Distribution Characteristics and Driving Mechanisms of Organic Matter in Sediment of Lakes in China: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Overview of the Area of Investigation of Lake Sediments
3. Status and Trends of OM Content in Lake Sediments
3.1. Poyang Lake
3.2. Taihu Lake
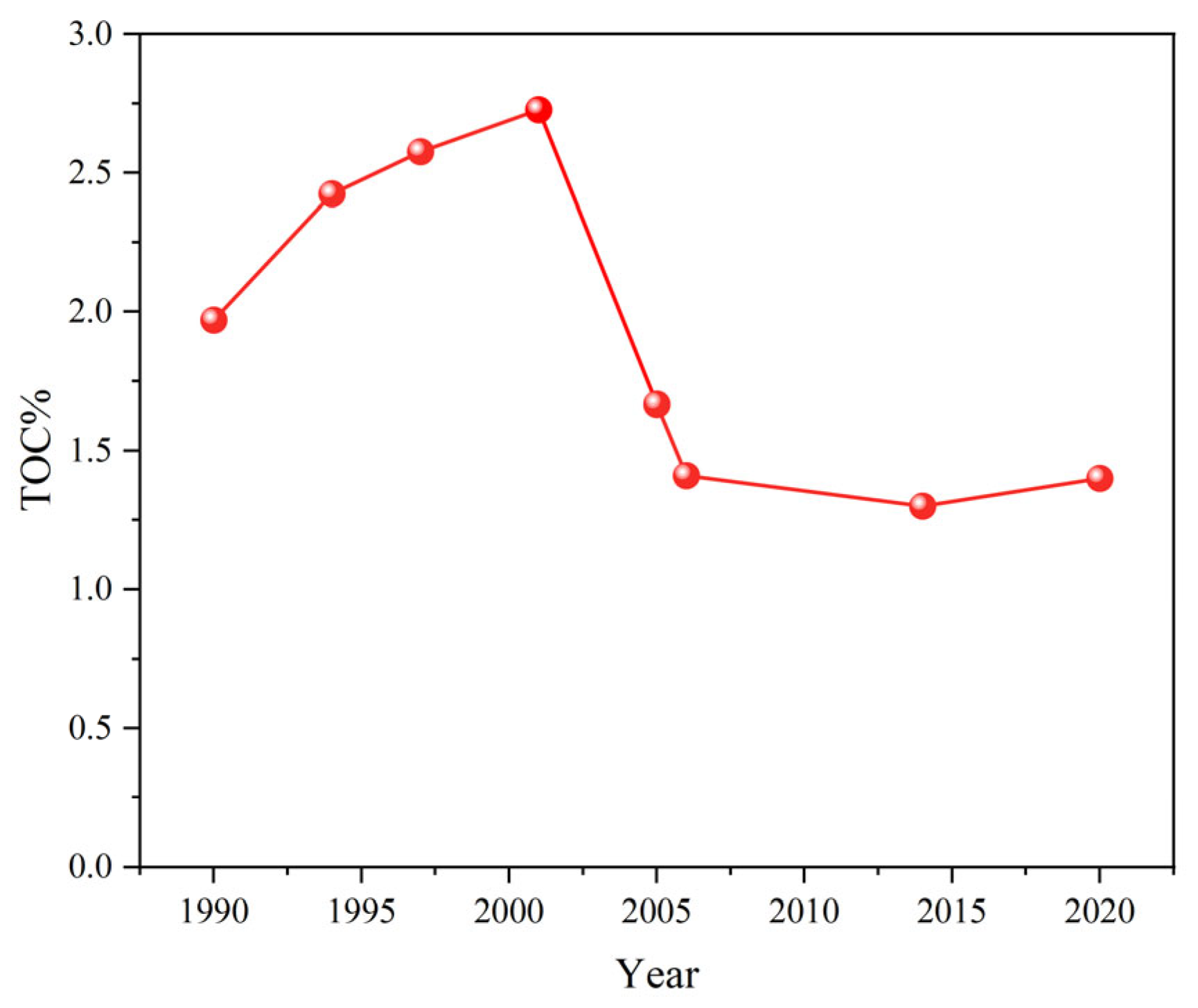
3.3. Qinghai Lake
3.4. Hulun Lake
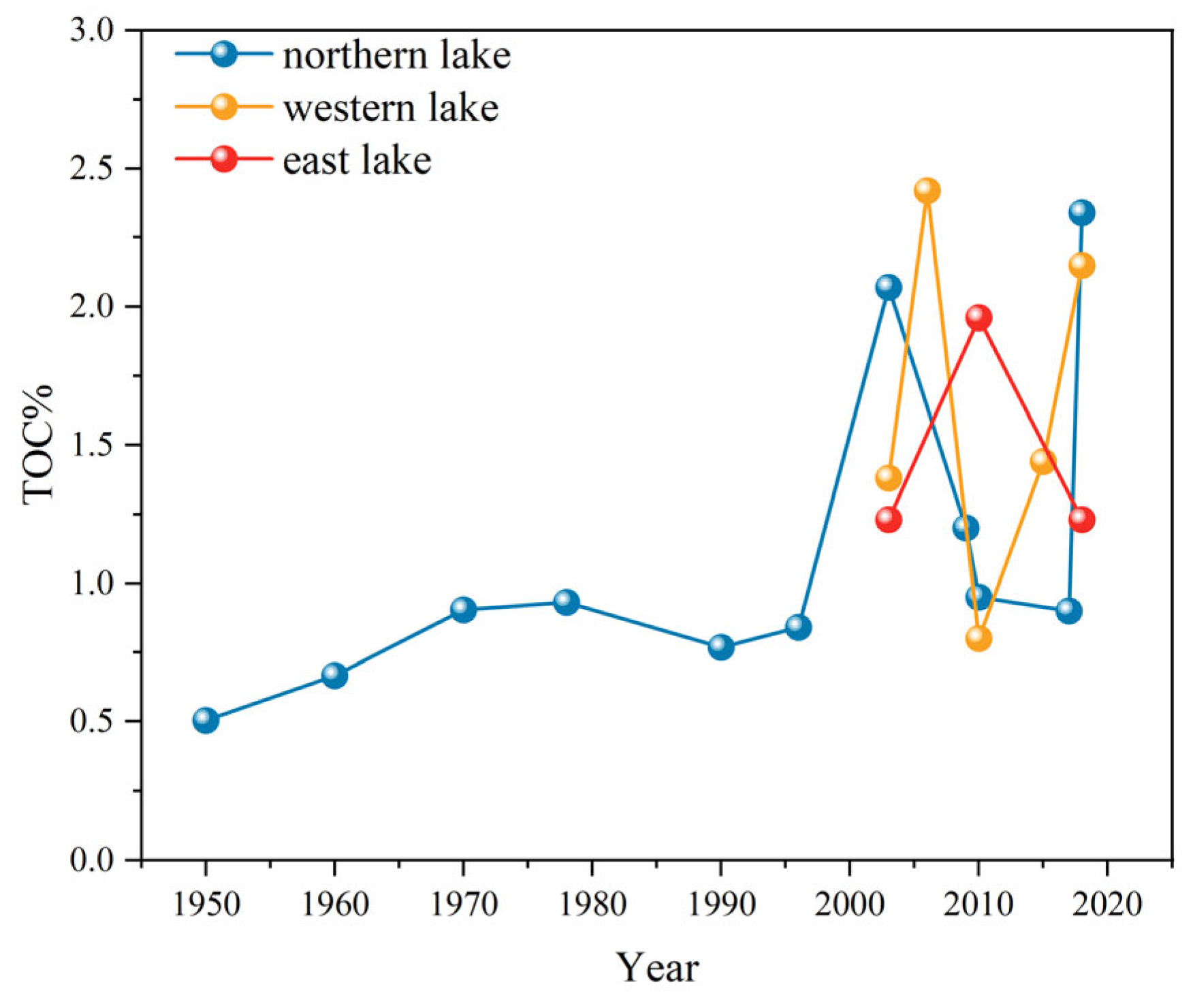
3.5. Comparative Analysis of OM in Lake Sediments
4. Sources of OM in Lake Sediments
4.1. OM Concepts and Groupings
4.2. OM Source Classification
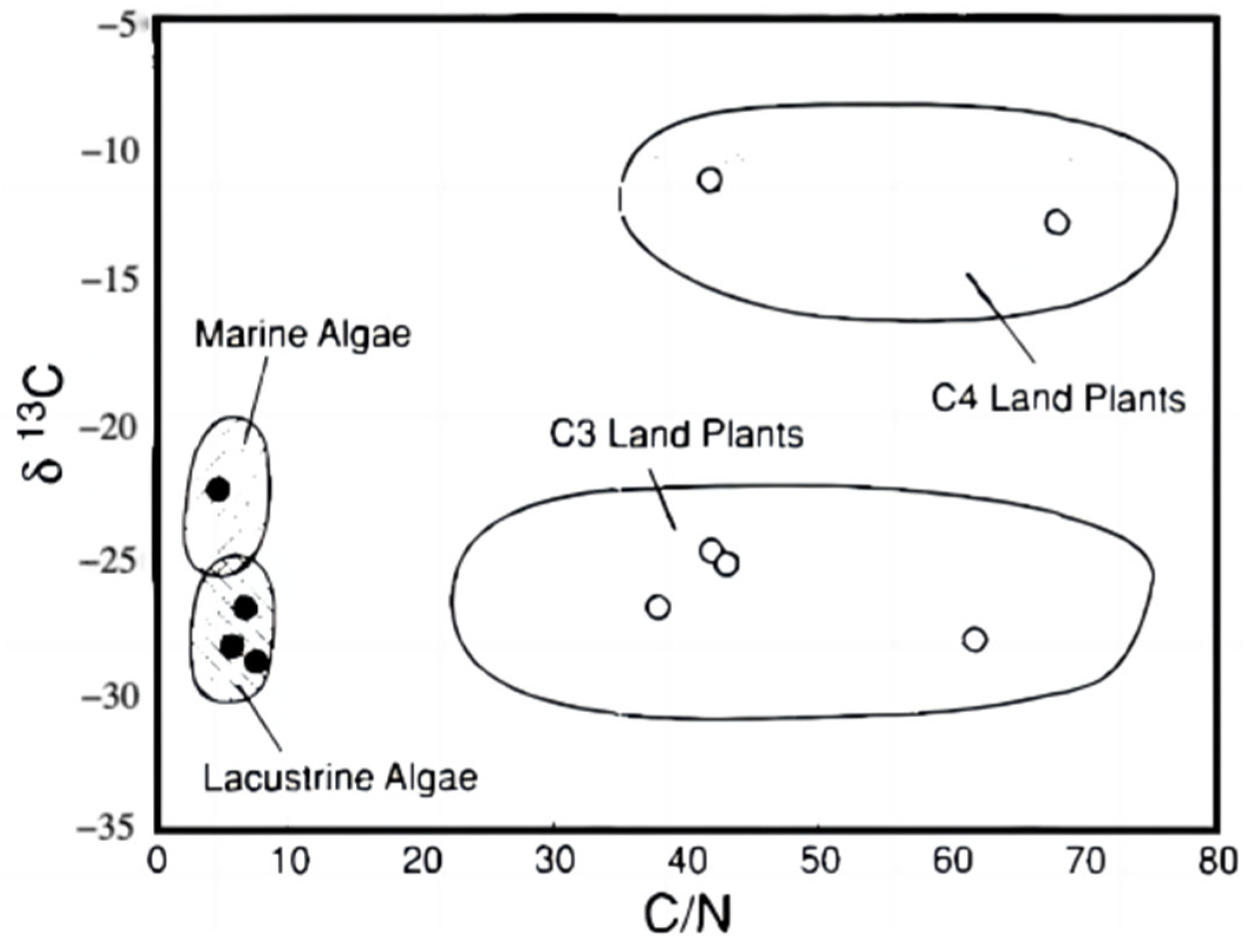
4.3. OM Source Analysis
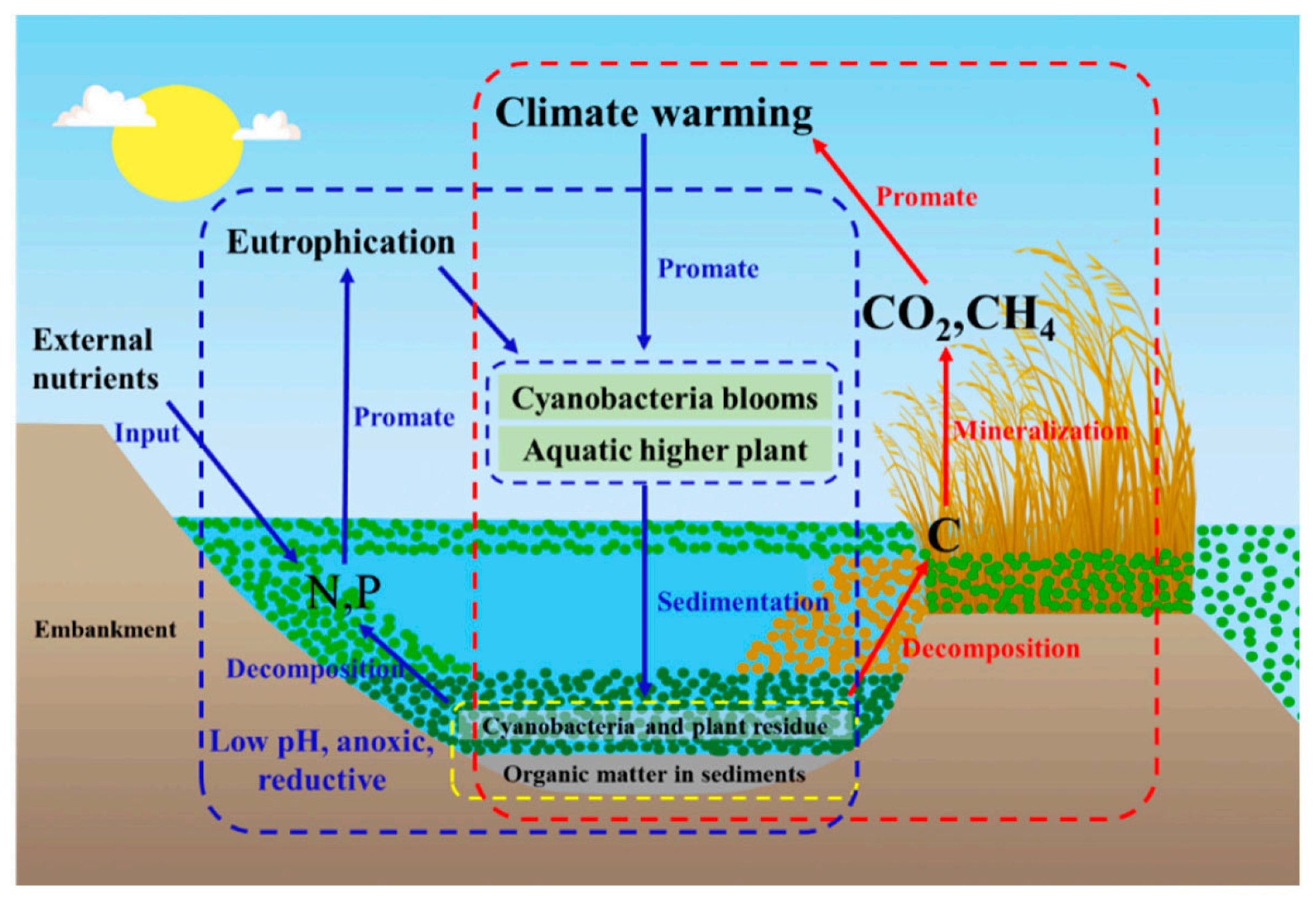
5. Factors Affecting OM Content in Lake Sediments
6. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qu, Q. China’s Five Great Lakes. Educ. Geogr. 2002, 6, 18. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Chen, H.; Yu, Z.; Wu, J.; Zhu, Q.; Peng, C.; Wang, Y.; Qin, B. Carbon accumulation and sequestration of lakes in China during the Holocene. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015, 21, 4436–4448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Y.; Huang, T.; Ning, C.; Sun, T.; Tao, P.; Wang, J.; Sun, Q. Changes of DOM and its correlation with internal nutrient release during cyanobacterial growth and decline in Lake Chaohu, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 124, 769–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Wu, F.; Liu, C.; Fu, P.; Li, W.; Wang, L.; Liao, H.; Guo, J. Characteristics of organic phosphorus fractions in different trophic sediments of lakes from the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River region and Southwestern Plateau, China. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 152, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Lai, G. The basic characteristics and recent trends of ecological environment in Poyang Lake. Gansu Sci. Technol. 2009, 25, 47–49. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Ye, J. Wetlands of Jiangxi; China Forestry Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Jiao, L.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, R.; Feng, S.; Wang, J. Effects of organic matter content and composition on ammonium adsorption in lake sediments. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 6179–6187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J. Simulation of Non-Point Source Pollution in TaihuLake Basin Based on SWAT Model and Analysis of Its Impact Factors. Master’s Thesis, Jiangsu Ocean University, Lianyungang, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Ji, Z.; Li, X.; Long, Z.; Pei, Y. Comprehensive analysis of the migration and transformation of nutrients between sediment and overlying water in complex habitat systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 852, 158433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zan, F.; Huo, S.; Xi, B.; Zhu, C.; Liao, H.; Zhang, J.; Yeager, K.M. A 100-year sedimentary record of natural and anthropogenic impacts on a shallow eutrophic lake, Lake Chaohu, China. J. Environ. Monit. 