A Review on Climate Change Impacts on Freshwater Systems and Ecosystem Resilience
Abstract
1. Introduction
- To synthesize recent (2010–2025) peer-reviewed research on climate-driven changes in freshwater systems including hydrological shifts, thermal dynamics, and ecosystem responses across rivers, lakes, wetlands, ponds, and groundwater in diverse climatic regions.
- To identify and analyze critical knowledge, data, and methodological gaps that limit cross-system understanding and hinder the translation of climate-science evidence into actionable freshwater management and resilience planning.
- To evaluate and integrate adaptation and governance strategies including nature-based solutions, Integrated Water Resources Management (IWRM), the Water–Energy–Food–Ecosystem (WEFE) nexus, and emerging technological tools (AI, GIS, and remote sensing) within a unified DPSIR (Drivers-Pressures-States-Impacts-Responses) framework to guide evidence-based, regionally adaptable water-management decisions.
2. Methodology
3. Climate Change Impacts on Freshwater Systems and Strategies for Adaptation
3.1. Climate Change and Hydrological Shift
3.1.1. Impact of Climate Change on Precipitation Patterns, Snowmelt Timing, and River Flow Dynamics
3.1.2. Effects of Hydrological Changes on Water Availability, Quality, and Ecosystem Functioning
3.2. Rising Temperatures and Water Temperature
3.2.1. Impact of Rising Temperatures on Water Temperature Regimes in Rivers, Lakes Ponds
3.2.2. Impact on Aquatic Ecosystems, Species Distribution, and Thermal Stratification Processes
3.3. Vulnerable Freshwater Systems: Shallow Lakes and Ponds
3.3.1. Shallow Lakes: Vulnerability to Warming, Stratification, and Nutrient Stress
3.3.2. Ponds: Disappearance from Permafrost Thaw and Evaporation Loss
3.4. Implications for Water Management
3.4.1. Climate Change and Water Management Strategies
3.4.2. Role of Emerging Technology in Water Management
3.4.3. Adaptive Strategies for Water Management
3.5. Policy Relevance and Use for Decision-Makers
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mock, C.N.; Nugent, R.; Kobusingye, O.; Smith, K.R. (Eds.) Disease Control Priorities: Injury Prevention and Environmental Health, 3rd ed.; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; Volume 7, ISBN 978-1-4648-0522-6. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. Sustainable Management of Water Resources in Agriculture; OECD Studies on Water; OECD: Paris, France, 2010; ISBN 978-92-64-08345-5. [Google Scholar]
- Lili, R.; Yanlei, D.; Shurong, D. The Impact of Water Resource Constraints on Industrial Linkages in the Yellow River Basin. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1360451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamushka, V.I. Indicators of Environmental Sustainability in Water Resources Management. JSM Environ. Sci. Ecol. 2022, 10, 1080. [Google Scholar]
- Muigua, K. Adopting Holistic Approaches to Biodiversity Conservation and Water Resources Management for Sustainable Development. Sustain. Dev. 2021. Available online: https://kmco.co.ke/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/Adopting-Holistic-Approaches-to-Biodiversity-Conservation-and-Water-Resources-Management-for-Sustainable-Development-Kariuki-Muigua-November-2021.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2025).
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Safe and Sustainable Water Resources Strategic Research Action Plan 2012–2016; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2012.
- Salimi, S.; Almuktar, S.A.A.A.N.; Scholz, M. Impact of Climate Change on Wetland Ecosystems: A Critical Review of Experimental Wetlands. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 286, 112160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, C.M.; Sharma, S.; Gray, D.K.; Hampton, S.E.; Read, J.S.; Rowley, R.J.; Schneider, P.; Lenters, J.D.; McIntyre, P.B.; Kraemer, B.M.; et al. Rapid and Highly Variable Warming of Lake Surface Waters around the Globe. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 10773–10781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K.E. Conceptual Framework for Changes of Extremes of the Hydrological Cycle with Climate Change. Clim. Change 1999, 42, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takele, G.S.; Gebrie, G.S.; Gebremariam, A.G.; Engida, A.N. Future Climate Change and Impacts on Water Resources in the Upper Blue Nile Basin. J. Water Clim. Change 2022, 13, 908–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokulil, M.T.; De Eyto, E.; Maberly, S.C.; May, L.; Weyhenmeyer, G.A.; Woolway, R.I. Increasing Maximum Lake Surface Temperature under Climate Change. Clim. Change 2021, 165, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danladi Bello, A.-A.; Hashim, N.; Mohd Haniffah, M. Predicting Impact of Climate Change on Water Temperature and Dissolved Oxygen in Tropical Rivers. Climate 2017, 5, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubalcaba, J.G. Metabolic Responses to Cold and Warm Extremes in the Ocean. PLoS Biol. 2024, 22, e3002479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donat, M.G.; Alexander, L.V.; Yang, H.; Durre, I.; Vose, R.; Dunn, R.J.H.; Willett, K.M.; Aguilar, E.; Brunet, M.; Caesar, J.; et al. Updated Analyses of Temperature and Precipitation Extreme Indices since the Beginning of the Twentieth Century: The HadEX2 Dataset. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 2098–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markonis, Y.; Papalexiou, S.M.; Martinkova, M.; Hanel, M. Assessment of Water Cycle Intensification Over Land Using a Multisource Global Gridded Precipitation DataSet. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 11175–11187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vonk, J.E.; Tank, S.E.; Bowden, W.B.; Laurion, I.; Vincent, W.F.; Alekseychik, P.; Amyot, M.; Billet, M.F.; Canário, J.; Cory, R.M.; et al. Reviews and Syntheses: Effects of Permafrost Thaw on Arctic Aquatic Ecosystems. Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 7129–7167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wu, J. Water Resources and Sustainable Development. Water 2023, 16, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contractor, S.; Donat, M.G.; Alexander, L.V. Changes in Observed Daily Precipitation over Global Land Areas since 1950. J. Clim. 2021, 34, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremichael, A.; Kebede, A.; Woyessa, Y.E. Impact of Climate Change on Water Resource Potential and Sediment Yield of the Gibe III Watershed, Omo-Gibe Basin, Ethiopia. J. Water Clim. Change 2024, 15, 902–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musie, M.; Momblanch, A.; Sen, S. Exploring Future Global Change-Induced Water Imbalances in the Central Rift Valley Basin, Ethiopia. Clim. Change 2021, 164, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yao, T.; Xie, H.; Yang, K.; Zhu, L.; Shum, C.K.; Bolch, T.; Yi, S.; Allen, S.; Jiang, L.; et al. Response of Tibetan Plateau Lakes to Climate Change: Trends, Patterns, and Mechanisms. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2020, 208, 103269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Zhang, G.; Woolway, R.I.; Yang, K.; Wada, Y.; Wang, J.; Crétaux, J.-F. Widespread Societal and Ecological Impacts from Projected Tibetan Plateau Lake Expansion. Nat. Geosci. 2024, 17, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.; Laizé, C.L.R.; Acreman, M.C.; Flörke, M. How Will Climate Change Modify River Flow Regimes in Europe? Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakib, Z. Long-Term Trends in Precipitation Indices at Eastern Districts of Bangladesh. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Xu, B.; Ju, J.; Wu, C.; Dai, H.; Hu, B.X. Projection and Uncertainty of Precipitation Extremes in the CMIP5 Multimodel Ensembles over Nine Major Basins in China. Atmos. Res. 2019, 226, 122–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Ji, H.; Wen, J.; Wu, S.-Y.; Xu, M.; Tagle, F.; He, B.; Duan, W.; Li, J. The Characteristics of Regional Heavy Precipitation Events over Eastern Monsoon China during 1960–2013. Glob. Planet. Change 2019, 172, 414–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Ren, G.; Yang, S. Change in Precipitation over the Asian Continent from 1901–2016 Based on a New Multi-Source Dataset. Clim. Res. 2018, 76, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Wasko, C.; Lettenmaier, D.P. If Precipitation Extremes Are Increasing, Why Aren’t Floods? Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 8545–8551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasko, C.; Sharma, A. Global Assessment of Flood and Storm Extremes with Increased Temperatures. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donat, M.G.; Lowry, A.L.; Alexander, L.V.; O’Gorman, P.A.; Maher, N. More Extreme Precipitation in the World’s Dry and Wet Regions. Nat. Clim. Change 2016, 6, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabanli, İ. A Climate Change Impact: Variation In Precipitation Patterns, And Increased Drought Risk In Turkey. Sak. Univ. J. Sci. 2019, 23, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Trenberth, K. Changes in Precipitation with Climate Change. Clim. Res. 2011, 47, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, E.; Raffaele, F.; Giorgi, F. Impact of Climate Change on Snow Melt Driven Runoff Timing over the Alpine Region. Clim. Dyn. 2018, 51, 1259–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakol, A.; Rahmani, V.; Harrington, J. Changes in the Frequency of Hot, Humid Days and Nights in the Mississippi River Basin. Int. J. Climatol. 2020, 40, 4715–4730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Wasko, C. Trends and Changes in Streamflow with Climate. In Trends and Changes in Hydroclimatic Variables; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 275–304. ISBN 978-0-12-810985-4. [Google Scholar]
- Asadieh, B.; Krakauer, N.Y. Impacts of Changes in Precipitation Amount and Distribution on Water Resources Studied Using a Model Rainwater Harvesting System. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2016, 52, 1450–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymondi, R.R.; Cuhaciyan, J.E.; Glick, P.; Capalbo, S.M.; Houston, L.L.; Shafer, S.L.; Grah, O. Water Resources: Implications of Changes in Temperature and Precipitation. In Climate Change in the Northwest; Island Press/Center for Resource Economics: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; pp. 41–66. ISBN 978-1-59726-426-6. [Google Scholar]
- Tabari, H. Climate Change Impact on Flood and Extreme Precipitation Increases with Water Availability. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabari, H. Extreme Value Analysis Dilemma for Climate Change Impact Assessment on Global Flood and Extreme Precipitation. J. Hydrol. 2021, 593, 125932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Huang, Q.; Tang, Q.; Chen, X.; Yu, J.; Pozdniakov, S.P.; Wang, T. Increasing Annual and Extreme Precipitation in Permafrost-Dominated Siberia during 1959–2018. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lompi, M.; Mediero, L.; Caporali, E. Future Flood Hazard Assessment for the City of Pamplona (Spain) Using an Ensemble of Climate Change Projections. Water 2021, 13, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaubey, P.K.; Mall, R.K.; Jaiswal, R.; Payra, S. Spatio-Temporal Changes in Extreme Rainfall Events Over Different Indian River Basins. Earth Space Sci. 2022, 9, e2021EA001930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajracharya, S.; Maharjan, S.; Shrestha, F.; Shrestha, B.; Guo, W.; Liu, S.; Yao, X.; Khattak, G. The Status of Glaciers in the Hindu Kush-Himalayas from Satellite Data. AGU Fall Meet. Abstr. 2011, 2011, C43A-04. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Lu, X.; Park, E.; Tarolli, P. Impacts of Climate Change on Lake Fluctuations in the Hindu Kush-Himalaya-Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, A.B. Climate Change in the Hindu Kush Himalaya: Impacts on Water and Air; ICIMOD: Lalitpur, Nepal, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Khadka, N.; Chen, X.; Sharma, S.; Shrestha, B. Climate Change and Its Impacts on Glaciers and Glacial Lakes in Nepal Himalayas. Reg. Environ. Change 2023, 23, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joya, E.; Bromand, M.T.; Murtaza, K.O.; Dar, R.A. Current Glacier Status and ELA Changes since the Late Pleistocene in the Hindu Kush Mountains of Afghanistan. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2021, 219, 104897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, M.; Mahmood, S. Exploring Potential Glacial Lakes Using Geo-Spatial Techniques in Eastern Hindu Kush Region, Pakistan. Nat. Hazards Res. 2024, 4, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasa, R.B.; Rai, S.; Adhikari, D. Climate-Induced Disaster in Nepal: Assessing Impact of Glacial Lake Outburst Floods in Thame Valley, Solukhumbu. Nepal. J. Dev. Rural Stud. 2024, 21, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stimson Center. Investigating an Emerging Climate Hazard: Transboundary Glacial Floods on the China-Nepal Border. 22 July 2025. Available online: https://www.stimson.org/2025/investigating-an-emerging-climate-hazard-transboundary-glacial-floods-on-the-china-nepal-border/ (accessed on 20 August 2025).
- A Hidden Glacier Lake Caused the Deadly Bhotekoshi Flood, Scientists Say|The Farsight Nepal. Available online: https://farsightnepal.com/news/a-hidden-glacier-lake-caused-the-deadly-bhotekoshi-flood-scientists-say/ (accessed on 20 August 2025).
- India-Flash Floods (Media, IMD) (ECHO Daily Flash of 18 August 2025)-India | ReliefWeb. Available online: https://reliefweb.int/report/india/india-flash-floods-media-imd-echo-daily-flash-18-august-2025 (accessed on 20 August 2025).
- Flash Floods Kill Hundreds in Pakistan, India. DW, 16 August 2025. Available online: https://www.dw.com/en/flash-floods-kill-hundreds-in-pakistan-india/a-73656252 (accessed on 20 August 2025).
