Sodium p-Perfluorous Nonenoxybenzene Sulfonate (OBS) Induces Developmental Toxicity Through Apoptosis in Developing Zebrafish Embryos: A Comparison with Perfluorooctane Sulfonate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Zebrafish Maintenance and Embryo Collection
2.3. Embryo Developmental Toxicity Assays
2.4. Total RNA Extraction and Concentration Measurement
2.5. cDNA Synthesis and Real-Time qRT-PCR
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
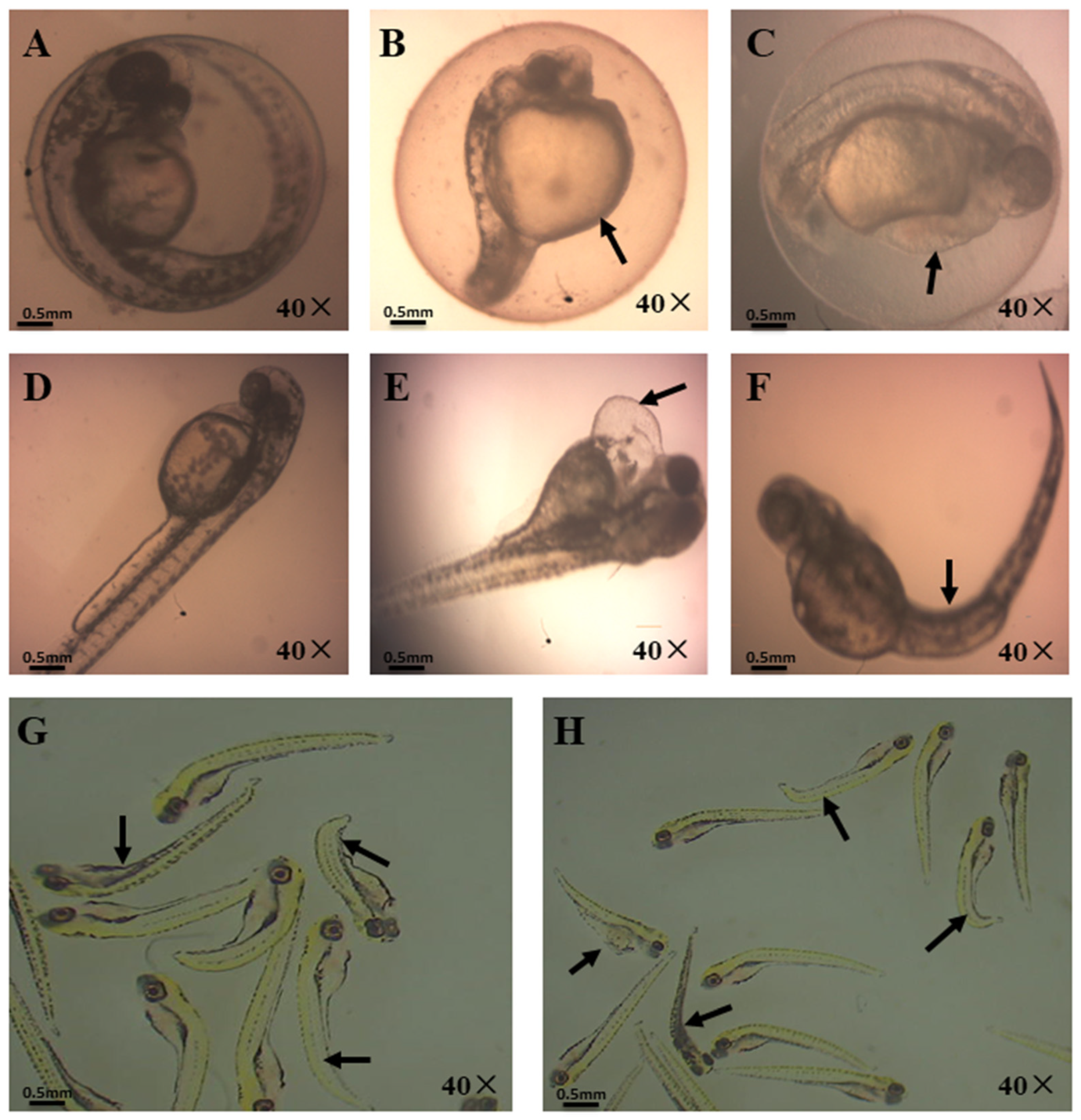
3.1. Effects of OBS on Zebrafish Embryo Developmental Morphology
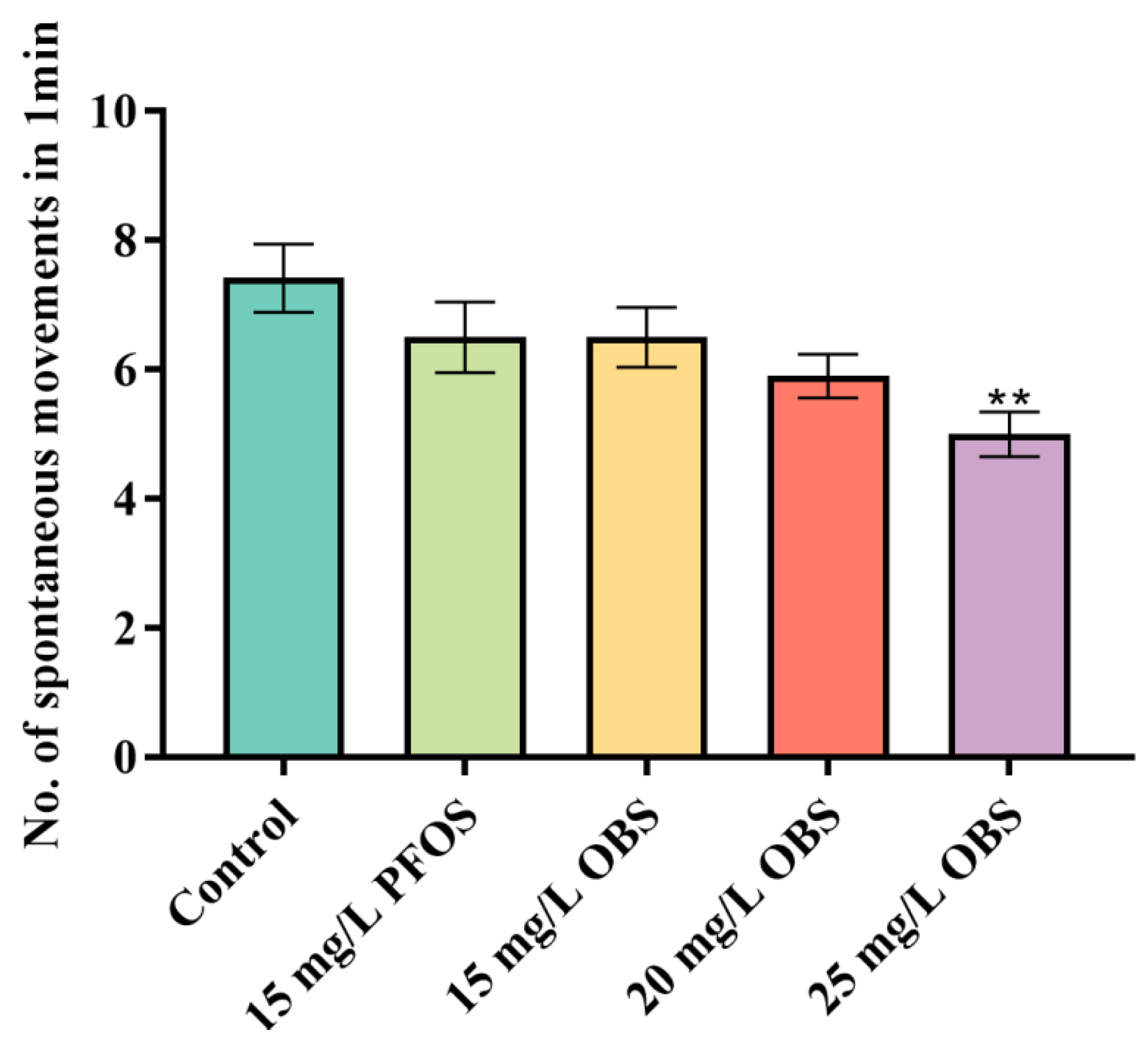
3.2. Effects of OBS on Spontaneous Movements in Zebrafish Embryos
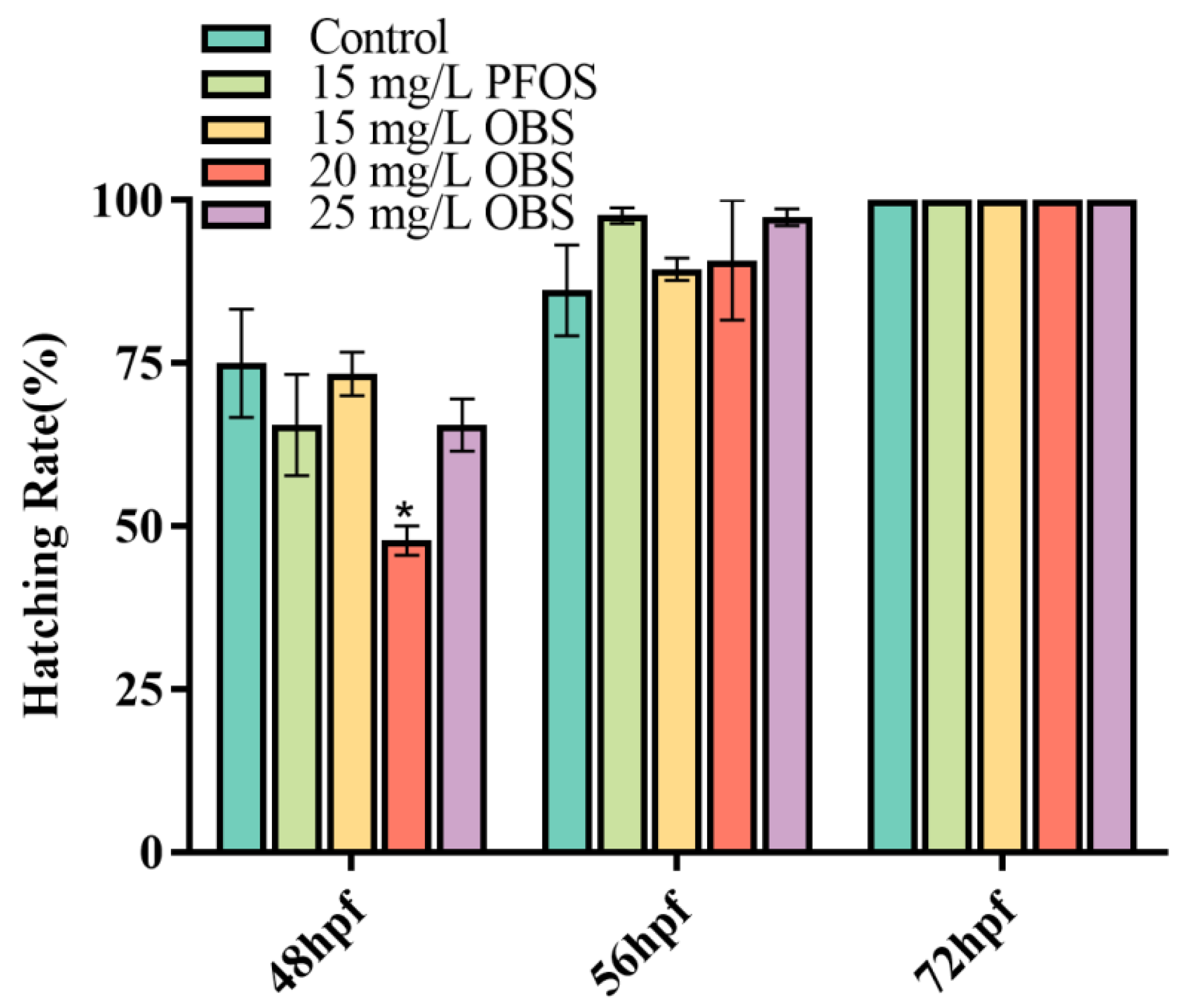
3.3. Effects of OBS on Zebrafish Embryo Hatching Rate
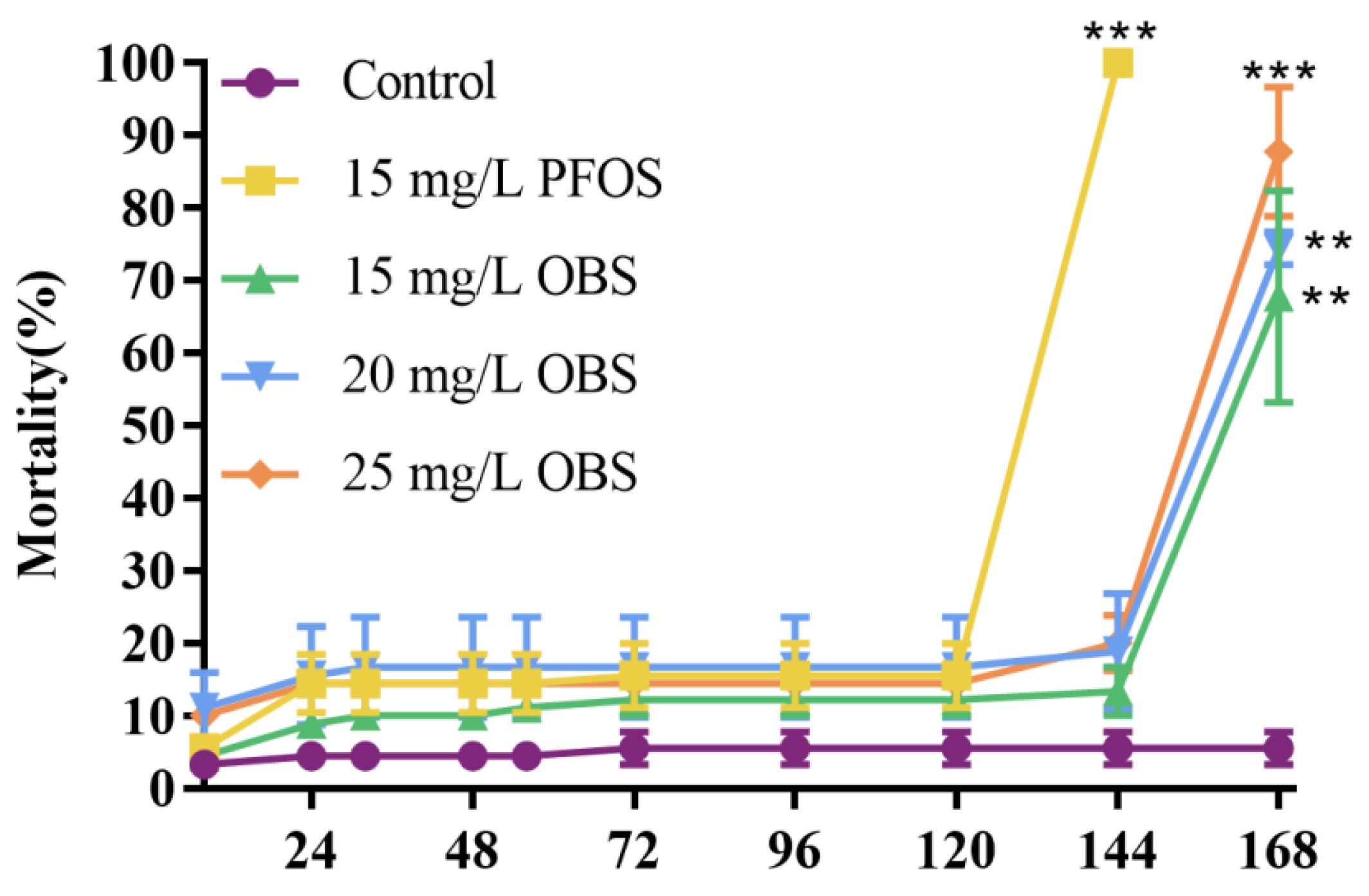
3.4. Effects of OBS Exposure on Zebrafish Embryo Mortality
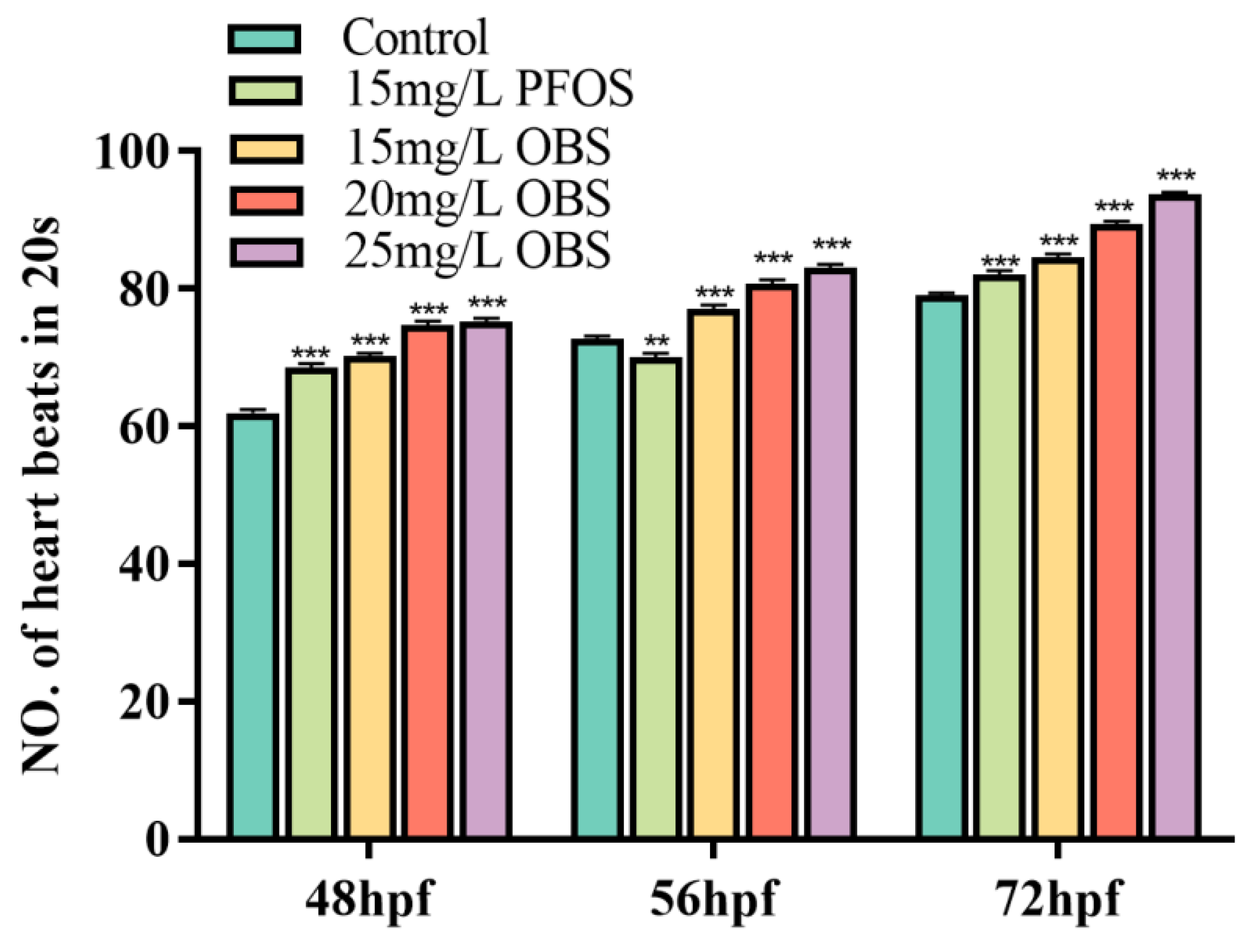
3.5. Effects of OBS Exposure on Zebrafish Embryo Heart Beat Rate
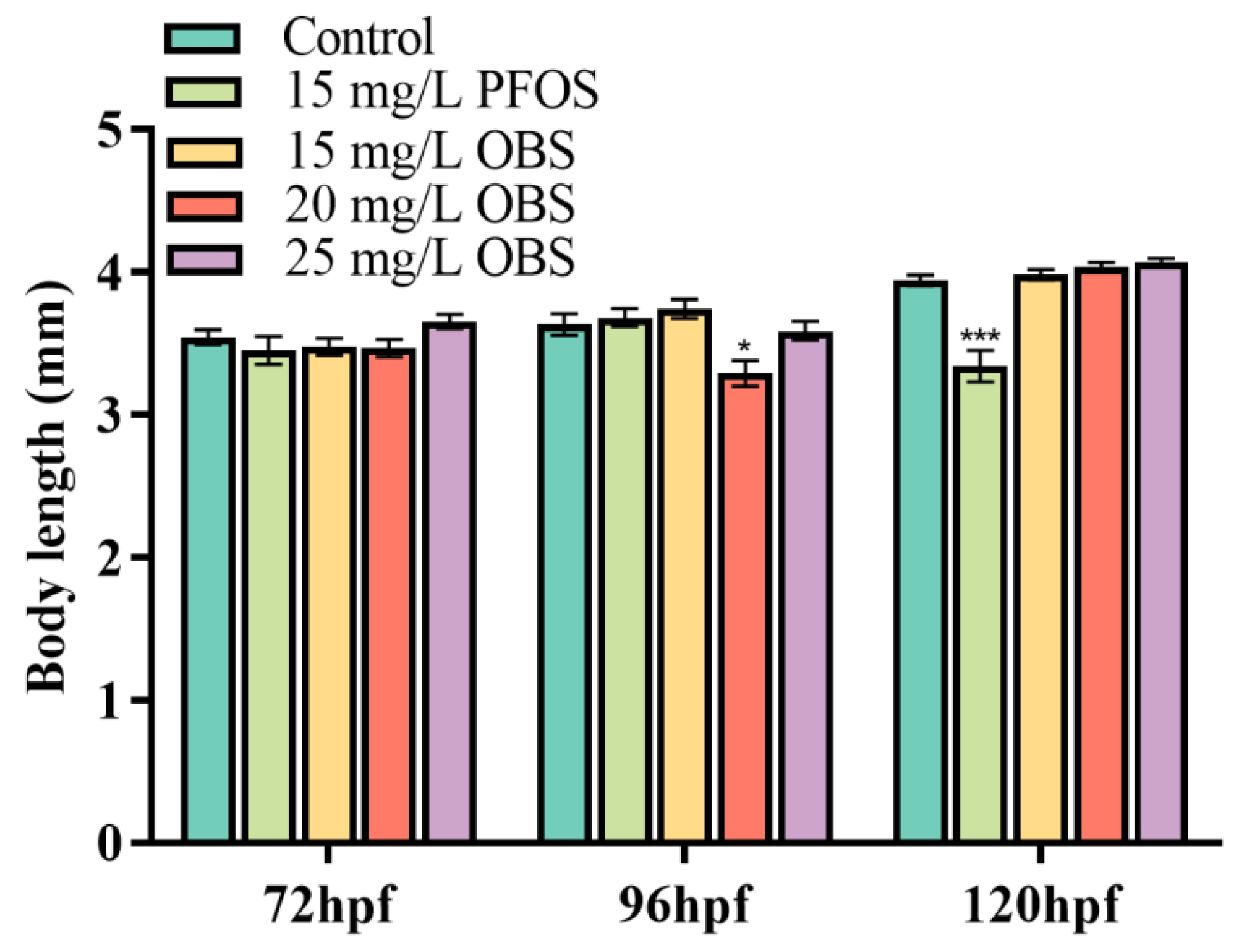
3.6. Effects of OBS Exposure on Zebrafish Larvae Body Length
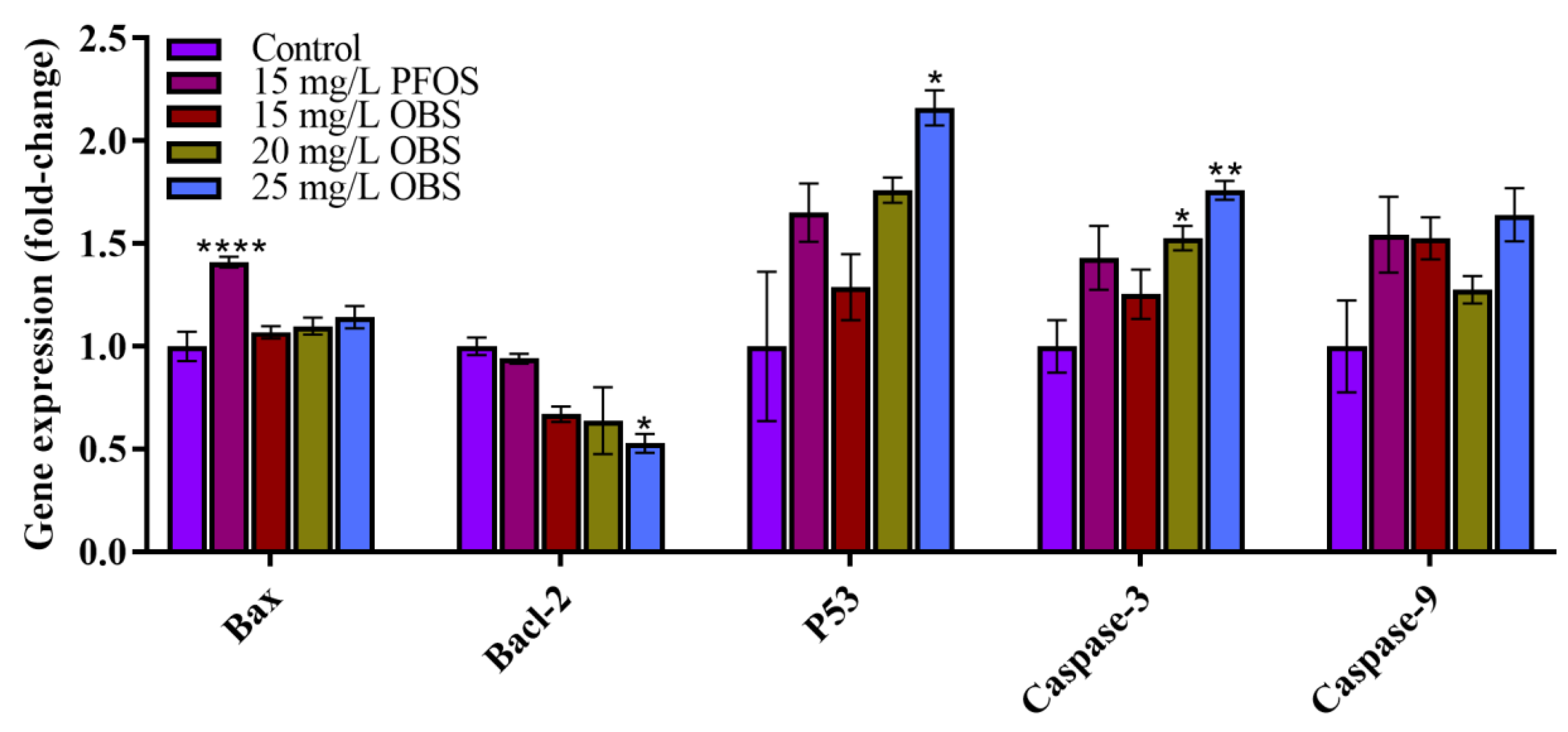
3.7. Effects of OBS Exposure on the Expression Levels of Key Genes in Zebrafish Embryos
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lindstrom, A.B.; Strynar, M.J.; Libelo, E.L. Polyfluorinated compounds: Past, present, and future. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 7954–7961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunderland, E.M.; Hu, X.C.; Dassuncao, C.; Tokranov, A.K.; Wagner, C.C.; Allen, J.G. A review of the pathways of human exposure to poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) and present understanding of health effects. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epid. 2019, 29, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, F.C.; Ludtke, S.; Thackray, C.; Pickard, H.M.; Haque, F.; Dassuncao, C.; Endo, S.; Schaider, L.; Sunderland, E.M. Binding of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) to Serum Proteins: Implications for Toxicokinetics in Humans. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 1055–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonato, T.; Pal, T.; Benna, C.; Di Maria, F. Contamination of the terrestrial food chain by per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) and related human health risks: A systematic review. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 961, 178337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, A.; Shan, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wan, J.; Ning, P.; Hong, C.; Tian, H.; et al. Hepatotoxicity induced in rats by chronic exposure to F-53B, an emerging replacement of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS). Environ. Pollut. 2024, 346, 123544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Y.; Qu, Y.; Huang, J.; Cagnetta, G.; Yu, G.; Weber, R. First assessment on degradability of sodium p-perfluorous nonenoxybenzene sulfonate (OBS), a high volume alternative to perfluorooctane sulfonate in fire-fighting foams and oil production agents in China. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 46948–46957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Shi, Y.; Li, C.; Song, X.; Qin, Z.; Cao, D.; Cai, Y. Discovery of a Novel Polyfluoroalkyl Benzenesulfonic Acid around Oilfields in Northern China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 14173–14181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Song, X.; Jin, Q.; Li, W.; He, S.; Cai, Y. Tissue distribution and bioaccumulation of a novel polyfluoroalkyl benzenesulfonate in crucian carp. Environ. Int. 2020, 135, 105418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yu, N.; Du, L.; Shi, W.; Yu, H.; Song, M.; Wei, S. Transplacental transfer of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances identified in paired maternal and cord sera using suspect and nontarget screening. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 3407–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, M.; Wang, X.; Tu, W.; Fu, Z.; Jin, Y. Bioaccumulation in the gut and liver causes gut barrier dysfunction and hepatic metabolism disorder in mice after exposure to low doses of OBS. Environ. Int. 2019, 129, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, W.; Martínez, R.; Navarro-Martin, L.; Kostyniuk, D.J.; Hum, C.; Huang, J.; Deng, M.; Jin, Y.; Chan, H.M.; Mennigen, J.A. Bioconcentration and Metabolic Effects of Emerging PFOS Alternatives in Developing Zebrafish. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 13427–13439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucci, K.; Bayoumi, M.; Stevack, K.; Watson-Leung, T.; Rochman, C.M. Microplastics may induce food dilution and endocrine disrupting effects in fathead minnows (Pimephales promelas), and decrease offspring quality. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 345, 123551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chernick, M.; Dong, W.; Xie, L.; Hinton, D.E. The role of chorion integrity on the bioaccumulation and toxicity of selenium nanoparticles in Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes). Aquat. Toxicol. 2025, 278, 107170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Lu, C.; Wang, X.; Du, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, B.; Wang, J.; Zhu, L. Comparison of the combined toxicity of PFOA and emerging alternatives: A comprehensive evaluation of oxidative damage, apoptosis and immunotoxicity in embryonic and adult zebrafish. Water Res. 2025, 273, 123028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; Hu, W.; Luo, Y.; Zhu, P.; You, S.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Wu, X.; Li, X. Impacts of PFOAC8, GenXC6, and their mixtures on zebrafish developmental toxicity and gene expression provide insight about tumor-related disease. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 160085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tong, Z.; Xie, W.; Wang, A.; Song, C.; Yao, W.; Wang, J. Pyraclostrobin induces developmental toxicity and cardiotoxicity through oxidative stress and inflammation in zebrafish embryos. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 358, 124490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.-H.; Gao, J.-M.; Huang, C.-J.; Li, C.-Q. Zebrafish models for assessing developmental and reproductive toxicity. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2014, 42, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.-Y.; Gan, X.; Shen, B.; Jiang, J.; Shen, H.; Lei, Y.; Liang, Q.; Bai, C.; Huang, C.; Wu, W.; et al. 6PPD and its metabolite 6PPDQ induce different developmental toxicities and phenotypes in embryonic zebrafish. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 455, 131601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Liang, H. The combined neurotoxicity of DBP and nano-TiO2 in embryonic zebrafish (Danio rerio) revealed by oxidative activity, neuro-development genes expression and metabolomics changes. Aquat. Toxicol. 