Temporal and Spatial Variation Characteristics of Seasonal Differences in Extreme Precipitation in China Monsoon Region in the Last 40 Years
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Area Summary
2.2. Data
2.3. Method
2.3.1. Extreme Precipitation Index
2.3.2. Mann–Kendall Trend Test and Sen Slope
3. Results
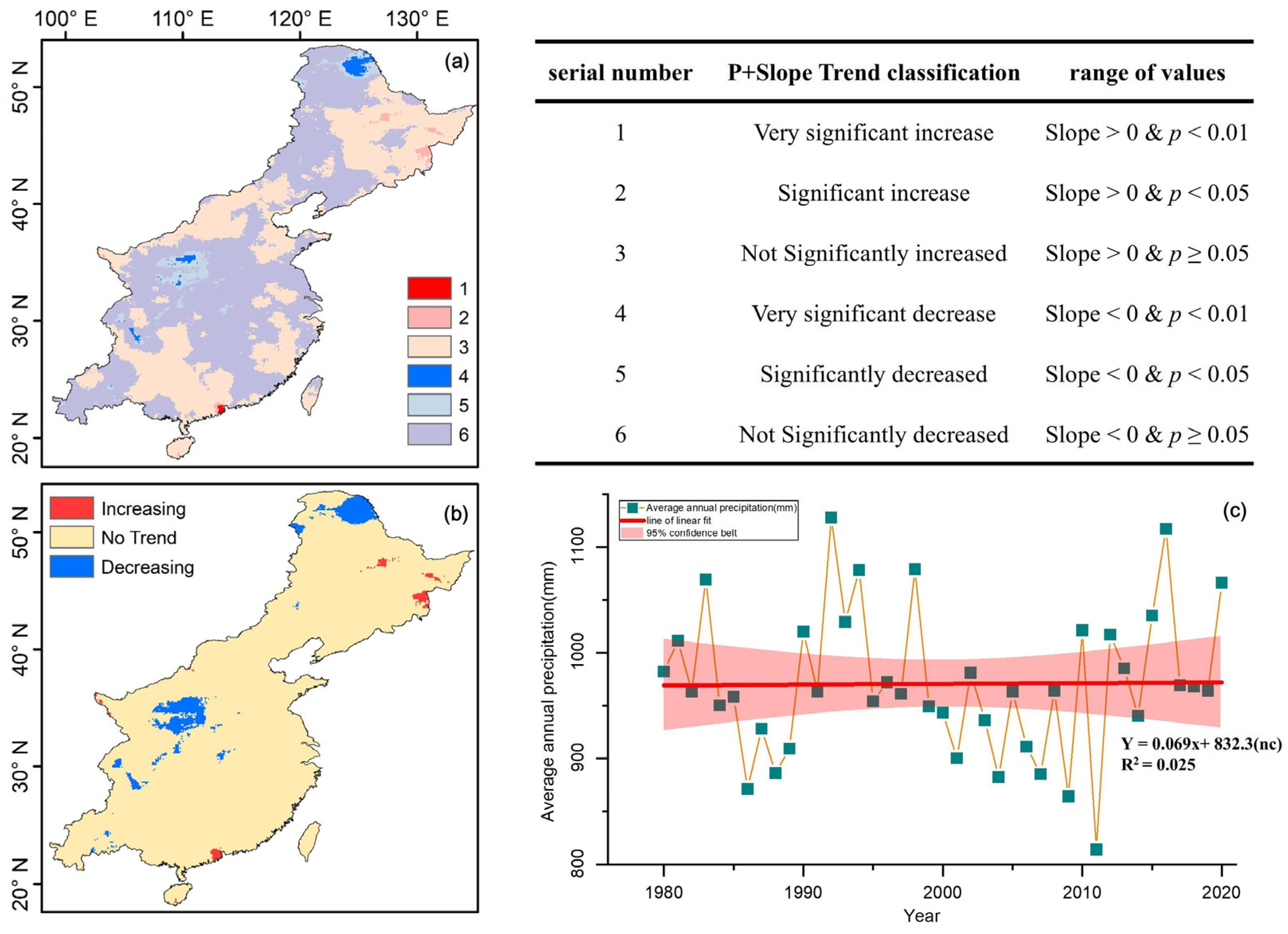
3.1. The Temporal and Spatial Variation Trend of Precipitation in Monsoon Region of China
3.2. Temporal and Spatial Variations in Seasonal Differences of Extreme Precipitation Intensity in Monsoon Region of China
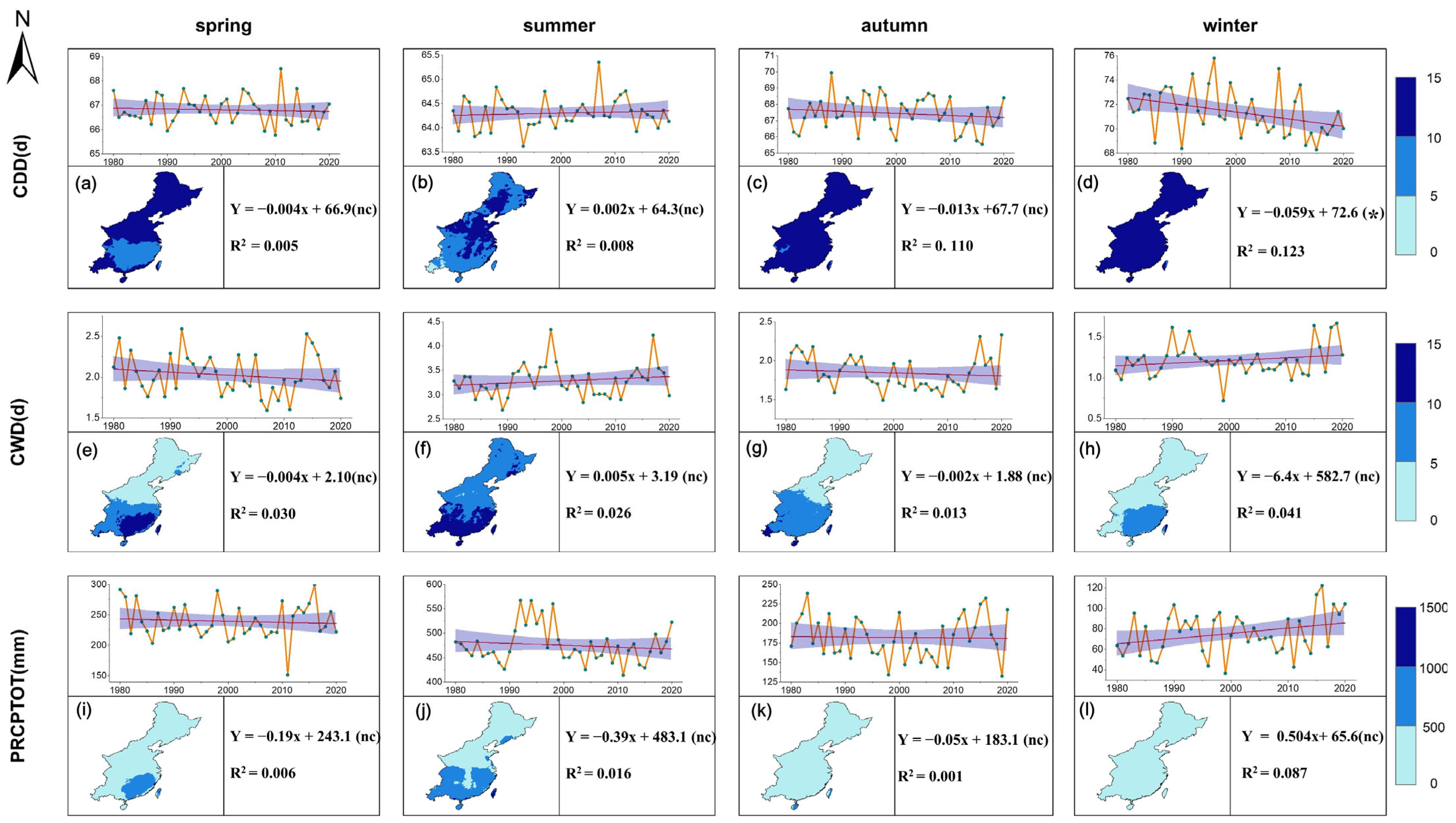
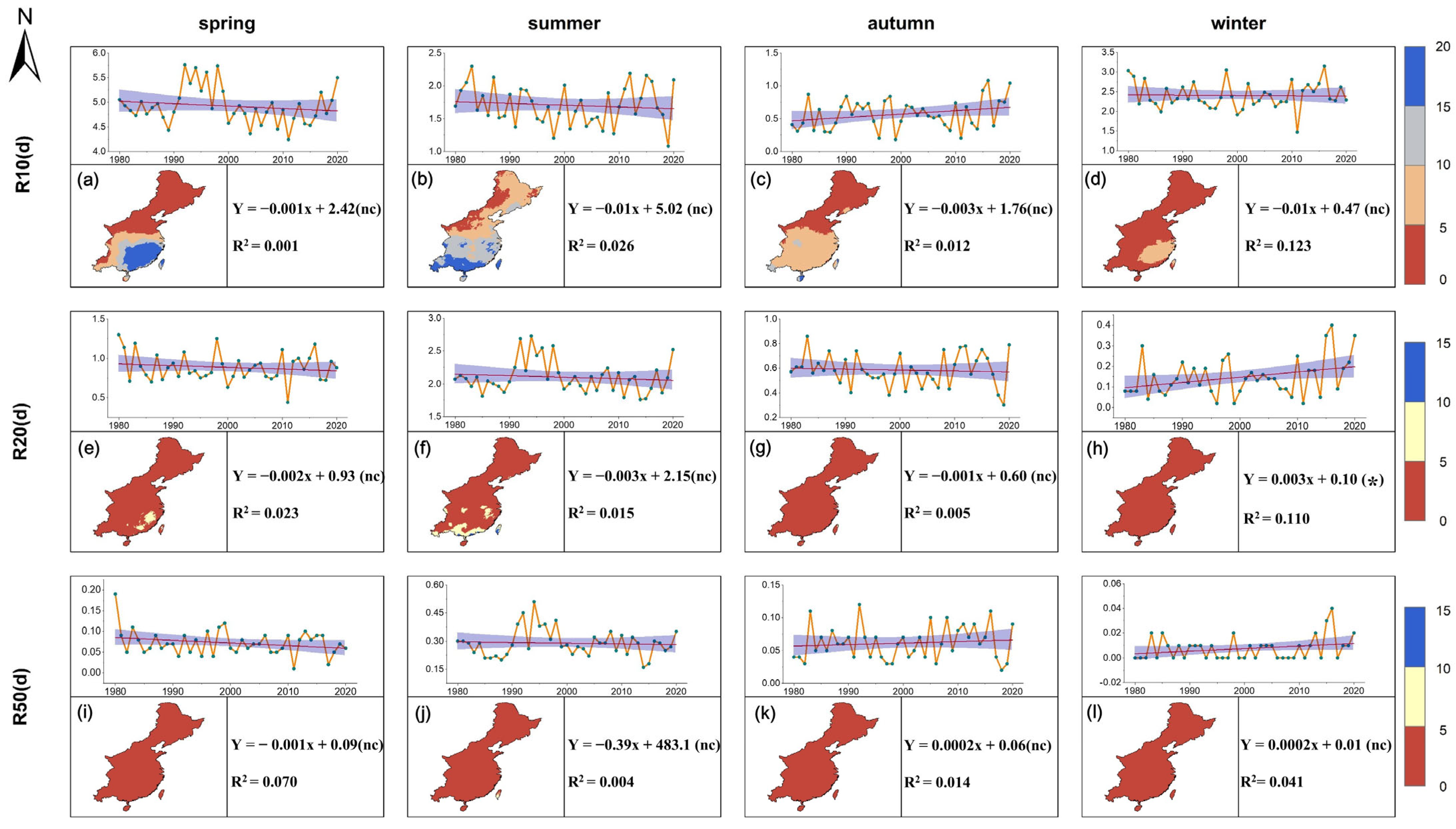
3.3. Temporal and Spatial Variations in Seasonal Differences in Extreme Precipitation Duration in the Monsoon Region of China
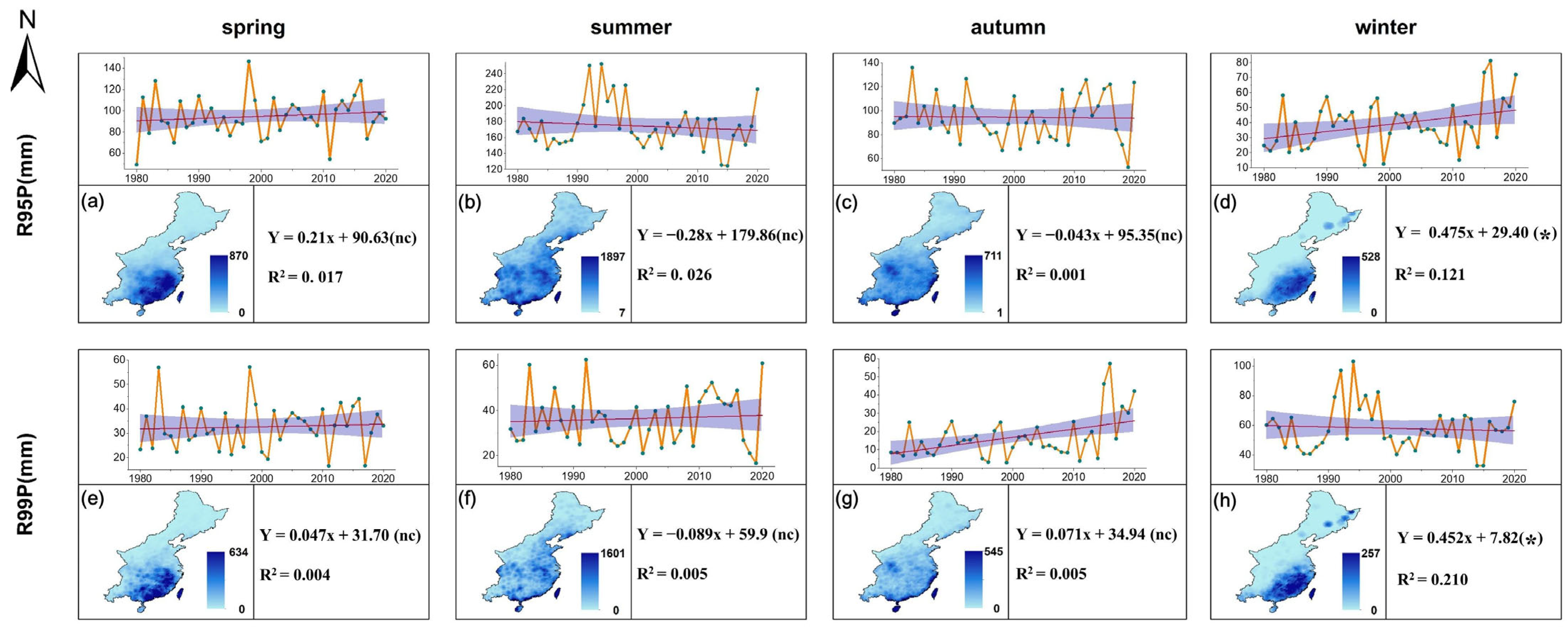
3.4. Temporal and Spatial Variations in Seasonal Differences of the Extreme Precipitation Threshold in the Monsoon Region of China
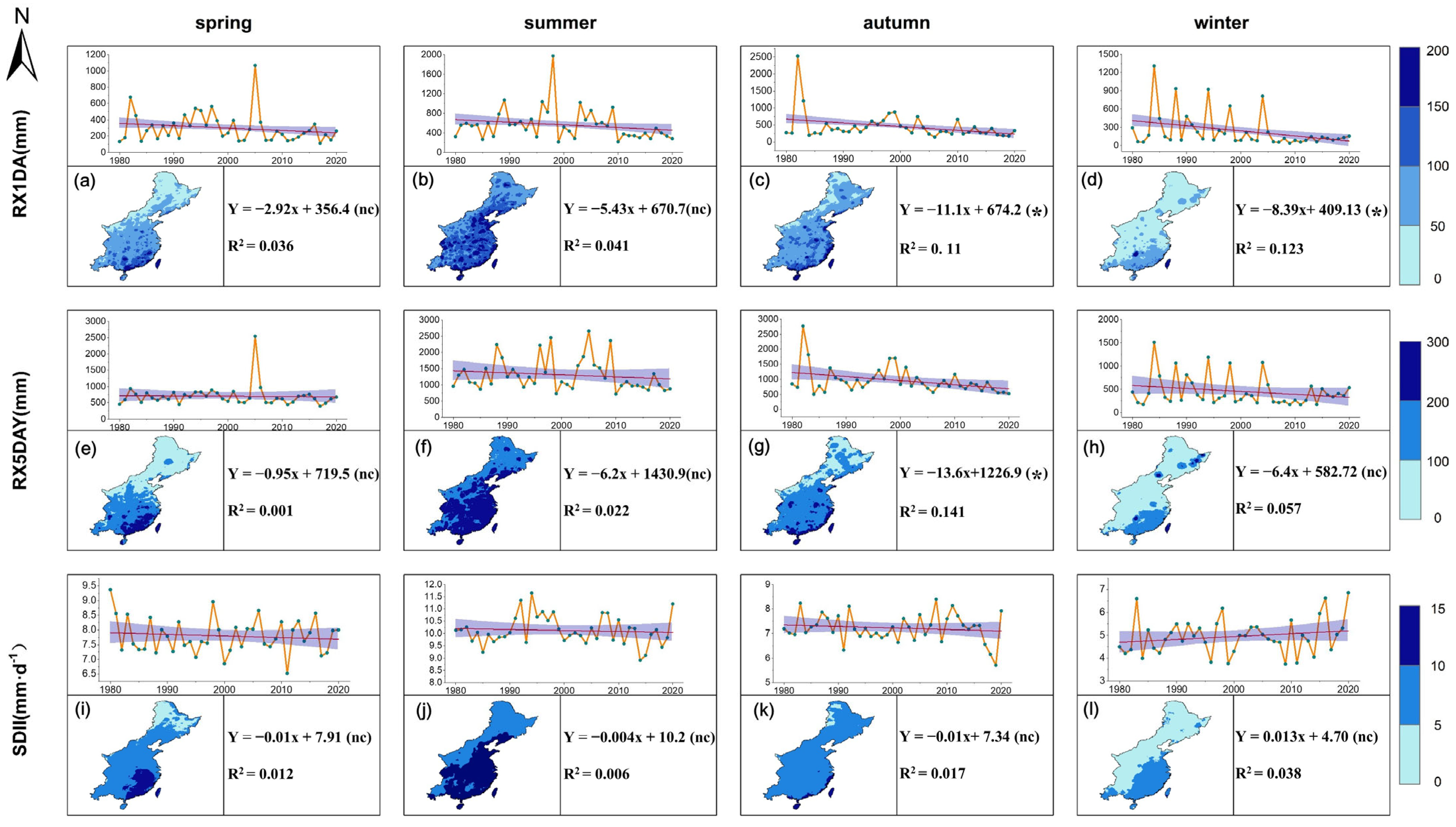
3.4.1. Temporal and Spatial Variations in Seasonal Differences of Absolute Threshold Index
3.4.2. Temporal and Spatial Variations in Seasonal Differences of Relative Threshold Index
4. Discussion
4.1. The Spatial and Temporal Differentiation Characteristics of Precipitation Trend
4.2. Seasonal and Spatial Differentiation of Extreme Precipitation Intensity
4.3. Dry and Wet Seasonal Dynamics of Extreme Precipitation Duration
4.4. Seasonal Sensitivity of Extreme Precipitation Threshold
4.5. The Actual Impact and Measures of Winter Precipitation Enhancement on Southern China
4.6. Comprehensive Discussion and Mechanism Correlation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frame, D.J.; Rosier, S.M.; Noy, I.; Harrington, L.J.; Carey-Smith, T.; Sparrow, S.N.; Stone, D.A.; Dean, S.M. Climate Change Attribution and the Economic Costs of Extreme Weather Events: A Study on Damages from Extreme Rainfall and Drought. Clim. Chang. 2020, 162, 781–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristie, L.E.; Jennifer, V.; Jane, W.B.; Jesse, E.B.; David, M.H.; Nicole, A.E.; Katie, H.; Colleen, E.R.; Shubhayu, S.; June, S.; et al. Extreme Weather and Climate Change: Population Health and Health System Implications. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2021, 42, 293–315. [Google Scholar]
- Maximilian, K.; Anders, L.; Leonie, W. The Effect of Rainfall Changes on Economic Production. Nature 2022, 601, 223–227. [Google Scholar]
- Pascale, S.; Lucarini, V.; Feng, X.; Porporato, A.; Hasson, S.U. Projected changes of rainfall seasonality and dry spells in a high greenhouse gas emissions scenario. Clim. Dyn. 2015, 46, 1331–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siyan, D.; Ying, S.; Xuebin, Z. Attributing Observed Increase in Extreme Precipitation in China to Human Influence. Environ. Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 095005. [Google Scholar]
