Water Quality Management in the Age of AI: Applications, Challenges, and Prospects
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. AI for Water Quality Monitoring
2.1. Application of AI in Real-Time Water Quality Monitoring
2.2. AI Combined with RS and Unmanned Monitoring: Expanding New Dimensions in Water Quality Monitoring
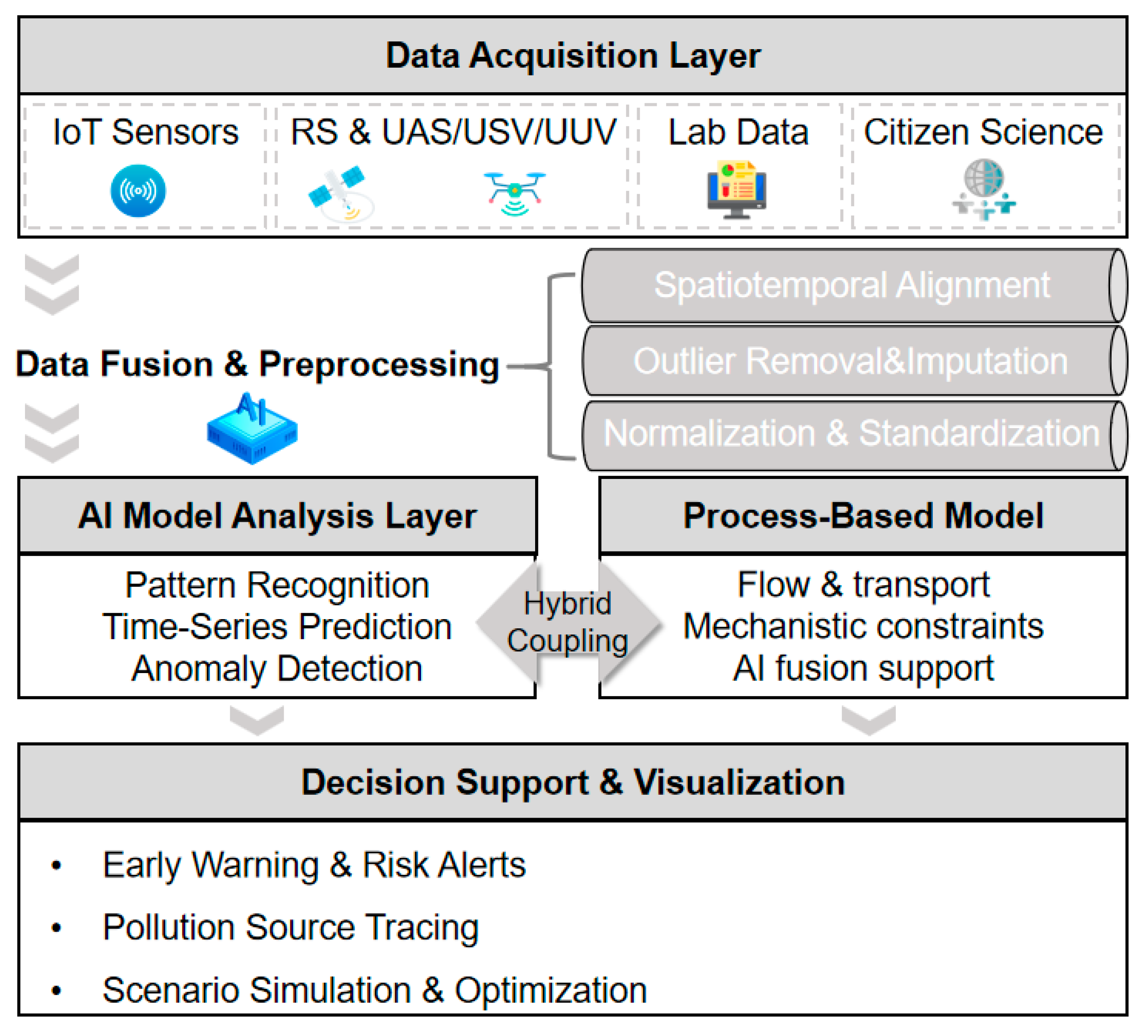
2.3. Multi-Source Data Fusion and Intelligent Analysis
3. The Application of AI in Water Quality Prediction
3.1. Water Quality Prediction Based on Historical and Real-Time Data
3.2. AI Coupled with Process-Based Models (PBM)
4. The Application of AI in Smart Water Environment Management
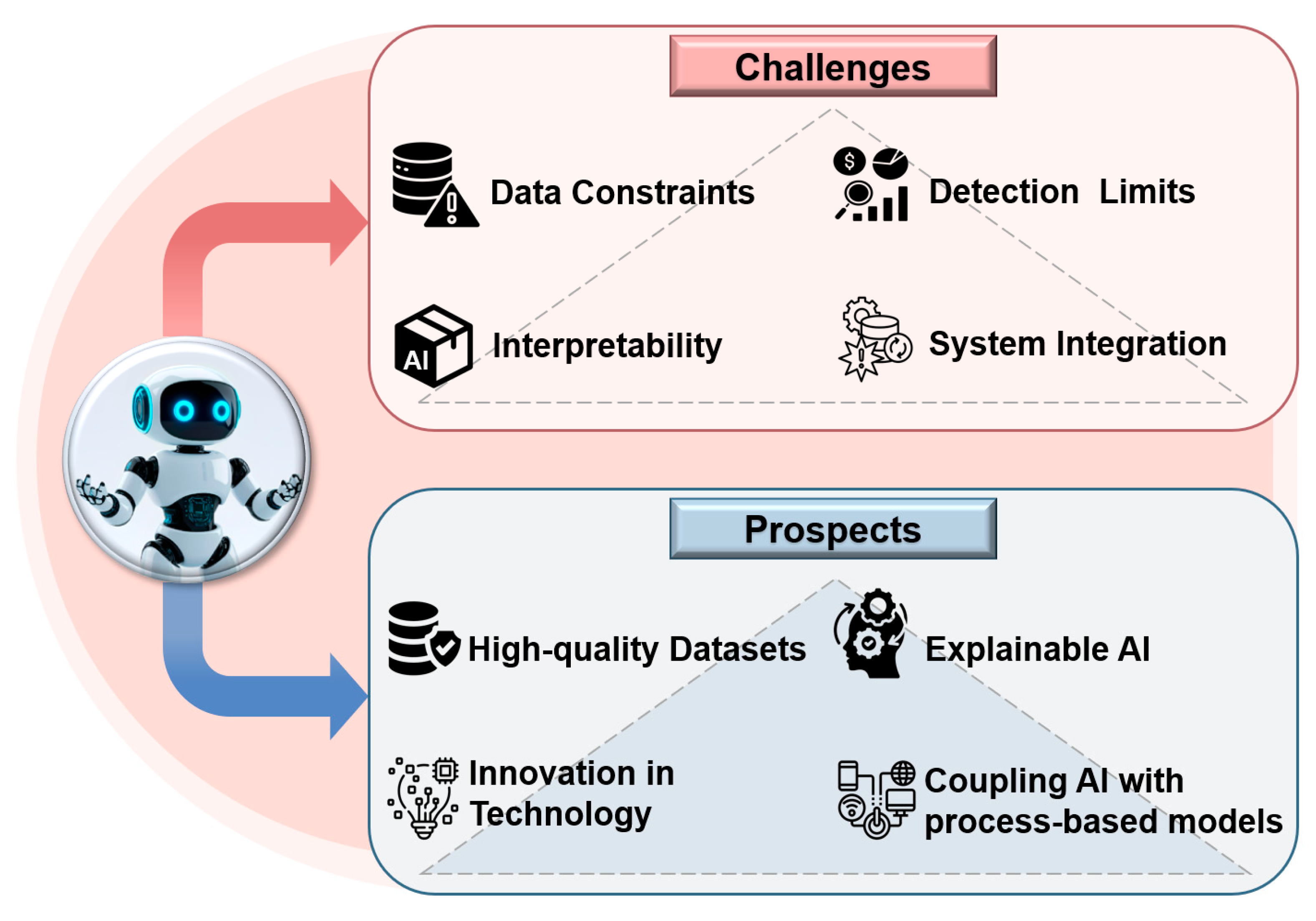
5. Conclusions and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial intelligence |
| ANN | Artificial Neural Networks |
| APIs | application programming interfaces |
| ARD | average relative deviation |
| ARIMA | Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average |
| BOD5 | 5-day Biochemical Oxygen Demand |
| Boosting-IPW-PLS | Boosting-Iterative Predictor Weighting-Partial Least Squares |
| BPA | Bisphenol A |
| CDOM | Colored Dissolved Organic Matter |
| Chl-a | chlorophyll-a |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Networks |
| COD | chemical oxygen demand |
| DDMs | data-driven models |
| DEET | N,N-diethyltoluamide |
| DL | Deep Learning |
| DO | dissolved oxygen |
| DP | dissolved phosphorus |
| DSS | Decision Support Systems |
| DT | Decision Trees |
| EC | Electrical Conductivity |
| ECs | emerging contaminants |
