Could the Presence of Ferrihydrite in a Riverbed Impacted by Mining Leachates Be Linked to a Reduction in Contamination and Health Indexes?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
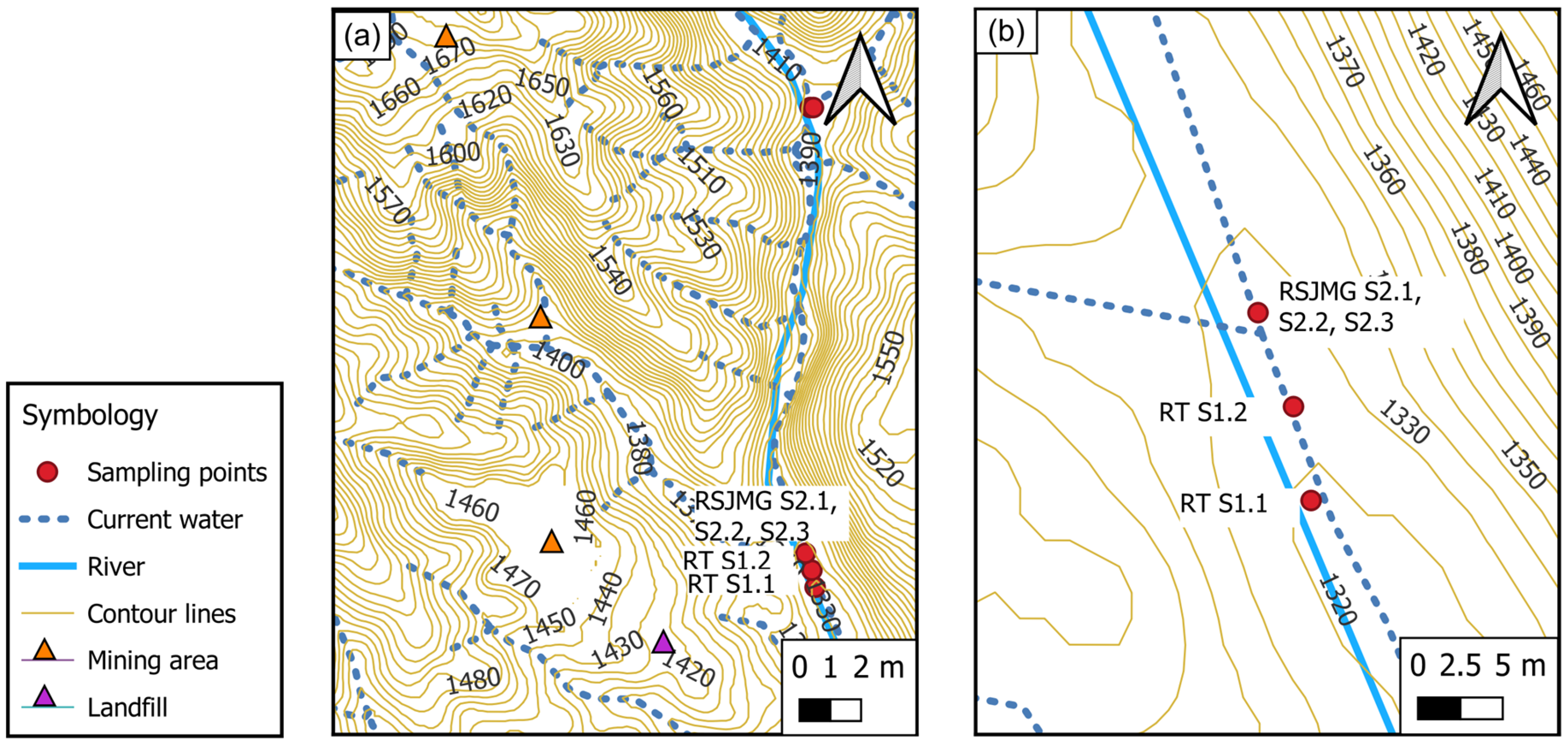
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Analysis of Physicochemical Parameters of Water Samples
2.3. Digestion of the Sample
2.4. Elemental Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Pollution Index
| Element | Permissible Standard Concentration (mg/L) |
|---|---|
| As | 0.025 |
| Cr | 0.05 |
| Ni | 0.07 |
| Zn | 5 |
| Fe | 0.3 |
| Mn | 0.15 |
| Cu | 2 |
| Cd | 0.005 |
| Pb | 0.01 |
2.7. Health Risk Assessment
Chronic Daily Intake
2.8. Non-Carcinogenic Risk
2.8.1. Risk Quotient for Ingestion and Dermal Route
2.8.2. Hazard Index
2.9. Carcinogenic Risk Index
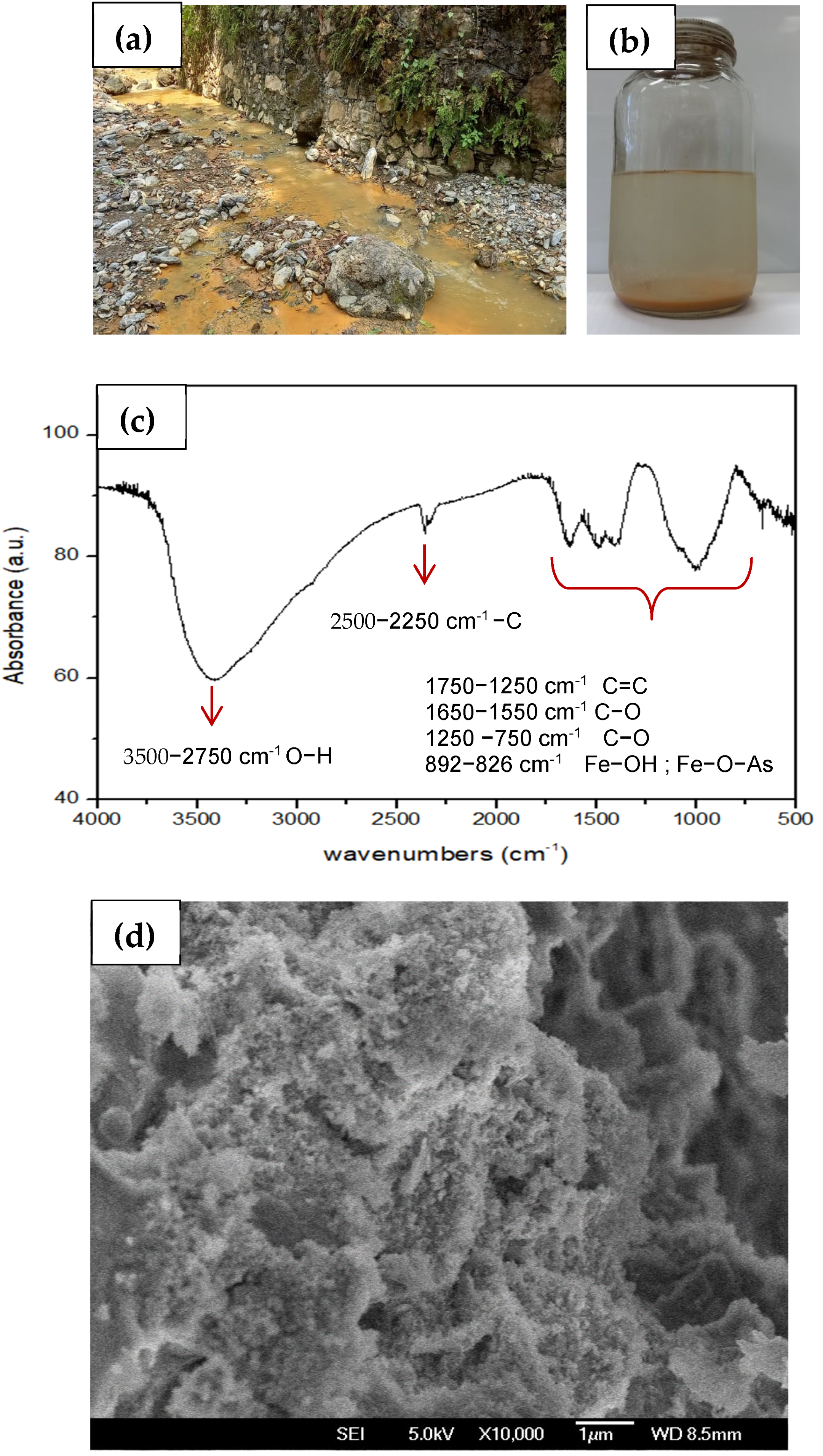
2.10. Analysis of Sedimented Solids in the Sampled Water from Point RSJMG S2.3
2.10.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy of Sediment
2.10.2. Fourier Transformation Infrared Spectroscopy
3. Results
3.1. Analyses of Physicochemical Parameters of River Water Samples
3.2. Analysis of Elements
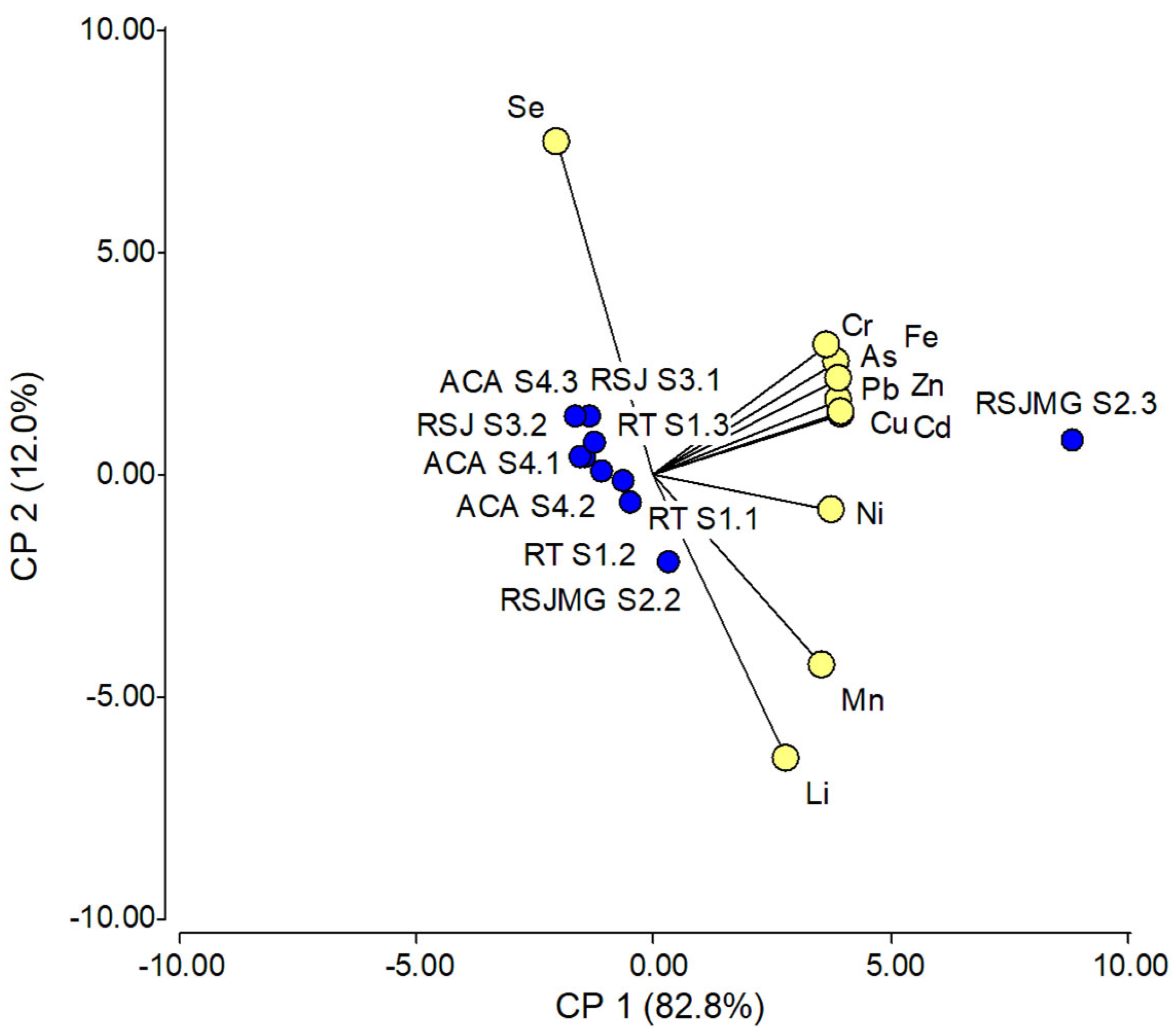
3.3. Principal Component Analysis
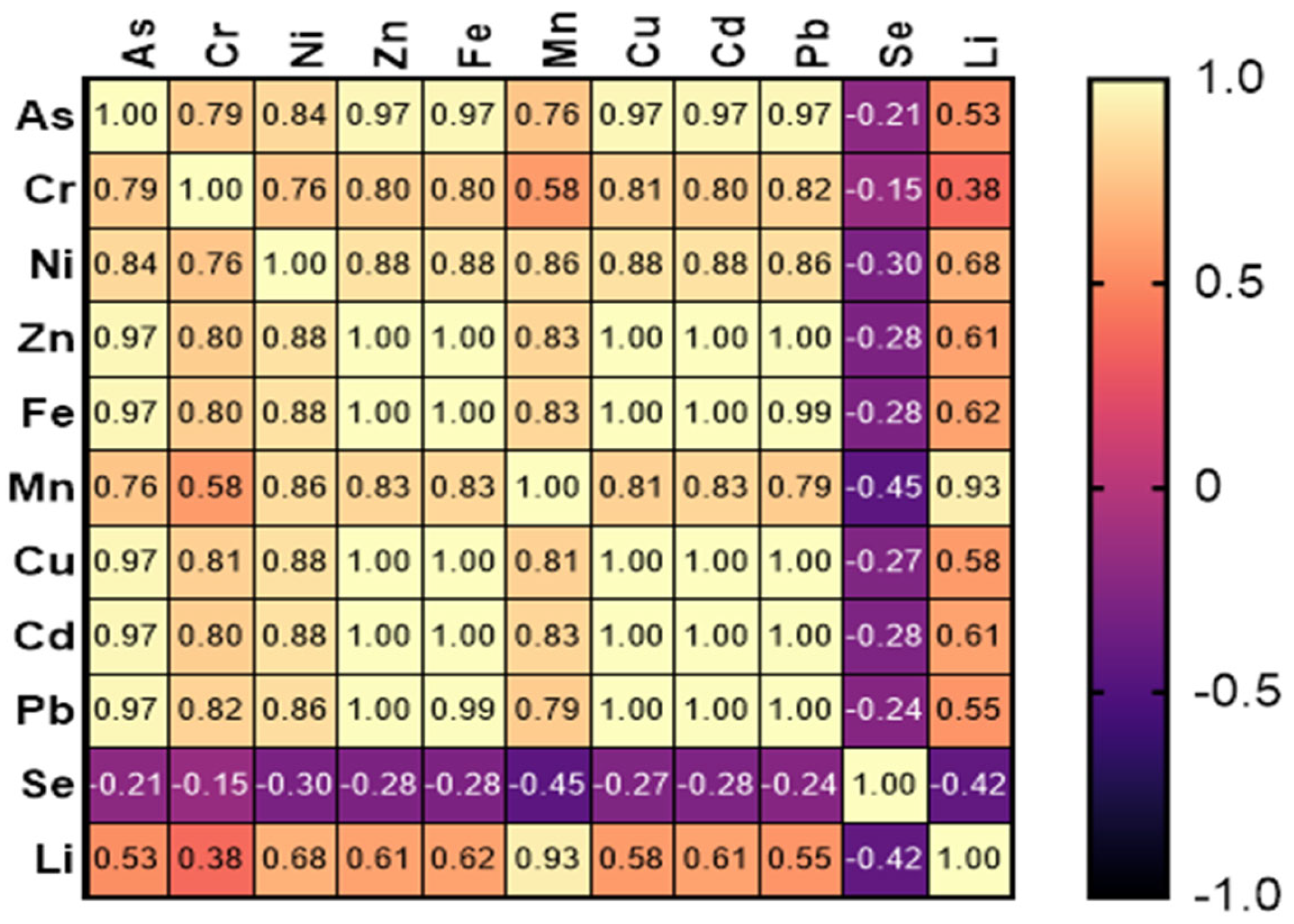
3.4. Pearson’s Correlation
3.5. Pollution Index
3.6. Chronic Daily Intake
3.7. Risk Quotient for Oral and Dermal Ingestion
3.8. Hazard Index
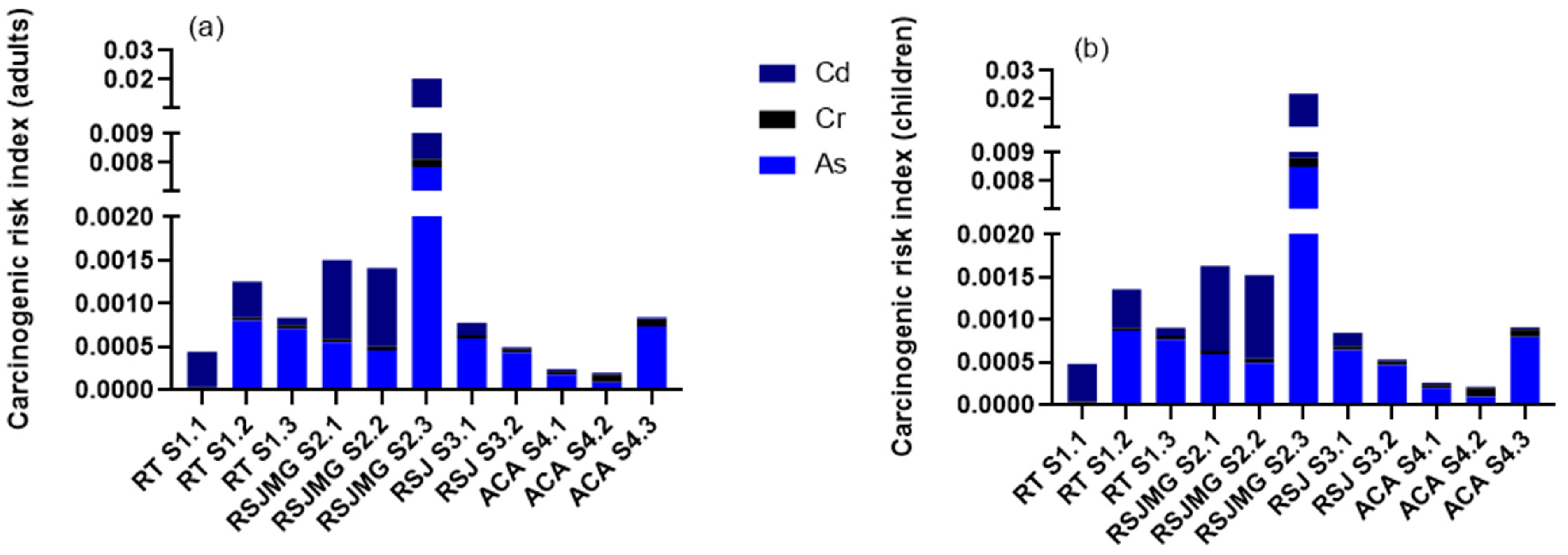
3.9. Carcinogenic Risk Index
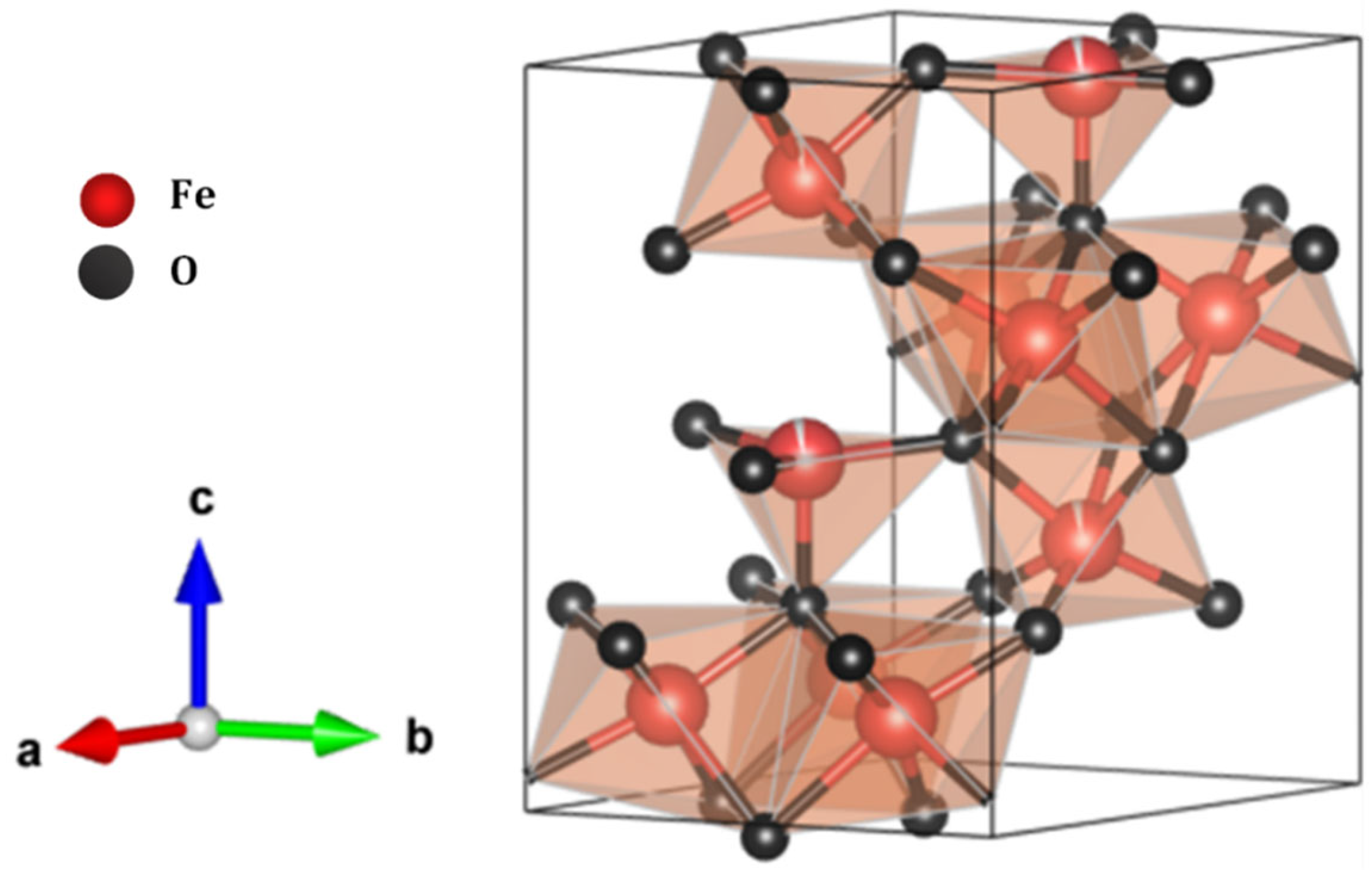
3.10. Analysis of Solids in Leachate-Contaminated Water and Proposal for PTE Reduction Through Ferrihydrite Generation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zamora-Ledezma, C.; Negrete-Bolagay, D.; Figueroa, F.; Zamora-Ledezma, E.; Ni, M.; Alexis, F.; Guerrero, V.H. Heavy metal water pollution: A fresh look about hazards, novel and conventional remediation methods. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 22, 101504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issac, M.N.; Kandasubramanian, B. Effect of microplastics in water and aquatic systems. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 19544–19562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, M.K.; Shahriar, A.; Ullah Jim, K. Water pollution in Bangladesh and its impact on public health. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomaszewska, B.; Akkurt, G.G.; Kaczmarczyk, M.; Bujakowski, W.; Keles, N.; Jarma, Y.A.; Baba, A.; Bryjak, M.; Kabay, N. Utilization of renewable energy sources in desalination of geothermal water for agriculture. Desalination 2021, 513, 115151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikiru, S.; Abiodun, O.J.A.; Sanusi, Y.K.; Sikiru, Y.A.; Soleimani, H.; Yekeen, N.; Haslija, A.B.A. A comprehensive review on nanotechnology application in wastewater treatment a case study of metal-based using green synthesis. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Nord, N.B.; Bester, K.; Vollertsen, J. Microplastics removal from treated wastewater by a biofilter. Water 2020, 12, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hama Aziz, K.H.; Mustafa, F.S.; Omer, K.M.; Hama, S.; Hamarawf, R.F.; Rahman, K.O. Heavy metal pollution in the aquatic environment: Efficient and low-cost removal approaches to eliminate their toxicity: A review. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 17595–17610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nnaji, N.D.; Onyeaka, H.; Miri, T.; Ugwa, C. Bioaccumulation for heavy metal removal: A review. SN Appl. Sci. 2023, 5, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyoti, D.; Sinha, R.; Faggio, C. Advances in biological methods for the sequestration of heavy metals from water bodies: A review. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 94, 103927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Barceló, D.; Clougherty, R.J.; Gao, B.; Harms, H.; Tefsen, B.; Vithanage, M.