- Alexander, L.V.; Zhang, X.; Peterson, T.C.; Caesar, J.; Gleason, B.; Klein Tank, A.M.G.; Haylock, M.; Collins, D.; Trewin, B.; Rahimzadeh, F.; et al. Global Observed Changes in Daily Climate Extremes of Temperature and Precipitation. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, D05109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westra, S.; Alexander, L.V.; Zwiers, F.W. Global Increasing Trends in Annual Maximum Daily Precipitation. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 3904–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, R.W.; Parlange, M.B.; Naveau, P. Statistics of Extremes in Hydrology. Adv. Water Resour. 2002, 25, 1287–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Gorman, P.A. Precipitation Extremes Under Climate Change. Curr. Clim. Change Rep. 2015, 1, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zittis, G.; Almazroui, M.; Alpert, P.; Ciais, P.; Cramer, W.; Dahdal, Y.; Fnais, M.; Francis, D.; Hadjinicolaou, P.; Howari, F.; et al. Climate Change and Weather Extremes in the Eastern Mediterranean and Middle East. Rev. Geophys. 2022, 60, e2021RG000762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myhre, G.; Alterskjær, K.; Stjern, C.W.; Hodnebrog, Ø.; Marelle, L.; Samset, B.H.; Sillmann, J.; Schaller, N.; Fischer, E.; Schulz, M.; et al. Frequency of Extreme Precipitation Increases Extensively with Event Rareness under Global Warming. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trenberth, K.E.; Dai, A.; Rasmussen, R.M.; Parsons, D.B. The Changing Character of Precipitation. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2003, 84, 1205–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirabayashi, Y.; Mahendran, R.; Koirala, S.; Konoshima, L.; Yamazaki, D.; Watanabe, S.; Kim, H.; Kanae, S. Global Flood Risk under Climate Change. Nat. Clim. Change 2013, 3, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolentino, P.L.M.; Williams, R.D.; Hurst, M.D. Natural Flood Risk Management in Tropical Southeast Asia: Prospects in the Biodiverse Archipelagic Nation of the Philippines. WIREs Water 2025, 12, e70000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aura, C.M.; Nyamweya, C.; Musa, S.; Ogari, Z.; Owoko, W.; Osore, M.; May, L.; Njiru, J.M. The Quantification of the Extent of Flooding on Selected Major Afrotropical Lakes to Guide Management Implications. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1062289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, A.E.; Zaki, M.M. The Impact of Global Climatic Changes on the Aquatic Environment. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, A.W.; Gobler, C.J. Harmful Algal Blooms: A Climate Change Co-Stressor in Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems. Harmful Algae 2020, 91, 101590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azanza, R.; Rivera, P.P.; Orizar, I.; Jacinto, G.; David, L.; Vargas-Nguyen Vm, V. Harmful Algal Blooms (HABs) Management in Tropical Marine Food Production Areas Amidst Climate Change. Trans. NAST PHL 2024, 46, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, D.; Fujisaki-Manome, A.; Wang, J.; Kessler, J.; Chu, P. Modeling Changes in Ice Dynamics and Subsurface Thermal Structure in Lake Michigan-Huron between 1979 and 2021. Ocean Dyn. 2023, 73, 201–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Lan, J.; Qin, B.; Luo, L.; Jin, J.; Zhu, G.; Wu, Z. Effects of the Long-Term Climate Change and Selective Discharge Schemes on the Thermal Stratification of a Large Deep Reservoir, Xin’anjiang Reservoir, China. Water 2022, 14, 3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, R.; Woolway, R.I.; Saari, M.; Pulkkanen, M.; Kløve, B. Six Decades of Thermal Change in a Pristine Lake Situated North of the Arctic Circle. Water Resour. Res. 2022, 58, e2021WR031543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugdale, S.J.; Allen Curry, R.; St-Hilaire, A.; Andrews, S.N. Impact of Future Climate Change on Water Temperature and Thermal Habitat for Keystone Fishes in the Lower Saint John River, Canada. Water Resour. Manag. 2018, 32, 4853–4878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaib, N.A.; Quinn, T. Reassessing the Source of Long-Period Comets. Science 2009, 325, 1234–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bryant, M.D. Global Climate Change and Potential Effects on Pacific Salmonids in Freshwater Ecosystems of Southeast Alaska. Clim. Change 2009, 95, 169–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smol, J.P.; Douglas, M.S.V. Crossing the Final Ecological Threshold in High Arctic Ponds. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 12395–12397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tye, S.P.; Siepielski, A.M.; Bray, A.; Rypel, A.L.; Phelps, N.B.D.; Fey, S.B. Climate Warming Amplifies the Frequency of Fish Mass Mortality Events across North Temperate Lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. Lett. 2022, 7, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Xu, J.; Meng, X.; Wang, Y.; Yan, B.; Hong, X. Impact of Climate Variability on Blue and Green Water Flows in the Erhai Lake Basin of Southwest China. Water 2019, 11, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krochta, M.; Anlauf-Dunn, K.; Bugni, D.; Chang, H. Effects of Climate Change on Stream Temperature and Salmonid Habitats in a Cascades River Basin. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 387, 125843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comte, L.; Buisson, L.; Daufresne, M.; Grenouillet, G. Climate-induced Changes in the Distribution of Freshwater Fish: Observed and Predicted Trends. Freshw. Biol. 2013, 58, 625–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capon, S.J.; Stewart-Koster, B.; Bunn, S.E. Future of Freshwater Ecosystems in a 1.5 °C Warmer World. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 784642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaak, D.J.; Wollrab, S.; Horan, D.; Chandler, G. Climate Change Effects on Stream and River Temperatures across the Northwest U.S. from 1980–2009 and Implications for Salmonid Fishes. Clim. Change 2012, 113, 499–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, J.G.; Scheller, R.M. Effects of Climate Warming on Fish Thermal Habitat in Streams of the United States. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1996, 41, 1109–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heino, J.; Virkkala, R.; Toivonen, H. Climate Change and Freshwater Biodiversity: Detected Patterns, Future Trends and Adaptations in Northern Regions. Biol. Rev. 2009, 84, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushal, S.S.; Likens, G.E.; Jaworski, N.A.; Pace, M.L.; Sides, A.M.; Seekell, D.; Belt, K.T.; Secor, D.H.; Wingate, R.L. Rising Stream and River Temperatures in the United States. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2010, 8, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Meerhoff, M.; Davidson, T.A.; Trolle, D.; Søndergaard, M.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Beklioglu, M.; Brucet, S.; Volta, P.; González-Bergonzoni, I.; et al. Climate Change Impacts on Lakes: An Integrated Ecological Perspective Based on a Multi-Faceted Approach, with Special Focus on Shallow Lakes. J. Limnol. 2014, 73, 88–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havens, K.; Paerl, H.; Phlips, E.; Zhu, M.; Beaver, J.; Srifa, A. Extreme Weather Events and Climate Variability Provide a Lens to How Shallow Lakes May Respond to Climate Change. Water 2016, 8, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerhoff, M.; Teixeira-de Mello, F.; Kruk, C.; Alonso, C.; González-Bergonzoni, I.; Pacheco, J.P.; Lacerot, G.; Arim, M.; Beklioğlu, M.; Brucet, S.; et al. Environmental Warming in Shallow Lakes. In Advances in Ecological Research; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 46, pp. 259–349. ISBN 978-0-12-396992-7. [Google Scholar]
- Fragoso, C.R.; Motta Marques, D.M.L.; Ferreira, T.F.; Janse, J.H.; Van Nes, E.H. Potential Effects of Climate Change and Eutrophication on a Large Subtropical Shallow Lake. Environ. Model. Softw. 2011, 26, 1337–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooij, W.M.; Janse, J.H.; De Senerpont Domis, L.N.; Hülsmann, S.; Ibelings, B.W. Predicting the Effect of Climate Change on Temperate Shallow Lakes with the Ecosystem Model PCLake. Hydrobiologia 2007, 584, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golosov, S.; Terzhevik, A.; Zverev, I.; Kirillin, G.; Engelhardt, C. Climate Change Impact on Thermal and Oxygen Regime of Shallow Lakes. Tellus A Dyn. Meteorol. Oceanogr. 2012, 64, 17264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccioni, F.; Casenave, C.; Lemaire, B.J.; Le Moigne, P.; Dubois, P.; Vinçon-Leite, B. The Thermal Response of Small and Shallow Lakes to Climate Change: New Insights from 3D Hindcast Modelling. Earth Syst. Dyn. 2021, 12, 439–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, L.; Kirika, A. Changes in Shallow Lake Functioning: Response to Climate Change and Nutrient Reduction. Hydrobiologia 2003, 506–509, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feuchtmayr, H.; Moran, R.; Hatton, K.; Connor, L.; Heyes, T.; Moss, B.; Harvey, I.; Atkinson, D. Global Warming and Eutrophication: Effects on Water Chemistry and Autotrophic Communities in Experimental Hypertrophic Shallow Lake Mesocosms. J. Appl. Ecol. 2009, 46, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, J. Anthropogenic Climate Change Impacts on Ponds: A Thermal Mass Perspective. BioRisk 2010, 5, 193–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, M.J.; Greaves, H.M.; Sayer, C.D.; Hassall, C.; Milin, M.; Milner, V.S.; Marazzi, L.; Hall, R.; Harper, L.R.; Thornhill, I.; et al. Pond Ecology and Conservation: Research Priorities and Knowledge Gaps. Ecosphere 2021, 12, e03853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orság, M.; Meitner, J.; Fischer, M.; Svobodová, E.; Kopp, R.; Mareš, J.; Spurný, P.; Pechar, L.; Beděrková, I.; Hanuš, J.; et al. Estimating Heat Stress Effects on the Sustainability of Traditional Freshwater Pond Fishery Systems under Climate Change. Water 2023, 15, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Mishra, P.K.; Islam, A.; Alam, N.M. Simulation of Water Temperature in a Small Pond Using Parametric Statistical Models: Implications of Climate Warming. J. Environ. Eng. 2016, 142, 04015085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahr, J. Ecotoxicology of Organisms Adapted to Life in Temporary Freshwater Ponds in Arid and Semi-Arid Regions. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1997, 32, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paull, S.H.; Johnson, P.T.J. How Temperature, Pond-Drying, and Nutrients Influence Parasite Infection and Pathology. EcoHealth 2018, 15, 396–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andresen, C.G.; Lougheed, V.L. Disappearing Arctic Tundra Ponds: Fine-scale Analysis of Surface Hydrology in Drained Thaw Lake Basins over a 65 Year Period (1948–2013). J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2015, 120, 466–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautio, M.; Dufresne, F.; Laurion, I.; Bonilla, S.; Vincent, W.F.; Christoffersen, K.S. Shallow Freshwater Ecosystems of the Circumpolar Arctic. Écoscience 2011, 18, 204–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.L.; Brown, L.C. Thermal Regime of High Arctic Tundra Ponds, Nanuit Itillinga (Polar Bear Pass), Nunavut, Canada. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2024, 28, 3931–3945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Shi, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, W. Lake Changes in Inner Mongolia over the Past 30 Years and the Associated Factors. Water 2022, 14, 3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Wang, X.; Sang, Y.; Tang, S.; Jin, L.; Yang, H.; Ottlé, C.; Bernus, A.; Wang, S.; Wang, C.; et al. Optimizing Lake Surface Water Temperature Simulations Over Large Lakes in China With FLake Model. Earth Space Sci. 2021, 8, e2021EA001737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Erler, A.R.; Chandan, D.; Peltier, W.R. Great Lakes Basin Heat Waves: An Analysis of Their Increasing Probability of Occurrence Under Global Warming. Front. Water 2021, 3, 782265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhady, H.U.; Fujisaki-Manome, A.; Cannon, D.; Gronewold, A.; Wang, J. Climate Change-Induced Amplification of Extreme Temperatures in Large Lakes. Commun. Earth Environ. 2025, 6, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shi, K.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Woolway, R.I.; Piao, S.; Jeppesen, E. Climate Change Drives Rapid Warming and Increasing Heatwaves of Lakes. Sci. Bull. 2023, 68, 1574–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurlimann, A.; Moosavi, S.; Browne, G.R. Urban Planning Policy Must Do More to Integrate Climate Change Adaptation and Mitigation Actions. Land Use Policy 2021, 101, 105188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-C.; Wang, C.-L. Enhancing Urban Flood Resilience: Interdisciplinary Integration of Climate Adaptation, Flood Control, and Land-Use Planning from 3PA to 4PA. J. Water Clim. Change 2024, 15, 1961–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niekerk, W.V.; Duncker, L.; Maditse, K.; Davis, C.; Pieterse, A. Water Sensitive Urban Planning as Adaptation Strategy. In Proceedings of the 54th ISOCARP Congress, Bodø, Norway, 1–5 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Refsgaard, J.C.; Arnbjerg-Nielsen, K.; Drews, M.; Halsnæs, K.; Jeppesen, E.; Madsen, H.; Markandya, A.; Olesen, J.E.; Porter, J.R.; Christensen, J.H. The Role of Uncertainty in Climate Change Adaptation Strategies—A Danish Water Management Example. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Change 2013, 18, 337–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadaali, J.; Barani, G.-A.; Qaderi, K.; Hessari, B. Analysis of the Effects of Water Management Strategies and Climate Change on the Environmental and Agricultural Sustainability of Urmia Lake Basin, Iran. Water 2018, 10, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.I.; Farooq, M.; Muscolo, A.; Rehman, A. Crop Diversification and Saline Water Irrigation as Potential Strategies to Save Freshwater Resources and Reclamation of Marginal Soils-a Review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 28695–28729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beniston, M.; Stoffel, M.; Hill, M. Impacts of Climatic Change on Water and Natural Hazards in the Alps: Can Current Water Governance Cope with Future Challenges? Examples from the European “ACQWA” Project. Environ. Sci. Policy 2011, 14, 734–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crossman, J.; Futter, M.N.; Oni, S.K.; Whitehead, P.G.; Jin, L.; Butterfield, D.; Baulch, H.M.; Dillon, P.J. Impacts of Climate Change on Hydrology and Water Quality: Future Proofing Management Strategies in the Lake Simcoe Watershed, Canada. J. Great Lakes Res. 2013, 39, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worqlul, A.; Dile, Y.T.; Ayana, E.; Jeong, J.; Adem, A.; Gerik, T. Impact of Climate Change on Streamflow Hydrology in Headwater Catchments of the Upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Water 2018, 10, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sordo-Ward, A.; Granados, A.; Iglesias, A.; Garrote, L.; Bejarano, M. Adaptation Effort and Performance of Water Management Strategies to Face Climate Change Impacts in Six Representative Basins of Southern Europe. Water 2019, 11, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phene, C.J.; Beale, O.W. High-Frequency Irrigation for Water Nutrient Management in Humid Regions. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1976, 40, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, V.P.; Shrestha, N.; Urfels, A.; Ray, A.; Khadka, M.; Pavelic, P.; McDonald, A.J.; Krupnik, T.J. Implementing Conjunctive Management of Water Resources for Irrigation Development: A Framework Applied to the Southern Plain of Western Nepal. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 283, 108287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risal, A.; Urfels, A.; Srinivasan, R.; Bayissa, Y.; Shrestha, N.; Paudel, G.P.; Krupnik, T.J. Impact of Climate Change on Water Resources and Crop Production in Western Nepal: Implications and Adaptation Strategies. Hydrology 2022, 9, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdi, B.; Lehner, B.; Gombault, C.; Michaud, A.; Beaudin, I.; Sottile, M.