| FL | Fuzzy Logic |
| GIS | Geographic Information System |
| GP | Genetic Programming |
| GRU | Gated Recurrent Unit |
| GUI | graphical user interface |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| K-Means | K-Means clustering |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| MLM | Modified Local Model |
| MLPNN | multilayer perceptron neural networks |
| MLR | multiple linear regression |
| NN | Neural Network |
| NH3-N | Ammonia Nitrogen |
| NH4+ | Ammonium nitrogen |
| NO3-N | Nitrate Nitrogen |
| NSE | Nash-Sutcliffe Efficiency |
| ORP | Oxidation-Reduction Potential |
| P2P | point-to-point |
| PBM | process-based models (or Process-Based Models) |
| PGAI | Process-Guided AI |
| PGDL | process-guided deep learning |
| PSO-SVR | particle swarm optimization-support vector regression |
| R2 | coefficient of determination |
| RF | Random Forests |
| RNN | Recurrent Neural Networks |
| RMSE | root-mean-square error |
| RS | Remote Sensing |
| S2P | sequence-to-point |
| S2S | sequence-to-sequence |
| SDG 6 | Sustainable Development Goal 6 |
| SSL | suspended sediment load |
| SVM | Support Vector Machines |
| TDS | Total Dissolved Solids |
| TN | Total Nitrogen |
| TP | Total Phosphorus |
| TSS | Total Suspended Solids |
| UAS | Unmanned Aerial Systems |
| UMP | Unmanned Monitoring Platforms |
| USV | Unmanned Surface Vehicles |
| UUV | Unmanned Underwater Vehicles |
| WANN | Wavelet-Neural Networks |
| WQI | Water Quality Index |
| WSVR | Wavelet-Support Vector Regression |
| XAI | explainable AI |
