Sediment Transport Constraints for Restoration of the Ebro Delta
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
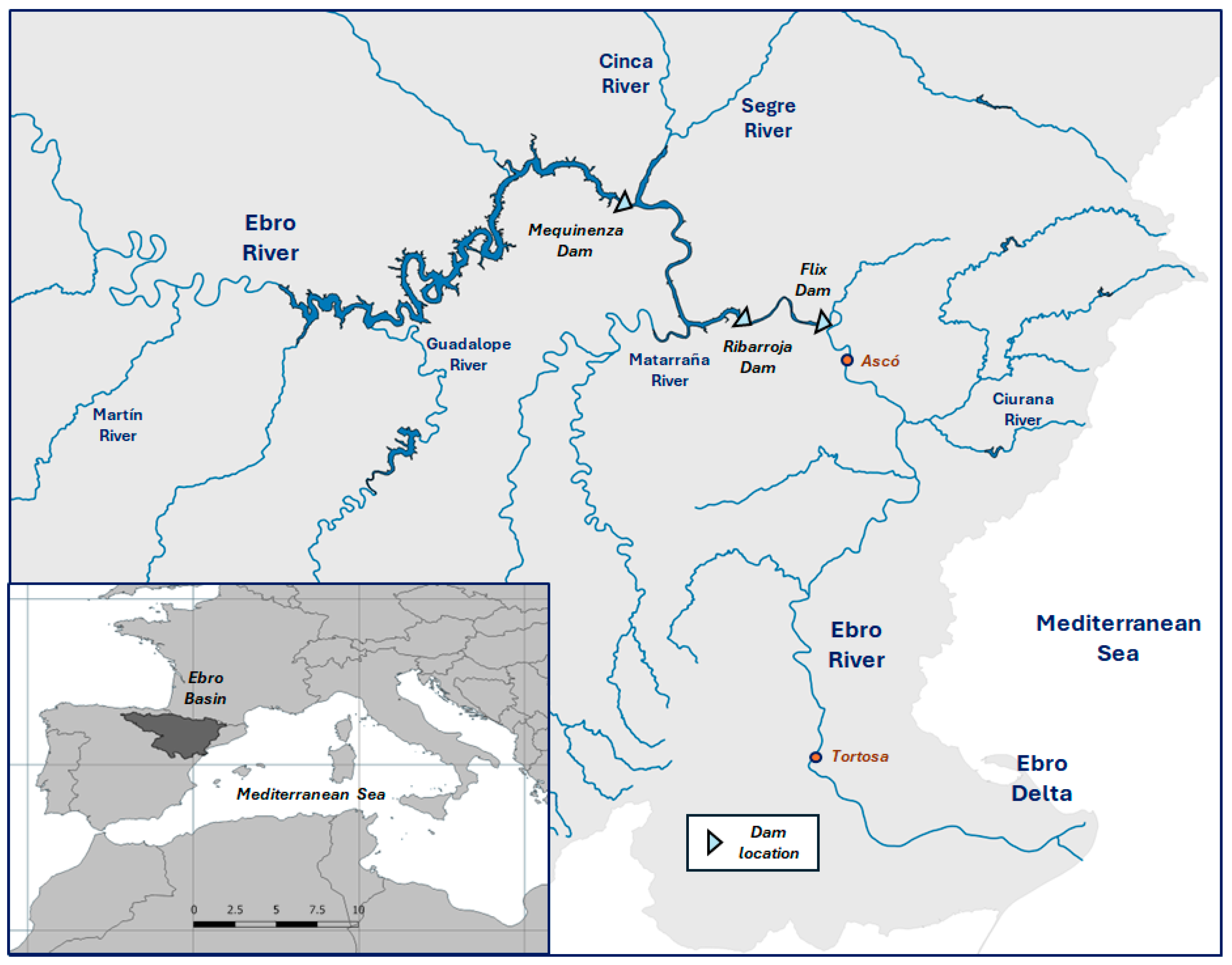
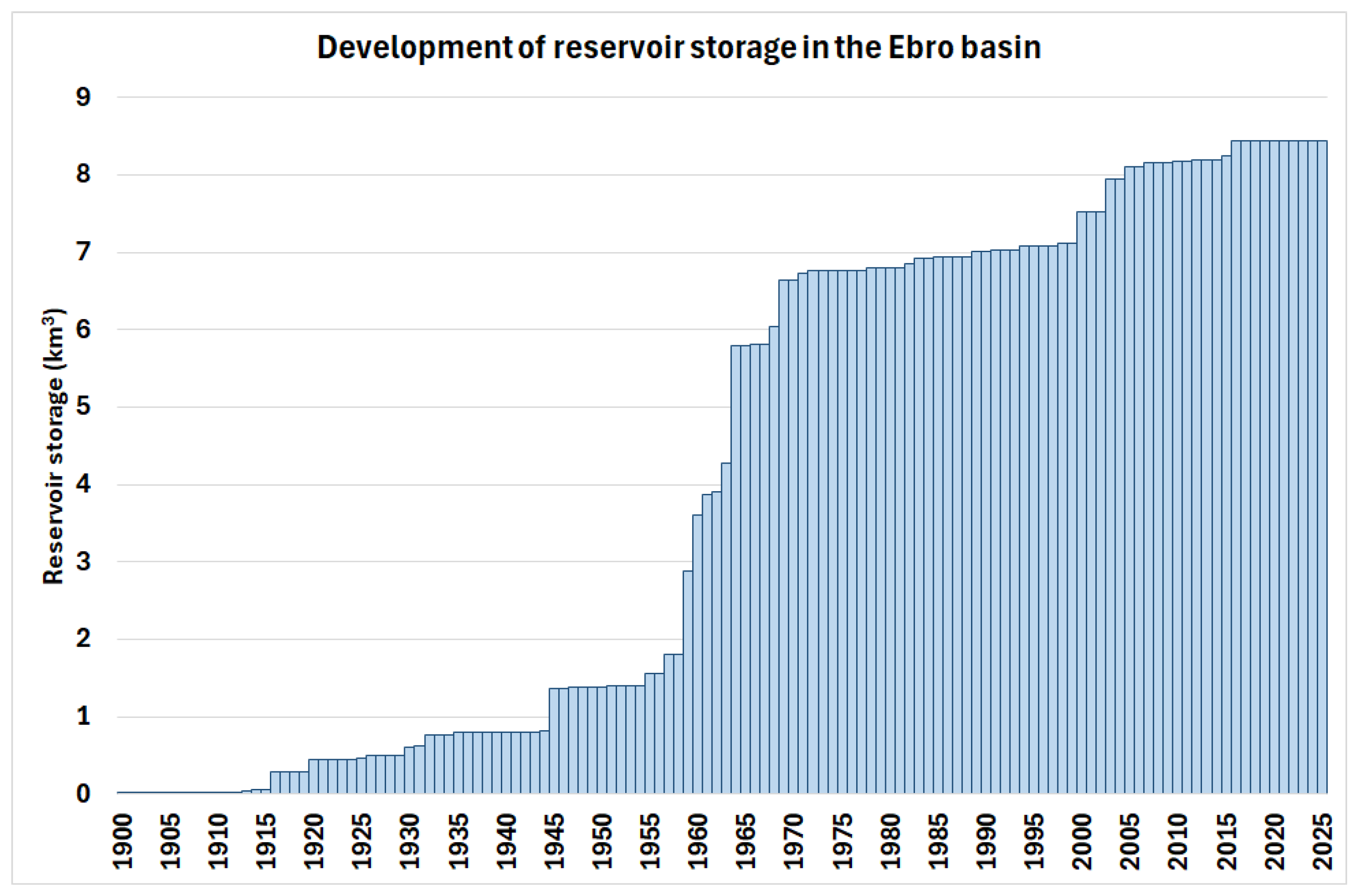
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Development of the Sediment Transport Rating Curve
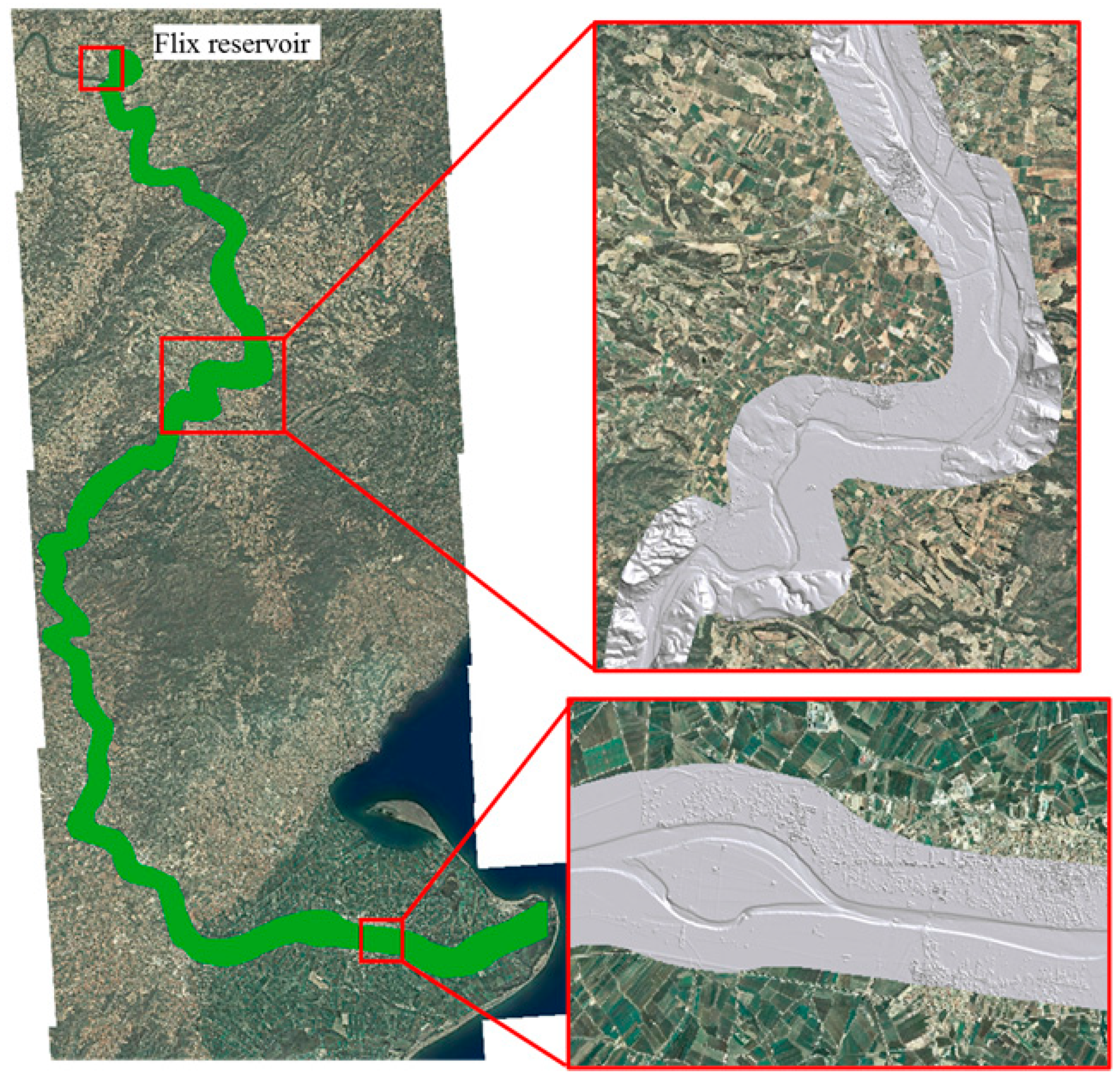
2.2.1. Hydrodynamic Model Setup
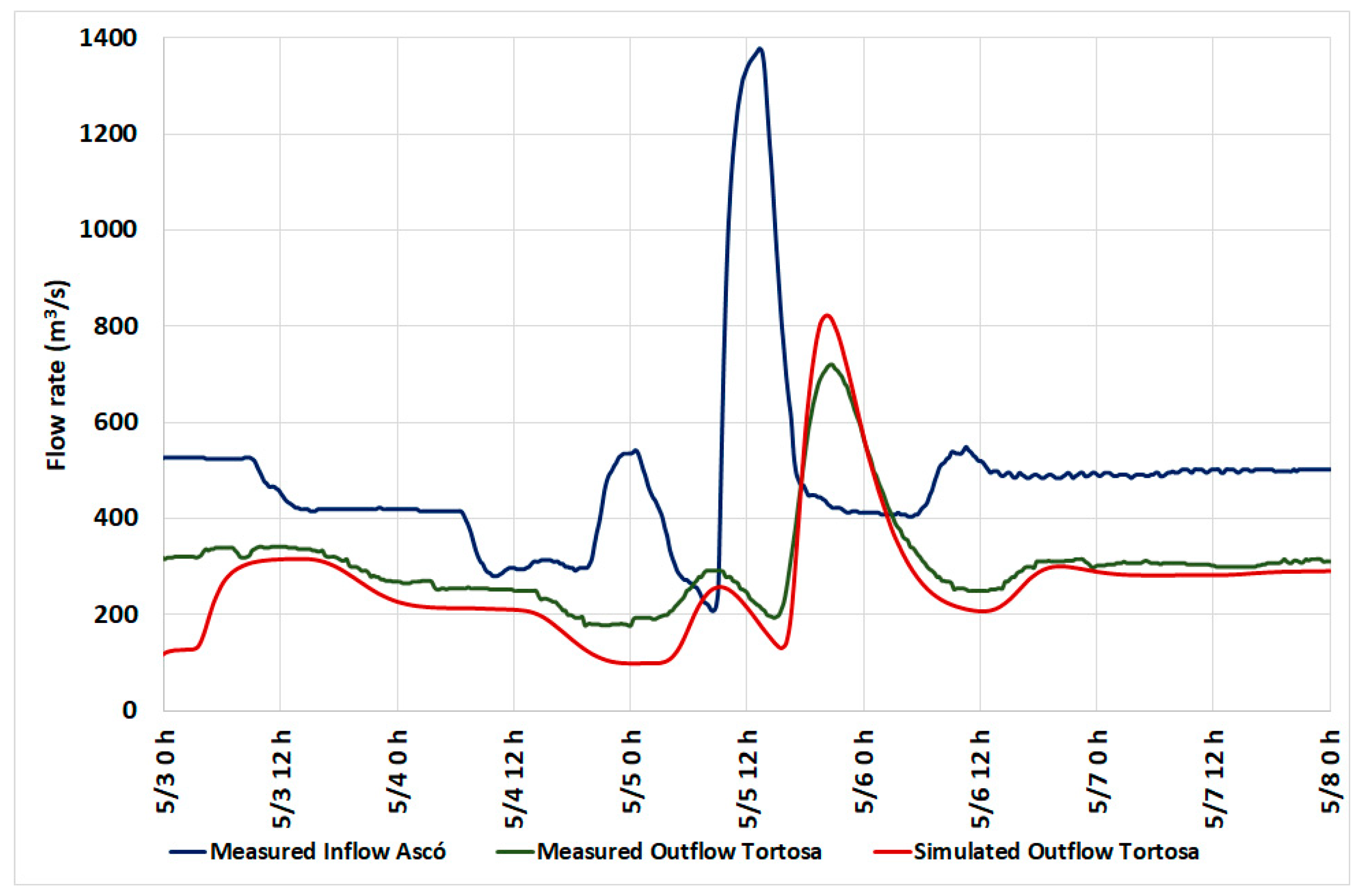
2.2.2. Model Calibration
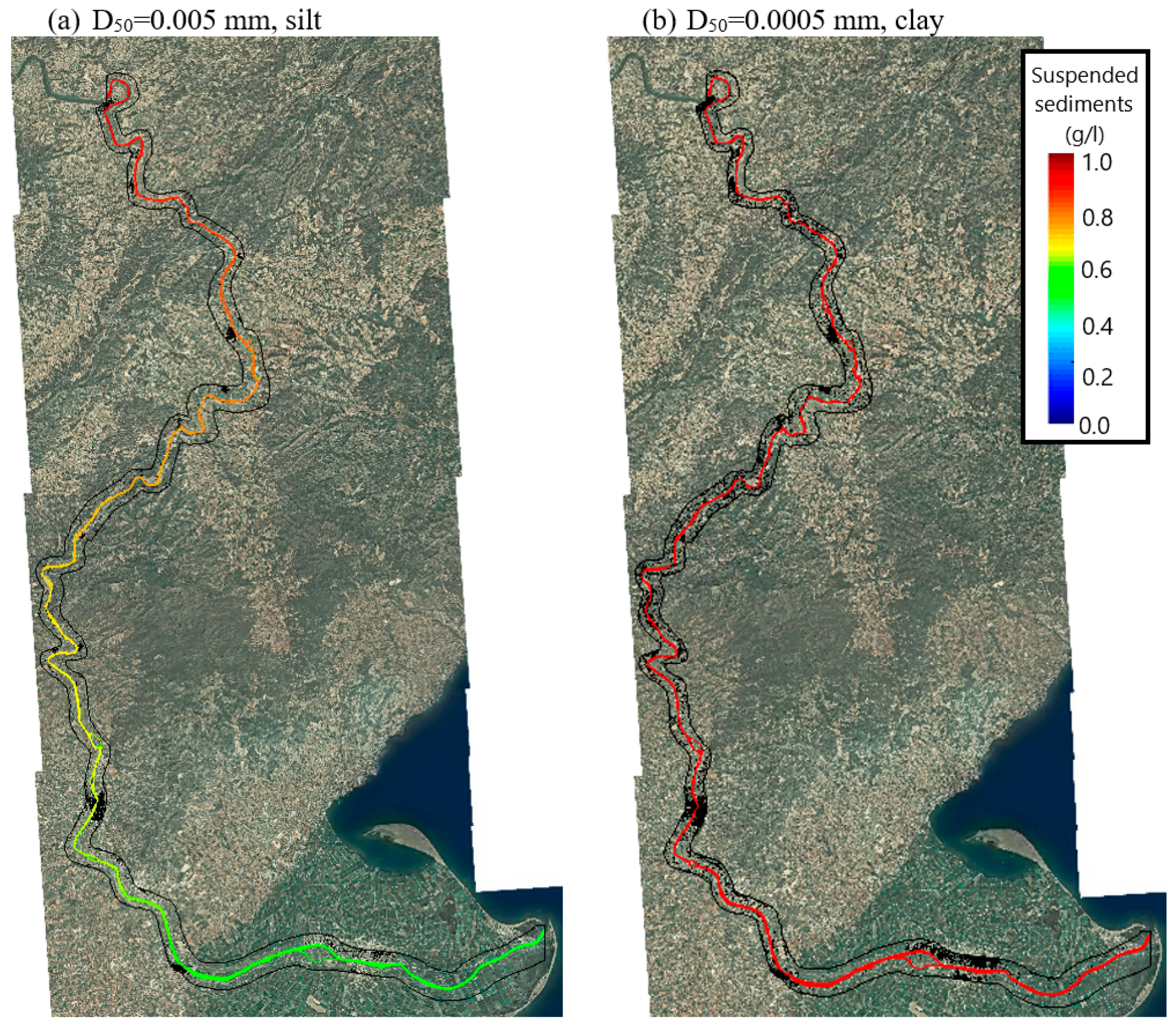
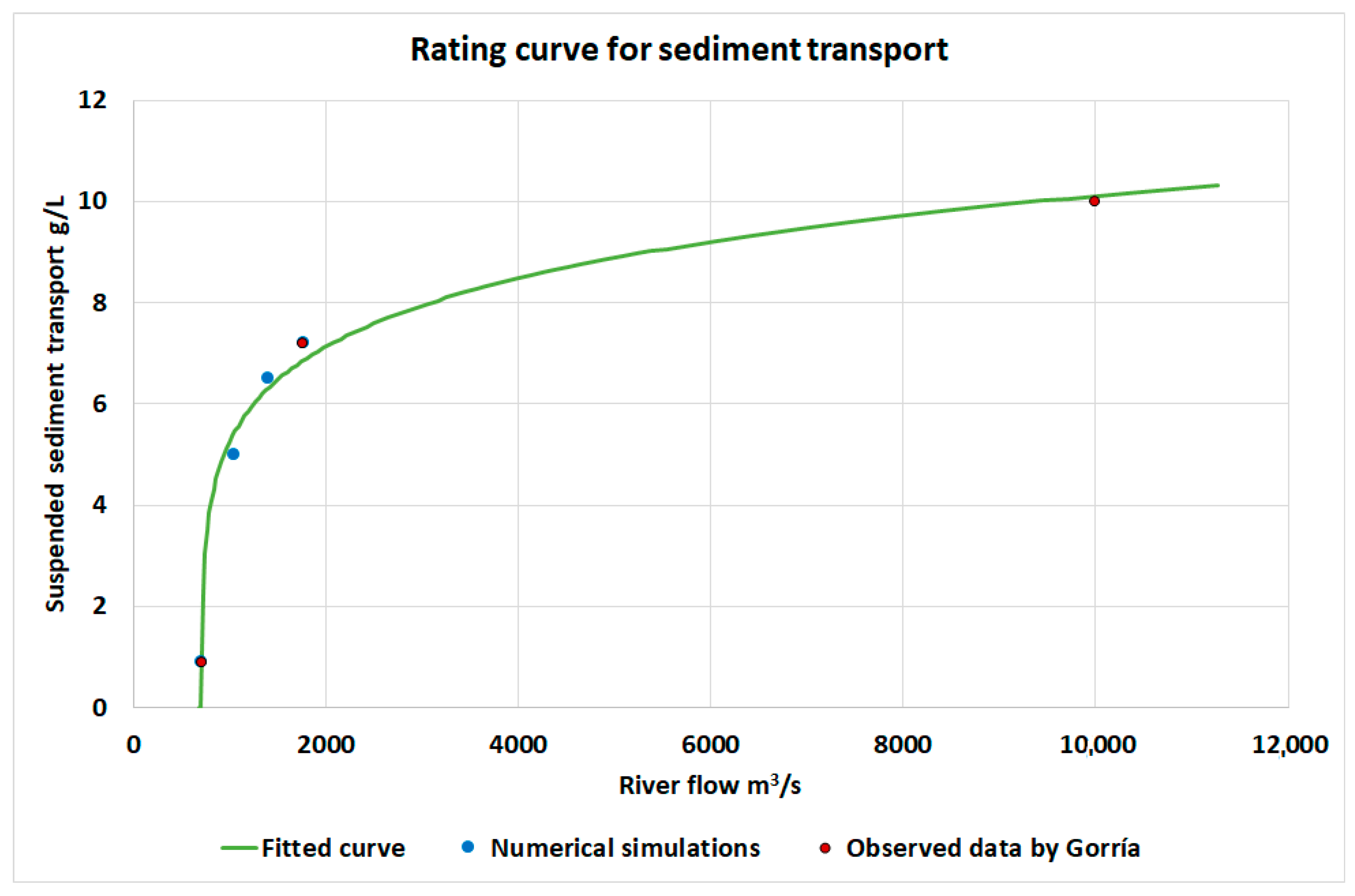
2.2.3. Rating Curve for Sediment Transport
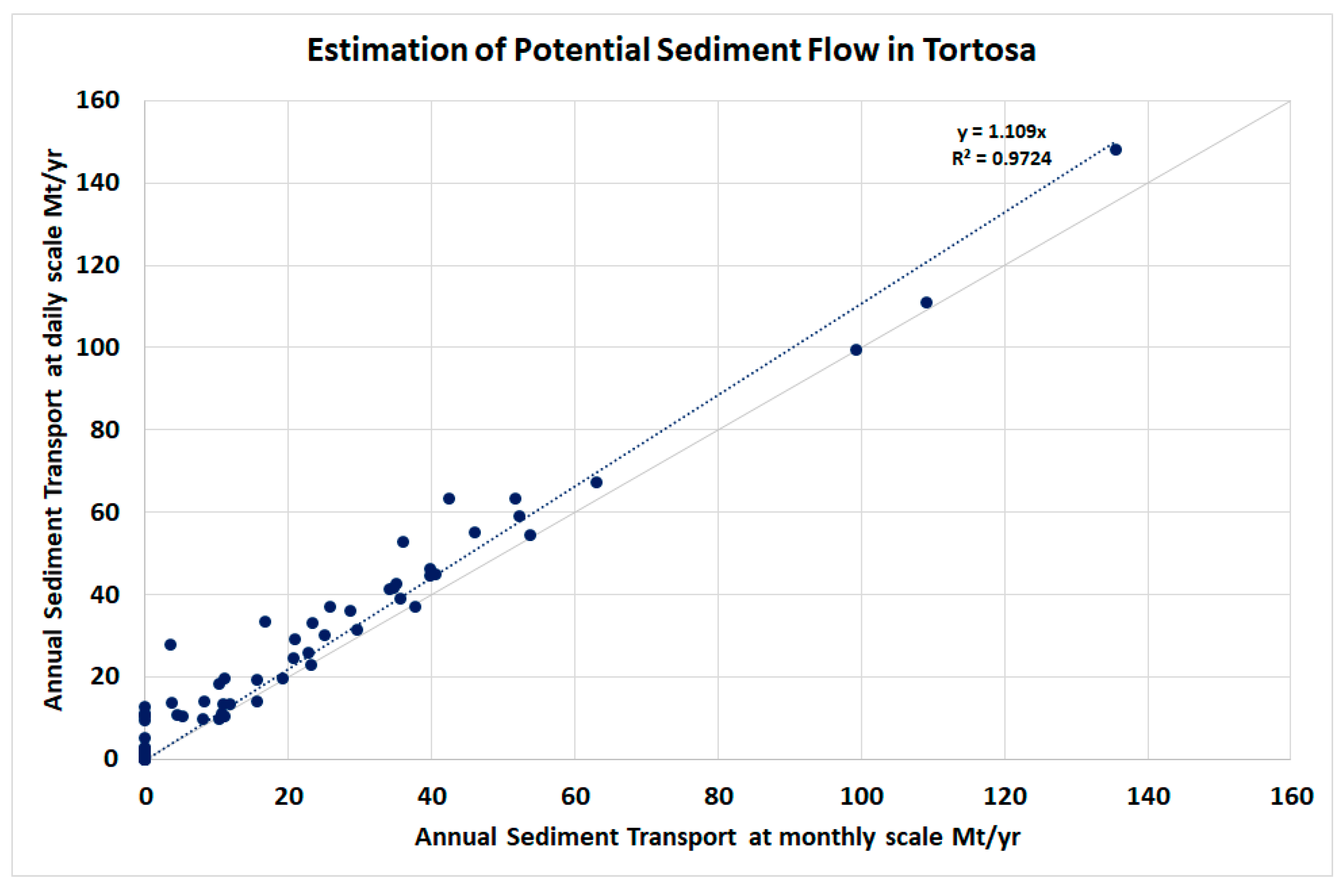
2.3. Potential Sediment Transport
2.3.1. Potential Sediment Transport Under Observed Hydrologic Regime
2.3.2. Potential Sediment Transport Under a Natural Hydrologic Regime
2.3.3. Projected Potential Sediment Transport Under a Natural Hydrologic Regime
2.3.4. Projected Potential Sediment Transport Under an Altered Hydrologic Regime
3. Results and Discussion
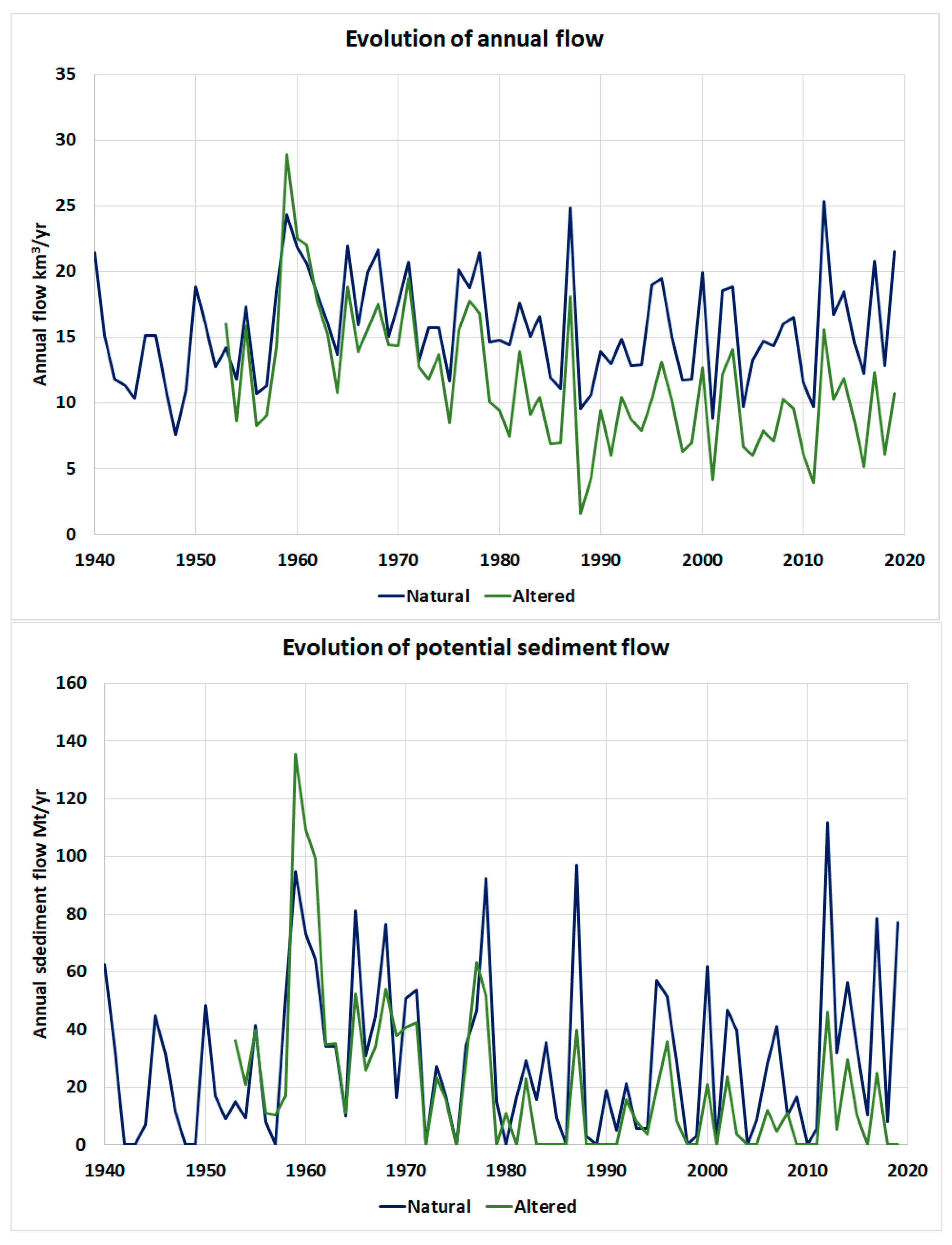
3.1. Current Potential Sediment Transport Under Natural and Altered Conditions
3.2. Potential Sediment Transport Under Climate Projections
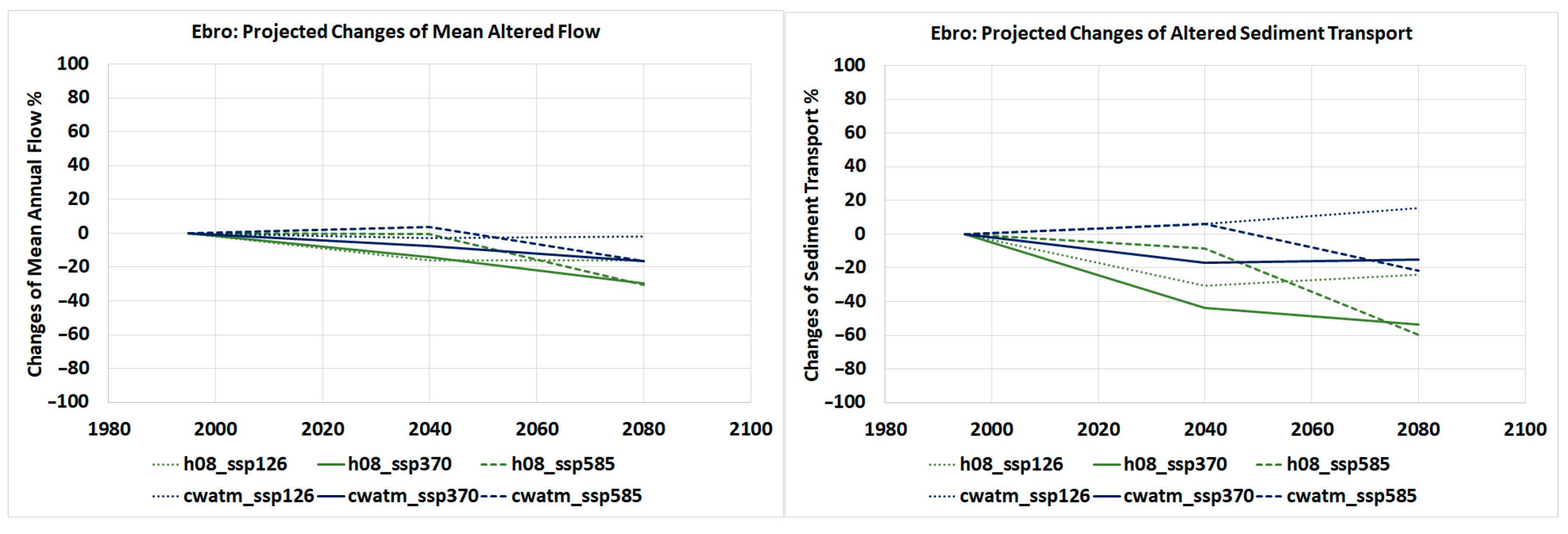
3.2.1. Sediment Transport Under Natural Conditions
3.2.2. Sediment Transport Under Altered Conditions
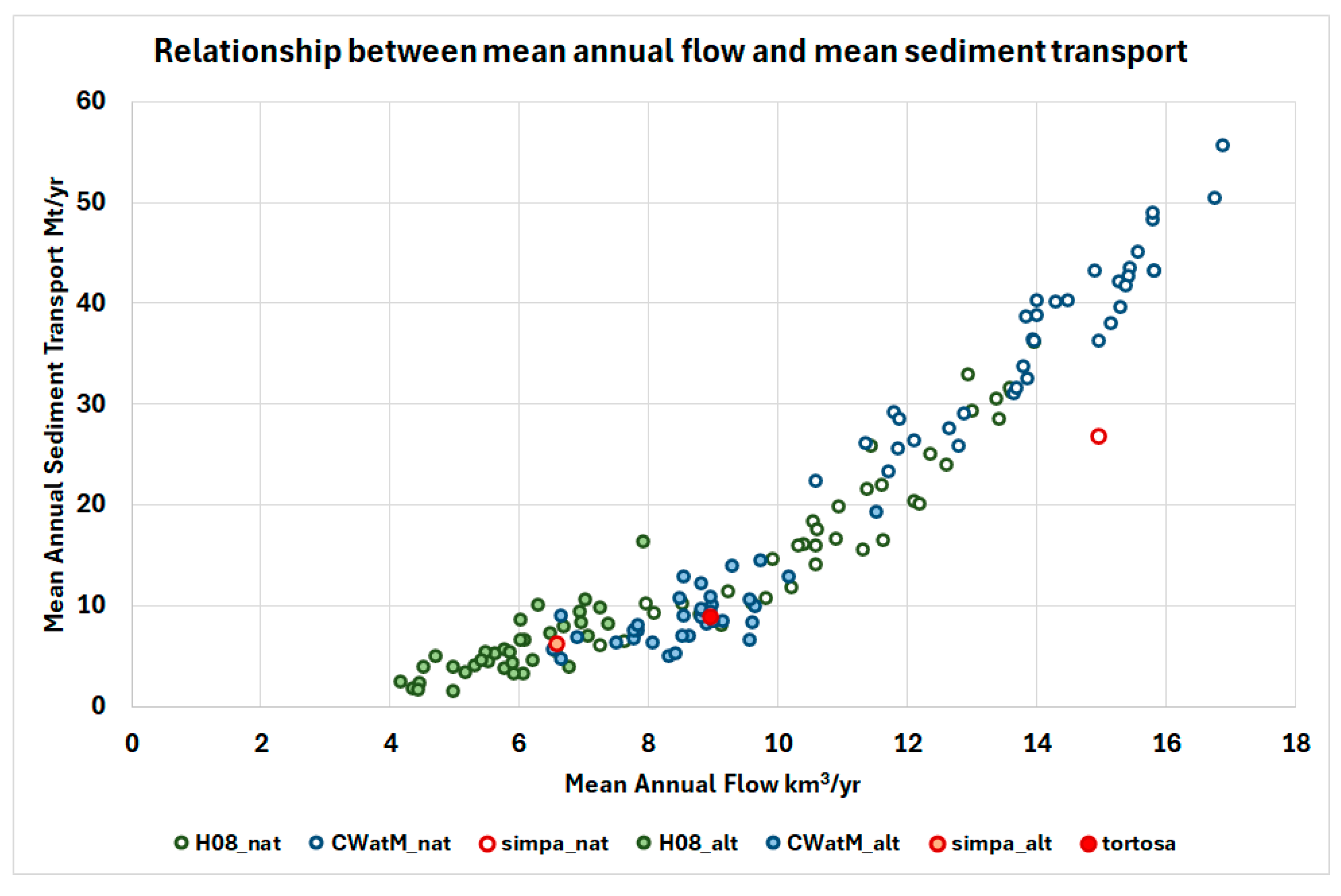
3.3. Relationship Between Annual Flow and Sediment Transport
3.4. Limitations of the Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AR6 | 6th Assessment Report |
| CHE | Confederación Hidrográfica del Ebro (Ebro Basin Authority) |
| CWatM | Community Water Model |
| ICOLD | International Commission on Large Dams |
| IPCC | Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change |
| ISIMIP | Inter-Sectoral Impact Model Intercomparison Project |
| SAIH | Automated Hydrologic Information System |
| SIMPA | Integrated System for Rainfall–Runoff Modelling |
| SSP | Shared Socioeconomic Pathway |
| SWE | Shallow Water Equations |
Appendix A
Description of the Hydrodynamic Model
References
- Batalla, R.J.; Vericat, D.; Tena, A. The fluvial geomorphology of the lower Ebro (2002–2013): Bridging gaps between management and research. Cuad. Investig. Geográfica 2014, 40, 29–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vericat, D.; Batalla, R.J. Sediment transport in a large impounded river: The lower Ebro, NE Iberian Peninsula. Geomorphology 2006, 79, 72–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanques, A.; Plana, F.; Maldonado, A. Recent influence of man on the Ebro margin sedimentation system, northwestern Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Geol. 1990, 95, 247–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailova, M.V. Transformation of the Ebro River Delta under the impact of intense human-induced reduction of sediment runoff. Water Resour. 