CFD Investigation of Spray and Water Curtain Systems in Mine Ventilation: Airflow Paths, Velocity Variations, and Influence Patterns
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Model
2.1. Turbulence Model
2.2. Air–Droplet Coupling Model
2.3. Water Curtain Porous Medium Model
2.4. Pressure-Swirl Atomizer Model
2.5. Rotating Cutterhead
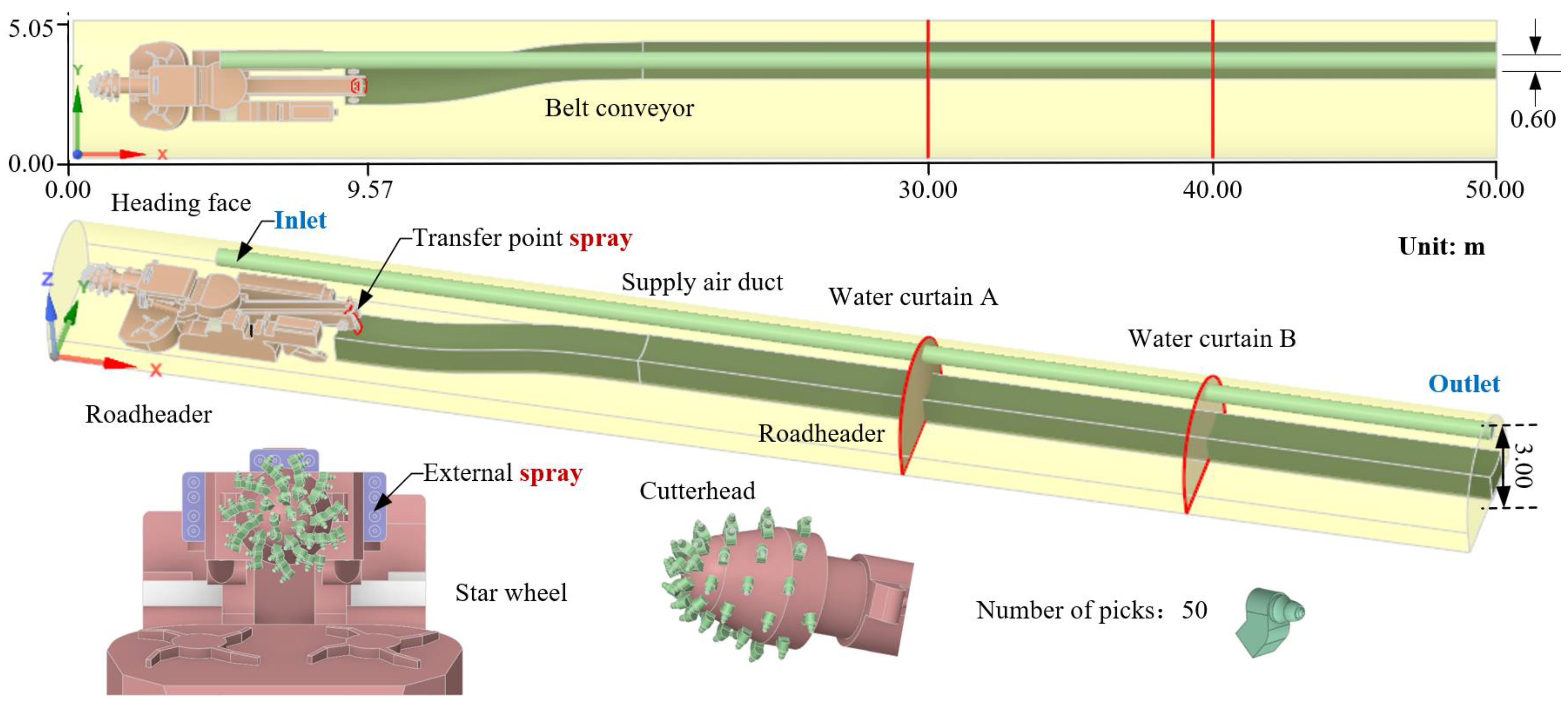
3. Case Description
3.1. Geometric Model
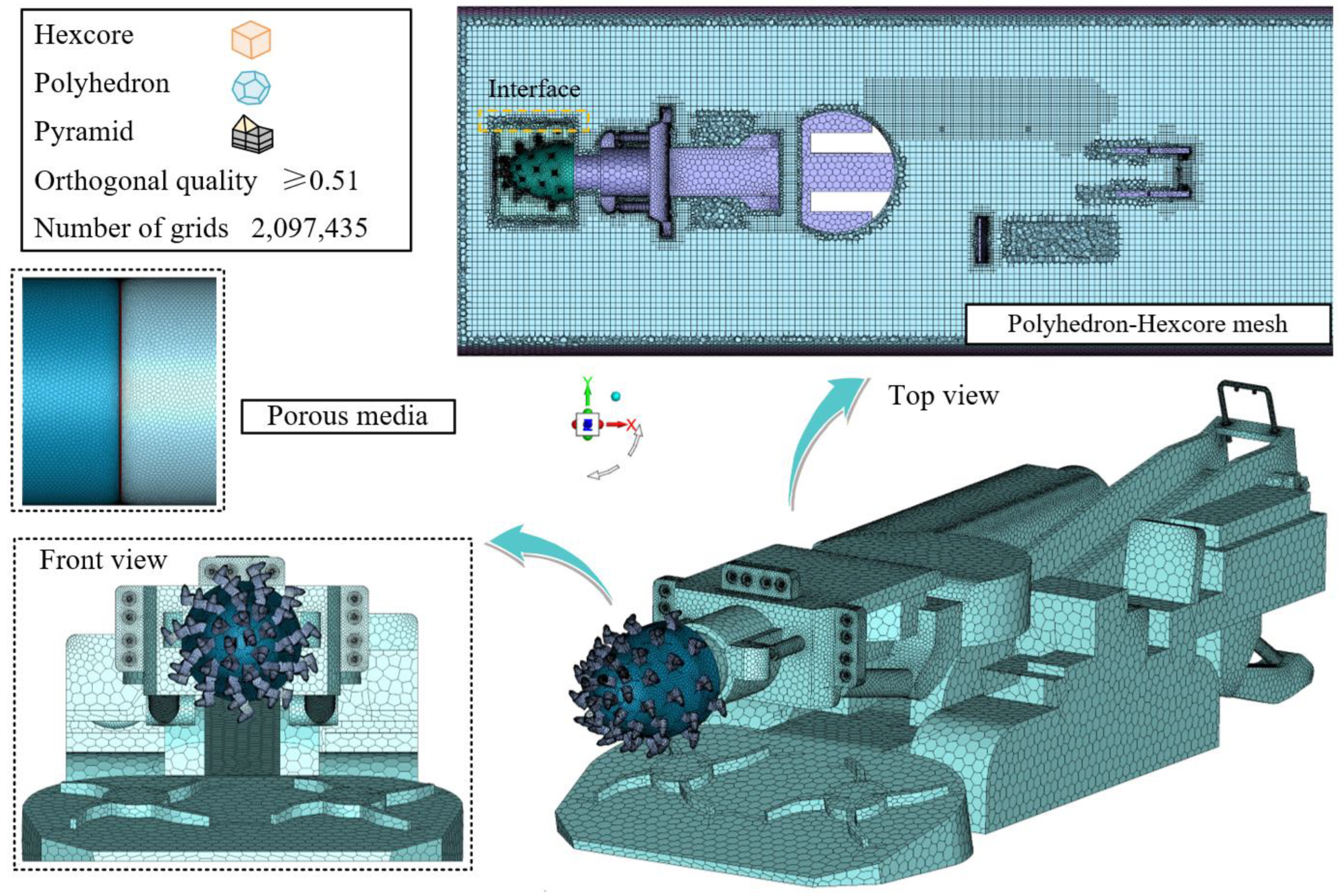
3.2. Mesh Details
3.3. Boundary Conditions
3.4. Solver and Numerical Details
4. Results and Discussion
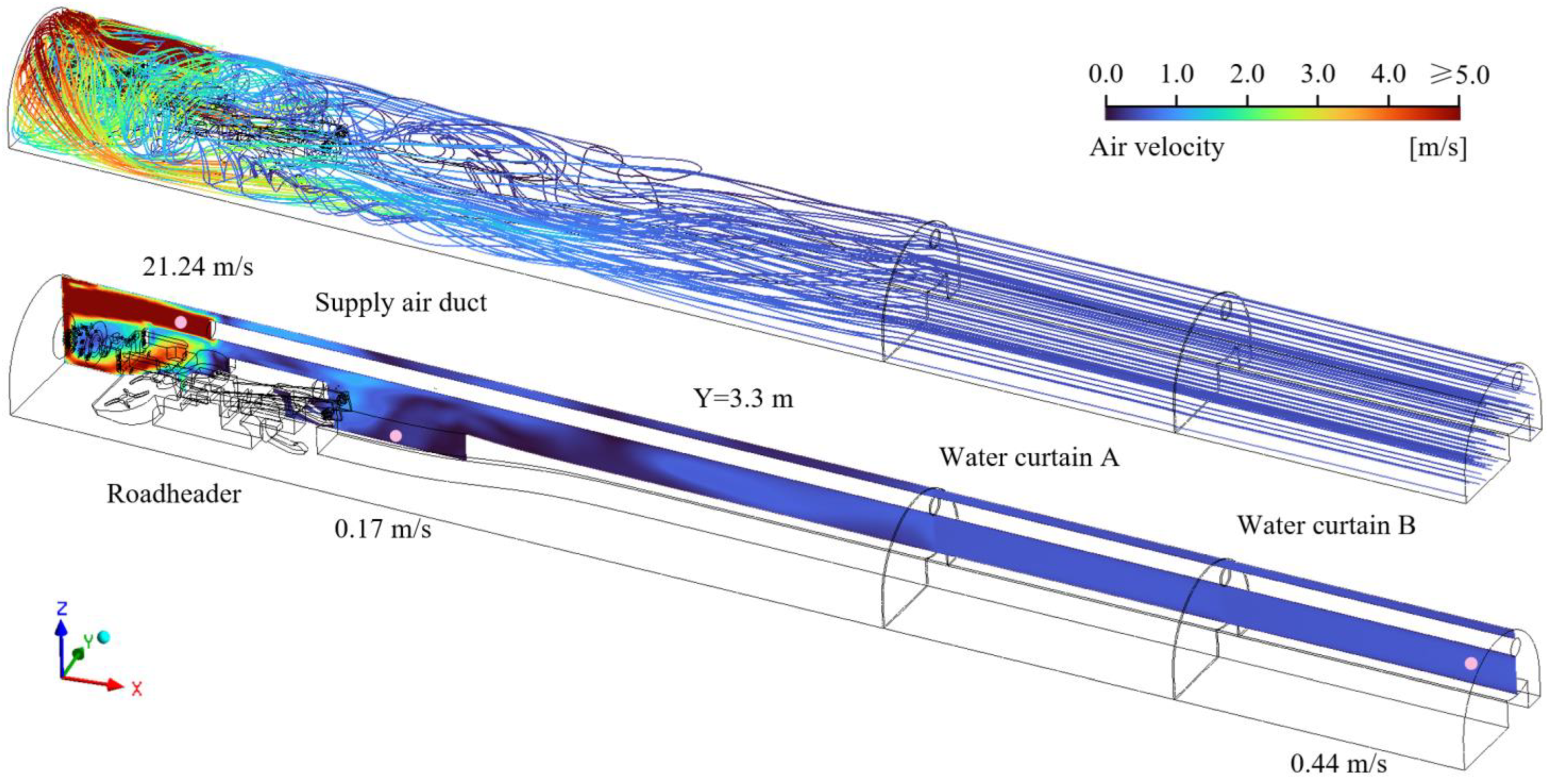
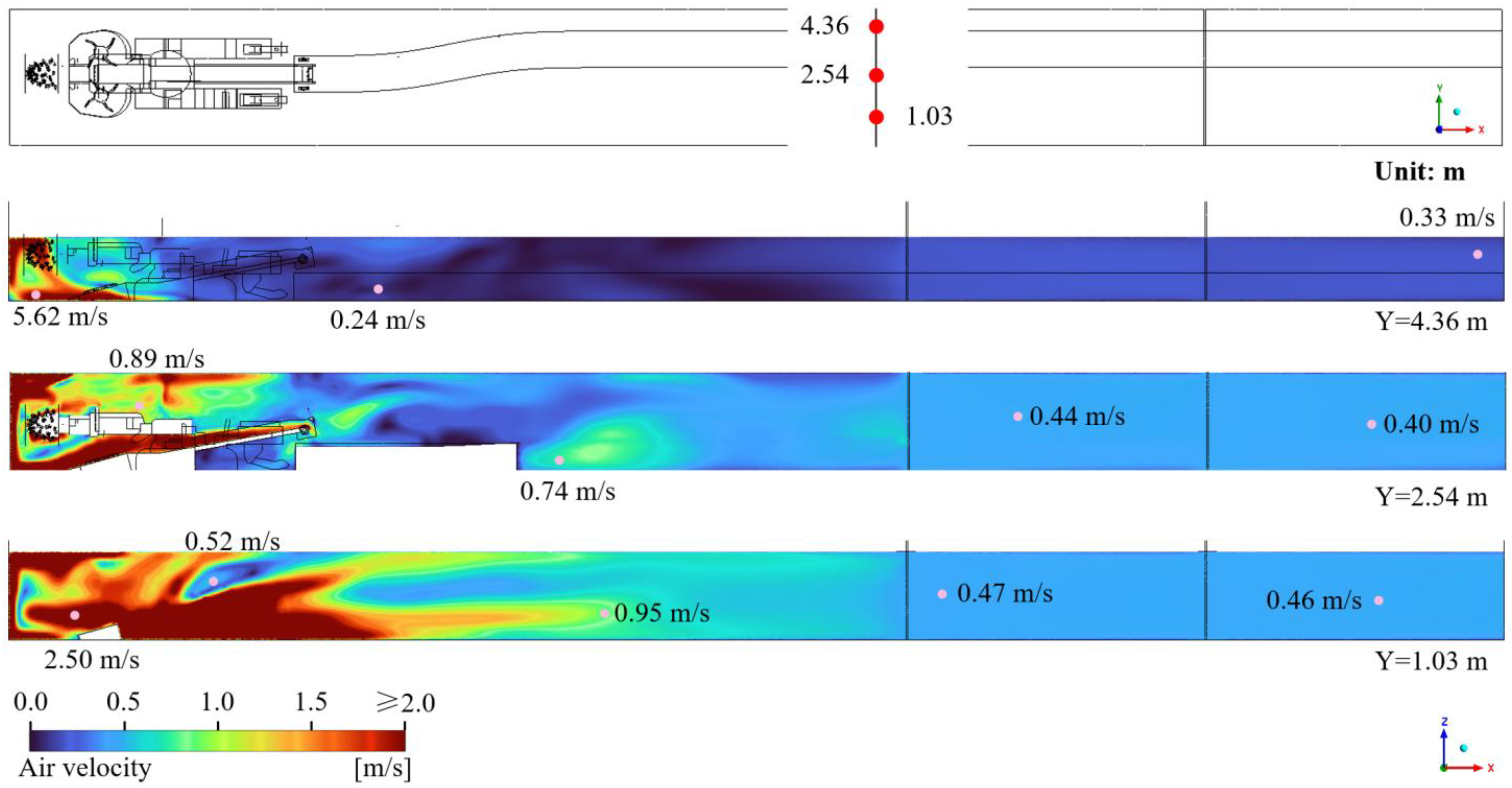
4.1. Airflow Field in a Tunnel Under Halted Operations
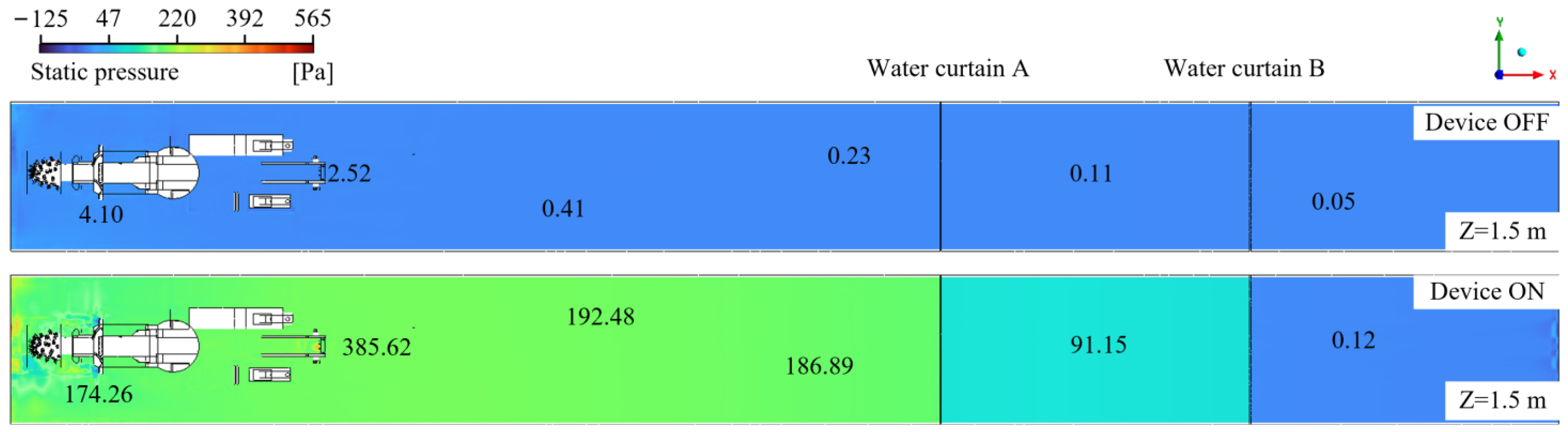
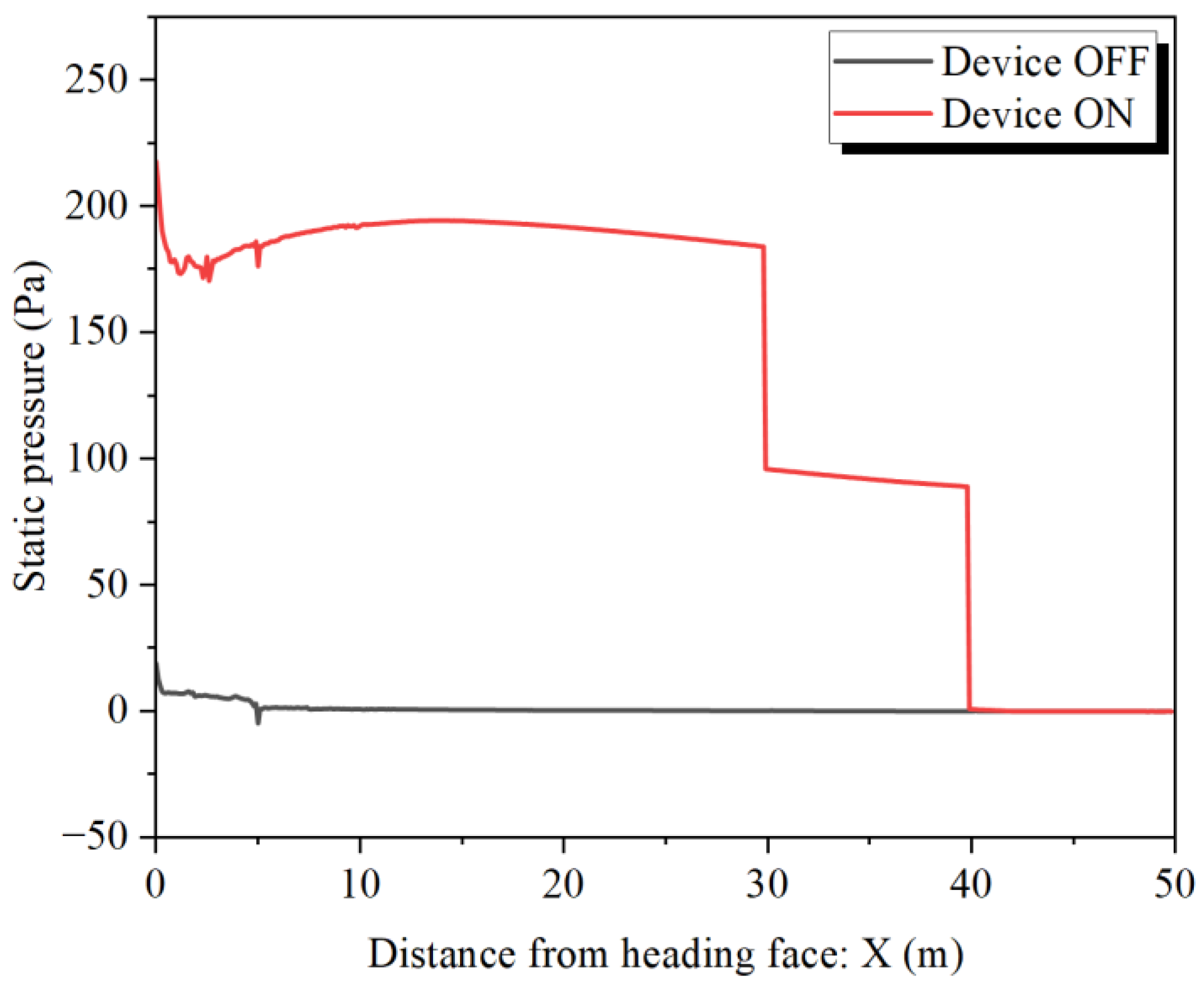
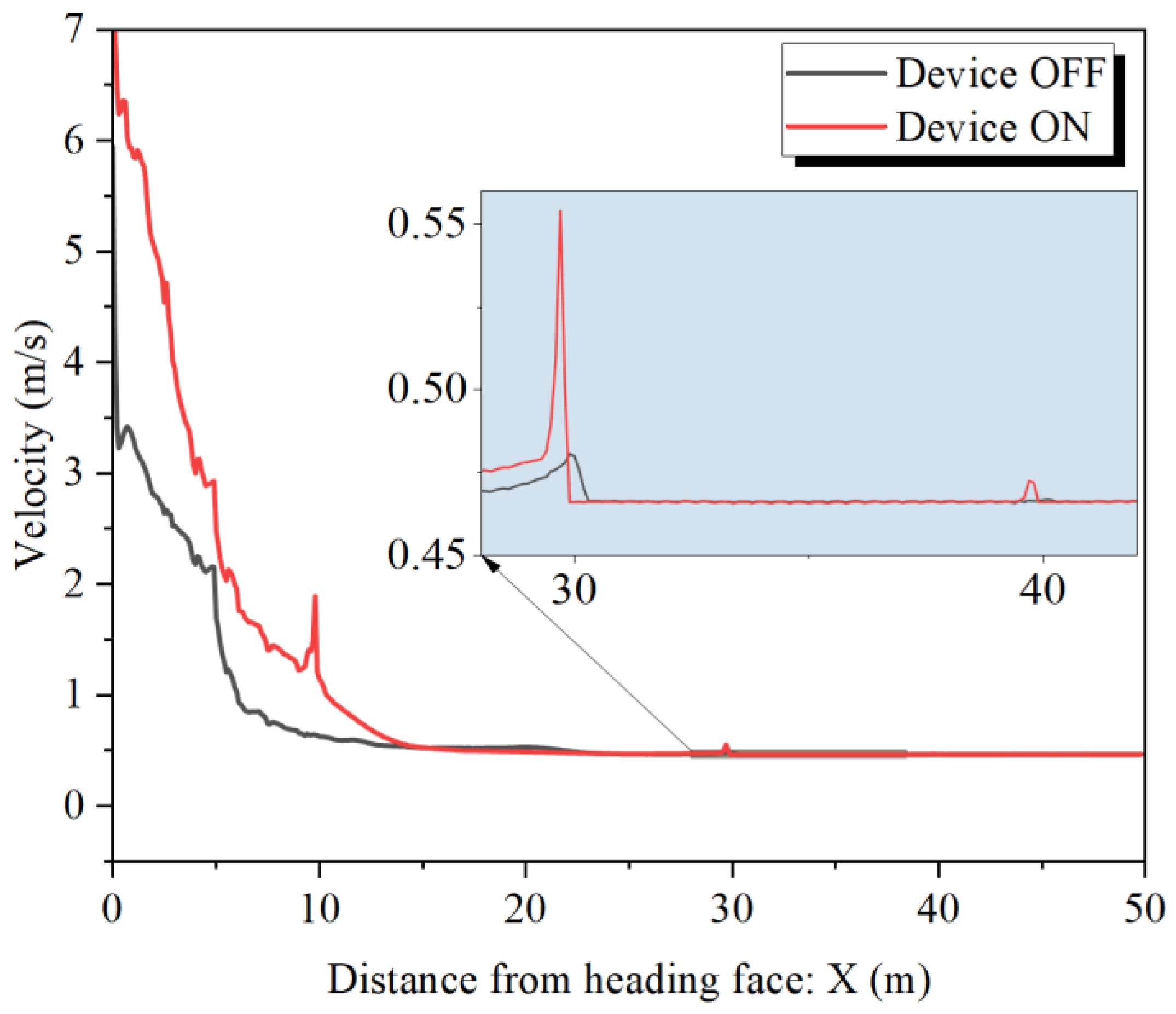
4.2. Impact of Spraying and Water Curtain on Airflow Field
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CFD | Computational Fluid Dynamics |
| RANS | Reynolds-averaged approach |
| SST | Shear Stress Transport |
| DPM | Discrete Phase Model |
References
- Laney, A.S.; Weissman, D.N. Respiratory diseases caused by coal mine dust. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2014, 56 (Suppl. 10), S18–S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seaman, C.E.; Shahan, M.R.; Beck, T.W.; Mischler, S.E. Design of a water curtain to reduce accumulations of float coal dust in longwall returns. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2020, 30, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Z.; Wang, P.F.; Li, S.L.; Chen, S.Q. Development and application of air-assisted spraying device for dust suppression on tunnel boring machine. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2025, 159, 106469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.; Chen, Y.P.; Xu, G.; Huang, J.X.; Ghosh, A.; Liu, W.V. Numerical study of coal dust behaviours and experimental investigation on coal dust suppression efficiency of surfactant solution by using wind tunnel tests. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2021, 43, 2173–2188. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, W.; Ouyang, X.P.; Zhu, W.J. Investigation of Water Spraying Distribution by Multi-points Characterization System in Simulation Tunnel. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2023, 32, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Fang, L. An analytical scaling law model framework for short-time dust emission from belt conveyor. Adv. Powder Technol. 2024, 35, 104613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.B.; Nie, W.; Guo, C.; Peng, H.T.; Ma, Q.X.; Xu, C.W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Q.Y. Optimization of spray dust suppression device in return air tunnel of a coal mine based on CFD technology. Build. Environ. 2021, 203, 108059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Nie, W.; Xu, C.W.; Peng, H.T.; Zhang, C.C.; Li, S.L.; Yue, N.; Liu, Z.Q.; Yang, S.B.; Ma, Q.X.; et al. A study of the spray atomization and suppression of tunnel dust pollution based on a CFD-based simulation. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 123632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Zhang, H.; Xue, T.; Fang, L. A multi-factor CFD simulation to dust suppression in dynamic tunnel excavation. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2025, 159, 106458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, W.; Guo, C.; Zhang, S.B.; Peng, H.T.; Xu, C.W.; Ma, Q.X.; Yuan, M.Y.; Zhou, W.W.; Guo, L.D.; Cheng, L. Optimization of spraying dust reduction technology of continuous miner machine and the dust environment in a tunnel, based on computational fluid dynamics (CFD) technology. Powder Technol. 2022, 398, 117044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.T.; Peng, Y.F.; Nie, W.; Liu, F.; Xu, C.W. Atomization law and dust reduction effect of air-atomizing nozzles determined by CFD and experiments. Energy 2025, 318, 134822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.X.; Nie, W.; Yang, S.B.; Xu, C.W.; Peng, H.T.; Liu, Z.Q.; Guo, C.; Cai, X.J. Effect of spraying on coal dust diffusion in a coal mine based on a numerical simulation. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 114717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Zhang, Z.M.; Wu, Y.H.; Gao, Z.H. Research on the application mechanism of water mist curtain smoke blocking and heat blocking in tunnels. Indoor Built Environ. 2024, 34, 330–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, W.; Yang, B.; Du, T.; Peng, H.T.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.L. Dynamic dispersion and high-rise release of coal dust in the working surface of a large-scale mine and application of a new wet dust reduction technology. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 351, 131356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olewski, T.; Basha, O.; Waldram, S.; Mannan, S.; Vechot, L. Mitigation of LNG Dispersion Using Two Dimensional (2D) Water Curtains. In Proceedings of the 22nd Hazards Symposium—Process Safety and Environmental Protection, Liverpool, UK, 11–14 April 2011; pp. 308–314. [Google Scholar]
- Menter, F.R. Zonal two equation k-w turbulence models for aerodynamic flows. In Proceedings of the 23rd Fluid Dynamics, Plasmadynamics, and Lasers Conference, Orlando, FL, USA, 6–9 July 1993; p. 2906. [Google Scholar]
- Menter, F.R. Two-equation eddy-viscosity turbulence models for engineering applications. AIAA J. 1994, 32, 1598–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnov, P.E.; Menter, F.R. Sensitization of the SST turbulence model to rotation and curvature by applying the Spalart–Shur correction term. J. Turbomach. 2009, 131, 041010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bec, J.; Cencini, M.; Hillerbrand, R. Heavy particles in incompressible flows: The large Stokes number asymptotics. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 2007, 226, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxey, M.R. The gravitational settling of aerosol particles in homogeneous turbulence and random flow fields. J. Fluid Mech. 2006, 174, 441–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffman, P.G. The lift on a small sphere in a slow shear flow. J. Fluid Mech. 1965, 22, 385–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelides, E.E.; Sommerfeld, M.; Wachem, B.V. Multiphase Flows with Droplets and Particles, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Gosman, A.D.; Loannides, E. Aspects of computer simulation of liquid-fueled combustors. J. Energy 1983, 7, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Li, L.L.; Guo, J.S.; Liu, Y.W.; Huang, X.R. Time scale of directional change of active Brownian particles. Phys. Lett. A 2022, 427, 127934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsi, S.A.; Alexander, A.J. An investigation of particle trajectories in two-phase flow systems. J. Fluid Mech. 2006, 55, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansys® Fluent, Release 25.1. Help System, Fluent Theory Guide. ANSYS, Inc.: Canonsburg, PA, USA, 2025.
