Human Impacts on Heavy Metals in Lake Sediments of Northern China: History, Sources, and Trend Prediction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sampling
2.2. Dating
2.3. Heavy Metal Analysis
2.4. Geoaccumulation Index Method
2.5. Potential Ecological Hazard Index Method
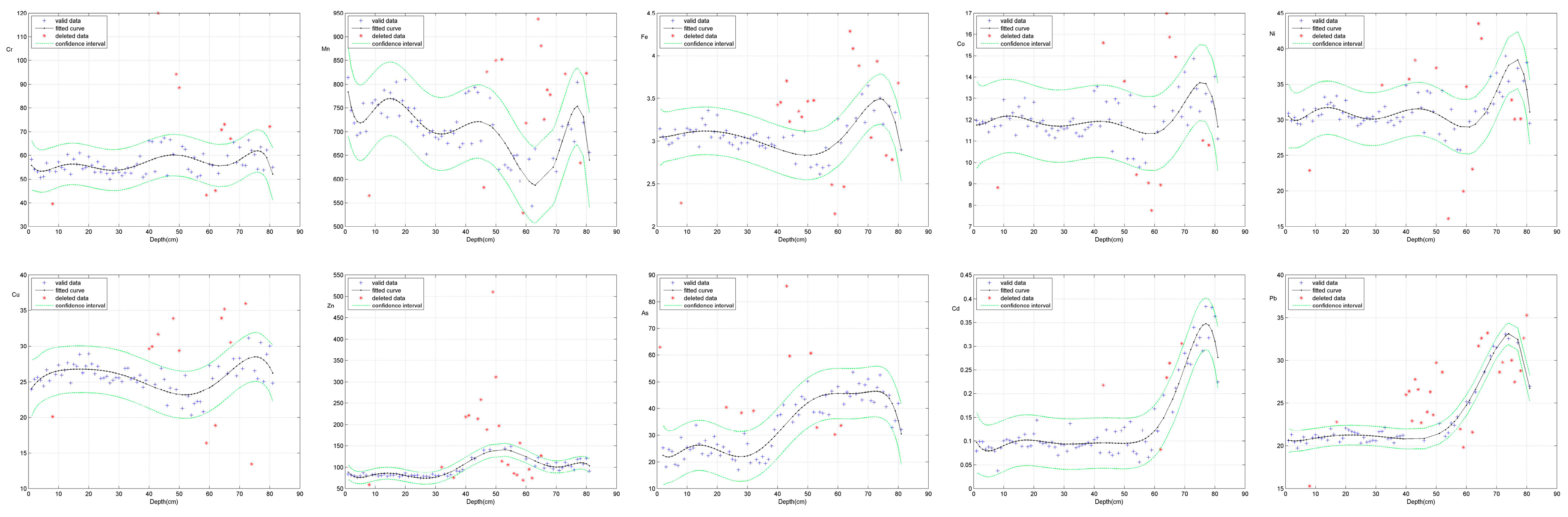
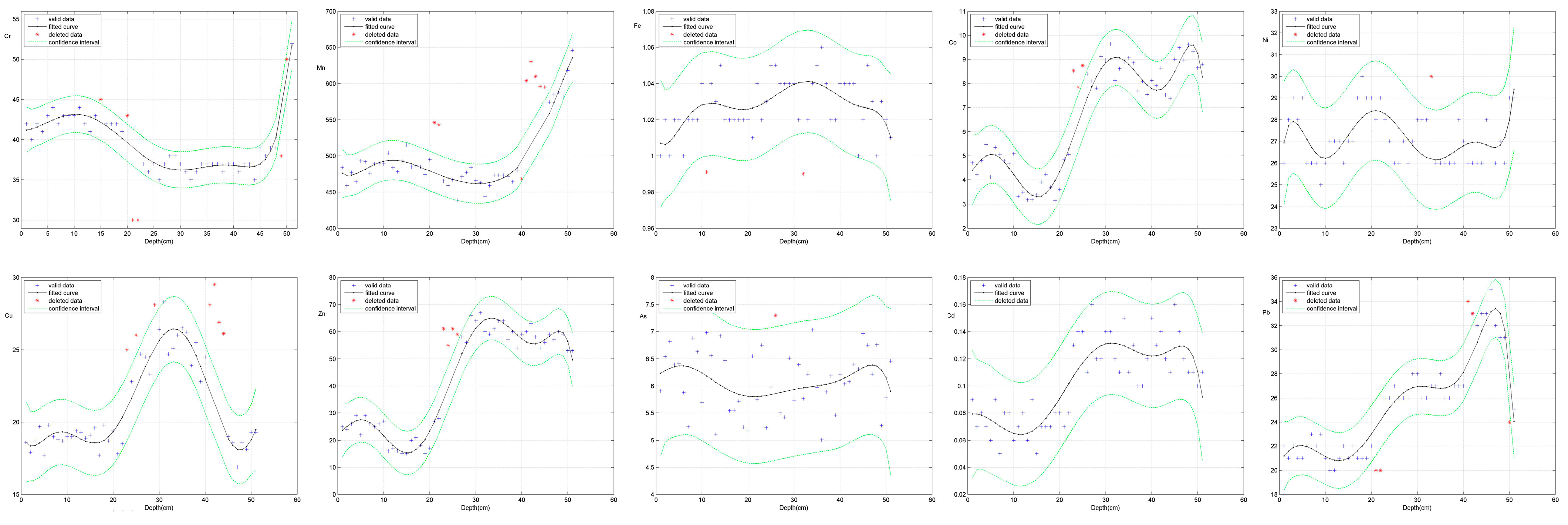
2.6. Evolution Prediction Method
2.7. Statistic Analysis
3. Results
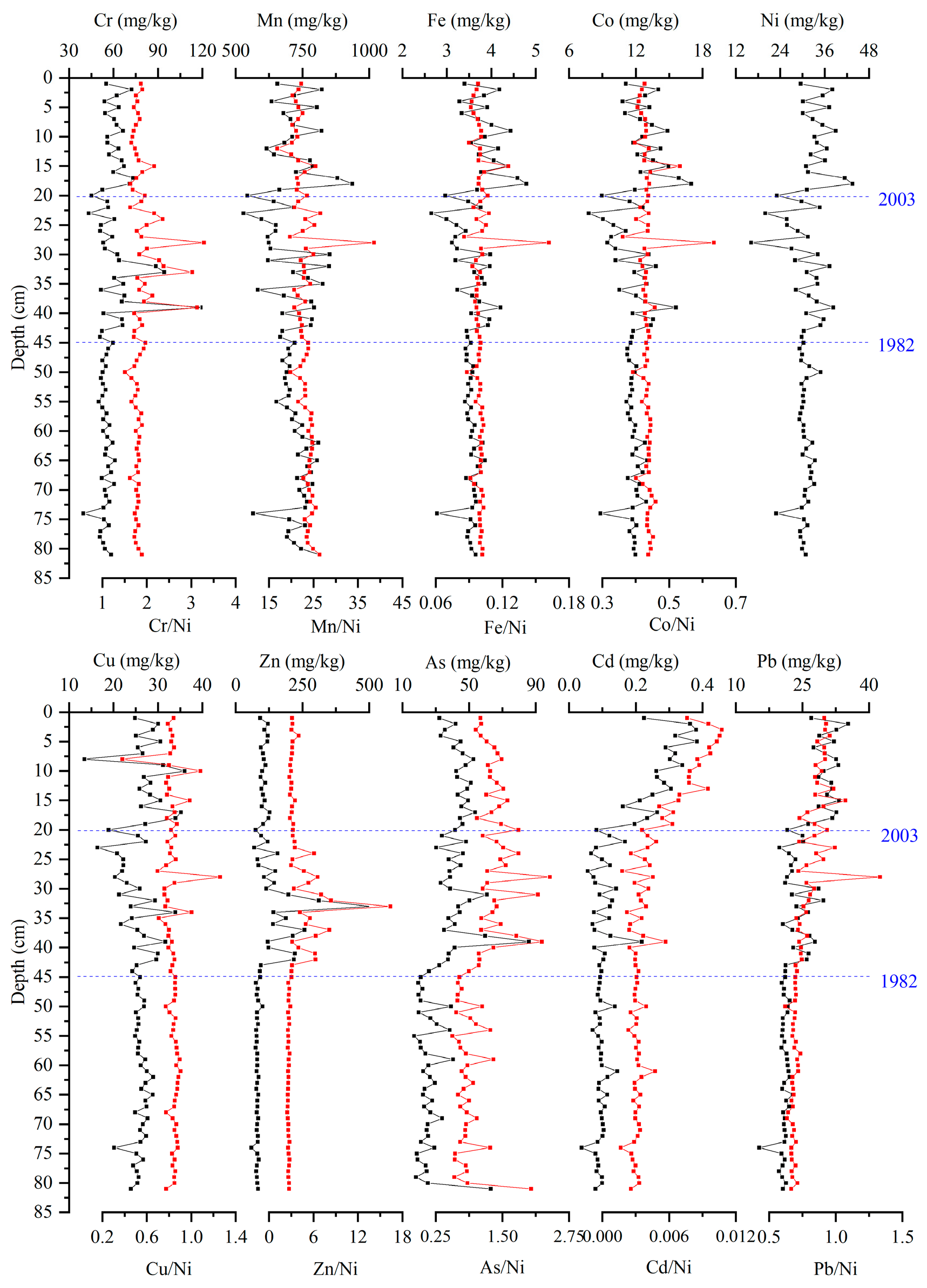
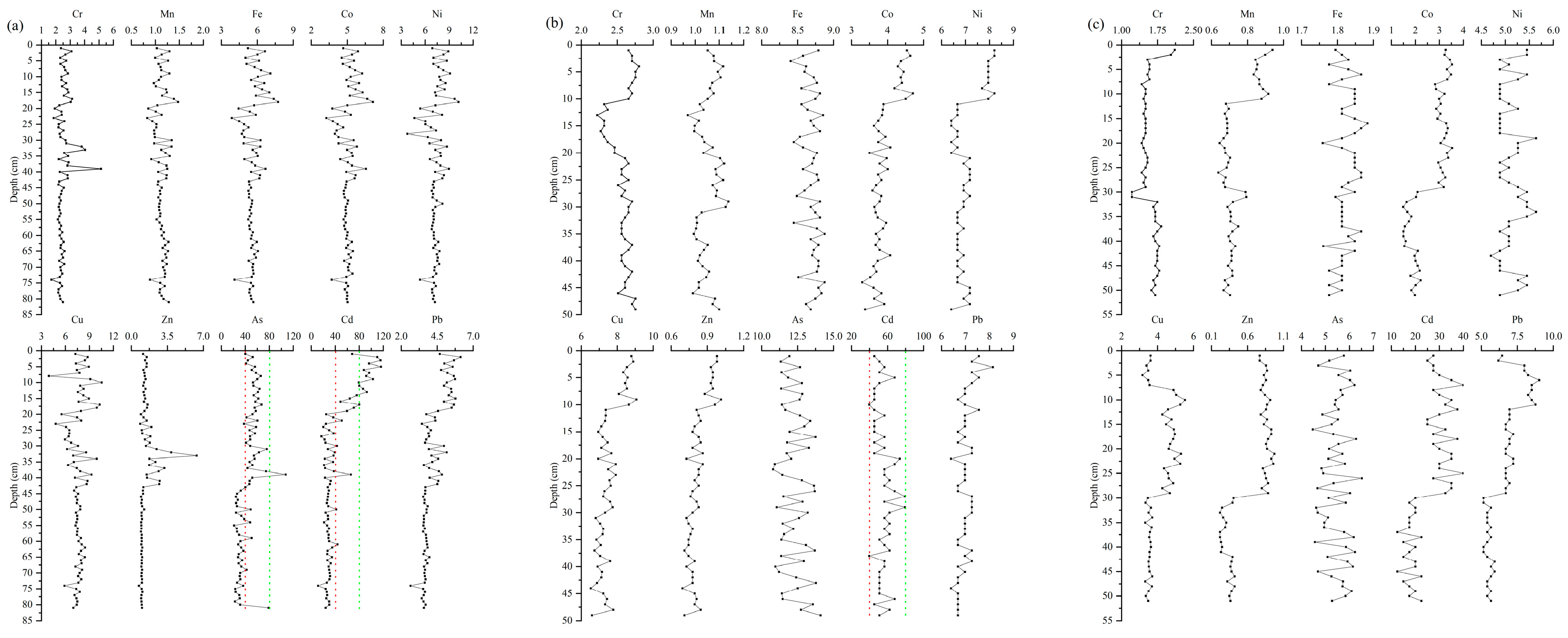
3.1. Vertical Distribution Characteristics of Heavy Metals in Sediments of CG
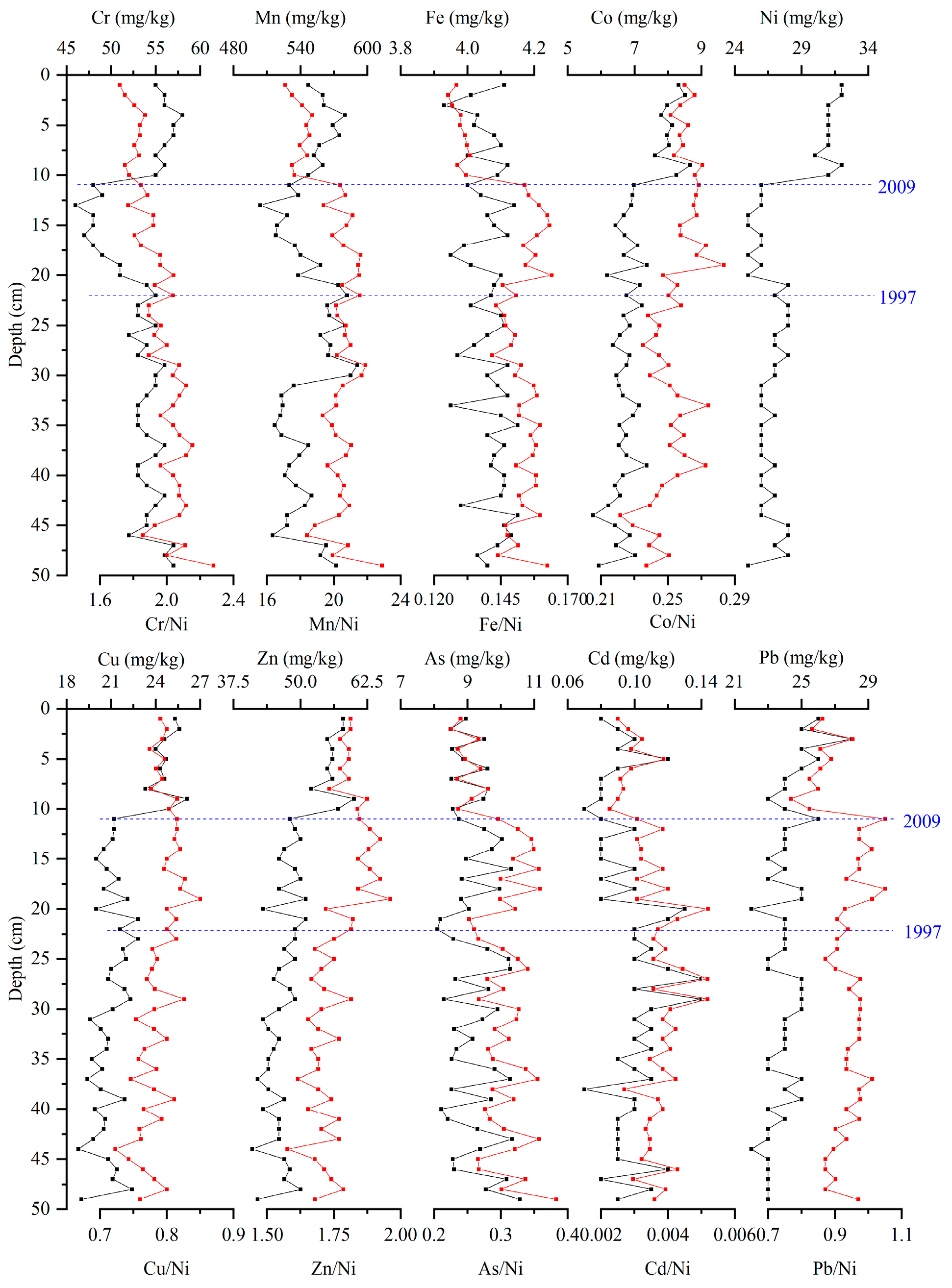
3.2. Vertical Distribution Characteristics of Heavy Metals in Sediments of WLS
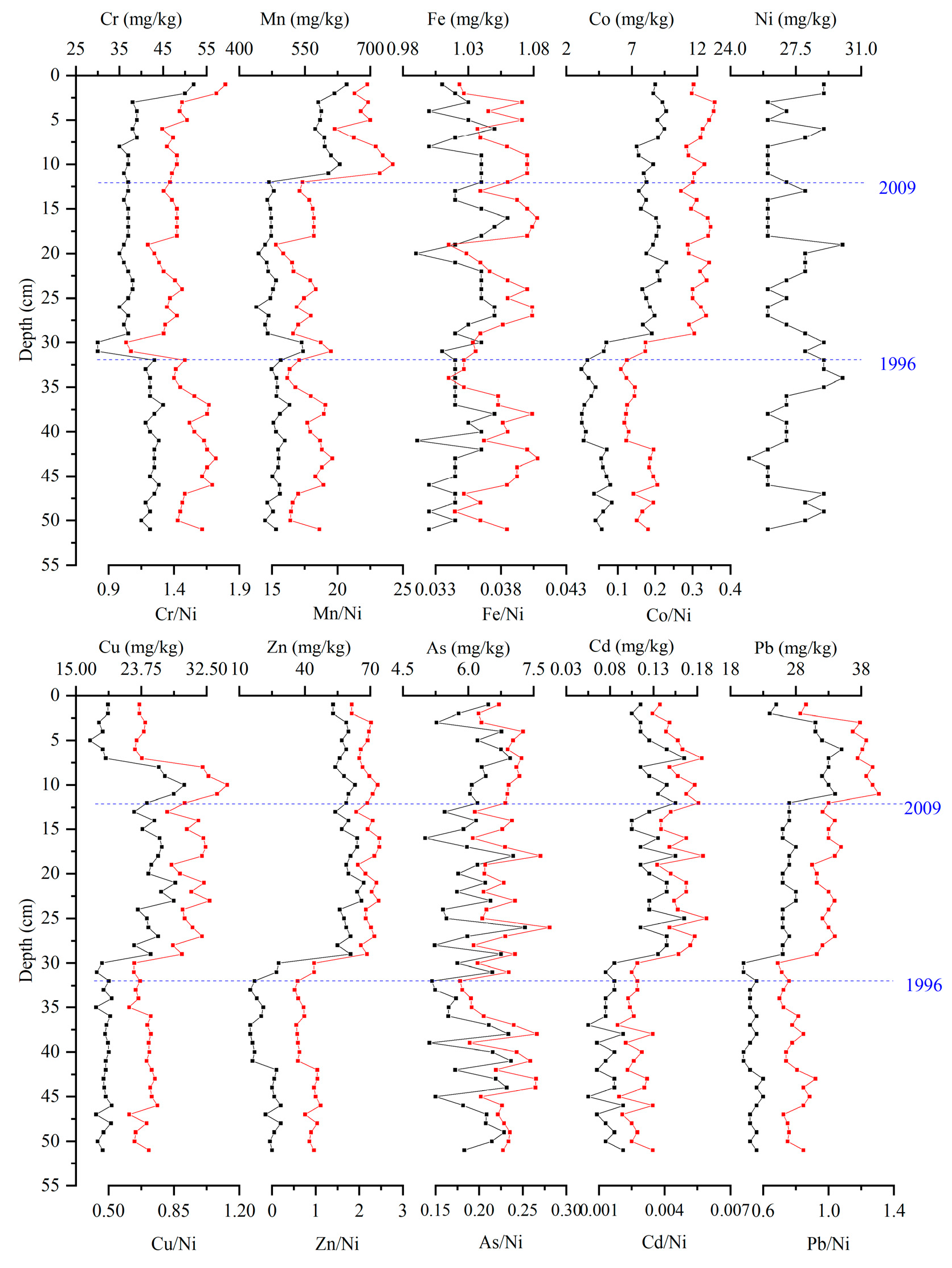
3.3. Vertical Distribution Characteristics of Heavy Metals in Sediments of BST
3.4. Pollution History of Heavy Metals
4. Discussion
4.1. Heavy Metal Evolutionary History of Lake Sediments
4.2. Pollution Status of Heavy Metals
4.3. Potential Ecological Hazard Assessment of Lake Sediments
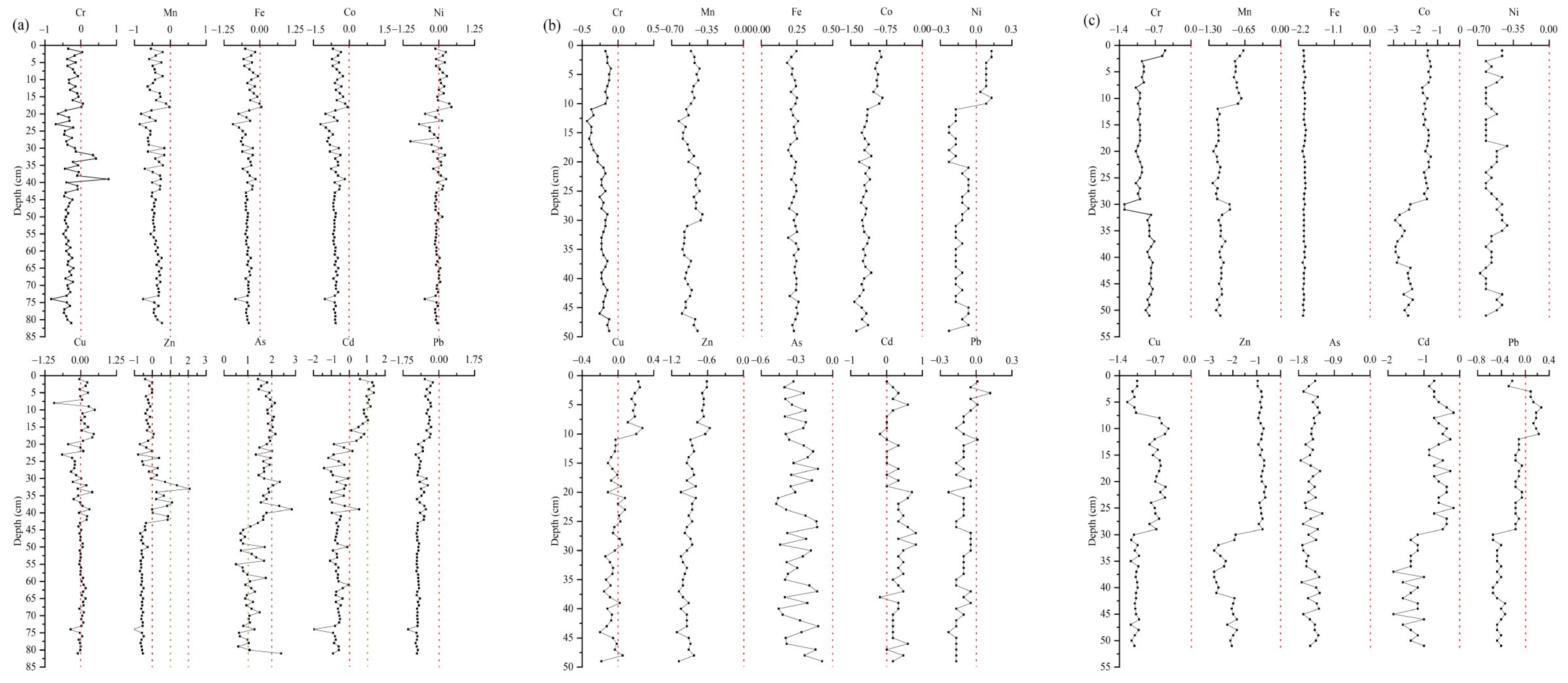
4.4. Source Apportionment of Heavy Metals in Lake Sediments
4.4.1. Correlation Analysis of Heavy Metal
4.4.2. Factor Analysis of Heavy Metals
4.5. Comparison of the History of Heavy Metal Pollution
4.6. Evolution Prediction of Heavy Metal Elements in Lake Sediments
4.7. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, D.P.; Yu, R.D.; Chen, J.; Leng, X.; Zhao, D.H.; Jia, H.T.; An, S.Q. Ecological risk of heavy metals in lake sediments of China: A national-scale integrated analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 334, 130206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, D.P.; Human, L.R.D.; Adams, J.B. Wetland plants as indicators of heavy metal contamination. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 92, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.Q.; Gu, J.X.; Gao, Z.J.; Lyu, J.; Sun, F.H.; Wu, C.S.; Liu, X.; Hong, W.L.; Lin, Y.S.; Wang, H.; et al. Distribution, Potential Sources, and Risks of Heavy Metal Contamination in the Huaihe River: Insights from Water and Sediment Analysis. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.Y.; Yang, Y.; Zang, S.Y.; Ren, X.X.; Xue, Z.C.; Wang, Y.; Sun, L.; Wu, C.W.; Li, J.D.; Liu, Y.X.; et al. Spatial and Temporal Variations in Heavy Metals in Lake and Reservoir Sediments in China: A Pollution Status and Risk Assessment. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Pan, X.M.; Wang, Q.Y.; Ge, G.; Huang, Y. Toxic effects of heavy metals on the freshwater benthic organisms in sediments and research on quality guidelines in Poyang Lake, China. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 3779–3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.X.; Li, M.; Zhao, C.D.; Yang, K.; Li, K.; Peng, M.; Yang, Z.F.; Liu, F.; Liu, Y.G.; Bai, R.J.; et al. Concentrations of toxic metals and ecological risk assessment for sediments of major freshwater lakes in China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2015, 157, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.X.; Lu, Y.; Li, H.P.; Tu, Y.; Liu, B.Y.; Yang, Z.G. Assessment of heavy metal contamination, distribution and source identification in the sediments from the Zijiang River, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, R.F.; Yue, F.J.; Zhu, Z.Z.; Liu, X.L.; Zhang, L.Y. Temporal and spatial variation of heavy metals in coastal wetlands around the Bohai Sea and analysis of their sources. China Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 6025–6038. [Google Scholar]
- Varol, M. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediments of the Tigris River (Turkey) using pollution indices and multivariate statistical techniques. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 195, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, X.; Gui, S.F.; Huang, H.; Zhang, H.J.; Wang, C.Y.; Guo, W. Ecological risk assessment and source identification for heavy metals in surface sediment from the Liaohe River protected area, China. Chemosphere 2017, 175, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.F.; Wu, Y.; Han, J.G.; Li, P.P. The current status of heavy metal in lake sediments from China: Pollution and ecological risk assessment. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 5454–5466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.Y.; Yu, M.C.; Yuan, Q.K.; Meng, Y.; Qie, Y.K.; Shang, Z.M.; Luan, F.B.; Zhang, D.L. Spatial distribution, pollution assessment, and source identification of heavy metals in the Yellow River. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 436, 129309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Qin, B.Q.; Zhu, G.W.; Song, C.Q.; Deng, J.M.; Xue, B.; Gong, Z.J.; Wang, X.L.; Wu, J.L.; Shi, K.; et al. Importance and main ecological and environmental problems of lakes in China. Sci. Bull. 2022, 67, 3503–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.H.; Li, L.; Wu, X.Q. Analysis of the Sources of Soil Heavy Metals in Geological High-Background Areas at a Large Spatial Scale. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sharkawy, M.; Alotaibi, M.O.; Li, J.; Du, D.; Mahmoud, E. Heavy Metal Pollution in Coastal Environments: Ecological Implications and Management Strategies: A Review. Sustainability 2025, 17, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zang, S.Y. Relationship between polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and particle size in dated core sediments in Lake Lianhuan, Northeast China. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 461, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, Q.F.; Li, G.; Liu, Z.Y. Distribution, source and pollution level of heavy metals in river sediments from South China. Catena 2018, 170, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.J.; Sun, L.; Zang, S.Y. Pollution history, source and transport path for PAHs in dated sediment cores from four lakes in Northern China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 374, 133994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Liu, E.F.; Zhang, E.L.; Li, K.; Shen, J. Spatial