From Land to Water: The Impact of Landscape on Water Quality Through Linear Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
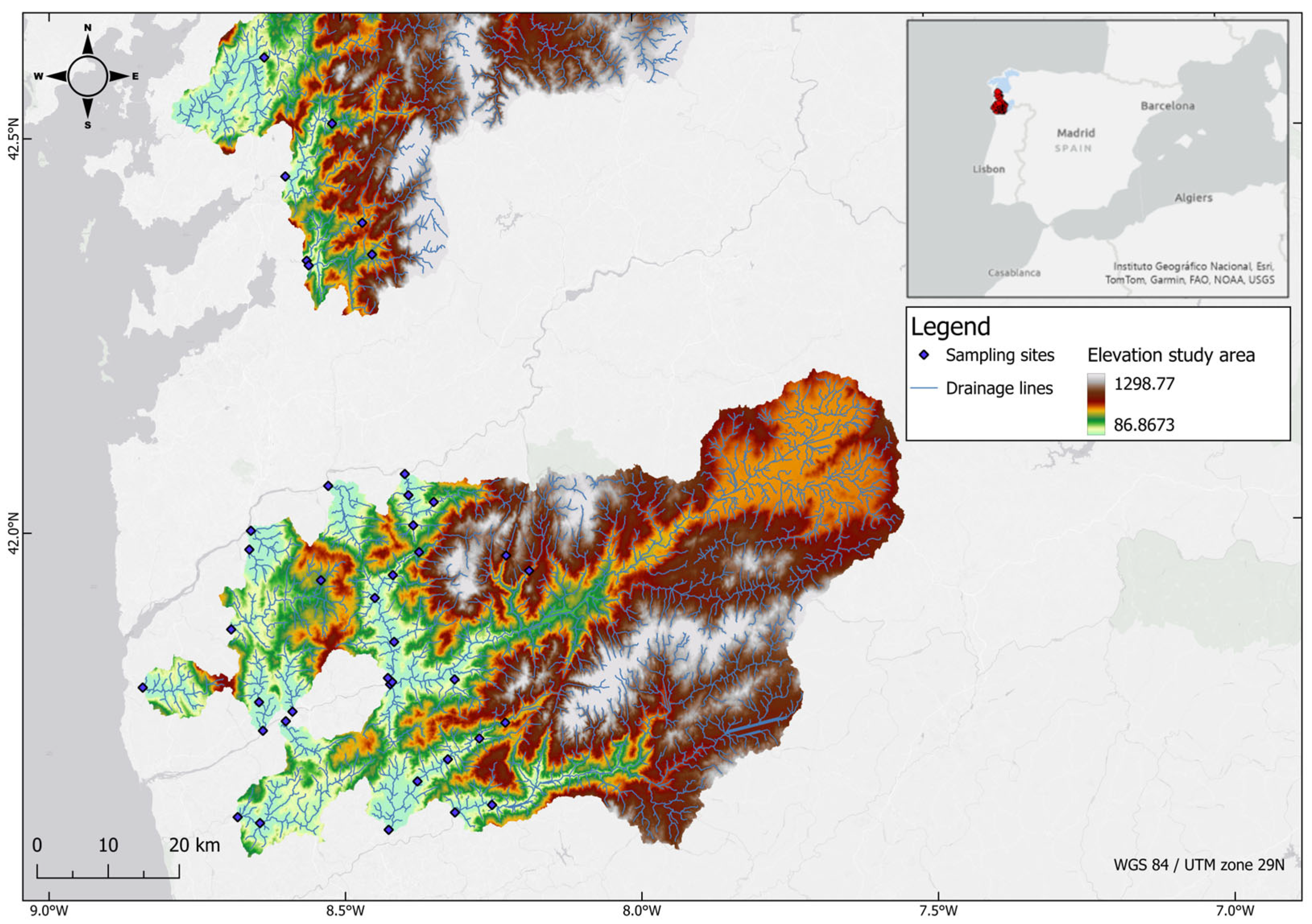
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data and Variable Selection for Water Quality Analysis
2.2.1. Water Quality Assessment Using Benthic Macroinvertebrate Assemblages
2.2.2. Landscape Metrics
2.3. Data Analysis
2.3.1. Linear Regression Models for Water Quality Prediction
2.3.2. Model Assessment
3. Results and Discussion
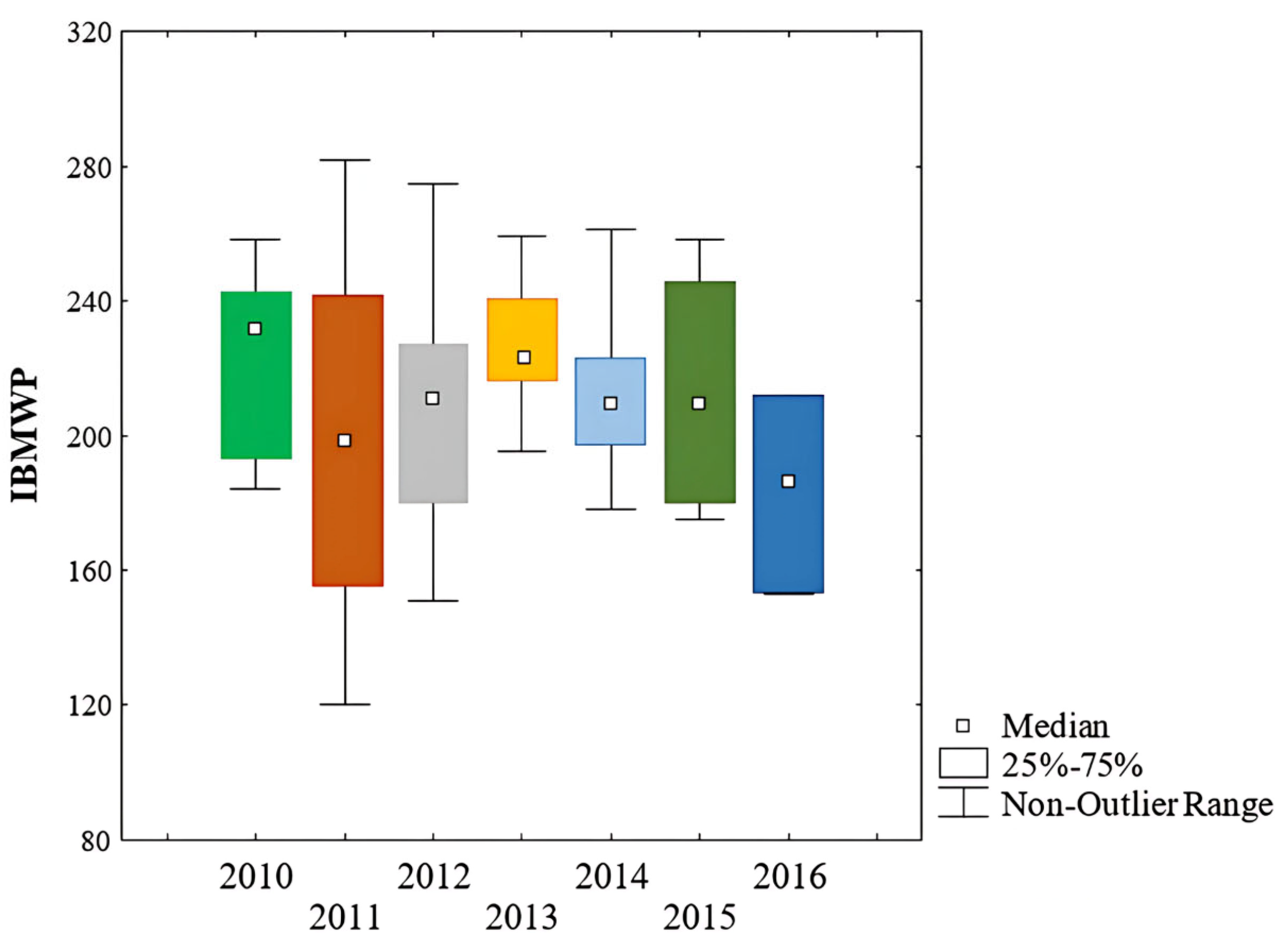
3.1. Macroinvertebrate Diversity and Water Quality
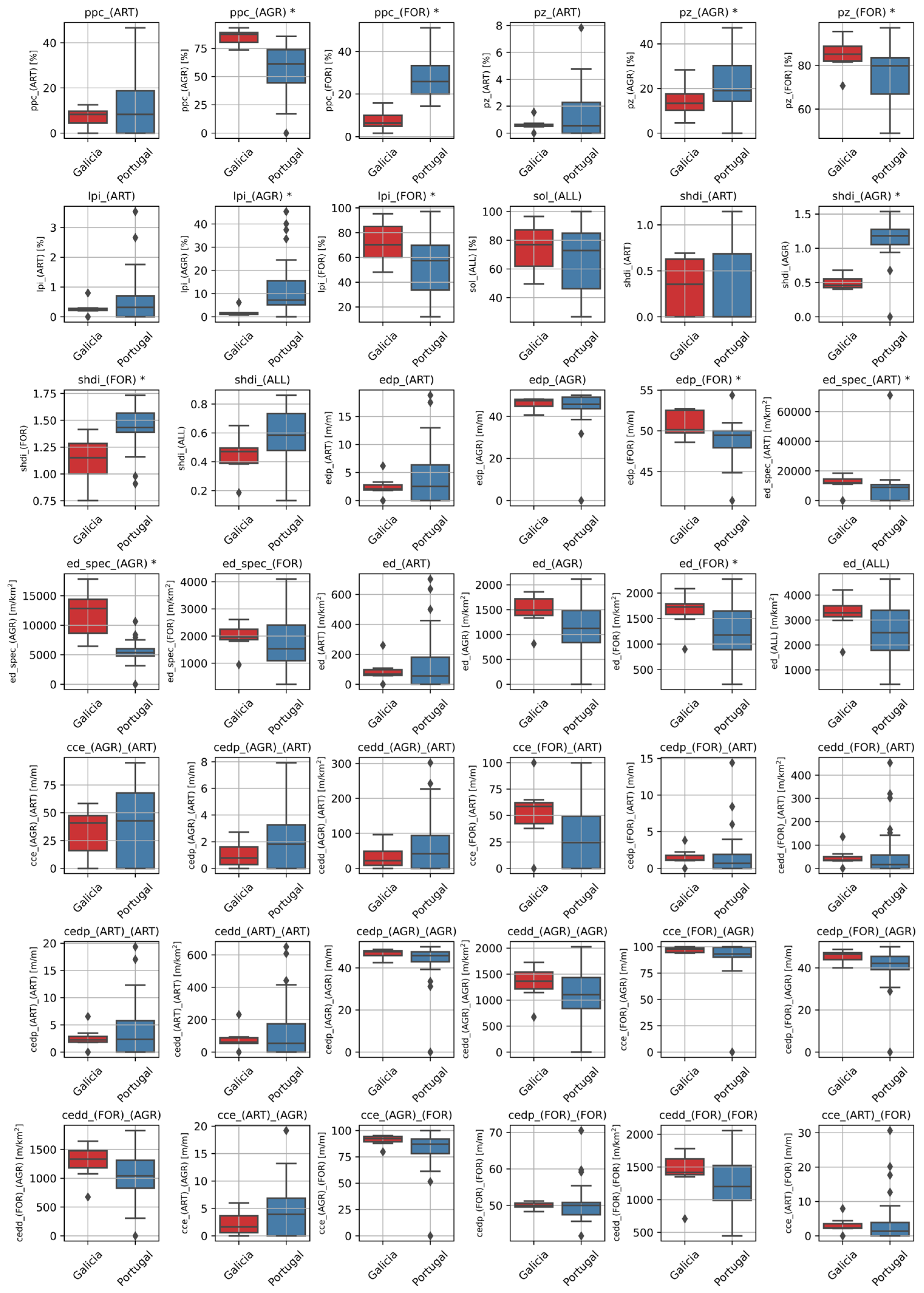
3.2. Landscape Metrics Assessment
3.3. Global Model Results
3.4. Best Models
3.5. Final Considerations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berking, J. Water Management in Ancient Civilizations; Edition Topoi: Berlin, Germany, 2018; ISBN 9783981836967. [Google Scholar]
- Nilson Bezerra Campos, J. A Gestão Integrada Dos Recursos Hídricos: Uma Perspectiva Histórica. Rev. Eletrônica Gestão E Tecnol. Ambient. 2013, 1, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lewis, E.W.; Staddon, C.; Sirunda, J. Urban Water Management Challenges and Achievements in Windhoek, Namibia. Water Pract. Technol. 2019, 14, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widianingsih, I.; Riswanda, R.; Paskarina, C. Governing Water, Engaging Community: Indonesian Water Security Roadmap. J. Gov. 2020, 5, 202–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Yang, L.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, X.; Wu, W.; Li, Y.; Jiang, D. Water Resource Synergy Management in Response to Climate Change in China: From the Perspective of Urban Metabolism. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 163, 105095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terêncio, D.P.S.; Fernandes, L.F.S.; Cortes, R.M.V.; Moura, J.P.; Pacheco, F.A.L. Flood Risk Attenuation in Critical Zones of Continental Portugal Using Sustainable Detention Basins. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 721, 137727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehana, S.; Sireesha Naidu, G. Development of Hydro-Meteorological Drought Index under Climate Change—Semi-Arid River Basin of Peninsular India. J. Hydrol. 2021, 594, 125973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wu, J. Drinking Water Quality and Public Health. Expo. Health 2019, 11, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.M.B.; Monteiro, S.M.; Cortes, R.M.V.; Pacheco, F.A.L.; Fernandes, L.F.S. Seasonal Effect of Land Use Management on Gill Histopathology of Barbel and Douro Nase in a Portuguese Watershed. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 764, 142869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshesha, T.W.; Wang, J.; Melaku, N.D. Modelling Spatiotemporal Patterns of Water Quality and Its Impacts on Aquatic Ecosystem in the Cold Climate Region of Alberta, Canada. J. Hydrol. 2020, 587, 124952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 Establishing a Framework for Community Action in the Field of Water Policy. 2000. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2000/60/oj/eng (accessed on 1 October 2025).
- Skoulikaris, C.; Zafirakou, A. River Basin Management Plans as a Tool for Sustainable Transboundary River Basins’ Management. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 14835–14848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, L.; Mackay, E.B.; Cardoso, A.C.; Baattrup-Pedersen, A.; Birk, S.; Blackstock, K.L.; Borics, G.; Borja, A.; Feld, C.K.; Ferreira, M.T.; et al. Protecting and Restoring Europe’s Waters: An Analysis of the Future Development Needs of the Water Framework Directive. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 1228–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostert, E. The European Water Framework Directive and Water Management Research. Phys. Chem. Earth 2003, 28, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mello, K.; da Costa, D.R.; Valente, R.A.; Vettorazzi, C.A. Multicriteria Evaluation for Protected Area Definition Aiming at Water Quality Improvement. Floresta e Ambiente 2018, 25, e20160134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, L.; Pereira, A.; Oliveira, A.; Fernandes, A.; Sanches Fernandes, L.F.; Pacheco, F.A.L. An Assessment of Groundwater Contamination Risk with Radon Based on Clustering and Structural Models. Water 2019, 11, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhurtun, P.; Lesven, L.; Ruckebusch, C.; Halkett, C.; Cornard, J.P.; Billon, G. Understanding the Impact of the Changes in Weather Conditions on Surface Water Quality. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, N.; Tyagi, S. Influences of Natural and Anthropogenic Factors on Surface and Groundwater Quality in Rural and Urban Areas. Front. Life Sci. 2015, 8, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voza, D.; Vukovic, M.; Takic, L.; Nikolic, D.; Mladenovic-Ranisavljevic, I. Application of Multivariate Statistical Techniques in the Water Quality Assessment of Danube River, Serbia. Arch. Environ. Prot. 2015, 41, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, A.J.; Carlson, A.K.; Creed, I.F.; Eliason, E.J.; Gell, P.A.; Johnson, P.T.J.; Kidd, K.A.; MacCormack, T.J.; Olden, J.D.; Ormerod, S.J. Emerging Threats and Persistent Conservation Challenges for Freshwater Biodiversity. Biol. Rev. 2019, 94, 