Abstract
Under the dual pressures of global climate change and rapid urbanization, urban drainage systems (UDS) face severe challenges caused by extreme precipitation events and altered surface hydrological processes. The drainage paradigm is shifting toward resilient systems integrating grey and green infrastructure, necessitating a comprehensive review of the design and operation of grey infrastructure. This study systematically summarizes advances in urban stormwater process-wide regulation, focusing on drainage network design optimization, siting and control strategies for flow control devices (FCDs), and coordinated management of Quasi-Detention Basins (QDBs). Through graph theory-driven topological design, real-time control (RTC) technologies, and multi-objective optimization algorithms (e.g., genetic algorithms, particle swarm optimization), the research demonstrates that decentralized network layouts, dynamic gate regulation, and stormwater resource utilization significantly enhance system resilience and storage redundancy. Additionally, deep learning applications in flow prediction, flood assessment, and intelligent control exhibit potential to overcome limitations of traditional models. Future research should prioritize improving computational efficiency, optimizing hybrid infrastructure synergies, and integrating deep learning with RTC to establish more resilient and adaptive urban stormwater management frameworks.
1. Introduction
Under the context of global climate change, the intensified spatiotemporal anomalies in precipitation patterns have precipitated extreme weather phenomena characterized as “wet-dry whiplash” [1]. Concurrently, urbanization has fundamentally altered hydrological processes at both watershed and urban micro-watershed scales through irreversible land surface modifications. A case study of Chennai’s tank system in India reveals that natural water storage areas experienced an average reduction of 43% in surface area between 1971 and 2005, with urban expansion directly accounting for 26.19% of storage capacity loss, while impervious surface proliferation increased runoff coefficients by 11.3% [2]. The dual stressors of climate change and attenuated surface response capabilities have rendered Urban Drainage Systems (UDS) increasingly vulnerable to functional failure. Governments and the public face significant economic and environmental risks. For instance, the catastrophic “July 20” extreme rainfall event in Zhengzhou, Henan Province (China) and the extreme rainfall in Western Europe in July 2021 caused economic losses exceeding USD 17 billion and 40 billion, respectively [3]. Furthermore, when stormwater runoff carries surface pollutants into natural water bodies, it poses a severe threat to public health and resident safety [4]. This urgency necessitates comprehensive investigations into urban stormwater management strategies and systematic optimization of infrastructure configurations to enhance urban hydrological resilience.
The process of stormwater from generation to discharge in urban areas involves a series of hydrological stages (Figure 1), including precipitation, interception, infiltration, runoff generation, flow concentration, treatment, and discharge, while involving the coordination of Green Infrastructure (GI), Blue Infrastructure (BI), and Grey Infrastructure (GREI) [5]. Traditionally, urban drainage systems have predominantly focused on GREI components such as storm-sewer networks, detention basins, floodwalls, and wastewater treatment plants, while neglecting the roles of GI (e.g., green roofs) and BI (e.g., wetlands and lakes). Technologies including rain gardens, infiltration trenches, permeable pavements, and bioretention basins represent engineering implementations of GI. These approaches are variably termed as Low Impact Development (LID), Best Management Practices (BMP), Sustainable Urban Drainage Systems (SUDS), or Water Sensitive Urban Design (WSUD) depending on regional technical frameworks [6]. These nature-based solutions enhance stormwater evapotranspiration and facilitate gradual infiltration into underground aquifers through multi-level retention by vegetation [7].
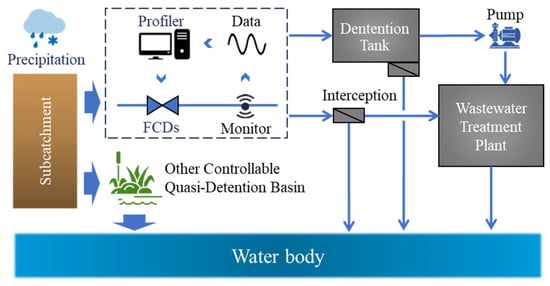
Figure 1.
Collection, treatment, and discharge of stormwater in urban areas.
However, current research on Green Infrastructure (GI) facilities remains predominantly confined to empirical parameter comparisons (e.g., runoff reduction rates, peak flow delay times) [8]. In contrast, Grey Infrastructure (GREI) demonstrates superior engineering controllability: gate systems enable dynamic retention regulation through real-time flow monitoring data-driven controls, enhancing emergency response capabilities during rainfall events [9]; grey infrastructure achieves higher spatial utilization efficiency, whereas GI implementations require substantial land areas, with GI retrofits occupying approximately 15% of the study region in a specific case [10], rendering them often impractical in land-constrained urban environments; grey infrastructure maintains measurable runoff interception efficiency during storm events [11], while Low Impact Development (LID) retention capacity undergoes rapid attenuation due to infiltration saturation and surface runoff [12].
Under the dual drivers of increasing extreme climate events and accelerated global urbanization, urban stormwater management is undergoing a paradigm shift from single-objective engineering approaches and grey infrastructure dominance toward integrated blue–green–grey infrastructure systems. With rapid advancements in Real-Time Control (RTC) technologies such as reactive control and Model Predictive Control (MPC), along with iterative upgrades in decision-support tools including optimization algorithms and machine learning, modern drainage system storage facilities are progressively evolving into smart control frameworks with dynamic responsiveness.
