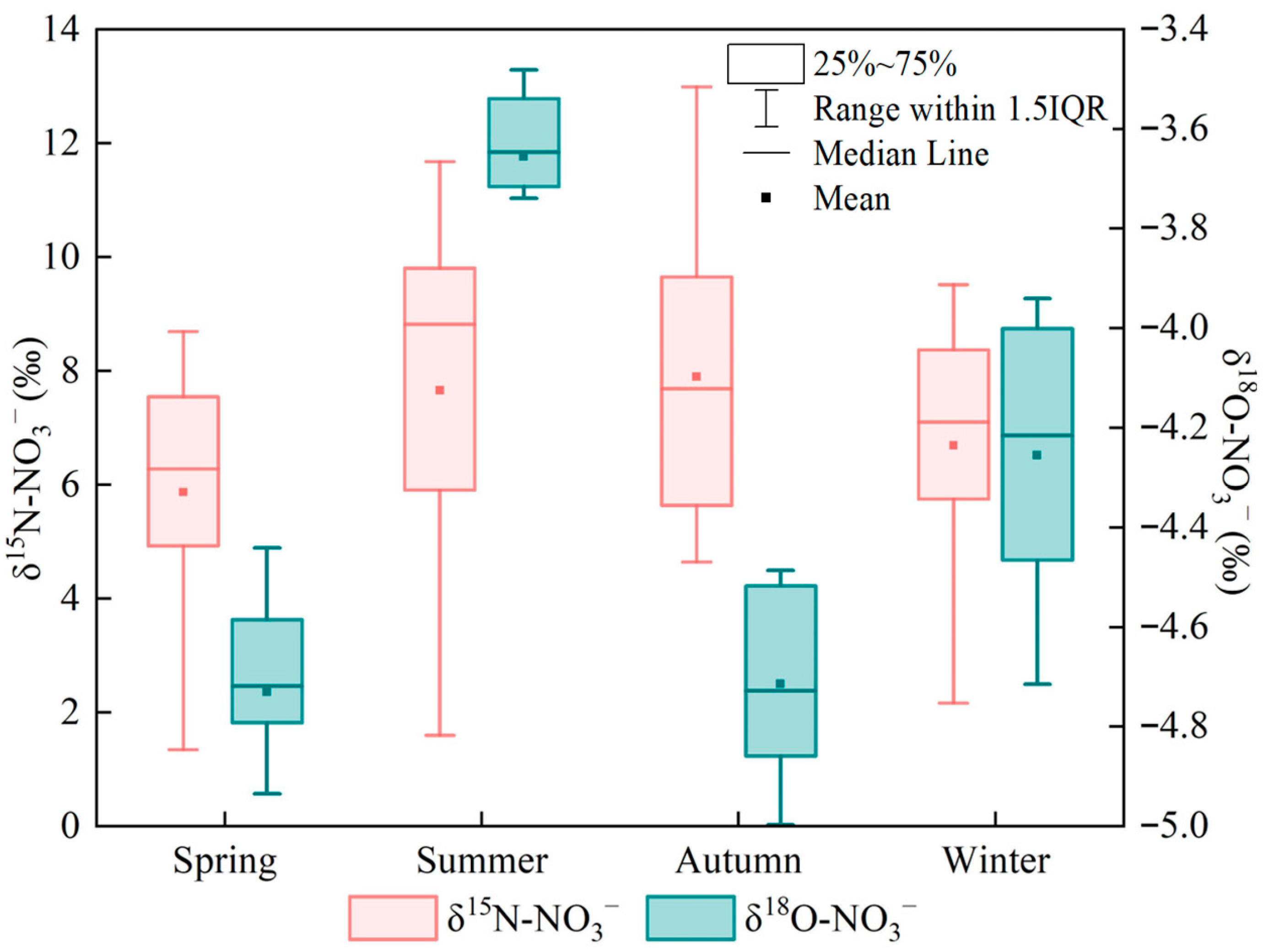
3.2. Seasonal Variability in Nitrate Isotope Signatures in the Upper Xin’an River Basin
3.3. Nitrate Source Apportionment
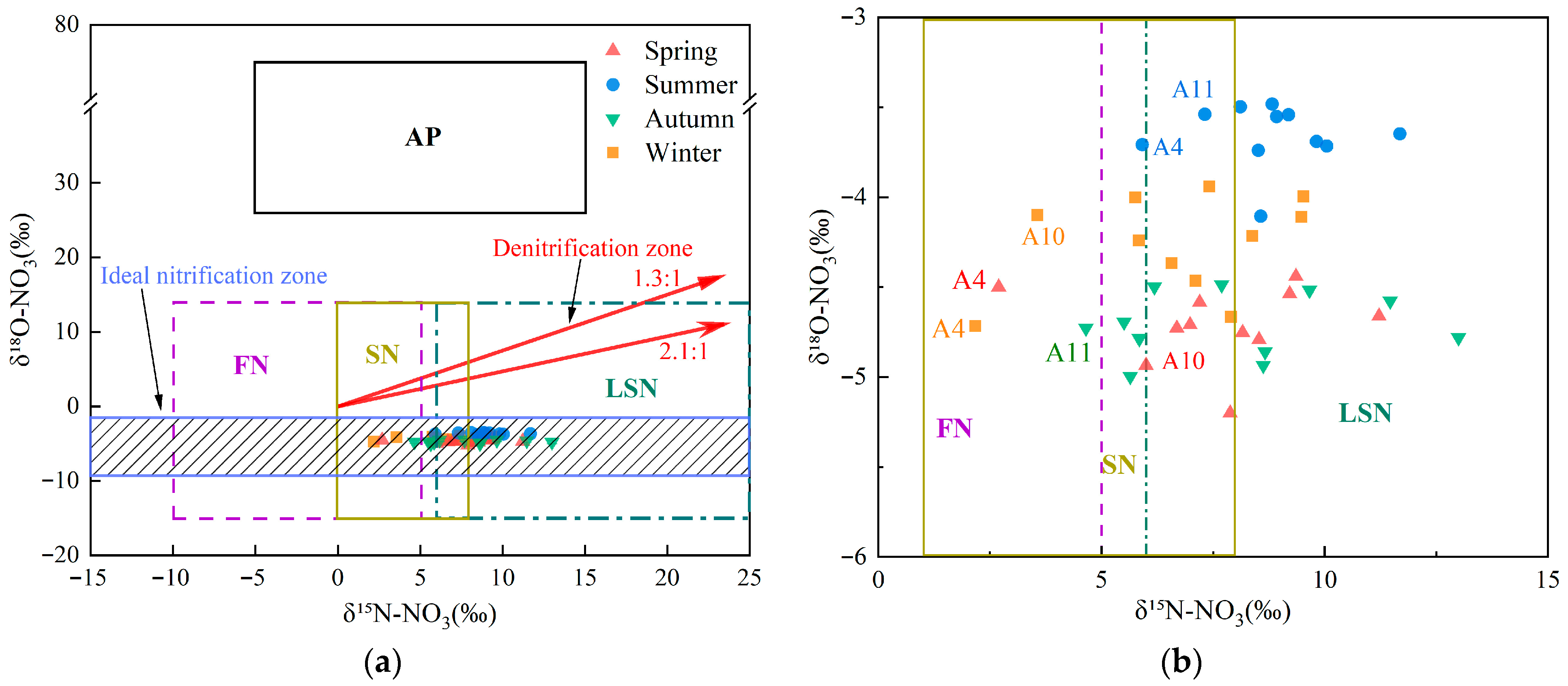
3.4. Nitrate Transport and Transformation Processes
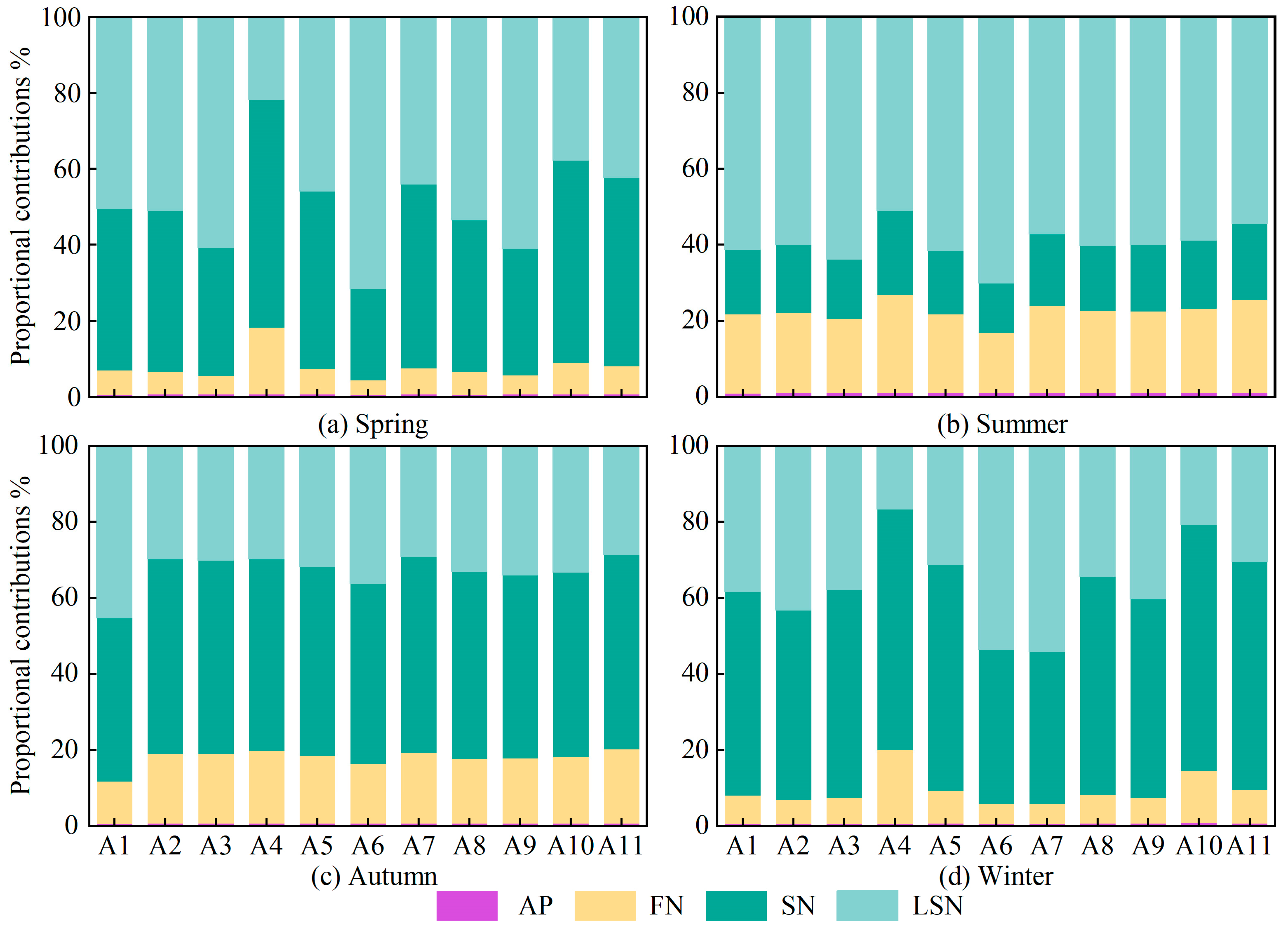
3.5. Quantifying Nitrate Source Contributions with the MixSIAR Model
4. Discussion
4.1. Uncertainties and Limitations
4.2. Comparison with Other Studies
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The concentrations of TN, NO3−-N and NH4+-N all exhibited significant seasonal differences (p < 0.05). In the upper Xin’an River basin, TN concentrations ranged from 0.72 to 4.08 mg/L (mean ± SD = 2.30 ± 0.48 mg/L). NO3−-N was the predominant form of inorganic nitrogen in the basin’s surface waters. Except in spring, when NO3−-N accounted for 48.9% of TN, NO3−-N contributed more than 72% of TN in the other three seasons.
- (2)
- In the upper Xin’an River basin, the mean δ15N–NO3− values among seasons followed the order summer > autumn > winter > spring. δ18O–NO3− exhibited significant seasonal differences (p < 0.05), with mean values following the order summer > winter > autumn > spring. Nitrate in the study area mainly originated from fertilizers, soil nitrogen, and livestock/sewage manure inputs, and its transformation processes within the basin were dominated by nitrification.
- (3)
- The MixSIAR results showed that LSN was the main nitrate source in spring and summer, with contributions of 49.2% and 59.9%, respectively; SN dominated in autumn (49.2%) and winter (54.1%); and FN made relatively high contributions in summer (21.5%) and autumn (17.3%). The contribution of AN was negligible in all seasons.