2012, 14, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, F. Dynamically Monitoring of Hulun Lake Based on Multi-source Remote Sensing Data. Geospat. Inf. 2019, 17, 83–85. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Yao, B.; Wang, S.; Huang, Y. Understanding the changes of optically active substances (OACs) in Hulun Lake in the past 35 years and its indication to the degradation of aquatic ecology. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 377, 134286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Li, C.; Zhao, H.; Tian, H.; Song, Q.; Kou, Z. The Climate Change and Its Effect on the Water Environment in the Hulun Lake Wetland. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2007, 29, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, G.; Wang, W.; Ma, Y.; Ma, J. The influence of Lunbeier wetland on grassland ecological environment. Inn. Mong. Water Resour. 2006, 2, 49–50. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.; Li, X. Qinghai Lake for Nearly 20 Years the Change and Evolution of Waters of Lake. J. Palaeogeogr. 2006, 8, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Cao, S.; Cao, G. Analysis on the drive of temperature and precipitation changes to vegetation phenology of the Qinghai Lake basin in the past 15 years. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 29, 249–255. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, H.; Gu, H.; Shi, J.; Wei, C. Study on changes of vegetation fraction and its driving factors in Qinghai Lake basin based on RS and GIS. Resour. Dev. Mark. 2016, 32, 827–831. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Li, X.; Cui, B.; Peng, H.; Yin, W. Trend of stream flow in Lake Qinghai Basin during the past 50 years(1956–2007)—Take Buha River and Shaliu River for examples. J. Lake Sci. 2010, 22, 757–766. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.; Qu, F.; Zhang, H.; Tao, B. The analysis on the productive potential and sustainable utilization of grassland resources in Qinghai Lake Region. Chin. J. Grassl. 2007, 29, 78–83. [Google Scholar]
- Jiangxi Academy of Environmental Protection Sciences. Water Quality Prediction and Planning of Poyang Lake; Jiangxi Academy of Environmental Protection Sciences: Nanchang, China, 1988; Volume 16, p. 7. [Google Scholar]
- State Environmental Protection Administration. Study on Eutrophication of Poyang Lake; State Environmental Protection Administration: Beijing, China, 1993; pp. 69–79.
- Japan International Cooperation Agency. Investigation on Water Quality Protection Countermeasure Plan of Poyang Lake in China; Japan International Cooperation Agency: Tokyo, Japan, 1993; p. 34. [Google Scholar]
- Jiangxi Academy of Sciences. Water Quality Monitoring of Poyang Lake; Jiangxi Academy of Sciences: Nanchang, China, 1999; p. 23. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, G.; Long, X.; Xing, J. Research Report on the Impact of Five Major Water Systems in Jiangxi Province on the Ecological Environment of Poyang Lake; Jiangxi Academy of Sciences: Nanchang, China, 2008; p. 79. [Google Scholar]
