Abstract
Rainwater needs to be recognized as a natural water source for domestic use, but finding viable processes to remove its contaminants is essential. The aim of this work was to compare the UV/H2O2 and UV/Fenton-like processes for the oxidation of 3,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid (3,5-DHBA) in rainwater. The reactions were assessed using ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) and molecular fluorescence spectroscopies, and the results showed the formation of new and similar chromophoric compounds in both processes, which were subsequently degraded. At environmentally relevant concentrations of chemical oxidants, namely H2O2 at 10−4 M, the chromophoric organic compounds in solution were degraded within 24 h by the UV/H2O2 process and within 4 h by the UV/Fenton-like process. However, when the concentration of H2O2 was increased by one order of magnitude for the UV/H2O2 process (from 10−4 M to 10−3 M), oxidation rates were similar and nearly complete after 4 h for both UV/H2O2 and UV/Fenton-like processes. These findings highlight that the presence of more oxidizing agents in the oxidation system improves the synergistic effect, leading to a greater contribution of the free radical oxidation pathway, particularly through hydroxyl radicals. Thus, by increasing the concentration of H2O2 in the UV/H2O2 process to 10−3 M, it was possible to achieve a similar level of oxidation (close to 100% after 4 h, as indicated by a decrease in fluorescence intensity) as the UV/Fenton-like process at environmentally relevant concentrations (10−4 M), but using fewer chemical reactants, since UV/H2O2 process does not require Fe(III) as catalyst and oxidant. Therefore, the UV/H2O2 process can be considered a simpler and cleaner process for removing organic contaminants from rainwater.
1. Introduction
Many people worldwide still lack access to safe drinking water, making freshwater scarcity one of the most pressing global challenges [1]. To reduce dependence on conventional water sources, it is crucial to explore alternative resources, such as rainwater [2]. However, it is well known that rainwater may contain organic pollutants [3], in addition to inorganic pollutants [4], as a result of rainout and washout processes. Santos et al. [5] showed that dissolved organic matter (DOM) extracted from rainwater in Portugal mostly contains aliphatic structures, with only a minor aromatic component (2–7%). Despite the low content of aromatic compounds in rainwater, their presence highlights the need to eliminate them before rainwater can be safely used for domestic purposes.
Small aromatic compounds, such as benzoate and phenol derivatives, have been found in rainwater and other types of atmospheric water [6,7,8,9]. Various studies have shown that small aromatic compounds are naturally degraded in atmospheric waters, mainly due to the attack of hydroxyl radicals [10,11,12], which are considered among the most important oxidants present in the atmospheric aqueous phase [13,14]. Furthermore, in atmospheric waters, sunlight has also been shown to be an important oxidant agent in the presence of chemical oxidants, such as Fe(III) and H2O2 (Fenton-like reaction), due to the simultaneous photogeneration of hydroxyl radicals, which, in turn, accelerate the degradation of organic compounds in rainwater [12,13]. Therefore, light and chemical oxidants may be simultaneously used to study the degradation of aromatic compounds in rainwater for treatment and subsequent safe use. Since 3,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid (3,5-DHBA) is a small aromatic compound substituted with carboxyl and hydroxyl groups (hydroxyacid), with characteristics resembling tracers of biomass burning [15,16], it has been considered a suitable model compound to study oxidation in rainwater [17,18]. To the best of our knowledge, only five studies have addressed the oxidation of 3,5-DHBA in the aqueous phase, four of which used concentrations relevant to atmospheric waters [17,19,20,21], and two used higher concentrations [18,21]. Gelencsér et al. [17] and Hoffer et al. [18] showed that Fenton-like oxidation of 3,5-DHBA produced new chromophoric compounds similar to humic-like substances. Santos and Duarte [19] highlighted that Fenton-like oxidation of 3,5-DHBA in the absence of light produced new chromophoric compounds that were completely degraded after 24 h of reaction, and Santos et al. [20] showed that the new intermediate products were also aromatic compounds, such as 2,4,6-trihydroxybenzoic acid, 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic acid, and tetrahydroxybenzene, suggesting that hydroxylation plays a key role in the Fenton-like oxidation during the night. Ferreira et al. [21] studied the oxidation of a mixture of small aromatic compounds, including benzoic, 3,5-dihydroxybenzoic, and syringic acids, in rainwater using the UV/H2O2 process, and new chromophoric compounds were initially formed but were fully degraded at a later stage. Moreover, only the study of Ferreira et al. [21] applied these processes to real rainwater samples with the purpose of their treatment, with results reflecting the influence of dissolved organic and inorganic species in rainwater, and the possible occurrence of parallel reactions or competition for chemical oxidants and/or UV light.
UV light is, per se, an oxidizing agent that affects organic compounds present in water by inducing their direct and sensitized photolysis and by promoting the photogeneration of radical species [13]. When combined with oxidation processes that occur naturally in atmospheric waters, such as the Fenton-like reaction, it enhances radical production, mainly hydroxyl radicals, thereby accelerating the oxidation of organic compounds [22]. However, for rainwater treatment, which usually involves less contaminated waters, avoiding the use of Fe(III) is advantageous, as it reduces the need for added chemicals. Therefore, the UV/H2O2 process, which primarily uses UV light to photolyze H2O2 and to produce hydroxyl radicals that attack organic molecules, emerges as a promising alternative for the degradation of organic compounds in rainwater [21]. In fact, both the UV/Fenton-like and UV/H2O2 processes are advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) that have been widely applied in wastewater treatment to oxidize organic pollutants [23,24,25], aiming for partial or complete mineralization into CO2 and H2O, depending on treatment conditions and target water quality. Given their effectiveness, comparing these processes for rainwater purification becomes increasingly important.