- (4)
- In summer and autumn, the contributions of LSN, SN and FN showed only minor variability among monitoring sites, whereas in spring and winter they differed markedly between sites. At monitoring sites located in areas with intensive human activities and livestock farming, LSN made the largest contribution, whereas in areas with intensive agricultural activity, SN and FN were the primary sources.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, W.M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.Q.; Zhang, W.R. Sources and health risks of nitrate pollution in surface water in the Weihe River watershed, China. J. Mt. Sci. 2022, 19, 2226–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Wang, N.; Guo, Y.X. Research Hotspots and Trends of Lake Ecosystem Services Based on Bibliometric Analysis. Environ. Sci. Res. 2024, 37, 1253–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, D.M.; De Baets, B.; Van Cleemput, O.; Hennessy, C.; Berglund, M.; Boeckx, P. Use of a Bayesian isotope mixing model to estimate proportional contributions of multiple nitrate sources in surface water. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 161, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nestler, A.; Berglund, M.; Accoe, F. Isotopes for improved management of nitrate pollution in aqueous resources: Review of surface water field studies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2011, 18, 519–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Bi, Z.L.; Shan, Z.X.; Ren, L.J.; Li, Q. Distribution and Sources of Nitrate in Surface Water of China. Environ. Sci. 2020, 41, 1594–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.T.; Xi, B.D.; Xu, Q.G.; Gao, R.T.; Lu, Y.; Huang, J.; Liu, H.L. Application of stable isotope techniques in the study of nitrate pollution in surface water. J. Lake Sci. 2013, 25, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.Q.; Niu, Y.; Yu, H.; Gou, P.; Hou, Q.Y.; Lu, X.F.; Wu, Y.L. Effect of rainfall-runoff process on sources and transformations of nitrate using a combined approach of dual isotopes, hydrochemical and Bayesian model in the Dagang River basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 837, 155674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.N.; Xu, H.; Jiang, W.; Zhan, X.; Zhu, G.W.; Sun, H.W.; Zhang, Y.L. Source apportionment of nitrate in typical mountainous rivers of the Qiandao Lake watershed based on nitrogen and oxygen isotope techniques. Environ. Sci. 2025, 46, 2232–2241. Available online: https://www.hjkx.ac.cn/hjkx/ch/html/20250426.htm (accessed on 10 September 2025).
- Zhang, J.; Cao, M.D.; Jin, M.G.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Z.X.; Kang, F.X. Identifying the source and transformation of riverine nitrates in a karst watershed, North China: Comprehensive use of major ions, multiple isotopes and a Bayesian model. J. Contam Hydrol. 2022, 246, 103957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Li, Y.L.; Chen, Y.M.; Li, X.; Ren, S.H. Analysis of spatiotemporal distribution and sources of nitrogen in the lower Qinhe River using nitrogen and oxygen isotope techniques. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2025, 45, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, D.M.; Botter, J.; De Baets, B.; Accoe, F.; Nestler, A.; Taylor, P.; Boeckx, P. Present limitations and future prospects of stable isotope methods for nitrate source identification in surface- and groundwater. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1159–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, C.; Elliott, E.M.; Wankel, S.D. Tracing Anthropogenic Inputs of Nitrogen to Ecosystems. In Stable Isotopes in Ecology and Environmental Science, 2nd ed.; Michener, R., Lajtha, K., Eds.; Blackwell Publishing: Malden, MA, USA, 2007; pp. 231–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Gao, H.B.; Long, B.; Wu, J.F. Research progress in tracing nitrate pollution in groundwater by coupling nitrate isotopes with multiple tracers. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2024, 35, 970–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.Y.; Ma, Y.Y.; Li, G.W.; Tang, W.Z.; Du, C.L. Research progress in the application of stable isotope techniques to the analysis of nitrate pollution sources in water bodies. J. Environ. Eng. Technol. 2023, 13, 1373–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, M.F.; Reichert, P.; Bernasconi, S.M.; Barbieri, A.; McKenzie, J.A. Modelling nitrogen and oxygen isotope fractionation during denitrification in a lacustrine redox-transition zone. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2003, 67, 2529–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granger, J.; Wankel, S.D. Isotopic overprinting of nitrification on denitrification as a ubiquitous and unifying feature of environmental nitrogen cycling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E6391–E6400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohl, D.H.; Shearer, G.B.; Commoner, B. Fertilizer Nitrogen: Contribution to Nitrate in Surface Water in a Corn Belt Watershed. Science 1971, 174, 1331–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Chen, D. Coupling stable isotopes and water chemistry to assess the role of hydrological and biogeochemical processes on riverine nitrogen sources. Water Res. 2019, 150, 418–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, T.; Li, Z.; Lu, L.H.; Wang, L.W.; He, W.F.; Zhang, Y.Y. Research progress and prospects of stable isotope mixing models. Earth Environ. 2025, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saka, D.; Antwi, E.O.; Skrzypek, G.; Adu-Gyamfi, J.; Heng, L.; Attiogbe, F. Tracing sulfate sources in a tropical agricultural catchment with a stable isotope Bayesian mixing model. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.W.; Semmens, B.X. Incorporating uncertainty and prior information into stable isotope mixing models. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, B.C.; Jackson, A.L.; Ward, E.J.; Parnell, A.C.; Phillips, D.L.; Semmens, B.X. Analyzing mixing systems using a new generation of Bayesian tracer mixing models. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.N.; Cui, J.J.; Bai, L.Y.; Yu, X.J.; Dai, J.L. Research progress on methods for nitrate source apportionment in watershed water environment. Environ. Eng. 2023, 41, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Hu, Q.; Shen, W.; Guo, J.; Yang, L.; Yuan, Q.; Lu, X.; Wang, L. Identification of nitrate sources of groundwater and rivers in complex urban environments based on isotopic and hydro-chemical evidence. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 871, 162026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.L.; Liu, S.L.; Wan, H.Y.; Yan, K.; Tao, Y.J.; Wang, H.S. Analysis of nitrate sources in surface water of northern Yantai based on nitrogen and oxygen isotopes and MixSIAR model. China Geol. 2024, 51, 2066–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.C.; Xu, H.; Yu, J.; Liu, M.L.; Shan, L.; Cheng, X.L.; Kang, L.J. Impact of urban distribution on nutrient concentrations in the Xin’an River system and Qiandao Lake. Res. Environ. Sci. 2022, 35, 864–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Wang, J.Y.; Luan, B.J.; Wang, S.R.; Huo, Z.G. Source tracing analysis of nitrogen in the upper reach of Xin’an River Basin based on SWAT model. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 175, 113554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.Q. Analysis of nitrogen and phosphorus pollution and countermeasures in the Xin’an River Basin of Huangshan City. J. Green Sci. Technol. 2022, 24, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.F.; Hu, R.H.; Fang, M. Ecological hidden dangers and prevention of water resources in the Xin’an River Basin. Anhui Agric. Sci. Bull. 2014, 20, 101–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.C.; Xu, H.; Kang, L.J.; Zhu, G.; Paerl, H.W.; Li, H.; Liu, M.; Zhu, M.; Zou, W.; Qin, B.; et al. Nitrate sources and transformations in a river-reservoir system: Response to extreme flooding and various land use. J. Hydrol. 2024, 638, 131491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Wu, N.; Fang, J.L.; Gao, J.X.; Zhou, X.T.; Feng, C.Y. Ecosystem services and their value for reducing phosphorus non-point source pollution in the upper Xin’an River. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2015, 26, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cai, J.; Yuan, H.W.; Xu, L.H.; Wei, Z.Z.; Chen, X.Y. Spatio-temporal evolution and multi-scenario prediction of habitat quality in the Xin’an River Basin. J. Yunnan Agric. Univ. (Soc. Sci.) 2022, 16, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.; Liu, X.H.; Xiao, Y.X.; Luo, R.L.; Pang, J.Y.; Cheng, H.X. Analysis and prediction of spatiotemporal changes of ecosystem carbon storage in the Xin’an River Basin based on PLUS and InVEST models. Geoscience 2024, 38, 574–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.R.; Zeng, Q.M.; Chen, L.G.; Sun, B.; Zhu, Q. Spatiotemporal variation of net anthropogenic nitrogen input and its response to ecological compensation in the Xin’an River Basin. J. Ecol. Rural. Environ. 2021, 37, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Ye, C.L. Current situation and control measures of agricultural non-point source pollution in the Xin’an River Basin of Huangshan City. Anhui Agric. Sci. Bull. 2013, 19, 101+107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.B. Analysis of hydrological elements in the upper Xin’an River Basin. Water Resour. Dev. Manag. 2023, 9, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Zhang, J.M.; Lin, Y.X.; Li, Z.W.; Xiao, W.H. Runoff variation characteristics and attribution analysis in the upper reaches of the Xin’an River Basin. J. Nat. Resour. 