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Wells, M. “Potentially toxic element”—Something that means everything means nothing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 11922–11925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieder, R.; Benbi, D.K. Potentially toxic elements in the environment—A review of sources, sinks, pathways and mitigation measures. Rev. Environ. Health 2023, 39, 561–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón-Segura, M.E.; Ramírez-Guzmán, A.; Talavera-Mendoza, O.; Carbajal-López, Y.; Martínez-Valenzuela, M.C.; Mora-Herrera, M.E.; Salinas-Alcántara, L.; Hurtado-Brito, P. Genotoxic biomonitoring in children living near the El Fraile mine tailings in northern Guerrero State, Mexico. Toxics 2022, 10, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovar-Sánchez, E.; Cervantes-Ramírez, T.; Castañeda-Bautista, J.; Gómez-Arroyo, S.; Ortiz-Hernández, L.; Sánchez-Salinas, E.; Mussali-Galante, P. Response of Zea mays to multimetal contaminated soils: A multibiomarker approach. Ecotoxicology 2018, 27, 1161–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landin-Sandoval, V.J.; Mendoza-Castillo, D.I.; Bonilla-Petriciolet, A.; Aguayo-Villarreal, I.A.; Reynel-Avila, H.E.; Gonzalez-Ponce, H.A. Valorization of agri-food industry wastes to prepare adsorbents for heavy metal removal from water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, J.; Del Sol Hernández Bernal, M.; Rodríguez, N.P.; Goguitchaichvili, A. Magnetic susceptibility prospecting and Geochemical Characterization of Taxco’s Mining Waste Dam Guerrero I (Mexico). Quaternary 2023, 6, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, S.; De la Rosa, J.D.; De la Campa, A.M.S.; González-Castanedo, Y.; Fernández-Caliani, J.C.; Gonzalez, I.; Romero, A. Contribution of mine wastes to atmospheric metal deposition in the surrounding area of an abandoned heavily polluted mining district (Rio Tinto mines, Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 449, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetter, C.W.; Boving, T.; Kreamer, D. Contaminant Hydrogeology, 3rd ed.; Waveland Press, Inc.: Long Grove, IL, USA, 2018; Available online: https://books.google.com.mx/books?hl=es&lr=&id=ZXE8DwAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PR1&ots=RCSYdENYum&sig=FBwJ4hHgaKu53BL_zPGs13IWvBo&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q&f=false (accessed on 15 June 2023).