2024, 269, 106881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamila, S.; Dey, K.K.; Islam, S.; Chattopadhyay, A. Mixture of arsenic and chromium alters antioxidant, DNA repair and tumor suppressor gene expressions in zebrafish brain at environmental concentrations. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 155, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, B.; Liu, Z.; Xia, X. Developmental toxicity and alteration of gene expression in zebrafish embryo exposed to 6-benzylaminopurine. Chemosphere 2019, 233, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Guideline for the Testing of Chemicals Test No. 236: Fish Embryo Acute Toxicity (FET) Test; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2013; p. 22. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Sun, L.; Mennigen, J.A.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Q.; Tu, W. Developmental toxicity of the novel PFOS alternative OBS in developing zebrafish: An emphasis on cilia disruption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 409, 124491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel, R. DarT: The embryo test with the Zebrafish Danio rerio—A general model in ecotoxicology and toxicology. ALTEX 2002, 19, 38–48. [Google Scholar]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Q.; Hu, W.; Liu, F.; Dong, S.; Peng, X.; Zhong, Y.; Chen, C.; Zuo, Y.; Ge, C.; Li, W.; et al. Dipropyl phthalate induces craniofacial chondrogenic defects in zebrafish embryos. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 290, 117603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Mo, J.; Li, J.; Wu, K. Exploring developmental toxicity of microplastics and nanoplastics (MNPS): Insights from investigations using zebrafish embryos. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 933, 173012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haridevamuthu, B.; Murugan, R.; Seenivasan, B.; Meenatchi, R.; Pachaiappan, R.; Almutairi, B.O.; Arokiyaraj, S.; Arockiaraj, J. Synthetic azo-dye, Tartrazine induces neurodevelopmental toxicity via mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in zebrafish embryos. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 461, 132524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Zhao, H.; Ding, J.; Jing, C.