Groundwater Suitability for Irrigation in the Hennaya Region, Northwest Algeria: A Hydrochemical and GIS-Based Multi-Criteria Assessment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Methodology Framework
2.3. Groundwater Data Acquisition and Analysis
2.3.1. Gibbs Diagram
2.3.2. Piper Diagram
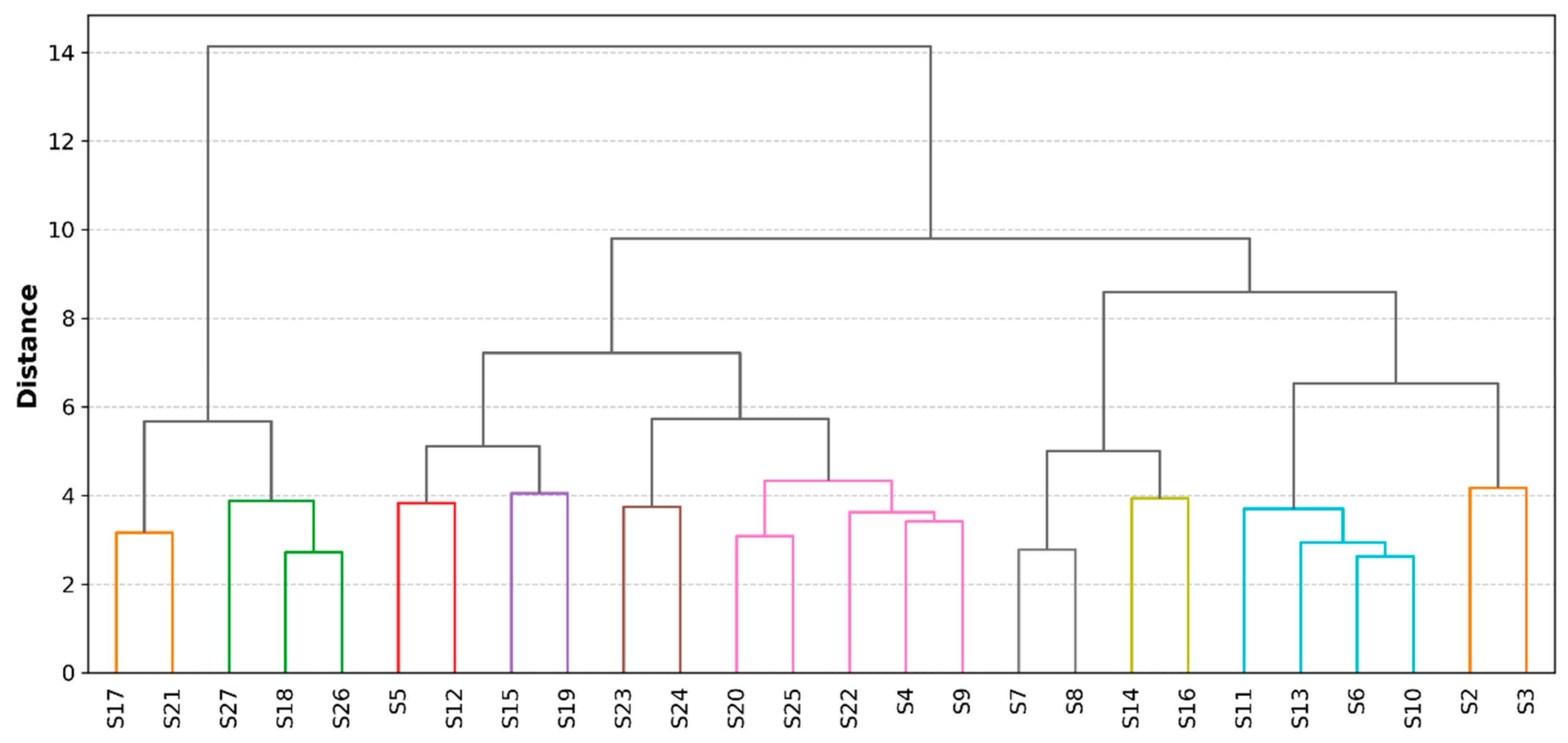
2.4. Hierarchical Clustering Analysis
2.5. Groundwater Quality Evaluation for Irrigation
2.5.1. Groundwater Quality Criteria for Irrigation Purpose
2.5.2. Water Quality Index
- Selecting a parameter and allocating a weight:
- Proportional weight calculation. Equation (9) was applied to calculate the proportional weight (Wi) in this phase.
- Rating scale for quality assignment quality. Equation (10) was used to establish the quality rating scale (qi) for each parameter.
- Sub-index value determination WQI calculation. In this phase, the sub-index values (SIi) for all chemical properties are calculated by multiplying the proportional weight, as given in Equation (11) [72], then summing all the sub-indices from all samples of the study area together to get the final WQI (Equation (4)).
2.5.3. The Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP)
- Defining and elucidating the context of the problem;
- Dividing the decision-making problem into levels, starting at the top with the decision’s objective, moving down to specify criteria and options, and ending with a collection of alternatives;
- Making pairwise comparison matrices and determining the relative weights;
- Assessing the accuracy of the pairwise comparisons can be done by computing the consistency index (CI) and the consistency ratio (CR).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Hydrochemical Analysis Results
3.2. Hydrogeochemical Evaluation
3.3. Origin of Hydrogeochemistry
3.3.1. Gibbs Plot
- (a)
- Position and Distribution of Samples
- (b)
- Dominant Geochemical Processes
- (c)
- Hydrogeological Implications: as outlined below:
- i.
- Aquifer Characteristics: The wells and boreholes studied are at medium depths (between 35 to 110 m), which contributes to the observed water–rock interaction patterns. The intermediate Na+/(Na++ Ca2+) ratios (around 0.5) likely indicate a mixed aquifer, composed of both carbonate formations (calcium source) and silicate formations containing sodium feldspars (sodium source).
- ii.
- Residence Time and Flow Dynamics: The dominance of rock–water interaction processes suggests a moderate to long residence time of water in the aquifer. The perpetual flow characteristics of discharge sources (S26 and S27) indicate active groundwater circulation within the system, which influences the overall hydrochemistry.
- iii.
- Climatic and Drainage Influence: The evaporation signature in the upper part of the diagram, combined with the high drainage characteristics of the aquifer, suggests a complex interplay between climatic conditions and hydrogeological factors in determining the final water chemistry.
- iv.
- Relative Homogeneity: The clustering of samples in a relatively restricted area of the diagram suggests a certain homogeneity in the geochemical processes controlling water chemistry across the studied aquifer, despite variations in well depths.