Current research trends focus on runoff reduction through Low Impact Development (LID) facilities, sewer overflow control, and the performance and implementation effectiveness of LID [13,14,15]. However, grey infrastructure, as a critical cornerstone of urban drainage systems, has not been a research hotspot, resulting in a lack of comprehensive reviews. With advancements in control technologies and machine learning, and to lay the groundwork for the long-term development of green–grey infrastructure while clarifying the design and control processes of grey facilities, it is imperative to conduct a comprehensive review and outlook on grey infrastructure. The research framework of this paper is grounded in the flow process of stormwater within urban drainage systems, encompassing two primary grey infrastructure components: drainage networks and Quasi-Detention Basins (QDBs). It provides a detailed analysis of their design and control, while integrating discussions on the application of graph theory-driven design techniques and advanced control technologies—such as fuzzy logic control, predictive control, and deep learning—within the system.
This review focuses on Green Infrastructure (GI) and Grey Infrastructure (GREI) with active regulation capabilities in urban stormwater management systems, systematically analyzing the design and control of drainage networks and Quasi-Detention Basins (QDB) (including rainwater tanks/cisterns, detention basins, and retention ponds), while providing perspectives on grey–green infrastructure coupling, computational process enhancement, and deep learning applications. In the presented case studies, to compare original conditions with optimized scenarios, four metrics from both environmental and economic dimensions were selected, including CSO reduction rate, flood volume reduction rate, storage capacity utilization rate, and economic loss reduction rate. These parameters directly or indirectly reflect the enhancement of UDS resilience.
This study conducted a literature search using Web of Science, setting the publication years between 2015 and 2025. The keywords “urban drainage system” and “rain” were selected as topics to define the initial scope. Additional terms “network” and “storage” were added as subject keywords, resulting in 129 relevant articles. Similarly, combining “detention tank”, “detention pond”, “storage tank”, and “detention tank” with Boolean operators retrieved 158 related articles. After further supplementation and screening of the above literature, a total of 150 articles were included in the analysis.
The paper is organized as follows: Section 2 introduces drainage network design and resilience assessment based on spatial layout principles, along with siting and control strategies for flow control devices; Section 3 reviews design methodologies, two primary control approaches, and coordinated operation of QDB; Section 4 discusses future research directions for urban drainage systems; and conclusions are drawn in Section 5.
2. Drainage Network
Drainage networks constitute the most critical component of urban drainage systems, responsible for conveying stormwater and wastewater from sub-catchments to wastewater treatment plants, thereby preventing urban flooding and protecting urban water bodies from combined sewer overflow (CSO) contamination. In essence, the fundamental objectives of urban drainage network systems during rainfall events are controlling CSO, sanitation sewer overflow (SSO), and flood inundation.
2.1. Design Process of Drainage Networks
Urban hydrological model development imposes specific requirements on drainage network topological information, where well-structured and more resilient underground drainage networks enhance model accuracy and reliability. During the preliminary planning of drainage networks, resilience enhancement objectives should be integrated into the topology generation process, as systematic optimization at the planning stage proves more cost-effective than post-construction retrofits and modifications [16]. Current drainage network topology configurations predominantly rely on designer experience rather than established scientific principles, frequently resulting in systems with either oversimplified drainage pathways or excessively complex topologies that are prone to systemic failures during extreme rainfall events or pipe blockages [17].
2.1.1. Spatial Layout-Based Design
Classical drainage network design approaches prioritize gravity-driven drainage requirements, with pipe slope, diameter, and burial depth serving as control parameters. Moeini and Afshar (2017) [18] integrated the constrained Arc-Based Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm (ABACOA) with the Tree Growing Algorithm (TGA) to design nodal cover depths satisfying pipe slope constraints, subsequently employing three pipe-cutting methods from Moeini and Afshar (2013) [19] to construct feasible tree-structured layouts. Duque et al. (2020) [20] proposed an iterative mathematical optimization framework addressing sewer network layout and hydraulic design through: (1) mixed-integer programming (MIP, an optimization problem that integrates characteristics of both Linear Programming and Integer Programming) for generating tree-structured network layouts; (2) dynamic programming (DP, a mathematical method for optimizing multistage decision processes) for determining pipe diameters and invert elevations; and (3) iterative scheme updating of cost functions in layout selection models until reaching iteration limits or convergence criteria. While these studies address layout selection and hydraulic design in drainage networks, they lack topological optimization considerations.
Drainage networks can be spatially categorized into centralized systems and decentralized systems. Traditional centralized systems relying on single drainage pathways present critical vulnerabilities: (1) peak flows during extreme rainfall events may overwhelm Wastewater Treatment Plant (WWTP) processes or generate Combined Sewer Overflow/Sanitary Sewer Overflow (CSO/SSO) contamination [21]; (2) system failures (e.g., blockages) can trigger cascading network collapse leading to widespread junction ponding [22].