849–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekholm, P.; Lehtoranta, J.; Taka, M.; Sallantaus, T.; Riihimäki, J. Diffuse Sources Dominate the Sulfate Load into Finnish Surface Waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 748, 141297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guadie, A.; Yesigat, A.; Gatew, S.; Worku, A.; Liu, W.; Minale, M.; Wang, A. Effluent Quality and Reuse Potential of Urban Wastewater Treated with Aerobic-Anoxic System: A Practical Illustration for Environmental Contamination and Human Health Risk Assessment. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 40, 101891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, N.; Nafees, M.; Ge, L.; Khan, M.H.; Bilal, M.; Chan, W.P.; Lisak, G. Assessment of Industrial Wastewater for Potentially Toxic Elements, Human Health (Dermal) Risks, and Pollution Sources: A Case Study of Gadoon Amazai Industrial Estate, Swabi, Pakistan. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 419, 126450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez Andrés, N.; Martínez Santa-María, C.; Fernández Yuste, J. Are Wasterwater Treatment Plants Modifying Our Rivers? Cuad. De La Soc. Española De Cienc. For. 2019, 45, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.R.L.; Sanches Fernandes, L.F.; Cortes, R.M.V.; Pacheco, F.A.L. Assessing Anthropogenic Impacts on Riverine Ecosystems Using Nested Partial Least Squares Regression. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 583, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, A.R.; Sanches Fernandes, L.F.; Fontainhas-Fernandes, A.; Monteiro, S.M.; Pacheco, F.A.L. The Impact of Freshwater Metal Concentrations on the Severity of Histopathological Changes in Fish Gills: A Statistical Perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599–600, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, A.R.; Sanches Fernandes, L.F.; Fontainhas-Fernandes, A.; Monteiro, S.M.; Pacheco, F.A.L. From Catchment to Fish: Impact of Anthropogenic Pressures on Gill Histopathology. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 550, 972–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamadi, M.A.; Kavian, A. Effects of Rainfall Patterns on Runoff and Soil Erosion in Field Plots. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2015, 3, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasumana, C.; Fonseka, S.; Fernando, A.; Jayalth, K.; Amarasinghe, M.; Paranagma, P. Presence of Arsenic in Agrochemicals and Their Association with the Agricultural Chronic Kidney Disease in Sri Lanka. J. Toxicol. Health 2014, 104, 352–361. [Google Scholar]
