Early Warning Technology for Heavy Metal Contaminant Leakage Based on Self-Potential Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
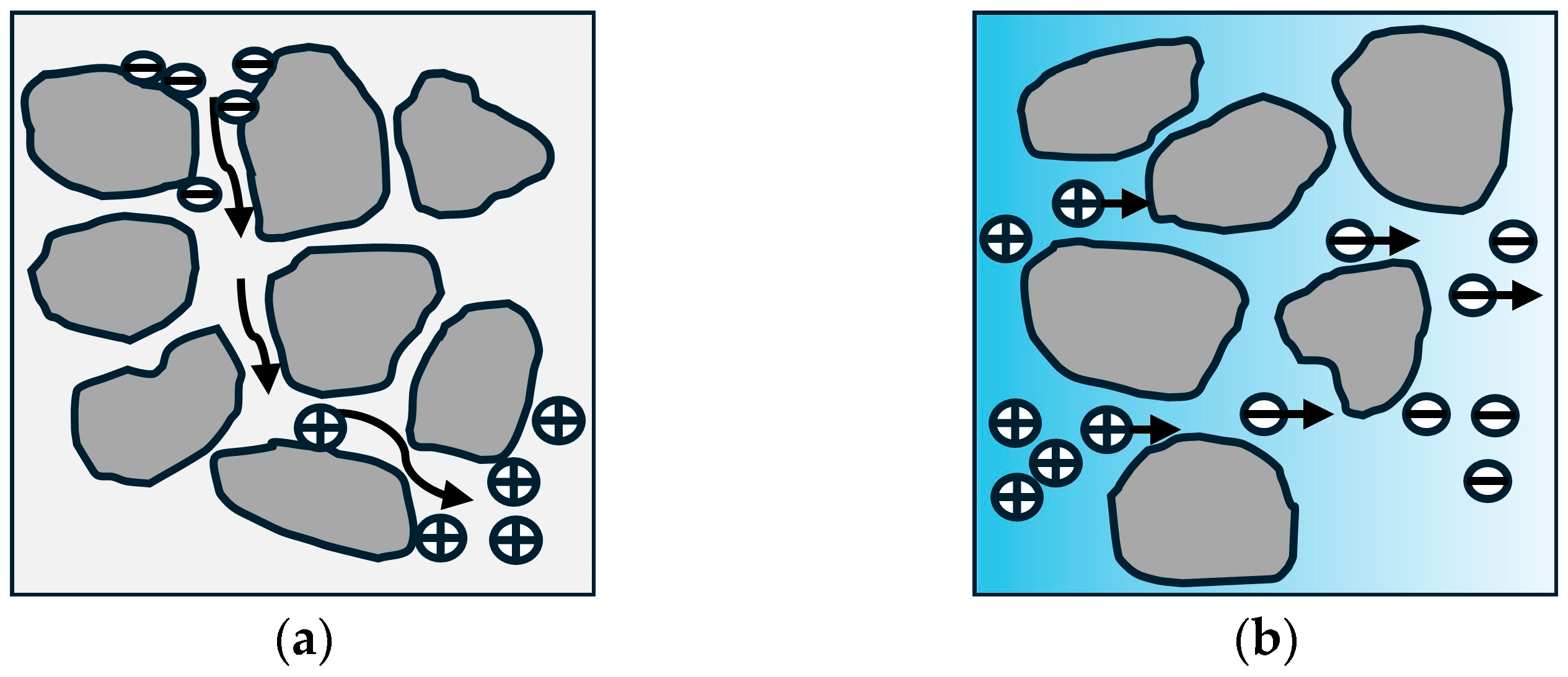
2.1. Formation Mechanisms of Natural Electric Fields
2.2. Governing Equations for Multiphysics Coupling
3. Case Studies
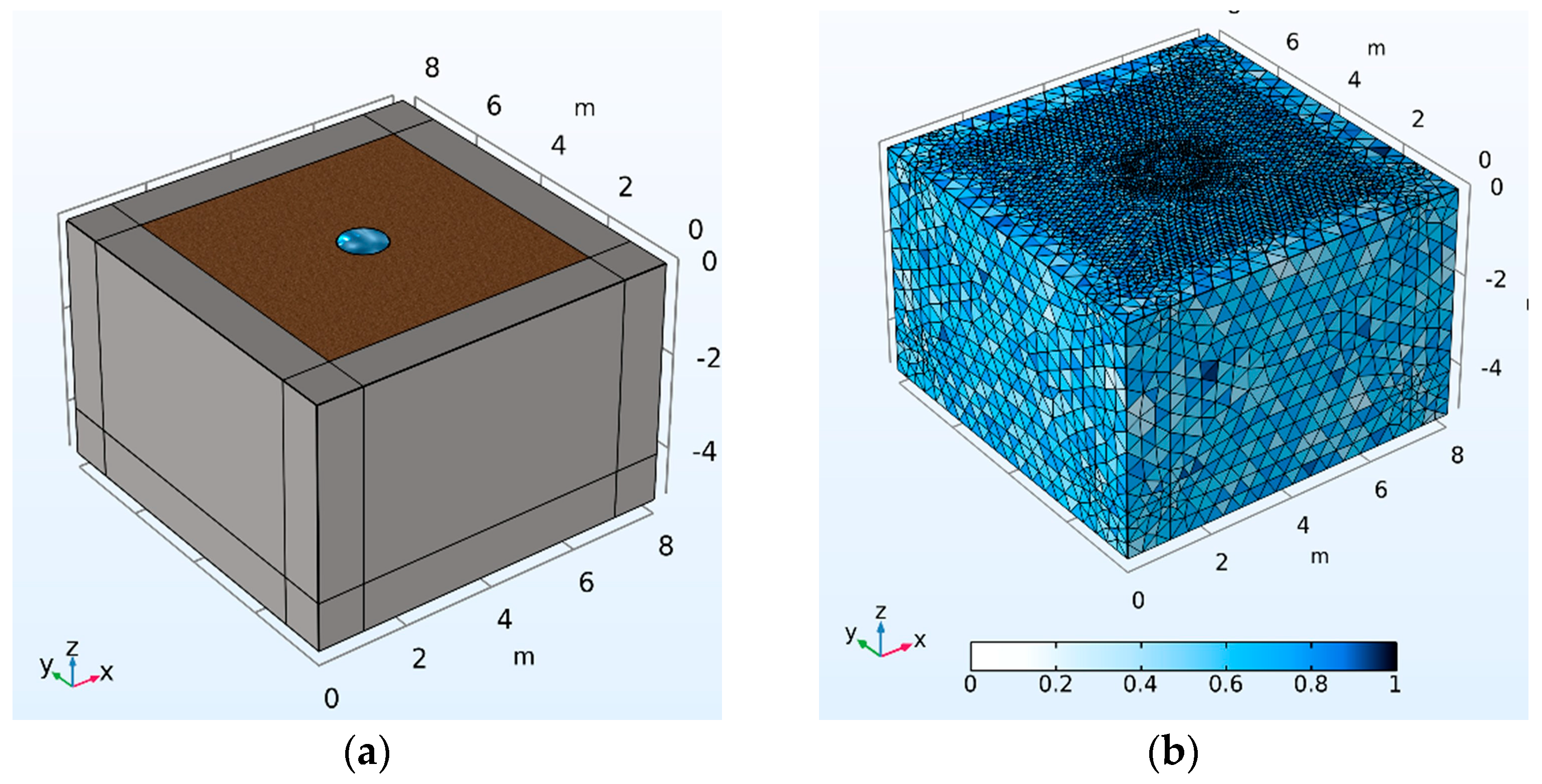
3.1. Numerical Modeling Framework
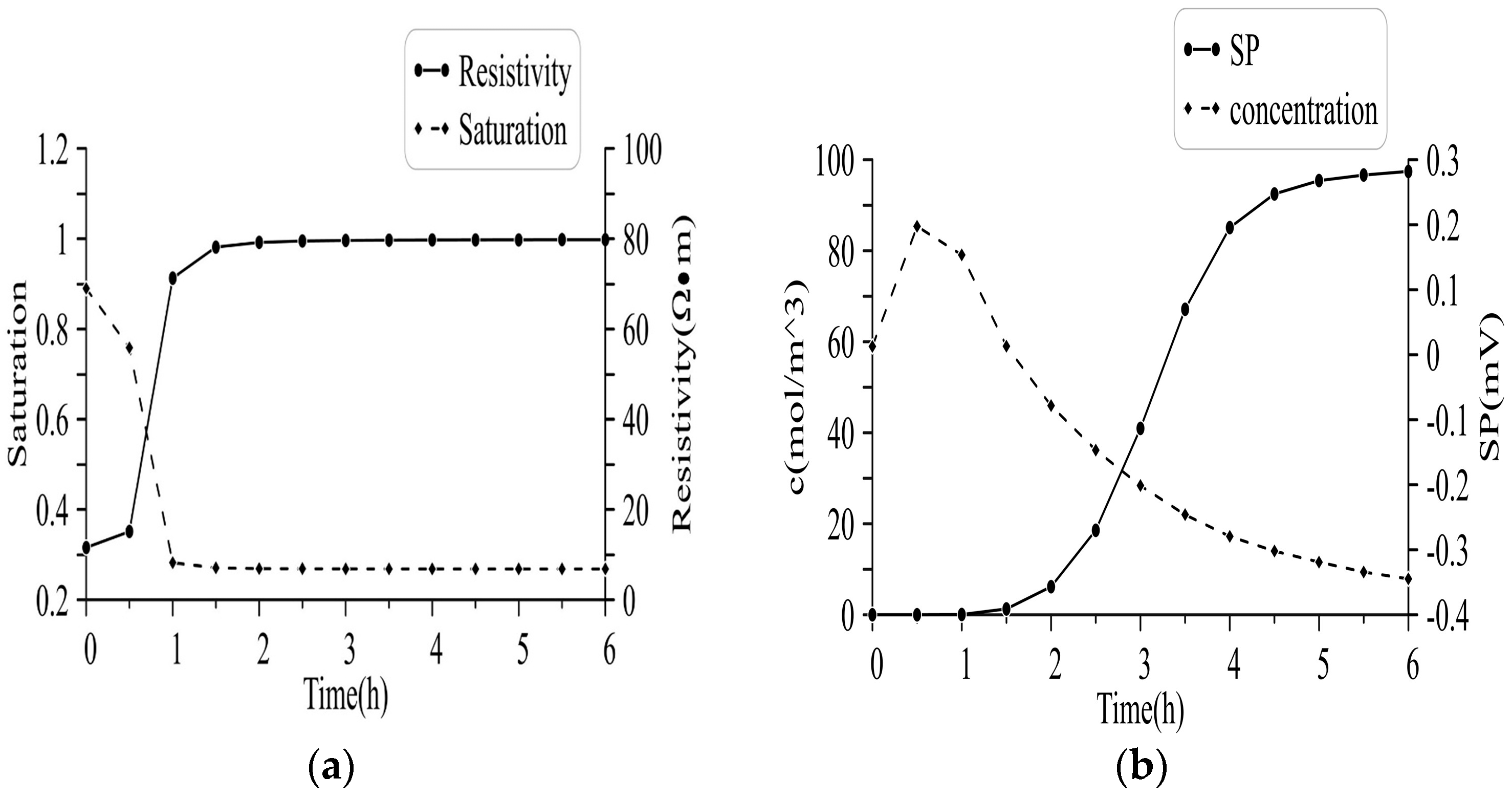
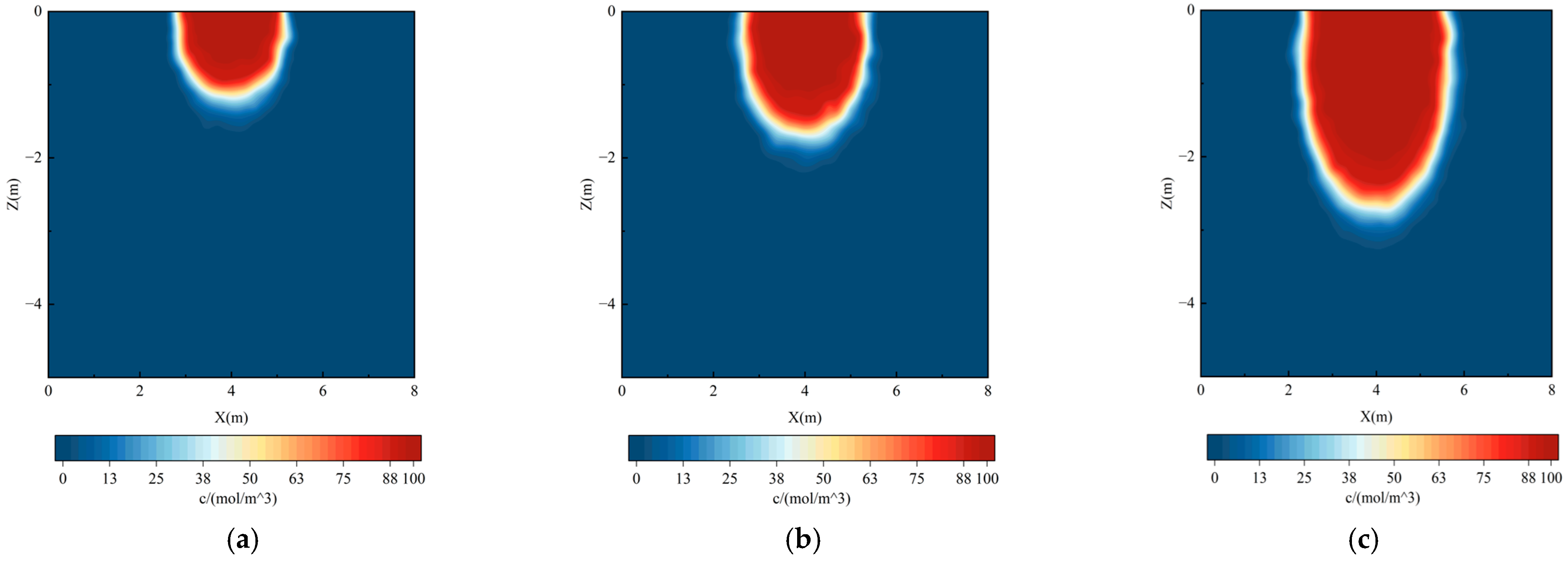
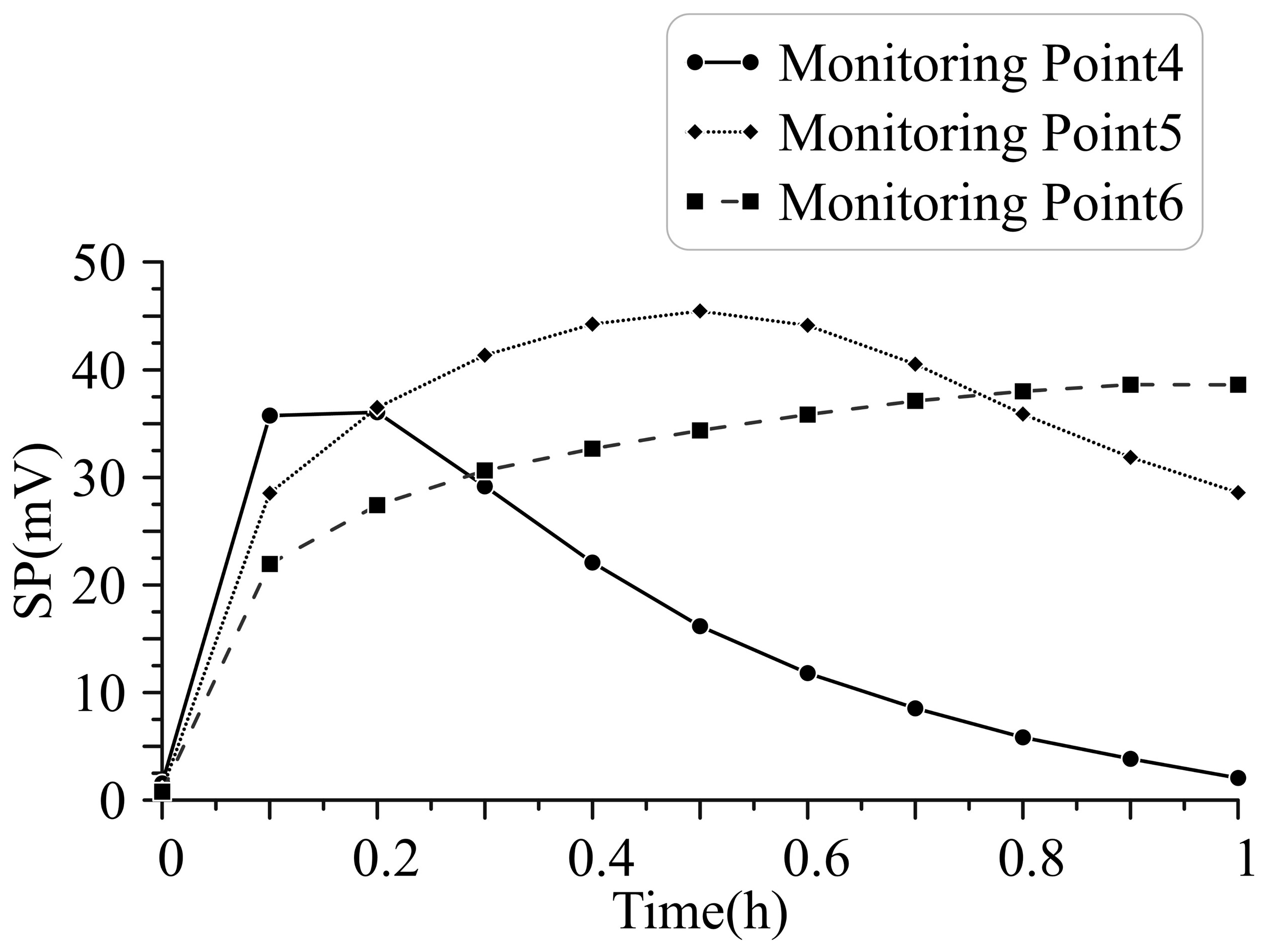
3.2. Case 1: Dynamic Response Mechanism and Lead Time Analysis
3.3. Case 2: Landfill Application and Monitoring Strategy Optimization
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, R.; Xie, X.; Hou, Q.; Han, D.; Song, J.; Huang, G. Spatial distribution, sources, and human health risk assessment of elevated nitrate levels in groundwater of an agriculture-dominant coastal area in Hainan Island, China. J. Hydrol. 2024, 634, 131088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suknark, P.; Buddhawong, S.; Wangyao, K. Investigating the effect of waste age and soil covering on waste characteristics prior to landfill mining using an electrical resistivity tomography technique. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 339, 117898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamal, M.; Di, Q.; Zhang, J.; Fu, C.; Ebrahim, S.; El-Raouf, A.A. Utilizing Ground-Penetrating Radar for Water Leak Detection and Pipe Material Characterization in Environmental Studies: A Case Study. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulsamad, F.; Revil, A.; Ahmed, A.S.; Coperey, A.; Karaoulis, M.; Nicais, S.; Peyras, L. Induced polarization tomography applied to the detection and the monitoring of leaks in embankments. Eng. Geol. 2019, 254, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Ye, Y. Identification of shallow subsurface targets using an improved transient electromagnetic radar method. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2024, 151, 105866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondracka, M.; Stan-Kleczek, I.; Sitek, S.; Ignatiuk, D. Evaluation of geophysical methods for characterizing industrial and municipal waste dumps. Waste Manag. 2021, 125, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Li, K.; Su, A.; Tang, H. Detection of landslide groundwater based on magnetic resonance sounding given complex topography. Eng. Geol. 2024, 331, 107453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, D.; Goeppert, N.; Goldscheider, N. New insights into particle transport in karst conduits using comparative tracer tests with natural sediments and solutes during low-flow and high-flow conditions. Hydrol. Process. 2022, 36, e14472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Hong, C.; Yuan, S.; Wu, P. Development and Verification of a Vertical Graphene Sensor for Tunnel Leakage Monitoring. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 17, 3962–3972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sears, R.G.; Rigoulot, S.B.; Occhialini, A.; Morgan, B.; Kakeshpour, T.; Brabazon, H.; Barnes, C.N.; Seaberry, E.M.; Jacobs, B.; Brown, C.; et al. Engineered gamma radiation phytosensors for environmental monitoring. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2023, 21, 1745–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Jiang, S.; Ou, J.; Kouadio, K.L.; Xiong, B. Multifaceted anomaly detection framework for leachate monitoring in landfills. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 368, 122130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revil, A.; Ghorbani, A.; Zhao, X.; Mouyeaux, A.; Barrere, L.; Richard, J.; Peyras, L.; Vaudelet, P. Groundwater flow paths using combined self-potential, electrical resistivity, and induced polarization signals. Geophys. J. Int. 2024, 239, 798–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, P.; Piegari, E.; Di Maio, R.; Vitagliano, E.; Soupios, P.; Milano, L. Monitoring time evolution of self-potential anomaly sources by a new global optimization approach. Application to organic contaminant transport. J. Hydrol. 2019, 575, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Huo, Z.