Efficient Oily Wastewater Treatment via Electrocoagulation: Process Optimization and Sludge Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
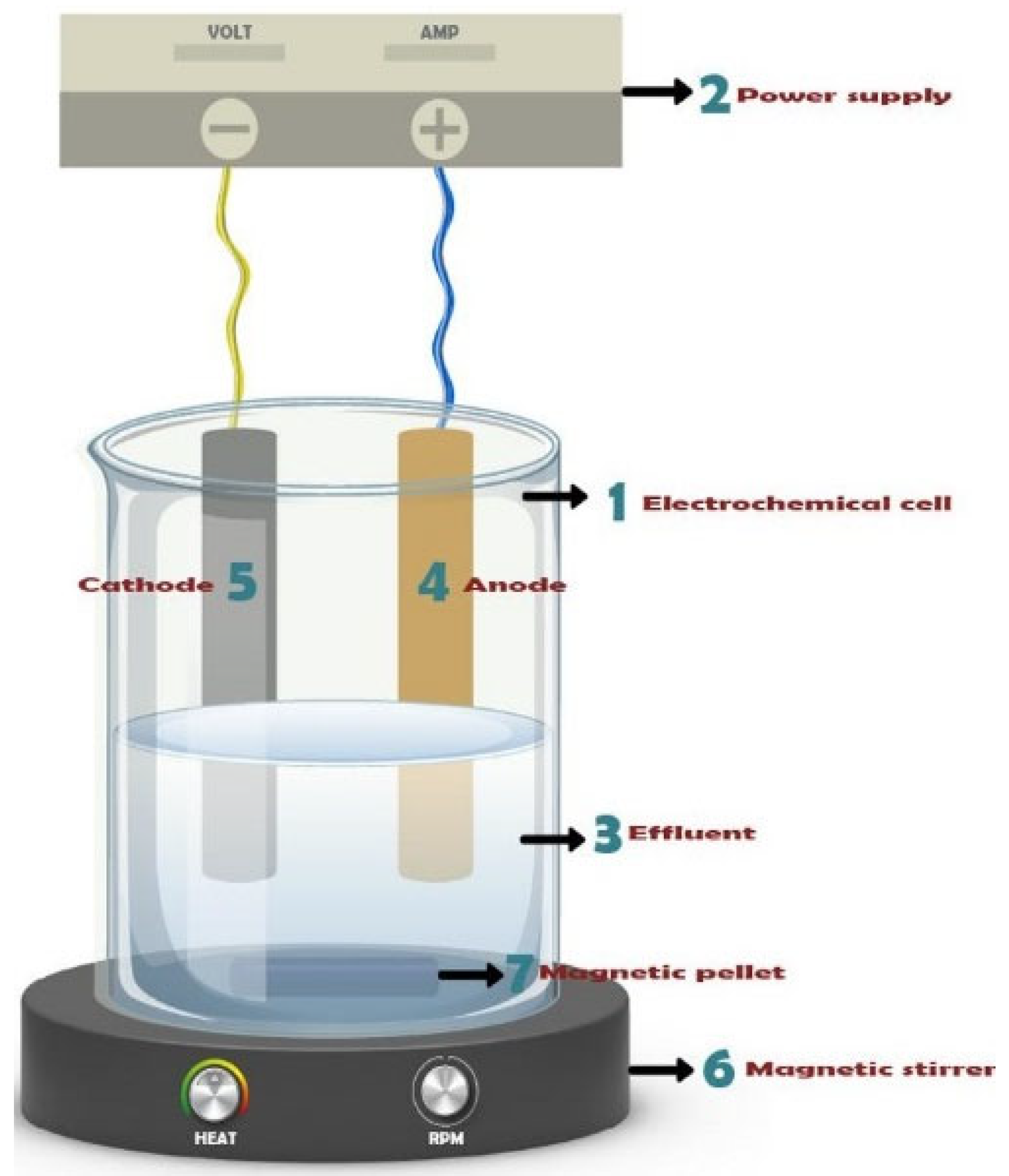
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