-F.; Blondlot, A. Simulated Impacts of Climate Change and Agricultural Land Use Change on Surface Water Quality with and without Adaptation Management Strategies. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 213, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Steenhuis, T.S.; Davis, K.F.; van der Werf, W.; Ritsema, C.J.; Pacenka, S.; Zhang, F.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Du, T. Diversified Crop Rotations Enhance Groundwater and Economic Sustainability of Food Production. Food Energy Secur. 2021, 10, e311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainuddin, M.; Karim, F.; Gaydon, D.S.; Kirby, J.M. Impact of Climate Change and Management Strategies on Water and Salt Balance of the Polders and Islands in the Ganges Delta. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, A.; Madhav, S.; Mishra, R.; Srivastav, A.L.; Garg, P. Impact of Climate Change on Water Resources, Challenges and Mitigation Strategies to Achieve Sustainable Development Goals. Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, T.; Alfredo, K.; Fisher, J. Sustainable Water Management in Urban, Agricultural, and Natural Systems. Water 2014, 6, 3934–3956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leigh, N.G.; Lee, H. Sustainable and Resilient Urban Water Systems: The Role of Decentralization and Planning. Sustainability 2019, 11, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.A.; Sayed, S.; Abdoulhalik, A.; Moutari, S.; Oyedele, L. Applications of Machine Learning to Water Resources Management: A Review of Present Status and Future Opportunities. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 441, 140715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouma, Y.O.; Cheruyot, R.; Wachera, A.N. Rainfall and Runoff Time-Series Trend Analysis Using LSTM Recurrent Neural Network and Wavelet Neural Network with Satellite-Based Meteorological Data: Case Study of Nzoia Hydrologic Basin. Complex Intell. Syst. 2022, 8, 213–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayhomayoon, Z.; Ghordoyee-Milan, S.; Jaafari, A.; Arya-Azar, N.; Melesse, A.M.; Kardan Moghaddam, H. How Does a Combination of Numerical Modeling, Clustering, Artificial Intelligence, and Evolutionary Algorithms Perform to Predict Regional Groundwater Levels? Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 203, 107482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Role of Artificial Intelligence in Improving Water Resource Management: From Demand Forecasting to Waste Reduction and Water Crisis Mitigation|Auctores. Available online: https://www.auctoresonline.org/article/role-of-artificial-intelligence-in-improving-water-resource-management-from-demand-forecasting-to-waste-reduction-and-water-crisis-mitigation (accessed on 20 August 2025).
- Jayaraman, P.; Nagarajan, K.; Partheeban, P.; Krishnamurthy, V. Critical Review on Water Quality Analysis Using IoT and Machine Learning Models. Int. J. Inf. Manag. Data Insights 2024, 4, 100210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Application of Geoai for Water Resource Monitoring in Eastern Ukraine. Technical Sciences Modern Trends of Social Transformations of Society in Conditions of Sustainable Development 214–215. Available online: https://eu-conf.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/MODERN-TRENDS-OF-SOCIAL-TRANSFORMATIONS-OF-SOCIETY-IN-CONDITIONS-OF-SUSTAINABLE-DEVELOPMENT.pdf#page=215 (accessed on 20 August 2025).
- Kayastha, R.B.; Steiner, N.; Kayastha, R.; Mishra, S.K.; McDonald, K. Comparative Study of Hydrology and Icemelt in Three Nepal River Basins Using the Glacio-Hydrological Degree-Day Model (GDM) and Observations From the Advanced Scatterometer (ASCAT). Front. Earth Sci. 2020, 7, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, G.; Avdan, U. Object-Based Water Body Extraction Model Using Sentinel-2 Satellite Imagery. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 50, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, K.H.; Menenti, M.; Jia, L. Surface Water Mapping and Flood Monitoring in the Mekong Delta Using Sentinel-1 SAR Time Series and Otsu Threshold. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machine Learning-Based Flood Risk Assessment in Urban Watershed: Mapping Flood Susceptibility in Charlotte, North Carolina. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2673-7086/5/3/43 (accessed on 20 August 2025).
- Duwal, S.; Liu, D.; Pradhan, P.M. Flood Susceptibility Modeling of the Karnali River Basin of Nepal Using Different Machine Learning Approaches. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2023, 14, 2217321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Jie, Y.; Zhang, X.; Jing, G.; Yang, Y.; He, B. GIS-Based Risk Assessment for Regional Flood Disaster. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Environmental Science and Information Application Technology, Wuhan, China, 4–5 July 2009; Volume 2, pp. 564–567. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S.; Cheng, X.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, H. GIS-Based Flood Risk Assessment in Suburban Areas: A Case Study of the Fangshan District, Beijing. Nat. Hazards 2017, 87, 1525–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigg, N.S. Framework and Function of Integrated Water Resources Management in Support of Sustainable Development. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katusiime, J.; Schütt, B. Integrated Water Resources Management Approaches to Improve Water Resources Governance. Water 2020, 12, 3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Radif, A. Integrated Water Resources Management (IWRM): An Approach to Face the Challenges of the next Century and to Avert Future Crises. Desalination 1999, 124, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albatayneh, A. Water Energy Food Nexus to Tackle Climate Change in the Eastern Mediterranean. Air Soil Water Res. 2023, 16, 11786221231170222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpandeli, S.; Naidoo, D.; Mabhaudhi, T.; Nhemachena, C.; Nhamo, L.; Liphadzi, S.; Hlahla, S.; Modi, A.T. Climate Change Adaptation through the Water-Energy-Food Nexus in Southern Africa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasul, G.; Sharma, B. The Nexus Approach to Water–Energy–Food Security: An Option for Adaptation to Climate Change. Clim. Policy 2016, 16, 682–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaniya, B.; Gunathilake, M.B.; Rathnayake, U. Ecosystem-Based Adaptation for the Impact of Climate Change and Variation in the Water Management Sector of Sri Lanka. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 8821329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandino, G.; Elliff, C.I.; Silva, I.R. Ecosystem-Based Management of Coastal Zones in Face of Climate Change Impacts: Challenges and Inequalities. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 215, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramova, E.; Locatelli, B.; Djoudi, H.; Somorin, O.A. Forests and Trees for Social Adaptation to Climate Variability and Change. WIREs Clim. Change 2012, 3, 581–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarano, F.R. Ecosystem-Based Adaptation to Climate Change: Concept, Scalability and a Role for Conservation Science. Perspect. Ecol. Conserv. 2017, 15, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staddon, C.; Ward, S.; De Vito, L.; Zuniga-Teran, A.; Gerlak, A.K.; Schoeman, Y.; Hart, A.; Booth, G. Contributions of Green Infrastructure to Enhancing Urban Resilience. Environ. Syst. Decis. 2018, 38, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, D.; O’Donnell, E.; Johnson, M.; Slater, L.; Thorne, C.; Zheng, S.; Stirling, R.; Chan, F.K.S.; Li, L.; Boothroyd, R.J. Green Infrastructure: The Future of Urban Flood Risk Management? WIREs Water 2021, 8, e1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geneletti, D.; Zardo, L. Ecosystem-Based Adaptation in Cities: An Analysis of European Urban Climate Adaptation Plans. Land Use Policy 2016, 50, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramova, E.; Locatelli, B.; Brockhaus, M.; Fohlmeister, S. Ecosystem Services in the National Adaptation Programmes of Action. Clim. Policy 2012, 12, 393–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Maktoumi, A.; Zekri, S.; El-Rawy, M.; Abdalla, O.; Al-Wardy, M.; Al-Rawas, G.; Charabi, Y. Assessment of the Impact of Climate Change on Coastal Aquifers in Oman. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munang, R.; Thiaw, I.; Alverson, K.; Mumba, M.; Liu, J.; Rivington, M. Climate Change and Ecosystem-Based Adaptation: A New Pragmatic Approach to Buffering Climate Change Impacts. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2013, 5, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

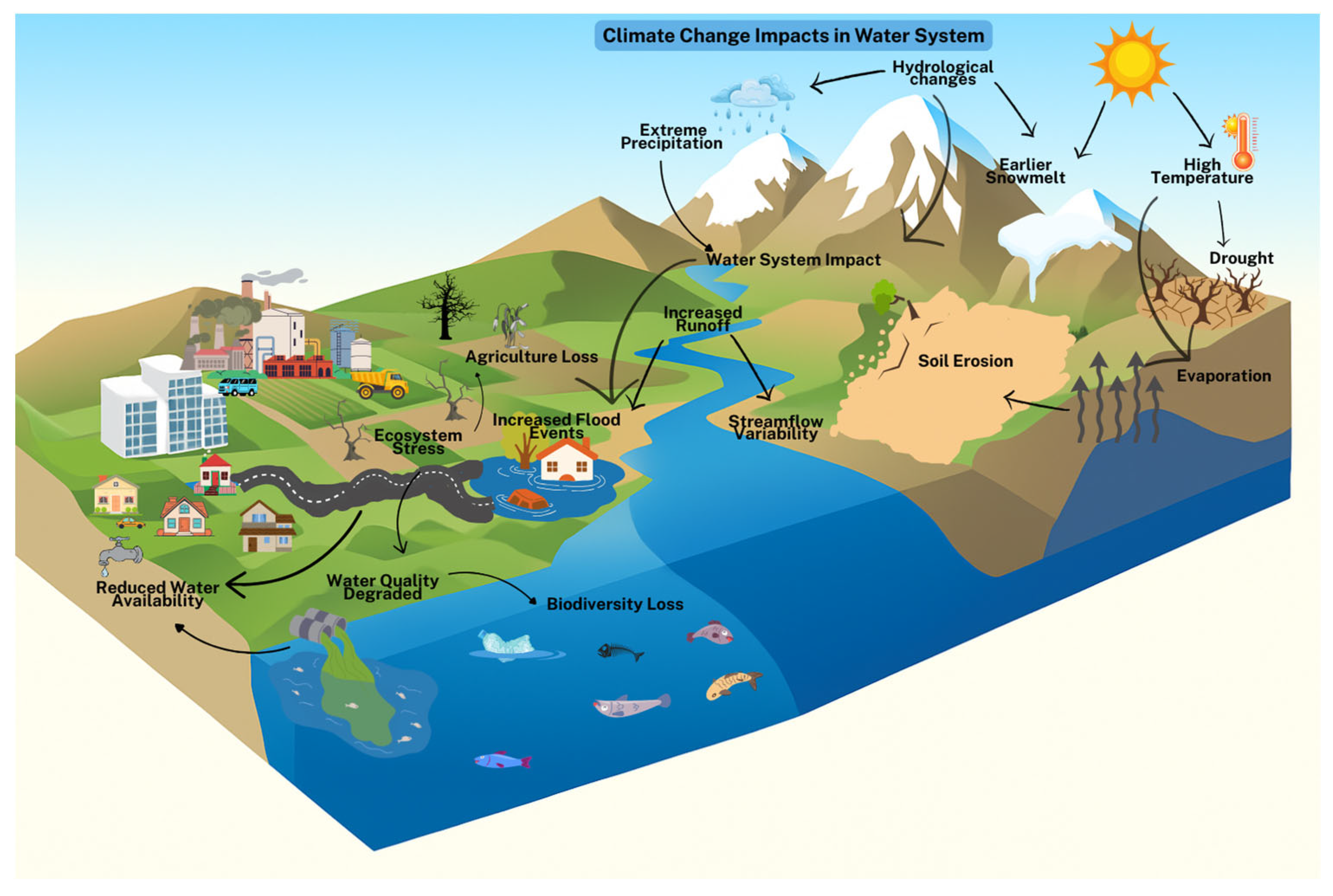

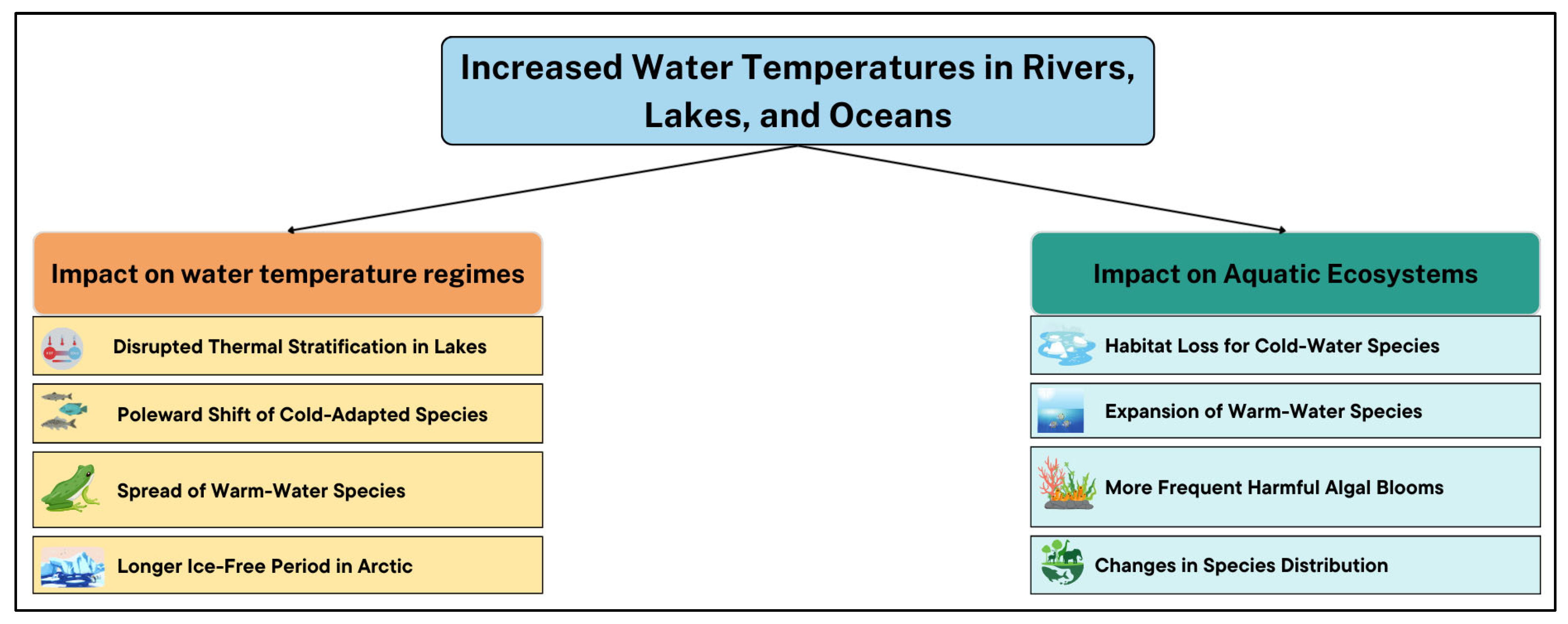
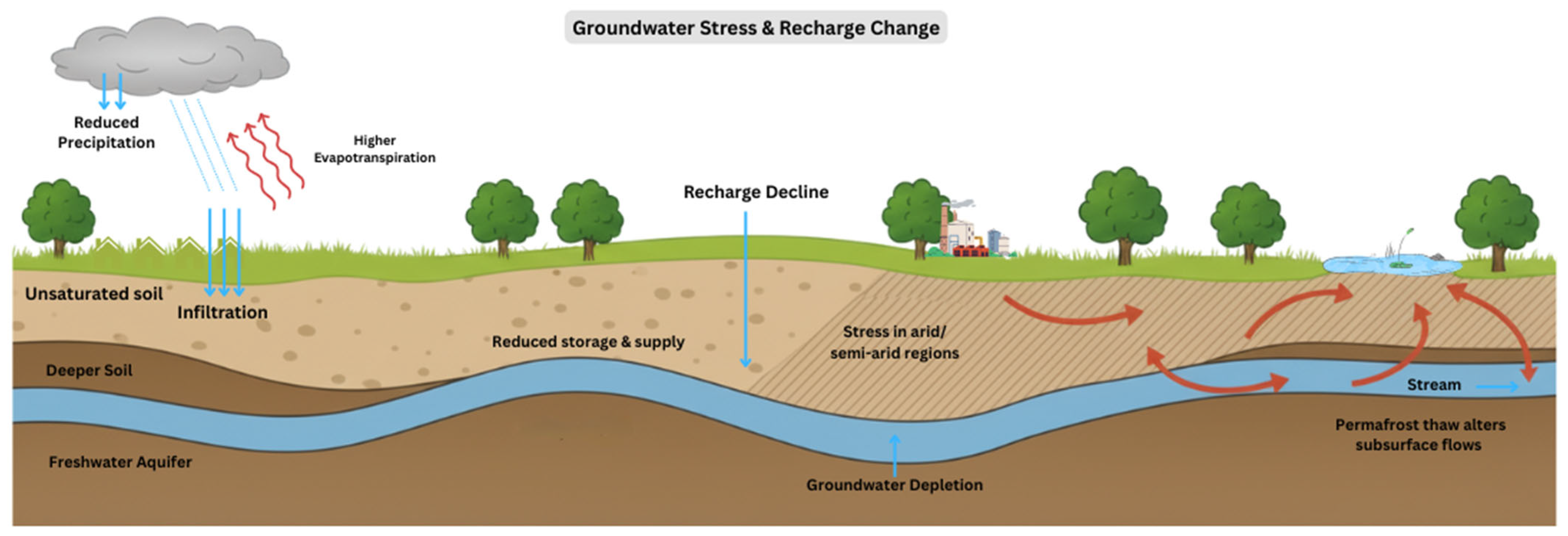
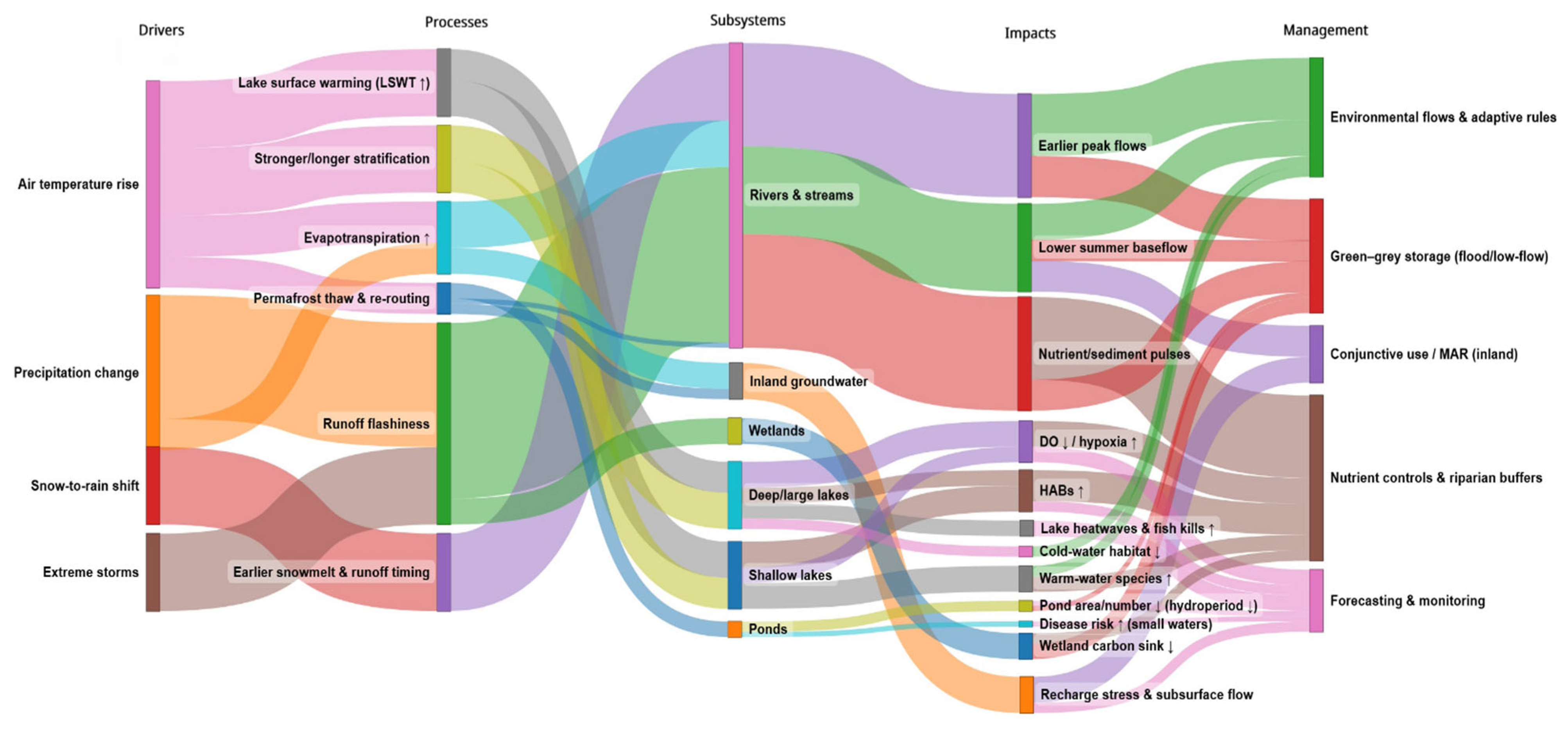
| Section | Number of Papers | Main Keywords | Data Sources/Databases | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Introduction and Background | 25 | Climate change; freshwater ecosystems; vulnerability | Web of Science; Scopus; ScienceDirect; Google Scholar | Foundational concepts and context |
| Hydrological Changes (Precipitation) | 50 | Precipitation extremes; snowmelt; river flows | Web of Science; Scopus; ScienceDirect; Google Scholar | Changing hydrological regimes |
| Thermal Regimes and Ecosystems | 40 | Water temperature; stratification; fish; algal blooms | Web of Science; Scopus; ScienceDirect; Google Scholar | Impacts on aquatic life and thermal processes |
| Water Resource Adaptation Strategies | 25 | IWRM; policy; governance; adaptation | Web of Science; Scopus; ScienceDirect; Google Scholar | Managing water under climate stress |
| Emerging Technologies and Modeling | 13 | AI; machine learning; remote sensing; GIS | Web of Science; Scopus; ScienceDirect; Google Scholar | Monitoring and prediction tools |
| Total (approx.) | ≈153 | Unique studies underlying the synthesis |
| Habitat/System | Climate Change Effects | Key Consequences | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rivers | Altered precipitation and snowmelt timing; stream warming of 0.22 °C/decade in NW U.S.; increased rainfall extremes in Asia and Europe | Earlier and more intense flows, flood risk, habitat loss for salmonids, reduced summer streamflow, altered irrigation reliability | [14,18,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,72,79,80,82] |
| Lakes (deep and large) | LSWT rise ~0.34 °C per decade globally; stronger stratification; hypoxia; more frequent heatwaves; increased algal blooms; reduced ice cover in >5000 lakes | Oxygen depletion, fish die-offs (6–34× increase projected), reduced cold-water habitats, expansion of warm-water fish, trophic instability | [8,11,16,21,22,67,68,74,101,102,103,104,105] |
