Wear Testing and Anti-Wear Performance Analysis of Surface Coating Materials for Stay Vanes of a Francis Turbine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Principle and Test Method of Sediment Wear Test
2.1. Test Principle
2.2. Test Method
3. Sediment Wear Test Device and Specimen Production
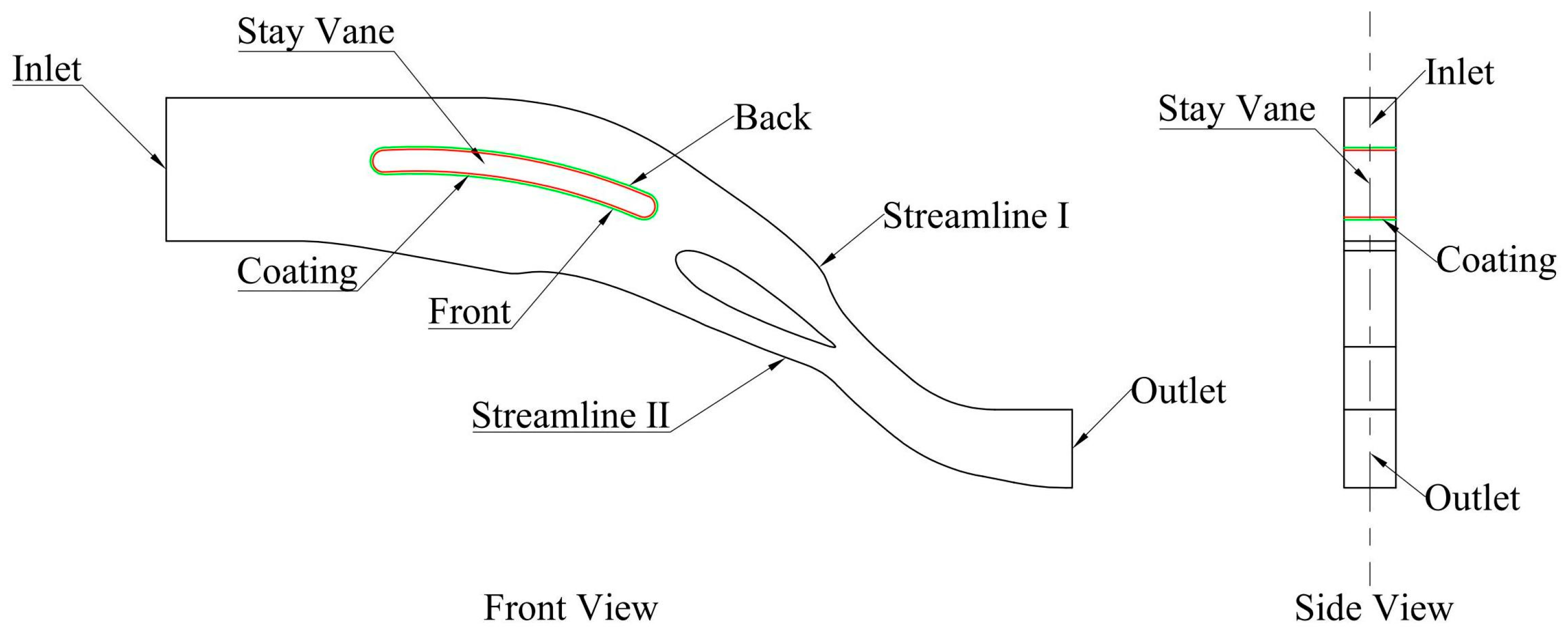
3.1. Design of Test Device
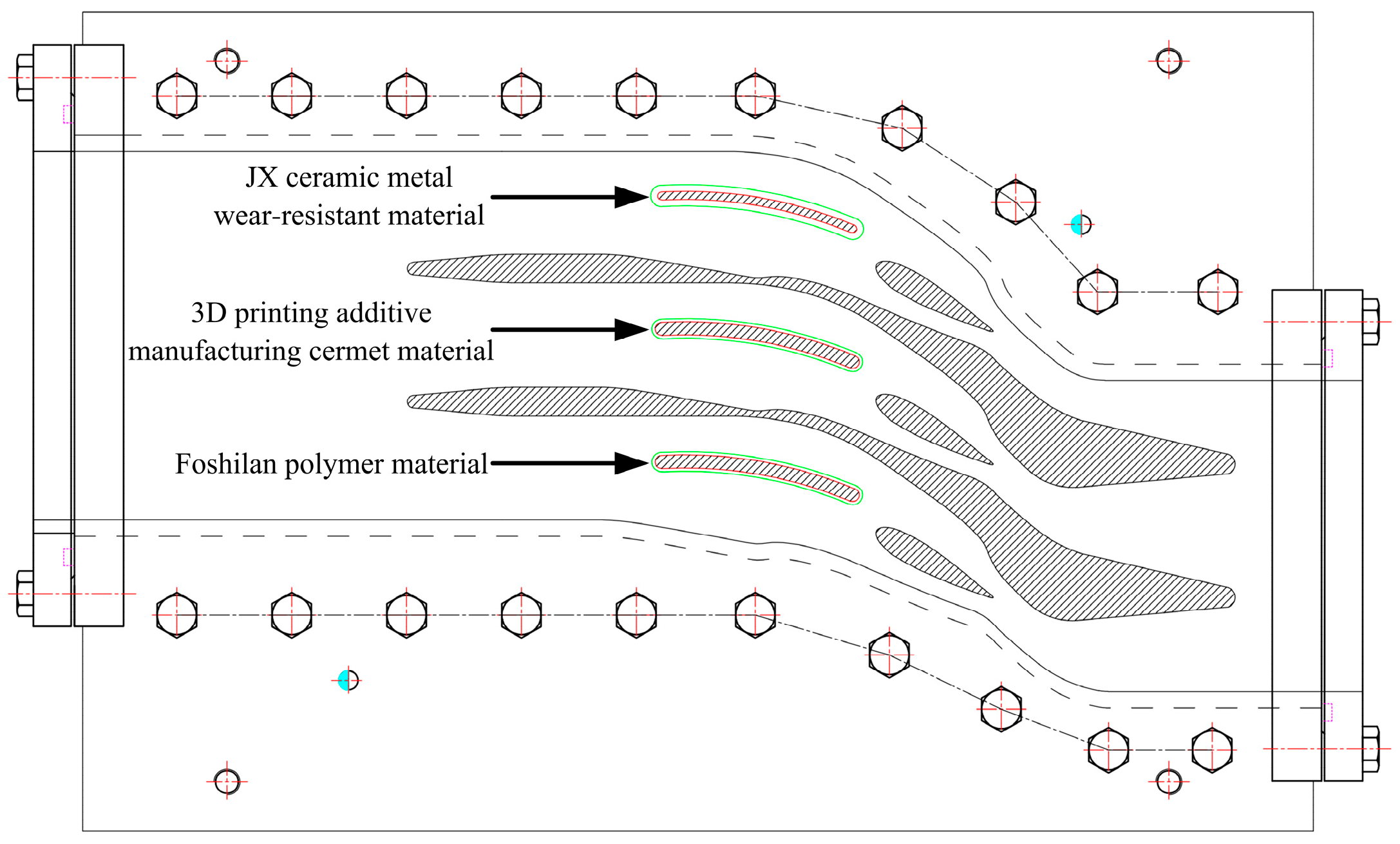
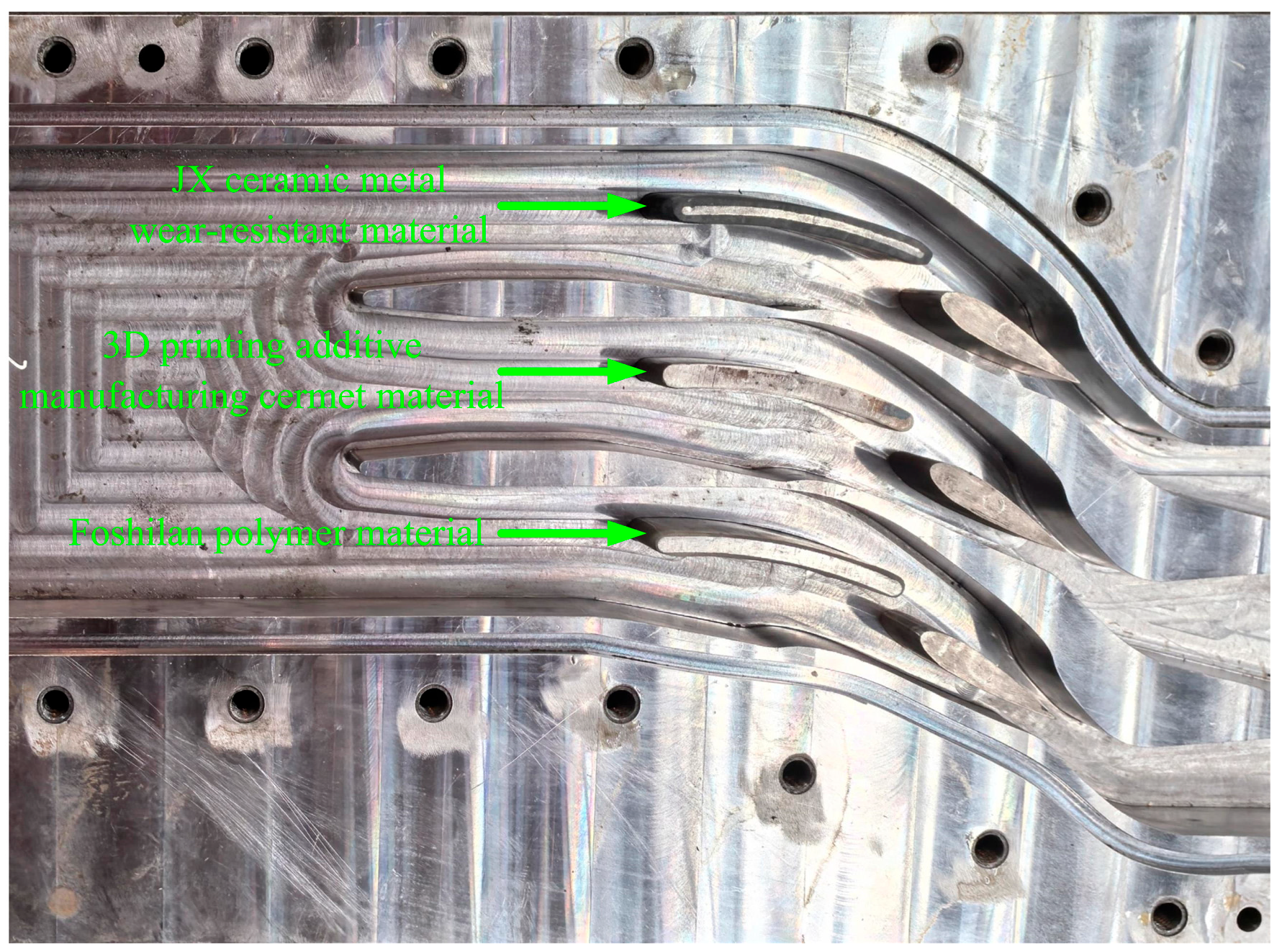
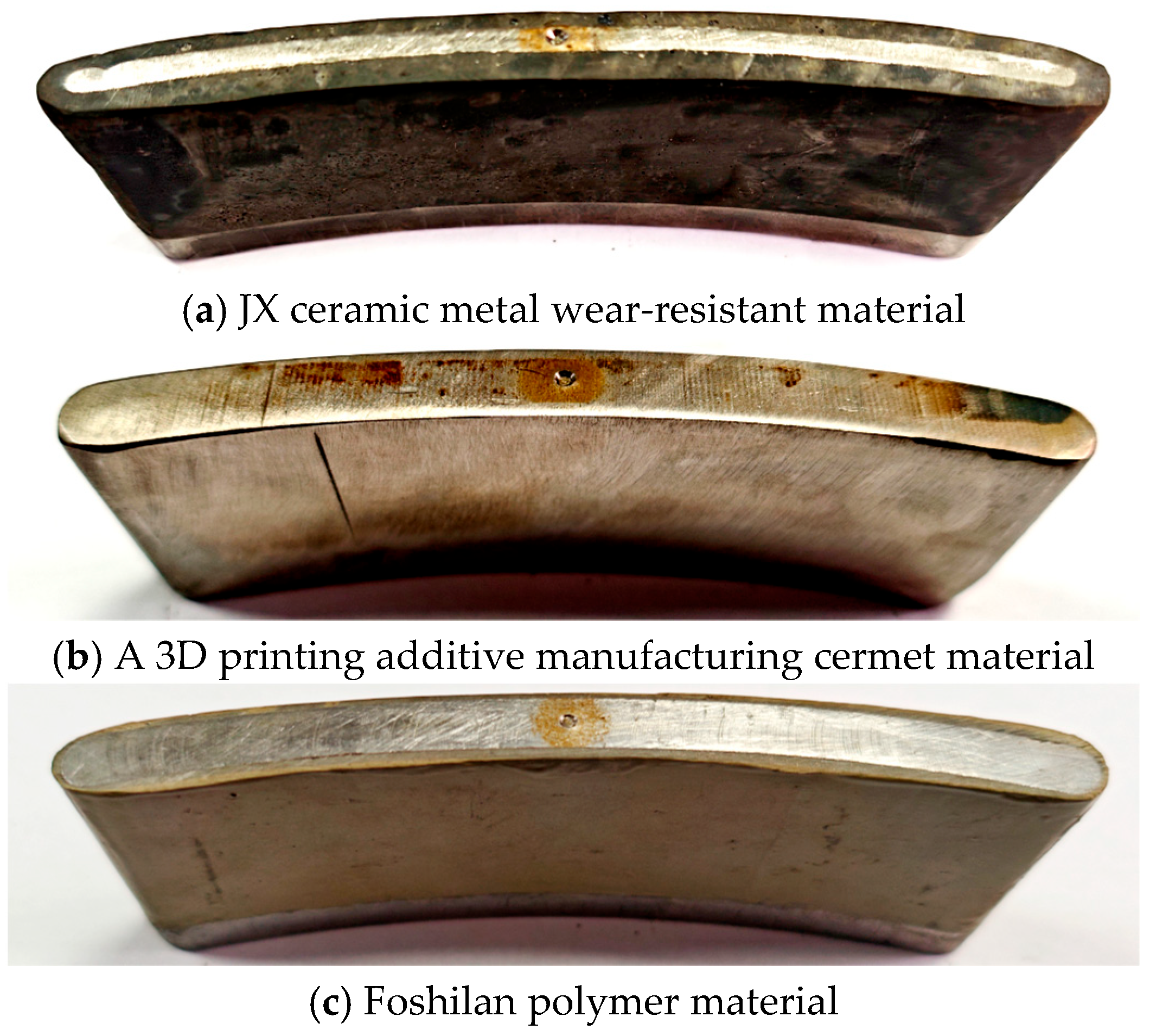
3.2. Specimen Making
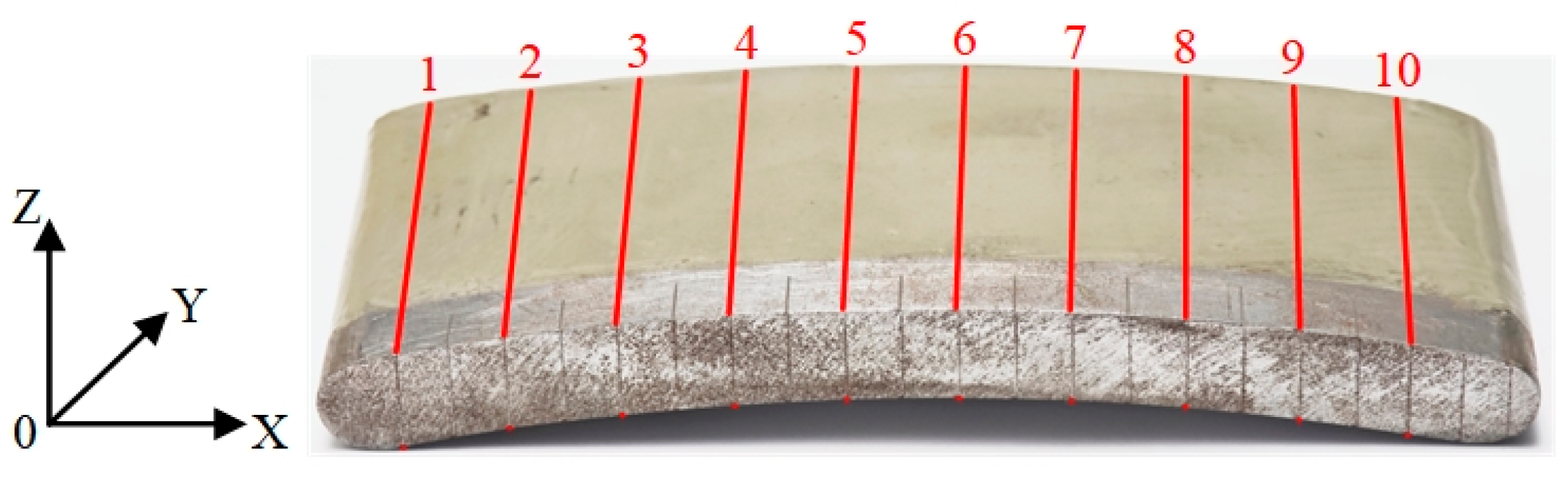
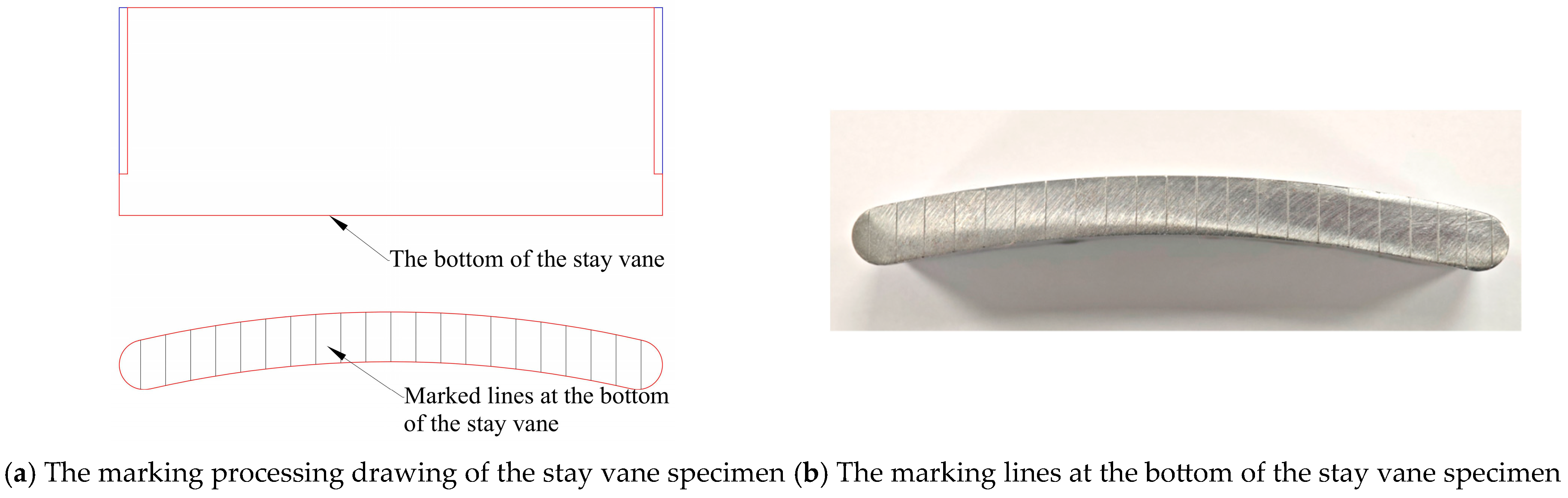
3.3. Specimen Test Positioning Mark
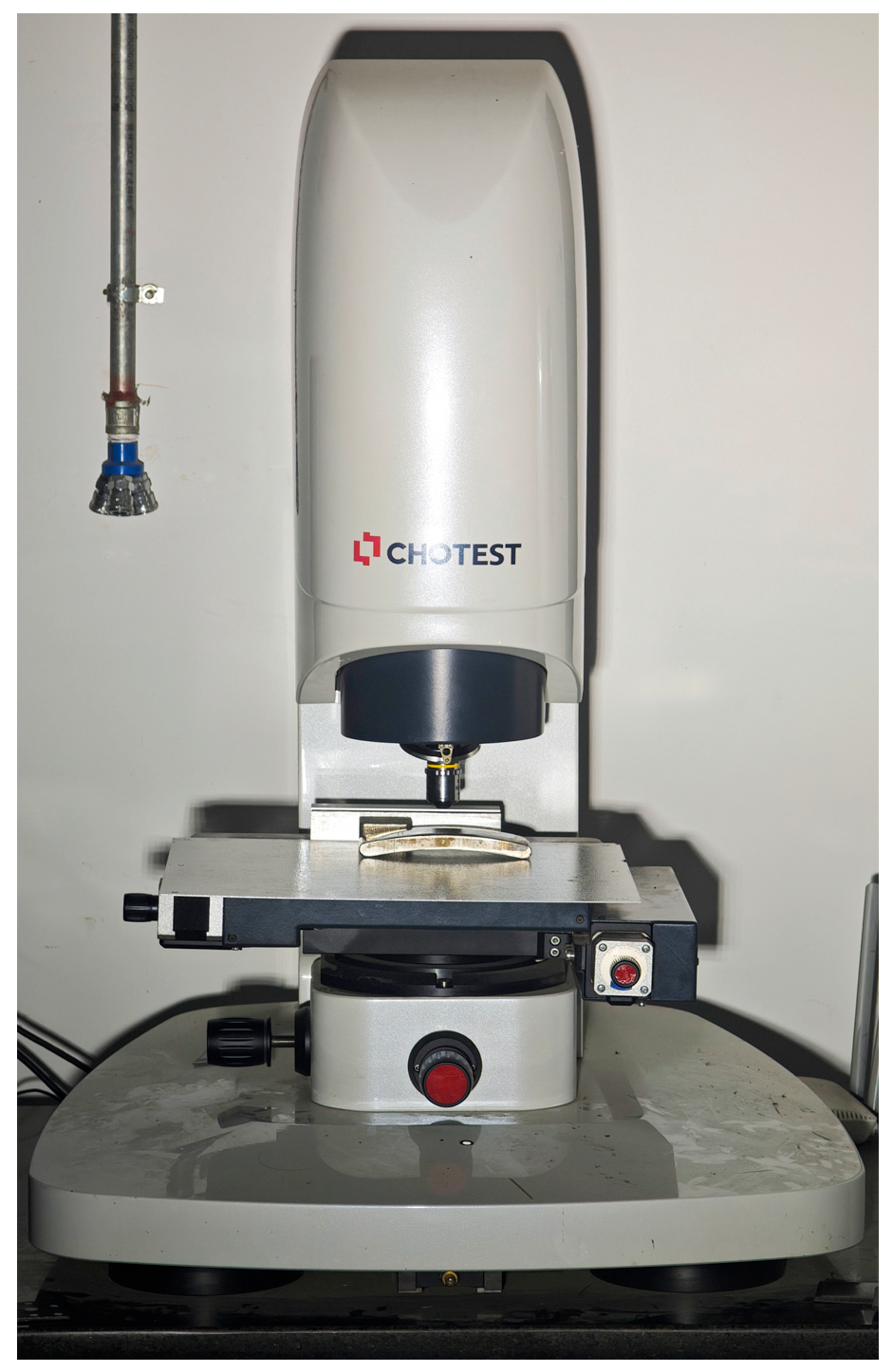
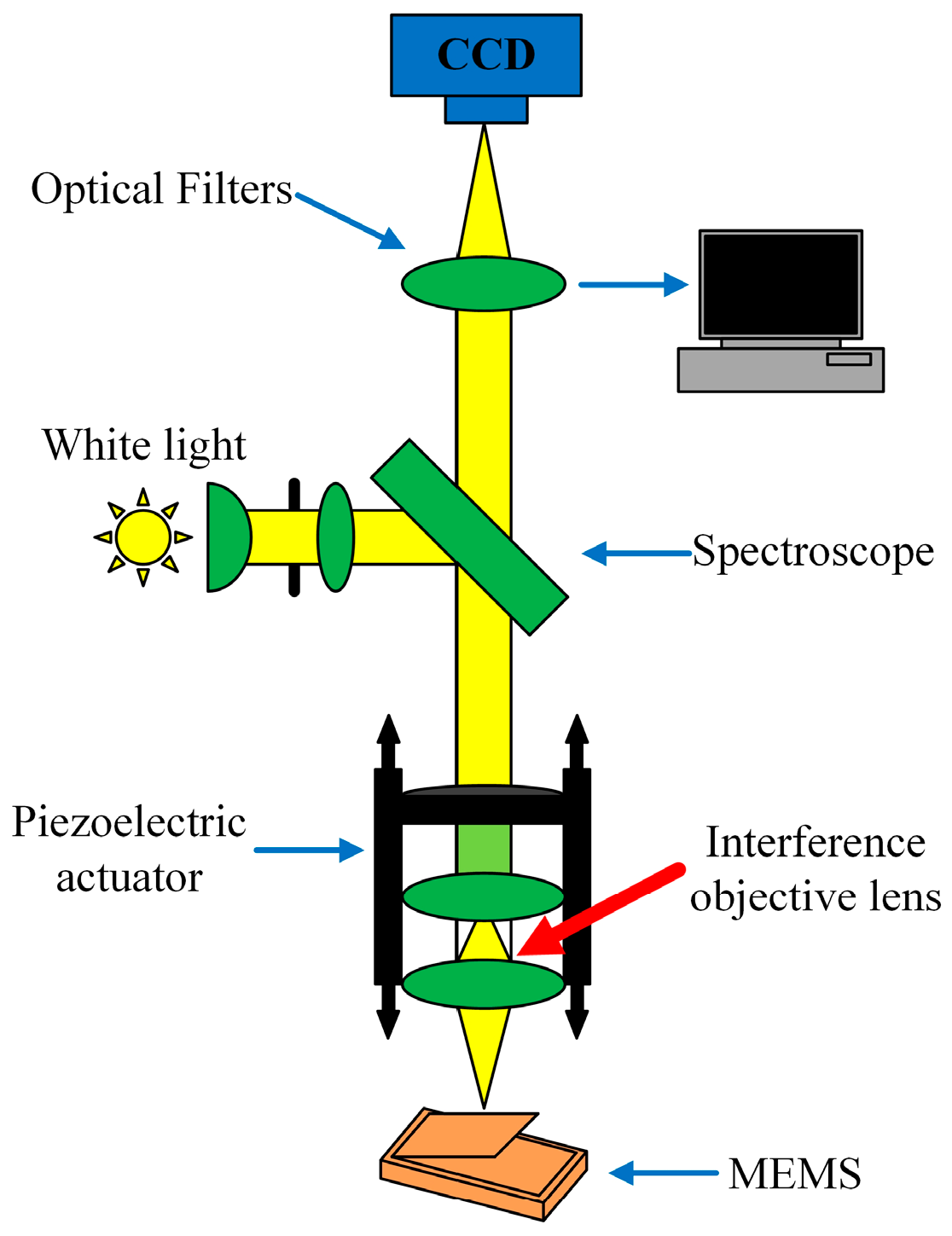
3.4. Construction of Sediment Wear Test System
4. Sediment Wear Test
4.1. Wear Test Parameters
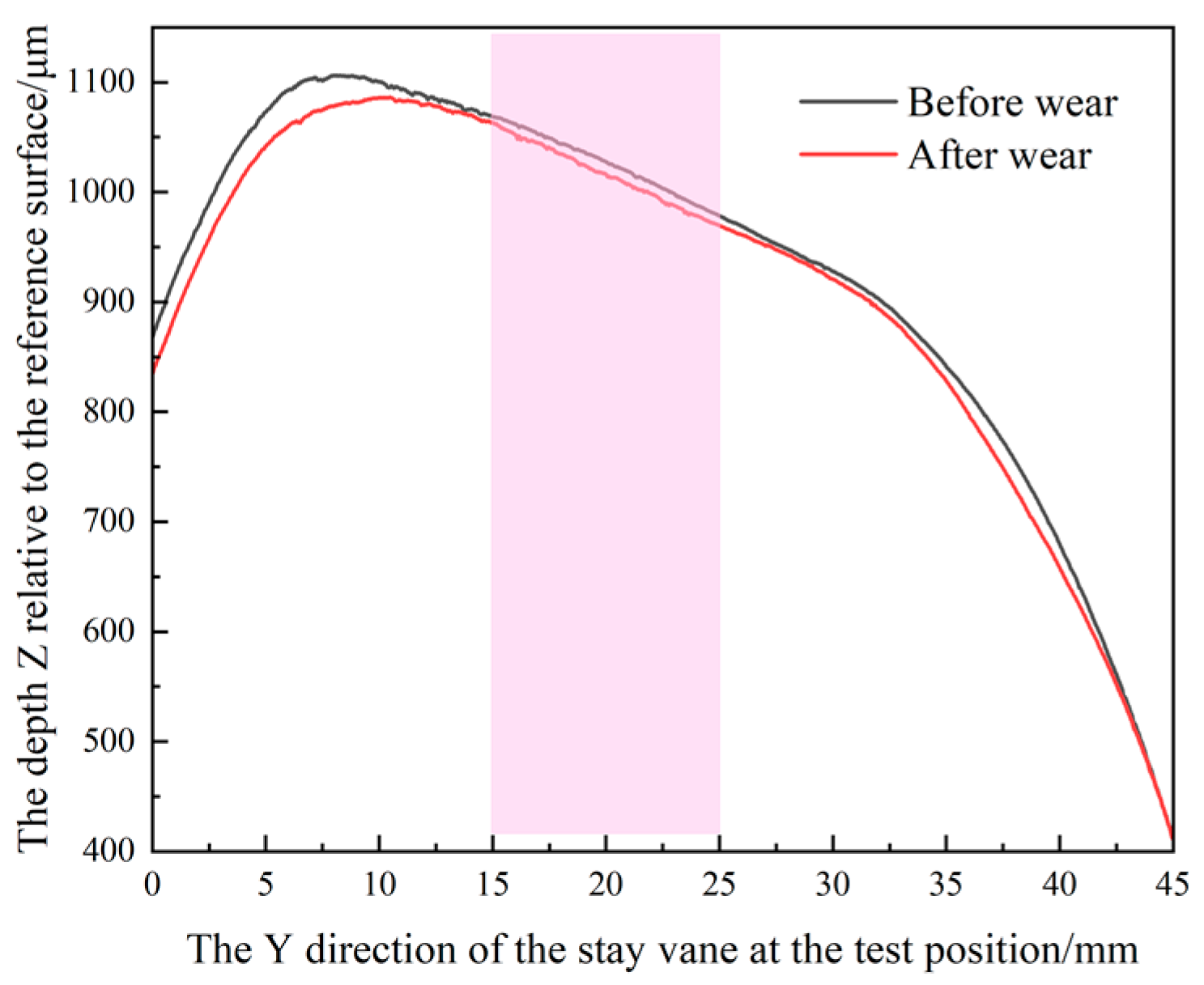
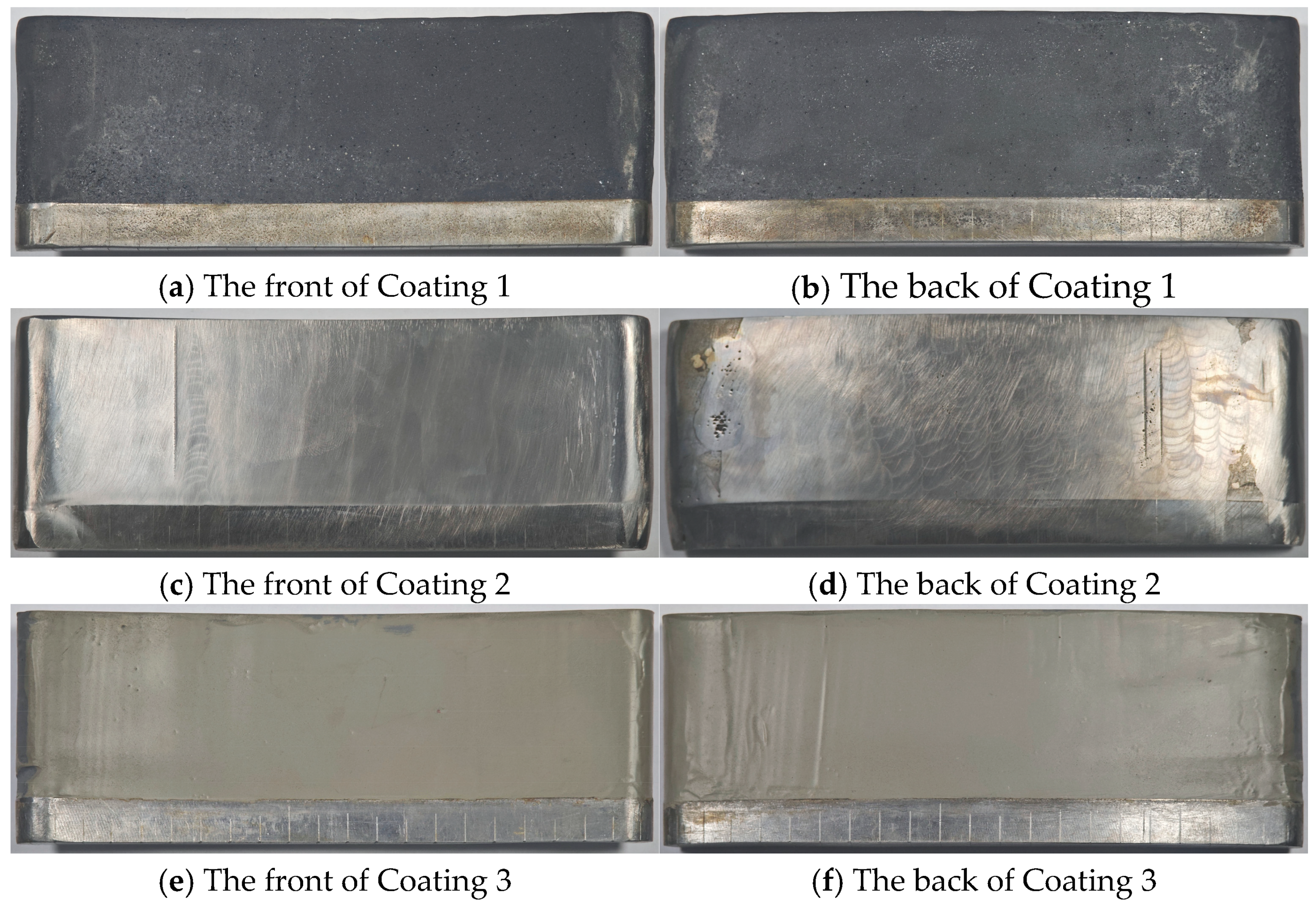
4.2. Test Results of Sediment Wear
4.3. Sediment Wear Test Results
5. Analysis of Anti-Wear Performance of Anti-Wear Coating Materials
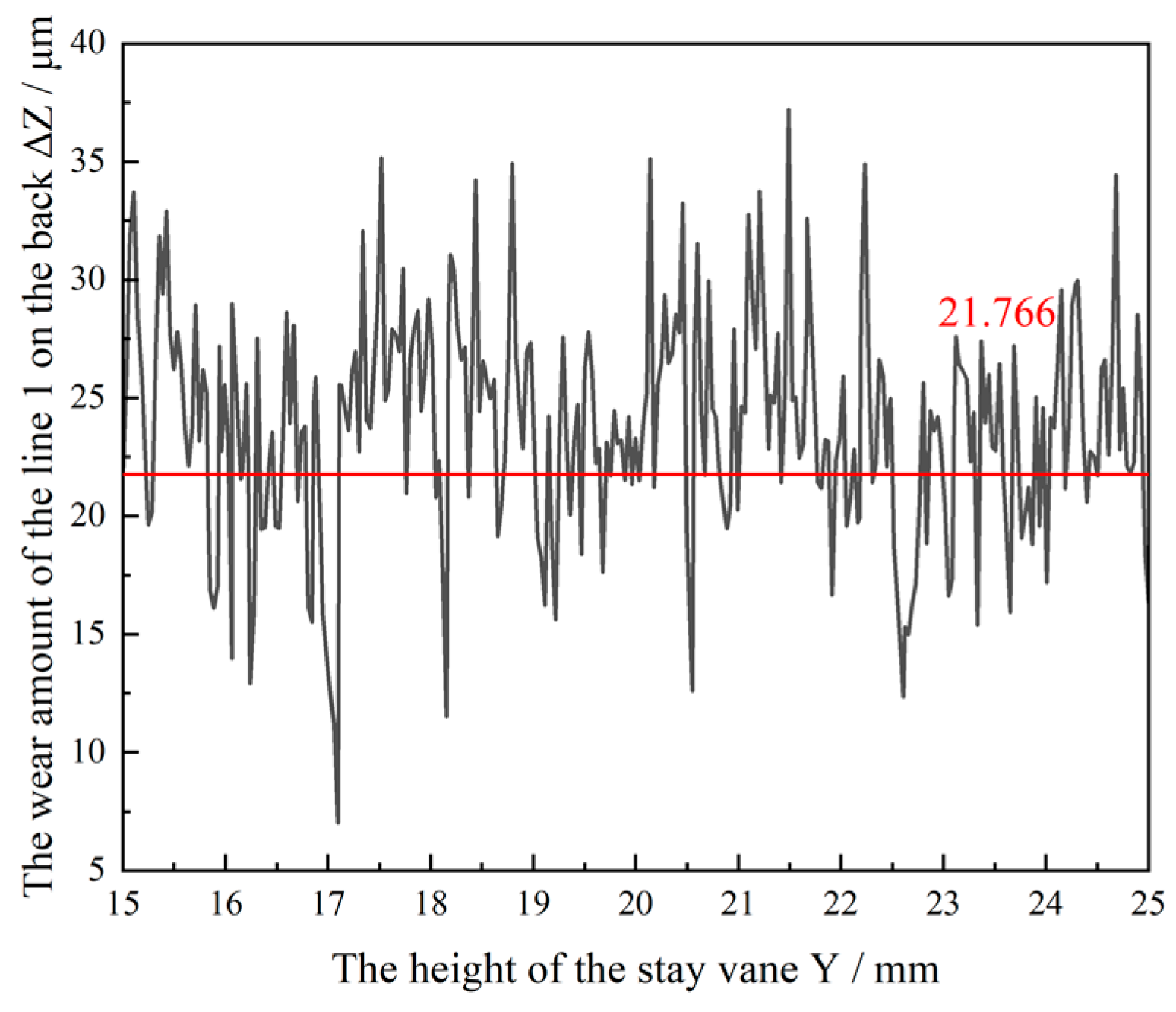