- Westra, S.; Alexander, L.V.; Zwiers, F.W. Global Increasing Trends in Annual Maximum Daily Precipitation. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 3904–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, T.C.; Zhang, X.; Brunet-India, M.; Vázquez-Aguirre, J.L. Changes in North American extremes derived from daily weather data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbero, R.; Fowler, H.J.; Lenderink, G.; Blenkinsop, S. Is the intensification of precipitation extremes with global warming better detected at hourly than daily resolutions? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 974–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchmeier-Young, M.C.; Zhang, X. Human influence has intensified extreme precipitation in North America. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 13308–13313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, E.; Barry, A.A.; Brunet, M.; Ekang, L.; Fernandes, A.; Massoukina, M.; Mbah, J.; Mhanda, A.; do Nascimento, D.J.; Peterson, T.C.; et al. Changes in temperature and precipitation extremes in western central Africa, Guinea Conakry, and Zimbabwe, 1955–2006. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, 13308–13313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegegne, G.; Melesse, A.M.; Alamirew, T. Projected changes in extreme precipitation indices from CORDEX simulations over Ethiopia, East Africa. Atmos. Res. 2021, 247, 105156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Sun, Y.; Li, C. Detection of Human Influence on Precipitation Extremes in Asia. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 5293–5304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donat, M.G.; Alexander, L.V.; Yang, H.; Durre, I.; Vose, R.; Caesar, J. Global land-based datasets for monitoring climatic ex-tremes. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 94, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donat, M.G.; Lowry, A.L.; Alexander, L.V.; O’Gorman, P.A.; Maher, N. Addendum: More extreme precipitation in the world’s dry and wet regions. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2016, 6, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zwiers, F.; Westra, S.; Alexander, L.V. A Global, Continental, and Regional Analysis of Changes in Extreme Precipitation. J. Clim. 2021, 34, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haibo, D.; Lisa, V.A.; Markus, G.D.; Tanya, L.; Arvind, S.; Jim, S.; Andries, K.; Gwangyong, C.; Hong, S.H.; Fumiaki, F.; et al. Precipitation from Persistent Extremes is Increasing in Most Regions and Globally. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 6041–6049. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, P.; Zhang, X.; Wan, H.; Pan, X. Trends in Total Precipitation and Frequency of Daily Precipitation Extremes over China. J. Clim. 2005, 18, 1096–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Yang, N.; Li, M.; Cheng, L.