- Zörb, C.; Senbayram, M.; Peiter, E. Potassium in Agriculture–Status and Perspectives. J. Plant Physiol. 2014, 171, 656–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameira, M.d.R.; Mota, M. Nitrogen Related Diffuse Pollution from Horticulture Production—Mitigation Practices and Assessment Strategies. Horticulturae 2017, 3, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Long, H.; Li, Y.; Tu, S.; Jiang, T. Non-Point Source Pollution in Response to Rural Transformation Development: A Comprehensive Analysis of China’s Traditional Farming Area. J. Rural Stud. 2020, 83, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, J.; Are, K.S.; Huang, Z.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Q. Livestock Grazing Significantly Accelerates Soil Erosion More than Climate Change in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: Evidenced from 137Cs and 210Pbex Measurements. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 285, 106643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clément, F.; Ruiz, J.; Rodríguez, M.A.; Blais, D.; Campeau, S. Landscape Diversity and Forest Edge Density Regulate Stream Water Quality in Agricultural Catchments. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 72, 627–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrington, B.M.; Aust, W.M.; Barrett, S.M.; Ford, W.M.; Dolloff, C.A.; Schilling, E.B.; Wigley, T.B.; Bolding, M.C. Forestry Best Management Practices Relationships with Aquatic and Riparian Fauna: A Review. Forests 2017, 8, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilary, B.; Chris, B.; North, B.E.; Angelica Maria, A.Z.; Sandra Lucia, A.Z.; Carlos Alberto, Q.G.; Beatriz, L.G.; Rachael, E.; Andrew, W. Riparian Buffer Length Is More Influential than Width on River Water Quality: A Case Study in Southern Costa Rica. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 286, 112132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, R.M.B.; Sanches Fernandes, L.F.; Pereira, M.G.; Cortes, R.M.V.; Pacheco, F.A.L. Water Resources Planning for a River Basin with Recurrent Wildfires. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 526, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uuemaa, E.; Roosaare, J.; Mander, Ü. Landscape Metrics as Indicators of River Water Quality at Catchment Scale. Hydrol. Res. 2007, 38, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yang, K.; Tai, J.; Shan, F. Review of the Relationship between Regional Landscape Pattern and Surface Water Quality. Shengtai Xuebao/Acta Ecol. Sin. 2011, 31, 3180–3189. [Google Scholar]
- McGarigal, K. FRAGSTATS: Spatial Pattern Analysis Program for Quantifying Landscape Structure; General Technical Report PNW-GTR-351; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Pacific Northwest Research Station: Portland, OR, USA, 1995. Available online: https://www.fs.usda.gov/pnw/pubs/pnw_gtr351.pdf (accessed on 24 August 2025).