distribution, contamination and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Erhai Lake, a large eutrophic plateau lake in southwest China. Catena 2016, 145, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Wang, X.D.; Gao, Y.L.; Yue, F.J.; Chen, W. Geochemical Indicators on the Central Tibetan Plateau Lake Sediments: Historical Climate Change and Regional Sustainability. Sustainability 2024, 16, 8186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Singh, S.P.; Sahu, S.; Bhattacharyya, R.; Maurya, A.S.; Kumar, N.; Rout, R.K.; Tripathy, G.R. Isotopic evidence of autochthonous organic matter acting as a major sink of anthropogenic heavy metals in modern lacustrine sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 349, 123964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogola, J.O.; Olale, K.; Mogwasi, R.; Mainya, O. Organochlorine pesticide residues in water and sediments in river Kibos-Nyamasaria in Kisumu County: An inlet river of Lake Victoria, Kenya. Sci. Afr. 2024, 23, e02094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.Z.; Luo, L.C.; Zhang, L.W.; Li, D.L.; Li, H.Y.; Xu, T.B.; Xu, J.; Zhang, H.C. The Occurrence of Microplastics Pollution in the Surface Water and Sediment of Lake Chenghai in Southwestern China. Water 2024, 16, 2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.F.; Sun, D.Y.; Sun, L.; Zhang, N.N.; Zhang, J.W.; Zang, S.Y. Sediment record of heavy metals over the last 150 years in Northeast China: Implications for regional anthropogenic activities. Ecotoxicology 2021, 30, 1354–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, L.S.; Ayoko, G.A.; Egodawatta, P.; Goonetilleke, A. Adsorption-desorption behavior of heavy metals in aquatic environments: Influence of sediment, water and metal ionic properties. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Sun, X.; Hu, Y.; Chen, G.; Xu, J.L. The influence of anthropogenic activities on heavy metal pollution of estuary sediment from the coastal East China Sea in the past nearly 50 years. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 181, 113872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, G.J. Progresses on 137Cs and 210Pbex Dating of Lake Sediments. Adv. Earth Sci. 1995, 10, 188–192, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Arnaud, F.; Magand, O.; Chaoron, E.; Bertrand, S.; Boës, X.; Charlet, F.; Mélières, M.-A. Radionuclide dating (210Pb, 137Cs, 241Am) of Recent Lake Sediments in a Highly Active Geodynamic setting (Lakes Puyehue and Icalma-Chilean Lake District). Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 366, 837–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walling, D.E.; He, Q. Use of fallout 137Cs in investigations of overbank sediment deposition on river floodplains. Catena 1997, 29, 263–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, Y.Y.; Huang, H.; Wang, X.D. Sedimentary Heavy Metal Pollution in the Huaihe River. Res. Environ. Sci. 2003, 16, 26–28. [Google Scholar]
- Sojka, M.; Jaskula, J. Heavy Metals in River Sediments: Contamination, Toxicity, and Source Identification—A Case Study from Poland. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2022, 19, 10502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, J. The Normalization problem of heavy metals in Sediments: A Case Study of Al. Donghai Mar. Sci. 1998, 16, 48–55, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.P.; Xu, C.X.; An, Z.Y.; Wang, S.M. Analysis and evaluation of the source of heavy metals in water of the River Changjiang. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 173, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | As | Cd | Pb | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CG | 46.7 | 636 | 2.74 | 11.9 | 21.4 | 17.1 | 80.4 | 8.0 | 0.099 | 28.8 |
| WLS | 41.4 | 520 | 2.31 | 10.3 | 19.5 | 14.4 | 59.1 | 7.5 | 0.053 | 17.2 |
| BST | 49.3 | 688 | 2.78 | 15.9 | 26.6 | 26.7 | 68.8 | 11.2 | 0.12 | 19.4 |