To the best of our knowledge, no study has compared the UV/Fenton-like and UV/H2O2 processes for the oxidation of organic compounds in rainwater with the purpose of real-world rainwater treatment applications. Therefore, the main aim of this study was to compare the oxidation of 3,5-DHBA by both processes in rainwater. First, the comparison was performed in water model solutions under environmentally relevant conditions and concentrations. Next, the effects of pH, H2O2 concentration, and time of reaction on the extent of oxidation in the UV/H2O2 process were evaluated, because this process does not require Fe(III). Finally, both processes were applied to a real rainwater sample, using a higher concentration of H2O2 in the UV/H2O2 process, and the results were compared. The oxidation reactions were evaluated by ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) and molecular fluorescence spectroscopies.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Experimental Procedure
The degradation of 3,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid (3,5-DHBA) was performed by UV/H2O2 and UV/Fe(III)/H2O2 (UV/Fenton-like) processes in water model solutions and in a rainwater sample. According to the process and the reactants needed, the model solutions were freshly prepared in ultrapure water from stock solutions of 3,5-DHBA (0.01 M), iron (III) chloride hexahydrate (FeCl3.6H2O) (0.01 M in 0.1 M HCl; [26]), and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) 30% (w/w). The concentrations used for the reactions were the following: 2 × 10−5 M for 3,5-DHBA, 5 × 10−6 M for Fe(III), and 10−4 M for H2O2. These concentration levels are in the range found in the atmospheric aqueous phase [13,17] and were like those used in the works of Santos and Duarte [19] and Santos et al. [12] for the study of the oxidation of small aromatic compounds in atmospheric waters. In order to evaluate the UV/Fenton-like process in the degradation of 3,5-DHBA, solutions containing 3,5-DHBA and Fe(III) were prepared, and the pH was adjusted to 5.0. Immediately after, H2O2 was added, and the solutions, placed in quartz tubes to prevent UV attenuation by glass, were positioned approximately 15 cm from the UV lamp in an incubator at 20 °C and exposed to UV light emitting at 254 nm (6 W). The extent of oxidation of 3,5-DHBA was evaluated using UV-Vis and molecular fluorescence spectroscopies at different reaction times, namely 0 h, 0.33 h, 0.67 h, 1 h, 2 h, 4 h, 6 h, and 24 h, immediately after the irradiation period in the incubator. For each reaction time, an independent quartz tube was used with the same volume (20 mL). At least two replicates of the above procedure were performed on different days. The same procedure was used to evaluate the UV/H2O2 process in the degradation of 3,5-DHBA, but without adding Fe(III) to the model solutions. The effect of the initial H2O2 concentration in the degradation of 3,5-DHBA by this process was tested for the concentrations of 10−4 M, 5 × 10−4 M, and 10−3 M. The effect of the pH was also tested for the pH values of 4.0, an acid pH for atmospheric waters; 5.0 and 6.0, neutral pH values for atmospheric waters; and 7.0, a basic pH for atmospheric waters [27]. The pH was adjusted using H2SO4 (0.1 M) and NaHCO3 (0.1 M) solutions, and, after the application of the oxidation processes, the pH values of the solutions varied by no more than 0.2 pH units. While testing the effect of the pH, the initial H2O2 concentration was 10−3 M. The controls of experiments were performed in solutions prepared in ultrapure water and containing only Fe(III) and H2O2, and only H2O2, for the UV/Fenton-like and UV/H2O2 processes, respectively. The UV-Vis and fluorescence spectra of controls did not show notable bands and changes with the course of the reaction (see Supplementary Materials Figure S1). Since a previous study by the authors [19] showed that the oxidation of 3,5-DHBA in ultrapure water by the Fenton-like process can occur at pH values between 4.0–5.0 in the absence of light, while oxidation by H2O2 does not occur, these control experiments were not repeated in the present study. Similarly to what was described for model solutions, the degradation of 3,5-DHBA was also evaluated in a rainwater sample at its natural pH (5.5) to test the influence of the matrix. For such, the sample was spiked with 3,5-DHBA and H2O2 for the UV/H2O2 process and with 3,5-DHBA, Fe(III), and H2O2 for the UV/Fenton-like process. For the sample, the oxidation was evaluated for the following reaction times: 0 h, 1 h, 2 h, 4 h, 6 h, and 24 h. The controls of sample oxidation were also performed by applying UV light, the UV/H2O2 process with an initial H2O2 concentration of 10−3 M, and the UV/Fenton-like process with an initial H2O2 concentration of 10−4 M.
Prior to use, all glass material was immersed for 30 min in a solution of NaOH (0.1 M), then rinsed with distilled water, followed by immersion for 24 h in a solution of HNO3 (4 M), and finally rinsed with ultrapure water.
2.2. Rainwater Sampling and Sample Preparation
A rainwater sample was collected on the roof of a building at the University of Aveiro, in the western part of the town of Aveiro (40°38′ N, 8°39′ W), on 30 April 2018. Rainwater sampling occurred through glass funnels (30 cm diameter) into glass bottles (5 L), placed inside polyvinyl chloride opaque tubes, protected from direct sunlight. The sampling containers were left open on a 24-hour basis, and the rainwater sample was the result of the collection of both wet and dry depositions [5]. After collection, the sample was divided into two aliquots. One of the aliquots was used for the measurement of the pH (5.5), and the second aliquot was filtered through hydrophilic polyvinylidene fluoride Millipore membrane filters with 0.45 μm of pore size and was refrigerated at 4 °C until its use as a matrix to perform the degradation of 3,5-DHBA and posterior analysis.
2.3. Analytical Instrumentation
UV-Vis spectra, in the range of 200–500 nm, were recorded on a Shimadzu (Düsseldorf, Germany) Model UV 210PC spectrophotometer, using quartz cells of 5 cm path lengths. Ultrapure water was used as a reference in order to obtain the baseline. The molecular fluorescence spectra were recorded on a Jasco FP-6500 spectrophotometer with a xenon lamp as the source of radiation, using a 1 cm quartz cell. Synchronous spectra with Δλ of 60 nm were acquired using excitation wavelengths from 220 nm to 500 nm (5 nm intervals), using 10 nm bandwidths on both the excitation and emission monochromators. Excitation-emission matrix (EEM) fluorescence spectra were acquired by concatenating emission spectra measured every 5 nm from 280 nm to 500 nm and using excitation wavelengths from 220 nm to 400 nm and 5 nm bandwidths on both excitation and emission monochromators. For each day of experimental work, the fluorescence blank spectrum (ultrapure water) was subtracted from the solutions spectra.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Degradation of 3,5-DHBA by Different Processes
Figure 1 shows the absorbance and synchronous fluorescence (Δλ = 60 nm) spectra of 3,5-DHBA in water during its oxidation by the UV/H2O2 and UV-Fenton-like processes under environmental concentrations and conditions, specifically at a pH value of 5.0 and with a hydrogen peroxide concentration of 10−4 M.
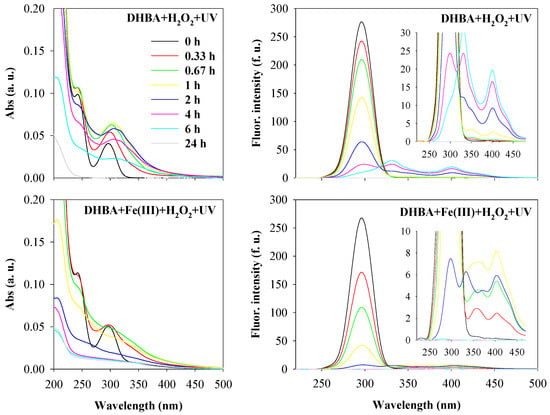
Figure 1.