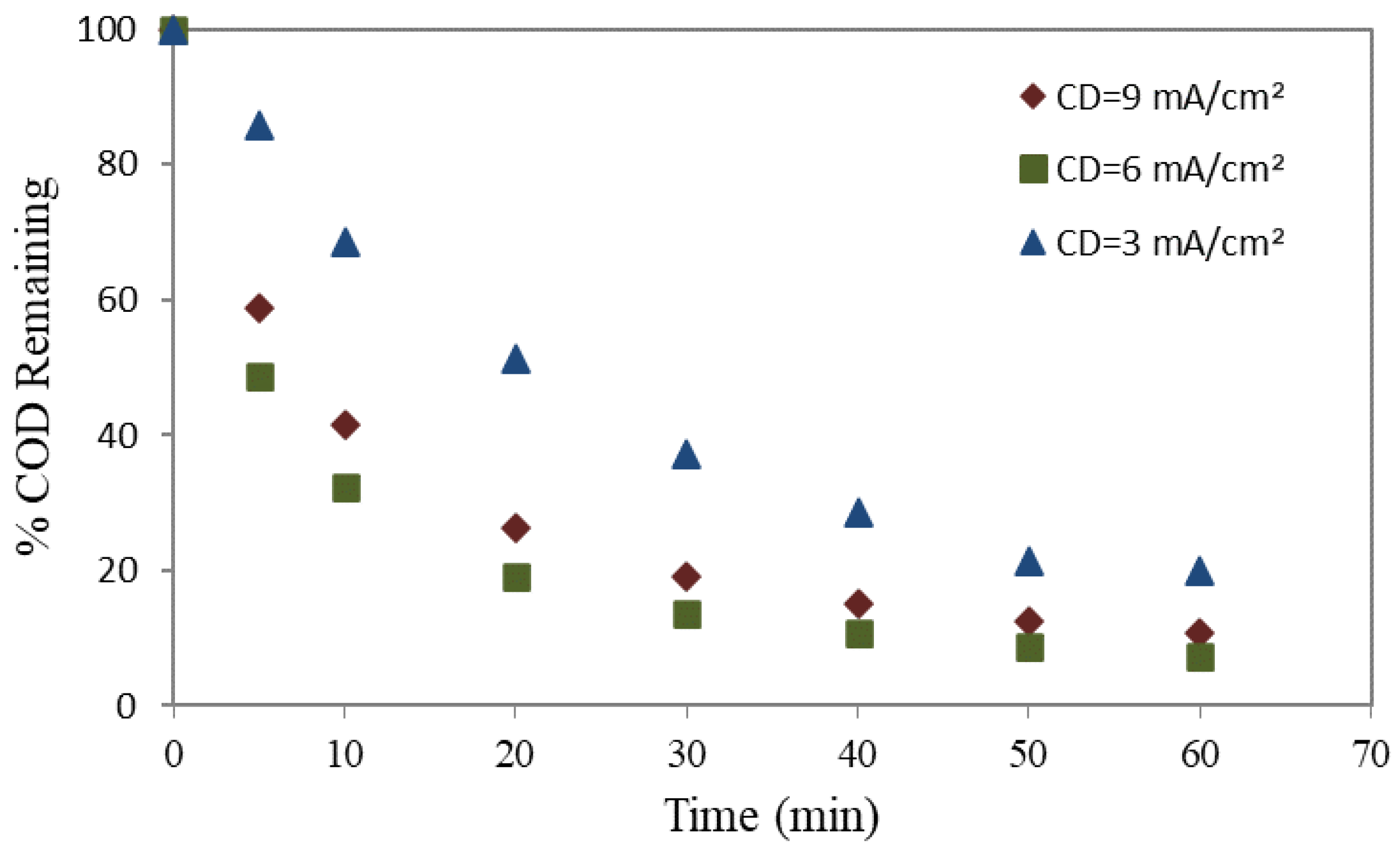
3.1. Current Density’s Impact on COD Removal Efficiency
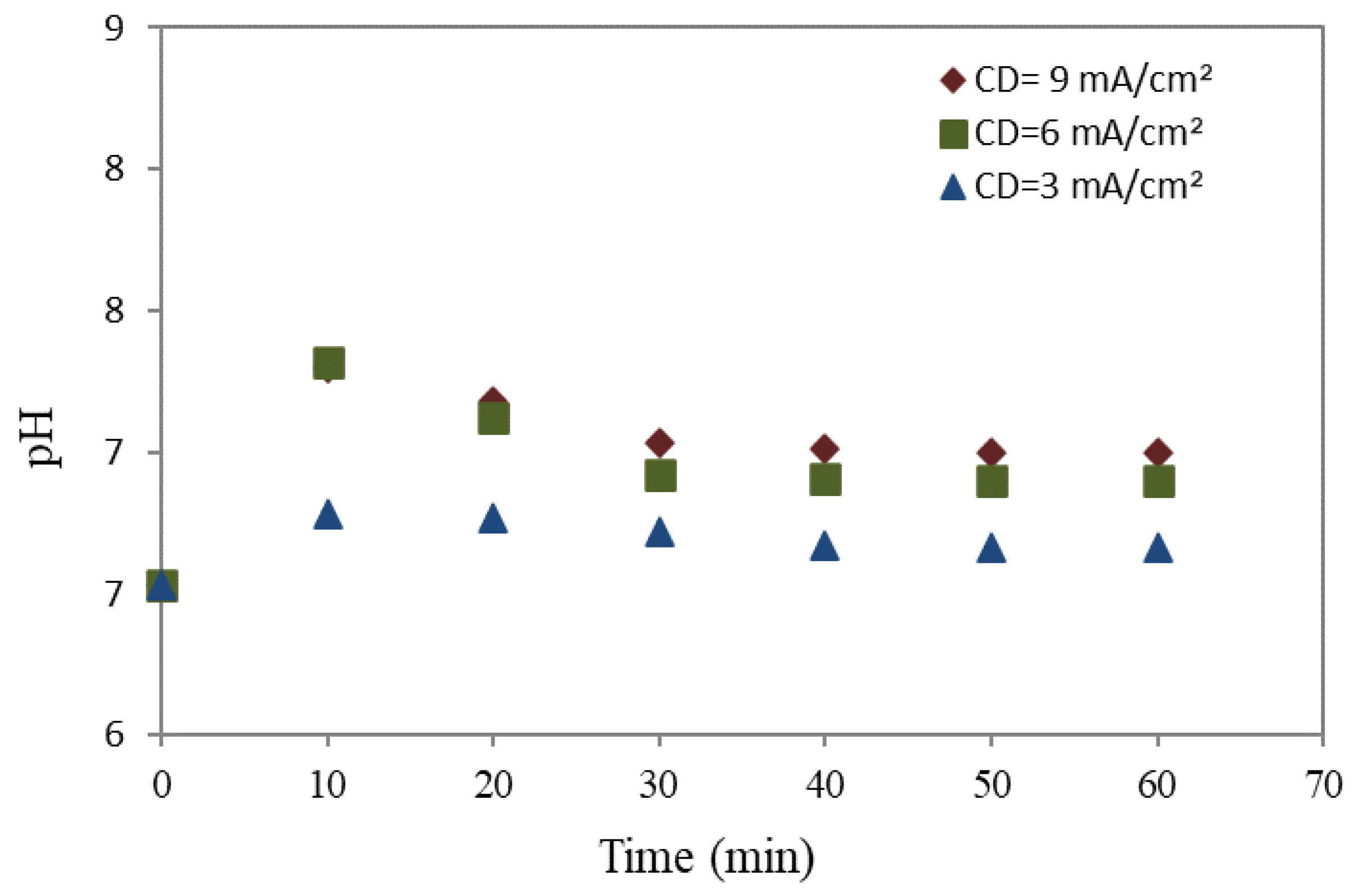
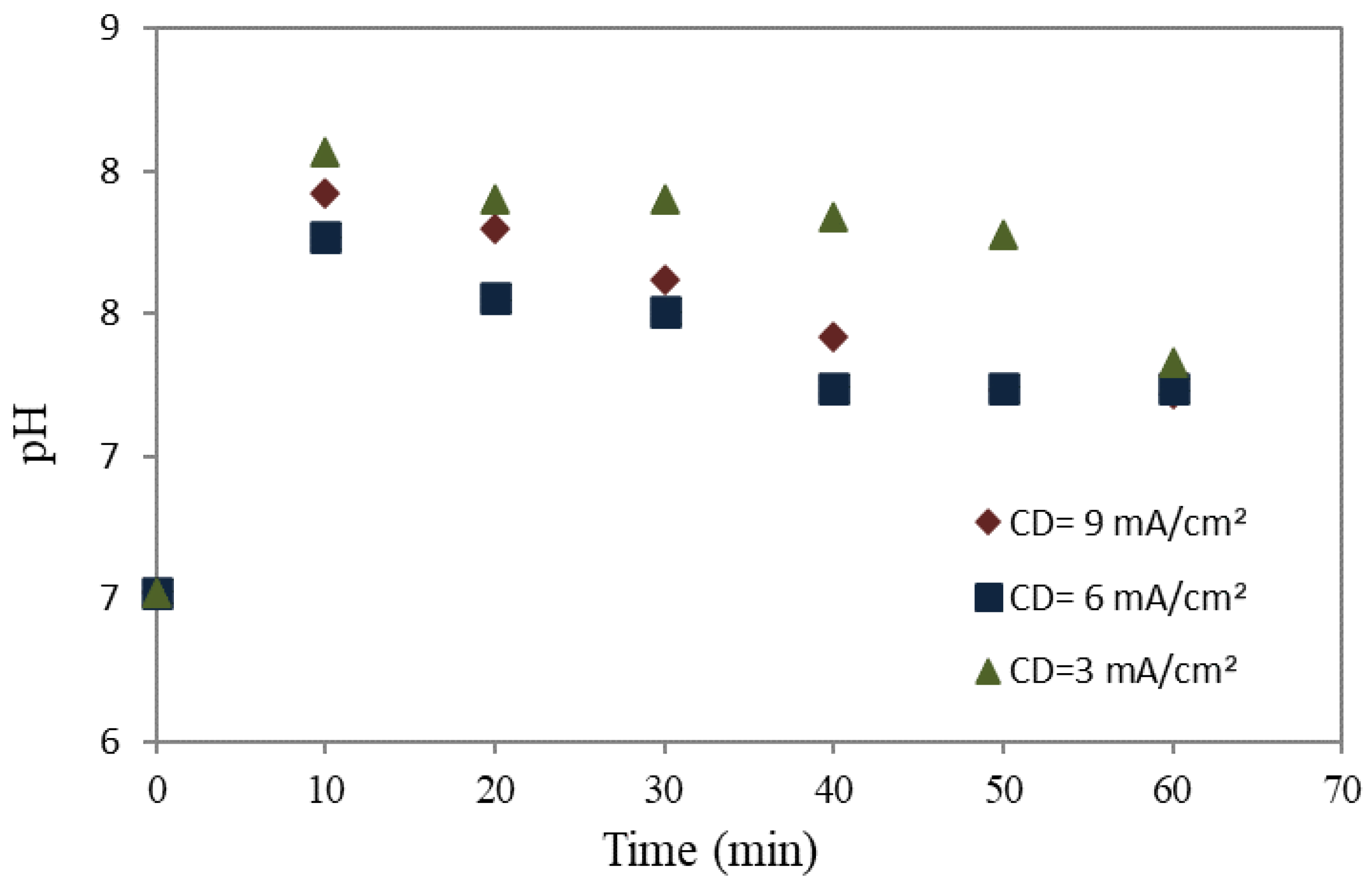