- Harbin Institute of Technology. Poyang Lake Ecosystem Service Function Investigation and Service Function Loss Assessment Research Work Report; Harbin Institute of Technology: Harbin, China, 2008; pp. 2–3. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Ni, D.; Jiao, L.; Jin, X.; Feng, M.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, W. Space-time Variety of Organic Matter and Nutrition Salt in Sediments from Poyang Lake. J. Environ. Eng. Technol. 2012, 2, 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Li, J.; Hu, K.; Zhang, D.; Lai, J. Compositions and sources of stable organic carbon and nitrogen isotopes in surface sediments of Poyang Lake. Zhongguo Huanjing Kexue/China Environ. Sci. 2014, 34, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Zhang, H.; Zou, C.; Wei, L.; Chang, F. Characteristics of n-alkanes in Modern Sediments of Poyang Lake and Its Biological Origins. J. Fujian Norm. Univ. 2014, 30, 111–118. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y. Study on the Influence of Dry-Wet Cycle on the Migration of PAHs in Lake Water-Fluctuating Zone. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Jiang, L. Trend analysis of flood peak/dry season flowrate in Poyang Lake Basin. J. Nat. Disasters 2008, 17, 75–80. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Q. Study of Source of Particulate Organic Matter in Migratory Bird Habitat in Poyang Lake. Master’s Thesis, East China University of Technology, Fuzhou, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Huang, L. Influence of quarrying in Poyang Lake on the ecological environment. Jiangxi Hydraul. Sci. Technol. 2008, 34, 740. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, X.; Chen, Z.; Lin, L.; Geng, B.R. Genotoxicity of emamectin benzoate on Rana zhenhaiensis tadpoles. Ningde Teach. Coll. 2010, 22, 373–376. [Google Scholar]
- Tice, R.R.; Agurell, E.; Anderson, D.; Burlinson, B.; Hartmann, A.; Kobayashi, H.; Miyamae, Y.; Rojas, E.; Ryu, J.C.; Sasaki, Y.F. Single cell gel/comet assay: Guidelines for in vitro and in vivo genetic toxicology testing. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2000, 35, 206–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Wu, W.; Mo, Z.; Wang, Z. Persistent organic pollutants in water and surface sediments of Taihu Lake in China and risk assessment. ChemosPhere 2003, 50, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H. Restoration Project of The Ecosystem In Tai Lake. Resour. Environ. Yangtza Basin 2001, 10, 173–178. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, M.; Liu, H.; Ren, L. Lake eutrophi-cation situation and countermeasures. China Environ. Manag. 1998, 6, 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Wan, G.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, D.; Huang, R. Environment records of lake sediment under different time scales-case study of grain size. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2003, 33, 563–568. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Jin, X.; Chu, Z. The sources of organic carbon and nitrogen in sediment of Taihu Lake. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2011, 31, 4661–4670. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F. Temporal and spatial variations of physico-chemical characteristicsin sediments of Taihu Lake, China. Master’s Thesis, Jinan University, Guangzhou, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X. Water Environmental Charactersand Sediment Oganic Matter Source Identification of Lake Taihu. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing University, Nanjing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, J.; Qi, C.; Zhang, X.; Han, R.; Huang, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, G. Spatial Distribution and Pollution Evaluation of Carbon, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus in Sediments of Zhushan Bay at Taihu Lake. Huan Jing Ke Xue 2019, 40, 5367–5374. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, T.; Yu, K.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y. Occurrence characteristics and environmental significance of nutrients over the past 100 years in the northern Taihu Basin, China. J. Soils Sediments 2023, 23, 2600–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Gao, J.; Zhao, G. Impacts of 20-year socio-economic development on the trend of aquatic environment of the Taihu lake. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2006, 15, 298–302. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, X.; Wu, H.; Xu, F. Analysis of pollution characteristics of main nutrients in Taihu Lake sediment. Water Resources Protection 2020, 36, 100–104. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, G. Eutrophic status and causing factors for a large, shallow and subtropical Lake Taihu, China. J. Lake Sci. 2008, 20, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Diao, W. Nutrition Evaluation on Surface Layer Sediment of Typical Estuarine Aquatic-terrestrial Ecotone in West Taihu Lake. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 29, 4–6. [Google Scholar]
- Xuan, Y. Distribution Characteristics of Sediment Nutrients in the Typical Accumulation Area of Algae Blooms in Taihu Lake. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing Normal University, Nanjing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, G.; Wang, J.; Jia, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Zhou, S. Determination of influencing factors on historical concentration variations of PAHs in West Taihu Lake, China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, P.; Zhang, H.; Shan, B. Vertical records of sedimentary PAHs and their freely dissolved fractions in porewater profiles from the northern bays of Taihu lake, Eastern China. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 98835–98844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Li, X.; Huang, L.; Zhao, T.; Han, X.; Gao, Q. Ceramization of contaminated sediment backfill technology and its effects of sediment remediation. Water·Resour. Prot. 2019, 35, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H. Environmental protection dredging in treatment of lake pollution internal cause. Port Waterw. Eng. 2000, 11, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Fang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Y. Research and Discussion on Ecological Dredging of Sediment in Taihu Lake; Chinese Hydraulic Engineering Society: Beijing, China, 2014; pp. 57–59. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Yang, B.; Dong, M.; Zhu, J. Study of sediment contaminants release based on different dredging cutter structures. Water Resour. Prot. 2017, 33, 74–78. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Su, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yu, J.; Jin, M. Lipid biomarker evidence for determining the origin and distribution of organic matter in surface sediments of Lake Taihu, Eastern China. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 77, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Su, Y.; Liu, Z.; Kong, L.; Yu, J.; Jin, M. Aliphatic hydrocarbon biomarkers as indicators of organic matter source and composition in surface sediments from shallow lakes along the lower Yangtze River, Eastern China. Org. Geochem. 2018, 122, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Lu, S.; Wang, D.; Xu, M.; Gan, S.; Jin, X. Nitrogen, Phosphorous and Organic Matter Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Their Pollution Status Evaluation of Sediments Nutrients in Lakeside Zones of Taihu Lake. China Environ. Sci. 2012, 32, 703–709. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, H.; Jiao, F. The Discussion on Distribution of Water Quality in East Tai Lake after Pulling Down the Enclosure. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2011, 36, 51–55. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Shi, W.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Z. Ecological environment succession and countermeasure of East Taihu Lake. China Environ. Sci. 2003, 23, 64–68. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.; Lei, Z.; Han, B. Effect of macrophytes on distribution on mineral elements esturay area of the East Lake Taihu. Ecol. Environ. 2009, 18, 1644–1648. [Google Scholar]
- Sha, Z.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; Du, J.; Hu, J.; Ma, Y.; Kong, F.; Wang, Z. Regional environmental change and human activity over the past hundred years recorded in the sedimentary record of Lake Qinghai, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 9662–9674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yu, B.; Dong, H. Study On Organic Matters In The Sediments From The Bottom Of The Qinghai Lake, China. Pet. Geol. Exp. 2006, 28, 375–379. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, M.; Fang, Y.; Ding, S.; Xiao, W.; Yu, C.; Wang, X.; Xu, Y. Heterogenous distribution and burial flux of black carbon in Chinese lakes and its global implication. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, J.; Tong, C.; Wang, T.; Wu, F.; Liu, M. Distribution characteristics and influencing factors of microplastics in intertidal zone sediments of the Yangtze Estuary. Chin. J. Ecol. 2021, 40, 2860–2871. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Cao, S.; Cao, G.; Zhao, H.; Chen, L.; Hou, Y. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Vegetation Net Primary Productivity and Their Drivers in Qinghai Lake Basin from 2000 to 2020. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2024, 31, 327–336. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Ma, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, D. Impact of land use and land cover change on environmental degradation in Lake Qinghai Watershed, northeast Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Land Degrad. Dev. 2009, 20, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X. A green fervor sweeps the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Science 2008, 321, 633–635. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X. Distribution of Nutrient Elements and Environmental Pollution Assessment in Sediment of Hulun Lake, Inner Mongolia. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2010, 29, 339–343. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, S.; Zan, F.; Xi, B.; Li, Q.; Zhang, J. Phosphorus fractionation in different trophic sediments of lakes from different regions, China. J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13, 1088–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Li, C.; Zhang, H. Vertical Distribution and Ecological Risk Assessment of Nutrients in Sediments of Hulun Lake. Water Resour. Power 2019, 37, 50–53. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Chen, J.; Jiang, X.; Li, H.; Wang, S. Release Effect of Surface Sediment Organic Matters in Lake Hulun. Res. Environ. Sci. 2021, 34, 812–823. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, Y.; Zang, S.; Xiao, H. The vertical variation of nutrients in a sediment core of delong lake reveals the anthropogenic effect. Ecotoxicology 2014, 23, 480–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Hou, X.; Huang, C.; Li, S.; Ma, X.; Yang, H.; Wu, W.; Chen, Z.; Huang, T. The influence of nutrients on the composition and quantity of buried organic carbon in a eutrophic plateau lake, Southwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 836, 155726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wu, C.; Xie, D.; Ma, J. Sources, Migration, Transformation, And Environmental Effects of Organic Carbon in Eutrophic Lakes: A Critical Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Wu, F.; Xiong, Y.; Li, F.; Du, X.; An, D.; Wang, L. Source characterization of sedimentary organic matter using molecular and stable carbon isotopic composition of n-alkanes and fatty acids in sediment core from Lake Dianchi, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 