Absorbance spectra (average spectra; left) and synchronous fluorescence spectra (Δλ = 60 nm; right) of 3,5-DHBA during oxidation by UV/H2O2 (DHBA + H2O2 + UV) and by UV/Fenton-like (DHBA + Fe(III) + H2O2 + UV) processes. Experimental conditions were as follows: [3,5-DHBA]0 = 2 × 10−5 M, [H2O2]0 = 10−4 M and initial pH = 5.0 for both processes; [Fe(III)]0 = 5 × 10−6 M for the UV/Fenton-like process. Spectra were recorded at oxidation times of 0, 0.33, 0.67, 1, 2, 4, 6, and 24 h, with the color code shown in the top left graph (which applies to all graphs).
The absorbance spectrum at the initial time of reactions shows two absorption bands, located at approximately 242 nm (principal band) and 296 nm (secondary band), which are attributed to the presence of 3,5-DHBA and its π–π* electronic transitions in the benzene ring and carboxylic (electron-withdrawing substituent) and hydroxyl (electron-donating substituent) groups [28]. Regarding the synchronous fluorescence spectrum of 3,5-DHBA, at time zero, a fluorescence band is located at 295 nm. For both degradation processes, the oxidation of 3,5-DHBA occurred when changes in the initial spectra were observed, suggesting the occurrence of chemical transformations in the initial compound. Synchronous fluorescence spectra highlight that, after 0.33 h of reaction, the fluorescence intensity of the band located at 295 nm decreased, followed by the appearance of two new bands at about 353 nm and 400 nm. After 2 h, a new band located at 335 nm is also visible, and then, over the course of the reactions, all bands tend to disappear up to 4 h for the UV/Fenton-like process and up to 24 h for the UV/H2O2 process. The appearance of new bands located at longer excitation wavelengths suggests the formation of new and more complex compounds [29], possibly due to the attack of hydroxyl radicals. These findings are in accordance with the studies of Santos and Duarte [19] and Santos et al. [20], which showed that the intermediate products formed through Fenton-like oxidation of 3,5-DHBA in water in the absence of light (at pH 4.5 and at 20 °C) were 2,4,6-trihydroxybenzoic and 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic acids and tetrahydroxybenzene, and suggested that the hydroxylation via hydroxyl radical attack was the main step of compound oxidation. In fact, since hydroxyl radicals can be photoproduced from hydrogen peroxide in atmospheric waters when present at concentration levels of 10−4 M [13], a similar occurrence is expected in the present study for both degradation processes that contemplate UV as a source of light (reaction 1, Table 1). On the other hand, with the course of reactions, the disappearance of absorbance and fluorescence bands suggests the total degradation of 3,5-DHBA and of the intermediate products formed. To confirm these findings, the reactions were also followed by EEM fluorescence spectroscopy, and the spectra obtained during the degradation of 3,5-DHBA by UV/H2O2 and UV/Fenton-like processes are presented in Figure 2.
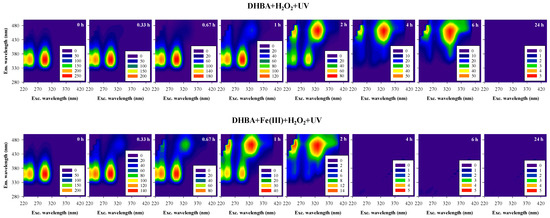
Figure 2.
Excitation-emission matrix (EEM) fluorescence spectra of 3,5-DHBA during oxidation by UV/H2O2 (DHBA + H2O2 + UV) and by UV/Fenton-like (DHBA + Fe(III) + H2O2 + UV) processes. Experimental conditions were: [3,5-DHBA]0 = 2 × 10−5 M, [H2O2]0 = 10−4 M and initial pH = 5.0 for both processes; [Fe(III)]0 = 5 × 10−6 M for the UV/Fenton-like process. EEM spectra were recorded at oxidation times of 0, 0.33, 0.67, 1, 2, 4, 6, and 24 h.
As shown in Figure 2, at the initial time, spectra of 3,5-DHBA exhibit two clear fluorescent bands with λexc/λem located at approximately 245/360 nm and 295/360 nm. Over the course of the reactions, the fluorescence intensities of the initial bands decreased, and new fluorescent bands appeared at longer emission wavelengths (λexc/λem at 245/460 nm and 325/460 nm), corroborating that new chromophoric compounds were formed, as suggested by the synchronous spectra. The red shift emission of bands initially located at 245 nm and 295 nm of excitation, and at 360 nm of emission, suggests an increase in the extent of the π-electron system, an increase in conjugated bonds in a chain structure, or structural modifications, such as the insertion of hydroxyl groups or distortions in planarity that affect electronic transitions [30]. Moreover, the slight shift toward higher excitation wavelengths suggests that solutions contain a higher amount of conjugated aromatic π-bond systems with electron-withdrawing functional groups, such as carbonyl [31]. In addition, it is important to point out that, for the UV/H2O2 process, the spectra after 1 h and 6 h of reaction are similar to those obtained after 20 min and 2 h of reaction by the UV/Fenton-like process, respectively. These findings suggest similar transformations for both degradation processes, as well as the presence of similar compounds or compounds with similar fluorescent characteristics, despite the delay for the UV/H2O2 process. Moreover, Figure 2 shows that no fluorescent band is visible after 4 h of reaction for the UV/Fenton-like process and after 24 h for the UV/H2O2 process, corroborating that the initial and formed chromophoric compounds were all photodegraded. The results indicate that the UV/Fenton-like reaction process transforms/degrades the 3,5-DHBA quicker than the UV/H2O2 process, which is possibly due to the absorption of UV radiation by the oxidants, Fe(III), H2O2, and both simultaneously (reactions 1–7, Table 1), originating higher quantities of reactive radical species in aqueous solutions, such as hydroxyl radicals, capable of degrading the organic compounds in water (reaction 9, Table 1). In fact, the more oxidizing agents are present in the oxidation system, the greater the synergic effect, resulting in an increased contribution of the free radical oxidation pathway. In addition, direct photolysis of 3,5-DHBA upon irradiation is also expected (reactions 10–11, Table 1). However, results also highlight that the total degradation of chromophoric compounds in water is possible using both degradation processes, though the UV/H2O2 process requires more time. The use of the UV/H2O2 process for degrading aromatic-like compounds in water has the advantage of not adding the oxidant and catalyst Fe(III), as occurs in the UV/Fenton-like process (which increases the iron content in water and, consequently, the absorbance of water, as observed in Figure 1 and in Supplementary Materials Figure S1). Based on these findings, the effect of hydrogen peroxide concentration on the degradation of 3,5-DHBA by the UV/H2O2 process was evaluated, testing higher concentrations of H2O2.
3.2. Effect of H2O2 Concentration on the Degradation of 3,5-DHBA by the UV/H2O2 Process
Figure 3 shows the absorbance and synchronous fluorescence (Δλ = 60 nm) spectra during the degradation of 3,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid in water by the UV/H2O2 process, at a pH value of 5.0, for hydrogen peroxide concentrations of 5 × 10−4 M and 1 × 10−3 M. The spectra obtained for the hydrogen peroxide concentration of 10−4 M were previously shown in Figure 1.