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Chen, T.; Liu, X. Rainfall seasonality changes and its possible teleconnections with global climate events in China. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 53, 3529–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenfeng, H.; Lingling, C.; Jianyun, S.; Junqiang, Y.; Qing, H.; Jing, C. Changes in Extreme Precipitation on the Tibetan Plateau and Its Surroundings: Trends, Patterns, and Relationship with Ocean Oscillation Factors. Water 2022, 14, 2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yao, X.; Ma, J.; Li, R. Research progress and prospects on summer extreme precipitation over the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Trans. Atmos. Sci. 2024, 47, 737–754. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, G.V.; Reddy, K.V.; Srinivasan, R.; Sridhar, V.; Umamahesh, N.; Pratap, D. Spatio-temporal analysis of rainfall extremes in the flood-prone Nagavali and Vamsadhara Basins in eastern India. Weather. Clim. Extrem. 2020, 29, 100265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, N.T.; Khoi, D.N.; Hoan, N.X.; Phung, N.K.; Dang, T.D. Spatiotemporal Trend Analysis of Precipitation Extremes in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam During 1980-2017. Int. J. Disaster Risk Sci. 2021, 12, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pirani, A., Connors, S.L., Péan, C., Chen, Y., Goldfarb, L., Gomis, M.I., Robin Matthews, J.B., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B. The Asian Monsoon; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bhardwaj, A.; Wasson, R.J.; Chow, W.T.L.; Ziegler, A.D. High-intensity monsoon rainfall variability and its attributes: A case study for Upper Ganges Catchment in the Indian Himalaya during 1901–2013. Nat. Hazards 2021, 105, 2907–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konda, G.; Chowdary, J.S.; Gnanaseelan, C.; Parekh, A. Improvement in the skill of CMIP6 decadal hindcasts for extreme rainfall events over the Indian summer monsoon region. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 21737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djakouré, S.; Amouin, J.; Kouadio, K.Y.; Kacou, M. Mesoscale Convective Systems and Extreme Precipitation on the West African Coast Linked to Ocean–Atmosphere Conditions during the Monsoon Period in the Gulf of Guinea. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, D.; Pang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Wu, Z. Large-scale dynamic, heat and moisture structures of monsoon-influenced precipitation in the East Asian monsoon rainy area. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2021, 147, 1007–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.; Ting, M. Low Pressure Systems and Extreme Precipitation in Southeast and East Asian Monsoon Regions. J. Clim. 2021, 34, 1147–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Jiang, D. The changes of monsoon area and monsoon precipitation in China during the mid-Holocene and the last glacial maximum. Sci. Bull. 2015, 60, 400–410. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y. Summer monsoon rainfalls in China. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 1992, 70, 373–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Li, J.; Wan, R.; Dong, X.; Ye, Q. Emergy-Theory-Based Evaluation of Typhoon Disaster Risk in China’s Coastal Zone. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Sun, X.; Tang, J.; Ji, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yang, X.-Q. Summer Regional Pentad Heat Wave in Eastern China and Their Possible Causes. Front. Earth Sci. 2020, 8, 598027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zheng, W.; Wang, S.; Kang, Y. Rain Belt and Flood Peak: A Study of the Extreme Precipitation Event in the Yangtze River Basin in 1849. Water 2021, 13, 2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Yin, S.; Yu, B.; Fan, C.; Wang, W.; Xie, Y. The most extreme rainfall erosivity event ever recorded in China up to 2022: The 7.20 storm in Henan Province. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2023, 27, 4563–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, V.K.; Rastogi, A.; Dua, S.; Basu, C. Healthcare Infrastructure, Resilience and Climate Change: Preparing for Extreme Weather Events; Routledge: Abingdon-on-Thames, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Dong, B.; Zhu, J. Anthropogenic impacts on changes in summer extreme precipitation over China during 1961–2014: Roles of greenhouse gases and anthropogenic aerosols. Clim. Dyn. 2022, 60, 2633–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, A.D.; Stevenson, D.S.; Bollasina, M.A. The role of anthropogenic aerosols in future precipitation extremes over the Asian Monsoon Region. Clim. Dyn. 2018, 52, 6257–6278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, H.E.; Vergopolan, N.; Pan, M.; Levizzani, V.; Van Dijk, A.I.; Weedon, G.P.; Brocca, L.; Pappenberger, F.; Huffman, G.J.; Wood, E.F. Global-scale evaluation of 22 precipitation datasets using gauge observations and hydrological modeling. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 6201–6217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, H.E.; Pan, M.; Roy, T.; Weedon, G.P.; Pappenberger, F.; Van Dijk, A.I.; Huffman, G.J.; Adler, R.F.; Wood, E.F. Daily evaluation of 26 precipitation datasets using Stage-IV gauge-radar data for the CONUS. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 207–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, H.E.; Wood, E.F.; Pan, M.; Fisher, C.K.; Miralles, D.G.; Van Dijk, A.I.; McVicar, T.R.; Adler, R.F. MSWEP V2 global 3-hourly 0.1 precipitation: Methodology and quantitative assessment. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 100, 473–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Jiang, W.; Wang, X.; Lu, J. Accuracy assessment of MSWEP precipitation products in Chinese mainland. Adv. Water Sci. 2018, 29, 455–464. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.; Xu, J.; Dong, B.; Hu, X.; Hu, H.; Yan, S.; Zhu, S.; He, K.; Shi, Z.; Chen, Y.; et al. GMCP: A Fully Global Multisource Merging-and-Calibration Precipitation Dataset (1-Hourly, 0.1°, Global, 2000–the Present). Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2025, 106, E596–E624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Pang, B.; Ren, M.; Shi, S.; Peng, D.; Zhu, Z.; Zuo, D. Evaluation of Performance of Three Satellite-Derived Precipitation Products in Capturing Extreme Precipitation Events over Beijing, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillmann, J.; Kharin, V.V.; Zwiers, F.W.; Zhang, X.; Bronaugh, D. Climate extremes indices in the CMIP5 multimodel ensemble: Part 2. Future climate projections. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 2473–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, N.M.; Saravanan, S. Extreme precipitation indices over India using CMIP6: A special emphasis on the SSP585 scenario. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 47119–47143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Xu, C.; Liu, F.; Song, L.; Cao, L.; Suo, N. Evaluation of CMIP6 models and multi-model ensemble for extreme precipitation over arid Central Asia. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kasri, J.; Lahmili, A.; Soussi, H.; Jaouda, I.; Bentaher, M. Trend Analysis of Meteorological Variables: Rainfall and Temperature. Civ. Eng. J. 2021, 7, 1868–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Q.; Jiang, J.C.; Jiao, F. Characteristics of Extreme Precipitation in Ansai District of Yan’an City, China. J. Appl. Ecol. 2021, 32, 1417–1423. [Google Scholar]
- Sytharith, P.; Saeed, R.; Liheang, B.; Sokhorng, B.; Panha, N.; Lin, L. An Analysis of Extreme Rainfall Events in Cambodia. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 1017. [Google Scholar]
- Anil, A.; Jun, M.; Hiroshi, I.; Kazuyoshi, S.; Umesh, C. Evaluating the Extreme Precipitation Indices and Their Impacts in the Volta River Basin in West Africa from a Nexus Perspective. Sustain. Nexus Forum 2025, 33, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Huangfu, J.; Huang, R.; Chen, W. Statistical analysis and a case study of tropical cyclones that trigger the onset of the South China Sea summer monsoon. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Li, Z.-L. Impacts of the Wave Train along the Asian Jet on the South China Sea Summer Monsoon Onset. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-M.; Gu, S.-X.; Jiang, R.-C.; Lu, G.-H.; Wu, Z.-Y.; Du, X.-X. The relationship between Pacific SSTA and Autumn Extreme Precipitation Events of China. MATEC Web Conf. 2018, 246, 02056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhou, T.; Wu, P.; Guo, Z.; Wang, M. Emergent constraints on future projections of the western North Pacific Subtropical High. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Yuan, J.; Peng, J.; Cao, X.; Duan, W.; Nan, Y.; Mao, M.; Feng, T. Role of the subtropical westerly jet wave train in the eastward-moving heavy rainfall event over southern China in winter: A case study. Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 11, 1107674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Ding, Y. Responses of South and East Asian summer monsoons to different land-sea temperature increases under a warming scenario. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2011, 56, 2718–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinsley, C.W. Reconstructing Atmospheric Changes in Monsoon Regions Using Eolian Dust; MBLWHOI Library: Woods Hole, MA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, B.; Lv, A.; Jia, S.; Zhu, W. Daily Precipitation Changes over Large River Basins in China, 1960–2013. Water 2016, 8, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Chen, H.; Wang, H. Detectable Human Influence on Changes in Precipitation Extremes Across China. Earth’s Future 2022, 10, e2021EF002409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-X.; Zeng, J.-S.; Tang, L.; Zhuang, D. Water vapor transport in the Pearl River basin and its influence on NDVI. ITM Web Conf. 2016, 7, 04007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Luo, Y.; Wu, C.; Zheng, D.; Liu, X.; Xu, W. Convective and Microphysical Characteristics of Extreme Precipitation Revealed by Multisource Observations Over the Pearl River Delta at Monsoon Coast. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2021GL097043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Jiang, Z.; Sun, X.; Li, W.; Li, L. How well do climate models simulate regional atmospheric circulation over East Asia? Int. J. Climatol. 2019, 40, 220–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.X.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, J.C.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, X. Spatial-temporal properties of moisture budget and associated large-scale circulation in the Yangtze River Basin. J. Lake Sci. 2008, 20, 733–740. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, J.-Y.; Ahn, J.-B.; Jhun, J.-G. Winter climate changes over East Asian region under RCP scenarios using East Asian winter monsoon indices. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 48, 577–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, F.; Yan, T.; Zhou, L.; Jiang, Y.; Li, W.; Fan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Mao, K.; Wu, W. Impact of sea ice decline in the Arctic Ocean on the number of extreme low-temperature days over China. Int. J. Clim. 2019, 40, 1421–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhou, T. The onset and seasonal march of East Asian summer monsoon from perspective of moist static energy. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2021, 66, 3744–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Li, L. A Lagrangian analysis of water vapor sources and pathways for precipitation in East China in different stages of the East Asian summer monsoon. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 977–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, B.; Minder, J.R. The impact of snow loss and soil moisture on convective precipitation over the Rocky Mountains under climate warming. Clim. Dyn. 2021, 56, 2915–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Gu, X.; Slater, L.J.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Kong, D. Urbanization-Induced Increases in Heavy Precipitation are Magnified by Moist Heatwaves in an Urban Agglomeration of East China. J. Clim. 2023, 36, 693–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Q.; Wang, Q.; Feng, G.; Jia, Z.; Liu, G. Roles of water vapor sources and transport in the intraseasonal and interannual variation in the peak monsoon rainfall over East China. Clim. Dyn. 2021, 57, 2153–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Sun, J.; Qiu, X.; Yang, Z. Five-Year Climatology of Local Convections in the Dabie Mountains. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Furtado, K.; Zhou, T.; Chen, H.; Li, J.; Guo, Z.; Xiao, C. The diurnal cycle of East Asian summer monsoon precipitation simulated by the Met Office Unified Model at convection-permitting scales. Clim. Dyn. 2018, 55, 131–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Xie, Z.; Tang, W.; Bueh, C.; Gong, Y.; Yan, J. Change in Extreme Precipitation Over Indochina Under Climate Change from a Lagrangian Perspective of Water Vapor. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 758664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Xu, J.; Ye, G.; Shen, W. The influence of different intensity of monsoon on typhoon precipitation: A comparative study of typhoons Soudelor and Maria. Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 11, 1251711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Yang, M.; Yuan, C. Temporal and Spatial Characteristics of Summer Extreme Precipitation in Eastern China and Possible Causalities. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2020, 8, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Xu, X.; Zhang, S.; Xu, H.; Cai, W. Response of remote water vapor transport to large topographic effects and the multi-scale system during the “7.20” rainstorm event in Henan Province, China. Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 11, 1106990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, P.; Lou, Y.; Chen, C.; Shen, C.; Hu, T. Assessing urban drainage pressure and impacts of future climate change based on shared socioeconomic pathways. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2024, 53, 101760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Li, X.; Du, S.; Zhan, Z. Hydraulic Facilities Characteristics along the Upstream Lanchang River. Curr. Trends Civ. Struct. Eng. 2020, 5, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Tan, F.; He, L.; Li, Y. The impact of winter meteorological conditions on agricultural production in 2018/2019. China Agric. Meteorol. 