The Construction of Check Dams on the Loess Plateau Has Prolonged Water Transmission Times and Altered Recharge Relationships
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
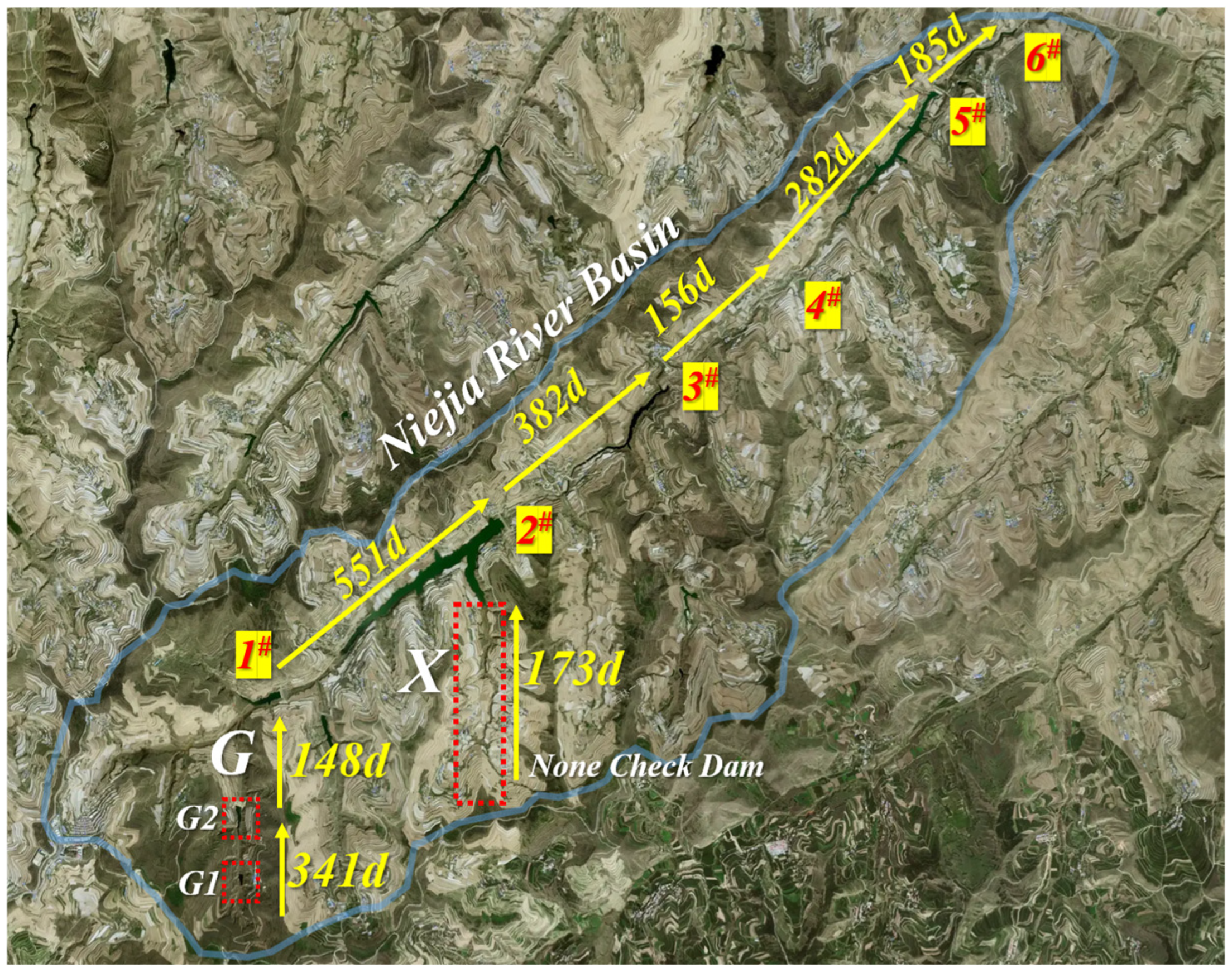
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Research Methods
2.2.1. Sample Collection
2.2.2. Determination and Analysis of Water Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotopes
- (1)
- Hydrogen and oxygen stable isotope determination
- (2)
- Calculation of deuterium excess
- (3)
- Least squares method for fitting the precipitation line, surface water line and groundwater line.
- (4)
- The end-member mixing model is used to calculate the proportion of water body source recharge.
- (5)
- Sine fitting isotope amplitude
- (6)
- The exponential model (EM) is used to calculate the water body transmission time.
- (7)
- Simulation of water vapor sources using the HYSPLIT backward trajectory model
- (8)
- The Pearson correlation coefficient is used to calculate the correlation between isotopes and meteorological factors.