473–474, 410–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L. Spatial Characteristics and Sources of Organic Matter in Top Sediment Layers of Lakes Datun and Changqiao. Master’s Thesis, Yunnan Normal University, Kunming, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, W.; Guo, N.; Xu, J.; Yu, H.; Niu, Y. Carbon and Nitrogen Isotope Characterization and Source Analysis of Sediments from Shallow Lakes in the Middle of Yangtze River. J. Hydroecology 2018, 39, 8–15. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J. TOC, CN Ratio and δ13 Corg Characteristics of Lake Surface Sediment in Northern Tibetan Plateau and its Environmental Significance. Master’s Thesis, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Q. Sources and Characterization of Organic Carbon and Nitrogen in Plateau Lake Sediments: Taking Dianchi Lake as Example. Ph. D. Thesis, East China Normal University, Shanghai, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wu, F.; Li, W.; Wang, L.; Guo, J.; Fu, P.; Zhang, R. Seasonal variation and vertical characteristics of the δ15N of particulate organic matterin Lake Hongfeng and Lake Baihua, Guizhou Province. J. Lake Sci. 2008, 20, 571–578. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P. Organic Carbon and Nitrogen Isotopic Characteristics of Tengchong Qinghai Lake Sediments During Last 1700 a and Paleo Environmental Reconstruction. Master’s Thesis, Yunnan Normal University, Kunming, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Wang, L.; Chen, J. Sources and selective preservation of organic matter in the karst watershed: Evidence from sediment records in a plateau deep lake, Southwestern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 4762–4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, P. Preservation of Elemental and Isotopic Source Identification of Sedimentary Organic Matter. Chem. Geol. 1994, 114, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; Niu, L.; Zhang, W.; Wang, C. Response of bacterial community compositions to different sources of pollutants in sediments of a tributary of Taihu Lake, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 13886–13894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Peng, Z.; Hu, W.; Zhu, J. Research on application of a new bottom trap technology to catch particles rich in nutrients in a large shallow lake. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 300, 113798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, W.; Yan, Y.; Liu, B.; Wang, T.; Mao, S.; Song, N.; Dou, H.; Ao, W.; Zou, C. Correction to: Organic Matter Pollution During the Spring Thaw in Hulun Lake Basin: Contribution of Multiform Human Activities. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 105, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, D. Response of Lake Sediment Organic Matter to Climate Change in the Past Century: A Case Study of Qinghai Lake. J. Lake Sci. 2022, 34, 1234–1245. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Xiao, J.; Wen, R.