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X. Uptake and toxicity of micro-/nanoplastics derived from naturally weathered disposable face masks in developing zebrafish: Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on aquatic life. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 343, 123129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarin, M.; Ny, A.; De Croze, N.; Maes, J.; Léonard, M.; Annaert, P.; de Witte, P.A.M. Pharmacokinetics in Zebrafish Embryos (ZFE) Following Immersion and Intrayolk Administration: A Fluorescence-Based Analysis. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, X.; Pang, S.; Sun, X.; Gao, J.; Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Li, X.; Wang, C. Evaluation of acute and developmental effects of difenoconazole via multiple stage zebrafish assays. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 175, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadzhiev, Y.; Wheatley, L.; Cooper, L.; Ansaloni, F.; Whalley, C.; Chen, Z.; Finaurini, S.; Gustincich, S.; Sanges, R.; Burgess, S.; et al. The miR-430 locus with extreme promoter density forms a transcription body during the minor wave of zygotic genome activation. Dev. Cell 2023, 58, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girigoswami, A.; Meenakshi, S.; Deepika, B.; Harini, K.; Gowtham, P.; Pallavi, P.; Girigoswami, K.J.A. Beneficial effects of bioinspired silver nanoparticles on zebrafish embryos including a gene expression study. DMPK 2024, 12, 177–192. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Li, G.; Huo, T.; Du, X.; Yang, Q.; Hung, T.-C.; Yan, W. Mechanisms of parental co-exposure to polystyrene nanoplastics and microcystin-LR aggravated hatching inhibition of zebrafish offspring. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 145766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Li, X.; Dong, S.; Zhao, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, M.; Shi, Y.; Ding, G. Developmental Toxicity and Cardiotoxicity Induced by PFOS and its Novel Alternative OBS in Early Life Stage of Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Water Air Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Huang, C.; Wang, L.; Ye, X.; Bai, C.; Simonich, M.T.; Tanguay, R.L.; Dong, Q. Toxicity, uptake kinetics and behavior assessment in zebrafish embryos following exposure to perfluorooctanesulphonicacid (PFOS). Aquat. Toxicol. 