Abstract
Nature-Based Solutions (NBSs) offer promising pathways to enhance ecological resilience and address urban water challenges, particularly in heritage cities where conventional gray infrastructure often fails to balance environmental needs with cultural preservation. This study proposes a strategic framework for the integration of NBSs into historic urban landscapes by employing Internal–External (IE) matrix modeling and an impact–uncertainty assessment, grounded in a structured evaluation of key internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats. The Internal Factor Evaluation (IFE) score of 2.900 indicates a favorable internal environment, characterized by the multifunctionality of NBS and their ability to reconnect urban populations with nature. Meanwhile, the External Factor Evaluation (EFE) score of 2.797 highlights moderate support from policy and public awareness but identifies barriers such as funding shortages and interdisciplinary coordination. Based on these findings, two strategies are developed: an SO (Strength–Opportunity) strategy, promoting community-centered and policy-driven NBS design, and a WO (Weakness–Opportunity) strategy, targeting resource optimization through legal support and cross-sectoral collaboration. This study breaks new ground by transforming theoretical NBS concepts into actionable, culturally sensitive planning tools that enable decision-makers to navigate the unique challenges of implementing adaptive stormwater and environmental management in historically constrained urban environments.
1. Introduction
The advent of climate change-induced extreme events has significantly elevated the urgency to safeguard cultural and natural heritage, as underscored by pivotal global frameworks such as the Sendai Framework 2015–2030 and the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. These directives emphasize the necessity of fortifying cultural and natural heritage as a cardinal strategy in enhancing urban resilience. In this context, the increasing incidence of flood events devastating cultural heritage and historic centers has become a focal concern, with recent analyses revealing the vulnerability of a substantial proportion of UNESCO World Heritage sites to flood hazards [1,2,3]. The ramifications of such events are profound, inflicting physical, chemical, and biological degradation upon invaluable heritage structures [4].
Contemporary urban stormwater management, predominantly reliant on conventional stormwater systems, has been increasingly scrutinized for its inadequacies and ecological repercussions [5,6]. This phenomenon has manifested in altered hydrological balances and hydraulic overloads, coupled with deteriorating water quality and ecological degradation [7]. Societal perspectives have evolved to critically assess these conventional strategies, advocating for sustainable and environmentally cognizant approaches [8]. Consequently, there is a pressing need to explore innovative stormwater management approaches that are adaptive, integrative, and most importantly, environmentally harmonious in their operation.
In alignment with the principles set forth by the International Union for Conservation of Nature, NBSs present a paradigm shift in addressing societal challenges through ecosystem-based approaches [9,10]. Particularly in stormwater management within heritage cities, NBSs offer a promising avenue to restore urban hydrological conditions and mitigate pollution [11]. Emphasizing green infrastructure, NBS seek to replicate natural water cycles and enhance urban biodiversity and resilience [12].
The implementation of NBSs in stormwater management necessitates a holistic consideration of environmental, social, and technological factors, transcending mere financial deliberations [13,14]. Projects that disregard environmental and human impacts in favor of short-term financial gains are increasingly deemed untenable, as they may exacerbate the long-term detriments of flood events and foment social discontent [15]. Despite the burgeoning body of research on sustainable stormwater management, a lacuna persists in studies facilitating the widespread adoption of NBS, particularly within the unique context of heritage cities.
This study creates a paradigm shift in sustainable urban development by translating theoretical principles of NBS into a practical, heritage-friendly implementation framework. Through a strategic SWOT analysis, we develop actionable tools that enable urban planners to reconcile ecological modernization with cultural preservation in limited historic environments. Our approach uniquely situates the performance of NBSs within the specific challenges of heritage cities, creating an actionable bridge between the imperatives of conservation and contemporary stormwater/environmental management needs. The study demonstrates how NBSs can be systematically integrated into heritage environments while maintaining their ecological efficacy and cultural authenticity, fundamentally redefining urban adaptation strategies.
2. Methods
2.1. Principles of the SWOT
SWOT, an acronym for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, is a strategic analytical tool originating from management research in the mid-20th century [16,17]. The initial phase of this study (Figure 1) employs the SWOT analysis method to identify internal and external factors influencing the implementation of stormwater management models based on NBS within historic urban natural infrastructure. The research commences with problem identification, followed by the determination of the research strategy and the establishment of the expert group size. The scope and application of the SWOT analysis are clarified through the development of a comprehensive master plan. To ensure representativeness and reliability, the selection of experts adheres to an established forward-looking methodology and is systematically categorized into four groups, each encompassing nine core elements: strengths (e.g., enhanced ecological understanding, AI data utilization), opportunities (e.g., policy advancements, technological innovations), weaknesses (e.g., conceptual limitations, quantitative challenges), and threats (e.g., barriers to interdisciplinary collaboration, limited public engagement). Subsequently, an in-depth evaluation is conducted using analytical tools, such as factor assessment, the ITE-EFE matrix, and the impact/uncertainty grid, ultimately leading to the formulation of an NBS strategy tailored to the characteristics of historic urban areas. Following the approach of Matyushenko et al. [13] and Shostak et al. [14], the minimum number of experts (Nexperts) was determined based on a pre-established error rate (ε) of 4%, as elucidated in Equation (1), resulting in a required panel size of 40.
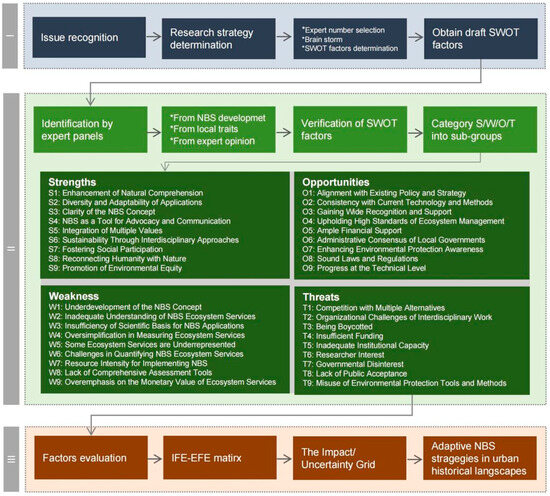
Figure 1.
Framework.
In this study, the error margin is set at 4% (ε = 0.04) to ensure both methodological rigor and practical feasibility in expert assessment. This level is considered optimal as it minimizes unnecessary recruitment while maintaining statistical confidence in the results. Such a threshold effectively reduces potential biases and uncertainties inherent in expert evaluations without imposing excessive demands on the research process. By implementing this approach, the study ensures adequate expert input to substantiate findings while maintaining operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Most participants were assistant professors or postdoctoral researchers, aged 27–42, with an average of six years of research experience in NBS- and heritage-related urban planning (Table S1). The selected factors were evaluated through an online questionnaire. Participants rated each theme on a 9-point Likert scale (1 = strongly disagree to 9 = strongly agree). Agreement levels were then expressed as percentages, with ratings between 6 and 9 considered positive responses. Subsequently, experts ranked the significance of each factor in their respective SWOT category using a weighted scoring system: 3 for the most significant, 2 for the second-most, and 1 for the third. The highest possible importance score for a single item was 120. In addition, the impact and uncertainty associated with each factor were assessed based on the arithmetic mean of expert ratings. These results were used to construct the impact–uncertainty grid, which identified priority themes and critical uncertainties in the implementation of NBSs in heritage cities [15,16].