Decentralized pipe network configurations exhibit advantages in flow distribution and higher redundancy compared to centralized layouts, resulting in greater resilience/recovery capacity. This resilience ensures that idle system capacity can be utilized when main drainage pipelines encounter failures, blockages, or insufficient storage capacity [23]. Such elastic storage mechanisms effectively mitigate or prevent overflow events. Researchers have classified decentralized network configurations into minimally reticulated and maximally reticulated systems based on their degree of network connectivity [24]. Bakhshipour et al. (2019a) [25] introduced the hanging gardens algorithm to generate network with arbitrary degree of centralization. The algorithm progressively decomposes an initially centralized layout into a decentralized configuration by incorporating candidate outlet lists. Subsequent optimization using the genetic algorithm (GA) refined the number, locations of discharge outlets, and pipe dimensions. The final design achieved over 25% reductions in total cost, maximum burial depth, and largest pipe diameter compared to centralized systems. Redundant pathways alleviate hydraulic pressure during peak flows and serve as alternative routes during pipeline failures (see Figure 2).
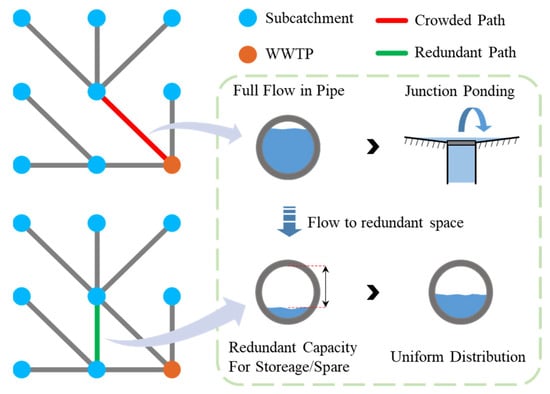
Figure 2.
Redundancy Pathways for Pipe Pressure Mitigation.
Decentralized networks, lacking optimization of redundant pathways, are prone to developing three flow direction errors—”ALL-UP”, “ALL-DOWN”, and “CYCLE”—which impede smooth water drainage. A subcatchment based on the potential outfall (SBPO) method has been employed for drainage network rationalization. This approach traces the potential discharge outlets for each drainage node through topological relationships, identifies control areas of nodes sharing identical potential drainage information as subcatchments, and calibrates stormwater distribution ratios among subcatchments to align with their respective drainage capacities. This classification strategy enables the delineation of control areas for specific discharge outlet combinations [26].
Another emerging approach in pipe network design is graph theory-driven pipeline path design, which applies graph theory principles by representing manholes as nodes and pipelines as edges [27]. This methodology selects feasible stormwater network solutions through topological analysis of urban drainage systems. In flat terrains where minimal elevation gradients complicate gravity-driven network layouts, [28] investigated graph theory applications for drainage network design in such areas. They developed the Loop by Loop Cutting Algorithm, which converts a base graph (containing all possible pipelines and manholes with multiple loops) into a tree-structured drainage layout through iterative loop-cutting. The optimal cutting strategy was subsequently minimized using GA, achieving high computational efficiency and significant construction cost reductions. Zhang et al. (2021) [29] employed a graph-based random walk sampling algorithm to stochastically generate models by constraining parameters such as pipe diameter and slope from upstream to downstream conduits. These designs were evaluated under varying rainfall durations and intensities using the Storm Water Management Model (SWMM), enabling the selection of optimal network configurations. Hesarkazzazi et al. (2022a) [30] enhanced network resilience by identifying critical nodes interacting with trunk pipelines through eigenvector centrality (node centrality). They designed three redundancy addition strategies (Upstream, Downstream, Centrality) to adjust network topology (via loop insertion). Their research demonstrated that decentralized networks outperformed centralized systems in redundancy design, reducing flood volumes by 30% under extreme rainfall (25-year return period) and exhibiting superior resilience during critical node/pipeline blockages. Hesarkazzazi et al. (2022b) [31] proposed a graph theory-based combinatorial multi-objective optimization framework for network design in a flat Iranian region and a steep Austrian area. Initial layouts were generated using open street map urban street networks combined with digital elevation model (DEM) and impervious layer data. A layout generator produced engineering-compliant networks, with multi-objective optimization algorithms selecting optimal configurations. Storm simulations confirmed the cost-resilience advantages of graph theory-based designs over random generation methods [32]. Graph theory-based network design represents a global structural strategy requiring only parameter constraint adjustments for regional adaptability, ensuring broad applicability.
By rationalizing the topological structure of drainage networks, critical design parameters, including control areas and flow directions, are clearly defined, thereby enhancing both data processing efficiency and authenticity of drainage network models. This structural clarity further facilitates the regulation of network storage capacity through flow control devices.
2.1.2. Resilience Assessment Framework
To evaluate the operational performance of designed pipe networks under varying rainfall events, specific metrics are required to assess their resilience (also termed restorative capacity). Butler et al. (2017) [33] define resilience as the degree to which the system minimizes level of service failure magnitude and duration over its design life when subject to exceptional conditions. Discipline-specific definitions exist; for instance, urban flood resilience is characterized as the resisting and restoring capacities of an urban system in coping with flood disasters [34]. This implies the ability to maintain essential drainage functions and minimize failure consequences during extreme events such as intense rainfall, pipeline blockages, or drainage equipment malfunctions.