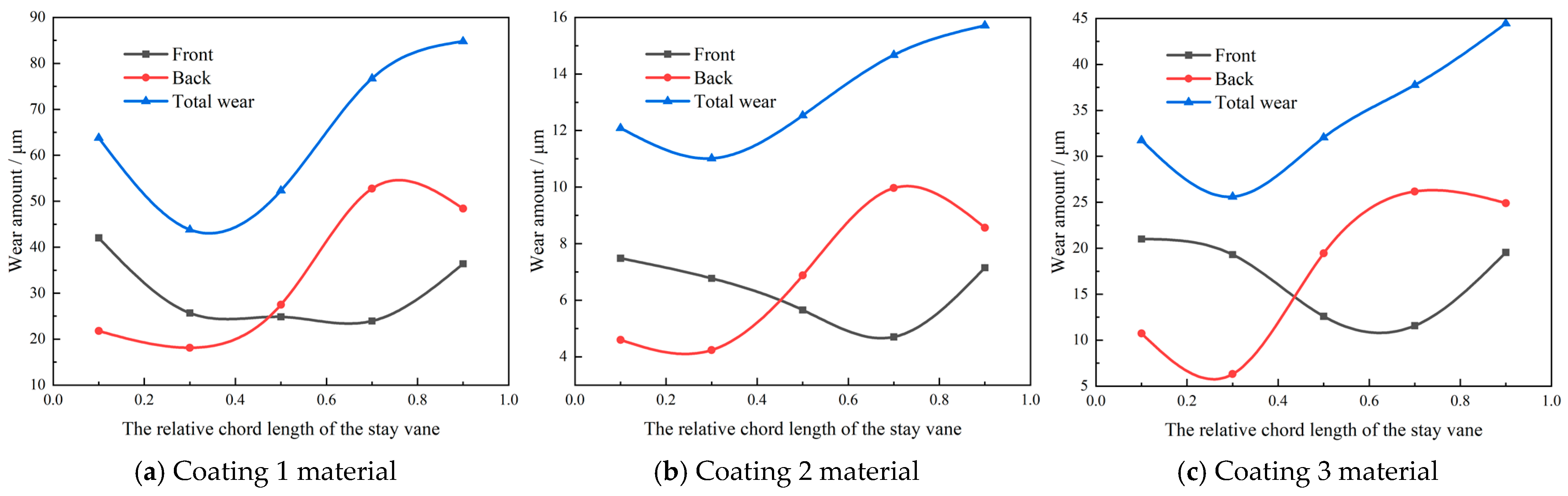
5.1. Wear Distribution of Specimens
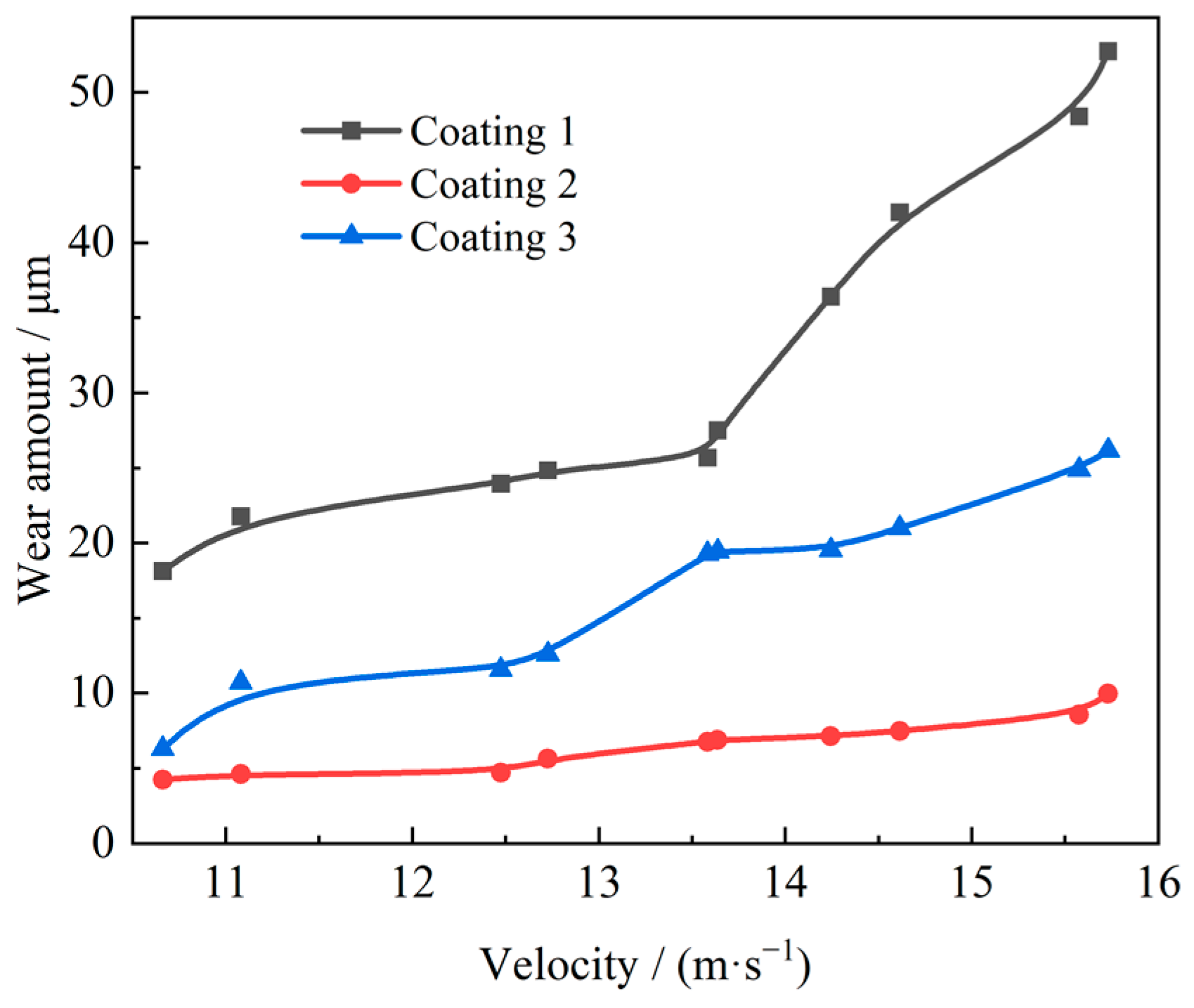
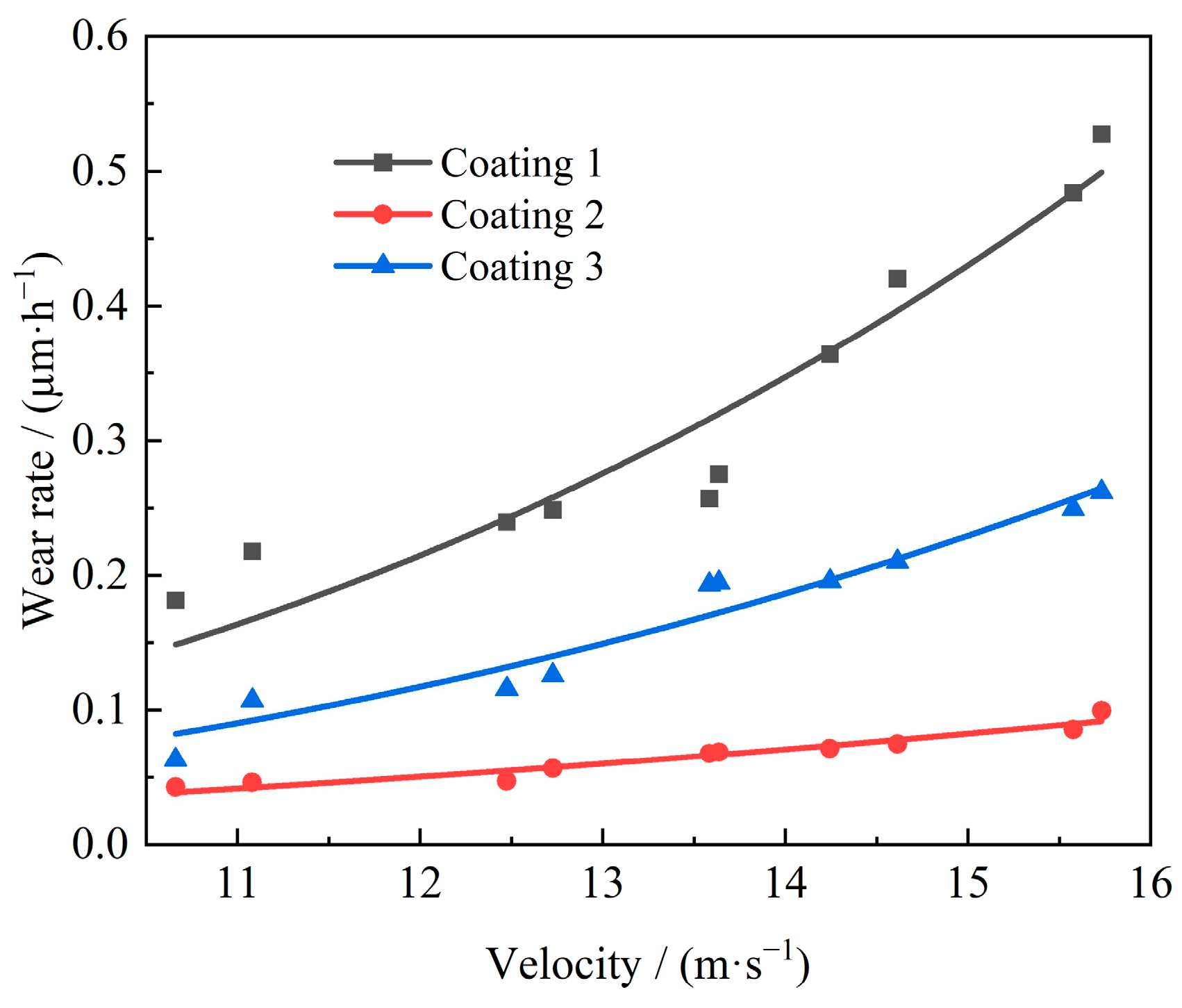
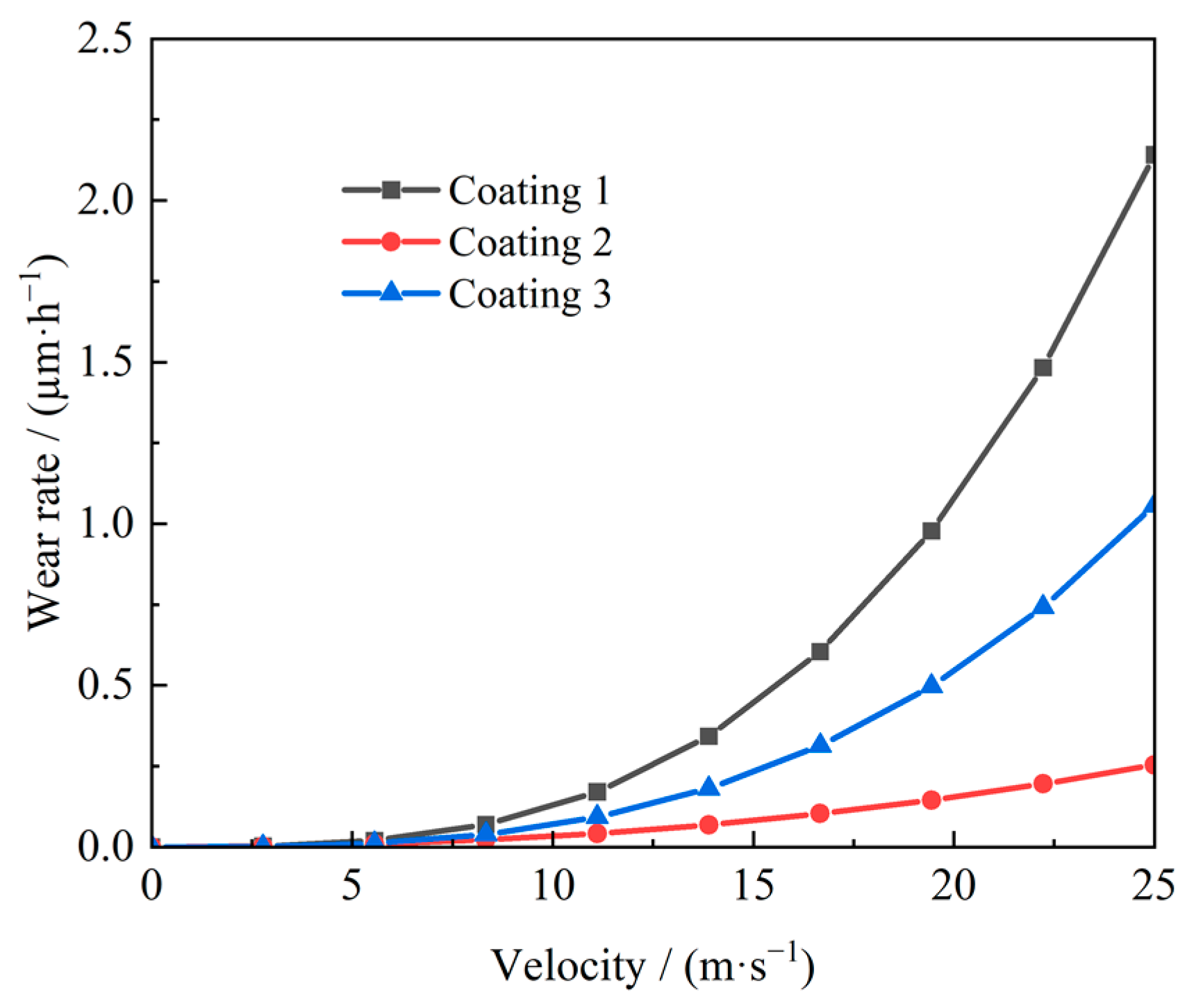
5.2. The Relationship Between Flow Velocity and Wear Amount
5.3. Establish Wear Model (Calculation Formula)
5.4. Wear Prediction
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matsuo, Y.; Yanagisawa, A.; Yamashita, Y. A global energy outlook to 2035 with strategic considerations for Asia and Middle East energy supply and demand interdependencies. Energy Strategy Rev. 2013, 2, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnie, I. Some reflections on the past and future of erosion. Wear 1995, 186–187, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, B.; Gao, Y.; Guo, X.; Li, Y. Research on Corrosion Protection Application of Polymer Composite Coating in Surface of Hydraulic Turbine Guide Vanes in Fuchunjiang Power Plant. Shanghai Coat. 2021, 59, 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, W.J.; Li, G.; Zhou, H.; Cui, T.; Shi, G. Research on Abrasion