2010, 98, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Du, Y.; Lam, P.K.S.; Wu, R.S.S.; Zhou, B. Developmental toxicity and alteration of gene expression in zebrafish embryos exposed to PFOS. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2008, 230, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagenaars, A.; Stinckens, E.; Vergauwen, L.; Bervoets, L.; Knapen, D. PFOS affects posterior swim bladder chamber inflation and swimming performance of zebrafish larvae. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 157, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrionuevo, W.; Burggren, W.J. O2 consumption and heart rate in developing zebrafish (Danio rerio): Influence of temperature and ambient O2. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 1999, 276, R505–R513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasamsetti, B.M.; Chon, K.; Kim, J.; Oh, J.-A.; Yoon, C.-Y.; Park, H.-H. Developmental Toxic Effects of Thiram on Developing Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryos. Toxics 2022, 10, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, A.; Mahmoodi, M.; Mohammadizadeh, F.; Mohamadi, M.; Hajizadeh, M.R.; Mirzaei, M.R.; Khanamani Falahati-pour, S.J. A novel copper (II) complex activated both extrinsic and intrinsic apoptotic pathways in liver cancerous cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 12280–12289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, J.; Hu, K.; Chen, T. AHR/cyp1b1 signaling-mediated extrinsic apoptosis contributes to 6PPDQ-induced cardiac dysfunction in zebrafish embryos. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 345, 123467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, M.; Ahmad, R.; Tantry, I.Q.; Ahmad, W.; Siddiqui, S.; Alam, M.; Abbas, K.; Moinuddin; Hassan, M.I.; Habib, S.; et al. Apoptosis: A Comprehensive Overview of Signaling Pathways, Morphological Changes, and Physiological Significance and Therapeutic Implications. Cells 2024, 13, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ijaz, S.; Iqbal, J.; Abbasi, B.A.; Tufail, A.; Yaseen, T.; Uddin, S.; Usman, K.; Ullah, R.; Bibi, H.; Inam, P.; et al. Current stage of preclinical and clinical development of guggulsterone in cancers: Challenges and promises. Cell Biol. Int. 2024, 48, 