2003, 30, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batalla, R.J.; Gómez, C.M.; Kondolf, G.M. Reservoir-induced hydrological changes in the Ebro River basin (NE Spain). J. Hydrol. 2004, 290, 117–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Santalla, I.; Navarro, N. Main threats in mediterranean coastal wetlands. The Ebro delta case. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Arcilla, A.; Cáceres, I.; Roux, X.L.; Hinkel, J.; Schuerch, M.; Nicholls, R.J.; Otero, d.M.; Staneva, J.; de Vries, M.; Pernice, U.; et al. Barriers and enablers for upscaling coastal restoration. Nat. Based Solut. 2022, 2, 100032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, J.W.; Ibáñez, C.; Pont, D.; Scarton, F. Status and Sustainability of Mediterranean Deltas: The Case of the Ebro, Rhône, and Po Deltas and Venice Lagoon. In Coasts and Estuaries: The Future; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, M.D.; Roberts, H.H. Drowning of the Mississippi Delta due to insufficient sediment supply and global sea-level rise. Nat. Geosci. 2009, 2, 488–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondolf, G.M.; Rubin, Z.K.; Minear, J.T. Dams on the Mekong: Cumulative sediment starvation. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 50, 5158–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Pan, C.; Wu, X.; Gao, S.; Wang, Z. The variations of sediment transport patterns in the outer Changjiang Estuary and Hangzhou Bay over the last 30 years. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2017, 122, 2999–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syvitski, J.P.M.; Vörösmarty, C.J.; Kettner, A.J.; Green, P. Impact of humans on the flux of terrestrial sediment to the global coastal ocean. Science 2005, 308, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, D.J.; Warne, A.G. Nile Delta in its destruction phase. J. Coast. Res. 1998, 14, 794–825. [Google Scholar]