Standardized resilience assessment metrics remain underdeveloped, with early evaluations focusing on subsystems of UDS. Behzadian et al. (2014) [35] employed the WaterMet2 model to evaluate hydraulic performance metrics of different water reuse schemes (rainwater harvesting and greywater recycling) in urban drainage systems. Resilience was quantified using failure duration expectation-based indices, followed by optimization via the multi-objective evolutionary algorithm NSGA-II to identify the most resilient solutions. Drawing from resilience assessment frameworks in water supply systems that employ concrete indicators [36], UDS can adopt analogous metric systems. Zhang et al. (2021) [29] conducted cost-resilience analyses for graph theory-generated layouts by evaluating environmental, social and technical impact severity.
The objective of resilience assessment lies in improving UDS during design phases or rehabilitating operational systems. Mohammadiun et al. (2018) [37] proposed a resilience design/rehabilitation method integrating Monte-Carlo simulation (MCS) and Copula functions. This approach calculates the probability distribution of external loads (rainfall) from historical data, subsequently generates synthetic rainfall events via inverse distribution functions to evaluate system failure probabilities, and employs the Non-dominated Sorting Differential Evolution iterative scheme to identify optimal interventions (e.g., relief tunnels, storage units) for enhancing resilience. Sweetapple et al. (2022) [38] developed a general resilience assessment methodology using middle-state-based evaluation, decomposing resilience into contributory components for global resilience analysis. Their study identified 14 potential system failure modes and proposed five intervention strategies. These frameworks not only quantify system resilience but also guide mitigation measures, thereby improving universal resilience.
Enhancing resilience during the pipe network design phase demonstrates greater cost-effectiveness compared to post-construction retrofitting [16]. Governmental guidance is critical in this regard, as exemplified by Fredrikstad in Norway, which integrated stormwater management into urban planning through the implementation of a municipal master plan (2008–2028) to improve risk management resilience [39].
In summary, urban drainage network design necessitates the deep integration of topological characteristics and resilience assessment frameworks to address extreme climatic events. Shanghai’s Combined Sewer System (CSS) serves as a paradigm for resilience-oriented design due to its unique network topology. The city center achieves substantial storage capacity (16 mm/hectare) through high-density pipelines and gentle slopes, significantly exceeding values in the Netherlands (5–7 mm/hectare) and Japan (6.1 mm/hectare) [40]. Other cities are actively developing analogous resilience assessment frameworks [41].
2.2. Key Elements in Pipeline Network Operation and Maintenance: Flow Control Devices
High costs and dense urban infrastructure often impede pipe network upgrades [42], making optimization of existing systems through Flow Control Devices (FCDs) a more viable approach. FCDs in drainage systems are critical facilities designed to regulate, restrict, or stabilize flow rates, pressures, and directions. Their functions encompass flood prevention, downstream facility protection, and serving as the physical medium for Real-Time Control (RTC) [43].
FCDs encompass diverse types, including orifice plates, control valves, weirs, and smart flow control devices. Strategic installation of FCDs at selected network locations maximizes sewer storage potential [44], offering three key advantages over constructing new grey infrastructure: (1) lower capital expenditure for FCDs; (2) no additional urban land occupation; and (3) enhanced operational flexibility for UDS under increasingly variable rainfall events. The following sections address the two most critical aspects of FCD implementation: siting and control. The control targets and effects of the FCD literature cited in this paper are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Control Optimization of Flow Control Devices (FCDs) in Selected Literature.
2.2.1. Optimal Siting of Flow Control Devices
To maximize the role of FCDs in dynamically utilizing network storage capacity, determining their optimal placement is essential, yet this critical aspect has historically received insufficient attention [58]. Improperly sited FCDs may fail to regulate flow, resulting in wasted investments, whereas strategically positioned devices can effectively enable in-sewer water storage. Leitão et al. (2018) [59] developed CENTAUR.loc, a geospatial database-driven placement model, to identify optimal FCD installation locations. This framework innovatively incorporates steady-state assumptions closer to real-world conditions through a simplified methodology based on the Manning-Strickler equation:
where Qmax is the full cross-section flow, n is the Manning roughness coefficient, A is the cross-section area, Rh is the hydraulic radius and J is the head loss per length of sewer (or the sewer slope). The CENTAUR.loc placement model implements five distinct reward functions, including maximizing storage capacity and minimizing discharge volume, thereby harnessing storage potential between 1983 m3 and 2070 m3. Muñoz et al. (2019) [60] expanded this work by conducting sensitivity analyses on parameters of these reward functions, developing the CENTAUR.rank algorithm to recursively evaluate different parameter value sets—effectively reallocating parameter weights. The generalized reward function demonstrated optimal coefficients, achieving maximal in-sewer storage, minimal FCD failure impacts, and maximal flow reduction. Reward function adjustments improved placement identification accuracy (rank correlation coefficient increased to 0.931) and enhanced model adaptability across diverse sewer networks.