- Liu, J.; Hou, K.; Tao, W.; Li, H.; He, D.; Ma, L.; Tang, H.; Wu, S.; Yang, K.; Li, X. A spatial distribution—Principal component analysis (SD-PCA) model to assess pollution of heavy metals in soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 859, 160112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aparicio, E.M. The risks of mining pollution and its impact on children. Thinkazos 2009, 12, 83–101. Available online: http://www.scielo.org.bo/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1990-74512009000200005 (accessed on 3 April 2023).
- Saldaña-Villanueva, K.; Pérez-Vázquez, F.J.; Ávila-García, I.P.; Méndez-Rodríguez, K.B.; Carrizalez-Yáñez, L.; Gavilán-García, A.; Vargas-Morales, J.M.; Van-Brussel, E.; Diaz-Barriga, F. A preliminary study on health impacts of Mexican mercury mining workers in a context of precarious employment. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2022, 71, 126925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archundia, D.; Prado-Pano, B.; Molina-Freaner, F. Potentially toxic elements in soil–plant–water-animal continuum in a mining area from Northwestern Mexico: Animal exposure pathways and health risks for children. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 46, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Bernal, J.M.; Ruiz-Huerta, E.A.; Armienta-Hernández, M.A.; Luna-Pabello, V.M. Evaluation of the removal of heavy metals in a natural wetland impacted by mining activities in Mexico. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa Gomez, D.; Sáez Salgado, E.; Mejías, O.; Pat-Espadas, A.M.; Pinedo Torres, L.A.; Jackson, L.; Parbhakar-Fox, A. Data integration of Critical Elements from mine waste in Mexico, Chile and Australia. Minerals 2022, 12, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-Ramírez, M.; Armienta-Hernández, M.A. Distribución de Fe, Zn, Pb, Cu, Cd y As originada por residuos mineros y aguas residuales en un transecto del Río Taxco en Guerrero. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Geológicas 2012, 29, 450–462. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, M.M.; Runkel, R.L.; McKnight, D.M. To Remediate or not? source identification in an acid mine drainage stream, Warden Gulch, Colorado. Mine Water Environ. 2023, 42, 383–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Liang, J.L.; Su, J.Q.; Jia, P.; Lu, J.L.; Zheng, J.; Wang, Z.; Feng, S.W.; Luo, Z.H.; Ai, H.X.; et al. Globally distributed mining-impacted environments are underexplored hotspots of multidrug resistance genes. ISME J. 2022, 16, 2099–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Yuhua, Z.; Qaidi, S.; Isleem, H.F.; Zaid, O.; Althoey, F.; Ahmad, J. Mine tailings-based geopolymers: A comprehensive review. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 24192–24212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Montoya, G.; Talavera-Mendoza, O.; Hernández-Flores, G.; Díaz-Villaseñor, E.; Ramírez-Guzmán, A.H.; Galarza-Brito, Z. Potentially toxic elements determination and chemical-microbiological analysis of potable water in Taxco de Alarcón, Guerrero. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Geológicas 2019, 36, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quevedo-Castañon, N.M.; Talavera-Mendoza, O.; Ramírez-Guzmán, A.H.; Dótor-Almazán, A.; Chávez-González, J.D.; Sampedro-Rosas, M.L.; Rosas-Acevedo, J.L. Fraccionamiento geoquímico de elementos potencialmente tóxicos en los jales mineros del Depósito Guerrero I de Taxco de Alarcón, Guerrero, México. Tlamati 2019, 10, 5–21. [Google Scholar]
- Pi-Puig, T.; Solé, J.; Gómez Cruz, A. Mineralogical study and genetic model of efflorescent salts and crusts from two abandoned tailings in the Taxco Mining District, Guerrero (Mexico). Minerals 2020, 10, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dótor Almazán, A.; Armienta Hernández, M.A.; Árcega Cabrera, F.; Talavera Mendoza, O. Procesos de transporte de arsénico y metales en aguas superficiales del distrito minero de Taxco, México: Aplicación de isótopos estables. Hidrobiológica 2014, 24, 245–256. [Google Scholar]
- Espinoza, E.; Armienta, M.A. Mobility and fractionation of Fe, Pb and Zn in river sediments from a silver and base-metals mining area: Taxco, México. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2007, 42, 1391–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ai, Y.; Zhou, J.; Xu, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Zhou, S. Effects of biochar on heavy metal speciation and microbial activity in red soil at a mining area. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 13491–13502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Chauhan, S.; Varjani, S.; Pandey, A.; Bhargava, P.C. Integrated approaches to mitigate threats from emerging potentially toxic elements: A way forward for sustainable environmental management. Environ. Res. 2022, 209, 112844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, V.H.T.; Kim, J.; Chang, S.; Chung, W. Bacterial biosorbents, an efficient heavy metals green clean-up strategy: Prospects, Challenges, and Opportunities. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Mendoza, A.G.; Flores-Trujillo, A.K.I.; Ramírez-Castillo, J.A.; Gallardo-Hernández, S.; Rodríguez-Vázquez, R. Effect of micro-nanobubbles on arsenic removal by Trichoderma atroviride for bioscorodite generation. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Osman, A.I.; Rooney, D.W.; Oh, W.; Yap, P. Remediation of heavy metals in polluted water by immobilized algae: Current Applications and Future Perspectives. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Trujillo, A.K.I.; Morales-Mendoza, A.G.; Rodríguez-Vázquez, R. Behavior of a mixture of metals for competiting adsorption sites of untreated and alkali-treated rice husk. Processes 2024, 12, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafique, M.; Hajra, S.; Tahir, M.B.; Gillani, S.S.A.; Irshad, M. A review on sources of heavy metals, their toxicity and removal technique using physico-chemical processes from wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 16772–16781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Gu, C.; Hong, Y.; Feng, X.; Zhu, M.; Wang, M.; Tan, W.; Wang, X. Fraction distribution of heavy metals and its relationship with iron in polluted farmland soils around distinct mining areas. Appl. Geochem. 2021, 130, 104969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, M.; Pacheco, J.S.L.; Noël, V.; Boye, K.; Fendorf, S. Organic compounds alter the preference and rates of heavy metal adsorption on ferrihydrite. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 750, 141485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ThomasArrigo, L.K.; Kaegi, R.; Kretzschmar, R. Ferrihydrite growth and transformation in the presence of ferrous iron and model organic ligands. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 13636–13647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheinost, A.C.; Abend, S.; Pandya, K.I.; Sparks, D.L. Kinetic controls on Cu and Pb sorption by ferrihydrite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 1090–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, K.H.; ThomasArrigo, L.K.; Kaegi, R.; Kretzschmar, R. Stabilization of ferrihydrite and lepidocrocite by silicate during Fe(II)-catalyzed mineral transformation: Impact on Particle Morphology and Silicate Distribution. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 5929–5938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Xie, Z.; Yang, Y.; Gao, B.; Wang, J. Effects of calcium on arsenate adsorption and arsenate/iron bioreduction of ferrihydrite in stimulated groundwater. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, M.; Min, X.; Ke, Y.; Lin, Z.; Yang, Z.; Wang, S.; Peng, N.; Yan, X.; Luo, S.; Wu, J.; et al. Recent progress in understanding the mechanism of heavy metals retention by iron (oxyhydr) oxides. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 141930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.O.; Liu, H.; Chu, Z.; Chen, T.; Zou, X.; Chen, D.; Zhang, X.; Hu, J. Adsorption of lead by kaolinite, montmorillonite, goethite and ferrihydrite: Performance and mechanisms based on quantitative analysis. Clay Miner. 2022, 57, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Xie, Q.; Chai, G.; Li, G. Simultaneous adsorption of As(III) and Cd(II) by ferrihydrite-modified biochar in aqueous solution and their mutual effects. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, Q.; Li, R.; Shen, N.; Li, J.; Shen, J.; Sun, X.; Han, W. Enhanced sequestration of chelated Cr (III) from aqueous by Al-containing ferrihydrite: New expectation of overall removal of various heavy metal complexes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 282, 120151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, K.; Wu, X.; Zhang, X.; Su, S.; Huang, Z.; Min, X.; Liu, Y.; Fang, M. Efficient adsorption of the Cd (II) and As (V) using novel adsorbent ferrihydrite/manganese dioxide composites. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 18627–18636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Wang, H.; Liu, H.; Yang, C.; Wei, Y.; Hou, D. Evaluation of the ability of ferrihydrite to bind heavy metal ions: Based on formation environment, adsorption reversibility and ageing. Appl. Geochem. 2014, 45, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association (APHA). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 22nd ed.; Rice, E.W., Baird, R.B., Eaton, A.D., Clesceri, L.S., Eds.; American Water Works Association (AWWA) and Water Environment Federation (WEF): Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, V.; Sharma, A.; Kumar, R.; Bhardwaj, R.; Thukral, A.K.; Rodrigo-Comino, J. Assessment of heavy-metal pollution in three different Indian water bodies by combination of multivariate analysis and water pollution indices. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2018, 26, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldovan, A.; Török, A.I.; Kovacs, E.; Cadar, O.; Mirea, I.C.; Micle, V. Metal contents and pollution indices assessment of surface water, soil, and sediment from the Arieș River Basin Mining Area, Romania. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, S.V.; Nithila, P.; Reddy, S.J. Estimation of heavy metals in drinking water and development of heavy metal pollution index. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A Environ. Sci. Eng. Toxicol. 1996, 31, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOM-127-SSA1-2021; Agua para uUo y Consumo Humano. Límites Permisibles de la Calidad del Agua. Norma Oficial Mexicana. Secretaría de Salud (SSA): Mexico City, Mexico, 2021.