- Darby, S.E.; Dunn, F.E.; Nicholls, R.J.; Cohen, S.; Zarfl, C.; Fekete, B.M. Fluvial sediment supply to a mega-delta reduced by shifting tropical-cyclone activity. Nat. Clim. Change 2015, 5, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauer, C.; Leitner, P.; Unfer, G.; Pulg, U.; Habersack, H.; Graf, W. The Role of Sediment and Sediment Dynamics in the Aquatic Environment. In Riverine Ecosystem Management; Aquatic Ecology Series; Schmutz, S., Sendzimir, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillén, J.; Palanques, A. Sediment dynamics and hydrodynamics in the lower course of a river highly regulated by dams: The Ebro River. Sedimentology 1992, 39, 567–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batalla, R.J.; Vericat, D. A review of sediment quantity issues: Examples from the river Ebro and adjacent basins (Northeastern Spain). Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2011, 7, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tena, A.; Batalla, R.J. The sediment budget of a large river regulated by dams (The lower River Ebro, NE Spain). J. Soils Sediments 2013, 13, 966–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polo, M.J.; Rovira, A.; García-Contreras, D.; Contreras, E.; Millares, A.; Aguilar, C.; Losada, M.A. Reservoir impacts downstream in highly regulated river basins: The Ebro delta and the Guadalquivir estuary in Spain. IAHS-AISH Proc. Rep. 2016, 373, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vericat, D.; Batalla, R.J.; Garcia, C. Breakup and reestablishment of the armour layer in a large gravel-bed river below dams: The lower Ebro. Geomorphology 2006, 76, 122–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibàñez, C.; Alcaraz, C.; Caiola, N.; Rovira, A.; Trobajo, R.; Alonso, M.; Duran, C.; Jiménez, P.J.; Munné, A.; Prat, N. Regime shift from phytoplankton to macrophyte dominance in a large river: Top-down versus bottom-up effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 416, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovira, A.; Ibàñez, C. Sediment management options for the lower Ebro River and its Delta. J. Soils Sediments 2007, 7, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galván, R. Plan de Acción Sobre el Delta del Ebro: Caracterización de los Sedimentos Existentes en los Embalses de Mequineza y Ribarroja. Technical Report Confederación Hidrográfica del Ebro. 2023. Available online: https://www.chebro.es/documents/20121/1548903/MEM01O2101381_MEQ_RIB_RG_v02.pdf/f44341b3-cf99-6bfd-f3a0-63e090a581f9?t=1709034433504 (accessed on 8 March 2024).
- CHE. Plan de Actuación para la Mejora de la Gestión del Régimen Sedimentario en el Ámbito del Delta del Ebro. Technical Report Confederación Hidrográfica del Ebro. 2021. Available online: https://www.chebro.es/documents/20121/1523790/Plan+Delta+gesti%C3%B3n+del+sedimento+Ebro+Documento+DGA_2_2_2021.pdf/6c3949e3-517e-830c-a5d5-dc886a2ebadc?t=1711959506330 (accessed on 24 March 2025).