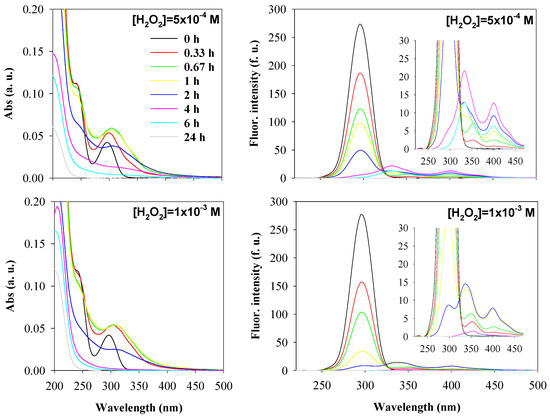
Figure 3.
Absorbance spectra (average spectra; left) and synchronous fluorescence spectra (Δλ = 60 nm; right) of 3,5-dihydroxybenxoic acid (DHBA) during oxidation by UV/H2O2 at different [H2O2]0: 5 × 10−4 M (first row), and 1 × 10−3 M (second row). Experimental conditions were as follows: [3,5-DHBA]0 = 2 × 10−5 M, and initial pH = 5.0. Spectra were recorded at oxidation times of 0, 0.33, 0.67, 1, 2, 4, 6, and 24 h, with the color code shown in the top left graph (which applies to all graphs).
To easily compare the effect of hydrogen peroxide concentration on the oxidation of 3,5-DHBA by the UV/H2O2 process, the extent of degradation during the reaction was calculated for each concentration, based on the decrease in absorbance of the principal band of the compound, as follows:
where At is the absorbance during the course of reaction at the time t, and A0 is the absorbance at the initial time (0 h). Figure 4 shows the extent of degradation (%) of 3,5-DHBA in a model solution by the UV/H2O2 process for peroxide concentrations of 1 × 10−4 M, 5 × 10−4 M, and 1 × 10−3 M.
Extent of oxidation (%) = (1 − At/A0) × 100
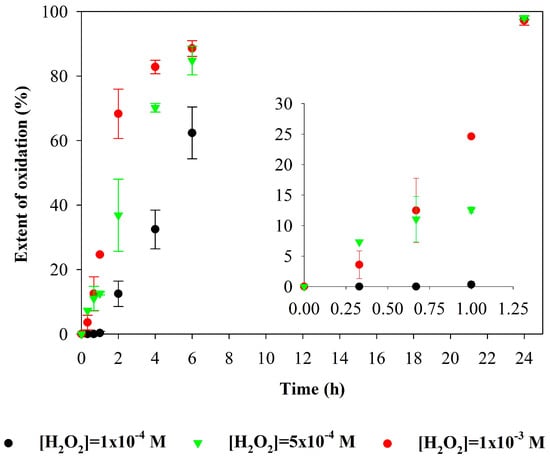
Figure 4.
Extent of degradation (%; average values and standard deviation) of 3,5-DHBA during UV/H2O2 process for [H2O2]0 of 1 × 10−4 M, 5 × 10−4 M, and 1 × 10−3 M, based on the decrease in absorbance of the principal band. Experimental conditions were as follows: [3,5-DHBA]0 = 2 × 10−5 M and pH 5.0.
The spectra depicted in Figure 1 and Figure 3 suggest that, as the hydrogen peroxide concentration increases from 10−4 M to 10−3 M, the rate of degradation of 3,5-DHBA and intermediate products formed also increases, as also highlighted in Figure 4. This is possibly due to the increased production of hydroxyl radicals and their consequent greater availability in solution to attack the organic compound. Absorbance and synchronous fluorescence spectra suggest that the degradation of 3,5-DHBA and its intermediate products occurred after 24 h for hydrogen peroxide concentrations of 10−4 M and 5 × 10−4 M and after 4 h for the concentration of 10−3 M. The EEM spectra (see Supplementary Materials Figure S2) confirm that hydrogen peroxide concentration affects the degradation rate of organic compounds in water, with 10−3 M being the most effective for degrading 3,5-DHBA and its intermediate products by the UV/H2O2 process. This concentration reduces the degradation time to approximately 4 h, which also reduces the operational time of the UV lamp.
3.3. Effect of pH on the Degradation of 3,5-DHBA Using the UV/H2O2 Process
In order to evaluate the effect of pH on the oxidation of 3,5-DHBA using the UV/H2O2 process, solutions with different initial pH values (4.0, 5.0, 6.0, and 7.0) were tested, all within the typical range found in rainwater [32]. The UV-Vis and fluorescence spectra obtained for these pH values are shown in the Supplementary Materials (see Supplementary Materials Figures S3 and S4), and the results were similar across the different pH values and consistent with those previously presented for the UV/H2O2 process at pH 5.0 (Figure 1 and Figure 2). To facilitate comparison, the effect of 3,5-DHBA degradation was calculated for each pH value based on the decrease in absorbance of the principal band of the compound, as was done for the hydrogen peroxide concentrations. Figure 5 shows the extent of degradation (%) of 3,5-DHBA in a model solution using the UV/H2O2 process at pH values of 4.0, 5.0, 6.0, and 7.0.
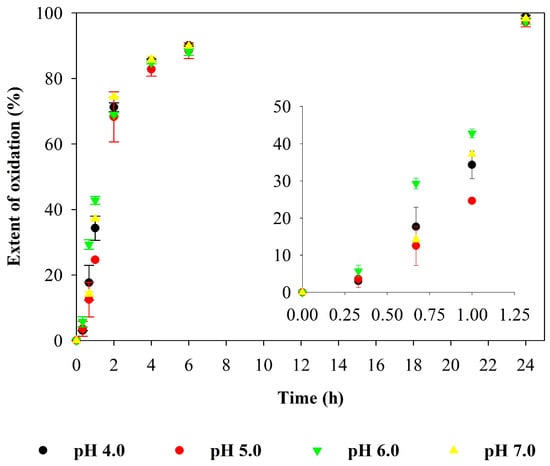
Figure 5.
Extent of degradation (%; average values and standard deviation) of 3,5-DHBA during UV/H2O2 process, at pH values of 4.0, 5.0, 6.0, and 7.0, based on the decrease in absorbance of the principal band. Experimental conditions were as follows: [3,5-DHBA]0 = 2 × 10−5 M and [H2O2]0: 1 × 10−3 M.