2.2. Description of Elements for SWOT
2.2.1. Description of Strengths
The implementation of NBSs in heritage cities presents several key advantages. These strengths span ecological, social, and cultural dimensions, enhancing urban sustainability and public well-being [17]. The Enhancement of Natural Comprehension (S1) reflects NBSs’ ability to raise awareness and appreciation of nature among urban populations [18]. Diversity and Adaptability of Applications (S2) highlights their flexibility in responding to the unique spatial and historical constraints of heritage environments [19]. A clear articulation of the NBS Concept (S3) supports broader stakeholder understanding and engagement [20]. NBSs also serve as effective tools for Advocacy and Communication (S4), promoting public discourse on sustainable urban development [21]. The Integration of Multiple Values (S5) enables NBSs to address ecological, historical, and cultural priorities concurrently [22]. Through Interdisciplinary Approaches (S6), NBSs bridge urban planning, ecology, and sociology to support holistic development strategies [23]. Fostering Social Participation (S7) emphasizes the role of community engagement in co-designing and maintaining NBS projects [24]. Reconnecting Humanity with Nature (S8) supports psychological and physiological health through increased contact with green space [25]. Finally, the Promotion of Environmental Equity (S9) positions NBSs as tools for reducing spatial and socio-environmental disparities [26].
2.2.2. Description of Weaknesses
Despite their benefits, NBSs face several limitations in heritage contexts. The Underdevelopment of the NBS Concept (W1) indicates a need for clearer theoretical grounding [27,28], while Inadequate Understanding of Ecosystem Services (W2) constrains recognition of their multifunctionality [10]. The Insufficiency of Scientific Basis (W3) highlights gaps in evidence-based practices tailored for heritage settings [29]. The Oversimplification in Measuring Services (W4) and Underrepresentation of Specific Services (W5) limit the comprehensive assessment of NBS performance [30,31]. Challenges in Quantifying Services (W6) further complicate valuation, making advocacy and integration more difficult [32]. The Resource Intensity of implementation (W7) can deter adoption in budget-constrained cities [33], while the Lack of Comprehensive Assessment Tools (W8) hampers planning and monitoring [34]. Finally, an Overemphasis on Monetary Value (W9) may obscure broader social and ecological contributions [35].
2.2.3. Description of Opportunities
Several external factors enhance the potential of NBSs in heritage cities. Alignment with Existing Policy and Strategy (O1) facilitates institutional support and integration [36], while Consistency with Current Technology (O2) aids implementation scalability [37]. Gaining Wide Recognition and Support (O3) reflects growing awareness among stakeholders [38], and High Standards of Ecosystem Management (O4) position NBSs as tools for biodiversity enhancement [39]. Ample Financial Support (O5) from sustainability-oriented funding programs may enable broader application [40,41], while Administrative Consensus (O6) among local governments can streamline decision-making [42]. NBSs also promote Environmental Awareness (O7) and benefit from Sound Laws and Regulations (O8) that legitimize their application [43,44]. Ongoing Technical Advancements (O9) improve NBS design and performance [45].
2.2.4. Description of Threats
NBSs face multiple challenges to their widespread adoption. Competition with Alternatives (T1) underscores the dominance of conventional infrastructure approaches [46], while Organizational Challenges (T2) highlight the complexities of interdisciplinary coordination [47]. Being Boycotted (T3) reflects possible opposition from skeptical stakeholders [48]. Insufficient Funding (T4) remains a significant barrier to long-term deployment [49], and Inadequate Institutional Capacity (T5) may hinder planning and execution [50]. A decline in Researcher Interest (T6) could slow innovation and refinement of best practices [12]. Governmental Disinterest (T7) and Lack of Public Acceptance (T8) may reduce legitimacy and engagement [42,51]. Finally, the Misuse of Tools and Methods (T9) could lead to poor outcomes or misalignment with conservation goals, undermining public trust and ecological value.
2.3. IFE-EFE Matrix
The Internal Factor Evaluation (IFE) matrix is a strategic instrument for assessing an organization’s internal milieu, encapsulating its strengths and weaknesses [18]. Concurrently, the External Factor Evaluation (EFE) matrix serves as a complementary tool for scrutinizing the external environment, pinpointing prevalent opportunities and threats [19]. Following the comprehensive SWOT analysis, these factors undergo a systematic evaluation via the IFE and EFE matrix.
In the IFE matrix, the internal factors of an organization, categorized as strengths and weaknesses, are first identified and listed. Each factor is assigned a weight (Wi), reflecting its relative importance, with the sum of all weights equal to 1.0. Subsequently, these factors are rated (Ri) on a 1 to 4 scale to indicate performance levels, with 1 denoting a major weakness and 4 a major strength. The weighted score for each factor is calculated by multiplying its weight by its rating (WSi = Wi × Ri). The total IFE score is the sum of these weighted scores (Total IFE = ∑WSi), offering a quantitative assessment of the organization’s internal strengths and weaknesses.
Similarly, in the EFE matrix, external factors, classified as opportunities and threats, are identified. Each external factor is weighted (Wj) and rated (Rj) on the same scale as in the IFE matrix to represent the effectiveness of the organization’s strategies in responding to these factors. The weighted score for each external factor is computed (WSi = Wj × Rj), and the total EFE score (Total EFE = ∑WSj) is obtained by summing these scores. This score provides a measure of how well the organization is positioned in relation to the external environment.
Subsequently, the Internal–External (IE) matrix is employed to analyze and ascertain the strategic positioning of each SWOT variable [20]. This matrix facilitates the delineation of the most apt strategies by correlating horizontal and vertical axes. The IE Matrix is based on the following two criteria: (1) the score from the IFE Matrix plotted on the vertical axis; (2) the score from the EFE Matrix plotted on the horizontal axis. The vertical axis of the IE matrix categorizes an IFE total weighted score ranging from 1.0 to 1.99 as indicative of a weak internal position. Scores spanning from 2.0 to 2.99 are deemed average, while a range of 3.0 to 4.0 is classified as strong. Scores fluctuate between a nadir of 1.0 and an apex of 4.0, averaging at 2.5. A score below 2.5 is interpreted as a weak internal standing, whereas a score exceeding 2.5 signifies a robust internal position [21]. On the horizontal axis, the EFE total weighted score is similarly stratified: scores between 1.0 and 1.99 are considered low, those from 2.0 to 2.99 are categorized as medium, and scores from 3.0 to 4.0 are deemed high.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Breakdown of Outcomes by SWOT Category
3.1.1. Strengths
Among the key themes identified across all four SWOT categories (Figure 2), ‘Reconnecting Humanity with Nature’ (S8) was highlighted as the most important strength of NBSs applied in heritage cities (score = 75). This was followed closely by ‘Integration of Multiple Values’ (S5) (score = 55) and ‘Diversity and Adaptability of Applications’ (S2) (score = 29). The respondents’ agreement with the themes presented to them as strengths ranged from 97% to 100% (Table 1).