3.2. Effect of Electrocoagulation on pH
3.3. Specific Energy Consumption
3.4. Anode Dissolution
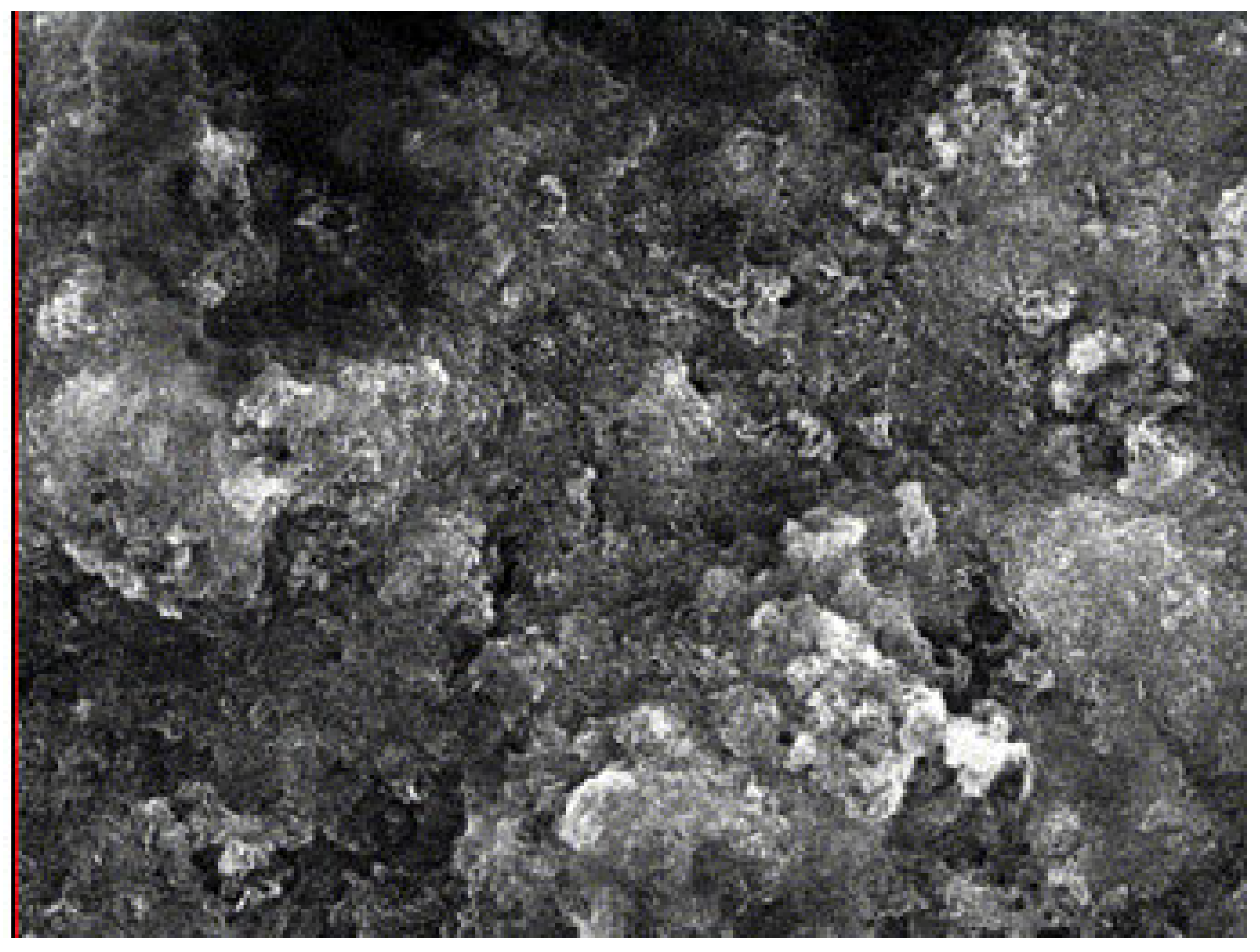
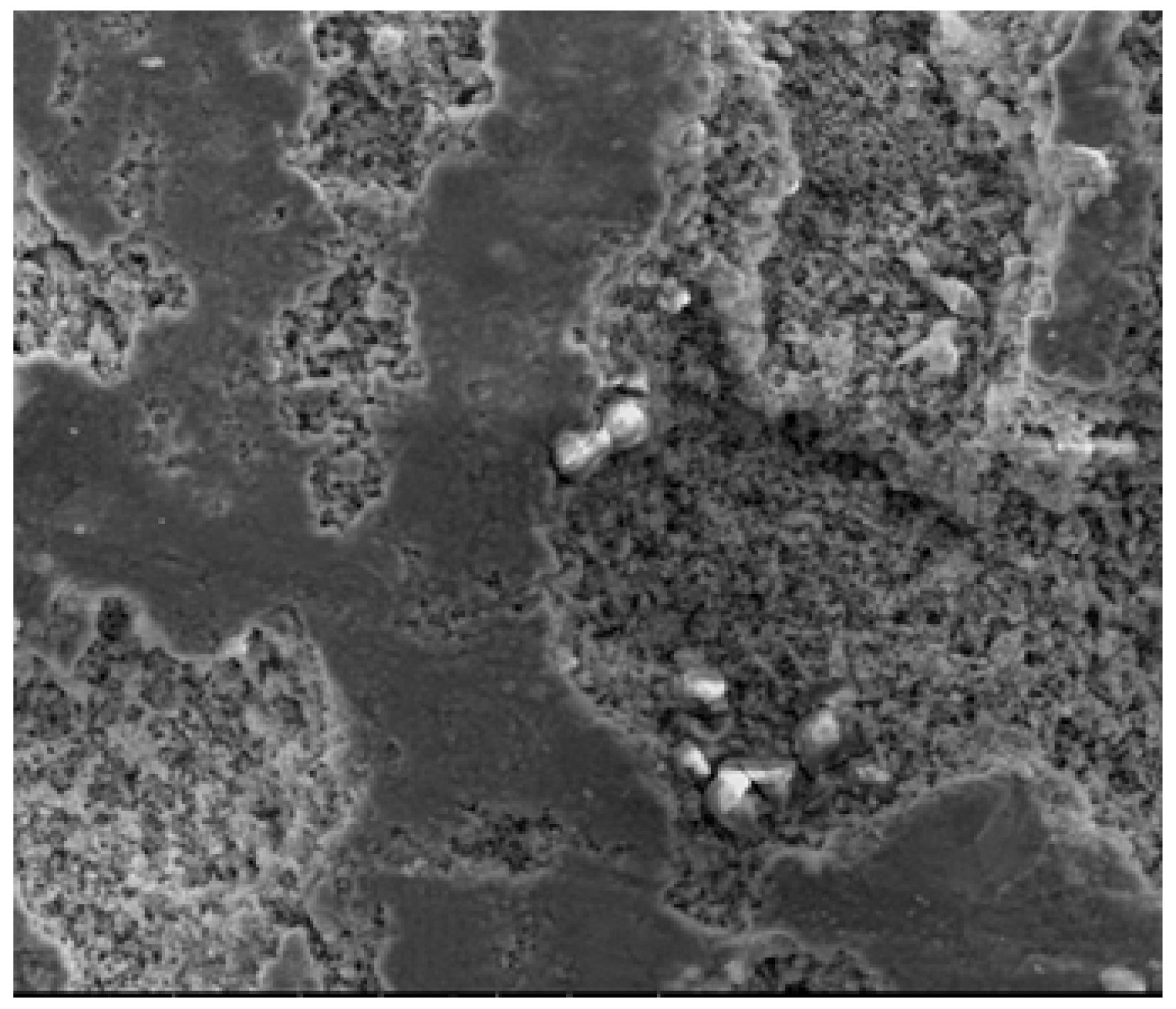
3.5. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) with Energy-Dispersive X-Ray Analysis (EDAX)
- The commercial mild steel is an alloy that may contain zinc as impurities or as a galvanizing coat, which may not dissolve through the process of electrocoagulation process.
- The industrial oily wastewater involving metalworking or corrosion inhibition may contain zinc product or residues, which is removed effectivity by iron hydroxide flocs co-precipitation.