- Tena, A.; Batalla, R.J.; Vericat, D.; López-Tarazón, J.A. Suspended sediment dynamics in a large regulated river over a 10-year period (the lower Ebro, NE Iberian Peninsula). Geomorphology 2011, 125, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondolf, G.M.; Gao, Y.; Annandale, G.W.; Morris, G.L.; Jiang, E.; Zhang, J.; Cao, Y.; Carling, P.; Fu, K.; Guo, Q.; et al. Sustainable sediment management in reservoirs and regulated rivers: Experiences from five continents. Earth’s Future 2014, 2, 256–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaud, F.; Piégay, H.; Béal, D.; Collery, P.; Vaudor, L.; Rollet, A.-J. Monitoring gravel augmentation in a large regulated river and implications for process-based restoration. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2017, 42, 2147–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiterer, K.; Gold, T.; Hauer, C.; Habersack, H.; Sindelar, C. Sediment Replenishment Along Rivers—Advection and Dispersion of Gravel Inputs. In Proceedings of the IAHR World Congress, Granada, Spain, 19–24 June 2022; pp. 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battisacco, E.; Franca, M.J.; Schleiss, A.J. Sediment replenishment: Influence of the geometrical configuration on the morphological evolution of channel-bed. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 8879–8894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, E.; Syvitski, J.; Zăinescu, F.; Nicholls, R.J.; Cohen, K.M.; Marriner, N.; Saito, Y.; Day, J.; Minderhoud, P.S.J.; Amorosi, A.; et al. Delta sustainability from the Holocene to the Anthropocene and envisioning the future. Nat. Sustain. 2024, 7, 1235–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICOLD. World Register of Dams. 2023. Available online: http://www.icold-cigb.net/ (accessed on 9 July 2020).
- Bladé, E.; Cea, L.; Corestein, G.; Escolano, E.; Puertas, J.; Vázquez-Cendón, E.; Dolz, J.; Coll, A. Iber: Herramienta de simulación numérica del flujo en ríos. Rev. Int. Metodos Numer. Para Calc. Diseno Ingenieria 2014, 30, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bladé Castellet, E.; Cea, L.; Corestein, G. Numerical modelling of river inundations. Ing. Agua 2014, 18, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santillán, D.; Cueto-Felgueroso, L.; Sordo-Ward, A.; Garrote, L. Influence of Erodible Beds on Shallow Water Hydrodynamics during Flood Events. Water 2020, 12, 