3.3.2. Piper Plot
3.4. Hierarchical Clustering Analysis Results
3.4.1. Parameter Clustering
3.4.2. Sample Clustering
3.5. Groundwater Quality Evaluation for Irrigation
3.5.1. Irrigation-Specific Indicators
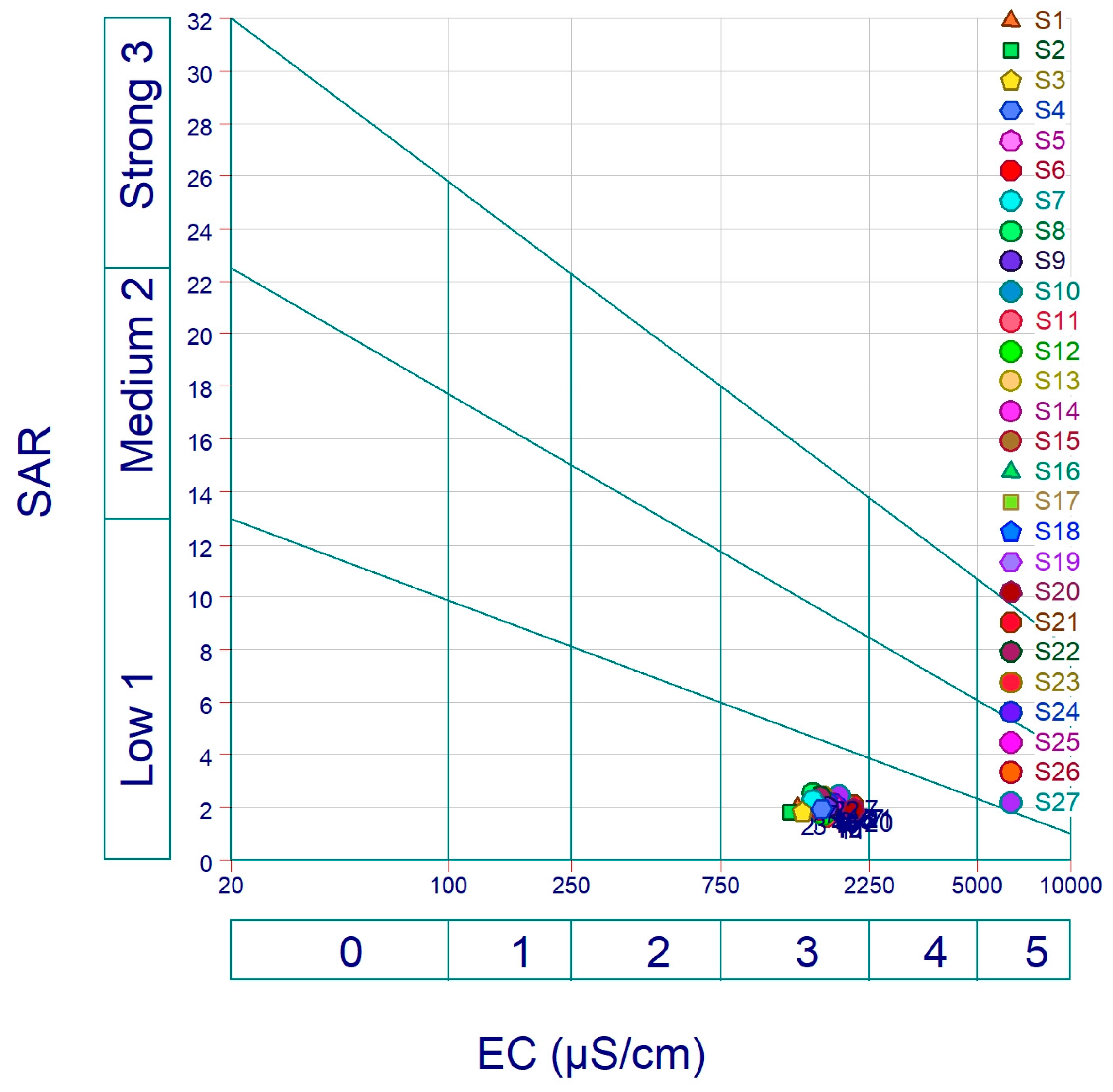
Sodium Adsorption Ratio (SAR)
Residual Sodium Carbonate (RSC)
Sodium Percentage (Na%)
Kelly’s Ratio (KR)
Permeability Index (PI)
Magnesium Hazard (MH)
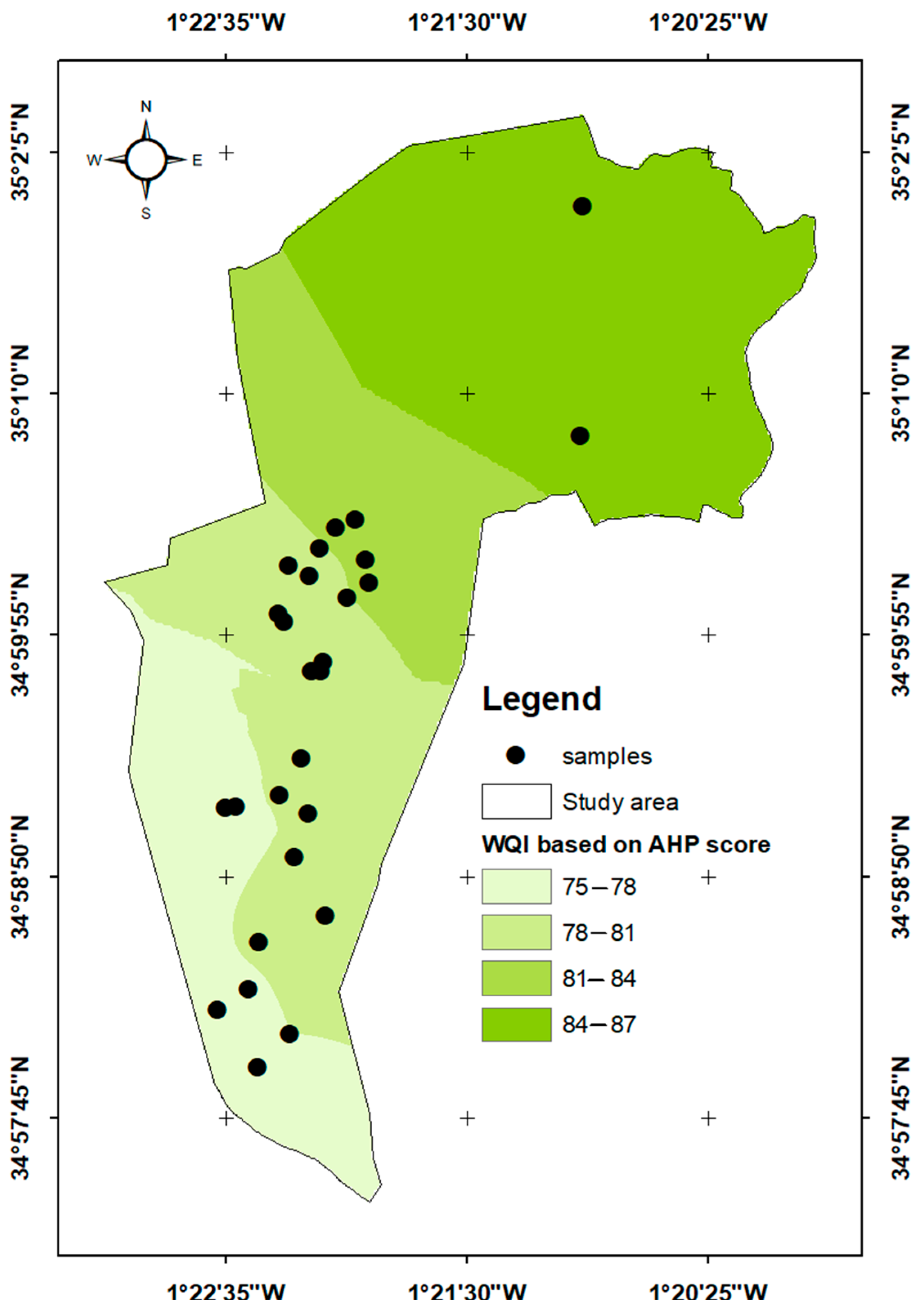
3.5.2. AHP-Based Water Quality Index
- Normalize the pairwise comparison matrix by dividing each element by the sum of its column.
- Calculate the average of each row to derive the weight for each criterion.
- Ensure that the weights sum to 1.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AHP | Analytic Hierarchy Process |
| Ca2+ | Calcium |
| CAT | Complete alkalimetric title |
| CE | Electrical Conductivity |
| CI | Consistency Index |
| Cl− | Chloride |
| CR | Consistency Ratio |
| FAO | Food and Agriculture Organization |
| GIS | Geographic Information System |
| Ha | Hectare |
| HCO3− | Bicarbonate |
| K+ | Potassium |
| MAX | Maximum |
| MCDA | Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis |
| MEAN | Arithmetic Mean |
| Mg2+ | Magnesium |
| MIN | Minimum |
| Na+ | Sodium |
| Na% | Sodium Percentage |
| NO2− | Nitrite |
| NO3− | Nitrate |
| P | Phosphorus |
| pH | Potential of Hydrogen |
| qi | Quality Rating Scale |
| RI | Random Index |
| RSC | Residual Sodium Carbonate |
| SAR | Sodium Adsorption Ratio |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| SO42− | Sulfate |
| TDS | Total Dissolved Solids |
| TH | Total Hardness |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| Wi | Proportional Weight |
| WQI | Water Quality Index |
References
- Lapworth, D.; Boving, T.; Brauns, B.; Dottridge, J.; Hynds, P.; Kebede, S.; Kreamer, D.; Misstear, B.; Mukherjee, A.; Re, V.; et al. Groundwater Quality: Global Challenges, Emerging Threats and Novel Approaches. Hydrogeol. J. 2023, 31, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derdour, A.; Abdo, H.G.; Almohamad, H.; Alodah, A.; Al Dughairi, A.A.; Ghoneim, S.S.M.; Ali, E. Prediction of Groundwater Quality Index Using Classification Techniques in Arid Environments. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dozier, A.Q.; Arabi, M.; Wostoupal, B.C.; Goemans, C.G.; Zhang, Y.; Paustian, K. Declining Agricultural Production in Rapidly Urbanizing Semi-Arid Regions: Policy Tradeoffs and Sustainability Indicators. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 085005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fertas, L.; Alouat, M.; Benmahamed, H. The Emergence of Irrigated Agriculture in Semi-Arid Zones in the Face of Climate Change and Urbanization in Peri-Urban Areas in Setif, Algeria. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malki, M.; Bouchaou, L.; Hirich, A.; Ait Brahim, Y.; Choukr-Allah, R. Impact of Agricultural Practices on Groundwater Quality in Intensive Irrigated Area of Chtouka-Massa, Morocco. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 574, 760–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar, S.; Kumari, B.; Gupta, S.K. Salinization of Coastal Groundwater Resource in the Perspective of Climate Change. In Fate and Transport of Subsurface Pollutants; Gupta, P.K., Bharagava, R.N., Eds.; Microorganisms for Sustainability; Springer: Singapore, 2021; Volume 24, pp. 315–326. ISBN 9789811565632. [Google Scholar]
- Jarraya-Horriche, F.; Benabdallah, S.; Ayadi, M. Groundwater Monitoring for Assessing Artificial Recharge in the Mediterranean Coastal Aquifer of Korba (Northeastern Tunisia). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, N.; Syakir Ishak, M.I.; Bhawani, S.A.; Umar, K. Various Natural and Anthropogenic Factors Responsible for Water Quality Degradation: A Review. Water 2021, 13, 2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkhiri, L.; Mouni, L. Hydrochemical Analysis and Evaluation of Groundwater Quality in El Eulma Area, Algeria. Appl. Water Sci. 2012, 2, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hailu, H.; Haftu, S. Hydrogeochemical Studies of Groundwater in Semi-Arid Areas of Northern Ethiopia Using Geospatial Methods and Multivariate Statistical Analysis Techniques. Appl. Water Sci. 2023, 13, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassri, I.; Harmouzi, H.; Tahri, L.; El Ouali, A.; Khattabi Rifi, S. Hydrogeochemical Assessment and Spatial Analysis of Groundwater Quality Parameters in North West of Morocco. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2024, S1658077X24000705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howladar, M.F.; Al Numanbakth, A.; Faruque, M.O. An Application of Water Quality Index (WQI) and Multivariate Statistics to Evaluate the Water Quality around Maddhapara Granite Mining Industrial Area, Dinajpur, Bangladesh. Environ. Syst. Res. 2018, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidiac, S.; El Najjar, P.; Ouaini, N.; El Rayess, Y.; El Azzi, D. A Comprehensive Review of Water Quality Indices (WQIs): History, Models, Attempts and Perspectives. Rev. Env. Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 22, 349–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, R.K. An Index-Number System for Rating Water Quality. J. Water Pollut. Control. Fed. 1965, 37, 300–306. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, S.E.; Adel Abdulrazzaq, K. Developing Water Quality Index to Assess the Quality of the Drinking Water. CivileJournal 2018, 4, 2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banda, T.; Kumarasamy, M. Development of a Universal Water Quality Index (UWQI) for South African River Catchments. Water 2020, 12, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azlaoui, M.; Zeddouri, A.; Haied, N.; Nezli, I.E.; Foufou, A. Assessment and Mapping of Groundwater Quality for Irrigation and Drinking in a Semi-Arid Area in Algeria. J. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 22, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakrout, A.; Meddah, B.; Ali Rahmani, S.E. Geochemical Assessment of Thermal Water in Bouhanifia Aquifer System: Suitability for Touristic Therapeutic Treatment. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, Z.; Leghrieb, Y.; Kouadri, S.; Al-Ansari, N.; Najm, H.M.; Mashaan, N.S.; Eldirderi, M.M.A.; Khedher, K.M. Hydro-Geochemistry and Groundwater Quality Assessment of Ouargla Basin, South of Algeria. Water 2022, 14, 2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdessamed, D.; Jodar-Abellan, A.; Ghoneim, S.S.M.; Almaliki, A.; Hussein, E.E.; Pardo, M.Á. Groundwater Quality Assessment for Sustainable Human Consumption in Arid Areas Based on GIS and Water Quality Index in the Watershed of Ain Sefra (SW of Algeria). Environ. Earth Sci. 2023, 82, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, N.; Ishak, M.I.S.; Ahmad, M.I.; Umar, K.; Md Yusuff, M.S.; Anees, M.T.; Qadir, A.; Ali Almanasir, Y.K. Modification of the Water Quality Index (WQI) Process for Simple Calculation Using the Multi-Criteria Decision-Making (MCDM) Method: A Review. Water 2021, 13, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L. The Analytic Hierarchy Process: Planning, Priority Setting, Resource Allocation; McGraw-Hill International Book Co.: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1980; ISBN 978-0-07-054371-3. [Google Scholar]
- Karakuş, C.B. Evaluation of Groundwater Quality in Sivas Province (Turkey) Using Water Quality Index and GIS-Based Analytic Hierarchy Process. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2019, 29, 500–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, A.; Tiwari, S.K.; Pandey, H.K.; Chaurasia, A.K.; Singh, S.; Singh, Y.V. Groundwater Quality Assessment Using Water Quality Index (WQI) under GIS Framework. Appl. Water Sci. 2021, 11, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbassi, A.R.; Mir Mohammad Hosseini, F.; Baghvand, A.; Nazariha, M. Development of Water Quality Index (WQI) for Gorganrood River. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2011, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semiromi, F.B.; Hassani, A.H.; Torabian, A.; Karbassi, A.R.; Lotfi, F.H. Evolution of a New Surface Water Quality Index for Karoon Catchment in Iran. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 64, 2483–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Han, L.X.; Zhang, H.; Peng, H. Evaluation and Analysis of Water Quality at the Dahuofang Reservoir Based on the Fuzzy Evaluation and Analytical Hierarchy Process. AMM 2013, 316–317, 748–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozdağ, A. Combining AHP with GIS for Assessment of Irrigation Water Quality in Çumra Irrigation District (Konya), Central Anatolia, Turkey. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 8217–8236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, H.; Avtar, R.; Kumar, P.; Tran, D.; Ty, T.; Behera, H.; Kurasaki, M. Groundwater Quality Assessment Using Fuzzy-AHP in An Giang Province of Vietnam. Geosciences 2019, 9, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, H.; Naik, P.K.; Rishi, M.S. A Comprehensive Water Quality Index Based on Analytical Hierarchy Process. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqbool, S.; Singh, V.; Patley, M.K.; Kinattinkara, S.; Arumugam, T. Evaluation of Groundwater Quality Potential Zones Using AHP and WIOA Models in Shopian District, Jammu and Kashmir, India: A GIS. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2024, 16, 100488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Tripathi, M.P.; Khalkho, D.; Dewangan, R.; Baghel, S.; Kuriqi, A. Groundwater Quality Evaluation for Drinking and Irrigation Using Analytical Hierarchy Process with GIS in Semi Critical Block of Chhattisgarh, India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2024, 83, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, I.; Fan, H.; Aslam, R.W.; Tariq, A.; Quddoos, A.; Sajjad, A.; Soufan, W.; Almutairi, K.F.; Ali, F. Integrated Geospatial and Geostatistical Multi-Criteria Evaluation of Urban Groundwater Quality Using Water Quality Indices. Water 2024, 16, 2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loganathan, S.; Sathiyamoorthy, M. Assessing Groundwater Contamination Risk in Industrial Zone of Ranipet District, Southern India: A Modified DRASTIC and Fuzzy-AHP Approach. Results Eng. 2024, 23, 102772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Lu, G.; Wu, M.; Li, Z.; Deng, Y.; Wu, J.; Hao, Y.; Mo, C.; Li, Q.; Wu, J.; et al. Quantification and Visualization of Groundwater Contamination Prevention Regionalization Based on Analytic Hierarchy Process Method (AHP) in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area, South China. J. Hydrol. 2024, 628, 130521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patoni, K.; Esteller, M.V.; Expósito, J.L.; Fonseca, R.M.G. Spatial Design of Groundwater Quality Monitoring Network Using Multicriteria Analysis Based on Pollution Risk Map. Environ. Earth Sci. 2024, 83, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allaoua, N.; Hafid, H.; Chenchouni, H. Exploring Groundwater Quality in Semi-Arid Areas of Algeria: Impacts on Potable Water Supply and Agricultural Sustainability. J. Arid. Land 2024, 16, 147–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DHWT. Bilan de L’hydraulique Agricole 2024; Hydraulics Directorate of the Wilaya of Tlemcen: Tlemcen, Algeria, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- INSID. Projet D’utilisation Des Eaux Usées Traitées Pour L’irrigation Du Périmètre de Hennaya (Tlemcen), Institut National Des Sols, de l’Irrigation et Du Drainage; Institut National des Sols, de l’Irrigation et du Drainage (INSID): Algiers, Algeria, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jezdan, O. Evaluation of Irrigation Water Quality and Soil Fertility. In Proceedings of the Training Course on Management and Methods of Using Treated Saline Water in Agricultural Irrigation and International Standards for Soil, Water, and Plant Analysis, Algiers, Algeria, 2–6 December 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bemmoussat, A. Impact of Agricultural Activity on the Quality of Groundwater in the Tafna Basin. Master’s Thesis, University of Abou Bekr Belkaid, Tlemcen, Algeria, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hayane, S.M. Contribution à L’étude Géologique et Hydrogéologique Du Bassin Versant de L’oued Sikkak (Région de Tlemcen); University of Oran: Oran, Algeria, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Baba Hamed, K.; Bouanani, A.; Terfous, E.; Bekkouche, A. Modele transitoire de la nappe des alluvions de la plaine d’hennaya (Tlemcen, NW-Algérie) transitory model of the alluvium aquifer of hennaya plaine (Tlemcen, NW-Algeria). LJEE 2005, 4, 7–17. [Google Scholar]