| Shallow Lakes | Strong surface-to-volume coupling makes them sensitive to rainfall/runoff; warming lowers nutrient thresholds for eutrophication; rainfall extremes disrupt stratification | Cyanobacterial blooms, oxygen stress, destabilized food webs, biodiversity loss (fish and zooplankton decline, phytoplankton increase) | [84,85,87,88,89,90,91,92,93] |
| Ponds | Sensitive to evaporation and rainfall timing; permafrost thaw causing drainage; heat extremes up to 40–45 °C; shortened hydroperiods | Disappearance in Arctic/Subarctic, biodiversity decline, disease transmission rise (parasites in snails, amphibian deformities), aquaculture threats | [92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100] |
| Wetlands | Increased evapotranspiration; drought-driven respiration > production; altered precipitation balance | Carbon release (sink → source), habitat degradation, loss of biodiversity | [7,101] |
| Groundwater | Declining recharge in arid/semi-arid zones; permafrost thaw altering flows; over-extraction worsens stress | Lower water tables, salinization, quality degradation, destabilized aquifers | [43,44,45,46] |
| Tools | Core Focus | Benefits | Challenges | Reference(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Machine Learning and Deep Learning | Forecasting rainfall, hydrodynamics, groundwater levels, flood susceptibility mapping | Improved accuracy in predicting water flow and flood-prone zones | Requires large datasets, computational resources, and model calibration complexities. | [126,134] |
| IoT and Geo-AI with Remote Sensing | Real-time water quality monitoring, mapping water bodies, detecting pollution, analyzing glacier melt | Early detection of anomalies; large-scale monitoring | sensor deployment and maintenance costs; data processing complexity; cloud cover and spatial and temporal resolution issues | [129,130,132] |
| GIS-based Risk Assessment and Integrated Models | Integrating socio-economic, hydrological, and environmental data for flood risk and vulnerability assessment | Identifies high-risk areas; guides targeted mitigation | Data availability and quality; requires stakeholder engagement | [136,137] |
| Strategy | Core Focus | Benefits | Challenges | Reference(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Integrated Water Resource Management (IWRM) | Coordinated management of water, land, and resources | Balances social, economic, and environmental needs | Requires institutional coordination and capacity | [138,139,140] |
| Nexus Approach | Integration of water, energy, food, and ecosystems beyond traditional water-centric planning | Optimizes resource use across sectors, reduces trade-offs and promotes co-benefits , enhances resilience to climate stress and addresses poverty and inequality in vulnerable regions | Requires cross-sectoral coordination, complex governance and institutional barriers and data and capacity gaps in developing regions | [141,142,143] |
| Ecosystem-based Approaches (EbA) | Use of natural ecosystems (e.g., wetlands, forests) to buffer climate impacts | Enhances biodiversity, improves resilience, cost-effective | Data scarcity, underfunding, limited integration into planning | [148,149,150,151] |
| Infrastructure Upgrades | Grey and green infrastructure to improve water retention and urban resilience | Reduces flood risk, manages runoff, provides co-benefits (e.g., cooling) | High initial costs, uneven access in under-resourced regions | [146,150,151] |
| Urban Green Solutions | Green roofs, permeable pavements, urban forests | Mitigates heat islands, improves water infiltration | Lack of baseline data, implementation hurdles | [150] |
| Crop Pattern Modification | Shift to less water-intensive crops | Enhances water-use efficiency in agriculture | May affect food production patterns and farmer acceptance | [110] |
| Managed Aquifer Recharge (MAR) | Recharging groundwater to counteract salinization and over-extraction | Secures freshwater supply, buffers drought | Technical complexity, site-specific hydrogeological requirements | [122,152] |
| Policy and Governance Reform | Cross-sectoral coordination, flexible adaptation frameworks | Enables integrated, long-term planning | Political resistance, institutional inertia | [106,153] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dahal, D.; Bhattarai, N.; Silwal, A.; Shrestha, S.; Shrestha, B.; Poudel, B.; Kalra, A. A Review on Climate Change Impacts on Freshwater Systems and Ecosystem Resilience. Water 2025, 17, 3052. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17213052
Dahal D, Bhattarai N, Silwal A, Shrestha S, Shrestha B, Poudel B, Kalra A. A Review on Climate Change Impacts on Freshwater Systems and Ecosystem Resilience. Water. 2025; 17(21):3052. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17213052
Chicago/Turabian StyleDahal, Dewasis, Nishan Bhattarai, Abinash Silwal, Sujan Shrestha, Binisha Shrestha, Bishal Poudel, and Ajay Kalra. 2025. "A Review on Climate Change Impacts on Freshwater Systems and Ecosystem Resilience" Water 17, no. 21: 3052. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17213052
APA StyleDahal, D., Bhattarai, N., Silwal, A., Shrestha, S., Shrestha, B., Poudel, B., & Kalra, A. (2025). A Review on Climate Change Impacts on Freshwater Systems and Ecosystem Resilience. Water, 17(21), 3052. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17213052