| Practically Unpollution | Slight Pollution | Slight to Moderate Pollution | Moderate Pollution | Moderate to High Pollution | High Pollution | Extreme Pollution | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pollution level | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| Igeo | ≤0 | 0–1 | 1–2 | 2–3 | 3–4 | 4–5 | >5 |
| Low | Moderate | Moderate to High | High | Extremely High | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eir | <40 | 40–80 | 80–160 | 80–320 | ≥320 |
| Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | As | Cd | Pb | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | 1 | 0.517 ** | 0.598 ** | 0.633 ** | 0.585 ** | 0.426 ** | 0.611 ** | 0.606 ** | 0.324 ** | 0.497 ** |
| Mn | 1 | 0.822 ** | 0.829 ** | 0.747 ** | 0.693 ** | 0.141 | 0.137 | 0.244 * | 0.389 ** | |
| Fe | 1 | 0.985 ** | 0.886 ** | 0.745 ** | 0.165 | 0.368 ** | 0.547 ** | 0.712 ** | ||
| Co | 1 | 0.898 ** | 0.757 ** | 0.167 | 0.360 ** | 0.510 ** | 0.660 ** | |||
| Ni | 1 | 0.715 ** | 0.220 * | 0.354 ** | 0.561 ** | 0.662 ** | ||||
| Cu | 1 | 0.065 | 0.144 | 0.372 ** | 0.465 ** | |||||
| Zn | 1 | 0.365 ** | 0.022 | 0.228 * | ||||||
| As | 1 | 0.443 ** | 0.596 ** | |||||||
| Cd | 1 | 0.887 ** | ||||||||
| Pb | 1 |
| Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | As | Cd | Pb | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | 1 | 0.617 ** | 0.041 | 0.271 | 0.551 ** | 0.359 * | 0.235 | −0.091 | 0.107 | 0.118 |
| Mn | 1 | −0.233 | 0.255 | 0.449 ** | 0.460 ** | 0.375 ** | 0.003 | 0.257 | 0.304 * | |
| Fe | 1 | −0.216 | −0.082 | −0.196 | −0.187 | −0.112 | 0.026 | −0.461 ** | ||
| Co | 1 | 0.869 ** | 0.947 ** | 0.929 ** | −0.247 | −0.274 | 0.504 ** | |||
| Ni | 1 | 0.932 ** | 0.881 ** | −0.206 | −0.136 | 0.409 ** | ||||
| Cu | 1 | 0.967 ** | −0.242 | −0.156 | 0.482 ** | |||||
| Zn | 1 | −0.202 | −0.274 | 0.443 ** | ||||||
| As | 1 | −0.066 | −0.098 | |||||||
| Cd | 1 | 0.061 | ||||||||
| Pb | 1 |
| Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | As | Cd | Pb | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | 1 | 0.158 | −0.290 * | −0.394 ** | 0.134 | −0.506 ** | −0.478 ** | 0.027 | −0.437 ** | −0.384 ** |