- Dwivedi, S.; Shikha, D. Water Pollution: Causes, Effects and Control; New Age International: New Delhi, India, 2016; Volume 16. [Google Scholar]
- Flotemersch, J.E.; Leibowitz, S.G.; Hill, R.A.; Stoddard, J.L.; Thoms, M.C.; Tharme, R.E. A Watershed Integrity Definition and Assessment Approach to Support Strategic Management of Watersheds. River Res. Appl. 2016, 32, 1654–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acuña-Alonso, C.; Fernandes, A.C.P.; Álvarez, X.; Valero, E.; Pacheco, F.A.L.; Varandas, S.D.G.P.; Terêncio, D.P.S.; Fernandes, L.F.S. Water Security and Watershed Management Assessed through the Modelling of Hydrology and Ecological Integrity: A Study in the Galicia-Costa (NW Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 143905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Deitch, M.J.; Gebremicael, T.G.; Angelini, C.; Ortals, C.J. Identifying Critical Source Areas of Non-Point Source Pollution to Enhance Water Quality: Integrated SWAT Modeling and Multi-Variable Statistical Analysis to Reveal Key Variables and Thresholds. Water Res. 2024, 253, 121286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohith, A.N.; Karki, R.; Veith, T.L.; Preisendanz, H.E.; Duncan, J.M.; Kleinman, P.J.A.; Cibin, R. Prioritizing Conservation Practice Locations for Effective Water Quality Improvement Using the Agricultural Conservation Planning Framework (ACPF) and the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT). J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 349, 119514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terry, J.; Lindenschmidt, K.-E. Water Quality and Flow Management Scenarios in the Qu’appelle River–Reservoir System Using Loosely Coupled WASP and CE-QUAL-W2 Models. Water 2023, 15, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- K. C., D.V.; Abdul Rahiman, A.W.; E., A.; J., A.K.; N., P. Water Quality Simulation Using the WASP Model for Eutrophication Control in a South Indian Reservoir. Water Pr. Technol. 2023, 18, 2740–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mummidivarapu, S.K.; Rehana, S.; Rao, Y.R.S. Mapping and Assessment of River Water Quality under Varying Hydro-Climatic and Pollution Scenarios by Integrating QUAL2K, GEFC, and GIS. Environ. Res. 2023, 239, 117250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zehra, R.; Singh, S.P.; Verma, J.; Kulshreshtha, A. Spatio-Temporal Investigation of Physico-Chemical Water Quality Parameters Based on Comparative Assessment of QUAL 2Kw and WASP Model for the Upper Reaches of Yamuna River Stretching from Paonta Sahib, Sirmaur District to Cullackpur, North Delhi Districts of North India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 480. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Z.; Yu, M.; Chen, H.; Zhao, H.; Huang, Y.; Su, W.; Xia, F.; Chang, S.X.; Brookes, P.C.; Dahlgren, R.A.; et al. Elevated Temperature Shifts Soil N Cycling from Microbial Immobilization to Enhanced Mineralization, Nitrification and Denitrification across Global Terrestrial Ecosystems. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 5267–5276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar-Rúa, S.; Acuña-Alonso, C.; Álvarez, X. Estimation of the Ecological Integrity of the Guadiana River Using Partial Least Squares Path Modelling and Simulation Scenarios. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 954, 176305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.C.P.; Sanches Fernandes, L.F.; Moura, J.P.; Cortes, R.M.V.; Pacheco, F.A.L. A Structural Equation Model to Predict Macroinvertebrate-Based Ecological Status in Catchments Influenced by Anthropogenic Pressures. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 681, 242–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatrabhuj; Meshram, K.; Mishra, U.; Omar, P.J. Integration of Remote Sensing Data and GIS Technologies in River Management System. Discov. Geosci. 2024, 2, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shravan Kumar, S.M.; Pandey, M.; Shukla, A.K. Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Riverbank Changes Using Remote Sensing and Geographic Information System. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2024, 136, 103692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, H.; Yaseen, Z.M.; Scholz, M.; Ali, M.; Gad, M.; Elsayed, S.; Khadr, M.; Hussein, H.; Ibrahim, H.H.; Eid, M.H.; et al. Evaluation and Prediction of Groundwater Quality for Irrigation Using an Integrated Water Quality Indices, Machine Learning Models and GIS Approaches: A Representative Case Study. Water 2023, 15, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraman, P.; Nagarajan, K.K.; Partheeban, P.; Krishnamurthy, V. Critical Review on Water Quality Analysis Using IoT and Machine Learning Models. Int. J. Inf. Manag. Data Insights 2024, 4, 100210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzubaidi, L.; Bai, J.; Al-Sabaawi, A.; Santamaría, J.; Albahri, A.S.; Al-dabbagh, B.S.N.; Fadhel, M.A.; Manoufali, M.; Zhang, J.; Al-Timemy, A.H.; et al. A Survey on Deep Learning Tools Dealing with Data Scarcity: Definitions, Challenges, Solutions, Tips, and Applications. J. Big Data 2023, 10, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taye, M.M. Understanding of Machine Learning with Deep Learning: Architectures, Workflow, Applications and Future Directions. Computers 2023, 12, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes; Fonseca, A.; Pacheco, F.; Sanches Fernandes, L. Water Quality Predictions through Linear Regression - A Brute Force Algorithm Approach. MethodsX 2023, 10, 102153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, J.; Kanwal, S.; Kim, J.; Nisar, M.W.; Naseem, U.; Hussain, A. Heart Disease Diagnosis Using the Brute Force Algorithm and Machine Learning Techniques. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2022, 72, 3195–3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riyad, W.A.; Yee, S.C.P.; Thinakaran, R.; Salam, Z.A.B.A. Comparative Evaluation of Numerous Optimization Algorithms for Compiling Travel Salesman Problem. J. Adv. Res. Dyn. Control Syst. 2020, 12, 877–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piçarra, J.M.; Gutiérrez-Marco, J.C.; Sá, A.A.; Meireles, C.; Gonzálezclavijo, E. Silurian Graptolite Biostratigraphy of the Galicia—Trás-Os-Montes Zone (Spain and Portugal). GFF 2006, 128, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobierno de España SIOSE. Sistema de Información de Ocupación Del Suelo de España. Ministerio de Transportes, Movilidad y Agencia urbana. 2017. Available online: https://www.siose.es/ (accessed on 25 September 2022).