Figure 5 highlights that the pH value does not introduce significant changes in the extent of degradation after 2 h. However, up to 1 h, the oxidation tended to be fastest at a pH of 6.0. In addition, regardless of the pH value between 4.0 and 7.0, the extent of degradation of 3,5-DHBA after 4 h is high, exceeding 83%; after 6 h, it surpasses 88%; and after 24 h, it is almost complete (higher than 97%). Since hydroxyl radicals are the main responsible for the degradation of 3,5-DHBA using the UV/H2O2 process, these results suggest that the amount of hydroxyl radicals produced is not affected by the pH within the tested range, at least for process times longer than 2 h [21].
3.4. Degradation of 3,5-DHBA in Rainwater by the UV/H2O2 and UV/Fenton-like Processes
Based on the previous results, the UV/H2O2 process with an initial H2O2 concentration of 10−3 M and the UV/Fenton-like process with an initial H2O2 concentration of 10−4 M were applied to a rainwater sample spiked with 3,5-DHBA and compared. First, the rainwater sample was characterized using UV-Vis and fluorescence spectroscopy, and the absorbance and EEM fluorescence spectra are shown in Figure 6.
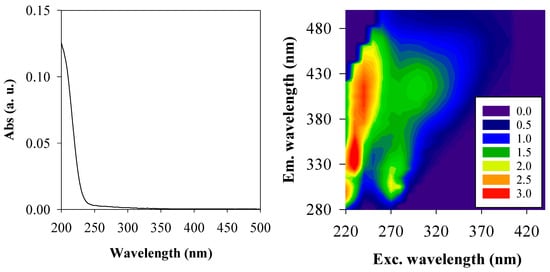
Figure 6.
Absorbance (average spectra; left) and EEM fluorescence (Δλ = 60 nm; right) spectra of the rainwater sample at its natural pH (5.5).
As shown in Figure 6, the UV-Vis spectrum of the sample is very similar to other rainwater samples [33,34], decreasing monotonically with increasing wavelength. Regarding the EEM fluorescence spectra of the sample, six bands with different excitation and emission wavelength maxima (λex/λem) can be highlighted: one generally assigned to humic-like compounds (A at λex/λem ≈ 230/410 nm), one usually assigned to marine humic-like compounds (M at λex/λem ≈ 300/410 nm), and four attributed to protein-like compounds, such as tryptophan (T1 at λex/λem ≈ 230/335 nm and T2 at λex/λem ≈ 280/335 nm) and tyrosine (B1 at λex/λem ≈ 220/300 nm and B2 at λex/λem ≈ 270/305 nm) [34]. The fluorescence intensity of these bands is low, indicating a low content of chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM), with intensity decreasing as the excitation wavelength increases. Furthermore, these fluorescence bands have also been identified in the EEM spectra of rainwater [33,34], reinforcing the common presence of CDOM in this type of water.

Table 1.
Reactions that may occur during oxidation of 3,5-DHBA in rainwater by the UV/H2O2 and UV/Fenton-like processes.
Table 1.
Reactions that may occur during oxidation of 3,5-DHBA in rainwater by the UV/H2O2 and UV/Fenton-like processes.
| No. | Reaction | Occurrence Process | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | H2O2 + hv → 2•OH | UV/H2O2, UV/Fenton-like | [35] |
| 2 | Fe(III) + H2O + hv → Fe(II) + •OH + H+ | UV/Fenton-like | [36] |
| 3 | Fe(III) + H2O2 + hv → Fe(O2H)2+ + H+ | UV/Fenton-like | [36] |
| 4 | Fe(O2H)2+→ Fe(II) + HO2• | UV/Fenton-like | [37] |
| 5 | Fe(II) + H2O2 → Fe(III) + •OH + OH− | UV/Fenton-like | [38] |
| 6 | Fe(III) + H2O → FeOH2+ + H+ | UV/Fenton-like | [39] |
| 7 | FeOH2+ + hv → Fe(II) + •OH | UV/Fenton-like | [36] |
| 8 | •OH + •OH → H2O2 | UV/H2O2, UV/Fenton-like | [40] |
| 9 | OH• + (C6H5O2)COOH → Products | UV/H2O2, UV/Fenton-like | [20] |
| 10 | (C6H5O2)COOH + hυ → (C6H5O2)COOH* | UV/H2O2, UV/Fenton-like | [13] |
| 11 | (C6H5O2)COOH* → Products | UV/H2O2, UV/Fenton-like | [13] |
| 12 | S + hυ → S* | UV/H2O2, UV/Fenton-like | [13] |
| 13 | S* + (C6H5O2)COOH → S + (C6H5O2)COOH* | UV/H2O2, UV/Fenton-like | [13] |
| 14 | S* + (C6H5O2)COOH → S-H• + (C6H5O2)COO• | UV/H2O2, UV/Fenton-like | [13] |
| 15 | S-H• + O2 → S + HO2• | UV/H2O2, UV/Fenton-like | [13] |
| 16 | HO2• → H2O2 + O2 | UV/H2O2, UV/Fenton-like | [13] |
| 17 | (C6H5O2)COO• → Products | UV/H2O2, UV/Fenton-like | [13] |
| 18 | S-H• → Products | UV/H2O2, UV/Fenton-like | [12,13] |
| 19 | S* + S → Products | UV/H2O2, UV/Fenton-like | [12,13] |
| 20 | S + OH• → Products | UV/H2O2, UV/Fenton-like | [12] |
Notes: (C6H5O2)COOH is the 3,5-DHBA; S is an organic photosensitizer.
As controls for the experiments, the oxidation of the rainwater sample (not spiked with 3,5-DHBA) by UV light, UV/H2O2 process with an initial H2O2 concentration of 10−3 M, and UV/Fenton-like process with an initial H2O2 concentration of 10−4 M were also evaluated (see Supplementary Materials Figures S5 and S6). The absorbance and fluorescence spectra resultant from the oxidation of the sample (not spiked with 3,5-DHBA) by UV light suggest the occurrence of direct photolysis of DOM upon irradiation (reactions 12–14, Table 1), as the intensity of bands decreased throughout time and disappeared after 24 h. Moreover, for both the UV/H2O2 and UV/Fenton-like processes applied to the rainwater sample (not spiked with 3,5-DHBA), the absorbance and fluorescence spectra show that the bands disappeared after 1 h (see Supplementary Materials Figures S4 and S5). These findings suggest that both processes enhance DOM oxidation in rainwater compared to UV oxidation alone, with hydroxyl radicals playing a crucial role in accelerating and improving the efficiency of DOM degradation.
Figure 7 shows the UV-Vis spectra and the synchronous fluorescence spectra, and Figure 8 shows the EEM fluorescence spectra, obtained during the oxidation of the sample spiked with 3,5-DHBA, by UV/H2O2 with an initial H2O2 concentration of 10−3 M and by UV/Fenton-like with an initial H2O2 concentration of 10−4 M, up to 24 h of reaction.