References
- Jones, E.R.; Bierkens, M.F.P.; Wanders, N.; Sutanudjaja, E.H.; van Beek, L.P.H.; van Vliet, M.T.H. Current Wastewater Treatment Targets Are Insufficient to Protect Surface Water Quality. Commun. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Mao, D.; Song, K.; Xiang, H.; Li, S.; Wang, Z. Effects of Landscape Changes on Water Quality: A Global Meta-Analysis. Water Res. 2024, 260, 121946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salerno, F.; Gaetano, V.; Gianni, T. Urbanization and Climate Change Impacts on Surface Water Quality: Enhancing the Resilience by Reducing Impervious Surfaces. Water Res. 2018, 144, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Xu, W.; Lin, Z. Algorithm for Monitoring Water Quality Parameters in Optical Systems Based on Artificial Intelligence Data Mining. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 28142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essamlali, I.; Nhaila, H.; Khaili, M.E. Advances in Machine Learning and IoT for Water Quality Monitoring: A Comprehensive Review. Heliyon 2024, 10, e27920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sela, L.; Sowby, R.B.; Salomons, E.; Housh, M. Making Waves: The Potential of Generative AI in Water Utility Operations. Water Res. 2025, 272, 122935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AI in Water Management Market Growth Rate, Industry Analysis with Key Companies 2025–2032. Available online: https://www.datamintelligence.com/research-report/ai-in-water-management-market (accessed on 13 May 2025).