2019, 34, 1771–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L. Current situation and countermeasures of rice industry development in Huangshan City. Anhui Agric. Sci. Bull. 2023, 29, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L. Present situation and countermeasures of rapeseed production in Anhui Province. Anhui Agric. Sci. Bull. 2016, 22, 61–62+64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.H. Study on agricultural non-point source pollution from tea plantations in the Xin’an River Basin. Anhui Agric. Sci. Bull. 2014, 20, 107–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Su, J.W.; Li, Z.; Wang, W.; Wang, Z.Y.; Chen, J. Hydrochemical characteristics and hydrogeochemical processes of groundwater in the upper reaches of Xin’an River Basin. East China Geol. 2023, 44, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Yang, C.G.; Qu, B.Q.; Li, Y.; Jin, J.; Luo, L.; Wu, Z.; Shi, K.; Zhu, G. Modeling the effects of climate change and land use/land cover change on sediment yield in a large reservoir basin in the East Asian Monsoonal Region. Water 2022, 14, 2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnell, A.C.; Inger, R.; Bearhop, S.; Jackson, A.L. Source partitioning using stable isotopes: Coping with too much variation. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigman, D.M.; Casciotti, K.L.; Andreani, M.; Barford, C.; Galanter, M.; Böhlke, J.K. Measurement of the oxygen isotopic composition of nitrate in sea-water and freshwater using the denitrifier method. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 4905–4912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.J.; Fu, X.F. Application progress of stable isotope ratio mass spectrometry in tracing the source of environmental pollutants. Exp. Anal. 2025, 3, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotrufo, M.F.; Wallenstein, M.D.; Boot, C.M.; Denef, K.; Paul, E. The Microbial Efficiency-Matrix Stabilization (MEMS) framework integrates plant litter decomposition with soil organic matter stabilization: Do labile plant inputs form stable soil organic matter? Glob. Change Biol. 2013, 19, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, N. Study on the effects of long-term fertilization and climatic factors on soil nutrient changes and production sustainability based on the APSIM model. Chin. Acad. Agric. Sci. 2021, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleber, M.; Johnson, M.G. Advances in understanding the molecular structure of soil organic matter. Adv. Agron. 2010, 106, 77–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.Y.; Wan, S.Q. Global response patterns of terrestrial plant species to nitrogen addition. New Phytol. 2008, 179, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhardt, M.; Müller, B.; Gächter, R.; Wehrli, B. Nitrogen removal in a small constructed wetland: An isotope mass balance approach. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 3313–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Liu, W.G.; Wang, Z.F.; Hu, J. Relationship of nitrate isotopic character to population density in the Loess Plateau of Northwest China. Appl. Geochem. 2013, 35, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, W.H.; Boeckx, P.; Stock, B.C.; Smith, H.G.; Bodé, S.; Upadhayay, H.R.; Semmens, B.X. A deconvolutional Bayesian mixing model approach for river basin sediment source apportionment. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, P.; Li, F.D.; Wei, A.Z.; Li, S.Q.; Ma, H.M. Quantification of nitrate sources and fates in rivers in an irrigated agricultural area using environmental isotopes and a Bayesian isotope mixing model. Chemosphere 2018, 208, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, F.J.; Li, S.L.; Liu, C.Q.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Ding, H. Tracing nitrate sources with dual isotopes and long term monitoring of nitrogen species in the Yellow River, China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushal, S.S.; Groffman, P.M.; Band, L.E.; Elliott, E.M.; Shields, C.A.; Kendall, C. Tracking nonpoint source nitrogen pollution in human-impacted watersheds. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 8225–8232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.F.; Qin, X.; Chen, L.X.; Jin, M.T.; Li, F.L. Using dual isotopes to evaluate sources and transformations of nitrate in the West Lake watershed, eastern China. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2015, 177–178, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.F.; Hu, J.; Wu, A.J.; Li, G.Y.; Zhang, W.L.; Li, F.L. Source apportionment of nitrate in different land use areas based on multi-isotopes. Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 1696–1705. Available online: https://www.hjkx.ac.cn/hjkx/ch/html/20210412.htm (accessed on 15 September 2025).