- Zakir, H.M.; Sharmin, S.; Akter, A.; Rahman, M.S. Assessment of health risk of heavy metals and water quality indices for irrigation and drinking suitability of waters: A case study of Jamalpur Sadar area, Bangladesh. Environ. Adv. 2020, 2, 100005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salcedo Sánchez, E.R.; Martínez, J.M.E.; Morales, M.M.; Talavera Mendoza, O.; Alberich, M.V.E. Ecological and health risk assessment of potential toxic elements from a mining area (water and sediments): The San Juan-Taxco River System, Guerrero, Mexico. Water 2022, 14, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Arsenic, Inorganic (CASRN 7440-38-2); Integrated Risk Information System (IRIS); U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1991. Available online: https://iris.epa.gov/ (accessed on 19 May 2025).
- Tashakor, M.; Modabberi, S. Human health risks associated with potentially harmful elements from urban soils of Hamedan City, Iran. Pollution 2021, 7, 709–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Chromium VI (CASRN 18540-29-9); IRIS; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Nickel, Soluble Salts (CASRN 7440-02-0); IRIS; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Zinc (CASRN 7440-66-6); IRIS; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Iron in Drinking-Water: Background Document for Development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001; Available online: https://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/dwq/chemicals/iron.pdf (accessed on 19 May 2025).
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Manganese (CASRN 7439-96-5); IRIS; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Faiz, Y.; Siddique, N.; Tufail, M. Pollution level and health risk assessment of road dust from an expressway. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2012, 47, 818–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Copper (CASRN 7440-50-8); IRIS; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Cadmium; IRIS; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Integrated Science Assessment for Lead (EPA/600/R-10/075F); U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Selenium; IRIS; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Selenium; IRIS; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Saleh, H.N.; Panahande, M.; Yousefi, M.; Asghari, F.B.; Oliveri Conti, G.; Talaee, E.; Mohammadi, A.A. Carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic risk assessment of heavy metals in groundwater wells in Neyshabur Plain, Iran. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2019, 190, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Toxicological Review of Inorganic arsenic (CAS No. 7440-38-2) in Support of Summary Information on the Integrated Risk Information System (IRIS); U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. Available online: https://iris.epa.gov/ChemicalLanding/&substance_nmbr=0278 (accessed on 19 May 2025).
- Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment (OEHHA). Public Health Goal for Cadmium in Drinking Water; California Environmental Protection Agency: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2001. Available online: https://oehha.ca.gov/water/chemicals/cadmium (accessed on 19 May 2025).
- Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment (OEHHA). Public Health Goal for Hexavalent Chromium in Drinking Water; California Environmental Protection Agency: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2001. Available online: https://oehha.ca.gov/water/chemicals/hexavalent-chromium-cr-vi (accessed on 19 May 2025).
- Aendo, P.; Netvichian, R.; Thiendedsakul, P.; Khaodhiar, S.; Tulayakul, P. Carcinogenic risk of Pb, Cd, Ni, and Cr and critical ecological risk of Cd and Cu in soil and groundwater around the municipal solid waste open dump in central Thailand. J. Environ. Public Health 2022, 1, 3062215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secretaría de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales (SEMARNAT). Norma Oficial Mexicana, NOM-001-SEMARNAT-2021, Que Establece los Límites Permisibles de Contaminantes en las Descargas de Aguas Residuales en Cuerpos Receptores Propiedad de la Nación; Secretaría de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales: Mexico City, Mexico, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- United States Environmental Protection Ambiental (USEPA). Water: Monitoring & Assessment. 2012. Available online: https://archive.epa.gov/water/archive/web/html/vms59.html (accessed on 19 May 2025).
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed.; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; Available online: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/254637/9789241549950-eng.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 14 November 2024).
- Wei, Q.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, T.; Farooq, U.; Chen, W.; Qi, Z. Insight into the effect of phosphate on ferrihydrite colloid-mediated transport of tetracycline in saturated porous media. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 80693–80704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tsang, Y.F.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, D.; Pan, X. Adsorption capacities of poorly crystalline Fe minerals for antimonate and arsenate removal from water: Adsorption properties and effects of environmental and chemical conditions. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2018, 20, 2169–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, C.; Palumbo, G.; Sellitto, V.M.; Rizzardo, C.; Tomasi, N.; Pinton, R.; Cesco, S. Characteristics of insoluble, high molecular weight iron-humic substances used as plant iron sources. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2012, 76, 1246–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Xu, L.; Wang, X.; Demopoulos, G.P. Infrared spectroscopic and X-ray diffraction characterization of the nature of adsorbed arsenate on ferrihydrite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2007, 71, 1643–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, X.; Qi, X.; Shu, B.; Zhang, X.; Li, K.; Wei, Y.; Wang, H. Removal and immobilization of arsenic from copper smelting wastewater using copper slag by in situ encapsulation with silica gel. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 394, 124833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, P.; Pichler, T. Competitive adsorption of As(III) and As(V) by ferrihydrite: Equilibrium, kinetics, and surface complexation. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvertstein, R.; Bassler, C.; Morrill, T. Spectrometric Identification of Organic Compounds, 4th ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Rong, Z.; Tang, X.; Wu, L.; Chen, X.; Dang, W. A novel method to synthesize scorodite using ferrihydrite and its role in removal and immobilization of arsenic. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 5848–5857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazacu, N.; Chilom, C.G.; Iftimie, S.; Bălășoiu, M.; Ladygina, V.P.; Stolyar, S.V.; Orelovich, O.L.; Kovalev, Y.S.; Rogachev, A.V. Biogenic ferrihydrite nanoparticles produced by Klebsiella oxytoca: Characterization, physicochemical properties and bovine serum albumin interactions. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Huerta, E.A.; Armienta-Hernández, M.A.; Dubrovsky, J.G.; Gómez-Bernal, J.M. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals and As in maize (Zea mays L.) grown close to mine tailings strongly impacts plant development. Ecotoxicology 2022, 31, 447–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashmi, I.; Roy, T.; Kartika, K.S.; Pal, R.; Coumar, V.; Kala, S.; Shinoji, K.C. Organic and Inorganic Fertilizer Contaminants in Agriculture: Impact on Soil and Water Resources; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 3–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, Q.; Asif, M.; Shaheen, S.; Hayat, M.T.; Ali, S. Cadmium Contamination in Water and Soil. In Cadmium Toxicity and Tolerance in Plants; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 141–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Ambiental (USEPA). National Primary Drinking Water Regulations; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/ground-water-and-drinking-water/national-primary-drinking-water-regulations (accessed on 14 November 2024).
- USGS. Mineral Commodity Summaries, Lithium. 2022. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/periodicals/mcs2022/mcs2022-lithium.pdf (accessed on 10 October 2024).
