Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Potential Drinking Water Sources Globally: Distributions, Monitoring Trends, and Risk Assessment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Sources of Information and Methodology
2.2. Data Treatment
2.3. Risk Assessment
3. Results and Discussion
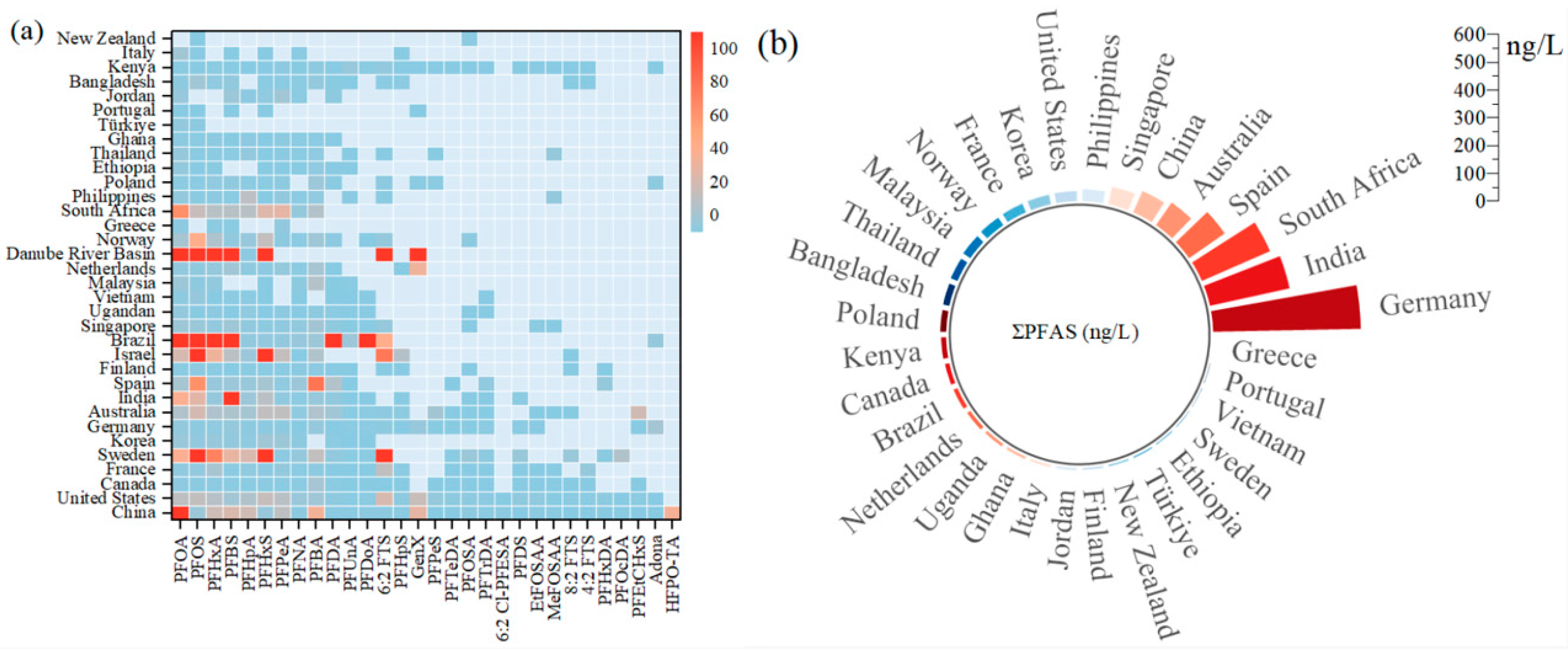
3.1. Concentration and Distribution Characteristics of PFAS in Potential Drinking Water Sources Worldwide
3.1.1. Low and Medium Concentrations of ΣPFAS
3.1.2. High Concentrations of ΣPFAS
3.1.3. High Presence Level of PFAS
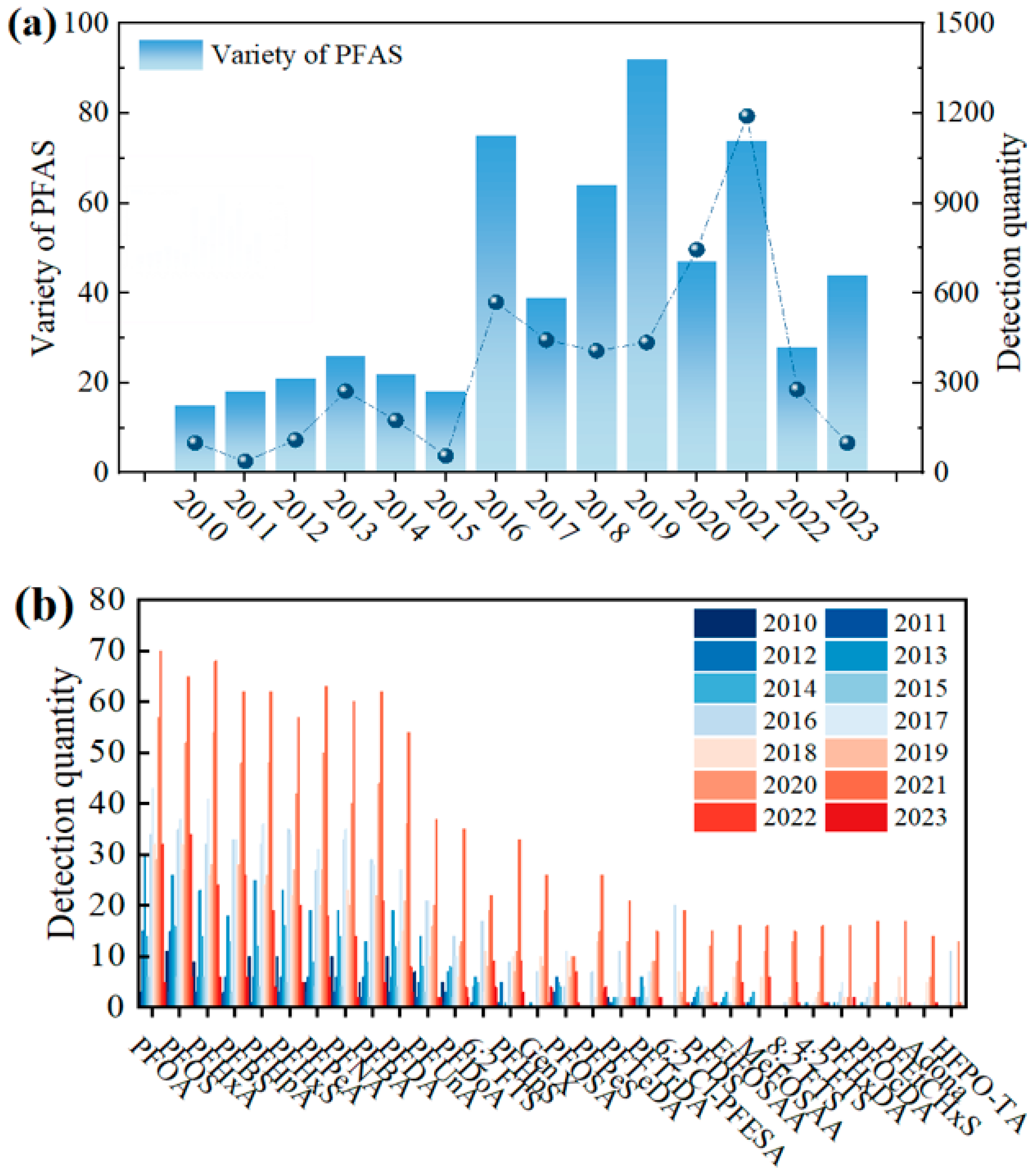
3.2. Monitor the Time-Series Changes in PFAS Species
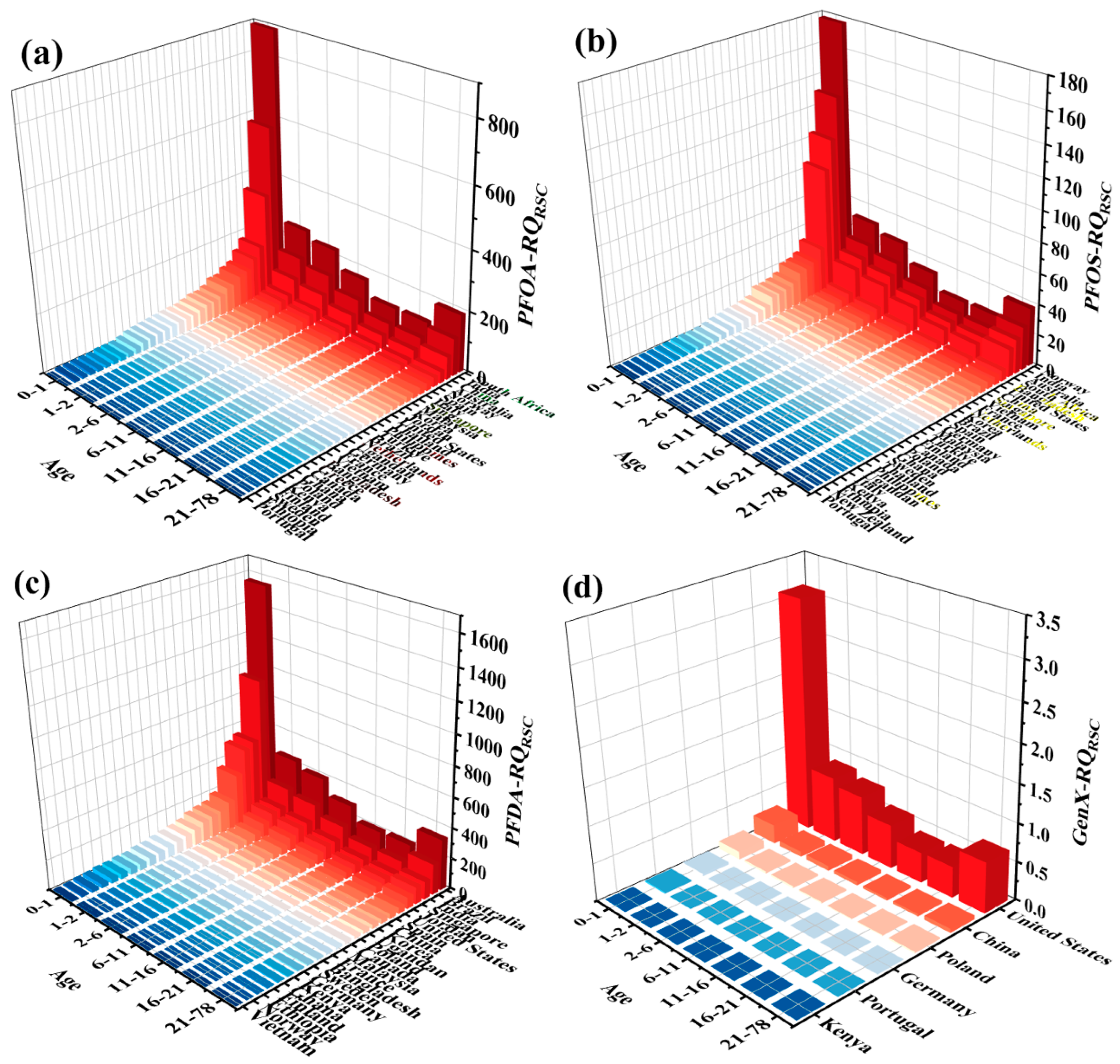
3.3. Global Risk Assessment of Potential Drinking Water Sources
3.4. The Health Impacts of PFAS
3.5. The Challenge of Reducing the Risk of PFAS
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schwichtenberg, T.; Bogdan, D.; Carignan, C.C.; Reardon, P.; Rewerts, J.; Wanzek, T.; Field, J.A. PFAS and Dissolved Organic Carbon Enrichment in Surface Water Foams on a Northern U.S. Freshwater Lake. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 14455–14464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurwadkar, S.; Dane, J.; Kanel, S.R.; Nadagouda, M.N.; Cawdrey, R.W.; Ambade, B.; Struckhoff, G.C.; Wilkin, R. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in water and wastewater: A critical review of their global occurrence and distribution. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 809, 151003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maclnnis, J.J.; Lehnherr, I.; Muir, D.C.G.; St Pierre, K.A.; St Louis, V.L.; Spencer, C.; De Silva, A.O. Fate and Transport of Perfluoroalkyl Substances from Snowpacks into a Lake in the High Arctic of Canada. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 10753–10762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Qu, Y.; Huang, J.; Weber, R. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in Chinese drinking water: Risk assessment and geographical distribution. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2021, 33, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, D.; Miaz, L.T. Spatial and Temporal Trends of Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Global Ocean and Coastal Waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 9527–9537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, K.Y.; Yamazaki, E.; Yamashita, N.; Taniyasu, S.; Murphy, M.B.; Horii, Y.; Petrick, G.; Kallerborn, R.; Kannan, K.; Murano, K.; et al. Transport of Perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) from an arctic glacier to downstream locations: Implications for sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 447, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lin, X.; Li, J.; Liu, P.; Lee, H.K.; Huang, Z. The sources and bioaccumulation of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in animal-derived foods and the potential risk of dietary intake. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-Q.; Hu, L.-X.; Liu, T.; Zhao, J.-H.; Yang, Y.-Y.; Liu, Y.-S.; Ying, G.-G. Per- and polyfluoralkyl substances (PFAS) in drinking water system: Target and non-target screening and removal assessment. Environ. Int. 2022, 163, 107219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorengard, M.; Bergstrom, S.; McCleaf, P.; Wiberg, K.; Ahrens, L. Long-distance transport of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in a Swedish drinking water aquifer. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 311, 119981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechner, M.; Knapp, H. Carryover of Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) and Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) from Soil to Plant and Distribution to the Different Plant Compartments Studied in Cultures of Carrots (Daucus carota ssp. Sativus), Potatoes (Solanum tuberosum), and Cucumbers (Cucumis sativus). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 11011–11018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, C.J.; Furdui, V.I.; Franklin, J.; Koerner, R.M.; Muir, D.C.G.; Mabury, S.A. Perfluorinated Acids in Arctic Snow: New Evidence for Atmospheric Formation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 3455–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, L.B.; Pickard, H.M.; Alvarez, D.A.; Becanova, J.; Keefe, S.H.; LeBlanc, D.R.; Lohmann, R.; Steevens, J.A.; Vajda, A.M. Uptake of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances by Fish, Mussel, and Passive Samplers in Mobile-Laboratory Exposures Using Groundwater from a Contamination Plume at a Historical Fire Training Area, Cape Cod, Massachusetts. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 5544–5557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, E.K.; Hall, L.M.; Brown, M.A.; Taylor-Manges, A.; Green, T.; Suchanec, K.; Furman, B.T.; Congdon, V.M.; Wilson, S.S.; Osborne, T.Z.; et al. Aquatic Vegetation, an Understudied Depot for PFAS. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2023, 34, 1826–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, J.-M.; Chen, D.; Han, F.-J.; Guo, Y.; Zeng, L.; Lu, X.; Wang, F. A short review on human exposure to and tissue distribution of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 1058–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.-J.; Wei, Y.-J.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Zhang, Y.-F. A review of cardiovascular effects and underlying mechanisms of legacy and emerging per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). Arch. Toxicol. 2023, 97, 1195–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsthuber, M.; Kaiser, A.M.; Granitzer, S.; Hassl, I.; Hengstschläger, M.; Stangl, H.; Gundacker, C. Albumin is the major carrier protein for PFOS, PFOA, PFHxS, PFNA and PFDA in human plasma. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown-Leung, J.M.; Cannon, J.R. Neurotransmission Targets of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substance Neurotoxicity: Mechanisms and Potential Implications for Adverse Neurological Outcomes. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2022, 35, 1312–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Ng, C. Absorption, distribution, and toxicity of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in the brain: A review. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2021, 23, 1623–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appel, M.; Forsthuber, M.; Ramos, R.; Widhalm, R.; Granitzer, S.; Uhl, M.; Hengstschläger, M.; Stamm, T.; Gundacker, C. The transplacental transfer efficiency of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS): A first meta-analysis. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B Crit. Rev. 2021, 25, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniou, E.; Colnot, T.; Zeegers, M.; Dekant, W. Immunomodulation and exposure to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances: An overview of the current evidence from animal and human studies. Arch. Toxicol. 2022, 96, 2261–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Liu, S.; Yang, J.; Zheng, S.; Sun, B. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) and cancer: Detection methodologies, epidemiological insights, potential carcinogenic mechanisms, and future perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 953, 176158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wackett, L.P. Confronting PFAS persistence: Enzymes catalyzing C-F bond cleavage. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2025, 50, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, C.N.; Castaneda, A.; Ornstein, E.; de Navarro, M.G.; McNamee, B.; Najera, S.; Calzadilla, D.; Quinete, N. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) composition and distribution in surface water of the Miccosukee Indian Reservation, Everglades and tributaries in the coastal environment of Miami, Florida. Environ. Res. 2025, 278, 121627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofiera, L.M.; Wintgens, T.; Kazner, C. Retention of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) and influencing factors by conventional and modified constructed wetlands treating municipal wastewater effluent. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2025, 39, 104319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, M.; Bonnet, B.; Hale, S.E.; Sørmo, E.; Cornelissen, G.; Ahrens, L.; Arp, H.P.H. Measurement and modelling of sorbent-amendment impacts on seasonal and long-term PFAS transport through unsaturated soil lysimeters. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 494, 138662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brusseau, M.L.; Guo, B. PFAS concentrations in soil versus soil porewater: Mass distributions and the impact of adsorption at air-water interfaces. Chemosphere 2022, 302, 134938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celis, J.E.; Espejo, W.; Bervoets, L.; Padilha, J.; Mello, F.V.; Sandoval, M.; Chiang, G.; Groffen, T. Bioaccumulation of per- and polyfluoroalkylated substances (PFAS) in marine invertebrates and fishes from Antarctica and different coastal areas of Chile. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2025, 219, 118300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manojkumar, Y.; Pilli, S.; Rao, P.V.; Tyagi, R.D. Sources, occurrence and toxic effects of emerging per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2023, 97, 107174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, J.; Bolan, N.S.; Kumar, M.; Nitai, A.S.; Ahmed, M.B.; Bolan, S.S.; Vithanage, M.; Rinklebe, J.; Mukhopadhyay, R.; Srivastava, P.; et al. Distribution, transformation and remediation of poly- and per-fluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in wastewater sources. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 164, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barisci, S.; Suri, R. Occurrence and removal of poly/perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in municipal and industrial wastewater treatment plants. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 84, 3442–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taher, M.N.; Al-Mutwalli, S.A.; Barisci, S.; Koseoglu-Imer, D.Y.; Dumee, L.F.; Shirazi, M.M.A. Progress on remediation of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) from water and wastewater using membrane technologies: A review. J. Water Process. Eng. 2024, 59, 104858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Pinkard, B.R.; Wang, S.; Novosselov, I.V. Review: Hydrothermal treatment of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Duan, J.; Tian, S.; Ji, H.; Zhu, Y.; Wei, Z.; Zhao, D. Short-chain per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in aquatic systems: Occurrence, impacts and treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 380, 122506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.; Shetti, N.P.; Basu, S.; Nadagouda, M.N.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Treatment technologies for removal of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in biosolids. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 453, 139964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Ibrar, I.; Al-Juboori, R.A.; Singh, L.; Ganbat, N.; Kazwini, T.; Karbassiyazdi, E.; Samal, A.K.; Subbiah, S.; Altaee, A. Updated review on emerging technologies for PFAS contaminated water treatment. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2022, 182, 667–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teymoorian, T.; Munoz, G.; Vo Duy, S.; Liu, J.; Sauvé, S. Tracking PFAS in Drinking Water: A Review of Analytical Methods and Worldwide Occurrence Trends in Tap Water and Bottled Water. ACS EST Water 2023, 3, 246–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riva, F.; Castiglioni, S.; Fattore, E.; Manenti, A.; Davoli, E.; Zuccato, E. Monitoring emerging contaminants in the drinking water of Milan and assessment of the human risk. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2018, 221, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jesus Gaffney, V.; Almeida, C.M.M.; Rodrigues, A.; Ferreira, E.; Benoliel, M.J.; Cardoso, V.V. Occurrence of pharmaceuticals in a water supply system and related human health risk assessment. Water Res. 2015, 72, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomaidi, V.S.; Tsahouridou, A.; Matsoukas, C.; Stasinakis, A.S.; Petreas, M.; Kalantzi, O.I. Risk assessment of PFASs in drinking water using a probabilistic risk quotient methodology. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 712, 136485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnbaum, L.S.; Post, G.B.; Gleason, J.A.; Cooper, K.R. Key scientific issues in developing drinking water guidelines for perfluoroalkyl acids: Contaminants of emerging concern. PLoS Biol. 2017, 15, e2002855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paige, T.; De Silva, T.; Buddhadasa, S.; Prasad, S.; Nugegoda, D.; Pettigrove, V. Background concentrations and spatial distribution of PFAS in surface waters and sediments of the greater Melbourne area, Australia. Chemosphere 2024, 349, 140791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coggan, T.L.; Anumol, T.; Pyke, J.; Shimeta, J.; Clarke, B.O. A single analytical method for the determination of 53 legacy and emerging per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in aqueous matrices. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 3507–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, D.; Moodie, D.; Green, M.P.; Mulder, R.A.; Clarke, B.O. Field-Based Distribution and Bioaccumulation Factors for Cyclic and Aliphatic Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in an Urban Sedentary Waterbird Population. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 8231–8244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, P.A.; Hoeksema, S.D.; Thompson, S.N.; Trayler, K.M. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) contamination in a microtidal urban estuary: Sources and sinks. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 193, 115215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batayi, B.; Okonkwo, O.J.; Daso, A.P. Poly- and perfluorinated substances in environmental water from the Hartbeespoort and Roodeplaat Dams, South Africa. Water SA 2021, 47, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groffen, T.; Wepener, V.; Malherbe, W.; Bervoets, L. Distribution of perfluorinated compounds (PFASs) in the aquatic environment of the industrially polluted Vaal River, South Africa. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 1334–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, M.; Campo, J.; Farré, M.; Pérez, F.; Picó, Y.; Barceló, D. Perfluoroalkyl substances in the Ebro and Guadalquivir river basins (Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 540, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignotti, E.; Casas, G.; Llorca, M.; Tellbuscher, A.; Almeida, D.; Dinelli, E.; Farre, M.; Barcelo, D. Seasonal variations in the occurrence of perfluoroalkyl substances in water, sediment and fish samples from Ebro Delta (Catalonia, Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607–608, 933–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, J.; Lorenzo, M.; Perez, F.; Pico, Y.; Farre, M.; Barcelo, D. Analysis of the presence of perfluoroalkyl substances in water, sediment and biota of the Jucar River (E Spain). Sources, partitioning and relationships with water physical characteristics. Environ. Res. 2016, 147, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campo, J.; Perez, F.; Masia, A.; Pico, Y.; Farre, M.; Barcelo, D. Perfluoroalkyl substance contamination of the Llobregat River ecosystem (Mediterranean area, NE Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 503–504, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skaar, J.S.; Ræder, E.M.; Lyche, J.L.; Ahrens, L.; Kallenborn, R. Elucidation of contamination sources for poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) on Svalbard (Norwegian Arctic). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 26, 7356–7363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, L.; Rakovic, J.; Ekdahl, S.; Kallenborn, R. Environmental distribution of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) on Svalbard: Local sources and long-range transport to the Arctic. Chemosphere 2023, 345, 140463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Fatowe, M.; Cui, D.; Quinete, N. Assessment of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in Biscayne Bay surface waters and tap waters from South Florida. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viticoski, R.L.; Wang, D.; Feltman, M.A.; Mulabagal, V.; Rogers, S.R.; Blersch, D.M.; Hayworth, J.S. Spatial distribution and mass transport of Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in surface water: A statewide evaluation of PFAS occurrence and fate in Alabama. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 836, 155524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Arevalo, E.; Strynar, M.; Lindstrom, A.; Richardson, M.; Kearns, B.; Pickett, A.; Smith, C.; Knappe, D.R.U. Legacy and Emerging Perfluoroalkyl Substances Are Important Drinking Water Contaminants in the Cape Fear River Watershed of North Carolina. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2016, 3, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petre, M.A.; Salk, K.R.; Stapleton, H.M.; Ferguson, P.L.; Tait, G.; Obenour, D.R.; Knappe, D.R.U.; Genereux, D.P. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in river discharge: Modeling loads upstream and downstream of a PFAS manufacturing plant in the Cape Fear watershed, North Carolina. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 831, 154763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Son, Y. Perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in surface water and sediments from two urban watersheds in Nevada, USA. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 751, 141622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, K.A.; Ray, H.; Gerrity, D.; Quinones, O.; Dano, E.; Prieur, J.; Vanderford, B.; Steinle-Darling, E.; Dickenson, E.R.V. Sources of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in an arid, urban, wastewater-dominated watershed. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 940, 173361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Chen, C.-E.; Zhang, D.; Tang, J. Emerging and legacy per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the rivers of a typical industrialized province of China: Spatiotemporal variations, mass discharges and ecological risks. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 986719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Shao, P.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Gai, N. Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in Rivers and Drinking Waters from Qingdao, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joerss, H.; Schramm, T.-R.; Sun, L.; Guo, C.; Tang, J.; Ebinghaus, R. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in Chinese and German river water—Point source- and country-specific fingerprints including unknown precursors. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Hong, P.; Ruan, Y.; Lin, H.; Xu, J.; Zhang, H.; Deng, S.; Wu, H.; Chen, L.; et al. Legacy and Emerging Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances Surveillance in Bufo gargarizans from Inlet Watersheds of Chaohu Lake, China: Tissue Distribution and Bioaccumulation Potential. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 13148–13160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, F.; Chen, F.; Wang, W.; Tang, H.; Gao, Y.; Meng, L. Occurrence and transport of novel and legacy poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances in coastal rivers along the Laizhou Bay, northern China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 198, 115909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zhang, J.; Hu, G.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H.; Wei, D.; Cai, D.; Yu, Y.; Li, X.; Ding, P.; et al. Characterization of the distribution, source, and potential ecological risk of perfluorinated alkyl substances (PFASs) in the inland river basin of Longgang District, South China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 287, 117642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.-B.; Hu, L.-X.; Yang, Y.-Y.; Wang, T.-T.; Liu, C.; Ying, G.-G. Contamination profiles and health risks of PFASs in groundwater of the Maozhou River basin. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 113996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Shen, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L. Tissue distribution of emerging per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in wild fish species from Qiantang river, east China: Comparison of 6:2 Cl-PFESA with PFOS. Environ. Res. 2024, 262, 119816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.-Y.; Lu, G.-H.; Piao, H.-T.; Chen, S.; Jiao, X.-C.; Gai, N.; Yamazaki, E.; Yamashita, N.; Pan, J.; Yang, Y.-L. Current Contamination Status of Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Tapwater from 17 Cities in the Eastern China and Their Correlations with Surface Waters. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2017, 99, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xie, Y.; Zhou, L.; Lu, G.; Li, Y.; Gao, P.; Hou, J. Co-accumulation characteristics and interaction mechanism of microplastics and PFASs in a large shallow lake. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 135780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, C.; Wang, Q.; Song, X.; Chen, X.; Fan, R.; Ding, D.; Liu, Y. Distribution, source identification and health risk assessment of PFASs and two PFOS alternatives in groundwater from non-industrial areas. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 152, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Song, L.; Zhao, Z.; Ma, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, H.; Ma, H.; Cai, M.; Codling, G.; Ebinghaus, R.; et al. Occurrence and trends in concentrations of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in surface waters of eastern China. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 820–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Meng, J.; Zhou, Y.; Song, N.; Zhao, Y.; Hong, M.; Yu, J.; Cao, L.; Dou, Y.; Kong, D. Transport and health risk of legacy and emerging per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the water cycle in an urban area, China: Polyfluoroalkyl phosphate esters are of concern. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 920, 171010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, S.M.; Zhang, S.; Tait, G.H.; Hoffman, K.; Collier, D.N.; Hoppin, J.A.; Stapleton, H.M. PFAS levels in paired drinking water and serum samples collected from an exposed community in Central North Carolina. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 895, 165091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokranov, A.K.; LeBlanc, D.R.; Pickard, H.M.; Ruyle, B.J.; Barber, L.B.; Hull, R.B.; Sunderland, E.M.; Vecitis, C.D. Surface-water/groundwater boundaries affect seasonal PFAS concentrations and PFAA precursor transformations. Environ. Sci. Process Impacts 2021, 23, 1893–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, E.; Zhu, Z.; Yin, D.; Qiu, Y.; Karrman, A.; Yeung, L.W.Y. A pilot study on extractable organofluorine and per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in water from drinking water treatment plants around Taihu Lake, China: What is missed by target PFAS analysis? Environ. Sci. Process Impacts 2022, 24, 1060–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starling, M.C.V.M.; Rodrigues, D.A.S.; Miranda, G.A.; Jo, S.; Amorim, C.C.; Ankley, G.T.; Simcik, M. Occurrence and potential ecological risks of PFAS in Pampulha Lake, Brazil, a UNESCO world heritage site. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 948, 174586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussabek, D.; Söderman, A.; Imura, T.; Persson, K.M.; Nakagawa, K.; Ahrens, L.; Berndtsson, R. PFAS in the Drinking Water Source: Analysis of the Contamination Levels, Origin and Emission Rates. Water 2022, 15, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuwald, I.J.; Huebner, D.; Wiegand, H.L.; Valkov, V.; Borchers, U.; Noedler, K.; Scheurer, M.; Hale, S.E.; Arp, H.P.H.; Zahn, D. Ultra-Short-Chain PFASs in the Sources of German Drinking Water: Prevalent, Overlooked, Difficult to Remove, and Unregulated. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 6380–6390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.; Alygizakis, N.; Androulakakis, A.; Galani, A.; Aalizadeh, R.; Thomaidis, N.S.; Slobodnik, J. Target and suspect screening of 4777 per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in river water, wastewater, groundwater and biota samples in the Danube River Basin. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 436, 129276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topaz, T.; Gridish, N.; Sade, T.; Zedaka, H.; Suari, Y.; Konomi, A.; Gkotsis, G.; Aleiferi, E.; Nika, M.-C.; Thomaidis, N.S.; et al. Exploring Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Microestuaries: Occurrence, Distribution, and Risks. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2024, 11, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauns, B.; Chandra, S.; Civil, W.; Lapworth, D.J.; MacDonald, A.M.; McKenzie, A.A.; Read, D.S.; Sekhar, M.; Singer, A.C.; Thankachan, A.; et al. Presence of emerging organic contaminants and microbial indicators in surface water and groundwater in urban India. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 362, 124983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelch, K.E.; McKnight, T.; Reade, A. 70 analyte PFAS test method highlights need for expanded testing of PFAS in drinking water. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 876, 162978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeNicola, M.; Lin, Z.; Quinones, O.; Vanderford, B.; Song, M.; Westerhoff, P.; Dickenson, E.; Hanigan, D. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances and organofluorine in lakes and waterways of the northwestern Great Basin and Sierra Nevada. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 166971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Liu, J.; Bao, K.; Chen, N.; Meng, B. Multicompartment occurrence and partitioning of alternative and legacy per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in an impacted river in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 138753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Wang, T.; Meng, J.; Wang, P.; Li, Q.; Lu, Y. Perfluoroalkyl substances in the Daling River with concentrated fluorine industries in China: Seasonal variation, mass flow, and risk assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 10009–10018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, Y.; Huang, J.; Liang, Z.; Liu, G.; Chen, D.; Guo, Y.; Wang, F. Occurrence and Ecological Risk Assessment of Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in Water and Sediment from an Urban River in South China. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 81, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Cheng, X.; Hua, X.; Jiang, B.; Tian, C.; Tang, J.; Li, Q.; Sun, H.; Lin, T.; Liao, Y.; et al. Emerging and legacy per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in water, sediment, and air of the Bohai Sea and its surrounding rivers. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ateia, M.; Maroli, A.; Tharayil, N.; Karanfil, T. The overlooked short- and ultrashort-chain poly- and perfluorinated substances: A review. Chemosphere 2019, 220, 866–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solan, M.E.; Koperski, C.P.; Senthilkumar, S.; Lavado, R. Short-chain per- and polyfluoralkyl substances (PFAS) effects on oxidative stress biomarkers in human liver, kidney, muscle, and microglia cell lines. Environ. Res. 2023, 223, 115424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Sheng, N.; Guo, Y.; Yeung, L.W.Y.; Dai, J.; Pan, Y. Nontargeted Identification and Temporal Trends of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in a Fluorochemical Industrial Zone and Adjacent Taihu Lake. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 7986–7996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, D.; Li, H.; Holzhausen, E.A.; Young, N.; Platz, E.A.; Walker, D.I.; Liang, D.; Aung, M.; Goodrich, J.A.; Setiawan, V.W.; et al. A scoping review on per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) and colorectal cancer: Evidence from in vitro, animal, and epidemiological studies. Environ. Int. 2025, 203, 109778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Wang, D.; Feng, L.; Wang, H.; Li, X. Prognostic associations of PFAS in ovarian cancer: Insights from exploratory analysis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 303, 119039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahi, S.; Winquist, A.; Troeschel, A.N.; Diver, W.R.; Hodge, J.M.; Deubler, E.; Patel, A.V.; Newton, C.C.; Teras, L.R. A case-cohort study of the association between per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) and breast cancer among participants in the American Cancer Society’s Cancer Prevention Study-II. Environ. Res. 2025, 285, 122381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siwakoti, R.C.; Rosario-Pabon, Z.; Vélez Vega, C.M.; Hao, W.; Alshawabkeh, A.; Cordero, J.F.; Watkins, D.J.; Meeker, J.D. Assessment of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) exposure and associations with oxidative stress biomarkers among pregnant women from the PROTECT cohort. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 973, 179130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byns, C.; Newell, K.; AbdElgawad, H.; Beemster, G.T.S.; Bervoets, L.; Groffen, T. Active biomonitoring of PFAS in Asian Clams: Associations with oxidative stress, respiration and condition index. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 385, 127067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Chung, S.; Wang, M. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) toxicity and mitigation of adipogenic dysregulation in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2025, 204, 115649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCall, J.R.; Sausman, K.T.; Brown, A.P.; Mead, R.N. In vitro cytotoxicity of six per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in human immune cell lines. Toxicol. Vitr. 2024, 100, 105910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iulini, M.; Russo, G.; Crispino, E.; Paini, A.; Fragki, S.; Corsini, E.; Pappalardo, F. Advancing PFAS risk assessment: Integrative approaches using agent-based modelling and physiologically-based kinetic for environmental and health safety. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2024, 23, 2763–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Ji, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, F.; Sheng, N.; Dai, J.; Pan, Y. Unveiling Priority Emerging PFAS in Taihu Lake Using Integrated Nontarget Screening, Target Analysis, and Risk Characterization. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2024, 58, 18980–18991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Shang, Y.; Bai, L.; Luo, S.; Seviour, T.W.; Guo, Z.; Ottosen, L.D.M.; Wei, Z. Complete defluorination of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) by ultrasonic pyrolysis towards zero fluoro-pollution. Water Res. 2023, 235, 119829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesan, A.K.; Lee, C.-S.; Gobler, C.J. Hydroxyl-radical based advanced oxidation processes can increase perfluoroalkyl substances beyond drinking water standards: Results from a pilot study. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 847, 157577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.-h.; Liang, X.-y.; Yang, S.-w.; Hu, Y.-y. Photochemical defluorination of aqueous perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) by VUV/Fe3+ system. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 239, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilić, N.; Andalib, A.; Lippert, T.; Knoop, O.; Franke, M.; Bräutigam, P.; Drewes, J.E.; Hübner, U. Ultrasonic degradation of GenX (HFPO-DA)—Performance comparison to PFOA and PFOS at high frequencies. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 472, 144630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.Y.; Ekpe, O.D.; Lee, H.-J.; Oh, J.-E. Perfluoroalkyl substances and pharmaceuticals removal in full-scale drinking water treatment plants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 123235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glover, C.M.; Quiñones, O.; Dickenson, E.R.V. Removal of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances in potable reuse systems. Water Res. 2018, 144, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Tang, W.; Xia, Z.; Wu, B.; Liu, H.; Fu, J.; Lu, Q.; Guo, L.; Gao, C.; Zhou, Q.; et al. Machine learning predicts the serum PFOA and PFOS levels in pregnant women: Enhancement of fatty acid status on model performance. Environ. Int. 2024, 190, 108837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Zhang, W.; Baccarelli, A.A.; Shen, Y. Predicting chemical ecotoxicity by learning latent space chemical representations. Environ. Int. 2022, 163, 107224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudlaff, M.; Sosnowska, A.; Gorb, L.; Bulawska, N.; Jagiello, K.; Puzyn, T. Environmental impact of PFAS: Filling data gaps using theoretical quantum chemistry and QSPR modeling. Environ. Int. 2024, 185, 108568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Teng, M.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhao, W.; Ruan, Y.; Leung, K.M.Y.; Wu, F. Insight into the binding model of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances to proteins and membranes. Environ. Int. 2023, 175, 107951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosnik, M.B.; Kephalopoulos, S.; Muñoz, A.; Aurisano, N.; Cusinato, A.; Dimitroulopoulou, S.; Slobodnik, J.; De Mello, J.; Zare Jeddi, M.; Cascio, C.; et al. Advancing exposure data analytics and repositories as part of the European Exposure Science Strategy 2020-2030. Environ. Int. 2022, 170, 107610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Uchida, T.; Inoue, T.; Iwasaki, Y.; Ito, R.; Akiyama, H. A Comprehensive Analysis of the per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) research landscape through AI-assisted text mining. J. Hazard. Mater. Lett. 2024, 5, 100121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haron, D.E.M.; Yoneda, M.; Hod, R.; Ramli, M.R.; Aziz, M.Y. Assessment of 18 endocrine disrupting chemicals in tap water samples from Klang Valley, Malaysia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 111062–111075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarebska, M.; Bajkacz, S.; Hordyjewicz-Baran, Z. Assessment of legacy and emerging PFAS in the Oder River: Occurrence, distribution, and sources. Environ. Res. 2024, 251, 118608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, E.K.; Aristizabal-Henao, J.; Timshina, A.; Ditz, H.L.; Camacho, C.G.; da Silva, B.F.; Coker, E.S.; Deliz Quiñones, K.Y.; Aufmuth, J.; Bowden, J.A. Assessment of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in the Indian River Lagoon and Atlantic coast of Brevard County, FL, reveals distinct spatial clusters. Chemosphere 2022, 301, 134478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz, G.; Mercier, L.; Duy, S.V.; Liu, J.; Sauvé, S.; Houde, M. Bioaccumulation and trophic magnification of emerging and legacy per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in a St. Lawrence River food web. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 309, 119739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wang, Q.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Y.; He, A.; Chen, Y.; Si, S. Biological effects of perfluoroalkyl substances on running water ecosystems: A case study in Beiluo River, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 468, 133808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tröger, R.; Köhler, S.J.; Franke, V.; Bergstedt, O.; Wiberg, K. A case study of organic micropollutants in a major Swedish water source—Removal efficiency in seven drinking water treatment plants and influence of operational age of granulated active carbon filters. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 135680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.-J.; Okvitasari, A.R.; Huang, F.-Y.; Tsai, C.-S. Characteristics, pollution patterns and risks of Perfluoroalkyl substances in drinking water sources of Taiwan. Chemosphere 2021, 264, 128579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Reinhard, M.; Tung Viet, N.; You, L.; He, Y.; Gin, K.Y.-H. Characterization of occurrence, sources and sinks of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in a tropical urban catchment. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 227, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Vestergren, R.; Xu, L.; Song, X.; Niu, X.; Zhang, C.; Cai, Y. Characterizing direct emissions of perfluoroalkyl substances from ongoing fluoropolymer production sources: A spatial trend study of Xiaoqing River, China. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 206, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Jorvekar, S.B.; Bhowmik, S.; Mohapatra, P.; Borkar, R.M. Comprehensive assessment of per and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) contamination in groundwater of Kamrup, Assam, India: Occurrence, health risks, and metabolomic insights. Environ. Sci. Process Impacts 2024, 26, 1601–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-M.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kim, M.-K.; Yang, H.; Lee, J.-E.; Son, Y.; Kho, Y.; Choi, K.; Zoh, K.-D. Concentration and distribution of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in the Asan Lake area of South Korea. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 381, 120909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Liu, X.; Mao, H.; Wang, S. Concentration, distribution, and bioconcentration of short- and long-chain perfluoroalkyl substances in the water, suspended particulate matter, and surface sediment of a typical semi-enclosed bay. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 890, 164416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boiteux, V.; Dauchy, X.; Bach, C.; Colin, A.; Hemard, J.; Sagres, V.; Rosin, C.; Munoz, J.-F. Concentrations and patterns of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances in a river and three drinking water treatment plants near and far from a major production source. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 583, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huff Chester, A.; Gordon, C.; Hartmann, H.A.; Bartell, S.E.; Ansah, E.; Yan, T.; Li, B.; Dampha, N.K.; Edmiston, P.L.; Novak, P.J.; et al. Contaminants of Emerging Concern in the Lower Volta River, Ghana, West Africa: The Agriculture, Aquaculture, and Urban Development Nexus. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2022, 41, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; He, X.; Liu, J.; Yao, Z.; Zhao, H.; Yu, D.; Liu, B.; Liu, T.; Zhao, W. Contamination of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the water source from a typical agricultural area in North China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 10, 1071134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.-G.; Ying, G.-G.; Liu, Y.-S.; Zhang, Q.-Q.; Chen, Z.-F.; Peng, F.-J.; Huang, G.-Y. Contamination profiles of perfluoroalkyl substances in five typical rivers of the Pearl River Delta region, South China. Chemosphere 2014, 114, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Liu, H.; Wei, X.; Li, W.; Chen, J.; Yang, W.; Qian, S.; Yao, J.; Wang, X. Dam operation altered profiles of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in reservoir. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafeiraki, E.; Costopoulou, D.; Vassiliadou, I.; Leondiadis, L.; Dassenakis, E.; Traag, W.; Hoogenboom, R.L.A.P.; van Leeuwen, S.P.J. Determination of perfluoroalkylated substances (PFASs) in drinking water from the Netherlands and Greece. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2015, 32, 2048–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunbiyi, O.D.; Massenat, N.; Quinete, N. Dispersion and stratification of Per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in surface and deep-water profiles: A case study of the Biscayne Bay area. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 909, 168413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Zeng, F. Distribution and Bioaccumulation of Perfluoroalkyl Acids in Xiamen Coastal Waters. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 2612853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Li, S.; Wang, W.; Sun, P.; Yin, C.; Li, X.; Yu, L.; Ren, G.; Peng, L.; Wang, F. Distribution and potential health risks of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in water, sediment, and fish in Dongjiang River Basin, Southern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 99501–99510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhu, H.; Li, B.; Hu, H.; Zhang, T.; Yamazaki, E.; Taniyasu, S.; Yamashita, N.; Sun, H. Distribution and primary source analysis of per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances with different chain lengths in surface and groundwater in two cities, North China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 108, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shields, M.R.; Puthigai, S.; Gregory, L.F.; Berthold, A.A. Distribution of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in the Rapidly Urbanizing Arroyo Colorado Watershed, Texas. J. Contemp. Water Res. Educ. 2024, 180, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melake, B.A.; Bervoets, L.; Nkuba, B.; Groffen, T. Distribution of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in water, sediment, and fish tissue, and the potential human health risks due to fish consumption in Lake Hawassa, Ethiopia. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 112033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Wu, N.; Li, W.; Niu, Z. Distribution, partitioning behavior and positive matrix factorization-based source analysis of legacy and emerging polyfluorinated alkyl substances in the dissolved phase, surface sediment and suspended particulate matter around coastal areas of Bohai Bay, China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brase, R.A.; Schwab, H.E.; Li, L.; Spink, D.C. Elevated levels of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in freshwater benthic macroinvertebrates from the Hudson River Watershed. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Jin, H.; Lu, B.; Lv, C.; Ji, Y.; Zhang, H.; Fan, R.; Zhao, N. Emerging poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances in water and sediment from Qiantang River-Hangzhou Bay. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 875, 162687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, V.E.; Silva Ferreira, A.C.; Cruzeiro, C.; Cardoso, P.G. Enhancement of per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) quantification on surface waters from marinas in the douro river, Portugal. Environ. Res. 2024, 262, 119805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Choo, G.; Kim, H.; Oh, J.-E. Evaluation of the current contamination status of PFASs and OPFRs in South Korean tap water associated with its origin. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 1505–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llewellyn, M.J.; Griffin, E.K.; Caspar, R.J.; Timshina, A.S.; Bowden, J.A.; Miller, C.J.; Baker, B.B.; Baker, T.R. Identification and quantification of novel per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) contamination in a Great Lakes urban-dominated watershed. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 941, 173325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleywegt, S.; Raby, M.; McGill, S.; Helm, P. The impact of risk management measures on the concentrations of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances in source and treated drinking waters in Ontario, Canada. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 748, 141195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussabek, D.; Persson, K.M.; Berndtsson, R.; Ahrens, L.; Nakagawa, K.; Imura, T. Impact of the Sediment Organic vs. Mineral Content on Distribution of the Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Lake Sediment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Capozzi, S.L.; Romanak, K.A.; Lehman, D.C.; Dove, A.; Richardson, V.; Greenberg, T.; McGoldrick, D.; Venier, M. The Ins and Outs of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in the Great Lakes: The Role of Atmospheric Deposition. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 9303–9313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carere, M.; Antoccia, A.; Buschini, A.; Frenzilli, G.; Marcon, F.; Andreoli, C.; Gorbi, G.; Suppa, A.; Montalbano, S.; Prota, V.; et al. An integrated approach for chemical water quality assessment of an urban river stretch through Effect-Based Methods and emerging pollutants analysis with a focus on genotoxicity. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 300, 113549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacInnis, J.; De Silva, A.O.; Lehnherr, I.; Muir, D.C.G.; St Pierre, K.A.; St Louis, V.L.; Spencer, C. Investigation of perfluoroalkyl substances in proglacial rivers and permafrost seep in a high Arctic watershed. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2022, 24, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hu, T.; Yang, L.; Guo, Z. The Investigation of Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Seasonal Freeze-Thaw Rivers During Spring Flood Period: A Case Study in Songhua River and Yalu River, China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2018, 101, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, Z. The investigation of the enrichment behavior of identified PFAS and unknown PFAA-precursors in water and suspended particulate matter of the surface microlayer: A case study in Tianjin (China). Water Res. 2024, 260, 121944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-E.; Yang, Y.-Y.; Zhao, J.-L.; Liu, Y.-S.; Hu, L.-X.; Li, B.-B.; Li, C.-L.; Ying, G.-G. Legacy and alternative per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in the West River and North River, south China: Occurrence, fate, spatio-temporal variations and potential sources. Chemosphere 2021, 283, 131301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, W.; Song, S.; Lu, Y.; Shi, Y.; Yang, S.; Wu, Q.; Wu, Y.; Jia, D.; Sun, J. Legacy and alternative per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in the Bohai Bay Rim: Occurrence, partitioning behavior, risk assessment, and emission scenario analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 168837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, C.; Han, J.; Sun, R.; Kong, X.; Wang, X.; He, X. Levels and spatial distribution of perfluoroalkyl substances in China Liaodong Bay basin with concentrated fluorine industry parks. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 101, 965–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, P.M.; Argos, M.; Kolpin, D.W.; Meppelink, S.M.; Romanok, K.M.; Smalling, K.L.; Focazio, M.J.; Allen, J.M.; Dietze, J.E.; Devito, M.J.; et al. Mixed organic and inorganic tapwater exposures and potential effects in greater Chicago area, USA. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 719, 137236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Reinhard, M.; Yin, T.; Nguyen, T.V.; Tran, N.H.; Yew-Hoong Gin, K. Multi-compartment distribution of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in an urban catchment system. Water Res. 2019, 154, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Pang, Y.; Luo, M.; Jiang, X.; Huang, J.; Li, Z. Multi-media distribution and risk assessment of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the Huai River Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 914, 169581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen Hoang, L.; Cho, C.-R.; Kannan, K.; Cho, H.-S. A nationwide survey of perfluorinated alkyl substances in waters, sediment and biota collected from aquatic environment in Vietnam: Distributions and bioconcentration profiles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 323, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Qv, Z.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, L. Natural biofilm as a potential integrative sample for evaluating the contamination and impacts of PFAS on aquatic ecosystems. Water Res. 2022, 215, 118233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weed, R.A.; Campbell, G.; Brown, L.; May, K.; Sargent, D.; Sutton, E.; Burdette, K.; Rider, W.; Baker, E.S.; Enders, J.R. Non-Targeted PFAS Suspect Screening and Quantification of Drinking Water Samples Collected through Community Engaged Research in North Carolina’s Cape Fear River Basin. Toxics 2024, 12, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chirikona, F.; Quinete, N.; Gonzalez, J.; Mutua, G.; Kimosop, S.; Orata, F. Occurrence and Distribution of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances from Multi-Industry Sources to Water, Sediments and Plants along Nairobi River Basin, Kenya. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefano, P.H.P.; Roisenberg, A.; D’Anna Acayaba, R.; Roque, A.P.; Bandoria, D.R.; Soares, A.; Montagner, C.C. Occurrence and distribution of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in surface and groundwaters in an urbanized and agricultural area, Southern Brazil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 30, 6159–6169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, M.; Ding, G.; Zhang, J.; Wei, L.; Xue, H.; Zhang, N.; Li, Y.; Chen, G.; Sun, Y. Occurrence and distribution of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in surface water and bottom water of the Shuangtaizi Estuary, China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 216, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Li, X.; Wang, M.; Xie, W. Occurrence and distribution of poly-and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in a surface flow constructed wetland. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 169, 106291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, Z.Y.; Kim, K.Y.; Oh, J.-E. The occurrence and distributions of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in groundwater after a PFAS leakage incident in 2018. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenka, S.P.; Kah, M.; Padhye, L.P. Occurrence and fate of poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in urban waters of New Zealand. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 428, 128257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Sun, R.; Han, J.; Han, G.; Yang, W.; He, X. Occurrence and inputs of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) from rivers and drain outlets to the Bohai Sea, China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 221, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Ren, N. Occurrence and Risk Assessment of per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Water Source Protection Area of Southeastern China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 913997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Han, J.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, J.; Sun, R.; Wang, X.; Han, G.; Yang, W.; He, X. Occurrence and seasonal variations of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) including fluorinated alternatives in rivers, drain outlets and the receiving Bohai Sea of China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 1223–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koulini, G.V.; Nambi, I.M. Occurrence of forever chemicals in Chennai waters, India. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2024, 36, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Niu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Occurrence of legacy and emerging poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances in water: A case study in Tianjin (China). Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scher, D.P.; Kelly, J.E.; Huset, C.A.; Barry, K.M.; Hoffbeck, R.W.; Yingling, V.L.; Messing, R.B. Occurrence of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in garden produce at homes with a history of PFAS-contaminated drinking water. Chemosphere 2018, 196, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, N.; Fauvelle, V.; Castro-Jimenez, J.; Lajaunie-Salla, K.; Pinazo, C.; Yohia, C.; Sempere, R. Occurrence of perfluoroalkyl substances in the Bay of Marseille (NW Mediterranean Sea) and the Rhone River. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 149, 110491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, G.; Labadie, P.; Botta, F.; Lestremau, F.; Lopez, B.; Geneste, E.; Pardon, P.; Dévier, M.-H.; Budzinski, H. Occurrence survey and spatial distribution of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl surfactants in groundwater, surface water, and sediments from tropical environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607–608, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liang, E.; Xu, X.; Xu, N. Occurrence, mass loading, and post-control temporal trend of legacy perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in the middle and lower Yangtze River. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 199, 115966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wei, L.; Luo, W.; Jiang, N.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, P.; Ga, B.; Pei, Z.; Li, Y.; Yang, R.; et al. Occurrence, spatial distribution, and sources of PFASs in the water and sediment from lakes in the Tibetan Plateau. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 443, 130170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, X.; Wei, Z.; Jing, P.; Lu, G.; Dian, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Y. The occurrence, spatial distribution, and well-depth dependence of PFASs in groundwater from a reclaimed water irrigation area. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 901, 165904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitmeyer, S.E.; Williams, A.M.; Duris, J.W.; Eicholtz, L.W.; Shull, D.R.; Wertz, T.A.; Woodward, E.E. Per- and polyfluorinated alkyl substances (PFAS) in Pennsylvania surface waters: A statewide assessment, associated sources, and land-use relations. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 888, 164161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smalling, K.L.; Romanok, K.M.; Bradley, P.M.; Morriss, M.C.; Gray, J.L.; Kanagy, L.K.; Gordon, S.E.; Williams, B.M.; Breitmeyer, S.E.; Jones, D.K.; et al. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in United States tapwater: Comparison of underserved private-well and public-supply exposures and associated health implications. Environ. Int. 2023, 178, 108033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Lei, H.; Lu, Y.; Xie, X.; Wang, P.; Liao, J.; Liang, Z.; Sun, B.; Wu, Z. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in water and sediment from a temperate watershed in China: Occurrence, sources, and ecological risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 890, 164207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Lu, Y.; Wang, P.; Lei, H.; Chen, N.; Liang, Z.; Jiang, X.; Li, J.; Cao, Z.; Liao, J.; et al. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in a subtropical river-mangrove estuary-bay system. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 464, 132937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boone, J.S.; Vigo, C.; Boone, T.; Byrne, C.; Ferrario, J.; Benson, R.; Donohue, J.; Simmons, J.E.; Kolpin, D.W.; Furlong, E.T.; et al. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in source and treated drinking waters of the United States. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 653, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobelius, L.; Hedlund, J.; Duerig, W.; Troger, R.; Lilja, K.; Wiberg, K.; Ahrens, L. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Swedish Groundwater and Surface Water: Implications for Environmental Quality Standards and Drinking Water Guidelines. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 4340–4349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigei, M.; Ahren, L.; Hazaymeh, A.; Dalahmeh, S.S. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in water and soil in wastewater-irrigated farmland in Jordan. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 137057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, M.; Gong, P.; Wang, C. Perfluorinated alkyl substances in snow as an atmospheric tracer for tracking the interactions between westerly winds and the Indian Monsoon over western China. Environ. Int. 2019, 124, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, N.-H.; Cho, C.-R.; Lee, J.-S.; Soh, H.-Y.; Lee, B.-C.; Lee, J.-A.; Tatarozako, N.; Sasaki, K.; Saito, N.; Iwabuchi, K.; et al. Perfluorinated alkyl substances in water, sediment, plankton and fish from Korean rivers and lakes: A nationwide survey. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 491, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.M.; Bharat, G.K.; Tayal, S.; Larssen, T.; Becanova, J.; Karaskova, P.; Whitehead, P.G.; Futter, M.N.; Butterfield, D.; Nizzetto, L. Perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in river and ground/drinking water of the Ganges River basin: Emissions and implications for human exposure. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 208, 704–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalonde, B.; Garron, C. Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in the Canadian Freshwater Environment. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2022, 82, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arinaitwe, K.; Keltsch, N.; Taabu-Munyaho, A.; Reemtsma, T.; Berger, U. Perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in the Ugandan waters of Lake Victoria: Spatial distribution, catchment release and public exposure risk via municipal water consumption. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 783, 164207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Yan, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Z.; Pang, Y. Perfluoroalkyl substances in the surface water and fishes in Chaohu Lake, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 75907–75920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Cai, Y.; Ma, L.; Lin, X.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. Perfluoroalkyl substances in water, sediment, and fish from a subtropical river of China: Environmental behaviors and potential risk. Chemosphere 2022, 288, 132513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, E.K.; Hall, L.M.; Brown, M.A.; Taylor-Manges, A.; Green, T.; Suchanec, K.; Furman, B.T.; Congdon, V.M.; Wilson, S.S.; Osborne, T.Z.; et al. PFAS surveillance in abiotic matrices within vital aquatic habitats throughout Florida. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 192, 115011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junttila, V.; Vähä, E.; Perkola, N.; Räike, A.; Siimes, K.; Mehtonen, J.; Kankaanpää, H.; Mannio, J. PFASs in Finnish Rivers and Fish and the Loading of PFASs to the Baltic Sea. Water 2019, 11, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikizoglu, B. PFOA and PFOS Pollution in Surface Waters and Surface Water Fish. Water 2024, 16, 2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reif, D.; Zoboli, O.; Wolfram, G.; Amann, A.; Saracevic, E.; Riedler, P.; Hainz, R.; Hintermaier, S.; Krampe, J.; Zessner, M. Pollutant source or sink? Adsorption and mobilization of PFOS and PFOA from sediments in a large shallow lake with extended reed belt. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 320, 115871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-McDevitt, M.E.; Dunn, M.; Habib, A.; Vojta, S.; Becanova, J.; Lohmann, R. Poly- and Perfluorinated Alkyl Substances in Air and Water from Dhaka, Bangladesh. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 41, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, L.; Gashaw, H.; Sjoholm, M.; Gebrehiwot, S.G.; Getahun, A.; Derbe, E.; Bishop, K.; Akerblom, S. Poly- and perfluoroalkylated substances (PFASs) in water, sediment and fish muscle tissue from Lake Tana, Ethiopia and implications for human exposure. Chemosphere 2016, 165, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Ai, Y.; Hu, J.; Xu, N.; Song, R.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, W.; Ni, J. Poly fluoroalkyl substances in Danjiangkou Reservoir, China: Occurrence, composition, and source appointment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 725, 138352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, D.Q.; Naidenko, O.V. Population-Wide Exposure to Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances from Drinking Water in the United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2020, 7, 931–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman-Bertinetti, S.L.; Gruber, K.J.; Remucal, C.K. Preferential Partitioning of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Freshwater Ice. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 15214–15223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Lei, M.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, M.; Chen, H.; Yang, W.; Wang, X. Presence and inputs of legacy and novel per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances from rivers and drainage outlets to Liaodong Bay, China. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2022, 56, 102684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebbink, W.A.; van Asseldonk, L.; van Leeuwen, S.P.J. Presence of Emerging Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in River and Drinking Water near a Fluorochemical Production Plant in the Netherlands. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2017, 51, 11057–11065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardian, M.G.E.; Boongaling, E.G.; Bernardo-Boongaling, V.R.R.; Gamonchuang, J.; Boontongto, T.; Burakham, R.; Arnnok, P.; Aga, D.S. Prevalence of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in drinking and source water from two Asian countries. Chemosphere 2020, 256, 127115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Shan, G.; Chen, M.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, L. Riverine inputs and source tracing of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in Taihu Lake, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Xie, Z.; Tang, J.; Sturm, R.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, G.; Ebinghaus, R. Seasonal variations and spatial distributions of perfluoroalkyl substances in the rivers Elbe and lower Weser and the North Sea. Chemosphere 2015, 129, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Xia, X.; Dong, J.; Xia, N.; Jiang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Y. Short- and long-chain perfluoroalkyl substances in the water, suspended particulate matter, and surface sediment of a turbid river. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 568, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lohmann, R.; Dassuncao, C.; Hu, X.C.; Weber, A.K.; Vecitis, C.D.; Sunderland, E.M. Source Attribution of Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in Surface Waters from Rhode Island and the New York Metropolitan Area. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2016, 3, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, G.; Giraudel, J.-L.; Botta, F.; Lestremau, F.; Devier, M.-H.; Budzinski, H.; Labadie, P. Spatial distribution and partitioning behavior of selected poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances in freshwater ecosystems: A French nationwide survey. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 517, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Fatowe, M.; Lemos, L.; Quinete, N. Spatial distribution of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in waters from Central and South Florida. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 84383–84395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Dong, B.; Wang, F.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Liu, Z.; Duan, X.; Bo, Y.; Peng, L. Spatial heterogeneity of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances caused by glacial melting in Tibetan Lake Nam Co due to global warming. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 478, 135468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.-G.; Ying, G.-G.; Zhao, J.-L.; Liu, Y.-S.; Jiang, Y.-X.; Zhang, Q.-Q. Spatiotemporal distribution and mass loadings of perfluoroalkyl substances in the Yangtze River of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 493, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, A.; Zhang, X.; Li, R.; Tu, W.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Mai, B. Spatiotemporal distribution, partitioning behavior and flux of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in surface water and sediment from Poyang Lake, China. Chemosphere 2022, 295, 133855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, G.; Fechner, L.C.; Geneste, E.; Pardon, P.; Budzinski, H.; Labadie, P. Spatio-temporal dynamics of per and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) and transfer to periphytic biofilm in an urban river: Case-study on the River Seine. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 23574–23582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, S.; Li, W.; Zhang, X.; He, Y.; Chu, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, S. Spatiotemporal variations and bioaccumulation of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances and oxidative conversion of precursors in shallow lake water. Chemosphere 2023, 313, 137527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Gao, L.; Chen, J.; He, X.; Wang, B. Spatiotemporal variations, sources and health risk assessment of perfluoroalkyl substances in a temperate bay adjacent to metropolis, North China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 115011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.; Thompson, K.; Dickenson, E.; Quinones, O.; Steinle-Darling, E.; Westerhoff, P. Sucralose and Predicted De Facto Wastewater Reuse Levels Correlate with PFAS Levels in Surface Waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2023, 10, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, B.F.; Aristizabal-Henao, J.J.; Aufmuth, J.; Awkerman, J.; Bowden, J.A. Survey of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in surface water collected in Pensacola, FL. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiu, R.-F.; Lee, H.-J.; Hsu, H.-T.; Gong, G.-C. Suspended particulate matter-bound per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in a river-coastal system: Possible correlation with transparent exopolymer particles. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 191, 114975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, G.; Liu, M.; Vo Duy, S.; Liu, J.; Sauvé, S. Target and nontarget screening of PFAS in drinking water for a large-scale survey of urban and rural communities in Québec, Canada. Water Res. 2023, 233, 119750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Li, Y.; Ma, L.; Chen, C.; Huang, J.; Yu, G. Temporal trends and transport of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in a subtropical estuary: Jiulong River Estuary, Fujian, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, G.; Budzinski, H.; Babut, M.; Lobry, J.; Selleslagh, J.; Tapie, N.; Labadie, P. Temporal variations of perfluoroalkyl substances partitioning between surface water, suspended sediment, and biota in a macrotidal estuary. Chemosphere 2019, 233, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Trend of PFAS concentrations and prediction of potential risks in Taihu Lake of China by AQUATOX. Environ. Res. 2024, 251, 118707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balgooyen, S.; Remucal, C.K. Tributary Loading and Sediment Desorption as Sources of PFAS to Receiving Waters. ACS EST Water 2022, 2, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penland, T.N.; Cope, W.G.; Kwak, T.J.; Strynar, M.J.; Grieshaber, C.A.; Heise, R.J.; Sessions, F.W. Trophodynamics of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in the Food Web of a Large Atlantic Slope River. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 6800–6811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madeira, C.L.; Acayaba, R.D.A.; Santos, V.S.; Villa, J.E.L.; Jacinto-Hernández, C.; Azevedo, J.A.T.; Elias, V.O.; Montagner, C.C. Uncovering the impact of agricultural activities and urbanization on rivers from the Piracicaba, Capivari, and Jundiaí basin in São Paulo, Brazil: A survey of pesticides, hormones, pharmaceuticals, industrial chemicals, and PFAS. Chemosphere 2023, 341, 139954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Shen, X.; Liu, W.; Covaci, A.; Yang, F. Occurrence and risk assessment of organophosphate esters in drinking water from Eastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 538, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Liu, Z.; Song, X.; Ding, X.; Ding, D. Legacy and emerging per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in multi-media around a landfill in China: Implications for the usage of PFASs alternatives. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 751, 141767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Age Range (Years) | Drinking Water Intake (L/day) | Body Weight (kg) |
|---|---|---|
| 0–1 | 0.595 | 7.8 |
| 1–2 | 0.245 | 11.4 |
| 2–6 | 0.337 | 17.4 |
| 6–11 | 0.455 | 31.8 |
| 11–16 | 0.562 | 56.8 |
| 16–21 | 0.722 | 71.6 |
| Adult (21–78) | 1.313 | 80.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Y.; Chang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Li, W. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Potential Drinking Water Sources Globally: Distributions, Monitoring Trends, and Risk Assessment. Water 2025, 17, 3280. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17223280
Zhou Y, Chang Y, Zhang D, Li W. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Potential Drinking Water Sources Globally: Distributions, Monitoring Trends, and Risk Assessment. Water. 2025; 17(22):3280. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17223280
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Yangyuan, Yu Chang, Dawei Zhang, and Weiying Li. 2025. "Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Potential Drinking Water Sources Globally: Distributions, Monitoring Trends, and Risk Assessment" Water 17, no. 22: 3280. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17223280
APA StyleZhou, Y., Chang, Y., Zhang, D., & Li, W. (2025). Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Potential Drinking Water Sources Globally: Distributions, Monitoring Trends, and Risk Assessment. Water, 17(22), 3280. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17223280