Resistance of Movable Guide Vane Protection Material for Hydraulic Turbine. Water Resour. Power 2023, 41, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wen, J.; Yang, Y. Development and Application of New Cavitation Treatment Process for Fixed Guide Blade of Turbine. Yunnan Water Power 2022, 38, 35–37. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Wen, Z. The application of Thermal Spraying Technology for Turbine flow-through Components in Shangmati Hydropower Station. Technol. Mark. 2021, 28, 49–51+54. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Feng, T.; Wu, Z.; Hu, Z.; Lv, J.; Ma, B.; Li, G. The application of Non-metallic anti-wear coatings in the flow-through components of Water turbines. Mech. Electr. Tech. Hydropower Stn. 2025, 48, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gang, Y.; Su, L.; Wang, T.; Cai, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Pang, J. Research on sediment erosion and anti-wear coating materials for water-intake components of hydraulic turbines in sandy rivers. Water 2024, 16, 2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B.; Gang, Y.; Xiao, M.; Yu, Z.; Jiang, D.; Pang, J.; Liu, X. Influence of tungsten carbide spray treatment on anti-wear performance of Francis turbine runner blades surface. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2024, 16, 16878132241284212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Kumar, M.; Singh, R.; Kumar, S. Microstructure and cavitation erosion performance of cold-sprayed WC-12Co and WC-17Co coatings on hydraulic turbine steels. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2024, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Kumar, D.; Goyal, R. Assessment of wear-resistance in hydro turbine steel: The impact of sediment erosion on a metal-ceramic coating. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2024; Volume 1411, p. 012003. [Google Scholar]
- Kashyzadeh, R.K.; Ridha, M.K.W.; Ghorbani, S. The influence of nanocoatings on the wear, corrosion, and erosion properties of AISI 304 and AISI 316L stainless steels: A critical review regarding hydro turbines. Corros. Mater. Degrad. 