- Olawade, D.B.; Wada, O.Z.; Ige, A.O.; Egbewole, B.I.; Olojo, A.; Oladapo, B.I. Artificial Intelligence in Environmental Monitoring: Advancements, Challenges, and Future Directions. Hyg. Environ. Health Adv. 2024, 12, 100114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnuru, A.; Madhuri, J.V.; Saravanan, S.; Vijayakumar, T.; Manimegalai, V.; Das, A. Data-Driven Approaches to Water Quality Monitoring: Leveraging AI, Machine Learning, and Management Strategies for Environmental Protection. J. Neonatal Surg. 2025, 14, 664–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frincu, R.M. Artificial Intelligence in Water Quality Monitoring: A Review of Water Quality Assessment Applications. Water Qual. Res. J. 2024, 60, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, M.; Farshforoush, N.; Bagheri, K.; Shemirani, A.I. Applications of Artificial Intelligence Technologies in Water Environments: From Basic Techniques to Novel Tiny Machine Learning Systems. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 180, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, M.H.; Melesse, A.M.; Reddi, L. A Comprehensive Review on Water Quality Parameters Estimation Using Remote Sensing Techniques. Sensors 2016, 16, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nallakaruppan, M.K.; Gangadevi, E.; Shri, M.L.; Balusamy, B.; Bhattacharya, S.; Selvarajan, S. Reliable Water Quality Prediction and Parametric Analysis Using Explainable AI Models. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 7520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, C.; Sun, L.; Guo, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W. A Deep Learning Algorithm for Multi-Source Data Fusion to Predict Water Quality of Urban Sewer Networks. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 318, 128533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wai, K.P.; Chia, M.Y.; Koo, C.H.; Huang, Y.F.; Chong, W.C. Applications of Deep Learning in Water Quality Management: A State-of-the-Art Review. J. Hydrol. 2022, 613, 128332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durgun, Y. Real-Time Water Quality Monitoring Using AI-Enabled Sensors: Detection of Contaminants and UV Disinfection Analysis in Smart Urban Water Systems. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2024, 36, 103409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, T.; Durlik, I.; Kostecka, E.; Kozlovska, P.; Łobodzińska, A.; Sokołowska, S.; Nowy, A. Integrating Artificial Intelligence Agents with the Internet of Things for Enhanced Environmental Monitoring: Applications in Water Quality and Climate Data. Electronics 2025, 14, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamyab, H.; Khademi, T.; Chelliapan, S.; SaberiKamarposhti, M.; Rezania, S.; Yusuf, M.; Farajnezhad, M.; Abbas, M.; Hun Jeon, B.; Ahn, Y. The Latest Innovative Avenues for the Utilization of Artificial Intelligence and Big Data Analytics in Water Resource Management. Results Eng. 2023, 20, 101566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Qian, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Curry, J. Recent Progress on Surface Water Quality Models Utilizing Machine Learning Techniques. Water 2024, 16, 3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soori, M.; Jough, F.K.G.; Dastres, R.; Arezoo, B. AI-Based Decision Support Systems in Industry 4.0, A Review. J. Econ. Technol. 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Zhang, T.; Du, W.; Meng, Q.; Xu, X.; Zhao, X. A Comprehensive Review of Machine Learning for Water Quality Prediction over the Past Five Years. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.-Y.; Cheng, C.-Y.; Cheng, S.-C.; Cheng, Y.-H.; Lo, W.-C.; Jiang, W.-L.; Nan, F.-H.; Chang, S.-H.; Ubina, N.A. A Low-Cost AI Buoy System for Monitoring Water Quality at Offshore Aquaculture Cages. Sensors 2022, 22, 4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanya, W.M.; Alawi, M.A.; Eugenio, I. Design and Development of Smart Water Quality Monitoring System Using IoT. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Res. Eng. (IJASRE) 2022, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakunt, P.S. Detection of Faults Based on Machine Learning Schemes in Wireless Sensor Networks. In Proceedings of the Signal Processing, Telecommunication and Embedded Systems with AI and ML Applications; Bhateja, V., Chakravarthy, V.V.S.S.S., Anguera, J., Ghosh, A., Flores Fuentes, W., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2025; pp. 127–137. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, X.; Cai, B.; Zou, Z.; Shao, H.; Yang, C.; Liu, Y. Artificial Intelligence Enhanced Fault Prediction with Industrial Incomplete Information. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2025, 224, 112063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Khondakar, K.R.; Mazumdar, H.; Kaushik, A.; Mishra, Y.K. AI and IoT: Supported Sixth Generation Sensing for Water Quality Assessment to Empower Sustainable Ecosystems. ACS EST Water 2025, 5, 490–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forhad, H.M.; Uddin, M.D.R.; Chakrovorty, R.S.; Ruhul, A.M.; Faruk, H.M.; Kamruzzaman, S.; Sharmin, N.; Jamal, A.S.I.M.; Haque, Md.M.-U.; Morshed, A.M. IoT Based Real-Time Water Quality Monitoring System in Water Treatment Plants (WTPs). Heliyon 2024, 10, e40746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Satapathy, A.; Srivastava, V.; Saxena, R. Revolutionizing Water Quality Management: The Impact of Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence. In Computational Automation for Water Security; Dubey, A.K., Srivastav, A.L., Kumar, A., Garcia Marquez, F.P., Giannakoudakis, D.A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2025; pp. 27–42. [Google Scholar]
- Desikan, J.; Singh, S.K.; Jayanthiladevi, A.; Bhushan, S.; Rishiwal, V.; Kumar, M. Hybrid Machine Learning-Based Fault-Tolerant Sensor Data Fusion and Anomaly Detection for Fire Risk Mitigation in IIoT Environment. Sensors 2025, 25, 2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmikantha, V.; Hiriyannagowda, A.; Manjunath, A.; Patted, A.; Basavaiah, J.; Anthony, A.A. IoT Based Smart Water Quality Monitoring System. Glob. Transit. Proc. 2021, 2, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeleke, I.A.; Nwulu, N.I.; Ogbolumani, O.A. A Hybrid Machine Learning and Embedded IoT-Based Water Quality Monitoring System. Internet Things 2023, 22, 100774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Kohli, M.; Kumar, R.; Bandral, S. IoT Based Underwater Robot for Water Quality Monitoring. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1033, 012013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, F.; Ding, J. Evaluation of Water Quality Based on a Machine Learning Algorithm and Water Quality Index for the Ebinur Lake Watershed, China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunda, N.S.K.; Gautam, S.H.; Mitra, S.K. Editors’ Choice—Artificial Intelligence Based Mobile Application for Water Quality Monitoring. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, B3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Feng, J. Attention Neural Network for Water Image Classification under IoT Environment. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Gao, F.; Chen, G. Wastewater Quality Monitoring System Using Sensor Fusion and Machine Learning Techniques. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1133–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cecconi, F.; Rosso, D. Soft Sensing for On-Line Fault Detection of Ammonium Sensors in Water Resource Recovery Facilities. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 10067–10076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foschi, J.; Turolla, A.; Antonelli, M. Soft Sensor Predictor of E. Coli Concentration Based on Conventional Monitoring Parameters for Wastewater Disinfection Control. Water Res. 2021, 191, 116806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, V.; Oinam, B.; Wieprecht, S. Machine Learning Approach for Water Quality Predictions Based on Multispectral Satellite Imageries. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 84, 102868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahat, S.H.; Steissberg, T.; Chang, W.; Chen, X.; Mandavya, G.; Tracy, J.; Wasti, A.; Atreya, G.; Saki, S.; Bhuiyan, M.A.E.; et al. Remote Sensing-Enabled Machine Learning for River Water Quality Modeling under Multidimensional Uncertainty. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 898, 165504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chebud, Y.; Naja, G.M.; Rivero, R.G.; Melesse, A.M. Water Quality Monitoring Using Remote Sensing and an Artificial Neural Network. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 4875–4887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.H. UAS-Based Real-Time Water Quality Monitoring, Sampling, and Visualization Platform (UASWQP). HardwareX 2022, 11, e00277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasudevan, S.K.; Baskaran, B. An Improved Real-Time Water Quality Monitoring Embedded System with IoT on Unmanned Surface Vehicle. Ecol. Inform. 2021, 65, 101421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Ma, S.; Liu, T.; Yao, S.; Li, S.; Gao, Y. Integrating UAV-Based Multispectral Data and Transfer Learning for Soil Moisture Prediction in the Black Soil Region of Northeast China. Agronomy 2025, 15, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihuoma, S.O.; Madramootoo, C.A.; Kalacska, M. Integration of Satellite Imagery and in Situ Soil Moisture Data for Estimating Irrigation Water Requirements. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 102, 102396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunia, M.; Laine, M.; Malve, O.; Kallio, K.; Kervinen, M.; Anttila, S.; Kotamäki, N.; Siivola, E.; Kettunen, J.; Kauranne, T. Data Fusion System for Monitoring Water Quality: Application to Chlorophyll-a in Baltic Sea Coast. Environ. Model. Softw. 2022, 155, 105465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigdeli, B.; Pahlavani, P.; Amirkolaee, H.A. An Ensemble Deep Learning Method as Data Fusion System for Remote Sensing Multisensor Classification. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 110, 107563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, M.; Liu, X.; Tong, Z.; Sudu, B.; Zhang, J.; Wang, R. Analysis of Water Quality Influencing Factors under Multi-Source Data Fusion Based on PLS-SEM Model: An Example of East-Liao River in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 907, 168126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priyanka, E.B.; Thangavel, S.; Mohanasundaram, R.; Anand, R. Solar Powered Integrated Multi Sensors to Monitor Inland Lake Water Quality Using Statistical Data Fusion Technique with Kalman Filter. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 25202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Ding, F.; Liu, L.; Yin, F.; Hao, M.; Kang, T.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, D. Monitoring Water Quality Parameters in Urban Rivers Using Multi-Source Data and Machine Learning Approach. J. Hydrol. 2025, 648, 132394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Quan, X.; Zhang, H.; Huang, L. Innovations of Water Pollution Traceability Technology with Artificial Intelligence. Earth Crit. Zone 2024, 1, 100009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Curzio, D.; Castrignanò, A.; Fountas, S.; Romić, M.; Viscarra Rossel, R.A. Multi-Source Data Fusion of Big Spatial-Temporal Data in Soil, Geo-Engineering and Environmental Studies. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ren, H.; Wu, B.; Ye, L. A Review of the Application of Machine Learning in Water Quality Evaluation. Eco-Environ. Health 2022, 1, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, R.; Kalia, A.; Boora, A.; Alfaisal, F.M.; Alharbi, R.S.; Berwal, P.; Alam, S.; Khan, M.A.; Qamar, O. Artificial Intelligence for Surface Water Quality Evaluation, Monitoring and Assessment. Water 2023, 15, 3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, G.-H.; Gwon, N.-H.; Cho, M.-J.; Park, J.-Y.; Baek, S.-S. Developing a Real-Time Water Quality Simulation Toolbox Using Machine Learning and Application Programming Interface. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 377, 124719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, L.; Pang, R.; Han, Z.; Wu, D.; Xie, B.; Su, Y. Current Applications and Future Impact of Machine Learning in Emerging Contaminants: A Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 53, 1817–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Huang, G.; Chi, M.; Shi, Y.; Jiang, J.; Feng, C.; Yan, Z.; Xu, Z. Prediction of Chemical Reproductive Toxicity to Aquatic Species Using a Machine Learning Model: An Application in an Ecological Risk Assessment of the Yangtze River, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 796, 148901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Driscol, J.; Sarigai, S.; Wu, Q.; Lippitt, C.D.; Morgan, M. Towards Synoptic Water Monitoring Systems: A Review of AI Methods for Automating Water Body Detection and Water Quality Monitoring Using Remote Sensing. Sensors 2022, 22, 2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Liu, L.; Ben, X.; Jin, D.