- Tanveer, M.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Wang, L. Lithium in environment and potential targets to reduce lithium toxicity in plants. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2019, 38, 1574–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakoor, N.; Adeel, M.; Azeem, I.; Ahmad, M.A.; Zain, M.; Abbas, A.; Hussain, M.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, P.; Li, Y.; et al. Interplay of higher plants with lithium pollution: Global trends, meta-analysis, and perspectives. Chemosphere 2023, 310, 136663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Peng, S.; Pei, L.; Zhou, K.; Wang, X. Integrated analysis of pollution characteristic and ecotoxicological effect reveals the fate of lithium in soil-plant systems: A Challenge to global sustainability. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 15755–15765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Harrison, F.E.; Aschner, M.; Bowman, A.B. Exposing the role of metals in neurological disorders: A focus on manganese. Trends Mol. Med. 2022, 28, 555–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, S.; Tripathy, B.; Kumar, M.S.; Das, A.P. Ecotoxicological consequences of manganese mining pollutants and their biological remediation. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2023, 5, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindner, S.; Lucchini, R.; Broberg, K. Genetics and epigenetics of manganese toxicity. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2022, 9, 697–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Mishra, S.; Sahu, H. A review of activated carbon to counteract the effect of iron toxicity on the environment. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2023, 5, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Zuo, R.; Teng, Y.; Ai, Y.; Yang, J. Influences of dissolved humic acid on Zn bioavailability and its consequences for thyroid toxicity. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 166, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Xi, S. The effects of heavy metals on human metabolism. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2019, 30, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Chakraborty, A.J.; Tareq, A.M.; Emran, T.B.; Nainu, F.; Khusro, A.; Idris, A.M.; Khandaker, M.U.; Osman, H.; Alhumaydhi, F.A.; et al. Impact of heavy metals on the environment and human health: Novel therapeutic insights to counter the toxicity. J. King Saud Univ. Sci./Maǧallaẗ Ǧāmiʹaẗ Al-Malik Saʹūd. Al-ʹUlūm 2022, 34, 101865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, W.; Alharthy, R.D.; Zubair, M.; Ahmed, M.; Hameed, A.; Rafique, S. Toxic and heavy metals contamination assessment in soil and water to evaluate human health risk. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Gupta, S.K. Application of Monte Carlo simulation for carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic risks assessment through multi-exposure pathways of heavy metals of river water and sediment, India. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 3465–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briffa, J.; Sinagra, E.; Blundell, R. Heavy metal pollution in the environment and their toxicological effects on humans. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, K.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Kim, K. Concentration, source, and total health risks of cadmium in multiple media in densely populated areas, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Garkal, A.; Sarode, L.; Bangar, P.; Mehta, T.; Singh, D.P.; Rawal, R. Understanding arsenic toxicity: Implications for environmental exposure and human health. J. Hazard. Mater. Lett. 2023, 5, 100090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossini, H.; Shafie, B.; Niri, A.D.; Nazari, M.; Esfahlan, A.J.; Ahmadpour, M.; Nazmara, Z.; Ahmadimanesh, M.; Makhdoumi, P.; Mirzaei, N.; et al. A comprehensive review on human health effects of chromium: Insights on induced toxicity. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 70686–70705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, M.; Anand, U.; Thiruvenkataswamy, S.; Babu, H.W.S.; Narayanasamy, A.; Prajapati, V.K.; Tiwari, C.K.; Gopalakrishnan, A.V.; Bontempi, E.; Sonne, C.; et al. A review of chromium (Cr) epigenetic toxicity and health hazards. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 882, 163483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirzaman, A.T.; Ebrahimi, P.; Niknezhad, S.; Vahidi, T.; Hosseinzadeh, D.; Akrami, S.; Ashrafi, A.M.; Velayatimehr, M.M.; Hosseinzadeh, R.; Kazemi, S. Toxic mechanisms of cadmium and exposure as a risk factor for oral and gastrointestinal carcinomas. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2023, 42, 9603271231210262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genchi, G.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Lauria, G.; Carocci, A.; Catalano, A. The Effects of Cadmium Toxicity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, M.; Itoh, H.; Sawada, N.; Tsugane, S. Exposure to environmental chemicals and cancer risk: Epidemiological evidence from Japanese studies. Genes Environ. 2023, 45, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, D.; Nabi, F.; Kama, R.; Li, S.; Wang, W.; Guo, Y.; Li, Z.M.; Li, H. The interaction between ferrihydrite and arsenic: A review of environmental behavior, mechanism and applied in remediation. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2024, 13, 100398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jambor, J.L.; Dutrizac, J.E. Occurrence and constitution of natural and synthetic ferrihydrite, a widespread iron oxyhydroxide. Chem. Rev. 1998, 98, 2549–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, P.; Singh, P.C.; Mishra, A.; Chauhan, P.S.; Dwivedi, S.; Bais, R.T.; Tripathi, R.D. Trichoderma: A potential bioremediator for environmental clean up. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2013, 15, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, P.K.; Vaish, A.; Dwivedi, S.; Chakrabarty, D.; Singh, N.; Tripathi, R.D. Biological removal of arsenic pollution by soil fungi. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 2430–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granchinho, S.C.R.; Franz, C.M.; Polishchuk, E.; Cullen, W.R.; Reimer, K.J. Transformation of arsenic(V) by the fungus Fusarium oxysporum melonis isolated from the alga Fucus gardneri. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2002, 16, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Qin, Z.; Xiahou, J.; Li, Y.; Yan, Y.; Feng, X.; Li, W.; Lan, S. Effects and mechanisms of Al substitution on the catalytic ability of ferrihydrite for Mn(II) oxidation and the subsequent oxidation and immobilization of coexisting Cr(III). J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 452, 131351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Yang, Z.; Yang, W.; Jiang, W.; Liao, Q.; Si, M.; Zhao, F. Ferrihydrite transformation impacted by coprecipitation of lignin: Inhibition or facilitation? J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 139, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Frandsen, C.; Wallace, A.F.; Legg, B.A.; Khalid, S.; Zhang, H.; Mørup, S.; Banfield, J.F.; Waychunas, G.A. Precipitation pathways for ferrihydrite formation in acidic solutions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2016, 172, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhu, M.; Lan, S.; Ginder-Vogel, M.; Fan, L.; Feng, X. Formation and secondary mineralization of ferrihydrite in the presence of silicate and Mn(II). Chem. Geol. 2015, 415, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weatherill, J.S.; Morris, K.; Bots, P.; Stawski, T.M.; Janssen, A.; Abrahamsen, L.; Blackham, R.; Shaw, S. Ferrihydrite formation: The Role of Fe13 Keggin Clusters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 9333–9342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, F.M.; Ehm, L.; Antao, S.M.; Lee, P.L.; Chupas, P.J.; Liu, G.; Strongin, D.R.; Schoonen, M.A.A.; Phillips, B.L.; Parise, J.B. The structure of ferrihydrite, a nanocrystalline material. Science 2007, 316, 1726–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, H.; Lin, Q.; Su, S.; Wang, Y.; Bai, L.; Wu, C. The effect of the ferrihydrite dissolution/transformation process on mobility of arsenic in soils: Investigated by coupling a two-step sequential extraction with the diffusive gradient in the thin films (DGT) technique. Geoderma 2019, 352, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rancourt, D.; Fortin, D.; Pichler, T.; Thibault, P.; Lamarche, G.; Morris, R.V.; Mercier, P.H.J. Mineralogy of a natural As-rich hydrous ferric oxide coprecipitate formed by mixing of hydrothermal fluid and seawater: Implications regarding surface complexation and color banding in ferrihydrite deposits. Am. Mineral. 2001, 86, 834–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Yao, L.; Lu, Y.; Peng, L.; Wu, P.; Shi, Z. Pb(II) and Cu(II) Adsorption and desorption kinetics on ferrihydrite with different morphologies. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2018, 82, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Tian, L.; Lu, Y.; Peng, L.; Wang, P.; Lin, J.; Cheng, T.; Dang, Z.; Shi, Z. Kinetics of Cd(ii) adsorption and desorption on ferrihydrite: Experiments and modeling. Environmental Science. Process. Impacts 2018, 20, 934–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karapınar, N. Removal of heavy metal ions by ferrihydrite: An opportunity to the treatment of acid mine drainage. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhu, R.; Xu, T.; Xu, Y.; Ge, F.; Xi, Y.; Zhu, J.; He, H. Co-adsorption of phosphate and zinc(II) on the surface of ferrihydrite. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 1148–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vala, A.K. Tolerance and removal of arsenic by a facultative marine fungus Aspergillus candidus. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 2565–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Root, R.A.; Farrell, J.; Ela, W.P.; Chorove, J. Effect of silicic acid on arsenate and arsenite retention mechanisms on 6-L ferrihydrite: A spectroscopic and batch adsorption approach. Appl. Geochem. 2013, 38, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


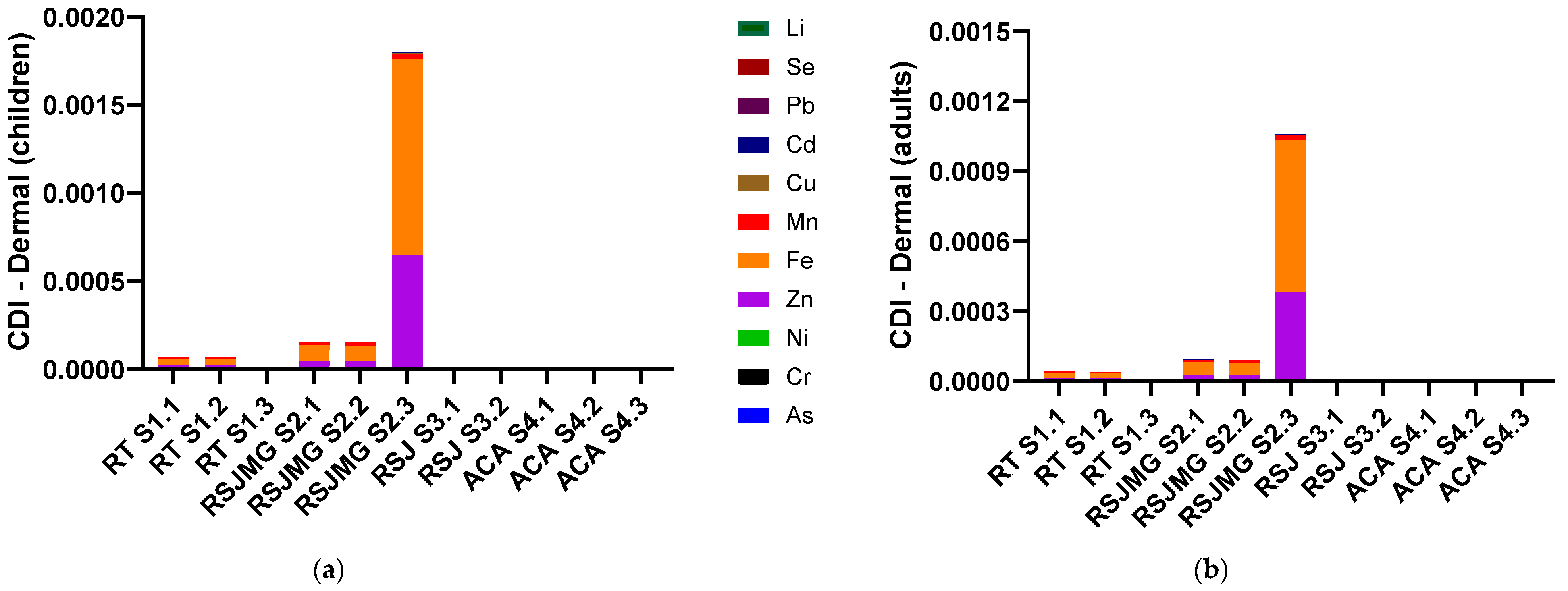

| Parameter | Asigned Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Adults | Children | |
| EC = Concentration of the element in water (mg/L) | ||
| IR = Ingestion rate (L/day) | 2.5 | 0.78 |
| FE = Frequency of exposure (day/year) | 350 | 350 |
| ED = Total duration of exposure (years) | 30 | 6 |
| BW = Average weight (kg) | 52 | 15 |
| AT = Average Exposure Time (Days) | 10,950 | 2190 |
| SA = Skin contact surface area (cm2) | 5700 | 2800 |
| AF = Skin adhesion factor | 0.07 | 0.07 |
| ABDSd = Dermal Adsorption Factor | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| ET = Exposure time (hour/day) | 0.58 | 0.58 |
| CF = Conversion factor (kg/mg) | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Element | Reference Dose (RfD) (mg/Kg·Day) | |
|---|---|---|
| Ingestion | Dermal | |
| As | 0.0003 [59] | 0.000123 [60] |
| Cr | 0.003 [61] | 0.000006 [60] |
| Ni | 0.02 [62] | 0.00540 [60] |
| Zn | 0.3 [63] | 0.06 [60] |
| Fe | 0.7 [64] | 0.14 [58] |
| Mn | 0.14 [65] | 0.00184 [66] |
| Cu | 0.04 [67] | 0.0120 [60] |
| Cd | 0.0005 [68] | 0.00001 [60] |
| Pb | 0.0035 [69] | 0.000525 [60] |
| Se | 0.005 [70] | 0.005 [71] |
| Sample | Temperature (°C) | Electrical Conductivity (μS/cm) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|
| RT S1.1 | 23.2 | 1640 | 7.90 |
| RT S1.2 | 23.7 | 1330 | 7.84 |
| RT S1.3 | 21.9 | 710 | 8.15 |
| RSJMG S2.1 | 25.8 | 2010 | 7.83 |
| RSJMG S2.2 | 25.8 | 2010 | 7.83 |
| RSJMG S2.3 | 25.8 | 2010 | 7.83 |
| RSJ S3.1 | 21.1 | 880 | 7.88 |
| RSJ S3.2 | 24.3 | 750 | 7.34 |
| ACA S4.1 | 23.2 | 1010 | 7.52 |
| ACA S4.2 | 23.4 | 1070 | 7.52 |
| ACA S4.3 | 24.3 | 880 | 7.52 |
| Sample | Element (mg/L) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As | Cr | Ni | Zn | Fe | Mn | Cu | Cd | Pb | Se | Li | |
| RT S1.1 | <L.D ± 0.00 | <L.D ± 0.00 | 0.011 ± 0.004 | 3.396 ± 0.132 | 6.158 ± 0.263 | 1.394 ± 0.038 | 0.026 ± 0.002 | 0.023 ± 0.0005 | 0.002 ± 0.00 | 0.008 ± 0.014 | 0.041 ± 0.001 |
| RT S1.2 | 0.012 ± 0.008 | <L.D ± 0.00 | 0.008 ± 0.002 | 3.216 ± 0.025 | 5.940 ± 0.104 | 1.279 ± 0.012 | 0.021 ± 0.001 | 0.024 ± 0.00 | 0.006 ± 0.001 | 0.014 ± 0.013 | 0.039 ± 0.00 |
| RT S1.3 | 0.010 ± 0.011 | <L.D ± 0.00 | 0.007 ± 0.001 | 0.220 ± 0.009 | 0.326 ± 0.036 | 0.199 ± 0.005 | 0.015 ± 0.008 | 0.005 ± 0.00 | 0.001 ± 0.002 | 0.018 ± 0.015 | 0.015 ± 0.00 |
| RSJMG S2.1 | 0.008 ±0.008 | <L.D ± 0.00 | 0.008 ± 0.005 | 7.651 ± 0.026 | 14.500 ± 0.302 | 2.712 ± 0.011 | 0.045 ± 0.003 | 0.052 ± 0.005 | 0.006 ± 0.002 | <L.D ± 0.00 | 0.080 ± 0.005 |
| RSJMG S2.2 | 0.007 ± 0.008 | 0.001 ± 0.001 | 0.008 ± 0.001 | 7.448 ± 0.565 | 14.190 ± 0.930 | 2.658 ± 0.093 | 0.040 ± 0.002 | 0.052 ± 0.001 | 0.006 ± 0.002 | <L.D ± 0.00 | 0.080 ± 0.002 |
| RSJMG S2.3 | 0.114 ± 0.003 | 0.012 ± 0.002 | 0.024 ± 0.002 | 103.547 ± 6.840 | 178.667 ± 10.351 | 5.097 ± 0.283 | 0.724 ± 0.035 | 0.697 ± 0.043 | 0.242 0.026 | <L.D ± 0.00 | 0.087 ± 0.003 |
| RSJ S3.1 | 0.009 ± 0.006 | <L.D ± 0.00 | 0.002 ± 0.001 | 0.253 ± 0.010 | 0.584 ± 0.688 | 0.008 ± 0.003 | 0.003 ± 0.001 | 0.008 ± 0.005 | 0.005 ± 0.004 | 0.029 ±0.025 | 0.029 ± 0.00 |
| RSJ S3.2 | 0.006 ± 0.007 | <L.D ± 0.00 | 0.002 ± 0.002 | 0.049 ± 0.008 | 0.236 ± 0.268 | 0.002 ± 0.001 | 0.001 ± 0.001 | 0.001 ± 0.00 | 0.002 ± 0.001 | 0.009 ± 0.008 | 0.007 ± 0.00 |