2025, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, E.; Stack, M.M. Erosion mapping of coated composites: Simulating conditions for tidal turbines blades. J. Bio- Tribo-Corros. 2025, 11, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolelli, G.; Berger, L.M.; Börner, T.; Koivuluoto, H.; Lusvarghi, L.; Lyphout, C.; Markocsan, N.; Matikainen, V.; Nylén, P.; Sassatelli, P.; et al. Tribology of HVOF- and HVAF-sprayed WC–10Co4Cr hardmetal coatings: A comparative assessment. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 265, 125–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, A.; Perumal, G.; Arora, H.S.; Grewal, H.S. Enhanced slurry and cavitation erosion resistance of deep cryogenically treated thermal spray coatings for hydroturbine applications. Renew. Energy 2021, 180, 1044–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abgottspon, A.; von Burg, M.; Staubli, T.; Felix, D. Analysis of hydro-abrasive erosion and efficiency changes measured on the coated Pelton turbines of HPP Fieschertal. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; Volume 774, p. 012030. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Pang, X.; Wang, Z.; Huang, D.; Liu, X.; Zeng, Y.; Yao, B.; Pang, J.; Gang, Y.; Hu, Y.; et al. Design and validation of a testing device for sediment-induced erosion based on similarity theory. Water 2025, 17, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zeng, Y. Sand Flow and Wear of Hydraulic Turbine; China Water Resources and Hydropower Press: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]





| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Head H (m) | 290 |
| Stay vanes | 12 |
| Guide vanes | 20 |
| Power P (MW) | 45.8 |
| Design flow rate Q (m3/s) | 17.6 |
| Runner blades (long + short) | 15 + 15 |
| Rotational speed n (r/min) | 500 |
| Particle Size/mm | The Weight Percentage of Sand Smaller Than a Certain Particle Size/% |
|---|---|
| 0.002 | 6.1 |
| 0.005 | 12.22 |
| 0.075 | 32.2 |
| 0.25 | 90 |
| 0.5 | 100 |
| Average particle size/mm | 0.21 mm |
| Coating Materials | Coefficient K | Speed Index n | Calculation Formula Ė |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coating 1 | 9.315 × 10−5 | 3.12 | Ė = 9.315 × 10−5 W3.12 |