128–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Zhu, H.; Huang, R.; Yan, B.; Xu, B.; Shi, Y.; Mao, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J. Roles of Cyt-c/Caspase-9/Caspase-3/Bax/Bcl-2 pathway in Cd-induced testicular injury in rats and the protective effect of quercetin. Toxicon 2024, 237, 107561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czabotar, P.E.; Garcia-Saez, A.J. Mechanisms of BCL-2 family proteins in mitochondrial apoptosis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 24, 732–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hu, G.; Guo, H.; Yang, W.; Li, X.; Ni, Y.; He, M.; Ding, P.; Yu, Y. Amino modifications exacerbate the developmental abnormalities of polystyrene microplastics via mitochondria-mediated apoptosis pathway in zebrafish larvae. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 958, 178031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umamaheswari, S.; Priyadarshinee, S.; Kadirvelu, K.; Ramesh, M. Polystyrene microplastics induce apoptosis via ROS-mediated p53 signaling pathway in zebrafish. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2021, 345, 109550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Lu, G.; Zhou, R.; Ma, Y. Thiacloprid-induced hepatotoxicity in zebrafish: Activation of the extrinsic and intrinsic apoptosis pathways regulated by p53 signaling pathway. Aquat. Toxicol. 2022, 246, 106147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Félix, L.M.; Vidal, A.M.; Serafim, C.; Valentim, A.M.; Antunes, L.M.; Monteiro, S.M.; Matos, M.; Coimbra, A.M. Ketamine induction of p53-dependent apoptosis and oxidative stress in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. Chemosphere 2018, 201, 730–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.-J.; Li, X.; Xu, Z.-Q.; Fang, K.-M.; Hong, H.-C.; Sun, H.-J.; Guan, D.-X.; Yu, X.-W. Environmentally relevant concentrations of arsenic induces apoptosis in the early life stage of zebrafish. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 227, 112883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Yao, X.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, J.; Liu, G.; Li, X.; Wang, C.; Yang, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhu, L.; et al. Environmentally relevant concentrations of butyl benzyl phthalate triggered oxidative stress and apoptosis in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio) liver: Combined analysis at physiological and molecular levels. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 160109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene Name | Forward Primer (5′–3′) | Reverse Primer (5′–3′) |