- Ribeiro, O. Portugal, o Mediterrâneo e o Atlântico, 2nd ed.; Letra Livre: Lisboa, Portugal, 2021; ISBN 978-989-8268-50-1. [Google Scholar]
- Queijeiro, J.; Blanco, D.; Álvarez, C. Climatic Zoning and Viticulture in Galicia (North West Spain) Zonage Viticole et Viticulture En Galice (Nord-Ouest de l’Espagne). In Proceedings of the 6th International Terroir Congress/VIe Congrès International des Terroirs Viticoles, Bordeaux, France, 2–8 July 2006; pp. 34–39. [Google Scholar]
- Harding, A.; Palutikof, J. The Climate System. The Physical Geography of the Mediterranean; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Pagés Valcarlos, J.L. Origen y Evolución Geomorfológica de Las Rías Atlánticas de Galicia. Rev. Soc. Geológica España 2000, 13, 393–403. [Google Scholar]
- Pedrosa, A.d.S.; Gonçalves, A.B.; Vieira, A.; Costa, F.d.S. Livro-Guia Da Viagem de Estudo Ao Litoral Norte e Serras Do Noroeste Português. 2010. Available online: https://repositorium.uminho.pt/entities/publication/4e9996a4-19de-4f2a-ab59-cdb276e331a0 (accessed on 1 October 2025).
- Alba-Tercedor, J.; Jáimez-Cuéllar, P.; Alvarez, M.; Avilés, J.; BONADA, N.; Casas, J.; Mellado-Díaz, A.; Ortega, M.; Pardo, I.; Prat, N.; et al. Caracterización Del Estado Ecológico de Ríos Mediterráneos Ibéricos Mediante El Índice IBMWP (Antes BMWP’). Limnetica 2002, 21, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alba-Tercedor, J. Macroinvertebrados Acuáticos y Calidad de Las Aguas de Los Ríos. In IV Simposio del Agua en Andalucía (SIAGA); Instituto Tecnológico Geominero de España: Madrid, Spain, 1996; Volume II, pp. 203–213. ISBN 84-7840-262-4. [Google Scholar]
- Armitage, P.D.; Moss, D.; Wright, J.F.; Furse, M.T. The Performance of a New Biological Water Quality Score System Based on Macroinvertebrates over a Wide Range of Unpolluted Running-Water Sites. Water Res. 1983, 17, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munné, A.; Prat, N. Use of Macroinvertebrate-Based Multimetric Indices for Water Quality Evaluation in Spanish Mediterranean Rivers: An Intercalibration Approach with the IBMWP Index. Hydrobiologia 2009, 628, 203–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto-Mendoza, M.T.; Vieira-Lanero, R.; Cobo, F. More Complexity Does Not Always Mean More Accuracy: The Case of IBMWP and METI in NW Spain. Ecohydrology 2015, 8, 595–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EEA. Copernicus Land Monitoring Service—EU—DEM; EEA: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2018; Available online: https://land.copernicus.eu/ (accessed on 1 October 2025).
- Kraemer, C.; Panda, S. Automatic ArcHydro for Watershed Delineation. In Proceedings of the 2009 Georgia Water Resources Conference, Kansas City, MO, USA, 17–21 May 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Adamczyk, J.; Tiede, D. ZonalMetrics—A Python Toolbox for Zonal Landscape Structure Analysis. Comput. Geosci. 2017, 99, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L.; Kelejian, H.H. Testing for Spatial Error Autocorrelation in the Presence of Endogenous Regressors. Int. Reg. Sci. Rev. 1997, 20, 153–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaño, J.; Palmer, A.; Sesé, A.; Cajal, B. Using the R-MAPE Index as a Resistant Measure of Forecast Accuracy. Psicothema 2013, 25, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salis, H.H.; Costa, A.; Moreira Vianna, J.H.; Azeneth Schuler, M.; Künne, A.; Sanches Fernandes, L.F.; Leal Pacheco, F.A. Hydrologic Modeling for Sustainable Water Resources Management in Urbanized Karst Areas. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zheng, B.; Liu, L. Biomonitoring and Bioindicators Used for River Ecosystems: Definitions, Approaches and Trends. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2010, 2, 1510–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cheng, L.; Kong, M.; Li, W.; Gong, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Cai, Y.; Li, K. Utility of a Macroinvertebrate-Based Multimetric Index in Subtropical Shallow Lakes. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 106, 105527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolédec, S.; Lamouroux, N.; Fuchs, U.; Mérigoux, S. Modelling the Hydraulic Preferences of Benthic Macroinvertebrates in Small European Stream. Freshw. Biol. 2006, 52, 145–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, S.; Baird, D.J.; Soares, A.M.V.M. Beyond Taxonomy: A Review of Macroinvertebrate Trait-based Community Descriptors as Tools for Freshwater Biomonitoring. J. Appl. Ecol. 2010, 47, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feio, M.J.; Ferreira, J.; Buffagni, A.; Erba, S.; Dörflinger, G.; Ferréol, M.; Munné, A.; Prat, N.; Tziortzis, I.; Urbanič, G. Comparability of Ecological Quality Boundaries in the Mediterranean Basin Using Freshwater Benthic Invertebrates. Statistical Options and Implications. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 476–477, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bieger, K.; Arnold, J.G.; Rathjens, H.; White, M.J.; Bosch, D.D.; Allen, P.M.; Volk, M.; Srinivasan, R. Introduction to SWAT+, a Completely Restructured Version of the Soil and Water Assessment Tool. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2017, 53, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dala-Corte, R.B.; Melo, A.S.; Siqueira, T.; Bini, L.M.; Martins, R.T.; Cunico, A.M.; Pes, A.M.; Magalhães, A.L.B.; Godoy, B.S.; Leal, C.G.; et al. Thresholds of Freshwater Biodiversity in Response to Riparian Vegetation Loss in the Neotropical Region. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 57, 1391–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzin, A.; Archaimbault, V.; Belliard, J.; Chauvin, C.; Delmas, F.; Pont, D. Ecological Assessment of Running Waters: Do Macrophytes, Macroinvertebrates, Diatoms and Fish Show Similar Responses to Human Pressures? Ecol. Indic. 2012, 23, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acuña-Alonso, C.; Novo, A.; Rodríguez, J.L.; Varandas, S.; Álvarez, X. Modelling and Evaluation of Land Use Changes through Satellite Images in a Multifunctional Catchment: Social, Economic and Environmental Implications. Ecol. Inf. 2022, 71, 101777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministerio de Obras Públicas y Urbanismo Real Decreto 849/1986, de 11 de Abril, Por El Que Se Aprueba El Reglamento Del Dominio Público Hidráulico, Que Desarrolla Los Títulos Preliminar I, IV, V, VI y VII de La Ley 29/1985, de 2 de Agosto, de Aguas. 1986. Available online: https://www.boe.es/buscar/act.php?id=BOE-A-1986-10 (accessed on 1 October 2025).