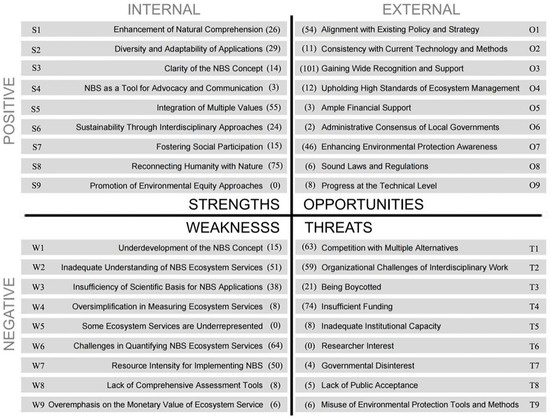
Figure 2.
SWOT themes with their total importance score.

Table 1.
Strengths of the NBS framework in the historic urban landscapes identified.
In heritage cities, where contemporary urbanization often precipitates a disjunction from natural environs, NBSs emerge as a pivotal instrument for re-establishing the symbiosis between urbanity and nature (S8) [22]. This reintegration transcends mere esthetic enhancement, delving into significant psychological and physiological ramifications. Empirical evidence robustly correlates exposure to natural elements with a diminution in stress levels, an augmentation in mental health, and an overall amelioration in human well-being [23].
Regarding S5, NBSs diverge markedly from traditional urban development paradigms that typically concentrate on isolated objectives [24]. These solutions inherently amalgamate ecological, historical, and cultural values, a synthesis of paramount importance in heritage cities where the preservation of cultural and historical identity is as imperative as urban progression. NBSs proffer a multifaceted platform that harmonizes these often conflicting interests, ensuring that urban development initiatives both respect and accentuate the historical milieu [25]. This methodology not only safeguards cultural heritage but also amplifies the esthetic and ecological value of urban landscapes.
Pertaining to S2, the unique challenges endemic to heritage cities, such as spatial constraints and the imperative of historical integrity preservation, necessitate versatile and bespoke solutions [26]. NBS, in their intrinsic adaptability, are tailored to accommodate the specific requirements and limitations unique to varied urban contexts. This flexibility extends to a spectrum of urban challenges, encompassing the management of stormwater, the mitigation of urban heat island effects, the enhancement of air quality, and the augmentation of recreational spaces [27,28]. The capacity of NBSs to be customized across diverse scenarios underscores their utility as a comprehensive tool in urban planning, rendering them efficacious in a broad array of urban settings [29].
‘Promotion of Environmental Equity’ (S9) (score = 0) emerged as the least emphasized strength. This finding underscores a paradigm where the preservation of architectural sanctity and cultural heritage predominates, potentially relegating environmental equity to a subordinate status [30]. Such a hierarchical approach could precipitate a diminished valuation of NBSs’ role in fostering environmental equity, especially when juxtaposed against the more tangible and immediate benefits, such as esthetic augmentation and historical conservation. Environmental equity, quintessentially, entails the provision of equitable access to pristine and salubrious environments for all echelons of society, irrespective of socio-economic stratification. However, within the ambit of heritage cities, the conceptual grasp and recognition of environmental equity appear to be less pronounced [31], in stark contrast to the scenario in more contemporary urban landscapes. This lacuna in understanding and emphasis could feasibly culminate in a diminished perceived significance of this facet of NBS.
3.1.2. Weaknesses
‘Challenges in Quantifying NBS Ecosystem Services’ (W6) was highlighted as the most important weakness of NBSs applied in heritage cities (score = 64) (Table 2). This was followed closely by ‘Inadequate Understanding of NBS Ecosystem Services’ (W2) (score = 51) and ‘Resource Intensity for Implementing NBS’ (W7) (score = 50). The respondents’ agreement with the themes presented to them as strengths ranged from 65% to 100%.

Table 2.
Weaknesses of the NBS framework in the historic urban landscapes identified.
W6 underscores the complexity inherent in evaluating and quantifying the ecological benefits provided by NBSs. Heritage cities, with their intricate blend of historical and modern elements, present a particularly challenging landscape for accurately assessing the ecosystem services of NBS [32]. This difficulty is compounded by the multifaceted nature of these services, which include biodiversity enhancement, air and water purification, and climate regulation, among others. The challenge lies not only in quantifying these services but also in effectively communicating their value to stakeholders and policymakers, which is crucial for securing support and funding for NBS initiatives [33].
W2 highlights a knowledge gap regarding the full spectrum of benefits that NBSs can provide. In heritage cities, where the primary focus often lies in preserving cultural and historical assets, the broader ecological and social benefits of NBS may be overlooked or insufficiently understood [34]. This lack of comprehensive understanding can hinder the integration of NBSs into urban planning and reduce their effectiveness in addressing environmental and societal challenges. It also impacts the ability of decision-makers to make informed choices about the implementation of NBSs and allocate resources where they are most needed.
W7 points to the significant resources required for the implementation of NBS, including financial investment, human capital, and time. In heritage cities, where resources may already be stretched thin due to the demands of maintaining historical sites and infrastructure, finding additional resources for NBSs can be particularly challenging. This situation is exacerbated by the often higher costs associated with adapting NBSs to fit the unique constraints and requirements of heritage environments [35]. The resource-intensive nature of NBSs can thus act as a deterrent to their adoption, especially in cases where the immediate and direct benefits are not easily quantifiable or visible.
‘Some Ecosystem Services are Underrepresented’ (W5) (score = 0) emerged as the least emphasized weakness. In heritage cities, the focus often lies on tangible and immediate benefits like esthetic enhancement, cultural preservation, and urban beautification. These benefits are more visible and easily quantifiable compared to certain ecosystem services. As a result, less apparent ecosystem services, such as microclimate regulation, biodiversity support, or soil enrichment, may be underemphasized or overlooked in planning and discussion. Additionally, there might be a general lack of awareness or understanding among stakeholders, including city planners, policymakers, and the public, about the full range of ecosystem services that NBSs can provide [36]. This lack of understanding can lead to an unintentional undervaluation of certain services, particularly those that are less direct or more complex to measure, such as mental health benefits or cultural ecosystem services. Moreover, some ecosystem services, especially regulating and supporting services, are inherently challenging to quantify and communicate effectively [35]. These services, such as nutrient cycling, habitat provision, and genetic diversity, are critical for long-term ecological balance but may not be immediately perceptible to urban populations. The difficulty in demonstrating their value in concrete terms may contribute to their underrepresentation.