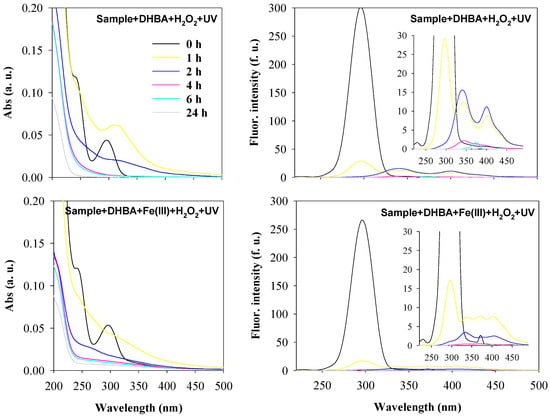
Figure 7.
Absorbance spectra (average spectra; left) and synchronous fluorescence spectra (Δλ = 60 nm; right) of a rainwater sample spiked with 3,5-DHBA during oxidation by UV/H2O2 (Sample + DHBA + H2O2 + UV) and by UV/Fenton-like (Sample + DHBA + Fe(III) + H2O2 + UV) processes. Experimental conditions were as follows: initial pH = 5.5 for both reactions; [H2O2]0 = 10−3 M for the UV/H2O2 process; [Fe(III)]0 = 5 × 10−6 M and [H2O2]0 = 10−4 M for the UV/Fenton-like process. Spectra were recorded at oxidation times of 0, 1, 2, 4, 6, and 24 h, with the color code shown in the top left graph (which applies to all graphs).
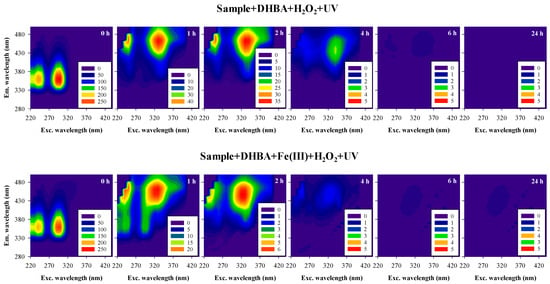
Figure 8.
Excitation-emission matrix (EEM) fluorescence spectra of a rainwater sample spiked with 3,5-DHBA during oxidation by UV/H2O2 (Sample + DHBA + H2O2 + UV) and by UV/Fenton-like (Sample + DHBA + Fe(III) + H2O2 + UV) processes. Experimental conditions were as follows: pH = 5.5 for both reactions; [H2O2]0 = 10−3 M for the UV/H2O2 process; [Fe(III)]0 = 5 × 10−6 M and [H2O2]0 = 10−4 M for the UV/Fenton-like process. EEM spectra were recorded at oxidation times of 0, 1, 2, 4, 6, and 24 h.
The absorbance and fluorescence spectra resultant from the oxidation of the sample spiked with 3,5-DHBA by the UV/H2O2 process with an initial H2O2 concentration of 10−3 M and using the UV/Fenton-like process with an initial H2O2 concentration of 10−4 M highlight that both processes oxidize the 3,5-DHBA, the intermediate products formed, and the DOM in rainwater. However, the UV/Fenton-like process tends to oxidize slightly faster, as indicated by the lower absorbance and fluorescence intensities at comparable reaction times. Nevertheless, after 4 h of oxidation, both processes effectively degraded most chromophoric compounds, reaching close to 100% removal as evaluated by fluorescence spectroscopy. In addition, absorbance spectroscopy indicated degradations higher than 83% after 4 h, 86% after 6 h, and 100% after 24 h, based on the decrease of the principal band of 3,5-DHBA. Moreover, the results of the oxidation of 3,5-DHBA by both oxidation processes in rainwater were similar to those observed in water model solutions with similar H2O2 concentrations, including the new fluorescent bands formed. This suggests that the compounds formed in model water solutions were similar to those formed in rainwater, which may also be due to the low chromophoric content of DOM in rainwater. However, since the presence of chromophoric DOM in rainwater may act as a photosensitizer, it could contribute to indirect photolysis and sensitized photolysis of 3,5-DHBA (reactions 12–17, 1, 9, Table 1; [13]). In addition, the photosensitizer itself may be degraded (reactions 18–20, Table 1). Therefore, the chromophoric DOM in rainwater may compete with 3,5-DHBA for oxidation agents, such as hydroxyl radicals and/or UV light [12,21], but since it originates radical species, they may act as oxidizing agents for degrading the organic compounds in rainwater. A summary of the main possible reactions involved in the oxidation of 3,5-DHBA in rainwater by the UV/H2O2 and the UV/Fenton-like processes is shown in Table 1.
Overall, after 4 h, the oxidation of 3,5-DHBA in rainwater yields similar results when performed using the UV/H2O2 process with an initial H2O2 concentration of 10−3 M and the UV/Fenton-like process with an initial H2O2 concentration of 10−4 M. In the UV/Fenton-like process, the presence of additional oxidizing agents enhances the synergistic effect, leading to an increase in free radical oxidation, mainly via hydroxyl radicals. In contrast, the UV/H2O2 process, despite having fewer oxidizing agents, achieves the same oxidation level due to the higher H2O2 concentration.
4. Conclusions
The study of the oxidation of 3,5-DHBA in rainwater by UV/H2O2 and UV/Fenton-like processes resulted in important conclusions. The absorbance and fluorescence spectra obtained during oxidation by both processes at environmentally relevant concentrations suggest the formation of new and similar chromophoric compounds, which are completely degraded after 24 h by the UV/H2O2 process and after 4 h by the UV/Fenton-like process. In the UV/H2O2 process, increasing the H2O2 concentration from environmentally relevant (10−4 M) to one order of magnitude higher (10−3 M) leads to a higher oxidation rate, while the pH of the solution, ranging from 4 to 7, does not affect the oxidation after 2 h. A similar extent of oxidation of 3,5-DHBA in rainwater was obtained after 4 h with both the UV/H2O2 process (with an initial H2O2 concentration of 10−3 M) and the UV/Fenton-like process (with an initial H2O2 concentration of 10−4 M). Nevertheless, although both processes lead to similar oxidation extents, mainly due to the attack of hydroxyl radicals, the UV/H2O2 process requires fewer reactants, which offers an advantage for its application in rainwater treatment.