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, H.; Tan, J.; Wang, T. Groundwater flow monitoring using time-lapse electrical resistivity and Self Potential data. J. Appl. Geophys. 2021, 193, 104411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.S.; Revil, A.; Steck, B.; Vergniault, C.; Jardani, A.; Vinceslas, G. Self-potential signals associated with localized leaks in embankment dams and dikes. Eng. Geol. 2019, 253, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Cui, Y.-a.; Xie, J.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, P.; Liu, H.; Liu, J. Seepage detection in earth-filled dam from self-potential and electrical resistivity tomography. Eng. Geol. 2022, 306, 106750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Huang, Q.; Han, P.; Zhang, Y.; Mo, C.; Li, S.; Jougnot, D. Characterization of rainwater infiltration within a controlled experiment by self-potential monitoring and modeling. J. Hydrol. 2025, 660, 133348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Qian, X.; Xu, Y.; Nai, C.; Liu, Y. Neglected flow direction detection in landfill water cycle: Precise characterization of leachate distribution through joint inversion of electrical resistivity and self-potential data. Water Cycle 2024, 5, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehanee, S.A.; Essa, K.S.; Soliman, K.S.; Diab, Z.E. A fast imaging method for the interpretation of self-potential data with application to geothermal systems and mineral investigation. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 13548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, K.; Jougnot, D.; Huang, Q.; Looms, M.C.; Linde, N. Advancing quantitative understanding of self-potential signatures in the critical zone through long-term monitoring. J. Hydrol. 2020, 585, 124771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.; Jardani, A.; Ahmed, A.S.; Revil, A.; Brigaud, L.; Begassat, P.; Dupont, J.P. Redox potential distribution of an organic-rich contaminated site obtained by the inversion of self-potential data. J. Hydrol. 2017, 554, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldi, M.; Guarracino, L.; Jougnot, D. An effective excess charge model to describe hysteresis effects on streaming potential. J. Hydrol. 2020, 588, 124949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rembert, F.; Jougnot, D.; Luquot, L.; Guerin, R. Interpreting Self-Potential Signal during Reactive Transport: Application to Calcite Dissolution and Precipitation. Water 2022, 14, 1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Huang, Q.; Tang, M.; Xue, L.; Han, P. Self-potential variations associated with the slip of Huangnibazi Landslide. J. Appl. Geophys. 2024, 220, 105275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-F.; Chen, H.; Deng, J.-Z.; Liu, S.-M.; Tang, W.-W.; Wang, S. Three-dimensional forward modeling and response characteristics analysis of foundation pit leakage electric-field considering electrokinetic effect. Appl. Geophys. 