The relatively low level of agreement (65%) on ‘Overemphasis on the Monetary Value of Ecosystem Services’ (W9) suggests a nuanced perspective among experts. One plausible explanation for this could be the inherent challenge in quantifying the value of ecosystem services in purely monetary terms, especially in the unique context of heritage cities. These cities often prioritize the preservation of cultural and historical values, which may not always align neatly with economic valuations [37]. Additionally, the benefits of NBSs, such as esthetic enhancement, cultural significance, and biodiversity support, often transcend straightforward economic metrics, making them challenging to encapsulate in monetary terms. This complexity might lead to a varied understanding and appreciation of the true value of ecosystem services.
3.1.3. Opportunities
‘Gaining Wide Recognition and Support’ (O3) was highlighted as the most important opportunity of NBSs applied in heritage cities (score = 101) (Table 3). This was followed closely by ‘Alignment with Existing Policy and Strategy’ (O1) (score = 54) and ‘Enhancing Environmental Protection Awareness’ (O7) (score = 43). The respondents’ agreement with the themes presented to them as strengths ranged from 92% to 100%.

Table 3.
Opportunities of the NBS framework in the historic urban landscapes identified.
O3 underscores the growing acknowledgement and endorsement of NBSs. This recognition is vital for fostering a supportive environment where NBSs can flourish. The widespread acceptance of NBSs is likely due to increasing awareness of their multifaceted benefits [38], not just in enhancing urban esthetics and preserving historical sites but also in improving ecological resilience and public well-being. This broadening support base can drive more integrated and sustainable urban planning practices.
O1 indicates that NBSs are increasingly being recognized as compatible with and integral to existing urban development policies and strategies [39]. This alignment is crucial for the seamless integration of NBSs into the urban fabric of heritage cities, where conserving historical and cultural integrity is paramount. The congruence of NBSs with current policy frameworks facilitates their adoption and implementation, ensuring that these solutions complement and enhance heritage conservation efforts.
O7 reflects the opportunity for NBSs to elevate the public consciousness about ecological stewardship. In heritage cities, where the focus has traditionally been on preserving cultural heritage, NBSs offer a platform to highlight the importance of environmental conservation. This heightened awareness can lead to more informed and engaged citizenry, advocating for and supporting sustainable urban development initiatives that respect both cultural heritage and ecological sustainability.
The low scores for ‘Ample Financial Support’ (O5) and ‘Administrative Consensus of Local Governments’ (O6) as opportunities in the application of NBSs in heritage cities reflect significant challenges in the practical implementation of these initiatives. The limited emphasis on financial support, with a score of 3, may stem from a broader fiscal reality where heritage city budgets are often stretched thin, with a significant portion allocated to the preservation and maintenance of historical sites [40]. Funding for new, innovative environmental projects like NBSs can thus be limited, as these initiatives might not be seen as immediately crucial compared to more traditional preservation efforts. Additionally, the allocation of funds for NBSs may be hindered by difficulties in demonstrating their short-term economic returns, especially when their benefits are ecological or social in nature, and not easily quantifiable in monetary terms.
The minimal score of 2 for ‘Administrative Consensus of Local Governments’ highlights the complexity of achieving coordinated and unified government support for NBSs. In heritage cities, where urban planning and conservation policies are often deeply entrenched, introducing and integrating new concepts like NBSs can encounter institutional inertia and resistance to change [41]. Moreover, the multifaceted nature of NBSs—spanning environmental, cultural, and social domains—requires a harmonized approach across various administrative departments, which can be challenging to achieve due to differing priorities, perspectives, and bureaucratic processes [42]. These challenges underscore the need for a more integrated approach to urban planning in heritage cities, one that not only values historical preservation but also embraces innovative solutions for sustainable urban development.
3.1.4. Threats
‘Insufficient Funding’ (T4) was highlighted as the most important threat of NBSs applied in heritage cities (score = 74) (Table 4). This was followed closely by ‘Competition with Multiple Alternatives’ (T1) (score = 63) and ‘Organizational Challenges of Interdisciplinary Work’ (T2) (score = 59). The respondent’s agreement with the themes presented to them as strengths ranged from 42% to 100%.

Table 4.
Threats of the NBS framework in the historic urban landscapes identified.
T4 reflects the fiscal constraints in allocating resources towards NBSs in heritage cities, where funding is often prioritized for maintaining and restoring historical sites. The challenge is exacerbated in contexts where the economic benefits of NBSs are not immediately apparent or are difficult to quantify, causing a reluctance to divert funds from traditional urban projects to innovative ecological solutions [43]. This financial limitation hinders the full realization of NBSs’ potential in enhancing urban environments both esthetically and ecologically.
T1 indicates the presence of established urban development strategies that NBSs must contend with. In heritage cities, where conventional approaches to urban development and preservation are deeply ingrained, NBSs can be perceived as competing rather than complementary solutions [24]. This competition can lead to skepticism or resistance from stakeholders accustomed to traditional methods, impeding the adoption of NBSs as a viable strategy.
T2 highlights the complexity inherent in implementing NBSs, which require collaboration across diverse fields, such as ecology, urban planning, history, and sociology [44]. In heritage cities, aligning these interdisciplinary efforts with existing bureaucratic structures and processes can be particularly challenging [45]. These organizational hurdles can slow down or even stall the integration of NBSs, despite their recognized benefits in reestablishing the connection between urban environments and nature, preserving cultural heritage, and addressing unique urban challenges through adaptable and multifaceted approaches.
The negligible emphasis on ‘Researcher Interest’ (T6) (score = 0) as a threat to NBSs in heritage cities, paired with a low agreement level of 44%, suggests a complex dynamic in the academic and scientific community’s engagement with NBSs. This outcome may indicate a perception that researchers’ interest in NBS, particularly in the context of heritage cities, is already robust or steadily growing, driven by the increasing global focus on sustainable urban development and ecological conservation [46,47]. The burgeoning interest in integrating environmental solutions with urban planning, especially in areas of historical significance, is likely fueling academic curiosity and research endeavors. Moreover, the interdisciplinary nature of NBS—encompassing ecology, urban planning, history, and cultural studies—can appeal to a wide range of researchers, further mitigating the threat of diminished academic interest. However, the relatively low agreement percentage could reflect an underlying concern about the sustainability of this interest over time, particularly in terms of securing consistent funding for research and overcoming potential institutional barriers within academia.
3.2. IFE-EFE Matrix
The IE matrix (Figure 3) serves as a strategic tool, providing a visual representation of an organization’s or project’s strategic posture based on the IFE and EFE scores. The IE matrix analysis for NBS in heritage cities reveals a strategic position where internal strengths can be harnessed to exploit external opportunities and address weaknesses and threats. As the field of NBS continues to evolve, it is imperative to maintain a dynamic strategic approach that is responsive to both internal capabilities and external environmental factors. Regular review and adaptation of strategies based on ongoing evaluation will be crucial to the successful implementation and expansion of NBSs in heritage cities.