- Tew, R.; Simon, T.; Gedeon, D.; Ibrahim, M.; Rong, W. An initial non-equilibrium porous-media model for CFD simulation of Stirling regenerators. In Proceedings of the 4th International Energy Conversion Engineering Conference and Exhibit (IECEC), San Diego, CA, USA, 26–29 June 2006; p. 4003. [Google Scholar]
- Gorgun, E.; Dogu, Y.; Aksit, M.F. Investigation of Flow Behavior and Porous Medium Resistance Coefficients for Metallic-Cloth Fibers. Fibers 2020, 8, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, D.P.; Nouar, I.; Senecal, P.K.; Rutland, J.; Martin, J.K.; Reitz, R.D.; Hoffman, J.A. Pressure-swirl atomization in the near field. SAE Trans. 1999, 108, 471–484. [Google Scholar]
- Senecal, P.K.; Schmidt, D.P.; Nouar, I.; Rutland, C.J.; Reitz, R.D.; Corradini, M.L. Modeling high-speed viscous liquid sheet atomization. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 1999, 25, 1073–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, C. Zum Zerfall eines Flüssigkeitsstrahles. ZAMM-J. Appl. Math. Mech. Z. Für Angew. Math. Mech. 1931, 11, 136–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dombrowski, N.; Hooper, P.C. The effect of ambient density on drop formation in sprays. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1962, 17, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonello, N.; Eude, Y.; de Meux, B.D.L.; Ferrand, M. Frozen Rotor and Sliding Mesh Models Applied to the 3D Simulation of the Francis-99 Tokke Turbine with Code_Saturne. In Proceedings of the 2nd Workshop on Transient Operation of Francis Turbines (Francis-99), Lulea, Sweden, 14–15 December 2016. [Google Scholar]