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Cui, L.; Yamagata, H. Organic geochemical investigations of the Dali Lake sediments in northern China: Implications for environment and climate changes of the last deglaciation in the East Asian summer monsoon margin. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2017, 140, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Lake | Source Types | Main Source Contribution | OM Tracers | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poyang Lake | Aquatic macrophytes, soil, phytoplankton | Soil | 13C, 15N, C/N | [18] |
| Datun Lake | Terrestrial sewage, soil, phytoplankton | Terrestrial sewage 40.95%, phytoplankton 32.93% | 13C, 15N, C/N | [76] |
| Changqiao Lake | Terrestrial sewage, soil, phytoplankton | Terrestrial sewage 32.75%, soil 39.85% | 13C, 15N, C/N, TOC, TN | [76] |
| Lu Lake | Soil, phytoplankton | Soil | 13C, 15N, C/N, TOC, TN | [77] |
| Lakes of Northern Tibet Plateau | C3 plants, aquatic plants, phytoplankton, lacustrine algae | Plankton algae, lacustrine algae | 13C, C/N | [78] |
| Dianchi Lake | Terrestrial vegetation, terrestrial sewage, macrophyte | Terrestrial vegetation, terrestrial sewage | 13C, 15N, C/N | [79] |
| Lake Hongfeng and Lake Baihua | Industry wastes, phytoplankton, terrigenous organic debris | Industry wastes, phytoplankton | C/N, 15N | [80] |
| Qinghai Lake | Terrigenous, phytoplankton | Phytoplankton | 13C, 15N, C/N | [81] |
| Hulun Lake | Aquatic plants | Aquatic plants | C/N | [74] |
| Hulun Lake | Terrigenous, autogenesis | Terrigenous 80% | 13C, C/N | [71] |
| Qinghai Lake | C3 terrestrial plants, lacustrine algae | C3 terrestrial plants | 13C, 14C | [63] |
| East Bays of Taihu lake | Macrophytes, diatoms, terrestrial higher plants | Macrophytes, diatoms | 13C, C/N | [55] |
| Meiliang Bay of Lake Taihu | Terrestrial plants, algae, aquatic vascular plants | Algae | 13C, 15N, C/N | [39] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, C.; Ran, F.; Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Fan, C. Distribution Characteristics and Driving Mechanisms of Organic Matter in Sediment of Lakes in China: A Review. Water 2025, 17, 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091294
Zhao C, Ran F, Liu S, Wang L, Fan C. Distribution Characteristics and Driving Mechanisms of Organic Matter in Sediment of Lakes in China: A Review. Water. 2025; 17(9):1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091294
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Chun, Fuyuan Ran, Sihong Liu, Liujiang Wang, and Chunzhen Fan. 2025. "Distribution Characteristics and Driving Mechanisms of Organic Matter in Sediment of Lakes in China: A Review" Water 17, no. 9: 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091294
APA StyleZhao, C., Ran, F., Liu, S., Wang, L., & Fan, C. (2025). Distribution Characteristics and Driving Mechanisms of Organic Matter in Sediment of Lakes in China: A Review. Water, 17(9), 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091294