3.6. Effect of Anode Material
3.7. Residual Metal Ions and Assessment of Secondary Contamination
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mohammed, M.N.; Abdullah, O.I.; Jweeg, M.J.; Aljibori, H.S.S.; Abdullah, T.A.; Alawi, N.M.; Rasheed, R.T.; Meharban, F.; Hamzah, H.T.; Al-Obaidi, Q. Comprehensive Review on Wastewater Treatment using Nanoparticles: Synthesis of Iron Oxide Magnetic Nanoparticles, Publication Trends via Bibliometric Analysis, Applications, Enhanced Support Strategies, and Future Perspectives. ASEAN J. Sci. Eng. 2025, 5, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriipsalu, M.; Marques, M.; Maastik, A. Characterization of oily sludge from a wastewater treatment plant flocculation-flotation unit in a petroleum refinery and its treatment implications. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2008, 10, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdy, S.A.; Al-Naseri, H. Effect of Magnesium Oxide Nanoparticles (MgO) on Wastewater Treatment and Electric Current Generation Using Microbial Fuel Cell Technology. Tikrit J. Eng. Sci. 2024, 31, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, P.; Mishra, I.M. Treatment and reclamation of hydrocarbon-bearing oily wastewater as a hazardous pollutant by different processes and technologies: A state-of-the-art review. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2018, 35, 73–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B. Human health hazards of wastewater. In High-risk Pollutants Wastewate; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 125–139. [Google Scholar]
- Mokif, L.A.; Jasim, H.K.; Abdulhusain, N.A. Petroleum and oily wastewater treatment methods: A mini review. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 49, 2671–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansam, A.M.; Thamer, A.A.; Aljibori, H.S.S.; Mohammed, M.N.; Abdullah, O. Effect of Nanoparticles Flow to Improve the Oil Refineries Wastewater. Int. Rev. Mech. Eng. 2024, 18, 351. [Google Scholar]
- Mahdy, S.A. Biodegradability enhancement of oily wastewater by an SBR treatment methods. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference Proceedings, Al-Amarah, Iraq, 1–2 February 2022; AIP Publishing: Melville, NY, USA; Volume 2809. [Google Scholar]
- Adetunji, A.I.; Olaniran, A.O. Treatment of industrial oily wastewater by advanced technologies: A review. Appl. Water Sci. 2021, 11, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waheed Khafaji, S.O.; Diab, M.A.; El-Sabban, H.A.; Jumanazarov, D.; Atamurotov, F.; Almehizia, A.A. Intensified wastewater treatment using In 2 S 3 on activated carbon derived from waste tire: Peroxydisulfate activation via visible-light, characterization, composition, pH influence, and mechanism. Chem. Eng. Process Process Intensif. 2025, 214, 110352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuhasel, K.; Kchaou, M.; Alquraish, M.; Munusamy, Y.; Jeng, Y.T. Oily wastewater treatment: Overview of conventional and modern methods, challenges, and future opportunities. Water 2021, 13, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Obaidi, Q.; Ibrahim, D.S.; Mohammed, M.N.; Abdullah, O.; Selem, N.Y. A Comprehensive Analysis of the Hydrogen Generation Technology Through Electrochemical Water and Industrial Wastewater Electrolysis. Pol. J. Chem. Technol. 2024, 26, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansam, A.; Al-Obaidi, Q.; Rand, N. Study of prototypes for biofuel production Extraction from biodegradation in oxygen-free environments Processing Wastewater. Sol. Energy Sustain. Dev. J. 2025, 14, 522–539. [Google Scholar]
- Jamaly, S.; Giwa, A.; Hasan, S.W. Recent improvements in oily wastewater treatment: Progress, challenges, and future opportunities. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 37, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, M.; Waqed, H.H.; Naglaa, F.; Soliman, P.K.S.; Mohammad, I.K.; Ibrahm, M.; Farruh, A.; Ahmadjon, A.; Diab, M.A. Enhanced wastewater purification and photocatalytic green energy production via a novel CaIn2S4-coupled BiFeO3 nanocomposite: Characterization and mechanistic insights. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 75, 108048. [Google Scholar]
- El-Gohary, F.; Tawfik, A.; Mahmoud, U. Comparative study between chemical coagulation/precipitation (C/P) versus coagulation/dissolved air flotation (C/DAF) for pre-treatment of personal care products (PCPs) wastewater. Desalination 2020, 252, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochando-Pulido, J.M.; Vellido-Pérez, J.A.; González-Hernández, R.; Martínez-Férez, A. Optimization and modeling of two-phase olive-oil washing wastewater integral treatment and phenolic compounds recovery by novel weak-base ion exchange resins. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 249, 117084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Mukherjee, D.; Koirala, N.; Hu, G.; Lee, K.; Zhao, M.; Li, J. Microbubble and nanobubble-based gas flotation for oily wastewater treatment: A review. Environ. Rev. 2022, 30, 359–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunbiyi, O.; Liu, Z. Air flotation techniques for oily wastewater treatment, in Advan. Technol. In Wastewater Treatment; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 153–172. [Google Scholar]