- Bemmoussat, A.; Adjim, M.; Bensaoula, F. Irrigation with Treated Wastewaters and the Protection of Hennaya Groundwater—Tlemcen, Algeria. J. Water Land Dev. 2019, 43, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OPEN LAB. Laboratoire D’analyses et Contrôle de Qualité et Conformité Agriculture et Agroalimentaire, Détergents, Cosmétique et Parfums, Parapharmaceutique, Matériaux Polymères, Analyse Environnementale et d’Eaux—BULLETIN D’ANALYSE; OPEN LAB: Tokyo, Japan, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Shankar, K.; Aravindan, S.; Rajendran, S. Hydrochemical Profile for Assessing the Groundwater Quality of Paravanar River Sub-Basin, Cuddalore District, Tamil Nadu, India. Curr. World Env. 2006, 1, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, R.J. Mechanisms Controlling World Water Chemistry. Science 1970, 170, 1088–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marandi, A.; Shand, P. Groundwater Chemistry and the Gibbs Diagram. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 97, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, A.M. A Graphic Procedure in the Geochemical Interpretation of Water-Analyses. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1944, 25, 914–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmegam, U.; Chidambaram, S.; Prasanna, M.V.; Sasidhar, P.; Manikandan, S.; Johnsonbabu, G.; Dheivanayaki, V.; Paramaguru, P.; Manivannan, R.; Srinivasamoorthy, K.; et al. A Study on the Mixing Proportion in Groundwater Samples by Using Piper Diagram and Phreeqc Model. Chin. J. Geochem. 2011, 30, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, M.; Gao, Z.; Chen, Q.; Wu, G.; Li, F. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Water Quality Assessment of Groundwater in the Yishu River Basin. Acta Geophys. 2020, 68, 877–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.P.; Malik, A.; Mohan, D.; Sinha, S. Multivariate Statistical Techniques for the Evaluation of Spatial and Temporal Variations in Water Quality of Gomti River (India)—A Case Study. Water Res. 2004, 38, 3980–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, S.; Kazama, F. Assessment of Surface Water Quality Using Multivariate Statistical Techniques: A Case Study of the Fuji River Basin, Japan. Environ. Model. Softw. 2007, 22, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.H. Hierarchical Grouping to Optimize an Objective Function. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1963, 58, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeonov, V.; Stratis, J.A.; Samara, C.; Zachariadis, G.; Voutsa, D.; Anthemidis, A.; Sofoniou, M.; Kouimtzis, T. Assessment of the Surface Water Quality in Northern Greece. Water Res. 2003, 37, 4119–4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xia, X.H.; Yang, Z.F.; Wang, F. Assessment of Water Quality in Baiyangdian Lake Using Multivariate Statistical Techniques. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2012, 13, 1213–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, L.A. Diagnosis and Improvement of Saline and Alkali Soils; Agricultural Handbook No. 60; US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1954. [Google Scholar]
- Eaton, F.M. Significance of Carbonates in Irrigation Waters. Soil Sci. 1950, 69, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelo, C.A.J.; Postma, D. Geochemistry, Groundwater and Pollution, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; ISBN 978-0-415-36428-7. [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox, L.V. Classification and Use of Irrigation Water; US Department of Agriculture, Circular 969: Washington, DC, USA, 1955. [Google Scholar]
- Mansouri, Z.; Dinar, H.; Belkendil, A.; Bakelli, O.; Drias, T.; Assadi, A.A.; Khezami, L.; Mouni, L. Integrated Groundwater Quality Assessment for Irrigation in the Ras El-Aioun District: Combining IWQI, GIS, and Machine Learning Approaches. Water 2025, 17, 1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obiefuna, G.; Sheriff, A. Assessment of Shallow Ground Water Quality of Pindiga Gombe Area, Yola Area, NE, Nigeria for Irrigation and Domestic Purposes. Res. J. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 3, 131–141. [Google Scholar]
- Doneen, L.D. Notes on Water Quality in Agriculture; Water Science and Engineering Paper 4001; Department of Water, University of California: Davis, CA, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Imad, H.U.; Akhund, M.A.; Ali, M.; Pathan, A.A.; Ahmed, A. Non-Volumetric Pricing Is a Threat to Water Reserves. Civ. Eng. J. 2019, 5, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, K.; Elango, L. Groundwater Quality and Its Suitability for Domestic and Agricultural Use in Tondiar River Basin, Tamil Nadu, India. Env. Monit Assess 2012, 184, 3887–3899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çadraku, H.S. Groundwater Quality Assessment for Irrigation: Case Study in the Blinaja River Basin, Kosovo. Civ. Eng. J. 2021, 7, 1515–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusatli, O.T.; Camur, M.Z.; Yazicigil, H. Susceptibility Indexing Method for Irrigation Water Management Planning: Applications to K. Menderes River Basin, Turkey. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.; Kim, K. Development of a Water Quality Loading Index Based on Water Quality Modeling. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 1534–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadiq, R.; Haji, S.A.; Cool, G.; Rodriguez, M.J. Using Penalty Functions to Evaluate Aggregation Models for Environmental Indices. J Env. Manag. 2010, 91, 706–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasanthavigar, M.; Srinivasamoorthy, K.; Vijayaragavan, K.; Rajiv Ganthi, R.; Chidambaram, S.; Anandhan, P.; Manivannan, R.; Vasudevan, S. Application of Water Quality Index for Groundwater Quality Assessment: Thirumanimuttar Sub-Basin, Tamilnadu, India. Env. Monit Assess 2010, 171, 595–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, B.; Roy, S.; Bera, A.; Adhikary, P.P.; Bera, B.; Sengupta, D.; Bhunia, G.S.; Shit, P.K. Geospatial Assessment of Groundwater Quality for Drinking through Water Quality Index and Human Health Risk Index in an Upland Area of Chota Nagpur Plateau of West Bengal, India. In Spatial Modeling and Assessment of Environmental Contaminants; Shit, P.K., Adhikary, P.P., Sengupta, D., Eds.; Environmental Challenges and Solutions; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 327–358. ISBN 978-3-030-63421-6. [Google Scholar]