3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cueto-Felgueroso, L.; Santillán, D.; García-Palacios, J.H.; Garrote, L. Comparison between 2D shallow-water simulations and energy-momentum computations for transcritical flow past channel contractions. Water 2019, 11, 1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghan-Souraki, D.; López-Gómez, D.; Bladé-Castellet, E.; Larese, A.; Sanz-Ramos, M. Optimizing sediment transport models by using the Monte Carlo simulation and deep neural network (DNN): A case study of the Riba-Roja reservoir. Environ. Model. Softw. 2024, 175, 105979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Gómez, D.; de Blas-Moncalvillo, M.; Castejón-Zapata, M.; Gassó-Sánchez, Á.; Bladé, E.; Sanz-Ramos, M.; Dehghan-Souraki, D.; Garrote-de Marco, L.; Santillán-Sánchez, D.; Soria-García, J.M.; et al. Análisis del transporte de sedimentos en el curso bajo del río Ebro mediante modelización numérica de una avenida controlada. Ing. Agua 2024, 28, 246–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Gómez, D.; de Blas-Moncalvillo, M.; Cuéllar-Moro, V. Herramientas para la gestión sostenible de la sedimentación en el embalse de Marmolejo (España). Ing. Agua 2024, 28, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Ramos, M.; López-Gómez, D.; Bladé, E.; Dehghan-Souraki, D. A CUDA Fortran GPU-parallelised hydrodynamic tool for high-resolution and long-term eco-hydraulic modelling. Environ. Model. Softw. 2023, 161, 105628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibàñez, C.; Prat, N.; Canicio, A. Changes in the hydrology and sediment transport produced by large dams on the lower Ebro river and its estuary. Regul. Rivers Res. Manag. 1996, 12, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Gao, S.; Wang, Z.; Pan, C.; Wu, X.; Wang, Q. Morphodynamic modeling of a large inside sand bar and its dextral morphology in a convergent estuary: Qiantang Estuary, China. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2017, 122, 1434–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrela, T.y.L. Quintas El sistema integrado de modelización precipitación-aportación SIMPA. Ing. Civ. 1996, 104, 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- CEDEX. Evaluación de Recursos Hídricos en Régimen Natural en España (1940/41–2017/18). Centro de Estudios y Experimentación de Obras Públicas. Ministerio de Fomento y Ministerio para la Transición Ecológica. 2020. Available online: https://www.miteco.gob.es/content/dam/miteco/es/agua/temas/evaluacion-de-los-recursos-hidricos/cedex-informeerh2019_tcm30-518171.pdf (accessed on 19 May 2021).