| ACA S4.1 | 0.001 ± 0.002 | 0.003 ± 0.002 | 0.004 ± 0.001 | 0.161 ± 0.027 | 0.721 ± 0.267 | 0.030 ± 0.001 | 0.017 ± 0.005 | 0.001 ± 0.0005 | 0.002 ± 0.005 | 0.005 ± 0.010 | 0.013 ± 0.00 |
| ACA S4.2 | 0.011 ± 0.002 | 0.001 ± 0.002 | 0.004 ± 0.002 | 0.071 ± 0.058 | 1.409 ± 0.498 | 0.037 ± 0.009 | 0.006 ± 0.003 | 0.001 ± 0.001 | 0.001 ± 0.004 | 0.022 ± 0.004 | 0.012 ± 0.001 |
| ACA S4.3 | 0.003 ± 0.007 | 0.002 ± 0.003 | 0.003 ± 0.003 | 0.145 ± 0.024 | 0.453 ± 1.24 | 0.037 ± 0.004 | 0.020 ± 0.002 | 0.001 ± 0.0005 | 0.001 ± 0.001 | 0.011 ± 0.015 | 0.0130 ± 0.00 |
| NOM 127 a | 0.010 | 0.050 | 0.070 | - | 0.300 | 0.150 | 2.000 | 0.003 | 0.010 | 0.04 | - |
| WHO b | 0.010 | 0.050 | 0.070 | - | - | 0.080 | 2 | 0.003 | 0.01 | 0.04 | - |
| USEPA c | 0.010 | 0.100 | 0.100 | 5 | 0.300 | 0.05 | 1.300 | 0.005 | 0.015 | 0.05 | - |
| NOM-001 d | 0.400 | 1.500 | 4.000 | 20 | - | - | 6 | 0.400 | 0.400 | - | - |
| Sample | Pollution Index | Level of Contamination |
|---|---|---|
| RSJMG S2.3 | 8491.56 | H |
| RSJMG S2.1 | 635.60 | H |
| RSJMG S2.2 | 626.66 | H |
| RT S1.2 | 301.45 | H |
| RT S1.1 | 282.27 | H |
| RSJ S3.1 | 104.37 | H |
| RT S1.3 | 63.52 | H |
| ACA S4.2 | 25.99 | M |
| ACA S4.1 | 20.07 | M |
| ACA S4.3 | 17.92 | M |
| RSJ S3.2 | 15.74 | M |
| Oral | Dermal | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Element | HQ Average | Max | Min | HQ Average | Max | Min |
| Adults | ||||||
| As | 2.515 | 17.467 | 0.000 | 0.0005 | 0.003 | 0.000 |
| Cr | 0.046 | 0.189 | 0.020 | 0.0002 | 0.0007 | 8.1 × 10−5 |
| Ni | 0.017 | 0.056 | 0.004 | 5.0 × 10−6 | 1.6 × 10−5 | 1.3 × 10−6 |
| Zn | 1.762 | 15.912 | 0.008 | 0.0007 | 0.006 | 2.9 × 10−6 |
| Fe | 1.336 | 11.767 | 0.016 | 0.0005 | 0.004 | 6.1 × 10−6 |
| Mn | 0.403 | 1.679 | 0.0005 | 0.0024 | 0.010 | 3.3 × 10−6 |
| Cu | 0.096 | 0.834 | 0.001 | 2.5 × 10−5 | 0.0002 | 3.0 × 10−7 |
| Cd | 7.259 | 64.234 | 0.092 | 0.0288 | 0.254 | 0.0003 |
| Pb | 0.325 | 3.183 | 0.004 | 0.0002 | 0.001 | 2.3 × 10−6 |
| Se | 0.097 | 0.264 | 0.000 | 7.7 × 10−6 | 2.0 × 10−5 | 0.000 |
| Children | ||||||
| As | 2.720 | 18.893 | 0.000 | 0.0008 | 0.005 | 0.000 |
| Cr | 0.050 | 0.205 | 0.027 | 0.0003 | 0.001 | 0.0001 |
| Ni | 0.019 | 0.061 | 0.005 | 8.5 × 10−6 | 2.8 × 10−5 | 2.3 × 10−6 |
| Zn | 1.906 | 17.210 | 0.008 | 0.001 | 0.010 | 5.0 × 10−6 |
| Fe | 1.445 | 12.727 | 0.017 | 0.0009 | 0.008 | 1.0 × 10−5 |
| Mn | 0.436 | 1.815 | 0.0005 | 0.004 | 0.017 | 5.6 × 10−6 |
| Cu | 0.104 | 0.902 | 0.004 | 4.3 × 10−5 | 0.0004 | 5.1 × 10−7 |
| Cd | 7.851 | 69.476 | 0.100 | 0.049 | 0.433 | 0.0006 |
| Pb | 0.035 | 3.442 | 0.004 | 0.0002 | 0.003 | 3.9 × 10−6 |
| Se | 0.105 | 0.286 | 0.047 | 1.3 × 10−5 | 3.5 × 10−5 | 0.000 |
| Element | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | As | Cr | Ni | Zn | Fe | Mn | Cu | Cd | Pb | Se | HI |
| Adults | |||||||||||
| RT S1.1 | 0.000 | 0.026 | 0.025 | 0.522 | 0.406 | 0.462 | 0.030 | 2.160 | 0.026 | 0.077 | 3.733 |
| RT S1.2 | 1.793 | 0.026 | 0.019 | 0.494 | 0.391 | 0.424 | 0.024 | 2.222 | 0.075 | 0.126 | 5.594 |
| RT S1.3 | 1.588 | 0.031 | 0.017 | 0.034 | 0.022 | 0.066 | 0.017 | 0.463 | 0.018 | 0.163 | 2.418 |
| RSJMG S2.1 | 1.230 | 0.190 | 0.018 | 1.176 | 0.955 | 0.898 | 0.051 | 4.844 | 0.075 | 0.000 | 9.438 |
| RSJMG S2.2 | 1.025 | 0.021 | 0.018 | 1.145 | 0.935 | 0.881 | 0.046 | 4.783 | 0.075 | 0.000 | 8.928 |
| RSJMG S2.3 | 17.471 | 0.026 | 0.056 | 15.918 | 11.771 | 1.689 | 0.835 | 64.489 | 3.185 | 0.000 | 115.440 |
| RSJ S3.1 | 1.332 | 0.026 | 0.005 | 0.039 | 0.038 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.771 | 0.062 | 0.264 | 2.543 |
| RSJ S3.2 | 0.973 | 0.026 | 0.005 | 0.008 | 0.016 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.093 | 0.009 | 0.086 | 1.216 |
| ACA S4.1 | 0.410 | 0.026 | 0.008 | 0.022 | 0.030 | 0.012 | 0.023 | 0.123 | 0.004 | 0.105 | 0.763 |
| ACA S4.2 | 0.205 | 0.062 | 0.009 | 0.025 | 0.048 | 0.010 | 0.019 | 0.093 | 0.031 | 0.043 | 0.544 |
| ACA S4.3 | 1.639 | 0.057 | 0.010 | 0.011 | 0.093 | 0.012 | 0.007 | 0.123 | 0.013 | 0.206 | 2.171 |
| Children | |||||||||||
| RT S1.1 | 0.000 | 0.028 | 0.027 | 0.565 | 0.439 | 0.501 | 0.032 | 2.341 | 0.029 | 0.083 | 4.044 |
| RT S1.2 | 1.940 | 0.028 | 0.021 | 0.535 | 0.423 | 0.460 | 0.026 | 2.408 | 0.081 | 0.136 | 6.058 |
| RT S1.3 | 1.718 | 0.033 | 0.018 | 0.037 | 0.023 | 0.072 | 0.018 | 0.502 | 0.019 | 0.176 | 2.617 |
| RSJMG S2.1 | 1.330 | 0.206 | 0.019 | 1.272 | 1.034 | 0.975 | 0.056 | 5.252 | 0.081 | 0.000 | 10.225 |
| RSJMG S2.2 | 1.108 | 0.022 | 0.020 | 1.239 | 1.011 | 0.956 | 0.050 | 5.185 | 0.081 | 0.000 | 9.672 |
| RSJMG S2.3 | 18.898 | 0.028 | 0.061 | 17.221 | 12.735 | 1.833 | 0.903 | 69.910 | 3.446 | 0.000 | 125.034 |
| RSJ S3.1 | 1.441 | 0.028 | 0.005 | 0.042 | 0.042 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.836 | 0.067 | 0.286 | 2.753 |
| RSJ S3.2 | 1.053 | 0.028 | 0.005 | 0.008 | 0.017 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.100 | 0.010 | 0.093 | 1.316 |
| ACA S4.1 | 0.443 | 0.028 | 0.008 | 0.024 | 0.032 | 0.013 | 0.025 | 0.134 | 0.005 | 0.113 | 0.826 |
| ACA S4.2 | 0.222 | 0.067 | 0.010 | 0.027 | 0.051 | 0.011 | 0.021 | 0.100 | 0.033 | 0.047 | 0.589 |
| ACA S4.3 | 1.773 | 0.061 | 0.011 | 0.012 | 0.100 | 0.013 | 0.007 | 0.134 | 0.014 | 0.223 | 2.349 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morales-Mendoza, A.G.; Flores-Trujillo, A.K.I.; Del-Razo, L.M.; Peña-Ocaña, B.A.; Missirlis, F.; Rodríguez-Vázquez, R. Could the Presence of Ferrihydrite in a Riverbed Impacted by Mining Leachates Be Linked to a Reduction in Contamination and Health Indexes? Water 2025, 17, 2167. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152167
Morales-Mendoza AG, Flores-Trujillo AKI, Del-Razo LM, Peña-Ocaña BA, Missirlis F, Rodríguez-Vázquez R. Could the Presence of Ferrihydrite in a Riverbed Impacted by Mining Leachates Be Linked to a Reduction in Contamination and Health Indexes? Water. 2025; 17(15):2167. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152167
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorales-Mendoza, Asunción Guadalupe, Ana Karen Ivanna Flores-Trujillo, Luz María Del-Razo, Betsy Anaid Peña-Ocaña, Fanis Missirlis, and Refugio Rodríguez-Vázquez. 2025. "Could the Presence of Ferrihydrite in a Riverbed Impacted by Mining Leachates Be Linked to a Reduction in Contamination and Health Indexes?" Water 17, no. 15: 2167. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152167
APA StyleMorales-Mendoza, A. G., Flores-Trujillo, A. K. I., Del-Razo, L. M., Peña-Ocaña, B. A., Missirlis, F., & Rodríguez-Vázquez, R. (2025). Could the Presence of Ferrihydrite in a Riverbed Impacted by Mining Leachates Be Linked to a Reduction in Contamination and Health Indexes? Water, 17(15), 2167. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152167