- Abbasi, T. Water Quality Indices; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; ISBN 978-0-444-54304-2. [Google Scholar]
- Bessedik, M.; Abdelbaki, C.; Badr, N.; Tiar, S.M.; Megnounif, A. Application of Water Quality Indices for Assessment of Influent and Effluent Wastewater from Wastewater Treatment Plant of Oran City, Algeria. DWT 2021, 236, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejashvini, A.; Subbarayappa, C.T.M.; Chowdappa, H.D.; Ramamurthy, V. Assessment of Irrigation Water Quality for Groundwater in Semi-Arid Region, Bangalore, Karnataka. Water Sci. 2024, 38, 548–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nageswara Rao, K.; Swarna Latha, P.; Ramesh Kumar, P.V. Groundwater Quality Assessment for Irrigation Use in the Godavari Delta Region of East Coast India Using IRWQI and GIS. Water Supply 2022, 22, 2612–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawo, N.S.; Karuppannan, S. Groundwater Quality Assessment Using Water Quality Index and GIS Technique in Modjo River Basin, Central Ethiopia. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2018, 147, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amalraj, A.; Pius, A. Assessment of Groundwater Quality for Drinking and Agricultural Purposes of a Few Selected Areas in Tamil Nadu South India: A GIS-Based Study. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2018, 4, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.M.; McClelland, N.I.; Deininger, R.A.; Tozer, R.G. A Water Quality Index-Do We Dare. Water Sew. Work. 1970, 117, 339–343. [Google Scholar]
- Uddin, M.G.; Nash, S.; Olbert, A.I. A Review of Water Quality Index Models and Their Use for Assessing Surface Water Quality. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 122, 107218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ŝtambuk-Giljanović, N. Comparison of Dalmatian Water Evaluation Indices. Water Environ. Res. 2003, 75, 388–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhart, C.E.; Schierow, L.; Sonzogni, W.C. An environmental quality index for the great lakes1. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1982, 18, 1025–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernie, N.; Saffran, K.; Cash, K.; Serge, H.; Haseen, K.; Saffran, K.; Williamson, D. Canadian Water Quality Guidelines for the Protection of Aquatic Life CCME WATER QUALITY INDEX 1 0 User’s Manual. Quality 1–5; Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment: Winnipeg, MB, Canada, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Dunn, G.W. Trends in Water Quality Variables at the Alberta/Saskatchewan Boundary; Report Prepared For: The Committee on Water Quality; Alberta Environmental Protection: Red Deer, AB, Canada, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Abrahão, R.; Carvalho, M.; da Silva, W.R., Jr.; Machado, T.; Gadelha, C.; Hernandez, M. Use of Index Analysis to Evaluate the Water Quality of a Stream Receiving Industrial Effluents. Water SA 2007, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumb, A.; Sharma, T.C.; Bibeault, J.-F. A Review of Genesis and Evolution of Water Quality Index (WQI) and Some Future Directions. Water Qual. Expo. Health 2011, 3, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutadian, A.D.; Muttil, N.; Yilmaz, A.G.; Perera, B.J.C. Development of a Water Quality Index for Rivers in West Java Province, Indonesia. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 85, 966–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Kumar, R.; Sharma, M.; Awasthi, A.; Kumar, M. Global Water Quality Indices: Development, Implications, and Limitations. Total Environ. Adv. 2024, 9, 200095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syeed, M.M.M.; Hossain, M.S.; Karim, M.R.; Uddin, M.F.; Hasan, M.; Khan, R.H. Surface Water Quality Profiling Using the Water Quality Index, Pollution Index and Statistical Methods: A Critical Review. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2023, 18, 100247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, R.; Berndtsson, R.; Hosseinzadeh, M.; Adamowski, J.F.; Abyaneh, M.R. A Critical Review on the Application of the National Sanitation Foundation Water Quality Index. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nong, X.; Shao, D.; Zhong, H.; Liang, J. Evaluation of Water Quality in the South-to-North Water Diversion Project of China Using the Water Quality Index (WQI) Method. Water Res. 2020, 178, 115781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.M.; McClelland, N.I.; Deininger, R.A.; O’Connor, M.F. A Water Quality Index—Crashing the Psychological Barrier. In Indicators of Environmental Quality; Thomas, W.A., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1972; pp. 173–182. ISBN 978-1-4684-2858-2. [Google Scholar]
- Nourbakhsh, Z.; Mehrdadi, N.; Moharamnejad, N.; Hassani, A.H.; Yousefi, H. Evaluating the Suitability of Different Parameters for Qualitative Analysis of Groundwater Based on Analytical Hierarchy Process. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 13175–13182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L. What Is the Analytic Hierarchy Process? In Proceedings of the Mathematical Models for Decision Support; Mitra, G., Greenberg, H.J., Lootsma, F.A., Rijkaert, M.J., Zimmermann, H.J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1988; pp. 109–121. [Google Scholar]