- Wu, Y.Q.; Ge, Y.X.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, G. Advances in soil organic nitrogen depolymerization and its regulation. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2025, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.G.; Kang, P.P.; Sun, Y. A stable isotope approach and its application for identifying nitrate source and transformation process in water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 1133–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.F.; Xia, Z.; Sang, C.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Li, D.; Liu, X.; Feng, J.; Han, X.; Liu, L.; et al. Soil resource status affects the responses of nitrogen processes to changes in temperature and moisture. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2019, 55, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Zheng, Q.; Zhu, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, F. Contribution of nitrate sources in surface water in multiple land use areas by combining isotopes and a Bayesian isotope mixing model. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 93, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Q.; Li, S.L.; Lang, Y.C.; Xiao, H.Y. Using δ15N- and δ18O-values to identify nitrate sources in karst ground water, Guiyang, southwest China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 6928–6933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widory, D.; Petelet-Giraud, E.; Négrel, P.; Ladouche, B. Tracking the sources of nitrate in groundwater using coupled nitrogen and boron isotopes: A synthesis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Wang, S.; Sun, H.; Li, T.; Tan, Q. Rainfall driven nitrate transport in runoff of hilly area by combining time-series monitoring of hydrochemistry and stable isotopes. J. Hydrol. 2025, 654, 132830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishizawa, M.; Shibata, S.; Klinkhammer, U.; Takai, K.; Le Bris, N. Nitrogen and oxygen isotope effects of ammonia oxidation by thermophilic Thaumarchaeota from a geothermal water stream. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 4492–4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, C.Y.; Wang, R.D.; Zhou, H.T.; Li, J.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.Y. Effects of autumn no-tillage on farmland wind erosion and soil physicochemical properties in Bashang region. J. Desert Res. 2022, 42, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.F.; Wang, C.X.; He, X.L.; Li, Y.N.; Wang, J.H.; Li, R. Study on the effects of winter irrigation during seasonal freezing–thawing period on soil microbial ecological properties. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 23586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Kazama, F. Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: A case study of the Fuji river basin, Japan. Environ. Model. Softw. 2007, 22, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhang, J.K.; Wang, S.Q.; Zhang, Q.R.; Zhang, Y.H.; He, J.H.; Cao, Y.S. Multivariate statistical analysis of chemical and stable isotopic data as indicative of groundwater evolution with reduced exploitation. Geosci. Front. 2023, 14, 101476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.Y.; Yu, H.B.; Wang, Q.S. Application of multivariate statistical techniques in assessment of surface water quality in Second Songhua River basin, China. J. Cent. South Univ. 2016, 23, 1040–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Y.; Yang, G.L.; Xie, Y.C.; Qu, X.K.; Li, T.T.; Shan, B.Q. Sources of nitrate and key transformation mechanisms in surface water of a piedmont agricultural area. Environ. Sci. 2025, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Source of Nitrates | δ15N–NO3− | δ18O–NO3− | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| AN | 0 | 3.0‰ | 57.2‰ | 6.5‰ |
| SN | 3.8‰ | 1.8‰ | −2.7‰ | 4.4‰ |
| FN | −2.1‰ | 0.7‰ | −4.1‰ | 2.7‰ |
| LSN | 10.3‰ | 3.1‰ | 5.9‰ | 7.0‰ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luan, B.; Wang, A.; Huo, Z.; Lin, X.; Zhang, M. Identification of Nitrate Sources in the Upper Reaches of Xin’an River Basin Based on the MixSIAR Model. Water 2025, 17, 3584. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17243584
Luan B, Wang A, Huo Z, Lin X, Zhang M. Identification of Nitrate Sources in the Upper Reaches of Xin’an River Basin Based on the MixSIAR Model. Water. 2025; 17(24):3584. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17243584
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuan, Benjie, Ai Wang, Zhiguo Huo, Xuqing Lin, and Man Zhang. 2025. "Identification of Nitrate Sources in the Upper Reaches of Xin’an River Basin Based on the MixSIAR Model" Water 17, no. 24: 3584. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17243584
APA StyleLuan, B., Wang, A., Huo, Z., Lin, X., & Zhang, M. (2025). Identification of Nitrate Sources in the Upper Reaches of Xin’an River Basin Based on the MixSIAR Model. Water, 17(24), 3584. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17243584