Overall, these findings point toward the adoption of a simpler process for treating rainwater contaminated with organic pollutants, promoting its use for domestic purposes, and supporting the establishment of legislation to regulate and encourage its integration into sustainable water resource management.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w17111618/s1, Figure S1: Absorbance spectra (average spectra; left) and synchronous fluorescence spectra (Δλ = 60 nm; right) of controls performed in water during oxidation by UV/H2O2 (H2O2 + UV) and by UV/Fenton-like (Fe(III) + H2O2 + UV) processes. Experimental conditions were as follows: [H2O2]0 = 10−4 M, and initial pH = 5.0 for both processes; [Fe(III)]0 = 5 × 10−6 M for the photo-Fenton-like process. Spectra were recorded at oxidation times of 0, 1, 2, 4, 6, and 24 h. Spectra were recorded at oxidation times of 0, 1, 2, 4, 6, and 24 h, with the color code shown in the top left graph (which applies to all graphs).; Figure S2: Excitation-emission matrix (EEM) fluorescence spectra of 3,5-DHBA during oxidation by UV/H2O2 at different [H2O2]0: 1 × 10−4 M (first row), 5 × 10−4 M (second row), and 1 × 10−3 M (third row). Experimental conditions were as follows: [3,5-DHBA]0 = 2 × 10−5 M, and initial pH = 5.0. EEM spectra were recorded at oxidation times of 0, 0.33, 0.67, 1, 2, 4, 6, and 24 h.; Figure S3: Absorbance spectra (average spectra; left) and synchronous fluorescence spectra (Δλ = 60 nm; right) of 3,5-DHBA during oxidation by UV/H2O2 at different initial pH values: 4.0 (first row), 5.0 (second row), 6.0 (third row), and 7.0 (fourth row). Experimental conditions were as follows: [H2O2]0: 1 × 10−3 M, and [3,5-DHBA]0 = 2 × 10−5 M. Spectra were recorded at oxidation times of 0, 0.33, 0.67, 1, 2, 4, 6, and 24 h, with the color code shown in the top left graph (which applies to all graphs).; Figure S4: Excitation-emission matrix (EEM) fluorescence spectra of 3,5-DHBA during oxidation by UV/H2O2 at different initial pH values: 4.0 (first row), 5.0 (second row), 6.0 (third row), and 7.0 (fourth row). Experimental conditions were as follows: [H2O2]0: 1 × 10−3 M, and [3,5-DHBA]0 = 2 × 10−5 M. EEM spectra were recorded at oxidation times of 0, 0.33, 0.67, 1, 2,.0 4, and 6 h.; Figure S5: Absorbance spectra (average spectra; left) and synchronous fluorescence spectra (Δλ = 60 nm; right) of a rainwater sample during oxidation by UV (Sample + UV), by UV/H2O2 (Sample + H2O2 + UV), and by UV/Fenton-like reaction (Sample + Fe(III) + H2O2 + UV). Experimental conditions were as follows: initial pH = 5.5 for both processes; [H2O2]0 = 10−3 M for the UV/H2O2; [Fe(III)]0 = 5 × 10−6 M and [H2O2]0 = 10−4 M for the UV/Fenton-like process. Spectra were recorded at oxidation times of 0, 1, 2, 4, 6, and 24 h, with the color code shown in the top left graph (which applies to all graphs).; Figure S6: Excitation-emission matrix (EEM) fluorescence spectra of a rainwater sample during oxidation by UV (Sample + UV), by UV/H2O2 (Sample + H2O2 + UV), and by UV/Fenton-like reaction (Sample + Fe(III) + H2O2 + UV). Experimental conditions were as follows: initial pH = 5.5 for both processes; [H2O2]0 = 10−3 M for the UV/H2O2; [Fe(III)]0 = 5 × 10−6 M and [H2O2]0 = 10−4 M for the UV/Fenton-like process. EEM spectra were recorded at oxidation times of 0, 1, 2, 4, 6, and 24 h.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.S.M.S.; formal analysis, P.S.M.S. and M.P.S.F.; funding acquisition, P.S.M.S. and A.C.D.; investigation, P.S.M.S. and M.P.S.F.; methodology, P.S.M.S. and M.P.S.F.; project administration, P.S.M.S.; resources, P.S.M.S. and A.C.D.; supervision, P.S.M.S. and A.C.D.; validation, P.S.M.S., M.P.S.F. and A.C.D.; visualization, P.S.M.S. and M.P.S.F.; writing—original draft, P.S.M.S. and M.P.S.F.; writing—review and editing, P.S.M.S., M.P.S.F. and A.C.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors wish to thank FCT/MCTES (PIDDAC) for financial support to CESAM (UID Centro de Estudos do Ambiente e Mar (CESAM) + LA/P/0094/2020) through national funds. Patrícia S.M. Santos is grateful for the support of the FCT Scientific Employment Stimulus—Individual 2017 (CEECIND/01835/2017; DOI:10.54499/CEECIND/01835/2017/CP1459/CT0017).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study will be made available by the authors on request.
Acknowledgments
The authors also thank Eva Silva for collaboration in experiments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- UNESCO World Water Assessment Programme. United Nations World Water Development Report 2023: Partnerships and Cooperation for Water; UNESCO Publishing: Paris, France, 2023; Available online: https://www.unwater.org/publications/un-world-water-development-report-2023 (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Sukanya, S.; Joseph, S. Alternative water resources in rural areas: Smart solutions for a sustainable future. In Water Resources Management for Rural Development: Challenges and Mitigation; Madhav, S., Srivastav, A.L., Izah, S.C., Hullebusch, E., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas, G.; Martinez-Varela, A.; Vila-Costa, M.; Jiménez, B.; Dachs, J. Rain Amplification of Persistent Organic Pollutants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 12961–12972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlasov, D.; Kasimov, N.; Eremina, I.; Shinkareva, G.; Chubarova, N. Partitioning and solubilities of metals and metalloids in spring rains in Moscow megacity. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 255–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, P.S.M.; Santos, B.H.E.; Duarte, A.C. First Spectroscopic Study on the Structural Features of Dissolved Organic Matter Isolated from Rainwater in Different Seasons. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 426, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinxteren, D.V.; Herrmann, H. Determination of Functionalised Carboxylic Acids in Atmospheric Particles and Cloud Water Using Capillary Electrophoresis/Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1171, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottrell, B.A.; Gonsior, M.; Isabelle, L.M.; Luo, W.; Perraud, V.; McIntire, T.M.; Pankow, J.F.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P.; Cooper, W.J.; Simpson, A.J. A regional study of the seasonal variation in the molecular composition of rainwater. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 77, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chon, K.; Kim, Y.; Bae, D.H.; Cho, J. Confirming anthropogenic influences on the major organic and inorganic constituents of rainwater in an urban area. Drink. Water Eng. Sci. 2015, 8, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyokova, O.V.; Artaev, V.B.; Lebedev, A.T. Priority and Emerging Pollutants in the Moscow Rain. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 1126–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhang, K.; Chen, H.; Wu, T.; Krzyaniak, M.; Wellons, A.; Bolla, D.; Douglas, K.; Zuo, Y. Iron-catalyzed photochemical transformation of benzoic acid in atmospheric liquids: Product identification and reaction mechanisms. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 3665–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Smith, J.; Laskin, A.; George, K.M.; Anastasio, C.; Laskin, J.; Dillner, A.M.; Zhang, Q. Molecular transformations of phenolic SOA during photochemical aging in the aqueous phase: Competition among oligomerization, functionalization, and fragmentation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 4511–4527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, P.S.M.; Cardoso, H.B.; Rocha-Santos, T.A.P.; Duarte, A.C. Oxidation of Benzoic Acid from Biomass Burning in Atmospheric Waters. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vione, D.; Maurino, V.; Minero, C.; Pelizzetti, E.; Harrison, M.A.J.; Olariu, R.-I.; Arsene, C. Photochemical Reactions in the Tropospheric Aqueous Phase and on Particulate Matter. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2006, 35, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, H.; Hoffmann, D.; Schaefer, T.; Braeuer, P.; Tilgner, A. Tropospheric Aqueous-Phase Free-Radical Chemistry: Radical Sources, Spectra, Reaction Kinetics and Prediction Tools. ChemPhysChem 2010, 11, 3796–3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, B.; Mayol-Bracero, O.L.; Guyon, P.; Roberts, G.C.; Decesari, S.; Facchini, M.C.; Artaxo, P.; Maenhaut, W.; Köll, P.; Andreae, M.O. Water-Soluble Organic Compounds in Biomass Burning Aerosols over Amazonia 1. Characterization by NMR and GC-MS. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2002, 107, 8047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoneit, B.R.T. Biomass Burning—A Review of Organic Tracers for Smoke from Incomplete Combustion. Appl. Geochem. 2002, 17, 129–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelencsér, A.; Hoffer, A.; Kiss, G.; Tombácz, E.; Kurdi, R.; Bencze, L. In-Situ Formation of Light-Absorbing Organic Matter in Cloud Water. J. Atmos. Chem. 2003, 45, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffer, A.; Kiss, G.; Blazsó, M.; Gelencsér, A. Chemical Characterization of Humic-Like Substances (HULIS) Formed from a Lignin-Type Precursor in Model Cloud Water. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L06115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, P.S.M.; Duarte, A.C. Fenton-Like Oxidation of Small Aromatic Acids from Biomass Burning in Water and in the Absence of Light: Implications for Atmospheric Chemistry. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 786–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, P.S.M.; Domingues, M.R.M.; Duarte, A.C. Fenton-Like Oxidation of Small Aromatic Acids from Biomass Burning in Atmospheric Water and in the Absence of Light: Identification of Intermediates and Reaction Pathways. Chemosphere 2016, 154, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.P.S.; Santos, P.S.M.; Duarte, A.C. Oxidation of Small Aromatic Compounds in Rainwater by UV/H2O2: Optimization by Response Surface Methodology. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 815, 152857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.; Ma, H.; Liao, J.; Rahaman, M.H.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Z. Comparison of Fenton, Ultraviolet–Fenton and Ultrasonic–Fenton Processes on Organics and Colour Removal from Pre-Treated Natural Gas Produced Water. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 15, 2411–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltran-Heredia, J.; Torregrosa, J.; Dominguez, J.R.; Peres, J.A. Comparison of the degradation of p-hydroxybenzoic acid in aqueous solution by several oxidation processes. Chemosphere 2001, 42, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Wang, X.; Ban, Y.; Ren, B. A Comparative Study of UV–Fenton, UV–H2O2 and Fenton Reaction Treatment of Landfill Leachate. Environ. Technol. 2011, 32, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, Z.U.H.; Gul, N.S.; Sabahat, S.; Sun, J.; Tahir, K.; Shah, N.S.; Muhammad, N.; Rahim, A.; Imran, M.; Iqbal, J.; et al. Removal of Organic Pollutants through Hydroxyl Radical-Based Advanced Oxidation Processes. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 267, 115564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignatello, J.J.; Oliveros, E.; MacKay, A. Advanced Oxidation Processes for Organic Contaminant Destruction Based on the Fenton Reaction and Related Chemistry. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 36, 1–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Pandis, S.N. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, D.H.; Fleming, I. Spectroscopic Methods in Organic Chemistry, 2nd ed.; McGraw-Hill: London, UK, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, T.; Li, M.; Xu, C.; Song, J.; Fan, X.; Li, J.; Jia, W.; Peng, P. Technical note: Chemical composition and source identification of fluorescent components in atmospheric water-soluble brown carbon by excitation-emission matrix spectroscopy with parallel factor analysis—potential limitations and applications. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2023, 23, 2613–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senesi, N. Molecular and Quantitative Aspects of the Chemistry of Fulvic Acid and Its Interactions with Metal Ions and Organic Chemicals. Part II. The Fluorescence Spectroscopy Approach. Anal. Chim. Acta 1990, 232, 77–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Gu, B.; LeBoeuf, E.J.; Pan, H.; Dai, S. Spectroscopic characterization of the structural and functional properties of natural organic matter fractions. Chemosphere 2002, 48, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerqueira, M.R.F.; Pinto, M.F.; Derossi, I.N.; Esteves, W.T.; Santos, M.D.R.; Matos, M.A.C.; Lowinsohn, D.; Matos, R.C. Chemical characteristics of rainwater at a southeastern site of Brazil. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2014, 5, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieber, R.J.; Whitehead, R.F.; Reid, S.N.; Willey, J.D.; Seaton, P.J. Chromophoric Dissolved Organic Matter (CDOM) in Rainwater, Southeastern North Carolina, USA. J. Atmos. Chem. 2006, 54, 21–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, P.S.M.; Santos, B.H.E.; Duarte, A.C. Seasonal and Air Mass Trajectory Effects on Dissolved Organic Matter of Bulk Deposition at a Coastal Town in South-Western Europe. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downes, A.; Blunt, T.P. The Effect of Sunlight upon Hydrogen Peroxide. Nature 1879, 20, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Yoon, J. Temperature Dependence of Hydroxyl Radical Formation in the hν/Fe3⁺/H2O2 and Fe3⁺/H2O2 Systems. Chemosphere 2004, 56, 923–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walling, C.; Weil, T. The Ferric Ion Catalysed Decomposition of Hydrogen Peroxide in Perchloric Acid Solution. Int. J. Chem. Kinet. 1974, 6, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardwick, T.J. The Rate Constant of the Reaction Between Ferrous Ions and Hydrogen Peroxide in Acid Solution. Can. J. Chem. 1957, 35, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milburn, R.M.; Vosburgh, W.C. A Spectrophotometric Study of the Hydrolysis of Iron(III) Ion. II. Polynuclear Species. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1955, 77, 1352–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buxton, G.V.; Greenstock, C.L.; Helman, W.P.; Ross, A.B. Critical Review of rate constants for reactions of hydrated electrons, hydrogen atoms and hydroxyl radicals (OH/O−) in Aqueous Solution. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1988, 17, 513–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).