- Saaty, T.L. Fundamentals of the Analytic Hierarchy Process. In The Analytic Hierarchy Process in Natural Resource and Environmental Decision Making; Schmoldt, D.L., Kangas, J., Mendoza, G.A., Pesonen, M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 15–35. ISBN 978-94-015-9799-9. [Google Scholar]
- Saaty, T.L. Decision Making with the Analytic Hierarchy Process. IJSSCI 2008, 1, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayers, R.S.; Westcot, D.W. Water Quality for Agriculture, FAO Irrigation and Drainage, Paper 29, Food and Agriculture Organization, Rome; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. The Quality of Water in Irrigation, FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper No. 29; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Water Quality in Agriculture: Risks and Risk Mitigation; FAO: Rome, Italy; IWMI: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2023; ISBN 978-92-5-138072-7. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality: Fourth Edition Incorporating First Addendum, 4th ed.; + 1st add.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; ISBN 978-92-4-154995-0. [Google Scholar]
- Sarath Prasanth, S.V.; Magesh, N.S.; Jitheshlal, K.V.; Chandrasekar, N.; Gangadhar, K. Evaluation of Groundwater Quality and Its Suitability for Drinking and Agricultural Use in the Coastal Stretch of Alappuzha District, Kerala, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2012, 2, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bemmoussat, A.; Adjim, M.; Bensaoula, F. Etude Des Eaux Souterraines de La Plaine d’Henaya (Bassin de La Tafna-NW Algerien). LARHYSS J. 2014, 11, 63–76, P-ISSN 1112-3680/E-ISSN 2521-9782. [Google Scholar]
- JORADP. Executive Decree No. 11–125 of 22 March 2011 on the Quality of Water for Human Consumption in Algeria. JORADP Off. J. Alger. Repub. 2011, 18, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- ANRH. National Agency of Water Resources: Monitoring of Water Quality in the Watershed of the Hammam Boughrara Dam. Internal Report; ANRH: Algiers, Algeria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Nisbet, M.; Verneaux, J. Composantes chimiques des eaux courantes. Discussion et proposition de classes en tant que bases d’interprétation des analyses chimiques. Annls Limnol. 1970, 6, 161–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.P. Calcium and Magnesium in Drinking-water: Public Health Significance. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 2010, 67, 612–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouanani, A. Hydrologie, Transport Solide et Modélisation. Etude de Quelques Sous Bassins de La Tafna (NW Algérie). Ph.D. Thesis, Université Abou Bekr Belkaid Tlemcen, Tlemcen, Algérie, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Hussein, E.E.; Derdour, A.; Zerouali, B.; Almaliki, A.; Wong, Y.J.; Ballesta-de los Santos, M.; Minh Ngoc, P.; Hashim, M.A.; Elbeltagi, A. Groundwater Quality Assessment and Irrigation Water Quality Index Prediction Using Machine Learning Algorithms. Water 2024, 16, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhouchette, H.; Boughariou, E.; Larayedh, O.; Bouri, S. Groundwater Quality Evaluation and Human Health Risks Assessment Using the WQI, NPI and HQnitrate Models: Case of the Sfax Intermediate Aquifer, Sahel Tunisia. Env. Geochem. Health 2022, 44, 2629–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheelbeek, P.F.; Chowdhury, M.A.H.; Haines, A.; Alam, D.S.; Hoque, M.A.; Butler, A.P.; Khan, A.E.; Mojumder, S.K.; Blangiardo, M.A.G.; Elliott, P.; et al. Drinking Water Salinity and Raised Blood Pressure: Evidence from a Cohort Study in Coastal Bangladesh. Env. Health Perspect 2017, 125, 057007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JORADP. Executive Decree No. 14–96 of 2 Jumada El Oula 1435 Corresponding to 4 March 2014 Amending and Supplementing Executive Decree No. 11–125 of 22 March 2011 Concerning the Quality of Drinking Water; JORADP: El-Mouradia, Alger, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bendida, A.; Kendouci, M.A.; Tidjani, A.E.-B. Characterization of Algerian Sahara groundwater for irrigation and water supply: Adrar region study case. J. Water Land Dev. 2021, 49, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPI. Potassium in Ecosystems Biogeochemical Fluxes of Cations in Agro- and Forest- Systems; International Potash Institute: Prague, Czechoslovakia, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Hamlat, A.; Guidoum, A. Assessment of Groundwater Quality in a Semiarid Region of Northwestern Algeria Using Water Quality Index (WQI). Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakouri, A.E. Hydrogeochemical characterization of groundwater of the middle ouerrha, taounate (RIF, MOROCCO). J. Water Sci. Environ. Technol. 2018, 3, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Derdour, A.; Mahamat Ali, M.M.; Chabane Sari, S.M. Evaluation of the Quality of Groundwater for Its Appropriateness for Drinking Purposes in the Watershed of Naâma, SW of Algeria, by Using Water Quality Index (WQI). SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejatijahromi, Z.; Nassery, H.R.; Hosono, T.; Nakhaei, M.; Alijani, F.; Okumura, A. Groundwater Nitrate Contamination in an Area Using Urban Wastewaters for Agricultural Irrigation under Arid Climate Condition, Southeast of Tehran, Iran. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 221, 397–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumont, S.; Camard, J.P.; Lefranc, A. Réutilisation Des Eaux Usées Épurées: Risques Sanitaires et Faisabilité En Île-de-France; ORS Ile-de-France: Saint-Denis, France, 2004; p. 80. [Google Scholar]
- Koussa, M. Étude Comparative Entre Les Méthodes d’interpolation Pour La Cartographie Des Nitrates: Cas d’application Les Eaux Souterraines de Djelfa, Algérie. Agric. For. J. 2018, 2, 18–25. [Google Scholar]
- Bouchard, D.C.; Williams, M.K.; Surampalli, R.Y. Nitrate Contamination of Groundwater: Sources and Potential Health Effects. J. AWWA 1992, 84, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, M.J. 8-Nitrates and Nitrites from Food and Water in Relation to Human Disease. In Nitrates and Nitrites in Food and Water; Hill, M., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Food Science, Technology and Nutrition; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 1996; pp. 163–193. ISBN 978-1-85573-282-7. [Google Scholar]