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, F. Hybrid Deep Learning Based Prediction for Water Quality of Plain Watershed. Environ. Res. 2024, 262, 119911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaee, T.; Khani, S.; Ravansalar, M. Artificial Intelligence-Based Single and Hybrid Models for Prediction of Water Quality in Rivers: A Review. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2020, 200, 103978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varadharajan, C.; Appling, A.P.; Arora, B.; Christianson, D.S.; Hendrix, V.C.; Kumar, V.; Lima, A.R.; Müller, J.; Oliver, S.; Ombadi, M.; et al. Can Machine Learning Accelerate Process Understanding and Decision-Relevant Predictions of River Water Quality? Hydrol. Process. 2022, 36, e14565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Xia, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G.; She, D.; Lei, J. Pollution Loads in the Middle-Lower Yangtze River by Coupling Water Quality Models with Machine Learning. Water Res. 2024, 263, 122191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, J.; Fan, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, C.; Hu, Q.; Cai, W.; Ju, H.; Gu, S. Deep Learning Model Based on Coupled SWAT and Interpretable Methods for Water Quality Prediction under the Influence of Non-Point Source Pollution. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 231, 109985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, J.S.; Jia, X.; Willard, J.; Appling, A.P.; Zwart, J.A.; Oliver, S.K.; Karpatne, A.; Hansen, G.J.A.; Hanson, P.C.; Watkins, W.; et al. Process-Guided Deep Learning Predictions of Lake Water Temperature. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 9173–9190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikmukhametov, T.; Jäschke, J. Combining Machine Learning and Process Engineering Physics towards Enhanced Accuracy and Explainability of Data-Driven Models. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2020, 138, 106834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Yen, N.; Pei, Y. A Physics-Coupled Deep Learning Framework for Hydrodynamic Diffusion Modeling in Watershed Systems: Integrating Spatiotemporal Networks and Environmental Constraints. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 34985–35003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; You, L.; Zhang, J.; He, Y.; Gin, K.Y.-H. Advancing Prediction of Emerging Contaminants in a Tropical Reservoir with General Water Quality Indicators Based on a Hybrid Process and Data-Driven Approach. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 430, 128492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Babovic, V. Improving Real-Time Forecasting of Water Quality Indicators with Combination of Process-Based Models and Data Assimilation Technique. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 66, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Babovic, V.; Gin, K.Y.H. A Comprehensive Integrated Catchment-Scale Monitoring and Modelling Approach for Facilitating Management of Water Quality. Environ. Model. Softw. 2019, 120, 104489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, H.V.; Dal Barco, M.K.; Cadau, M.; Harris, R.; Furlan, E.; Torresan, S.; Rubinetti, S.; Zanchettin, D.; Rubino, A.; Kuznetsov, I.; et al. Multi-Model Chain for Climate Change Scenario Analysis to Support Coastal Erosion and Water Quality Risk Management for the Metropolitan City of Venice. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, S.F.; Wada, I.U.; Ige, O.B.; Chianumba, E.C.; Adebayo, S.A. AI-Driven Predictive Maintenance and Optimization of Renewable Energy Systems for Enhanced Operational Efficiency and Longevity. Int. J. Sci. Res. Arch. 2024, 13, 2823–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.R.; Nallakaruppan, M.K.; Chengoden, R.; Koppu, S.; Iyapparaja, M.; Sadhasivam, J.; Sethuraman, S. Smart Water Resource Management Using Artificial Intelligence—A Review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickum, J.E.; Kuisma, S.; Bjornlund, H.; Stephan, R.M. Smart Water Management: The Way to (Artificially) Intelligent Water Management, or Just Another Pretty Name? Water Int. 2020, 45, 515–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geissen, V.; Mol, H.; Klumpp, E.; Umlauf, G.; Nadal, M.; van der Ploeg, M.; van de Zee, S.E.A.T.M.; Ritsema, C.J. Emerging Pollutants in the Environment: A Challenge for Water Resource Management. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2015, 3, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlivan, L.; Chapman, D.V.; Sullivan, T. Applying Citizen Science to Monitor for the Sustainable Development Goal Indicator 6.3.2: A Review. Environ. Monit Assess 2020, 192, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegarty, S.; Hayes, A.; Regan, F.; Bishop, I.; Clinton, R. Using Citizen Science to Understand River Water Quality While Filling Data Gaps to Meet United Nations Sustainable Development Goal 6 Objectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 783, 146953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zou, T.; Lai, Y. Novel Method for Industrial Sewage Outfall Detection: Water Pollution Monitoring Based on Web Crawler and Remote Sensing Interpretation Techniques. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 312, 127640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Performance Indicators | AI Methods | Traditional Methods | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Timeliness |
|
| [10,11] |
| Accuracy |
|
| [12,13] |
| Predictive Capability |
|
| [11,14,15] |
| Anomaly Detection Capability |
|
| [16,17] |
| Decision Support |
|
| [18,19,20] |
| Data Integration |
|
| [14,21] |
| Cost |
|
| [22,23] |
| AI Methods | Task | Data Source | Parameters | Results | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVM, ANN | Classification; Source prediction | IoT-based sensor collection system | Temperature, pH, Turbidity, DO, TDS, ORP, EC | Real-time monitoring; Remote transmission; Self-feedback and self-regulation; Low cost; Portable | [31] |
| K-Means | Classification; Automatic clustering analysis of sensor data | Underwater robot (sensors) | pH, Temperature, Turbidity, EC | Real-time underwater monitoring; Remote control & data upload; Suitable for large water bodies; Sustainable deployment; Low cost, minimal maintenance, compact design | [32] |
| RF, SVM, NN | Classification | Multispectral sensors | Escherichia coli (E. coli) | High accuracy | [16] |
| PSO-SVR | WQI prediction | Hyperspectral RS, In-situ data | Comprehensive water quality parameters (pH, DO, COD, BOD5, TN, TP, TDS, etc.) | High-precision; Suitable for large-scale dry area water quality estimation | [33] |
| LSTM | Real-time monitoring (aquaculture) | Buoy sensors | Temperature, Salinity, DO, Flow velocity | Low cost; Real-time data; Short-term prediction | [22] |
| CNN | Real-time monitoring | Smartphone camera-captured sensor images | E. coli | High accuracy (99.99%); Objective; Simple operation | [34] |
| CNN | Water image classification (pollution) | IoT-collected water images | Pollution type visual features (e.g., texture, oil stains, animal carcasses, etc.) | High precision; Enhanced features; Real-time monitoring/feedback | [35] |
| Boosting-IPW-PLS | Wastewater monitoring | Sensors | COD, TSS, Oil and Grease | High precision; Handles noise; Online monitoring | [36] |
| ANN | Sensor fault detection and replacement control | Sensors | NH4, pH, ORP, DO, TSS | High accuracy; Rapid fault ID; Automatic control replacement after fault detection | [37] |
| ANN | Prediction and disinfectant optimization control | Laboratory monitoring + sensors | E. coli | High-precision; Optimizes peracetic acid disinfectant usage | [38] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zou, S.; Ju, H.; Zhang, J. Water Quality Management in the Age of AI: Applications, Challenges, and Prospects. Water 2025, 17, 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111641
Zou S, Ju H, Zhang J. Water Quality Management in the Age of AI: Applications, Challenges, and Prospects. Water. 2025; 17(11):1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111641
Chicago/Turabian StyleZou, Shubin, Hanyu Ju, and Jingjie Zhang. 2025. "Water Quality Management in the Age of AI: Applications, Challenges, and Prospects" Water 17, no. 11: 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111641
APA StyleZou, S., Ju, H., & Zhang, J. (2025). Water Quality Management in the Age of AI: Applications, Challenges, and Prospects. Water, 17(11), 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111641