| Mn | 1 | −0.073 | 0.26 | 0.003 | −0.103 | 0.19 | 0.143 | 0.162 | 0.510 ** | |
| Fe | 1 | 0.294 * | −0.285 * | 0.379 ** | 0.334 * | −0.115 | 0.365 ** | 0.269 | ||
| Co | 1 | −0.144 | 0.614 ** | 0.980 ** | 0.081 | 0.842 ** | 0.807 ** | |||
| Ni | 1 | −0.278 * | −0.198 | −0.048 | −0.141 | −0.254 | ||||
| Cu | 1 | 0.733 ** | −0.016 | 0.654 ** | 0.527 ** | |||||
| Zn | 1 | 0.049 | 0.864 ** | 0.811 ** | ||||||
| As | 1 | 0.08 | 0.116 | |||||||
| Cd | 1 | 0.759 ** | ||||||||
| Pb | 1 |
| Heavy Metals | CG | WLS | BST | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | |
| Cr | 0.433 | 0.178 | 0.858 | 0.203 | 0.757 | −0.095 | 0.056 | −0.508 | 0.179 | −0.0246 |
| Mn | 0.885 | 0.015 | 0.144 | 0.169 | 0.787 | 0.279 | 0.183 | 0.018 | 0.843 | 0.003 |
| Fe | 0.887 | 0.375 | 0.185 | −0.024 | −0.033 | −0.798 | 0.071 | 0.308 | −0.119 | 0.453 |
| Co | 0.908 | 0.319 | 0.210 | 0.934 | 0.112 | 0.217 | −0.173 | 0.908 | 0.300 | 0.077 |
| Ni | 0.805 | 0.371 | 0.217 | 0.846 | 0.457 | 0.042 | −0.105 | −0.093 | −0.018 | −0.530 |
| Cu | 0.772 | 0.185 | 0.045 | 0.926 | 0.296 | 0.201 | −0.071 | 0.715 | −0.146 | 0.377 |
| Zn | 0.048 | 0.013 | 0.679 | 0.897 | 0.192 | 0.201 | −0.209 | 0.964 | 0.200 | 0.159 |
| As | 0.074 | 0.482 | 0.555 | −0.320 | 0.043 | 0.131 | −0.199 | 0.028 | 0.189 | −0.036 |
| Cd | 0.261 | 0.877 | 0.030 | −0.183 | 0.172 | 0.035 | 0.693 | 0.851 | 0.179 | 0.180 |
| Pb | 0.367 | 0.887 | 0.244 | 0.408 | 0.084 | 0.558 | 0.150 | 0.685 | 0.574 | 0.336 |
| Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | As | Cd | Pb | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1960s–1970s | CG | 55 | 740 | 3.08 | 11.9 | 30 | 26.9 | 80 | 29.5 | 0.11 | 22 |
| WLS | 56.5 | 565 | 4.05 | 6.5 | 26.5 | 20.7 | 46 | 10.1 | 0.1 | 23 | |
| BST | 42 | 478 | 1.01 | 4.8 | 28.7 | 18.7 | 25.7 | 6.55 | 0.07 | 21.3 | |
| 1970s–1980s | CG | 53 | 695 | 3.01 | 11.6 | 31 | 25.7 | 82 | 25.8 | 0.09 | 21 |
| WLS | 54.7 | 538 | 4.09 | 6.38 | 27 | 20.4 | 45.8 | 9.39 | 0.093 | 22.8 | |