|---|---|---|
| β-actin | CGAGCAGGAGATGGGAACC | CAACGGAAACGCTCATTGC |
| Bax | GGCTATTTCAACCAGGGTTCC | TGCGAATCACCAATGCTGT |
| p53 | GGGCAATCAGCGAGCAAA | ACTGACCTTCCTGAGTCTCCA |
| Caspase-3 | CCGCTGCCCATCACTA | ATCCTTTCACGACCATCT |
| Caspase-9 | AAATACATAGCAAGGCACC | CACAGGGAATCAAGAAAGG |
| Bcl-2 | TCACTCGTTCAGACCCTCAT | ACGCTTTCCACGCACAT |
| Malformation Percentage | Control | 15 mg/L PFOS | OBS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 mg/L | 20 mg/L | 25 mg/L | |||
| Yolk sac edema | 1.1 ± 1.1 | 12.2 ± 1.1 | 1.1 ± 1.1 | 1.1 ± 1.1 | 3.3 ± 1.9 |
| Pericardial edema | 0 | 6.7 ± 1.9 | 0 | 2.2 ± 1.1 | 1.1 ± 1.1 |
| Spinal curvature | 0 | 70 ± 1.9 | 3.3 ± 1.9 | 4.4 ± 1.1 | 6.7 ± 3.8 |
| Total | 1.1 ± 1.1 | 88.9 ± 2.2 | 4.4 ± 1.1 | 7.8 ± 1.1 | 11.1 ± 2.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zou, Y.; Huang, X.; Wang, X.; Xu, M.; Sun, Y. Sodium p-Perfluorous Nonenoxybenzene Sulfonate (OBS) Induces Developmental Toxicity Through Apoptosis in Developing Zebrafish Embryos: A Comparison with Perfluorooctane Sulfonate. Water 2025, 17, 2450. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162450
Zou Y, Huang X, Wang X, Xu M, Sun Y. Sodium p-Perfluorous Nonenoxybenzene Sulfonate (OBS) Induces Developmental Toxicity Through Apoptosis in Developing Zebrafish Embryos: A Comparison with Perfluorooctane Sulfonate. Water. 2025; 17(16):2450. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162450
Chicago/Turabian StyleZou, Yilong, Xueping Huang, Xianglian Wang, Manqing Xu, and Yong Sun. 2025. "Sodium p-Perfluorous Nonenoxybenzene Sulfonate (OBS) Induces Developmental Toxicity Through Apoptosis in Developing Zebrafish Embryos: A Comparison with Perfluorooctane Sulfonate" Water 17, no. 16: 2450. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162450
APA StyleZou, Y., Huang, X., Wang, X., Xu, M., & Sun, Y. (2025). Sodium p-Perfluorous Nonenoxybenzene Sulfonate (OBS) Induces Developmental Toxicity Through Apoptosis in Developing Zebrafish Embryos: A Comparison with Perfluorooctane Sulfonate. Water, 17(16), 2450. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162450