However, CENTAUR only optimizes single-FCD placement, whereas real-world networks require multiple controllers to meet operational targets. Manual determination of optimal multi-FCD configurations becomes time-consuming and error-prone, particularly when accounting for spatiotemporal rainfall-runoff variability. Eulogi et al. (2021) [61] developed a GA-based method to identify optimal multi-FCD placements in urban drainage networks, evaluating performance under rainfall events of varying intensities. Simulations validated the reliability of integrating CENTAUR with GA for multi-device siting. Building on this, Eulogi et al. (2022) [62] incorporated a prescreening method from W. Wang et al. (2021) [63], enabling large-scale network analysis under standard computational conditions. This framework extended placement optimization to FCD and Low-Impact Development (LID) configurations, demonstrating that combined FCD-LID deployments outperform standalone Real-Time Control (RTC) or LID in reducing Combined Sewer Overflow (CSO) volumes. Jalili et al. (2024) [64] advanced this research by optimizing FCD quantities, locations, and Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) control rules via GA. A primary GA phase identifies candidate locations, followed by a secondary optimization phase determining optimal FCD counts and PID parameters. Crucially, their study employs dynamic wave flood routing rather than static hydraulic assumptions, enabling precise simulation of network behavior under transient conditions.
2.2.2. Real-Time Control Strategies for Flow Control Devices
Urban drainage networks are dynamic and interconnected systems, where hydraulic changes at individual nodes—such as water depth and flow direction—can propagate through the network via mechanisms like backwater effects [65]. Models simulating dynamic flow routing better reflect real-world conditions by accounting for temporal flow variations and hydraulic interactions across network components, thereby accurately capturing the impacts of operational strategies, particularly those involving FCD adjustments. Heusch et al. (2012) [66] established a dynamic global control system for UDS in Quebec, forming the foundation for most FCD control frameworks discussed herein.
Drainage network control inherently involves contradictory objectives: rapid flow discharge may overwhelm downstream WWTPs, whereas delayed discharge risks exceeding system capacity, leading to CSO/SSO events and junction ponding [67]. Strategic FCD regulation enables redistribution of stormwater/sewage within residual network capacity, enhancing retention capabilities to create dynamic, resilient systems during rainfall events [68]. Remotely controllable FCDs in drainage networks primarily include pumps/pumping stations, gates, and offline storage tanks [43].
Model Computation and Predictive Analytics
Achieving optimal FCD control requires iterative model computations to evaluate future control outcomes for each solution. However, the time-intensive solving process of Saint–Venant equations may fail to deliver results within a single model time step [47]. Darsono and Labadie (2007) [45] proposed a neuro-optimal control algorithm based on a recurrent Jordan neural network architecture, optimizing combined sewer system flows and inline storage through dynamic, unsteady hydraulic modeling. This method addressed time-varying parameter adjustments between stormwater runoff predictions and hydraulic models across 5–15 min computational time intervals, satisfying real-time control constraints. Diverging from linear/nonlinear models, Joseph-Duran et al. (2015) [46] developed a hybrid linear model for large sewer networks, reducing computational burdens inherent in detailed physical models while enabling rapid feedback for control actions. Their approach enhanced WWTP treatment rates by leveraging storage capacities of retention tanks and pipelines. Li et al. (2022) [47] advanced swift hydraulic models incorporating two rapid-response frameworks: the first-order plus dead-time model for rising mains and the dynamic-shifting impulse-response filter for gravity sewers. These models reduced computation times by four orders of magnitude compared to conventional methods, enabling real-time control applications.
Accurate flow prediction is critical for real-time management and control of drainage systems. While traditional hydraulic models can provide precise flow predictions when rainfall patterns and network structures are fully characterized, their high computational complexity and parameter identification challenges limit applicability under data-scarce scenarios. To overcome these limitations, Alam et al. (2016) [69] evaluated eight mainstream machine learning algorithms on Internet of Things (IoT) data, demonstrating the potential of machine learning for high-accuracy predictions. Widely adopted data-driven methods include Artificial Neural Networks (ANN), Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM), and the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO). Zhang et al. (2018) [48] pioneered the integration of hydraulic models with recurrent neural networks (RNN) for FCD control, employing three RNN architectures—Elman, nonlinear autoregressive network with exogenous inputs (NARX), and LSTM—to identify sewer sections with residual storage capacity and predict system-wide flows. This approach enhanced control decision-making and response times, reducing overflow volumes from 10,544 m3 to 2566 m3 during a 50-year rainfall return period event through tunnel control. Sufi Karimi et al. (2019) [49] compared three data-driven methods (ANN, LSTM, and LASSO) for flow prediction under extreme weather conditions such as storms. ANN achieved robust performance across most monitoring locations, while LSTM excelled in scenarios with significant dynamic system variations. LASSO proved effective in feature selection, identifying key predictors for flow forecasting.
Predictions typically rely on prior observational data, but their accuracy degrades under missing data scenarios. Researchers have sought to address these limitations. Palmitessa et al. (2021) [50] employed LSTM for soft-sensing predictions of water depth, examining prediction accuracy under varying input features and data gaps. Their study revealed that LSTM compensates for missing historical water depth data by leveraging alternative inputs (e.g., rainfall intensity and temporal parameters). Integrating multiple input features—including water depth, rainfall intensity, and time—significantly enhances the predictive capability of LSTM networks.
Pump Operation and Control Strategies
Pumps are the most energy-intensive FCDs, making operational control critical for economic efficiency [70]. Pump control strategies primarily respond to inflow conditions, yet the inherent unpredictability of drainage system inflows complicates control logic. Traditional pump scheduling—relying on operator experience or fixed water level thresholds—fails to adapt to flow variability, resulting in frequent pump cycling, excessive energy consumption, and inadequate response to rainfall-induced flow surges [71].