- Xunta de Galicia Ley 7/2012, de 28 de Junio, de montes de Galicia. Boletín Oficial del Estado (BOE)/Diario Oficial de Galicia, 2012. Available online: https://www.boe.es/buscar/act.php?id=BOE-A-2012-11414 (accessed on 1 October 2025).
- Xunta de Galicia. Ley 6/2011, de 13 de octubre, de movilidad de tierras. Boletín Oficial del Estado (BOE)/Diario Oficial de Galicia, 2011. Available online: https://www.boe.es/buscar/pdf/2011/BOE-A-2011-17718-consolidado.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2025).
- Turner, S.; Pham, T.-T.-H. “Nothing Is like It Was before”: The Dynamics between Land-Use and Land-Cover, and Livelihood Strategies in the Northern Vietnam Borderlands. Land 2015, 4, 1030–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbelle-Rico, E.; López-Iglesias, E. Farmland Abandonment and Afforestation—Socioeconomic and Biophysical Patterns of Land Use Change at the Municipal Level in Galicia, Northwest Spain. Land 2024, 13, 1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotirov, M.; Arts, B. Integrated Forest Governance in Europe: An Introduction to the Special Issue on Forest Policy Integration and Integrated Forest Management. Land. Use Policy 2018, 79, 960–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.C.P.; Sanches Fernandes, L.F.; Cortes, R.M.V.; Leal Pacheco, F.A. The Role of Landscape Configuration, Season, and Distance from Contaminant Sources on the Degradation of Stream Water Quality in Urban Catchments. Water 2019, 11, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.C.P.; De Oliveira Martins, L.M.; Fernandes, L.F.S.; Pacheco, F.A.L. Effect of Landscape Metrics on Water Quality Over Three Decades: A Case Study of the Ave River Basin, Portugal. WIT Trans. Ecol. Environ. 2020, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.; Masante, D.; Jackson, B.; Cosby, B.; Emmett, B.; Jones, L. Fragmentation and Thresholds in Hydrological Flow-Based Ecosystem Services. Ecol. Appl. 2020, 30, e02046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, J.; Hemmings, B.; Fienen, M.N.; Knowling, M. Towards Improved Environmental Modeling Outcomes: Enabling Low-Cost Access to High-Dimensional, Geostatistical-Based Decision-Support Analyses. Environ. Model. Softw. 2021, 139, 105022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Rial, D.; Soto González, B.; García Vázquez, D.; Méndez-Martínez, G.; Pombal Diego, M.Á.; Garrido González, J. Freshwater Biodiversity Loss in Urbanised Rivers. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 156, 111150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle Junior, R.F.; Varandas, S.G.P.; Pacheco, F.A.L.; Pereira, V.R.; Santos, C.F.; Cortes, R.M.V.; Sanches Fernandes, L.F. Impacts of Land Use Conflicts on Riverine Ecosystems. Land. Use Policy 2015, 43, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, R.M.V.; Hughes, S.J.; Pereira, V.R.; da Graça Pinto Varandas, S. Tools for Bioindicator Assessment in Rivers: The Importance of Spatial Scale, Land Use Patterns and Biotic Integration. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 34, 460–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Nomenclature | Description | Units | Land Use Category | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ART | AGR | FOR | ALL | |||
| Artificial | Agriculture | Forest | All | |||
| ppc_(LUA) | percentage of land use patches | % | LUA | LUA | LUA | |
| pz_(LUA) | area proportion occupied by LUA | % | LUA | LUA | LUA | |
| lpi_(LUA) | area percentage occupied by the large land use patch of LUA | % | LUA | LUA | LUA | |
| sol_(LUA) | percentage of land occupied by the of LPI for each land use type. | % | LUA | |||
| shdi_(LUA) | Shannon’s diversity index of LUA | LUA | LUA | LUA | LUA | |
| ed_(LUA) | edge length LUA/total area | m/km2 | LUA | LUA | LUA | LUA |
| ed_spec_(LUA) | edge length LUA/area LUA | m/km2 | LUA | LUA | LUA | |
| edp_(LUA) | edge length of LUA by total edge length | m/m | LUA | LUA | LUA | |
| cce_(LUA)/(LUB) | edge length shared between LUA and LUB divided by the edge length of LUB | m/m | LUA and LUB | LUA and LUB | LUA and LUB | |
| cedp_(LUA)/(LUB) | edge length shared between LUA and LUB divided by the edge length of all land uses | m/m | LUA and LUB | LUA and LUB | LUA and LUB | |