- Garrote, L.; Sordo-Ward, A.; Bianucci, P. Assessment of Blue Water Availability for Agriculture in the Mediterranean. Proceedings of the 8th IAHR European Congress (Lisbon, 2024). 2024. Available online: https://www.iahr.org/library/infor?pid=30970 (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- Warszawski, L.; Frieler, K.; Huber, V.; Piontek, F.; Serdeczny, O.; Schewe, J. The inter-sectoral impact model intercomparison project (ISI-MIP): Project framework. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 3228–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weedon, G.P.; Balsamo, G.; Bellouin, N.; Gomes, S.; Best, M.J.; Viterbo, P. The WFDEI meteorological forcing data set: WATCH Forcing Data methodology applied to ERA-Interim reanalysis data. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 7505–7514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zeng, Y.; Wyman, B.; Dunne, J.P.; Horowitz, L.W.; Adcroft, A.J.; Ginoux, P.; Held, I.M.; John, J.G.; Krasting, J.P.; et al. The GFDL Earth System Model Version 4.1 (GFDL-ESM 4.1): Overall Coupled Model Description and Simulation Characteristics. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2020, 12, e2019MS002015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yukimoto, S.; Yoshimura, H.; Hosaka, M.; Sakami, T.; Tanaka, T.Y.; Shindo, E.; Tsujino, H.; Deushi, M.; Mizuta, R.; Yabu, S.; et al. Meteorological Research Institute-Earth System Model Version 1 (MRI-ESM1)—Model Description. In Technical Reports of the Meteorological Research Institute, No. 64; Meteorological Research Institute, Japan Meteorological Agency: Tsukuba, Japan, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sepulchre, P.; Caubel, A.; Ladant, J.-B.; Bopp, L.; Boucher, O.; Braconnot, P.; Brockmann, P.; Cozic, A.; Donnadieu, Y.; Dufresne, J.-L.; et al. IPSL-CM5A2—An Earth system model designed for multi-millennial climate simulations. Geosci. Model Dev. 2020, 13, 3011–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutjahr, O.; Putrasahan, D.; Lohmann, K.; Jungclaus, J.H.; von Storch, J.-S.; Brüggemann, N.; Haak, H.; Stössel, A. Max Planck Institute Earth System Model (MPI-ESM1.2) for the High-Resolution Model Intercomparison Project (HighResMIP). Geosci. Model Dev. 2019, 12, 3241–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellar, A.A.; Jones, C.G.; Mulcahy, J.P.; Tang, Y.; Yool, A.; Wiltshire, A.; O’Connor, F.M.; Stringer, M.; Hill, R.; Palmier, J.; et al. UKESM1: Description and Evaluation of the U.K. Earth System Model. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2019, 11, 4513–4558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanasaki, N.; Kanae, S.; Oki, T.; Masuda, K.; Motoya, K.; Shirakawa, N.; Shen, Y.; Tanaka, K. An integrated model for the assessment of global water resources—Part 1: Model description and input meteorological forcing. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2008, 12, 1007–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanasaki, N.; Kanae, S.; Oki, T.; Masuda, K.; Motoya, K.; Shirakawa, N.; Shen, Y.; Tanaka, K. An estimation of global virtual water flow and sources of water for major crops and livestock products using a global hydrological model. J. Hydrol. 2010, 384, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burek, P.; Satoh, Y.; Kahil, T.; Tang, T.; Greve, P.; Smilovic, M.; Guillaumot, L.; Zhao, F.; Wada, Y. Development of the Community Water Model (CWatM v1.04)—A high-resolution hydrological model for global and regional assessment of integrated water resources management. Geosci. Model Dev. 2020, 13, 3267–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sordo-Ward, A.; Granados, A.; Iglesias, I.; Garrote, L.; Bejarano, M.D. Adaptation Effort and Performance of Water Management Strategies to Face Climate Change Impacts in Six Representative Basins of Southern Europe. Water 2019, 11, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianucci, P.; Sordo-Ward, A.; Lama-Pedrosa, B.; Garrote, L. How do environmental flows impact on water availability under climate change scenarios in European basins? Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 911, 168566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paredes-Beltran, B.E.; Sordo-Ward, Á.; Martín-Carrasco, F.; Garrote, L. High-resolution estimates of water availability for the Iberian Peninsula under climate scenarios. Appl. Water Sci. 2024, 14, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehner, B.; Verdin, K.; Jarvis, A. New global hydrography derived from spaceborne elevation data. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2008, 89, 93–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CHE. Plan Hidrológico de la parte Española de la Demarcación Hidrográfica del Ebro Revisión para el Tercer Ciclo: 2022–2027. Memoria. Technical Report Confederación Hidrográfica del Ebro. 2022. Available online: https://www.chebro.es/documents/20121/1027081/00_PH3c_091_2023-01_Memoria_v01.pdf/f3036ada-67bf-9294-23ae-c627760a89cc?t=1675946692886 (accessed on 16 April 2025).