2019, 40, 337–339. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Tan, F.; Li, Y.; Li, X. The impact of winter meteorological conditions on Agricultural production in 2019/2020. Agric. Meteorol. China 2020, 41, 328–330. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, W.; Zhao, X.; Li, S. The impact of winter meteorological conditions on agricultural production in 2020/2021. Agric. Meteorol. China 2021, 42, 438–440. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Li, Y.; Fan, J.; Kong, F.; Zhang, D.; Hu, T. Future changes in urban drainage pressure caused by precipitation extremes in 285 cities across China based on CMIP6 models. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 91, 104404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Index | Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RX1day | −29.17/−77.49 * | −54.34/−154.07 ** | −110.45 **/−105.03 *** | −83.88 **/−94.57 ** |
| RX5day | −96.14/−277.10 * | −191.45/−568.46 * | −396.58 **/−397.21 *** | −351.64 **/−349.17 ** |
| SDII | −0.05/0.06 | −0.04/−0.31 ** | −0.06/−0.01 | 0.13/0.16 |
| R10 | −1056.92/8628.89 | −6441.06/−26829.76 ** | −3493.61/7676.98 | 6474.74 */6607.23 |
| R20 | −2871.49/1382.67 | −3168.85/−19416.98 *** | −1005.06/3173.35 | 3298.14 **/4898.14 * |
| R95p | −101.43/565.29 | −469.99/−1840.11 | 242.50/2234.15 | 1333.79 */1393.96 |
| R99p | −23.10/107.39 | −92.94/−367.17 | 49.85/453.73 | 260.21 */268.53 |
| CDD | −18.68 */0.00 | −0.76 **/−0.89 | 0.00/0.00 | 0.00/0.00 |
| CWD | 0.00/0.00 | −0.05/−0.02 | 0.20/1.76 * | 0.53/0.87 |
| R95ptot | −0.26 **/−0.43 * | 0.01/−0.31 * | 0.19/−0.00 | 0.29/0.90 |
| R99ptot | −0.08/−0.20 * | 0.00/−0.10 | 0.07/−0.13 | −0.09/0.25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sheng, K.; Li, R.; Chen, T.; Wang, L. Temporal and Spatial Variation Characteristics of Seasonal Differences in Extreme Precipitation in China Monsoon Region in the Last 40 Years. Water 2025, 17, 1672. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111672
Sheng K, Li R, Chen T, Wang L. Temporal and Spatial Variation Characteristics of Seasonal Differences in Extreme Precipitation in China Monsoon Region in the Last 40 Years. Water. 2025; 17(11):1672. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111672
Chicago/Turabian StyleSheng, Keding, Rui Li, Tongde Chen, and Lingling Wang. 2025. "Temporal and Spatial Variation Characteristics of Seasonal Differences in Extreme Precipitation in China Monsoon Region in the Last 40 Years" Water 17, no. 11: 1672. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111672
APA StyleSheng, K., Li, R., Chen, T., & Wang, L. (2025). Temporal and Spatial Variation Characteristics of Seasonal Differences in Extreme Precipitation in China Monsoon Region in the Last 40 Years. Water, 17(11), 1672. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111672