2.3. Data Processing Methods
3. Results
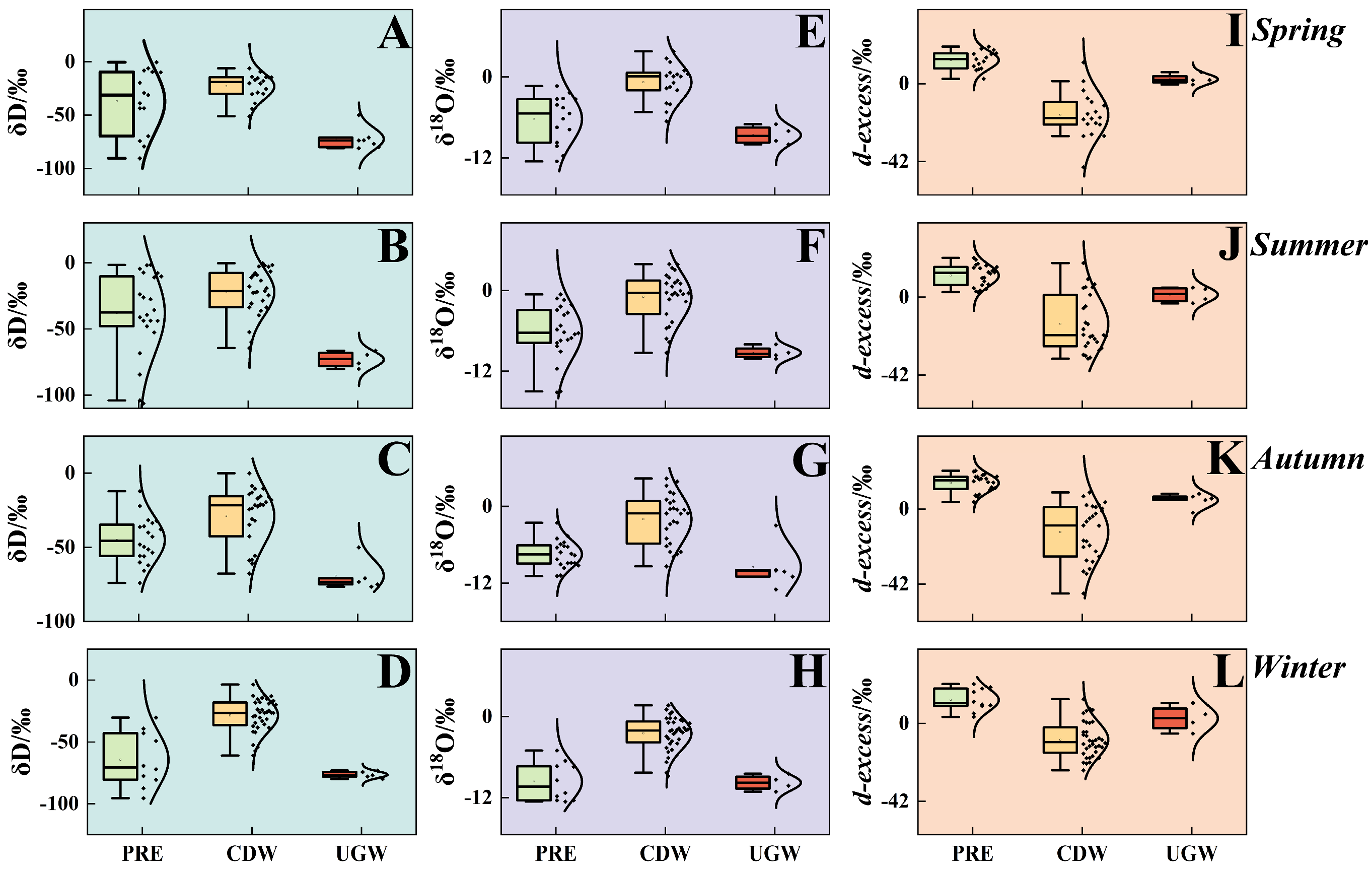
3.1. Seasonal Characteristics of Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotopes in Different Water
3.1.1. The Characteristics of δD and δ18O
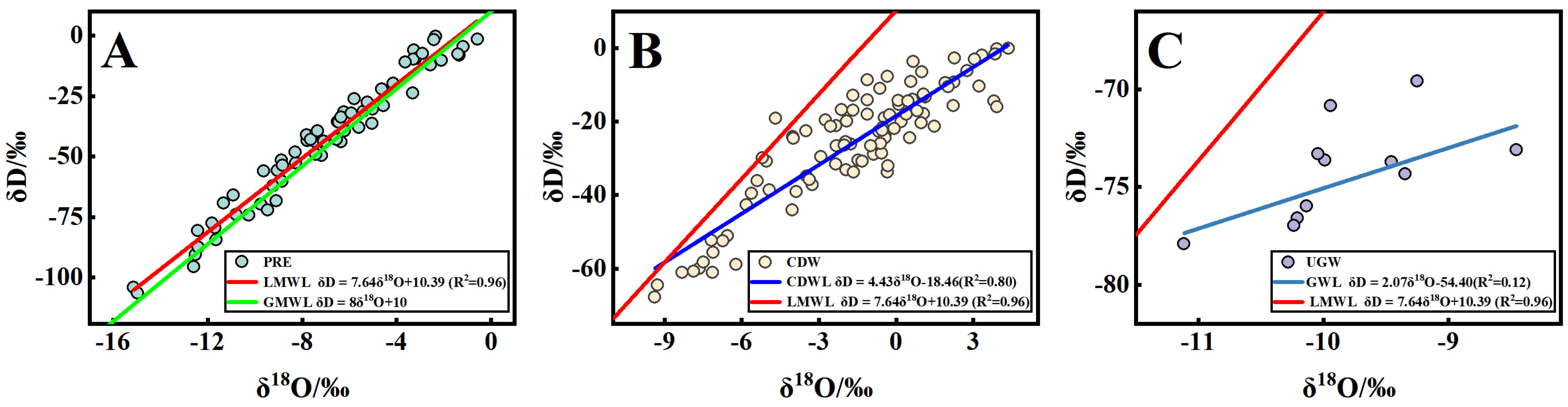
3.1.2. The Precipitation Line, Surface Water Line and Groundwater Line
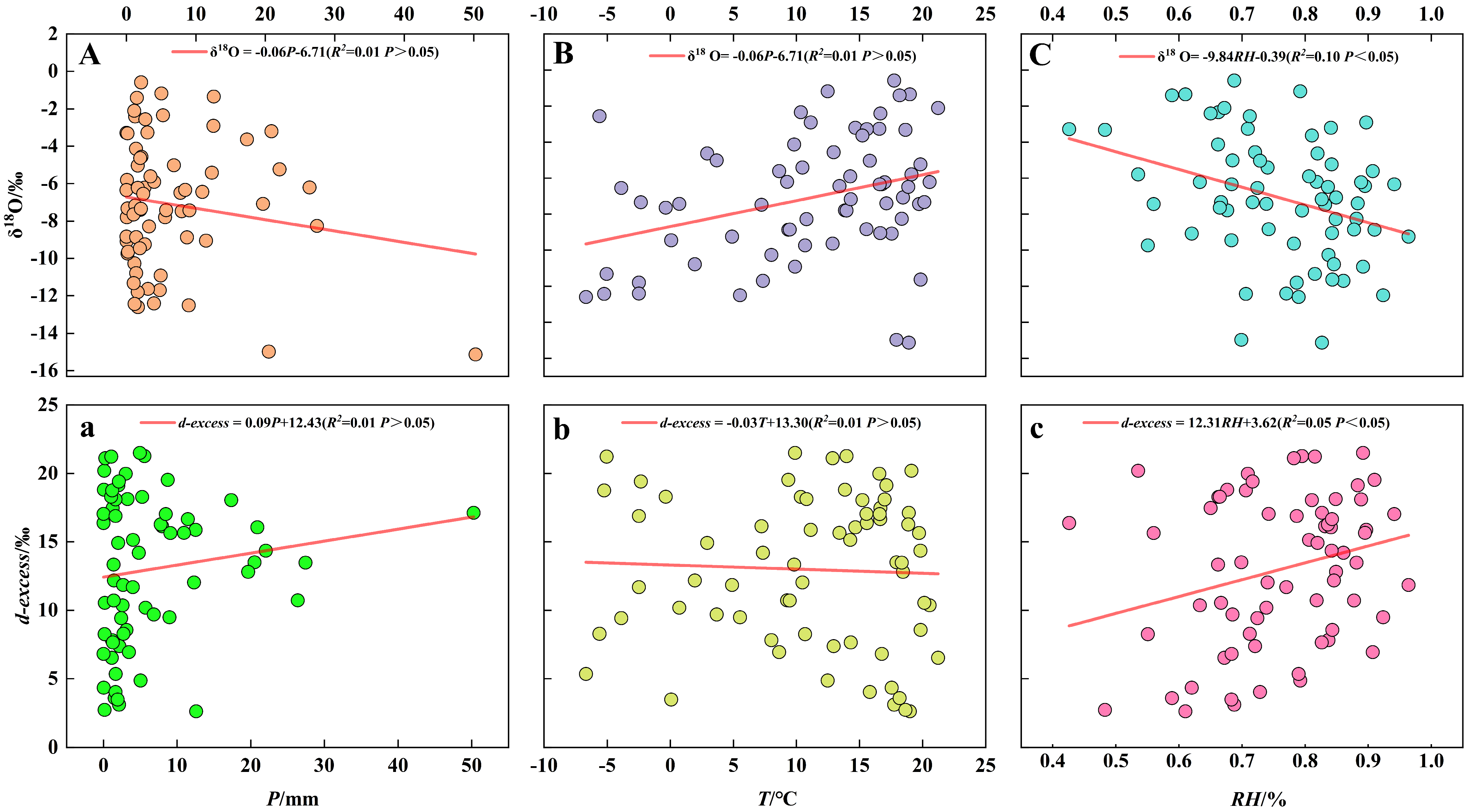
3.1.3. The Relationship Between PRE Isotopes and Meteorological Factors
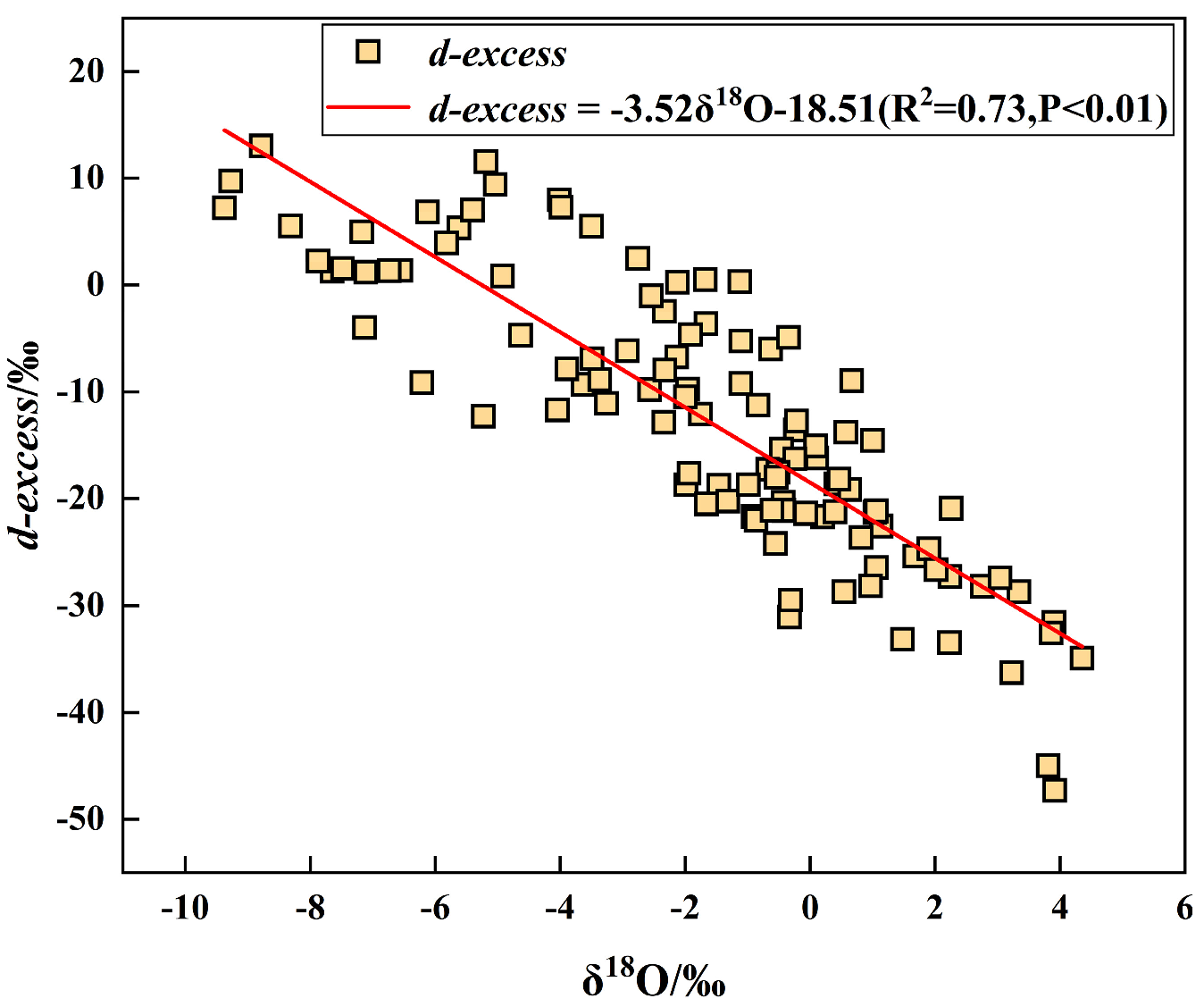
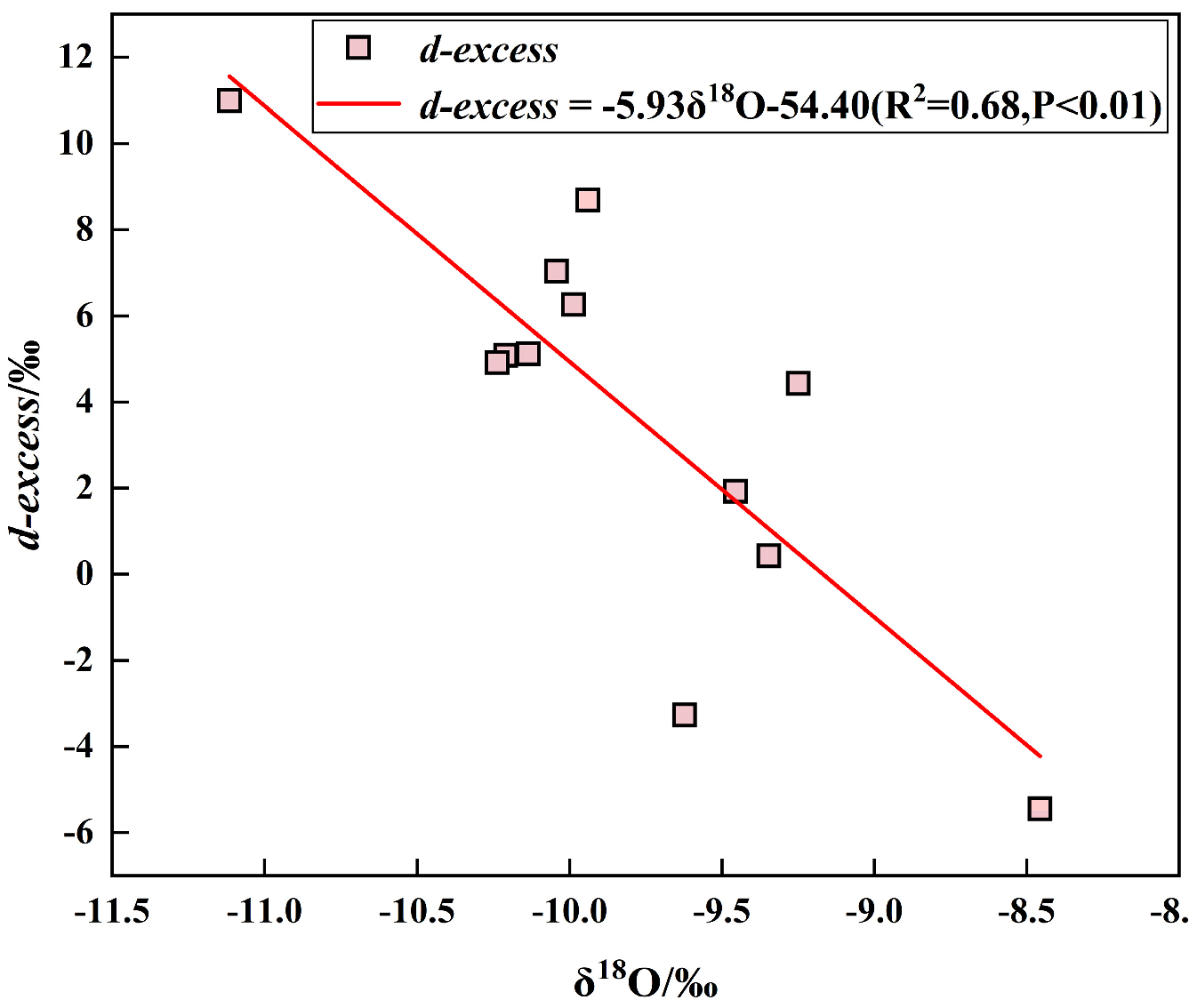
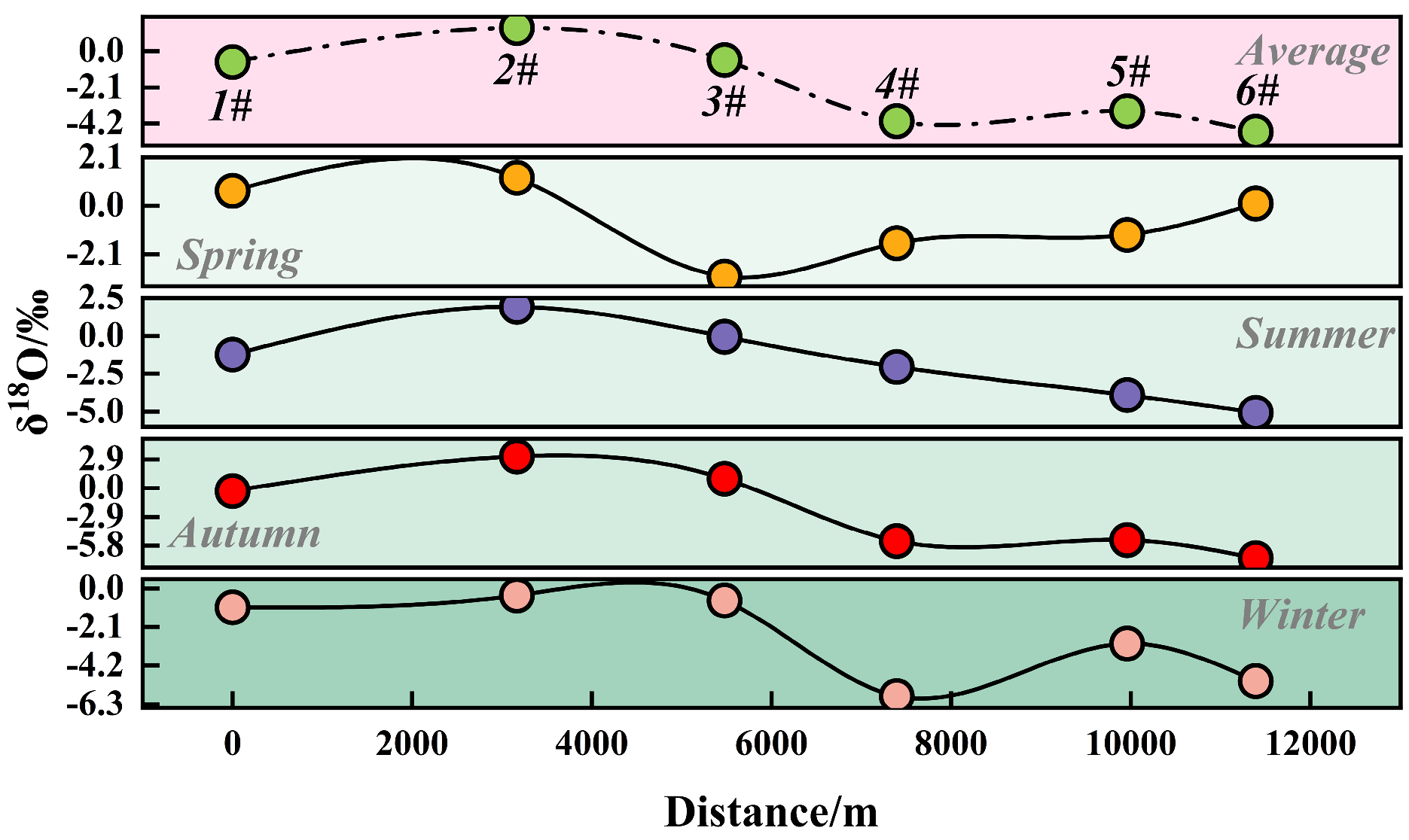
3.1.4. The Relationship Between δ18O and D-Excess Values of Surface Water and Groundwater and Distance
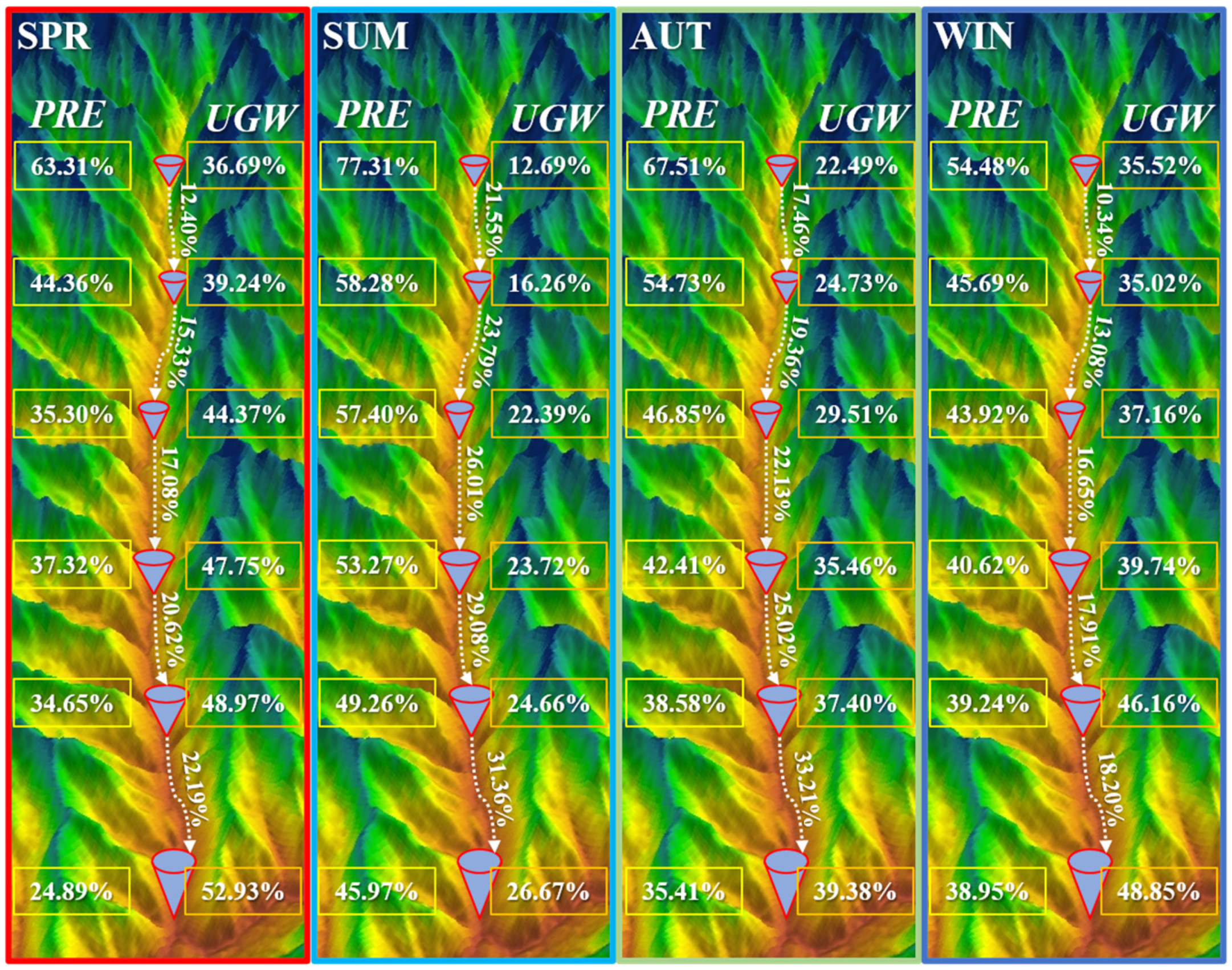
3.2. Different Water Replenishment Ratios
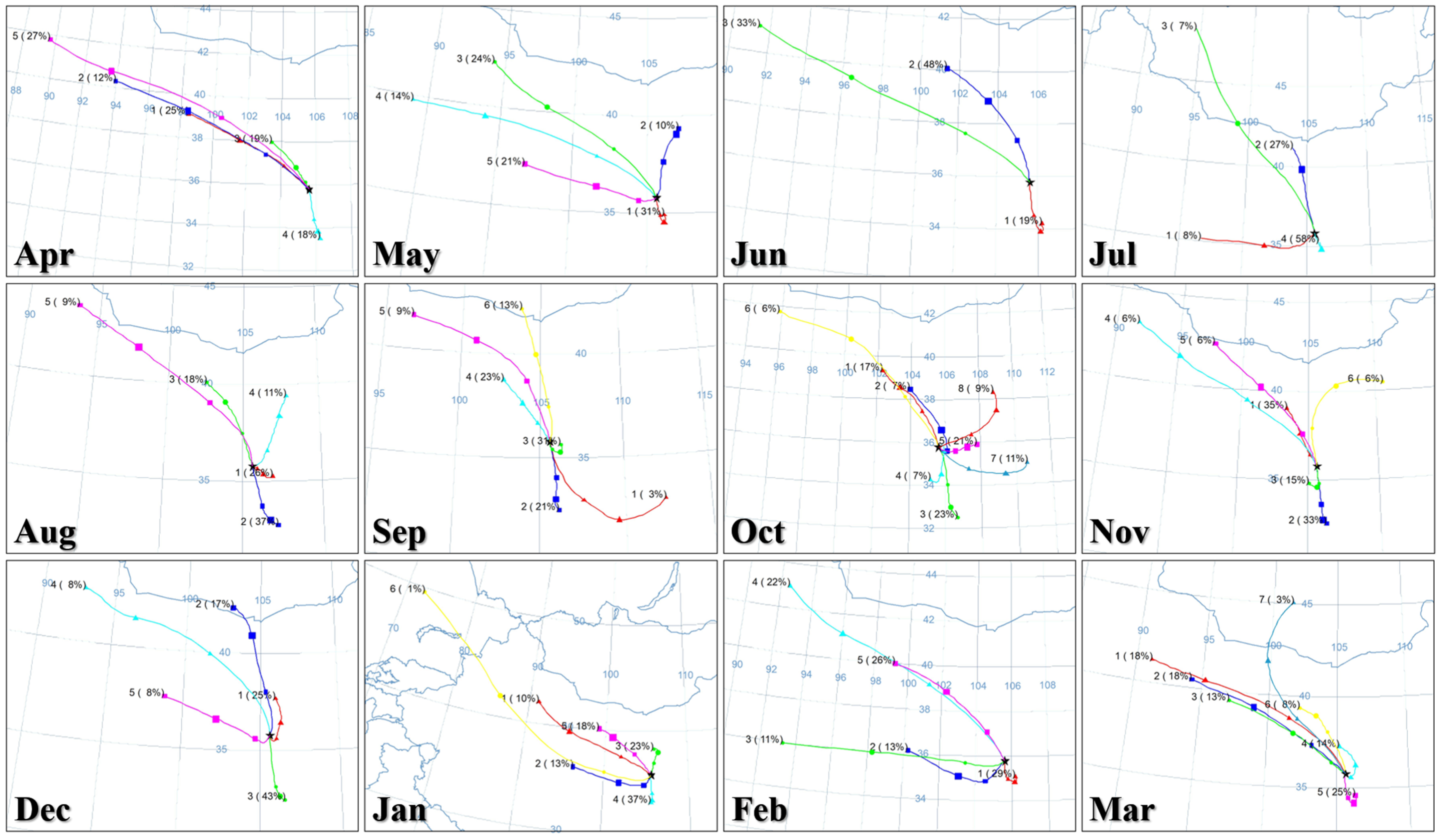
3.3. Calculation of Different Water Transmission Times
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Research Limitations and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fu, B.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Liang, W.; Miao, C. Hydrogeomorphic ecosystem responses to natural and anthropogenic changes in the Loess Plateau of China. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2017, 45, 223–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bo, F.; Li, C.; Yi, L.; Yang, G. Check dam in the Loess Plateau of China: Engineering for environmental services and food security. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 10298–10299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.D.; Fu, B.J.; He, C.S. Assessing the hydrological effect of the check dams in the Loess Plateau, China, by model simulations. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 2185–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, H. Isotopic variations in meteoric waters. Science 1961, 133, 1702–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, K.; Shen, H.; Yao, M.