Research addressing inflow pattern prediction remains limited, though inflow hydrographs can be derived through data observation or stochastic generation. Zhang et al. (2016) [72] developed a neural network-based model predicting pump system energy consumption and wastewater flows using historical data, subsequently applying an artificial immune network algorithm to solve nonlinear bi-objective optimization (minimizing energy use while maximizing wastewater throughput). Fecarotta and Cimorelli (2021) [53] formulated a mixed-integer nonlinear optimization problem (MINLP) framework, generating stochastic inflow patterns via auto-regressive moving average (ARMA) calibration and optimizing pump operations using open-source nonlinear mixed-integer programming. Optimized scheduling significantly extended pump runtime while reducing average operating power, indicating energy-efficient low-speed operation.
Research on pump control predominantly focuses on optimizing energy consumption/operational costs as control objectives through algorithmic approaches. Fecarotta et al. (2018) [73] developed a MINLP-based model coupled with a branch-and-bound nonlinear optimization algorithm to reduce pump energy usage. Rathnayake (2021) [52] formulated a generalized cost function incorporating pump mechanical energy, flow velocity, head, and efficiency, employing the Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm-II (NSGA-II) to minimize pollutant loads, wastewater treatment costs, and pump operational expenses. A limitation lies in its exclusive focus on single storage tanks and pumps, necessitating exploration of regional pump coordination. Addressing this limitation, Dai et al. (2022) [51] implemented a Rule-Based Control (RBC) strategy integrated with rainfall forecasting to coordinate regional multi-stage pump stations, optimizing network storage via pre-emptive drainage. This approach achieved 198% daytime and 293% nighttime capacity increases in storage utilization, alongside 96% reduction in pump cycling frequency, 12.2% lower energy intensity, and 30% reduced inflow variability at WWTPs. Zhao et al. (2024) [54] proposed a distributed optimal control method using ranking-based differential evolution (rank-DE) to globally optimize riverside combined sewer overflow (CSO) interceptors and decentralized pumps. By coordinating in-sewer storage and flow conveyance through alternating modes of maximized retention and prioritized drainage, overflow mitigation significantly improved.
Pump scheduling optimization demonstrates high cost-effectiveness in energy conservation [74]. However, research remains scarce on adapting pump operations to dynamic stormwater/sewage inflow patterns, necessitating future investigations to address this gap.
Distributed Gate Control Systems
Gates are distributed across drainage networks, necessitating distributed control strategies for effective regulation. Ruggaber et al. (2007) [55] designed and deployed CSONet, an embedded sensor network system enabling real-time, distributed, and decentralized control. This system collects data via distributed sensors and automates valve adjustments to modulate network storage capacity. Carbone et al. (2014) [75] implemented a distributed self-organizing gate system in an Italian city, simulating two scenarios—ungated networks versus smart gate actuators—using the SWMM. Gates dynamically adjusted their openings based on downstream pipe storage availability, prioritizing overflow reduction. During a 97.4 mm storm event, critical pipe filling degrees decreased by 22% after deploying distributed smart gates, demonstrating their ability to delay peak flows via temporary storage within existing network capacity. For decentralized gate control in urban combined sewer systems during storms, Rathnayake and Anwar (2019) [56] employed GA and NSGA-II to compute optimal orifice gate openings at each time step. Their model dynamically adjusted gate apertures using real-time feedback to simultaneously minimize pollutant loads and operational costs.
However, gate control may adversely affect hydraulic conditions at other network nodes, necessitating global optimization perspectives. Garofalo et al. (2017) [44] proposed a distributed RTC approach employing gossip-based algorithms in a decentralized real-time control system that coordinates water level sensors and electronically movable gates. This gossip protocol enables localized information exchange while estimating global average water levels. Compared to centralized control, distributed RTC effectively balances flows, reduces peak discharges, and demonstrates superior adaptability and fault tolerance—particularly under localized communication constraints. Luo et al. (2022) [57] developed dynamic programming with successive approximation considering the time lag of flow routing (DPSA-TL) combined with Model Predictive Control (MPC) for gate regulation. By decomposing multi-actuator control into sequential single-actuator subproblems, this method avoids solving high-dimensional Markov processes with complex state-transition equations. Compared to passive control, Rule-Based Control (RBC), and Evaluation Algorithm (EA), the DPSA-TL strategy achieved up to 16.5% greater CSO volume reduction during 3-year and 5-year return period events.
Studies that consider the impact of gate control on the hydraulic status of urban sewer systems are still limited, and further research is needed to address this gap.
Impacts of FCD Control on Wastewater Treatment Plant Performance
The regulation of FCDs alters hydraulic transmission time lags, peak flow distribution, and pollutant load fluxes within drainage networks, directly influencing the coupled fluctuations of WWTP inflow volume and quality. WWTP biological treatment processes exhibit high sensitivity to inflow dynamics—for instance, oxygen aeration rates in aerobic treatment must be adjusted several hours prior to drastic inflow variations [76]. Consequently, investigating WWTP inflow control is crucial for optimizing wastewater treatment processes.