- Yeit Haan, T.; Isma Nordin, P.M.; Ahmad Juanda, N.I.; Mohd Shafi, M.A.; Krishnan, P. A Review on Adsorption Process for the Treatment of Oily Wastewater. Adv. Environ. Eng. Res. 2023, 4, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhou, J.; Yan, Y.; Yang, L.; Xing, G.; Li, H.; Wu, P.; Wang, M.; Zheng, H. Application of coagulation/flocculation in oily wastewater treatment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 765, 142795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, R.H.; Abbar, A.H. Optimization of a combined electrocoagulation-electro-oxidation process for the treatment of Al-Basra Majnoon Oil field wastewater: Adopting a new strategy. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2023, 183, 109227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Obaidi, Q.; Aljibori, H.S.S.; Abdullah, T.A.; Mohammed, M.N.; Abdullah, O.I. Performance Investigation of Surface Modified Ceramic Microfilitration Membranes of Ionic Water Treatment. Environ. Res. Eng. Manag. 2024, 80, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Obaidi, Q.; Selem, N.Y.; Al-Dahhan, M.H. Emulsion liquid membrane (ELM) enhanced by nanoparticles and ionic liquid for extracting vanadium ions from wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 48576–48589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorram, A.G.; Fallah, N.; Nasernejad, B.; Afsham, N.; Esmaelzadeh, M.; Vatanpour, V. Electrochemical-based processes for produced water and oily wastewater treatment: A review. Chemosphere 2023, 338, 139565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Druskovic, M.; Vouk, D.; Posavcic, H.; Halkijevic, I.; Nad, K. The application of electrochemical processes in oily wastewater treatment: A review. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2021, 56, 1373–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, C.; Huang, G.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, S. Emerging usage of electrocoagulation technology for oil removal from wastewater: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 537–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasim, M.A.; AlJaberi, F.Y.A. Treatment of oily wastewater by electrocoagulation technology: A general review (2018–2022). J. Electrochem. Sci. Eng. 2023, 13, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, S.I. Mercury removal using Fe–Fe electrodes by electrocoagulation. Int. J. Mod. Eng. Res. 2013, 3, 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- Merma, A.G.; Santos, B.F.; Rego, A.S.; Hacha, R.R.; Torem, M.L. Treatment of oily wastewater from mining industry using electrocoagulation: Fundamentals and process optimization. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 15164–15176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uludag-Demirer, S.; Olson, N.; Ives, R.; Nshimyimana, J.P.; Rusinek, C.A.; Rose, J.B.; Liao, W. Techno-economic analysis of electrocoagulation on water reclamation and bacterial/viral indicator reductions of a high-strength organic wastewater—Anaerobic digestion effluent. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rubaiey, N.A.; Al-Barazanjy, M.G. Electrocoagulation Treatment of Oily Wastewater in the Oil Industry. J. Pet. Res. Stud. 2018, 8, 274–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, O.; Banat, F.; Srinivasakannan, C.; Radjenovic, J.; Hasan, S.W. Performance tests and removal mechanisms of aerated electrocoagulation in the treatment of oily wastewater. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 36, 101290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotovat, F.; Hosseini, M. Treatment of oily wastewater by electrocoagulation: Simultaneous optimization of oil removal efficiency and specific energy consumption. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 55, 104221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakizimana, J.N.; Gourich, B.; Chafi, M.; Stiriba, Y.; Vial, C.; Drogui, P.; Naja, J. Electrocoagulation process in water treatment: A review of electrocoagulation modeling approaches. Desalination 2017, 404, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghernaout, D.; Alghamdi, A.; Ghernaout, B. Electrocoagulation process: A mechanistic review at the dawn of its modeling. J. Environ. Sci. Allied Res. 2019, 2, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, M.; Katoch, S.S.; Kadier, A.; Singh, A. A review on electrocoagulation process for the removal of emerging contaminants: Theory, fundamentals, and applications. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 15252–15281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahedi, A.; Darban, A.; Taghipour, F.; Jamshidi-Zanjani, A. A review on industrial wastewater treatment via electrocoagulation processes. Curr. Opin Electrochem. 2020, 22, 154–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnisali, E.; Yan, Q.; Vayenas, D.V. Electrocoagulation as a revived wastewater treatment method–practical approaches: A review. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2022, 97, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlJaberi, F.Y.; Alardhi, S.M.; Ahmed, S.A.; Salman, A.D.; Juzsakova, T.; Cretescu, I.; Le, P.-C.; Chung, W.J.; Chang, S.W.; Nguyen, D.D. Can electrocoagulation technology be integrated with wastewater treatment systems to improve treatment efficiency? Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 113890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, L.H.; Drogui, P.; Mercier, G.; Blais, J.F. Electrochemical degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in creosote solution using ruthenium oxide on titanium expanded mesh anode. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 1118–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, K.; Abbassi, B.; Kinsley, C. Combined electrocoagulation and chemical coagulation in treating brewery wastewater. Water 2020, 12, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.A.; Mahdy, S.A.; Hussein, N.N. Synthesis of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles (TiO2) and Application for Reduction of Bacterial Growth. J. Nanostruct. 2024, 14, 1046–1057. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Yang, H.; Wen, T.; Wang, S.; Hu, B.; Wang, X. Removal of organic compounds by nanoscale zero-valent iron and its composites. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 792, 148546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, J.; Villegas, L.; Peralta-Hernández, J.M.; Salazar González, R. Removal of Acid Black 194 dye from water by electrocoagulation with aluminum anode. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2016, 51, 289–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbar, A.H.; Alkurdi, S.S. Performance evaluation of a combined electrocoagulation–electrooxidation process for the treatment of petroleum refinery wastewater. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Diyala, Iraq, 16–17 December 2020; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Şengil, İ.A. Treatment of dairy wastewaters by electrocoagulation using mild steel electrodes. J. Hazar. Mater. 2016, 137, 1197–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canizares, P.; Martinez, F.; Jiménez, C.; Sáez, C.; Rodrigo, M.A. Coagulation and electrocoagulation of oil-in-water emulsions. J. Hazar. Mater. 2008, 151, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, T.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Meng, H.; Wang, L. Research trends in electrochemical technology for water and wastewater treatment. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.A.; Mahdy, S.A.; Hussein, N.N. Anticancer properties of titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles obtained from Quercus infectoria plant extract. J. Nanostruct. 2024, 14, 492–504. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, S.F.; Christensen, M.L.; Jørgensen, M.K. Mechanisms behind pH changes during electrocoagulation. AIChE J. 2021, 67, e17384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetteh, E.; Rathilal, S. Evaluation of different polymeric coagulants for the treatment of oil refinery wastewater. Cogent Eng. 2020, 7, 1785756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godart, P.; Fischman, J.; Seto, K.; Hart, D. Hydrogen production from aluminum-water reactions subject to varied pressures and temperatures. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 11448–11458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, M.; Nagao, N.; Kawasaki, N.; Imai, A.; Toda, T. Improvement of COD removal by controlling the substrate degradability during the anaerobic digestion of recalcitrant wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 181, 838–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Naas, M.H.; Al-Zuhair, S.; Al-Lobaney, A.; Makhlouf, S. Assessment of electrocoagulation for the treatment of petroleum refinery wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 91, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Ali, A.B.; Samad, S.; Abdulrahman, A.; Osman, H.; Jumanazarov, D.; Atamurotov, F.; Mahariq, I. Sustainable and Electrostatically Engineered MXene-Based composite for environmental pollution remediation of Congo red dye and Cefixime from wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 369, 133164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupińska, I. Aluminium Drinking Water Treatment Residuals and Their Toxic Impact on Human Health. Molecules 2020, 25, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard Methods Committee of the American Public Health Association; American Water Works Association; Water Environment Federation. 3500-fe iron. In Standard Methods For the Examination of Water and Wastewater; Lipps, W.C., Baxter, T.E., Braun-Howland, E., Eds.; APHA Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2022; Available online: https://www.standardmethods.org/doi/abs/10.2105/SMWW.2882.055 (accessed on 30 November 2025).







| Varied Parameter | Optimal Value |
|---|---|
| Include conductivity | 1.536 ± 76 μS/cm |
| Oil content | 415 ± 20 mg/L |
| COD | 700 ± 35 mg/L |
| pH | 6.7 ± 0.3 |
| BOD | 80 ± 4 mg/L |
| TDS | 113,400 ± 400 mg/L |
| Element | Wt% | At% |
|---|---|---|
| CK | 11.44 | 22.38 |
| OK | 37.92 | 55.68 |
| SiK | 1.64 | 1.37 |
| Sak | 0.87 | 0.51 |
| FeK | 45.11 | 18.97 |
| ZnK | 3.02 | 1.08 |
| Matrix | Correction | ZAF |
| Element | Wt% | At% |
|---|---|---|
| CK | 9.59 | 14.57 |
| OK | 53.07 | 60.57 |
| AlK | 33.15 | 22.44 |
| Sik | 1.20 | 0.78 |
| SK | 1.78 | 1.01 |
| ClK | 1.21 | 0.63 |
| Matrix | Correction | ZAF |
| Anode Material | Current Density (mA/cm2) | Residual Fe (mg/L) | Residual Al (mg/L) | Regulatory Limit (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mild Steel | 3 | 0.85 | - | 0.2–0.3 (for Fe) |
| Mild Steel | 6 | 1.92 | - | 0.2–0.3 (for Fe) |
| Mild Steel | 9 | 3.45 | - | 0.2–0.3 (for Fe) |
| Aluminum | 3 | - | 0.45 | 0.1–0.2 (for Al) |
| Aluminum | 6 | - | 1.12 | 0.1–0.2 (for Al) |
| Aluminum | 9 | - | 2.85 | 0.1–0.2 (for Al) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Obaidi, Q.; Saeed, A.W.; Al Mesfer, M.K.; Danish, M.; Shah, M.; Ansari, K.B. Efficient Oily Wastewater Treatment via Electrocoagulation: Process Optimization and Sludge Analysis. Water 2025, 17, 3529. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17243529
Al-Obaidi Q, Saeed AW, Al Mesfer MK, Danish M, Shah M, Ansari KB. Efficient Oily Wastewater Treatment via Electrocoagulation: Process Optimization and Sludge Analysis. Water. 2025; 17(24):3529. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17243529
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Obaidi, Qusay, Ammar W. Saeed, Mohammed K. Al Mesfer, Mohd Danish, Mumtaj Shah, and Khursheed B. Ansari. 2025. "Efficient Oily Wastewater Treatment via Electrocoagulation: Process Optimization and Sludge Analysis" Water 17, no. 24: 3529. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17243529
APA StyleAl-Obaidi, Q., Saeed, A. W., Al Mesfer, M. K., Danish, M., Shah, M., & Ansari, K. B. (2025). Efficient Oily Wastewater Treatment via Electrocoagulation: Process Optimization and Sludge Analysis. Water, 17(24), 3529. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17243529