- Cea, L.; Puertas, J.; Vázquez-Cendón, M.E. Depth Averaged Modelling of Turbulent Shallow Water Flow with Wet-Dry Fronts. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2007, 14, 303–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.S. Modeling the tor-dotted crests, bedrock edges, and parabolic profiles of high alpine surfaces of the Wind River Range, Wyoming. Geomorphology 2002, 46, 35–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudd, S.M.; Furbish, D.J. Influence of chemical denudation on hillslope morphology. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2004, 109, F02001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paola, C.; Voller, V.R. A generalized Exner equation for sediment mass balance. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2005, 110, F04014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rijn, L.C. Sediment Transport, Part I: Bed Load Transport. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1984, 110, 1431–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulsby, R.L.; Whitehouse, R.J.S. Threshold of sediment motion in coastal environments. In Pacific Coasts and Ports’ 97: Proceedings of the 13th Australasian Coastal and Ocean Engineering Conference and the 6th Australasian Port and Harbour Conference; Centre for Advanced Engineering, University of Canterbury: Christchurch, New Zealand, 1997; Volume 1, pp. 145–150. [Google Scholar]
- Shields, A. Anwendung Der Aehnlichkeitsmechanik und der Turbulenzforschung Auf Die Geschiebebewegung. Ph.D. Thesis, Technical University Berlin, Berlin, Germany, 1936. [Google Scholar]
- van Rijn, L.C. Mathematical Modelling of Morphological Processes in the Case of Suspended Sediment Transport; Delft Hydraulics Laboratory: Delft, The Netherlands, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- van Rijn, L.C. Sediment Transport, Part II: Suspended Load Transport. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1984, 110, 1613–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanoni, V.A.; Brooks, N.H. Laboratory Studies of the Roughness and Suspended Load of Alluvial Streams; California Institute of Technology, Report E-68; Sedimentation Laboratory: Pasadena, CA, USA, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- van Leer, B. Towards the Ultimate Conservative Difference Scheme, V. A Second Order Sequel to Godunov’s Method. J. Comput. Phys. 1979, 32, 101–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

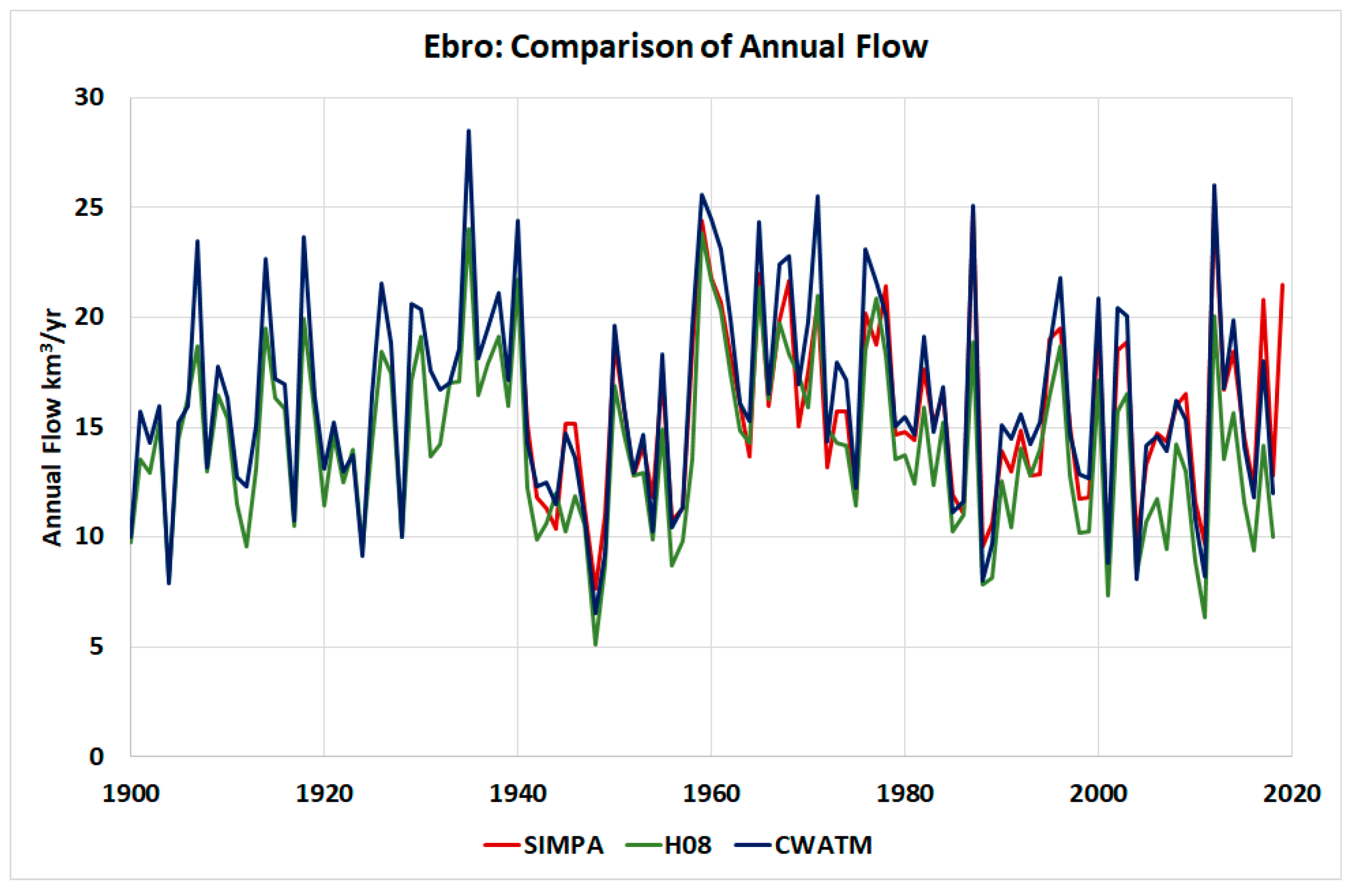
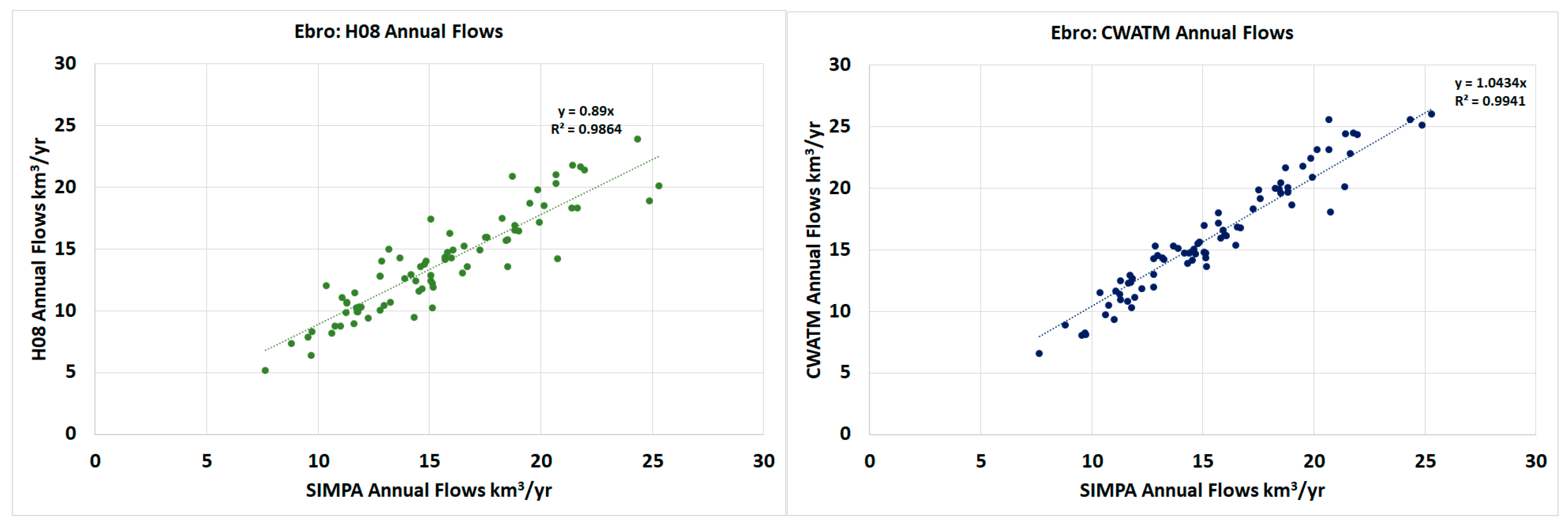
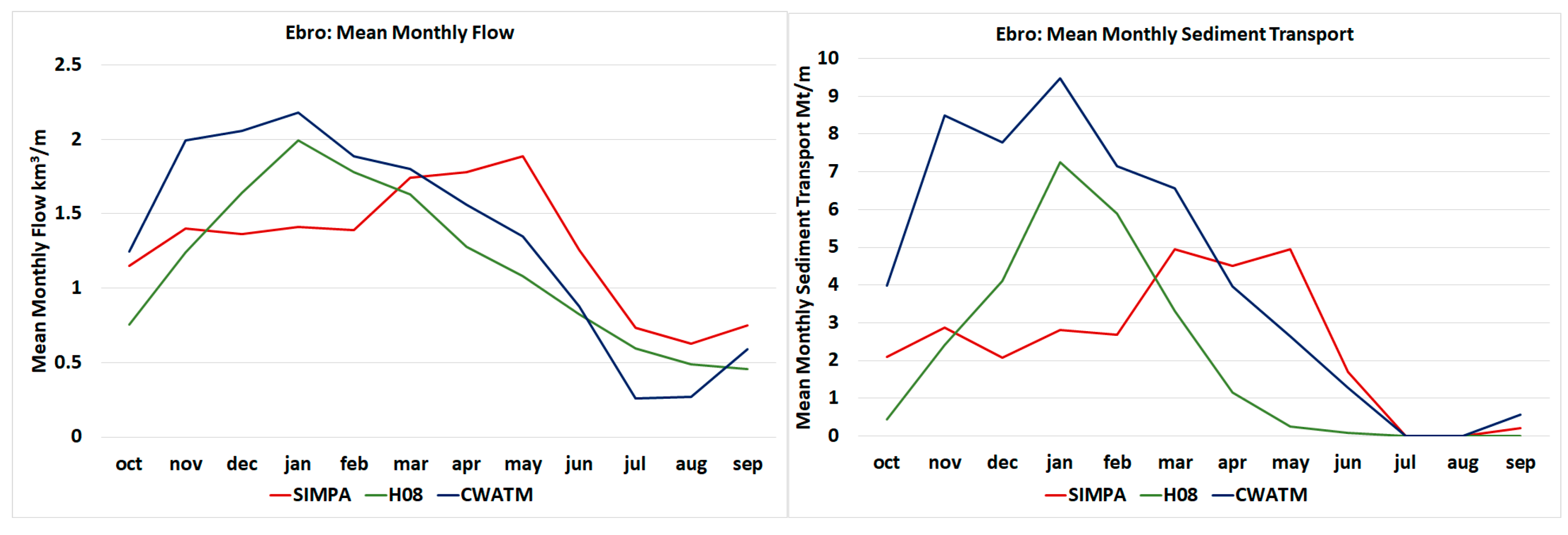
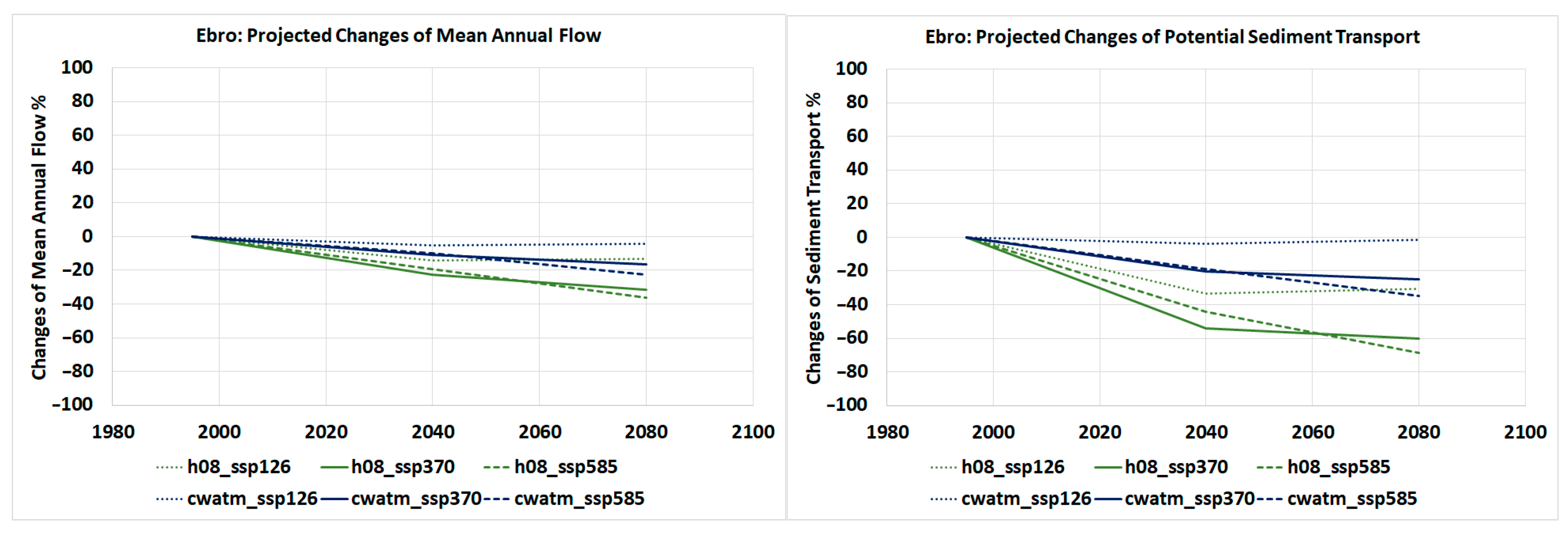
| Scenario | obsclim | obsclim | historic | ssp126 | ssp370 | ssp585 | ssp126 | ssp370 | ssp585 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Period | 79–18 | 74–13 | 74–13 | 20–59 | 20–59 | 20–59 | 60–99 | 60–99 | 60–99 |
| SIMPA | 14.97 | 15.19 | |||||||
| H08 | |||||||||
| gswp3 | 12.63 | 13.19 | |||||||
| gfdl | 13.45 | 12.12 | 10.61 | 11.64 | 12.20 | 10.22 | 9.14 | ||
| mrl | 13.40 | 12.37 | 11.33 | 12.97 | 13.62 | 11.45 | 9.94 | ||
| ipsl | 13.61 | 10.91 | 10.42 | 9.83 | 10.57 | 8.10 | 7.27 | ||
| mpi | 13.03 | 10.95 | 10.33 | 10.61 | 11.39 | 8.80 | 8.55 | ||
| ukesm1 | 13.98 | 11.63 | 9.63 | 9.24 | 10.62 | 7.64 | 7.97 | ||
| mean | 12.63 | 13.19 | 13.49 | 11.59 | 10.46 | 10.86 | 11.68 | 9.24 | 8.57 |
| CWatM | |||||||||
| gswp3 | 15.17 | 15.63 | |||||||
| gfdl | 15.84 | 15.31 | 13.66 | 14.98 | 15.46 | 13.88 | 12.66 | ||
| mrl | 15.59 | 15.81 | 15.28 | 16.90 | 16.78 | 15.81 | 14.03 | ||
| ipsl | 15.84 | 13.95 | 13.98 | 12.81 | 13.84 | 11.82 | 10.60 | ||
| mpi | 15.44 | 14.02 | 12.90 | 13.71 | 14.49 | 11.73 | 11.87 | ||
| ukesm1 | 15.40 | 14.92 | 13.82 | 12.13 | 14.30 | 11.89 | 11.38 | ||
| mean | 15.17 | 15.63 | 15.62 | 14.80 | 13.91 | 14.11 | 14.98 | 13.03 | 12.11 |