Early research focused on controlling WWTP inflow volumes. Fiorelli and Schutz (2009) [77] optimized a drainage network model with 24 storage tanks in Luxembourg, significantly reducing inflow variability at the WWTP. Ryu et al. (2015) [78] employed an auto-regressive moving average model with exogenous inputs (ARMAX) to assess storage functionality and WWTP impacts after converting a combined system to a separated system in South Korea. By testing network storage under hypothetical WWTP inflow conditions—1.5×, 2×, and 2.5× maximum daily design capacities—the system demonstrated 70 h, 11 h, and 3 h retention capacities, respectively, stabilizing WWTP inflows. Kroll et al. (2016) [79] addressed flow overload caused by land expansion in Belgium through local control by time slots and global control by ranked filling degree, restricting total WWTP inflows while minimizing CSO impacts. Simulations revealed superior flow stabilization under global control strategies. Sakson et al. (2018) [80] investigated WWTP inflow regulation in Poland, demonstrating that integrating storage tanks, in-sewer retention, and RTC systems effectively stabilizes inflows and reduces CSO volumes.
WWTP inflow quality critically influences subsequent treatment processes, making water quality prediction more pivotal than quantity forecasting. Langeveld et al. (2017) [81] developed an empirical model predicting both inflow quality and quantity, classifying water quality into four regimes: dry weather flow (DWF), initial wet weather flow (WWF), dilution phase during WWF, and post-WWF recovery. Their predictions showed strong agreement with measured NH3-N and COD concentration dynamics during wet weather events. Machine learning approaches leveraging historical data have gained traction for WWTP inflow quality/quantity prediction. R. Wang et al. (2021) [82] employed four methods—Linear Regression, Ridge Regression, ElasticNet Regression, and Lasso Regression—using historical meteorological data (precipitation, temperature) and inflow parameters (flow rate, COD, NH3-N) as training inputs. Simulations revealed Ridge Regression achieved highest accuracy in flow and COD predictions, while ElasticNet and Lasso Regression excelled in NH3-N forecasting. Li and Vanrolleghem (2022) [83,84] developed LSTM- and ANN-based influent generators for quality/quantity prediction. Their data-driven framework, integrated with random walk processes, addresses limited historical data scenarios, with lower Kullback–Leibler divergence values confirming closer alignment between generated and observed data distributions.
Integrating quality and quantity predictions enables WWTPs to holistically prepare for inflow variations, effectively bridging the final gap in rainfall-to-treatment process optimization.
3. Quasi-Detention Basin
Storage basins serve as critical infrastructure in urban stormwater management, intercepting initial high-pollutant runoff in combined systems and mitigating hydraulic shocks on downstream receiving waters by delaying peak discharge timing in separated systems. While previous studies often distinguish LID measures (e.g., rainwater tanks, detention basins) from storage basins in Green Infrastructure (GI), this study transcends conventional GI frameworks by proposing the “Quasi-Detention Basin (QDB)” concept, encompassing residential rainwater tanks, bioretention cells in LID facilities, and inline storage tanks within drainage networks. These QDB facilities share three defining characteristics:
(1) Substantial storage capacity: Temporarily storing stormwater runoff to regulate peak discharge and delay drainage timing, thereby alleviating network overload and downstream flood risks.
(2) Controllable inflow/outflow: Storage efficiency is constrained by inflow rates, volumetric capacity, and discharge rates, while extended retention enables preliminary water quality treatment.
(3) Spatially flexible deployment: QDB measures are distributable across upstream, midstream, and downstream sections of drainage systems, achieving holistic control through coordinated operation.
3.1. Design Process Optimization
3.1.1. Location–Capacity Integrated Design
The functional efficacy of QDBs is influenced by siting decisions and volumetric parameters. Traditional design methods, akin to conventional drainage network planning, rely heavily on empirical approaches, often neglecting dynamic interactive effects within system topologies.
With advancements in multi-objective optimization algorithms, siting and sizing are increasingly co-optimized. Volumetric parameters influence construction costs, while siting determines storage performance [85]. Baek et al. (2015) [86] developed a particle swarm optimization (PSO)-based framework for combined sewer networks in Seoul, South Korea, efficiently exploring permissible design zones to identify storage basin locations. Their optimized four-basin configuration achieved a 1.8% reduction in total volume against presets, with individual tank volumes reduced by up to 87.5%. Expanding on this, Ryu et al. (2017) [87] optimized siting and sizing for 10 potential storage basins in the same region. Ngo et al. (2016) [88] employed linear reservoir theory to minimize deviations between downstream peak flows and channel capacity, determining optimal basin configurations via the harmony search algorithm (HSA). This approach reduced downstream flood peaks by 33% under two rainfall duration scenarios. Wang et al. (2023) [89] introduced a novel framework integrating resilience characteristic metrics and simplified modeling. Leveraging linear superposition of system resilience principles, their method combines limited simulations with GA optimization to determine optimal storage tank placements.
Conventional modeling simulations typically assume static rainfall patterns, whereas actual rainfall exhibits spatial variability in intensity, directional movement, and propagation velocities [90]. Starzec et al. (2018) [91] incorporated rainfall movement dynamics into storage basin sizing by assigning distinct rainfall profiles to individual catchment subareas. Their analysis of four primary rainfall movement directions and varying velocities revealed significant impacts on facility dimensions. The results demonstrated that storage volumes accounting for rainfall movement exceeded static-condition designs by 108.41%, highlighting risks of underestimating storage facility sizing when neglecting spatiotemporal rainfall characteristics. Subsequent studies should prioritize integrating rainfall movement parameters.