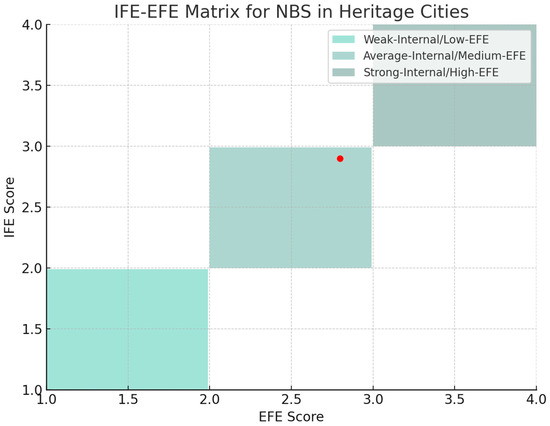
Figure 3.
IFE-EFE matrix for NBS in historic urban landscapes.
3.3. Internal Factor Evaluation (IFE)
The total IFE score of 2.900 (Table 5), which lies in the ‘average’ range but approaches the ‘strong’ classification, suggests that NBS initiatives have a more favorable internal environment with significant strengths. These strengths may include Integration of Multiple Values (S5) and Reconnecting Humanity with Nature (S8). The score also implies the presence of some weaknesses that need to be addressed, although they do not overshadow the strengths. These could be related to ‘Challenges in Quantifying NBS Ecosystem Services’ (W6).

Table 5.
The IFE-EFE scores.
The close proximity of the IFE score to the strong range suggests that the internal capabilities and resources dedicated to NBSs are solid and should be leveraged to capitalize on external opportunities. For instance, the strong internal capabilities can be used to better engage with stakeholders and the community, thereby improving the effectiveness of NBS and ensuring their alignment with local needs and values [48].
While the IFE score indicates a strong internal position, it is important to address the existing weaknesses to prevent them from undermining the strengths. To fortify the internal robustness of NBSs within heritage cities, a multifaceted strategy is imperative. This encompasses the development and deployment of standardized, interdisciplinary metrics for the empirical quantification of NBS ecosystem services, tailored to diverse urban heritage contexts [15,38]. Such an endeavor necessitates synergistic alliances with academic entities dedicated to pioneering models that intricately capture the ecological and socio-economic valuations of NBS. The integration of advanced technological tools, including Geographic Information Systems (GISs) and remote sensing, is pivotal for monitoring and evaluating the ecological impact of NBS, thus providing empirical substantiation of their benefits [26,49]. Investment in pilot projects is crucial, serving as prototypes to gauge the economic, environmental, and societal advantages of NBSs and to refine methodologies for ecosystem service quantification [40]. Furthermore, advocacy for legislative reform is essential, aimed at embedding the value of ecosystem services within the fabric of urban planning and development policies [39]. Through the implementation of these strategies, NBS initiatives can significantly enhance their internal capacity, ensuring a trajectory towards sustainability, resilience, and cultural enrichment in urban environments, while remaining adaptable to the dynamic interplay of internal capabilities and external exigencies.
3.4. External Factor Evaluation (EFE)
With an EFE score of 2.797, the external environment for NBSs in heritage cities is assessed to be moderately favorable. This score indicates that there are substantial opportunities available for the success of NBSs, including Gaining Wide Recognition and Support (O3) and Enhancing Environmental Protection Awareness (O7). However, there are threats that could impede progress, such as Competition with Multiple Alternatives (T1), Organizational Challenges of Interdisciplinary Work (T2), and Insufficient Funding (T4), which may affect funding and support.
Given that the EFE score is closer to 3.0 than to the midpoint of 2.5, this indicates that the NBS initiatives are well-positioned to take advantage of external opportunities. To optimize these opportunities, strategies could focus on the following: Participation in and orchestration of symposiums, workshops, and seminars, with a focus on sustainable urban development and heritage conservation [50], are crucial in establishing NBSs as the vanguard in these domains. Collaborative initiatives with educational institutions and environmental organizations are envisaged to develop comprehensive awareness programs [51], enlightening the populace on the criticality of environmental stewardship and the instrumental role of NBSs in achieving these conservation goals. Additionally, the creation of interactive, public installations at NBS sites is envisaged, serving an educational function by elucidating the ecological merits and heritage significance inherent in these spaces [52], thereby fostering a deeper public connection with these initiatives.
The EFE score, while in the medium range, also suggests a need for vigilance against potential threats. This entails initiating comprehensive comparative research that elucidates the distinctive advantages of NBSs, accentuating their contribution to biodiversity augmentation, cultural enrichment, and communal welfare, thereby underscoring their superiority over alternative methodologies. Strategic alliances ought to be cultivated with entities favoring different approaches, aiming to unearth synergistic opportunities that facilitate the integration of NBSs into expansive urban developmental frameworks [53]. Paramount to this strategy is the establishment of unambiguous communication protocols and collaborative infrastructures, which serve to optimize the functionality of interdisciplinary collectives, thereby streamlining both decision-making and executional processes. Investment in training programs is crucial, targeting the enhancement of cross-disciplinary competencies among team members, with a specific focus on fostering skills in cross-sectoral collaboration, conflict resolution, and holistic project management [54]. Diversification of funding sources is also imperative, extending beyond governmental grants to encompass private investments, public–private partnerships, and international agencies dedicated to sustainable development and heritage conservation [55]. This financial strategy should be complemented by the formulation of persuasive grant proposals and innovative crowdfunding campaigns, designed to vividly portray the multifaceted impacts of NBSs and attract a wide spectrum of potential investors. Lastly, the implementation of cost-efficient design and management practices in NBS projects is critical, ensuring the optimal utilization of available resources and maximizing their impact [56,57].
3.5. The Impact/Uncertainty Grid
The findings on the impact and uncertainty of various elements pertinent to NBS in heritage cities facilitated the creation of a dependency structure matrix (Figure 4). This matrix elucidates the relationship between the impact and predictability of each element. Notably, serials of strength (S8, S5, S1, S2, S9) and opportunity themes (i.e., O1, O3, O7, O6, O9, O4, and O2), despite exhibiting a profound impact on the subject matter, were not categorized as strategic areas, owing to their significant predictability. In contrast, elements like S6, S7, O8, and W7 warrant closer examination. These elements emerged as key uncertainties in the implementation of NBS systems, as indicated by their representation with dark red points in the matrix. Particular attention should be directed towards S6, S7, O8, and W7. These elements have been identified by experts as critical uncertainties, underscoring their potential to influence diverse scenarios in the implementation of NBS in heritage cities.
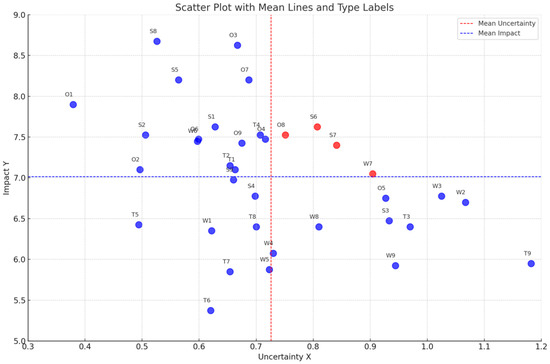
Figure 4.