| Scenario | obsclim | obsclim | historic | ssp126 | ssp370 | ssp585 | ssp126 | ssp370 | ssp585 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Period | 79–18 | 74–13 | 74–13 | 20–59 | 20–59 | 20–59 | 60–99 | 60–99 | 60–99 |
| SIMPA | 26.76 | 25.29 | |||||||
| H08 | |||||||||
| gswp3 | 23.83 | 28.58 | |||||||
| gfdl | 28.40 | 20.23 | 13.99 | 16.40 | 19.99 | 11.77 | 8.00 | ||
| mrl | 30.36 | 24.91 | 15.41 | 32.79 | 31.05 | 25.74 | 14.54 | ||
| ipsl | 31.55 | 16.55 | 15.95 | 10.61 | 18.26 | 9.17 | 5.91 | ||
| mpi | 29.27 | 19.72 | 15.86 | 15.83 | 21.46 | 8.98 | 10.11 | ||
| ukesm1 | 35.98 | 21.89 | 10.17 | 11.37 | 17.50 | 6.39 | 10.10 | ||
| mean | 23.83 | 28.58 | 31.11 | 20.66 | 14.28 | 17.40 | 21.65 | 12.41 | 9.73 |
| CWatM | |||||||||
| gswp3 | 37.87 | 42.09 | |||||||
| gfdl | 43.13 | 39.51 | 30.99 | 36.15 | 43.36 | 32.44 | 27.52 | ||
| mrl | 45.06 | 48.22 | 42.06 | 55.62 | 50.38 | 48.93 | 38.74 | ||
| ipsl | 43.13 | 36.35 | 36.17 | 25.73 | 38.52 | 29.10 | 22.32 | ||
| mpi | 42.58 | 40.16 | 28.96 | 31.52 | 40.13 | 23.19 | 25.52 | ||
| ukesm1 | 41.72 | 43.09 | 33.57 | 26.28 | 40.07 | 28.40 | 26.07 | ||
| mean | 37.87 | 42.09 | 43.12 | 41.47 | 34.35 | 35.06 | 42.49 | 32.41 | 28.03 |
| Scenario | obsclim | obsclim | historic | ssp126 | ssp370 | ssp585 | ssp126 | ssp370 | ssp585 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Period | 79–18 | 74–13 | 74–13 | 20–59 | 20–59 | 20–59 | 60–99 | 60–99 | 60–99 |
| Tortosa | 8.96 | 9.66 | |||||||
| SIMPA | 6.57 | 6.75 | |||||||
| H08 | |||||||||
| gswp3 | 6.21 | 6.72 | |||||||
| gfdl | 7.08 | 5.54 | 5.33 | 6.57 | 5.63 | 5.00 | 4.36 | ||
| mrl | 6.50 | 6.03 | 6.08 | 7.93 | 7.04 | 6.31 | 5.17 | ||
| ipsl | 6.94 | 5.78 | 6.69 | 6.79 | 5.50 | 4.54 | 4.47 | ||
| mpi | 6.97 | 5.79 | 5.88 | 7.38 | 6.10 | 4.45 | 5.43 | ||
| ukesm1 | 7.27 | 6.03 | 5.93 | 5.92 | 4.99 | 4.18 | 4.72 | ||
| mean | 6.21 | 6.72 | 6.95 | 5.84 | 5.98 | 6.92 | 5.85 | 4.90 | 4.83 |
| CWatM | |||||||||
| gswp3 | 8.91 | 9.35 | |||||||
| gfdl | 9.02 | 8.64 | 8.08 | 9.61 | 8.83 | 8.33 | 7.52 | ||
| mrl | 9.66 | 9.31 | 9.17 | 11.55 | 10.19 | 9.75 | 8.85 | ||
| ipsl | 9.02 | 8.53 | 9.00 | 8.44 | 8.50 | 6.92 | 6.53 | ||
| mpi | 8.97 | 8.56 | 7.78 | 9.59 | 8.84 | 6.67 | 7.85 | ||
| ukesm1 | 9.11 | 9.35 | 8.36 | 8.24 | 8.61 | 6.55 | 7.47 | ||
| mean | 8.91 | 9.35 | 9.15 | 8.88 | 8.48 | 9.49 | 8.99 | 7.64 | 7.64 |
| Scenario | obsclim | obsclim | historic | ssp126 | ssp370 | ssp585 | ssp126 | ssp370 | ssp585 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Period | 79–18 | 74–13 | 74–13 | 20–59 | 20–59 | 20–59 | 60–99 | 60–99 | 60–99 |
| Tortosa | 8.91 | 11.26 | |||||||
| SIMPA | 6.26 | 6.01 | |||||||
| H08 | |||||||||
| gswp3 | 4.49 | 6.46 | |||||||
| gfdl | 6.95 | 4.33 | 3.99 | 5.45 | 5.21 | 1.46 | 1.71 | ||
| mrl | 7.19 | 8.54 | 3.11 | 16.32 | 10.53 | 9.97 | 3.30 | ||
| ipsl | 9.32 | 3.74 | 7.80 | 3.76 | 5.32 | 3.81 | 2.24 | ||
| mpi | 8.18 | 5.57 | 5.34 | 8.07 | 6.48 | 1.60 | 4.48 | ||
| ukesm1 | 9.74 | 6.50 | 3.11 | 4.26 | 3.82 | 2.33 | 4.96 | ||
| mean | 4.49 | 6.46 | 8.27 | 5.74 | 4.67 | 7.57 | 6.27 | 3.83 | 3.34 |
| CWatM | |||||||||
| gswp3 | 8.09 | 9.30 | |||||||
| gfdl | 8.31 | 6.84 | 6.27 | 8.20 | 8.81 | 4.92 | 6.25 | ||
| mrl | 9.88 | 13.91 | 8.36 | 19.16 | 12.76 | 14.34 | 9.42 | ||
| ipsl | 8.31 | 6.93 | 10.01 | 5.12 | 10.65 | 6.77 | 5.59 | ||
| mpi | 10.81 | 8.93 | 6.65 | 10.56 | 9.58 | 4.60 | 7.39 | ||
| ukesm1 | 9.30 | 12.76 | 7.49 | 6.44 | 12.12 | 8.94 | 7.94 | ||
| mean | 8.09 | 9.30 | 9.32 | 9.87 | 7.75 | 9.90 | 10.78 | 7.91 | 7.32 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martin-Carrasco, F.; Santillán, D.; López-Gómez, D.; Iglesias, A.; Garrote, L. Sediment Transport Constraints for Restoration of the Ebro Delta. Water 2025, 17, 1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111620
Martin-Carrasco F, Santillán D, López-Gómez D, Iglesias A, Garrote L. Sediment Transport Constraints for Restoration of the Ebro Delta. Water. 2025; 17(11):1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111620
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartin-Carrasco, Francisco, David Santillán, David López-Gómez, Ana Iglesias, and Luis Garrote. 2025. "Sediment Transport Constraints for Restoration of the Ebro Delta" Water 17, no. 11: 1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111620
APA StyleMartin-Carrasco, F., Santillán, D., López-Gómez, D., Iglesias, A., & Garrote, L. (2025). Sediment Transport Constraints for Restoration of the Ebro Delta. Water, 17(11), 1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111620