| Coating 2 | 2.000 × 10−4 | 2.22 | Ė = 2.000 × 10−4 W2.22 |
| Coating 3 | 6.764 × 10−5 | 3.00 | Ė = 6.764 × 10−5 W3 |
| Month | Sand Content/(kg/m3) | Coating 1 | Coating 2 | Coating 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.022 | 4.45 | 0.7 | 2.28 |
| 2 | 0.026 | 4.75 | 0.74 | 2.43 |
| 3 | 0.029 | 5.87 | 0.92 | 3.01 |
| 4 | 1.088 | 213.09 | 33.36 | 109.15 |
| 5 | 1.055 | 213.52 | 33.42 | 109.37 |
| 6 | 1.315 | 257.55 | 40.31 | 131.92 |
| 7 | 3.734 | 755.71 | 118.29 | 387.08 |
| 8 | 4.528 | 916.4 | 143.44 | 469.39 |
| 9 | 2.186 | 428.14 | 67.02 | 219.3 |
| 10 | 1.453 | 294.07 | 46.03 | 150.62 |
| 11 | 0.482 | 94.4 | 14.78 | 48.35 |
| 12 | 0.0866 | 17.53 | 2.74 | 8.98 |
| Annual maximum wear amount/µm | 3205.48 | 501.75 | 1641.88 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Zeng, Y.; Pang, J.; Li, T.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Z.; Gan, L.; Huang, D. Wear Testing and Anti-Wear Performance Analysis of Surface Coating Materials for Stay Vanes of a Francis Turbine. Water 2025, 17, 1671. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111671
Hu Y, Zhang L, Liu X, Zeng Y, Pang J, Li T, Ma Y, Wang Z, Gan L, Huang D. Wear Testing and Anti-Wear Performance Analysis of Surface Coating Materials for Stay Vanes of a Francis Turbine. Water. 2025; 17(11):1671. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111671
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Yangyang, Lijie Zhang, Xiaobing Liu, Yongzhong Zeng, Jiayang Pang, Tianlin Li, Yuanjiang Ma, Zhongquan Wang, Longchao Gan, and Dong Huang. 2025. "Wear Testing and Anti-Wear Performance Analysis of Surface Coating Materials for Stay Vanes of a Francis Turbine" Water 17, no. 11: 1671. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111671
APA StyleHu, Y., Zhang, L., Liu, X., Zeng, Y., Pang, J., Li, T., Ma, Y., Wang, Z., Gan, L., & Huang, D. (2025). Wear Testing and Anti-Wear Performance Analysis of Surface Coating Materials for Stay Vanes of a Francis Turbine. Water, 17(11), 1671. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111671