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Chen, D. Assessment of streamflow components and hydrologic transit times using stable isotopes of oxygen and hydrogen in waters of a subtropical watershed in eastern China. J. Hydrol. 2020, 589, 125363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, J.; Zhao, C.; Wang, C.; Hao, W.; Meng, L.; Huang, C. Seasonal and spatial variations of water recharging in the Yangtze River using hydrogen and oxygen stable isotopes. J. Hydrol. 2024, 639, 131563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, M.D.; Gröcke, D.R.; Joshi, S.K.; Greenwell, H.C. Investigating groundwater recharge using hydrogen and oxygen stable isotopes in Kabul city, a semi-arid region. J. Hydrol. 2023, 626, 130187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Li, P.; He, X.; Zhang, Q. Tracing the sources and evaporation fate of surface water and groundwater using stable isotopes of hydrogen and oxygen. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 931, 172708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyssen, J.; Clymans, W.; Descheemaeker, K.; Poesen, J.; Vandecasteele, I.; Vanmaercke, M.; Walraevens, K. Impact of soil and water conservation measures on catchment hydrological response—A case in north Ethiopia. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 1880–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.; Li, P.; Cui, Z.; Li, Z. The influence of different check dam configurations on the downstream river topography and water–sediment relationship. J. Hydrol. 