2022, 19, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boleve, A.; Vandemeulebrouck, J.; Grangeon, J. Dyke leakage localization and hydraulic permeability estimation through self-potential and hydro-acoustic measurements: Self-potential ‘abacus’ diagram for hydraulic permeability estimation and uncertainty computation. J. Appl. Geophys. 2012, 86, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, L.A. Capillary Conduction of Liquids Through Porous Mediums. J. Appl. Phys. 1931, 1, 318–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayek, M. Analytical solution for steady vertical flux through unsaturated soils based on van Genuchten-Mualem model. J. Hydrol. 2024, 634, 131066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, A.; Vahab, M.; Broumand, P.; Khalili, N. An eXtended finite element method implementation in COMSOL multiphysics: Thermo-hydro-mechanical modeling of fluid flow in discontinuous porous media. Comput. Geotech. 2023, 159, 105458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onaa, C.; Olaobaju, E.A.; Amro, M.M. Experimental and numerical assessment of Light Non-Aqueous Phase Liquid (LNAPL) subsurface migration behavior in the vicinity of groundwater table. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 23, 101573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Huang, Y.; Illman, W.A.; Su, Y.; Miao, K. Migration behaviour of LNAPL in fractures filled with porous media: Laboratory experiments and numerical simulations. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2023, 253, 104118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aranda, N.; Elis, V.R.; Prado, R.L.; Miguel, M.G.; Alves de Godoy Leme, M.; Conicelli, B.; Guzman, O. Electrical resistivity methods to characterize the moisture content in Brazilian sanitary landfill. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawrea, A.; Zytner, R.G.; Donald, J. Enhanced GPR data interpretation to estimate in situ water saturation in a landfill. Waste Manag. 2021, 120, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y. Mapping and monitoring dense non-aqueous phase liquid source zone by fused surface and cross-borehole electrical resistivity tomography. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 478, 135618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

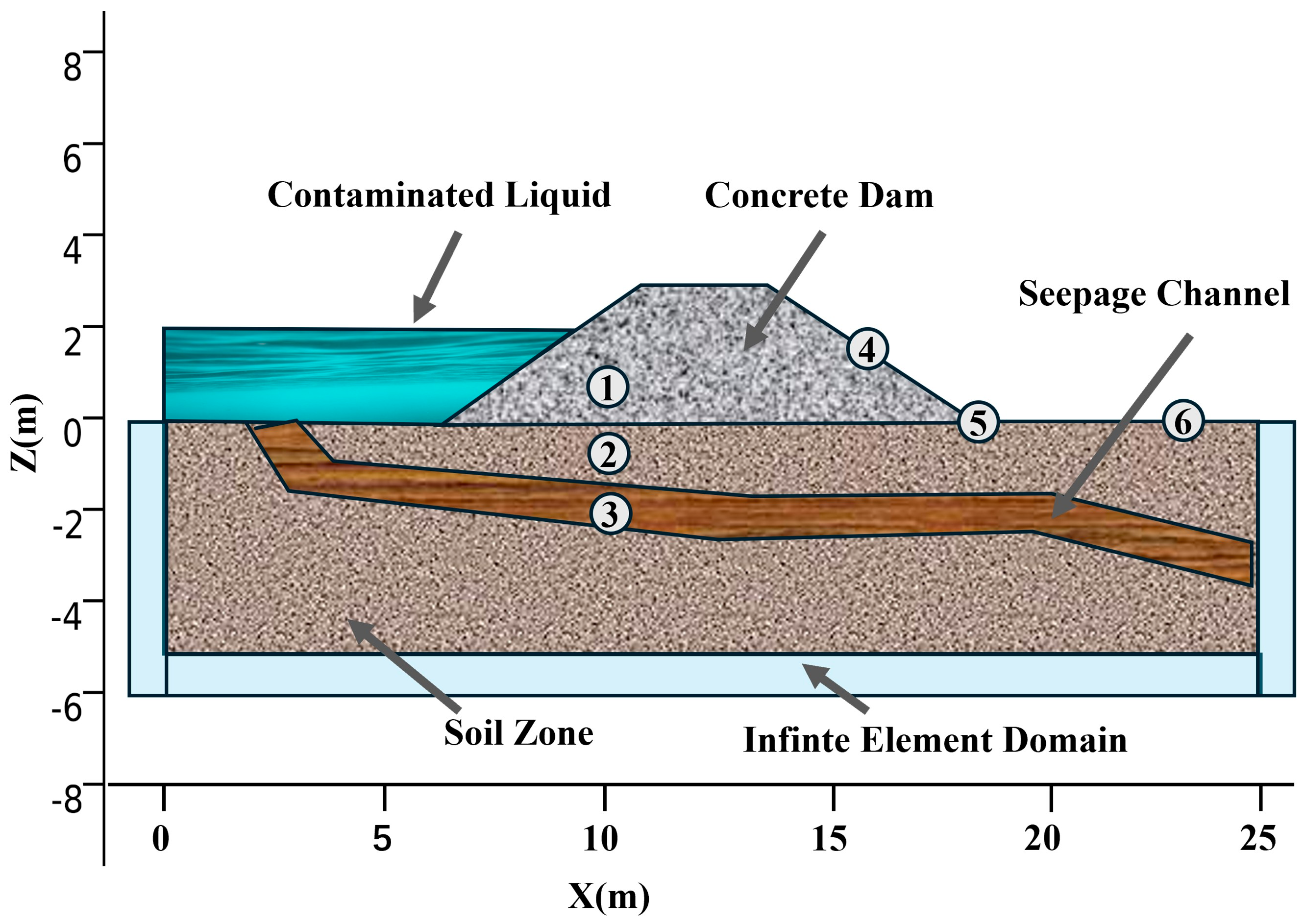

| Material Property | Soil | Contaminated Liquid |
|---|---|---|
| Permeability/(m2) | 1.3·10−11 | —— |
| Density/(kg/m3) | 1300 | 1000 |
| Porosity | 0.339 | 1 |
| Dynamic viscosity/(Pa·s) | —— | 0.001 |
| Concentration/(mol/m3) | 0.01 | 100 |
| Relative permittivity | Topp equation | —— |
| Electrical conductivity | Archie’s law | —— |
| Material Property | Concrete Dam | Seepage Channel |
|---|---|---|