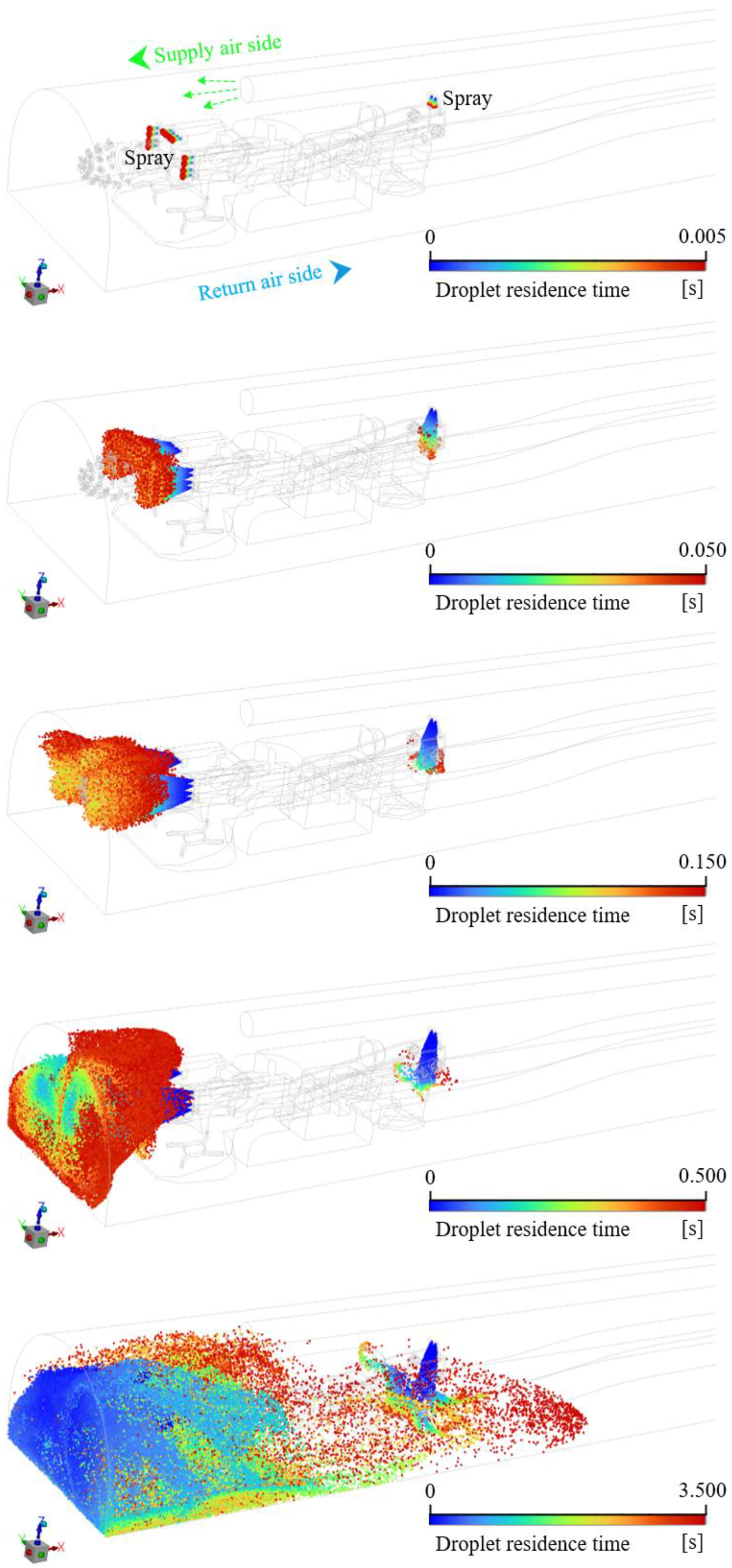
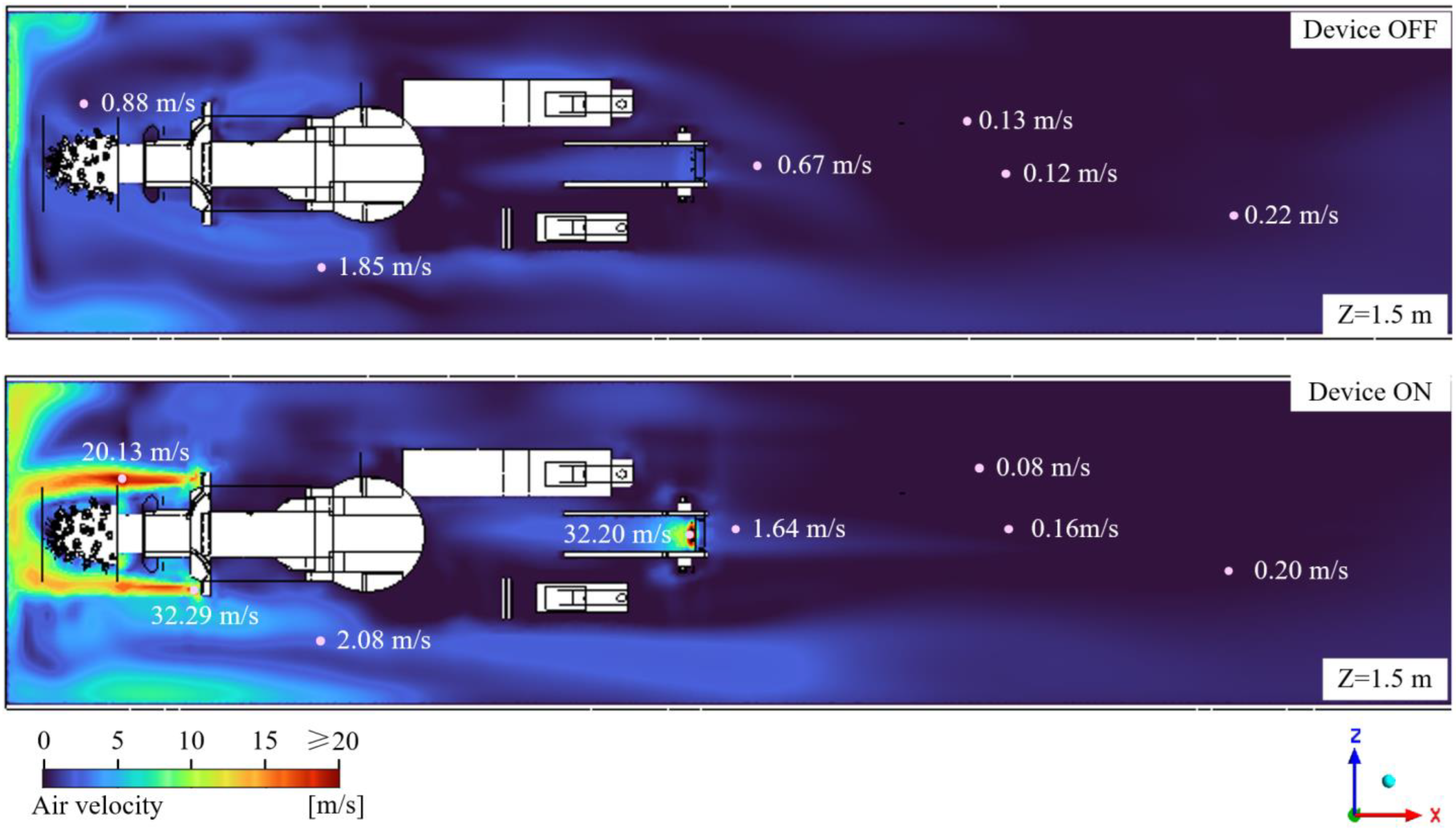
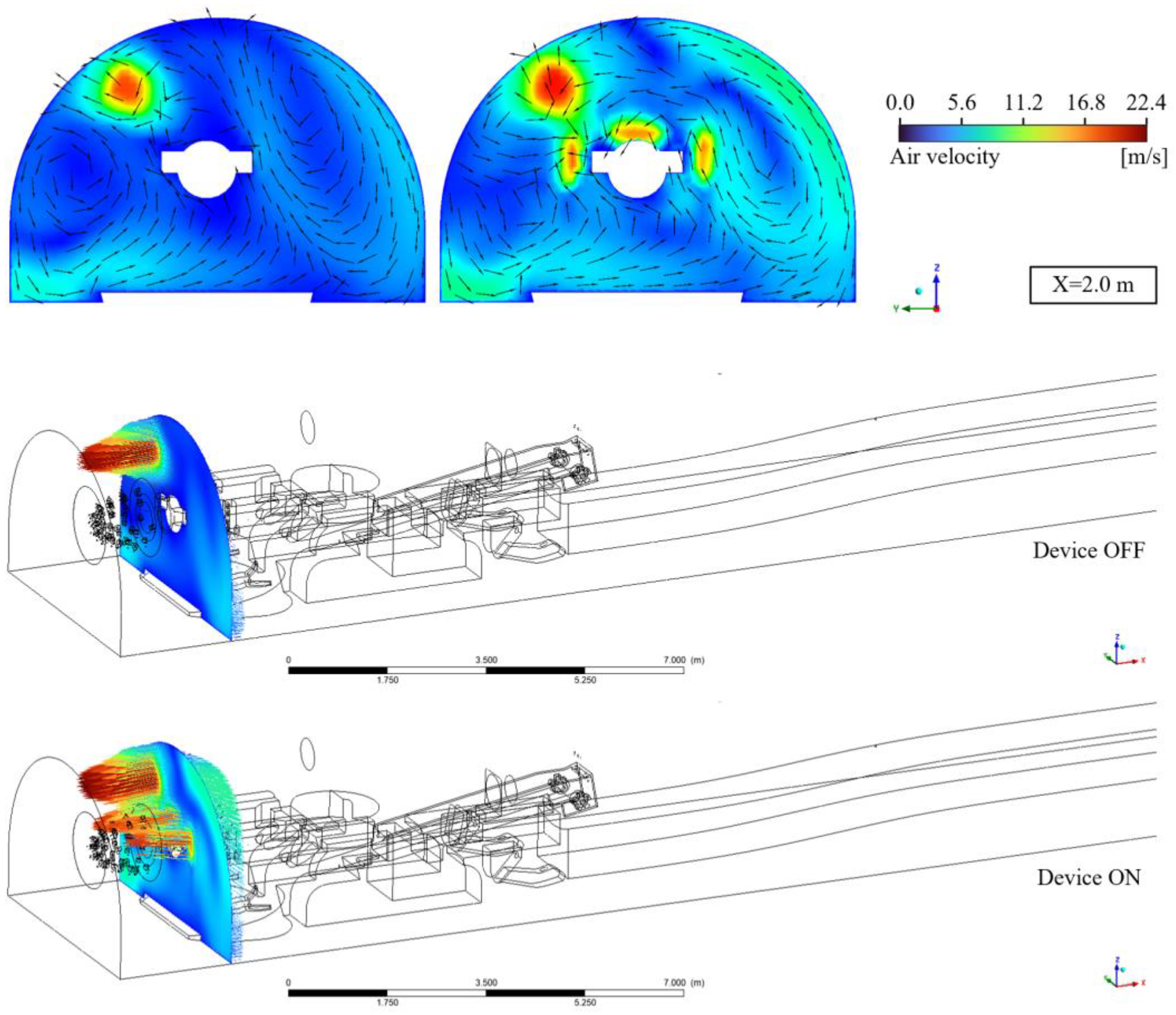
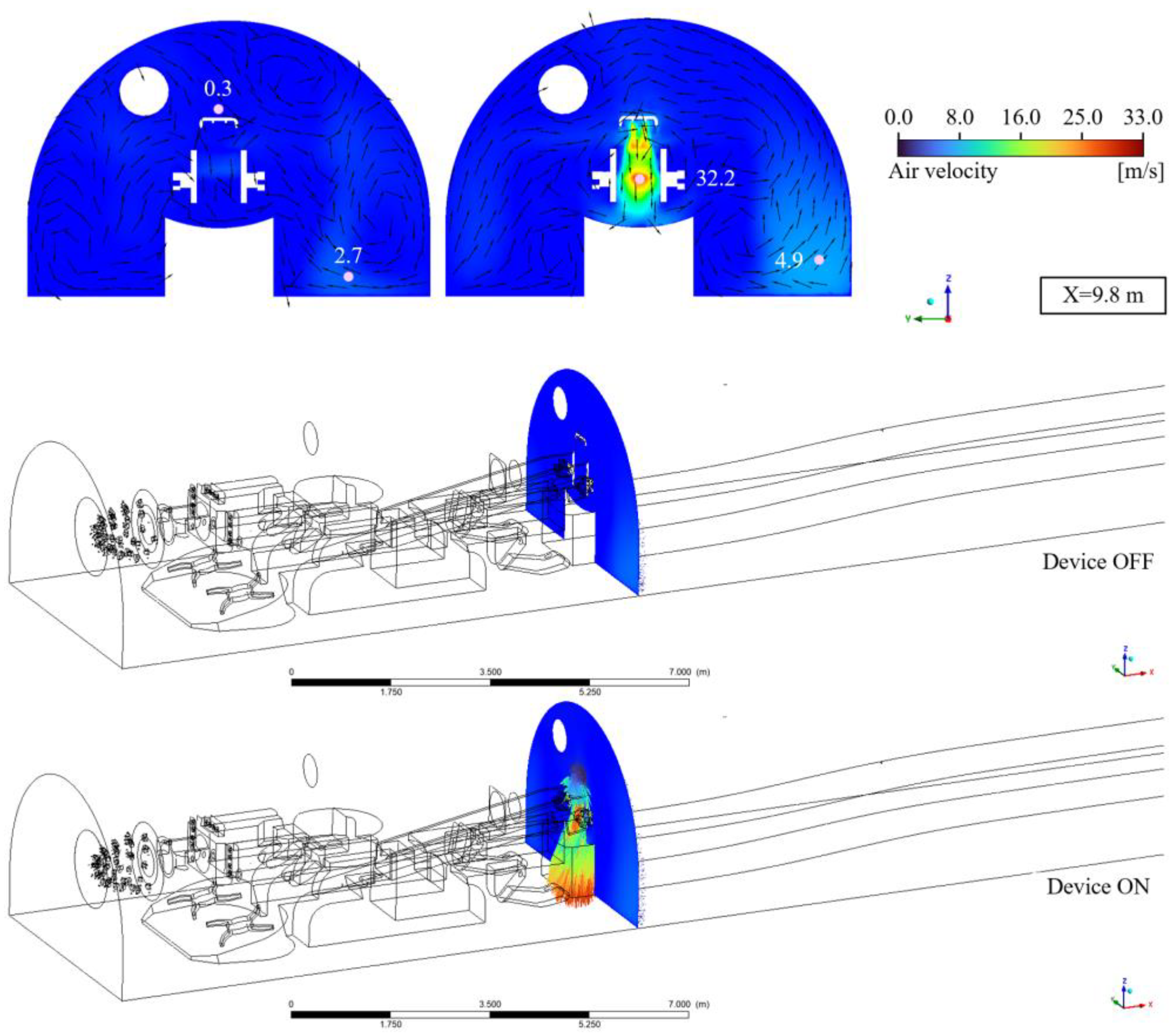
| Item | Name | Parameter |
|---|---|---|
| Turbulence Model | K–ω SST | Transient Double Precision |
| Inlet | Mass Flow Rate | 6.9355 kg/s |
| Sliding Mesh Motion | Rotational Area Rotational Velocity | Cutterhead 47.8 rev/min |
| Discrete Phase Model | Interaction | Interaction with Continuous Phase Update DPM Sources Every Flow Iteration DPM Iteration Interval (10) |
| Tracking Option | Max. Number of Steps (700) | |
| High-Res Tracking (ON) | ||
| Particle Treatment | Unsteady Particle Tracking Track with Fluid Flow Time Step | |
| Pressure Swirl Atomizer | Material | Water-liquid |
| Density | 998.2 kg/m3 | |
| Type | Pressure Swirl Atomizer | |
| Position | Cutterhead|Transfer point | |
| Total Flow Rate | 0.83 kg/s | |
| Upstream Pressure | 2.8 Mpa | |
| Injector Inner Diameter | 5 mm | |
| Spray Half Angle | 15° | |
| Azimuthal Angle | 0–360° | |
| Dispersion Angle | 7° | |
| Sheet Constant | 12 | |
| Ligament Constant | 0.5 |
| Item | Name | Parameter |
|---|---|---|
| Solution Methods | Solver | Couple |
| Time | Bounded Second Order Implicit | |
| Gradient | Least Squares Cell Based | |
| Pressure | PRESTO! | |
| Momentum | Third-Order MUSCL | |
| Turbulent Kinetic Energy | Third-Order MUSCL | |
| Specific Dissipation Rate | Third-Order MUSCL | |
| Time Advancement | Time Step Size | 0.0001 s |
| Max Iterations/Time Step | 20 | |