- Scippo, M.-L.; Badot, P.-M.; Bornert, G.; Desriac, N.; Dubois-Brissonnet, F.; Escobar-Gutiérrez, A.; Kesse-Guyot, E.; Mselli-Lakhal, L.; Lognay, G.C.; Martin, O.C.B.; et al. Évaluation des risques liés à la Consommation de Nitrates et Nitrites; Anses: Cedex, France, 2022; p. 275. [Google Scholar]
- Deliste, C.E.; et Schmidt, J.W. The Effects of Sulphur on Water and Aquatic Life in Canada in “‘Sulphur and Its Inorganic Derivatives in the Canadian Environment’”; National Research Council of Canada, NRC Associate Committee on Scientific Criteria for Environmental Quality: Ottawa, Ontario, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Nouayti, N.; Khattach, D.; Hilali, M. Evaluation de la qualité physico-chimique des eaux souterraines des nappes du Jurassique du haut bassin de Ziz (Haut Atlas central, Maroc) Assessment ofphysico-chemical quality of groundwaterof the Jurassic aquifers inhigh basin of Ziz (Central High Atlas, Morocco). J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2015, 6, 1068–1081. [Google Scholar]
- Houria, B.; Mahdi, K.; Zohra, T.F. Hydrochemical Characterisation of Groundwater Quality: Merdja Plain (Tebessa Town, Algeria). Civ. Eng. J. 2020, 6, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z. Groundwater Is Important for the Geochemical Cycling of Phosphorus in Rapidly Urbanized Areas: A Case Study in the Pearl River Delta. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 114079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meinikmann, K.; Hupfer, M.; Lewandowski, J. Phosphorus in Groundwater Discharge—A Potential Source for Lake Eutrophication. J. Hydrol. 2015, 524, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisbeth, C.S.; Jessen, S.; Bennike, O.; Kidmose, J.; Reitzel, K. Role of Groundwater-Borne Geogenic Phosphorus for the Internal P Release in Shallow Lakes. Water 2019, 11, 1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisbeth, C.S.; Kidmose, J.; Weckström, K.; Reitzel, K.; Odgaard, B.V.; Bennike, O.; Thorling, L.; McGowan, S.; Schomacker, A.; Kristensen, D.L.; et al. Dissolved Inorganic Geogenic Phosphorus Load to a Groundwater-Fed Lake: Implications of Terrestrial Phosphorus Cycling by Groundwater. Water 2019, 11, 2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattray, G. Geochemical Evolution of Groundwater in the Mud Lake Area, Eastern Idaho, USA. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 8251–8269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, S.; Pulido-Bosch, A.; Vallejos, Á.; Molina, L.; Llop, A.; MacDonald, A.M. Impact of Irrigated Agriculture on Groundwater-Recharge Salinity: A Major Sustainability Concern in Semi-Arid Regions. Hydrogeol. J. 2018, 26, 2781–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkarim, B.; Telahigue, F.; Abaab, N.; Boudabra, B.; Agoubi, B. AHP and GIS for Assessment of Groundwater Suitability for Irrigation Purpose in Coastal-Arid Zone: Gabes Region, Southeastern Tunisia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 30, 15422–15437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, E.A.; Derikvand, E.; Eslami, H.; Kharazi, H.G.; Razaz, M. Water Quality Studies Using Fuzzy-Analytic Hierarchical Procedure Method to Identify Their Suitability for Drinking, Industry, and Agriculture—A Case Study. Desalination Water Treat. 2021, 226, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraswat, A.; Nath, T.; Omeka, M.E.; Unigwe, C.O.; Anyanwu, I.E.; Ugar, S.I.; Latare, A.; Raza, M.B.; Behera, B.; Adhikary, P.P.; et al. Irrigation Suitability and Health Risk Assessment of Groundwater Resources in the Firozabad Industrial Area of North-Central India: An Integrated Indexical, Statistical, and Geospatial Approach. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1116220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chy, T.J.; Hasan, K.; Seum, A.B.A.; Mitu, K.N. Integrating Surface and Subsurface Influences to Assess Groundwater Potential in a Rapidly Urbanizing Temperate Region: A Geographic Information System-Analytical Hierarchy Process (GIS-AHP) Case Study of Shelby County, Tennessee. Green Technol. Sustain. 2025, 3, 100204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhav, S.; Ahamad, A.; Kumar, A.; Kushawaha, J.; Singh, P.; Mishra, P.K. Geochemical Assessment of Groundwater Quality for Its Suitability for Drinking and Irrigation Purpose in Rural Areas of Sant Ravidas Nagar (Bhadohi), Uttar Pradesh. Geol. Ecol. Landsc. 2018, 2, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
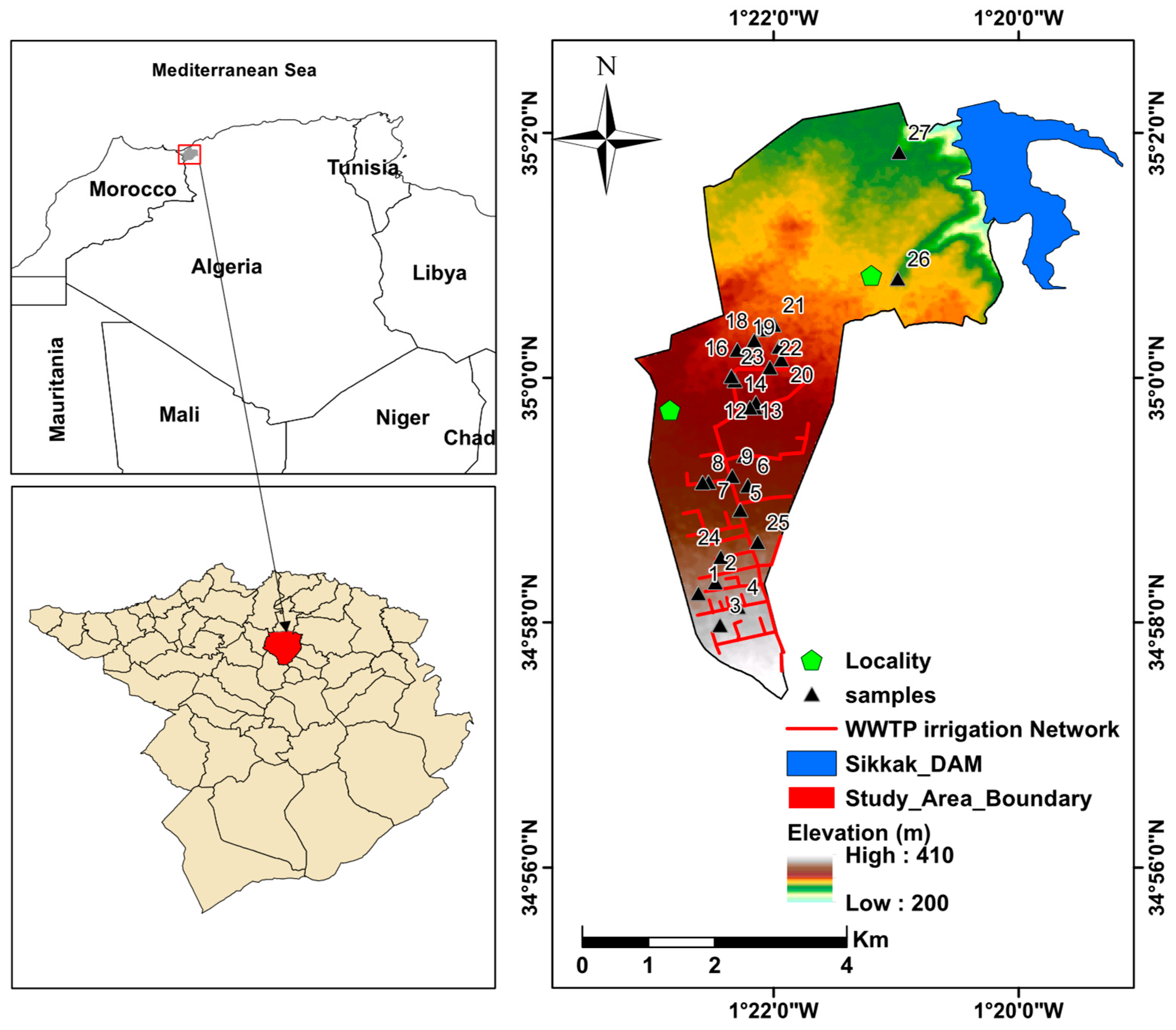
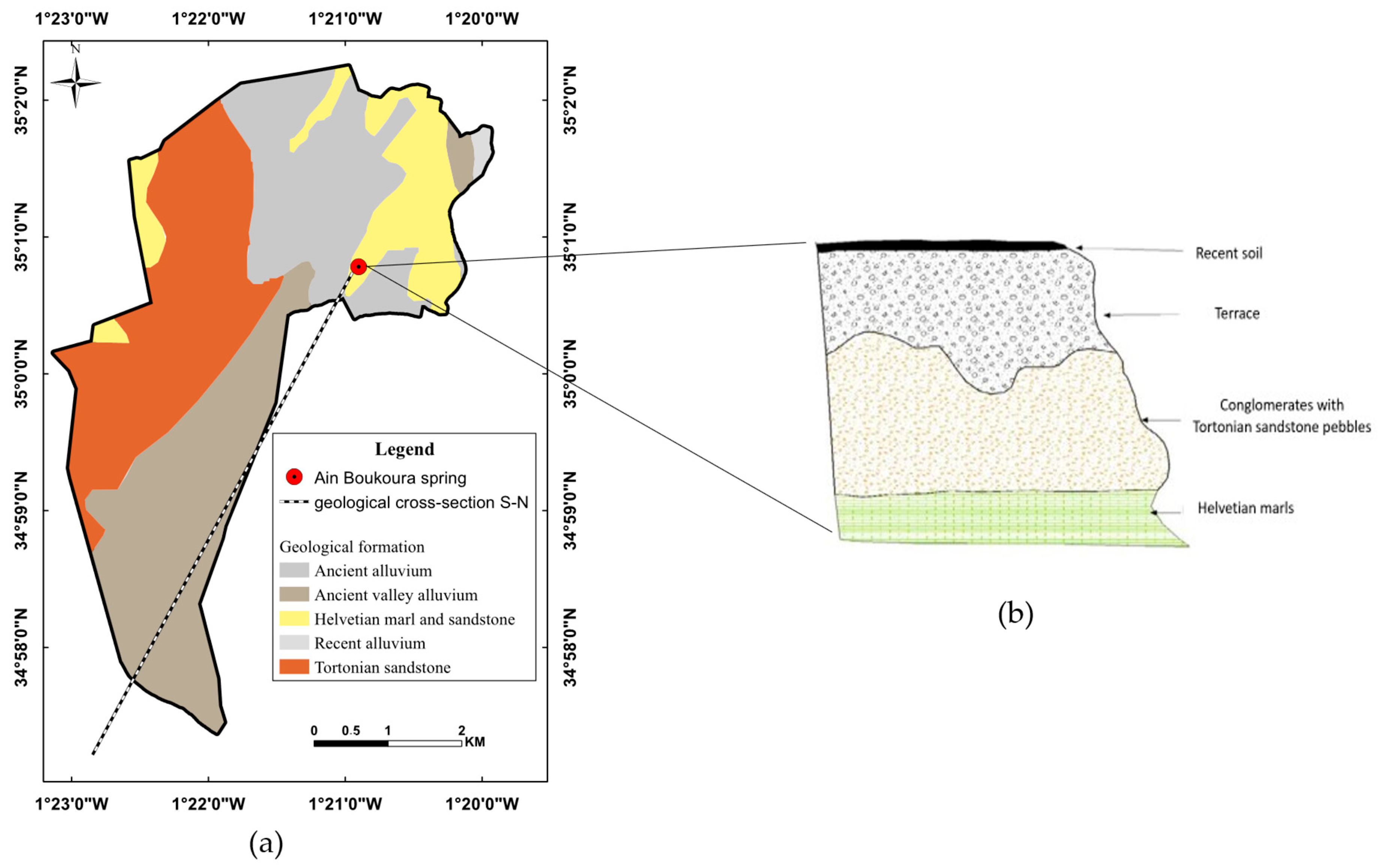
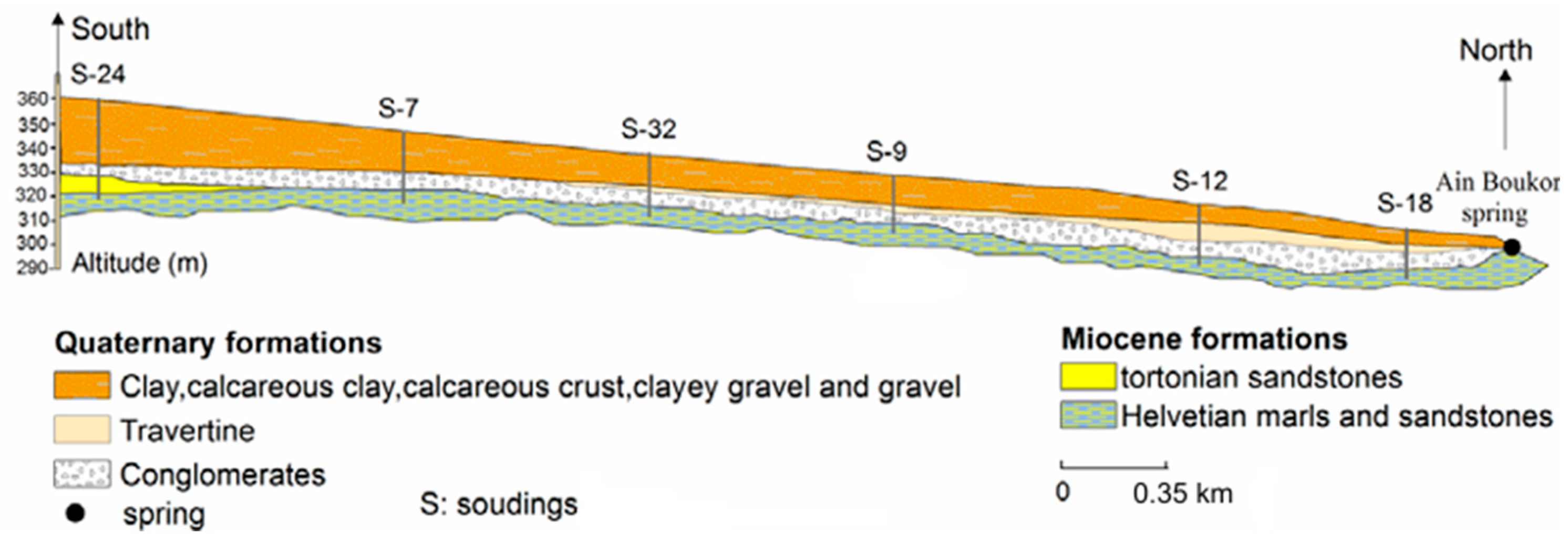
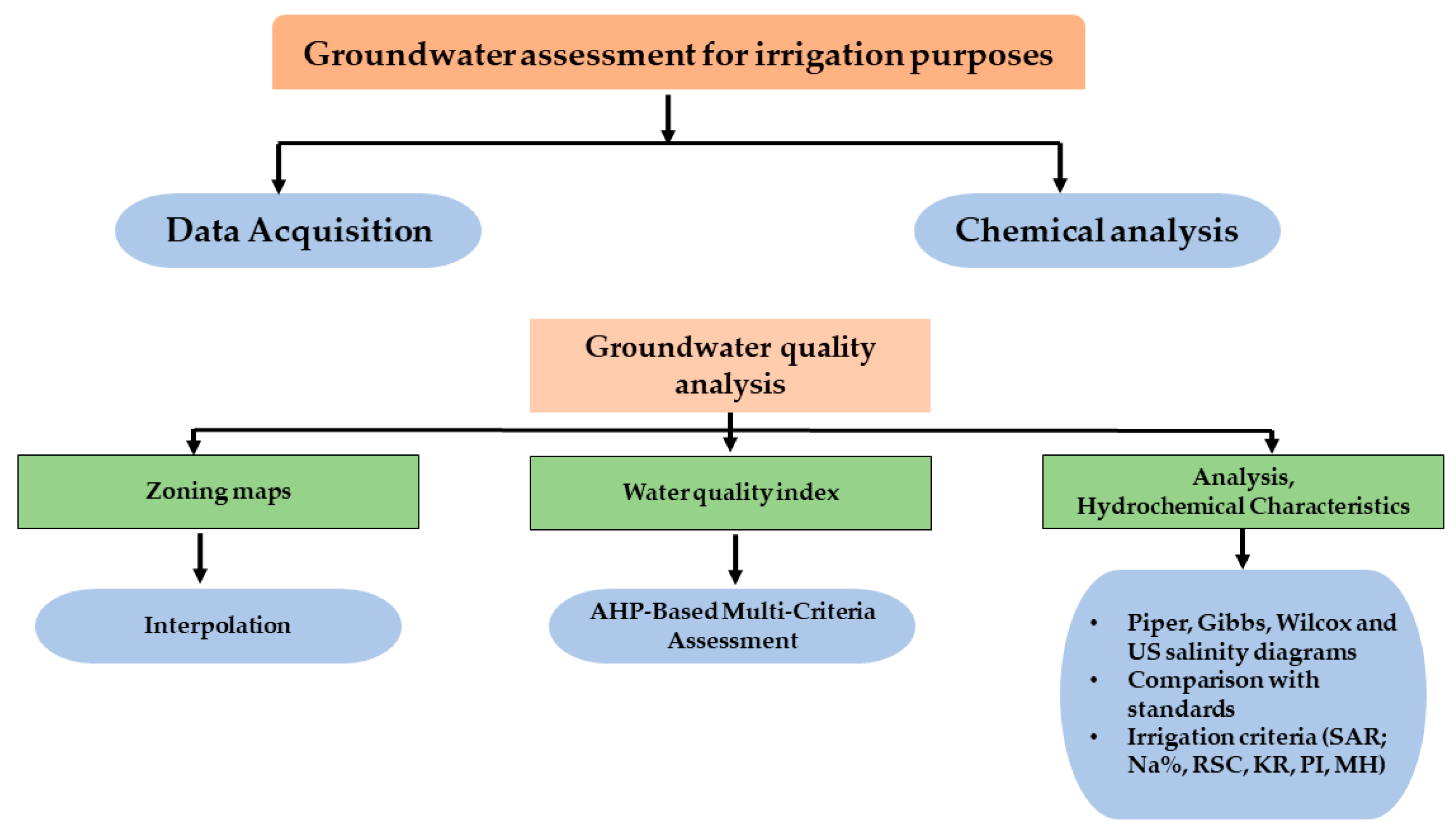





| Parameters | Unit | Analysis Protocol | Desirable Limits (FAO, WHO) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen Potential (pH) | - | ISO 10523:2008 [45] | 6.5–8.5 |
| Electrical Conductivity (EC) | µS/cm | ISO 7888:1985 [45] | 0–2800 |
| Total Dissolved Solids (TDSs) | mg/L | Rodier [45] | 0–2000 |
| Complete Alkalimetric Title (CAT) | mg as CaCO3 | ISO 9963-2/1994 [45] | 0–500 |
| Calcium (Ca2+) | mg/L | NFT 90-016 [45] | 0–200 |
| Magnesium (Mg2+) | mg/L | NFT 90-005 [45] | 0–50 |
| Potassium (K+) | mg/L | NFT 90-020 [45] | 0–12 |
| Sodium (Na+) | mg/L | NFT 90-019 [45] | 0–200 |
| Bicarbonates (HCO3−) | mg/L | Gravimetric Method [45] | 0–125 |
| Sulphates (SO42−) | mg/L | NFT 90-009 [45] | 0–400 |
| Chlorides (Cl−) | mg/L | NFT 90-014 [45] | 0–500 |
| Total Hardness (TH) | mg as CaCO3 | ISO 6059:1984 [45] | 0–200 |
| Nitrates (NO3−) | mg/L | NFT 90-012 [45] | 0–50 |
| Nitrites (NO2−) | mg/L | NFT 90-012 [45] | 0–3 |
| Phosphorus (P) | mg/L | ISO 6878:2004 [45] | 0–5 |
| Significance Values | Value Definitions |
|---|---|
| 1 | Both factors have equal deduction |
| 3 | Factor 1 is more important than factor 2 |
| 5 | Factor 1 is very important than factor 2 |
| 7 | Factor 1 has a stronger proposition than factor 2 |
| 9 | Factor 1 has absolute superiority over factor 2 |
| 2, 4, 6, 8 | Intermediate values |
| Parameter | Unit | Max | Min | Mean | Standard Deviation | Coefficient of Variation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | - | 8.02 | 7.09 | 7.73 | 0.15 | 2% |