2025, 656, 133046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Hou, J.; Huang, M.; Li, Z.; Xu, K.; Zhang, D.; Wang, C. Impact of soil and water conservation measures and precipitation on streamflow in the middle and lower reaches of the Hulu River Basin, China. Catena 2020, 195, 104792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Wang, C.; Yang, N.; Duan, L.; Yu, R.; Zhang, K.; Sun, P. Large-scale surface water-groundwater origins and connectivity in the Ordos Basin, China: Insight from hydrogen and oxygen isotopes. Environ. Res. 2023, 236, 116837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, K.J.; McDonnell, J.J. A review and evaluation of catchment transit time modeling. J. Hydrol. 2006, 330, 543–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, H.; Li, B.; Wang, Y. Characteristics of Streamflow Components in the Tarim River Basin Based on Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotopes. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Pekin. 2025, 61, 358–368. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, A.F.; Draxler, R.R.; Rolph, G.D.; Stunder, B.J.B.; Cohen, M.D.; Ngan, F. NOAA’s HYSPLIT atmospheric transport and dispersion modeling system. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc 2015, 96, 2059–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guanghe, X.; Huang, B.; Kunpeng, L.; Chen, J. Studies on Submersible Short-Circuit Blowing Based on Orthogonal Experiments, Back Propagation Neural Network Prediction, and Pearson Correlation Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 10321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Xiubao, S.; Guoyu, R. A review of seasonal division and change research. Prog. Geogr. 