| cedd_(LUA)/(LUB) | edge length shared between LUA and LUB divided by total area | m/km2 | LUA and LUB | LUA and LUB | LUA and LUB | |
| Rating | |PBIAS| | MAPE |
|---|---|---|
| High | 0–10% | 0–10% |
| Good | 10–15% | 10–20% |
| Reasonable | 15–25% | 20–50% |
| Low | >25% | >50% |
| Model ID | 36611 | 36698 | 153591 | 153678 | 153698 | 229124 | 341269 | 341765 | 356391 | 481290 | 481293 | 481296 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| nº of regressors | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Max (VIF) | 1.77 | 2.38 | 2.27 | 3.29 | 3.28 | 2.55 | 1.90 | 1.73 | 2.28 | 1.56 | 1.65 | 1.58 |
| R2 | 0.63 | 0.62 | 0.65 | 0.66 | 0.68 | 0.63 | 0.65 | 0.66 | 0.64 | 0.64 | 0.63 | 0.63 |
| R2 adjusted | 0.57 | 0.56 | 0.58 | 0.60 | 0.62 | 0.56 | 0.59 | 0.59 | 0.58 | 0.57 | 0.56 | 0.56 |
| max (p-value)—regression coefficients | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.04 |
| min (p-value)—error normality tests | 0.39 | 0.50 | 0.74 | 0.34 | 0.49 | 0.46 | 0.65 | 0.57 | 0.43 | 0.65 | 0.70 | 0.73 |
| min (p-value)—error heteroskedasticity | 0.42 | 0.32 | 0.34 | 0.24 | 0.21 | 0.23 | 0.51 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.57 | 0.68 | 0.33 |
| MAPE (Calibration) [%] | 26.80 | 29.92 | 26.73 | 28.67 | 27.08 | 31.78 | 31.09 | 32.01 | 31.95 | 29.39 | 29.03 | 29.39 |
| MAPE (Validation) [%] | 8.14 | 9.63 | 9.14 | 10.47 | 10.45 | 10.94 | 10.91 | 11.17 | 10.85 | 8.64 | 9.23 | 8.99 |
| PBIAS [%] | 3.74 | 1.33 | 8.27 | 5.05 | 7.82 | 8.27 | 9.04 | 9.36 | 7.70 | 6.98 | 6.61 | 7.68 |
| NRMSD [%] | 12.28 | 10.37 | 14.11 | 12.10 | 13.51 | 12.77 | 12.38 | 12.53 | 12.86 | 13.24 | 14.12 | 13.49 |
| Zscore | 0.71 | 1.60 | 0.40 | 1.23 | 1.65 | 1.06 | 1.08 | 1.00 | 1.05 | 0.86 | 0.90 | 1.25 |
| Model | 36611 | 36698 | 153591 | 153678 | 153698 | 229124 | 341269 | 341765 | 356391 | 481290 | 481293 | 481296 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nº of regressors | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| intercept | 344.7 | 459.1 | 465.5 | 572.7 | 574.1 | 403.7 | 379.7 | 399.4 | 409.0 | 461.5 | 452.8 | 442.1 |
| ppc(ART) | −2.9 | −2.4 | −2.6 | |||||||||
| pz_(ART) | −13.9 | |||||||||||
| ppc_(AGR) | 1.9 | 1.3 | 2.4 | 2.2 | 1.5 | 2.5 | ||||||
| ppc_(FOR) | −1.8 | −1.6 | −1.6 | −2.0 | −2.1 | −2.0 | ||||||
| lpi_(ART) | −26.4 | −23.7 | −26.9 | −31.8 | −28.3 | |||||||
| lpi_(FOR) | −1.1 | −1.9 | −1.9 | −1.8 | −1.6 | −1.8 | ||||||
| sol_(ALL) | −1.0 | −1.6 | −1.6 | −1.0 | −0.9 | −0.9 | ||||||
| shdi_(ART) | −73.2 | −62.7 | −66.5 | −72.7 | −63.8 | |||||||
| shdi_(ALL) | −196.1 | −214.9 | −211.8 | |||||||||
| 6_edp_(AGR) | −4.4 | −3.2 | −2.9 | −2.4 | ||||||||
| 6_edp_(ART) | −5.1 | |||||||||||
| cce_(AGR)_(ART) | −1.0 | −0.8 | −0.7 | −1.0 | ||||||||
| cedp_(AGR)_(AGR) | −3.1 | |||||||||||
| cedp_(FOR)_(AGR) | −2.6 | −5.4 | −5.7 | −3.1 | ||||||||
| cce_(AGR)_(FOR) | −2.5 | −2.0 | −1.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rosário, G.; Acuña-Alonso, C.; Álvarez, X.; Fernandes, L.F.; Terêncio, D.; Pereira, V.; Santos, C.; Lopes, M.; Pacheco, F.; Gorni, G.; et al. From Land to Water: The Impact of Landscape on Water Quality Through Linear Models. Water 2025, 17, 3088. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17213088
Rosário G, Acuña-Alonso C, Álvarez X, Fernandes LF, Terêncio D, Pereira V, Santos C, Lopes M, Pacheco F, Gorni G, et al. From Land to Water: The Impact of Landscape on Water Quality Through Linear Models. Water. 2025; 17(21):3088. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17213088
Chicago/Turabian StyleRosário, Gabriel, Carolina Acuña-Alonso, Xana Álvarez, Luís Filipe Fernandes, Daniela Terêncio, Vitor Pereira, Cátia Santos, Marisa Lopes, Fernando Pacheco, Guilherme Gorni, and et al. 2025. "From Land to Water: The Impact of Landscape on Water Quality Through Linear Models" Water 17, no. 21: 3088. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17213088
APA StyleRosário, G., Acuña-Alonso, C., Álvarez, X., Fernandes, L. F., Terêncio, D., Pereira, V., Santos, C., Lopes, M., Pacheco, F., Gorni, G., Varandas, S., & Fernandes, A. (2025). From Land to Water: The Impact of Landscape on Water Quality Through Linear Models. Water, 17(21), 3088. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17213088