| EC | µS/cm | 2010 | 1247 | 1622.07 | 125.04 | 8% |
| TDS | mg/L | 1930 | 990 | 1504.07 | 282.14 | 19% |
| CAT | mg/L as CaCO3 | 369 | 321 | 344.89 | 11.29 | 3% |
| Ca2+ | mg/L | 188.78 | 105.26 | 138.38 | 14.79 | 11% |
| Mg2+ | mg/L | 75.64 | 46.48 | 61.39 | 6.20 | 10% |
| K+ | mg/L | 4.52 | 1.17 | 2.04 | 0.54 | 27% |
| Na+ | mg/L | 141.26 | 95.24 | 116.13 | 9.47 | 8% |
| HCO3− | mg/L | 470 | 390 | 430.78 | 23.81 | 6% |
| SO42− | mg/L | 153.54 | 69.43 | 98.16 | 15.12 | 15% |
| Cl− | mg/L | 349.54 | 154.25 | 213.85 | 28.06 | 13% |
| TH | mg/L as CaCO3 | 550 | 334 | 432.37 | 58.21 | 13% |
| NO3− | mg/L | 145.38 | 46.72 | 85.45 | 20.70 | 24% |
| NO2− | mg/L | 1.45 | 0.41 | 0.77 | 0.22 | 28% |
| P | mg/L | 0.4 | 0.02 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 118% |
| SAR | Na% | RSC | KR | PI | MH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIN | 1.692 | 24.221 | −8.910 | 0.3208 | 99% | 48% |
| MAX | 2.550 | 36.976 | −1.701 | 0.5912 | 62% | 39% |
| MEAN | 2.074 | 29.732 | −4.909 | 0.4278 | 79% | 42% |
| SD | 0.173 | 2.410 | 1.375 | 0.050 | 0.071 | 1.877 |
| Parameter | Range | Suitability |
|---|---|---|
| SAR | <10 | Excellent |
| 10–18 | Good | |
| 18–26 | Doubtful | |
| >26 | Unsuitable | |
| RSC | <1.25 | Safe |
| 1.25–2.5 | Marginal | |
| >2.5 | Unsuitable | |
| Na% | <20 | Excellent |
| 20–40 | Good | |
| 40–60 | Permissible | |
| 60–80 | Doubtful | |
| >80 | Unsuitable | |
| KR | <1 | Suitable |
| 1–2 | Marginal | |
| >2 | Unsuitable | |
| PI | >75 | Suitable |
| 25–75 | Marginal | |
| <25 | Unsuitable | |
| MH | <50 | Suitable |
| 50–60 | Marginal | |
| >60 | Unsuitable |
| pH | EC | TDS | HCO3− | Cl | NO3− | SAR | %Na | RSC | KR | PI | MH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 1.00 | 0.20 | 0.25 | 0.50 | 0.33 | 1.00 | 0.20 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 1.00 |
| EC | 5.00 | 1.00 | 2.00 | 4.00 | 3.00 | 5.00 | 1.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 |
| TDS | 4.00 | 0.50 | 1.00 | 3.00 | 2.00 | 4.00 | 0.50 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 |
| HCO3− | 2.00 | 0.25 | 0.33 | 1.00 | 0.50 | 2.00 | 0.25 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Cl | 3.00 | 0.33 | 0.50 | 2.00 | 1.00 | 2.00 | 0.33 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 |
| NO3− | 1.00 | 0.20 | 0.25 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 1.00 | 0.33 | 0.50 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| SAR | 5.00 | 1.00 | 2.00 | 4.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 |
| %Na | 3.00 | 0.33 | 0.50 | 2.00 | 1.00 | 2.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| RSC | 3.00 | 0.33 | 0.50 | 2.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 |
| KR | 2.00 | 0.25 | 0.33 | 1.00 | 0.50 | 1.00 | 0.50 | 1.00 | 0.50 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| PI | 2.00 | 0.25 | 0.33 | 1.00 | 0.50 | 1.00 | 0.50 | 1.00 | 0.50 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| MH | 1.00 | 0.25 | 0.33 | 1.00 | 0.50 | 1.00 | 0.50 | 1.00 | 0.50 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| n | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RI | 0 | 0 | 0.58 | 0.90 | 1.12 | 1.24 | 1.32 | 1.41 | 1.45 | 1.49 | 1.51 | 1.48 | 1.56 | 1.57 | 1.58 |
| Criterion | pH | EC | TDS | HCO3− | Cl− | NO3− |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | 3.10% | 20.22% | 13.62% | 4.87% | 8.14% | 4.34% |
| Criterion | SAR | %Na | RSC | KR | PI | MH |
| Weight | 14.38% | 7.65% | 8.57% | 5.13% | 5.13% | 4.87% |
| S. No. | WQI Value | Water Quality Classification | S. No. | WQI Value | Water Quality Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 81.463 | Good | 15 | 74.322 | Good |
| 2 | 75.701 | Good | 16 | 79.084 | Good |
| 3 | 69.628 | Good | 17 | 84.243 | Good |
| 4 | 82.215 | Good | 18 | 81.025 | Good |
| 5 | 79.883 | Good | 19 | 80.665 | Good |
| 6 | 76.342 | Good | 20 | 85.044 | Good |
| 7 | 69.259 | Good | 21 | 86.479 | Good |
| 8 | 80.509 | Good | 22 | 82.261 | Good |
| 9 | 83.469 | Good | 23 | 76.876 | Good |
| 10 | 80.557 | Good | 24 | 79.515 | Good |
| 11 | 79.118 | Good | 25 | 82.952 | Good |
| 12 | 79.353 | Good | 26 | 81.910 | Good |
| 13 | 79.385 | Good | 27 | 88.713 | Good |
| 14 | 82.101 | Good |
| GWQI Range | Water Quality Class | Suitability for Irrigation |
|---|---|---|
| <50 | Excellent | Highly suitable; no restrictions |
| 50–100 | Good | Suitable; minor precautions |
| 100–200 | Poor | Marginally suitable; requires management (e.g., leaching, crop selection) |
| >300 | Unsuitable for drinking | Highly unsuitable |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Badraoui, A.; Abdelbaki, C.; Bessedik, M.; Tiar, S.M.; Berrezel, Y.A.; Ziane, M.; Slimani, A.; Souafi, A.; Boudadi, N.; Tischbein, B.; et al. Groundwater Suitability for Irrigation in the Hennaya Region, Northwest Algeria: A Hydrochemical and GIS-Based Multi-Criteria Assessment. Water 2025, 17, 3025. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17203025
Badraoui A, Abdelbaki C, Bessedik M, Tiar SM, Berrezel YA, Ziane M, Slimani A, Souafi A, Boudadi N, Tischbein B, et al. Groundwater Suitability for Irrigation in the Hennaya Region, Northwest Algeria: A Hydrochemical and GIS-Based Multi-Criteria Assessment. Water. 2025; 17(20):3025. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17203025
Chicago/Turabian StyleBadraoui, Abderrahim, Chérifa Abdelbaki, Madani Bessedik, Sidi Mohamed Tiar, Yacine Abdelbaset Berrezel, Mahdi Ziane, Amaria Slimani, Ahmed Souafi, Nourredine Boudadi, Bernhard Tischbein, and et al. 2025. "Groundwater Suitability for Irrigation in the Hennaya Region, Northwest Algeria: A Hydrochemical and GIS-Based Multi-Criteria Assessment" Water 17, no. 20: 3025. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17203025
APA StyleBadraoui, A., Abdelbaki, C., Bessedik, M., Tiar, S. M., Berrezel, Y. A., Ziane, M., Slimani, A., Souafi, A., Boudadi, N., Tischbein, B., & Kumar, N. (2025). Groundwater Suitability for Irrigation in the Hennaya Region, Northwest Algeria: A Hydrochemical and GIS-Based Multi-Criteria Assessment. Water, 17(20), 3025. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17203025