2024, 43, 826–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Huang, T.; Man, W.; Hu, H.; Long, Y.; Li, Z.; Pang, Z. Contribution of recycled moisture to precipitation: A modified D-excess-based model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2021GL095909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Hou, F.; Ni, B. Research on Stable Isotopes of Hydrogen and Oxygen in Atmospheric Precipitation in China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 1983, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Song, X.; Zhong, G. Comparative analysis of three methods for HYSPLIT atmospheric trajectories clustering. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Mi, N.; Mi, W.; Li, L. Spatial non-stationary characteristics between grass yield and its influencing factors in the Ningxia temperate grasslands based on a mixed geographically weighted regression model. J. Geogr. Sci. 2022, 32, 1076–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Qiu, Y. The difference in cloud water resources and precipitation on the eastern and western sides of the Liupan mountains caused by topographic effects. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Yang, K.; Lu, H.; Sun, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tang, Q. Weakened subtropical westerlies reduced early spring precipitation in the Southeast Tibetan Plateau. J. Clim. 2023, 36, 4363–4373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Du, R.; Cao, X.; Yu, H.; Xu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Peng, J. Evaporation dominates the loss of plateau lake in Southwest China using water isotope balance assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 873, 162415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreedevi, P.D.; Sreekanth, P.D.; Reddy, D.V. Deuterium excess of groundwater as a proxy for recharge in an evaporative environment of a granitic aquifer, South India. J. Geol. Soc. India 2021, 97, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Yin, L.; Ao, H.; Cheng, G.; Zhou, M.