The impact/uncertainty grid.
3.6. Strength + Opportunity (SO) Strategy
Formulating an expansion strategy for NBSs in heritage cities that fully integrates the strengths of interdisciplinary approaches (S6), social participation (S7), and opportunities presented by sound laws and regulations (O8) demands a synergistic approach. The strategy must weave these elements into a unified fabric that supports the holistic application of NBSs.
- (1)
- Interdisciplinary Policy Formulation (S6 + O8)
Establish policy think tanks that bring together urban planners, environmental scientists, legal experts, and heritage conservationists to draft NBS policies.
Create a regulatory sandbox where new interdisciplinary NBS approaches can be tested within the existing legal framework, with an eye towards informing and adapting future regulations.
- (2)
- Community-driven NBS Design and Implementation (S6 + S7)
Develop NBS projects through collaborative design processes that include local communities, cultural historians, ecologists, and city planners.
Leverage social science research to understand community needs and perceptions, ensuring NBS interventions are both culturally appropriate and environmentally sound.
- (3)
- Legislation-backed Participatory Platforms (S7 + O8)
Create participatory platforms mandated by law that require stakeholder engagement in the NBS implementation process.
Utilize digital tools and social media to facilitate widespread community input and feedback, which is integrated into the legislative process.
- (4)
- Integrated Strategies
Establishment of Cross-Sectoral NBS Committees: These committees will oversee the NBS initiatives, ensuring that the projects align with sustainability goals, community aspirations, and legal mandates. They will also serve as mediation bodies to reconcile interdisciplinary conflicts and facilitate compliance with regulations.
Implementation of Co-Designed NBS Projects: Utilize interdisciplinary teams to design NBS projects with a participatory approach, ensuring that the projects benefit from diverse expertise while directly involving community input. Develop a legal framework that supports community co-design as a standard practice in NBS project development.
Adaptation of Policies to Support NBS Integration: Revisit and revise current laws and regulations to accommodate the flexible and adaptive nature of NBS projects developed through interdisciplinary collaboration and social participation. Introduce legal provisions that incentivize community participation in NBS initiatives, such as tax benefits or grants for community-led projects.
3.7. Weakness + Opportunity (WO) Strategy
To address the integration of weakness (W7) and opportunity (O8) for the implementation of NBSs in heritage cities, a strategic approach must be developed that transforms the resource-intensity weakness into an opportunity through leveraging supportive laws and regulations. This strategic approach should focus on optimizing resource allocation and usage while ensuring a supportive and enabling regulatory environment.
- (1)
- Resource Optimization and Legal Synergy (W7 + O8)
Develop a comprehensive legal framework that incentivizes resource efficiency in NBS projects, such as tax credits for the use of local materials or subsidies for employing sustainable practices.
Advocate for regulations that streamline the approval processes for NBS initiatives, reducing bureaucratic resource drains and speeding up implementation.
- (2)
- Public–Private Partnerships for Resource Mobilization (W7 + O8)
Encourage public–private partnerships (PPPs) through supportive legislation, leveraging private sector innovation and investment to offset the resource intensity of NBS projects.
Design legal mechanisms that facilitate collaboration between the public sector, private entities, and non-profits for resource sharing in NBS initiatives.
- (3)
- Regulatory Frameworks Encouraging Resource-Sharing Communities (W7 + O8):
Introduce policies that support the formation of resource-sharing consortia among heritage city stakeholders, reducing individual investment burdens in NBS projects.
Implement laws that enable community-led NBS initiatives to access public funds and resources, fostering a cooperative approach to resource management.
- (4)
- Integrated Strategies
Resource Mapping and Legal Support: Initiate a resource-mapping exercise to identify and categorize local resources that can be utilized in NBS projects, supported by laws that prioritize their use. Enact policies that provide guidance on resource-efficient NBS techniques and offer legal support for projects that demonstrate resource optimization.
Education and Capacity Building: Implement education programs to build capacity in resource management and sustainable practices, ensuring that stakeholders are aware of the legal provisions that support these efforts. Use regulations to enforce mandatory training for NBS practitioners, focusing on resource-efficient designs and implementation strategies.
Monitoring, Reporting, and Legal Compliance: Establish a regulatory requirement for monitoring and reporting the resource intensity of NBS projects, encouraging transparency and accountability.
Create a legal obligation for NBS projects to adhere to resource-efficiency standards, with penalties for non-compliance and rewards for exemplary performance.
The integration of W7 and O8 acknowledges that while the resource intensity of implementing NBSs is a significant challenge, it also presents an opportunity to innovate and improve through supportive laws and regulations. By framing resource intensity as a factor that can be optimized and supported through legal means, this strategy not only addresses a critical weakness but also capitalizes on the existing opportunity to foster an environment conducive to the successful application of NBSs. This integrated approach ensures that the heritage cities benefit from NBSs that are resource-efficient and legally compliant, promoting sustainable urban development.
3.8. Limitation
Although this study provides systematic decision-making support for the strategic planning of NBSs in heritage cities through the SWOT-IE analysis framework, it is still necessary to recognize the following limitations: First, in terms of data sources, this study is mainly based on the evaluation opinions of the Chinese expert group. Although it ensures professionalism and pertinence, it may have regional biases to a certain extent and has not fully incorporated the actual demands of multiple subjects, such as local communities, enterprises, and government departments. Second, in terms of method application, the semi-quantitative IFE/EFE matrix adopted has structural advantages, but it is insufficient in accuracy compared with numerical models. Third, in terms of scope of application, although the proposed analysis framework is transferable, the unique urbanization process, climate characteristics, and governance system of Chinese heritage cities may affect the applicability of the research conclusions to other regions (especially cities with different development backgrounds). Subsequent research will focus on expanding from three aspects: expanding the scope of stakeholder participation to enhance the inclusiveness of the assessment, developing quantitative models to improve the accuracy of analysis, and verifying the adaptability of the framework in different regional contexts, so as to further enhance the scientific value and practical guidance of this method.
4. Conclusions
The findings reveal the unique contribution of implementing NBSs in heritage cities. The IE matrix shows that cultural value integration (“reconnecting people and nature”) represents an underutilized advantage that distinguishes heritage applications from traditional urban NBSs. The impact/uncertainty grid identifies policy coordination as a key opportunity but also reveals previously undocumented tensions between conservation requirements and ecological adaptation needs. Strategies based on the SWOT analysis reveal the need for a unique legal–ecological interdisciplinary framework when implementing NBSs in protected urban areas.
In terms of opportunities, challenges in quantifying ecosystem services are exacerbated in heritage contexts by conservation constraints. The strategic approach developed through SO and WO strategies further strengthens the potential of NBSs by providing innovative approaches to overcome funding constraints through cultural–ecological value bundling. As urban landscapes continue to evolve, the integration of NBSs demonstrates the possibility of creating sustainable, resilient, and culturally rich urban environments.