| BST | 43 | 485 | 1.01 | 5.07 | 26 | 19.2 | 26.7 | 6 | 0.07 | 22.3 | |
| 1980s–1990s | CG | 63 | 721 | 3.14 | 12.3 | 32 | 26.6 | 142 | 37.37 | 0.14 | 23 |
| WLS | 53.8 | 529 | 4.09 | 6.77 | 26.2 | 20.4 | 44.5 | 8.99 | 0.098 | 23.9 | |
| BST | 42.9 | 492 | 1.02 | 3.78 | 26.5 | 19.1 | 19 | 6.24 | 0.07 | 21.3 | |
| 1990s–2000s | CG | 62 | 667 | 2.82 | 10.6 | 28 | 22.5 | 175 | 42 | 0.1 | 23 |
| WLS | 53.8 | 567 | 4.07 | 6.7 | 27.2 | 21.5 | 47 | 9.16 | 0.114 | 24 | |
| BST | 38 | 505 | 1.02 | 4.1 | 29 | 18.7 | 21 | 5.67 | 0.07 | 20.8 | |
| 2000s–2010s | CG | 60 | 718 | 3.41 | 13.1 | 34 | 27.8 | 104 | 45.69 | 0.21 | 29 |
| WLS | 48.2 | 530 | 4.04 | 6.86 | 25.67 | 21.0 | 48.4 | 9.43 | 0.087 | 24.2 | |
| BST | 36.6 | 474 | 1.03 | 8.42 | 26.9 | 25.4 | 60 | 6.3 | 0.127 | 27 | |
| 2010s–2020s | CG | 61 | 727 | 3.29 | 12.6 | 34 | 27.2 | 107 | 41.69 | 0.32 | 31 |
| WLS | 56.1 | 561 | 4.05 | 8.13 | 31.2 | 24.7 | 56.3 | 9.02 | 0.088 | 25 | |
| BST | 40.4 | 602 | 1.02 | 8.74 | 27.2 | 21.2 | 57.2 | 6.3 | 0.122 | 30.9 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, R.; Zang, S.; Sun, L.; Ni, H. Human Impacts on Heavy Metals in Lake Sediments of Northern China: History, Sources, and Trend Prediction. Water 2025, 17, 2884. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17192884
Xie R, Zang S, Sun L, Ni H. Human Impacts on Heavy Metals in Lake Sediments of Northern China: History, Sources, and Trend Prediction. Water. 2025; 17(19):2884. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17192884
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Ruifeng, Shuying Zang, Li Sun, and Hongwei Ni. 2025. "Human Impacts on Heavy Metals in Lake Sediments of Northern China: History, Sources, and Trend Prediction" Water 17, no. 19: 2884. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17192884
APA StyleXie, R., Zang, S., Sun, L., & Ni, H. (2025). Human Impacts on Heavy Metals in Lake Sediments of Northern China: History, Sources, and Trend Prediction. Water, 17(19), 2884. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17192884