| Explicit Relaxation Factors | Momentum | 0.75 |
| Pressure | 0.75 | |
| Under-Relaxation Factors | Density | 1 |
| Body Force | 1 | |
| Turbulent Kinetic Energy | 0.8 | |
| Specific Dissipation Rate | 0.8 | |
| Turbulent Viscosity | 1 | |
| Discrete Phase Source | 0.9 | |
| Convergence Residual | Continuity | 1 × 10−4 |
| x-velocity | 1 × 10−4 | |
| y-velocity | 1 × 10−4 | |
| z-velocity | 1 × 10−4 | |
| k | 1 × 10−4 | |
| omega | 1 × 10−4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.-Y.; Li, Y.-T.; An, H.-Q.; Fang, L. CFD Investigation of Spray and Water Curtain Systems in Mine Ventilation: Airflow Paths, Velocity Variations, and Influence Patterns. Water 2025, 17, 1600. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111600
Wang C-Y, Li Y-T, An H-Q, Fang L. CFD Investigation of Spray and Water Curtain Systems in Mine Ventilation: Airflow Paths, Velocity Variations, and Influence Patterns. Water. 2025; 17(11):1600. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111600
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Cheng-Yan, Yi-Ting Li, Han-Qing An, and Le Fang. 2025. "CFD Investigation of Spray and Water Curtain Systems in Mine Ventilation: Airflow Paths, Velocity Variations, and Influence Patterns" Water 17, no. 11: 1600. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111600
APA StyleWang, C.-Y., Li, Y.-T., An, H.-Q., & Fang, L. (2025). CFD Investigation of Spray and Water Curtain Systems in Mine Ventilation: Airflow Paths, Velocity Variations, and Influence Patterns. Water, 17(11), 1600. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111600