This study shows that the successful integration of NBSs in heritage cities relies on tailoring standard approaches to address three specific factors: regulatory complexity, cultural asset sensitivity, and adaptive conservation needs. The framework provides practitioners with a targeted implementation roadmap that is different from the generic urban NBS guidelines. Therefore, the key to future urban development in heritage cities lies in embracing the holistic, adaptable, and integrative qualities of NBS.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w17142110/s1, Table S1: The Composition of Investigators.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.Z. and Y.L.; methodology, J.Z., Y.L. and R.M.A.I.; software, J.Z., Y.L. and R.M.A.I.; validation, R.M.A.I.; formal analysis, M.W. and J.Z.; investigation, J.Z., Y.L. and R.M.A.I.; resources, M.W. and S.K.T.; data curation, J.Z. and R.M.A.I.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.L., M.W. and S.K.T.; writing—review and editing, M.W.; visualization, J.Z.; supervision, M.W. and S.K.T.; project administration, M.W. and S.K.T.; funding acquisition, M.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation, China [grant numbers 2023A1515030158, 2025A1515012916], and Guangzhou City School (Institute) Enterprise Joint Funding Project, China [grant number 2024A03J0317].
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study because it was a non-interventional, anonymous online survey that did not involve any personally identifiable information or sensitive personal data. According to institutional guidelines and national bioethics regulations, such studies are exempt from formal IRB approval.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study. All participants were presented with a clear and detailed informed consent statement at the beginning of the questionnaire. This statement assured participants of anonymity, data protection, and the exclusive academic use of their responses. Participants were required to acknowledge the statement before proceeding with the survey.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Garrote, J.; Díez-Herrero, A.; Escudero, C.; García, I. A Framework Proposal for Regional-Scale Flood-Risk Assessment of Cultural Heritage Sites and Application to the Castile and León Region (Central Spain). Water 2020, 12, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimann, L.; Vafeidis, A.T.; Brown, S.; Hinkel, J.; Tol, R.S.J. Mediterranean UNESCO World Heritage at risk from coastal flooding and erosion due to sea-level rise. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porębska, A.; Godyń, I.; Radzicki, K.; Nachlik, E.; Rizzi, P. Built Heritage, Sustainable Development, and Natural Hazards: Flood Protection and UNESCO World Heritage Site Protection Strategies in Krakow, Poland. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesana, E.; Gagnon, A.; Ciantelli, C.; Cassar, J.; Hughes, J. Climate change impacts on cultural heritage: A literature review. WIREs Clim. Change 2021, 12, e710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jato-Espino, D.; Toro-Huertas, E.I.; Güereca, L.P. Lifecycle sustainability assessment for the comparison of traditional and sustainable drainage systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 817, 152959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nóblega Carriquiry, A.; Sauri, D.; March, H. Community Involvement in the Implementation of Sustainable Urban Drainage Systems (SUDSs): The Case of Bon Pastor, Barcelona. Sustainability 2020, 12, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todeschini, S. Innovative and Reliable Assessment of Polluted Stormwater Runoff for Effective Stormwater Management. Water 2024, 16, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roces García, J.; Sañudo-Fontaneda, L.; Ramírez, R.; Rodríguez, J.; Coupe, S.; Hunt, W.; Busto-Díez, A. Exploring social perception on Sustainable Drainage Systems: Insights from practitioners and academics. In Proceedings of the Novatech 2023 11e Conférence Internationale sur L’eau, Lyon, France, 3–7 July 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Pochwat, K. Assessment method for the hydraulic efficiency of urban drainage system components. J. Hydrol. 2025, 655, 132975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pochwat, K. Assessment of forced retention efficiency in stormwater drainage systems. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pochwat, K. Digital upgrade of drainage detention devices for forced retention. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 373, 123840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiolo, M.; Palermo, S.A.; Brusco, A.C.; Pirouz, B.; Turco, M.; Vinci, A.; Spezzano, G.; Piro, P. On the Use of a Real-Time Control Approach for Urban Stormwater Management. Water 2020, 12, 2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozer, L.; Hörschelmann, K.; Anguelovski, I.; Bulkeley, H.; Lazova, Y. Whose city? Whose nature? Towards inclusive nature-based solution governance. Cities 2020, 107, 102892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellar, J.A.C.; Popartan, L.A.; Pueyo-Ros, J.; Atanasova, N.; Langergraber, G.; Säumel, I.; Corominas, L.; Comas, J.; Acuña, V. Nature-based solutions in the urban context: Terminology, classification and scoring for urban challenges and ecosystem services. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 779, 146237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabisch, N.; Frantzeskaki, N.; Pauleit, S.; Naumann, S.; Davis, M.; Artmann, M.; Haase, D.; Knapp, S.; Korn, H.; Stadler, J.; et al. Nature-based solutions to climate change mitigation and adaptation in urban areas: Perspectives on indicators, knowledge gaps, barriers, and opportunities for action. Ecol. Soc. 2016, 21, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, P. Assessing the sustainable development of the historic urban landscape through local indicators. Lessons from a Mexican World Heritage City. J. Cult. Herit. 2020, 46, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, P.; Pereira Roders, A.R.; Colenbrander, B. Impacts of Common Urban Development Factors on Cultural Conservation in World Heritage Cities: An Indicators-Based Analysis. Sustainability 2018, 10, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirshenava, S.; Osanloo, M. Strategic planning of post-mining land uses: A semi-quantitative approach based on the SWOT analysis and IE matrix. Resour. Policy 2022, 76, 102585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capps, C.J.; Glissmeyer, M.D. Extending The Competitive Profile Matrix Using Internal Factor Evaluation And External Factor Evaluation Matrix Concepts. J. Appl. Bus. Res. (JABR) 2012, 28, 1059–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astika, I.M.; Suharyo, O. Internal and External Enviromental Strategy Analysis Using SWOT Matrix and QSPM. Int. J. Progress. Sci. Technol. 2021, 25, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banihashemi, S.A.; Rajaei, Z. Assessment of Environmental Conditions and Internal Capabilities Affecting University Strategies (IFE, EFE, SWOT & AHP Models). Int. J. Asian Soc. Sci. 2016, 6, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- van den Bosch, M.; Ode Sang, Å. Urban natural environments as nature-based solutions for improved public health—A systematic review of reviews. Environ. Res. 2017, 158, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandifer, P.A.; Sutton-Grier, A.E.; Ward, B.P. Exploring connections among nature, biodiversity, ecosystem services, and human health and well-being: Opportunities to enhance health and biodiversity conservation. Ecosyst. Serv. 2015, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.R.; Bledsoe, B.P.; Ferreira, S.; Nibbelink, N.P. Challenges to realizing the potential of nature-based solutions. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2020, 45, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neugarten, R.; Langhammer, P.; Osipova, E.; Bagstad, K.; Bhagabati, N.; Butchart, S.; Dudley, N.; Elliott, V.; Gerber, L.; Gutierrrez, C.; et al. Tools for Measuring, Modelling, and Valuing Ecosystem Services: Guidance for Key Biodiversity Areas, Natural World Heritage Sites, and Protected Areas; International Union for Conservation of Nature: Gland, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pacetti, T.; Cioli, S.; Castelli, G.; Bresci, E.; Pampaloni, M.; Pileggi, T.; Caporali, E. Planning Nature Based Solutions against urban pluvial flooding in heritage cities: A spatial multi criteria approach for the city of Florence (Italy). J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 41, 101081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghrabi, A.; Alyamani, A.; Addas, A. Exploring Pattern of Green Spaces (GSs) and Their Impact on Climatic Change Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies: Evidence from a Saudi Arabian City. Forests 2021, 12, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortinovis, C.; Zulian, G.; Geneletti, D. Assessing Nature-Based Recreation to Support Urban Green Infrastructure Planning in Trento (Italy). Land 2018, 7, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojinovic, Z.; Alves, A.; Gómez, J.P.; Weesakul, S.; Keerakamolchai, W.; Meesuk, V.; Sanchez, A. Effectiveness of small- and large-scale Nature-Based Solutions for flood mitigation: The case of Ayutthaya, Thailand. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 789, 147725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato-Huerta, J.; Geneletti, D. Environmental justice implications of nature-based solutions in urban areas: A systematic review of approaches, indicators, and outcomes. Environ. Sci. Policy 2022, 138, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anguelovski, I. New Directions in Urban Environmental Justice. J. Plan. Educ. Res. 2013, 33, 160–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borah, A.; Bardhan, R.; Bhatia, U. Protecting heritage: Insights into effective flood management using green infrastructure in a highly urbanized environment. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2023, 98, 104075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koko, I.A.; Misana, S.B.; Kessler, A.; Fleskens, L. Valuing ecosystem services: Stakeholders’ perceptions and monetary values of ecosystem services in the Kilombero wetland of Tanzania. Ecosyst. People 2020, 16, 411–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claudia, T.; Luigi, P. A Novel Paradigm to Achieve Sustainable Regeneration in Historical Centres with Cultural Heritage. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2016, 223, 693–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yung, E.H.K.; Chan, E.H.W. Implementation challenges to the adaptive reuse of heritage buildings: Towards the goals of sustainable, low carbon cities. Habitat Int. 2012, 36, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, V.; Barreira, A.P.; Loures, L.; Antunes, D.; Panagopoulos, T. Stakeholders’ Engagement on Nature-Based Solutions: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability 2020, 12, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, T.C.; Henneberry, J.; Gill, L. Comprehending the multiple ‘values’ of green infrastructure—Valuing nature-based solutions for urban water management from multiple perspectives. Environ. Res. 2017, 158, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, C.C.; Renaud, F.G. A review of public acceptance of nature-based solutions: The ‘why’, ‘when’, and ‘how’ of success for disaster risk reduction measures. Ambio 2021, 50, 1552–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharon, O.; Fishman, S.N.; Ruhl, J.B.; Olander, L.; Roady, S.E. Ecosystem services and judge-made law: A review of legal cases in common law countries. Ecosyst. Serv. 2018, 32, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medda, F.; Lipparini, F. Impact investment for urban cultural heritage. City Cult. Soc. 2021, 26, 100413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finewood, M.H.; Marissa, M.A.; Zivkovich, J. Green Infrastructure and the Hidden Politics of Urban Stormwater Governance in a Postindustrial City. Ann. Am. Assoc. Geogr. 2019, 109, 909–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremer, P.; Hamstead, Z.; Haase, D.; McPhearson, T.; Frantzeskaki, N.; Andersson, E.; Kabisch, N.; Larondelle, N.; Rall, E.; Baró, F.; et al. Key insights for the future of urban ecosystem services research. Ecol. Soc. 2016, 21, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toxopeus, H.; Polzin, F. Reviewing financing barriers and strategies for urban nature-based solutions. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 289, 112371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nesshöver, C.; Assmuth, T.; Irvine, K.N.; Rusch, G.M.; Waylen, K.A.; Delbaere, B.; Haase, D.; Jones-Walters, L.; Keune, H.; Kovacs, E.; et al. The science, policy and practice of nature-based solutions: An interdisciplinary perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 1215–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nofal, E. Participatory Design Workshops: Interdisciplinary Encounters within a Collaborative Digital Heritage Project. Heritage 2023, 6, 2752–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliasson, I.; Knez, I.; Fredholm, S. Heritage Planning in Practice and the Role of Cultural Ecosystem Services. Herit. Soc. 2019, 11, 44–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tengberg, A.; Fredholm, S.; Eliasson, I.; Knez, I.; Saltzman, K.; Wetterberg, O. Cultural ecosystem services provided by landscapes: Assessment of heritage values and identity. Ecosyst. Serv. 2012, 2, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet, A.; Locatelli, B.; Levrel, H.; Dendoncker, N.; Barnaud, C.; Conde, Y. Linking equity, power, and stakeholders’ roles in relation to ecosystem services. Ecol. Soc. 2019, 24, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajeethaveesin, T.; Panboonyuen, T.; Lawawironjwong, S.; Srestasathiern, P.; Jaiyen, S.; Jitkajornwanich, K. A Performance Comparison between GIS-based and Neuron Network Methods for Flood Susceptibility Assessment in Ayutthaya Province. Trends Sci. 2022, 19, 2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damayanti, V.; Dipowijoyo, H.; Kurniawan, K.R.; Rosbergen, J.; Timmer, P.; Wijayanto, P. Two Towns in Indonesia, One on the Coast, the Other “A City of One Thousand Rivers”: Historic Urban Landscape (HUL) Quick Scan Method Workshops and Publication of Handbook for Indonesian University Lecturers. Blue Pap. 2022, 1, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Calviño, L.; Rodríguez-Medina, J.; López-Facal, R. Heritage education under evaluation: The usefulness, efficiency and effectiveness of heritage education programmes. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2020, 7, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Kasraian, D.; Wesemael, P.J.V. Children and Urban Green Infrastructure in the Digital Age: A Systematic Literature Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bush, J. The role of local government greening policies in the transition towards nature-based cities. Environ. Innov. Soc. Transit. 2020, 35, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, C.; Polesie, T. Return on heritage investments: Measurable economic results of the conservation of rossared manor house. BDC Boll. Del Cent. Calza Bini 2013, 13, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanziola, J. Some more unequal than others: Alternative financing for museums, libraries and archives in England. Cult. Trends 2011, 20, 113–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Liu, M.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Su, J.; Zhou, S.; Bakhshipour, A.E.; Tan, S.K. Assessing hydrological performance for optimized integrated grey-green infrastructure in response to climate change based on shared socio-economic pathways. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 91, 104436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Fu, X.; Zhang, D.; Chen, F.; Su, J.; Zhou, S.; Li, J.; Zhong, Y.; Tan, S.K. Urban Flooding Risk Assessment in the Rural-Urban Fringe Based on a Bayesian Classifier. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