| Permeability/(m2) | 1.3∙10−13 | 1.3∙10−9 |
| Density/(kg/m3) | 1300 | 1000 |
| Porosity | 0.1 | 0.6 |
| Dynamic viscosity/(Pa·s) | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| Concentration/(mol/m3) | 0 | 0.01 |
| Relative permittivity | Topp equation | Topp equation |
| Electrical conductivity | Archie’s law | Archie’s law |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, F.; Li, H.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, G.; Jia, X. Early Warning Technology for Heavy Metal Contaminant Leakage Based on Self-Potential Method. Water 2025, 17, 2839. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17192839
Wang F, Li H, Zhang W, Liu Y, Wang G, Jia X. Early Warning Technology for Heavy Metal Contaminant Leakage Based on Self-Potential Method. Water. 2025; 17(19):2839. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17192839
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Feng, Hongli Li, Wei Zhang, Yansheng Liu, Guofu Wang, and Xiaobo Jia. 2025. "Early Warning Technology for Heavy Metal Contaminant Leakage Based on Self-Potential Method" Water 17, no. 19: 2839. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17192839
APA StyleWang, F., Li, H., Zhang, W., Liu, Y., Wang, G., & Jia, X. (2025). Early Warning Technology for Heavy Metal Contaminant Leakage Based on Self-Potential Method. Water, 17(19), 2839. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17192839