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, J. Isotopic evidence for the moisture origin and composition of surface runoff in the headwaters of the Heihe River basin. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2011, 56, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhao, Q.; Qin, X.; Gao, Q.; Lyu, C. Spatio-temporal distribution characteristics of hydrogen and oxygen isotope components in the Tuojia River and their influencing factors. J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 29, 1461–1469. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, M.; Chen, Y.; Khalil, M.M. Isotopic composition of groundwater resources in arid environments. J. Hydrol. 2022, 609, 127773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Gao, J.; Luo, L.; Zhao, A.; Niu, X.; Yu, W.; Chen, G. Temporal variations of stable isotopic compositions in atmospheric water vapor on the Southeastern Tibetan Plateau and their controlling factors. Atmos. Res. 2024, 303, 107328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, C.; Li, X.Y.; Fu, C.; Wu, H.; Wang, P.; Liu, J. Hydrometeorological processes and moisture sources in the northeastern Tibetan Plateau: Insights from a 7-yr study on precipitation isotopes. J. Clim. 2022, 35, 6519–6531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasechko, S.; Sharp, Z.D.; Gibson, J.J.; JeanBirks, S.; Yi, Y.; Fawcett, P.J. Uncertainties in transpiration estimates Reply. Nature 2014, 506, E2–E3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, C.; McDonnell, J.J. (Eds.) Isotope Tracers in Catchment Hydrology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Moazeni-Noghondar, S.; Golkarian, A.; Azari, M.; Asgari Lajayer, B. Study on soil water retention and infiltration rate: A case study in eastern Iran. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitambo, B.M.; Wongchuig, S.; Tshimanga, R.M.; Paris, A.; Blazquez, A.; Moreira, D.; Papa, F. Hydrogeological control of groundwater variations in the Congo River Basin revealed by GRACE water storage change decomposition. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2025, 62, 102810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.; Zhang, H.; Shi, Y. Cascade effects of triggered earthquakes of cascade dams: Taking Xiluodu and Xiangjiaba reservoirs as examples. Chin. J. Geophys. 2023, 66, 2470–2488. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bai, L.L.; Shi, P.; Wang, W.; Li, Z.B.; Yu, K.X.; Li, P.; Chen, W.F. Sediment sources and their impacts on a check dam-controlled watershed, Loess Plateau, China. J. Mt. Sci. 2023, 20, 1660–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deemer, B.R.; Harrison, J.A.; Li, S.; Beaulieu, J.J.; DelSontro, T.; Barros, N.; Vonk, J.A. Greenhouse gas emissions from reservoir water surfaces: A new global synthesis. BioScience 2016, 66, 949–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poff, N.L.; Zimmerman, J.K. Ecological responses to altered flow regimes: A literature review to inform the science and management of environmental flows. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| δ18O | d-excess | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | T | RH | P | T | RH | |
| Spring | 0.18 | −0.61 * | −0.51 * | 0.16 | 0.04 | −0.04 |
| Summer | −0.55 ** | −0.28 | −0.21 | 0.42 * | −0.15 | 0.35 |
| Autumn | −0.02 | −0.16 | −0.29 | 0.23 | 0.22 | 0.16 |
| Winter | 0.63 * | 0.70 * | −0.62 * | −0.34 | −0.30 | 0.32 |
| Tributary | Seasons | PRE/% | UGW/% | Recharge Downward/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| to G2 | ||||
| G1 | Spring | 51.27 | 48.73 | 9.89 |
| Summer | 68.94 | 31.06 | 13.45 | |
| Autumn | 56.71 | 43.29 | 10.36 | |
| Winter | 44.32 | 55.68 | 6.34 | |
| to 1# | ||||
| G2 | Spring | 45.21 | 44.9 | 7.92 |
| Summer | 55.38 | 31.17 | 15.78 | |
| Autumn | 52.65 | 36.99 | 16.38 | |
| Winter | 39.65 | 54.01 | 10.99 | |
| to 2# | ||||
| X | Spring | 48.12 | 51.88 | 12.55 |
| Summer | 62.33 | 37.67 | 26.39 | |
| Autumn | 65.01 | 34.99 | 24.55 | |
| Winter | 37.99 | 62.01 | 14.61 |
| Check Dams | PRE/d | UGW/d |
|---|---|---|
| 1# | 206 | 603 |
| 2# | 134 | 975 |
| 3# | 138 | 956 |
| 4# | 124 | 916 |
| 5# | 142 | 1001 |
| 6# | 115 | 789 |
| G1 | 125 | 372 |
| G2 | 151 | 478 |
| X | 106 | 245 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.-J.; Meng, C.; Cheng, Y.-T.; Wang, J. The Construction of Check Dams on the Loess Plateau Has Prolonged Water Transmission Times and Altered Recharge Relationships. Water 2025, 17, 3320. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17223320
Sun Y, Zhang Y, Liu X-J, Meng C, Cheng Y-T, Wang J. The Construction of Check Dams on the Loess Plateau Has Prolonged Water Transmission Times and Altered Recharge Relationships. Water. 2025; 17(22):3320. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17223320
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Yi, Yi Zhang, Xiao-Jun Liu, Chen Meng, Yu-Ting Cheng, and Jing Wang. 2025. "The Construction of Check Dams on the Loess Plateau Has Prolonged Water Transmission Times and Altered Recharge Relationships" Water 17, no. 22: 3320. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17223320
APA StyleSun, Y., Zhang, Y., Liu, X.-J., Meng, C., Cheng, Y.-T., & Wang, J. (2025). The Construction of Check Dams on the Loess Plateau Has Prolonged Water Transmission Times and Altered Recharge Relationships. Water, 17(22), 3320. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17223320