Storage basin siting and sizing must address not only cost considerations but also rainfall movement impacts on actual storage capacity during operation—a critical factor warranting further investigation.
3.1.2. Flood-Induced Economic Loss-Driven Design
Extreme precipitation events in rapidly urbanizing regions cause substantial economic losses and casualties [92], necessitating research on flood impacts and subsequent economic consequences. Adelodun et al. (2023) [93] investigated causal relationships between extreme precipitation indices (e.g., consecutive wet days, number of very heavy precipitation days), and flood-induced economic losses in South Korea. However, flood damage cost estimation remains challenging due to regional heterogeneity. Lee and Kim (2019) [94] proposed a reliability index through multi-dimensional flood damage analysis (MD-FDA), quantifying property values across residential, agricultural, and industrial zones. This framework integrates distance measure methods, calculating Euclidean distances between design scenarios and the utopian point after normalization:
where RV represents flood volume reliability, RN denotes node reliability, RD indicates flood damage reliability, and R is the dimensionless comprehensive reliability index. A value closer to 1 signifies higher overall system reliability. This reliability index can be applied to resilience assessment during the QDB design phase.
Incorporating flood damage costs into design processes can effectively reduce construction and operational expenses. Jamali et al. (2020) [95] proposed an integrated modeling framework using semi-continuous simulation approaches, coupling SWMM and Cellular-Automata Fast Flood Evaluation to simulate tank storage conditions and inundation depths caused by network overloads. A GIS module assessed flood damage costs, revealing that widespread rainwater harvesting system implementation could reduce expected annual flood damage costs by up to 30%. Choi et al. (2017) [96] developed a storage facility siting method based on flood damage costs, employing multi-dimensional flood damage analysis (MD-FDA) in a South Korean watershed to quantify flood loss relationships between flood volumes and economic impacts. Optimally siting three storage facilities under a 30-year rainfall scenario reduced flood volumes by 4866 m3 (67.9%) and economic losses by KRW 50.5 million (46.4%).
Future research should integrate flood damage considerations into QDB design processes and UDS resilience assessments, enabling comprehensive infrastructure evaluation and improvement.
3.1.3. Water Quality-Oriented Design Paradigm
Water quality control is emerging as a critical dimension in design strategies. Y. Zhang et al. (2024) [97] coupled location, quantity, size, and cost in storage basin design, achieving 48.16% total overflow reduction and 9.05% SS load reduction through multi-objective optimization. However, such QDB designs largely treat water quality control as a secondary outcome.
Several studies prioritize water quality as a primary design objective. Wang et al. (2017) [98] implemented a two-stage optimization framework for storage basin design in CZ City, China, employing the analytic hierarchy process (AHP) to rank flood nodes based on flood reduction rates and total soluble solid (TSS) reduction rates. Subsequent generalized pattern search (GPS) refined preliminary designs to balance flood mitigation, TSS reduction, and storage costs. Li et al. (2020) [99] adopted a similar AHP-based approach, comparing pollution control efficacy between decentralized storage tanks and terminal storage tanks to identify optimal configurations. Hermoso et al. (2018) [100] investigated basin sizing effects on pollutant load reduction and overflow frequency, evaluating performance via two efficiency indices. Simulations across basin volumes (0–100 m3/ha) identified optimal sizing thresholds. Z. Xu et al. (2020) [101] developed a multi-source pollution overflow model simulating basin overflow quantity/quality and proposed the overflow peak pollution interception (OPPI) method. By integrating pollutant concentration dynamics and interception criteria, OPPI determines basin volumes to control overflow contamination under varying antecedent dry days.
Water quality control has transitioned from passive co-benefits to goal-oriented objectives in urban drainage storage design. Future research should advance water quality-driven QDB frameworks by incorporating flood damage quantification metrics into assessment paradigms.
3.2. Control Strategies for Quasi-Detention Basins
Real-time control strategies for storage basins in urban drainage systems are broadly categorized into reactive control and predictive control.
1. Reactive Control
Reactive control employs manual, experience-driven rule-setting approaches tailored to specific regions and rainfall scenarios [102]. While quick to implement and operationally stable, this strategy passively triggers predefined actions based solely on current system states. Its limitations include over-reliance on operator expertise and limited transferability to catchment areas with distinct physical or climatic characteristics due to data source specificity [103].
2. Predictive control (Model predictive control)
Predictive control requires system modeling and optimization, hence termed Model Predictive Control (MPC). MPC dynamically generates control schemes using predicted rainfall events or flow variation patterns, optimizing storage release timing to benefit both drainage networks and downstream WWTPs [104]. MPC focuses on two operational modes: (1) Pre-storm release: Emptying storage facilities before anticipated rainfall to maximize retention capacity [105]; (2) Intra-storm release: Regulating storage discharges during rainfall events when inflow exceeds available capacity [106]. A key limitation of MPC lies in the requirement for models to generate control actions within time steps, demanding highly efficient optimization algorithms to compute results [11].
3.2.1. Reactive Control
Reactive control, also termed heuristic control, can be subdivided into two approaches: rule-based control (RBC) and fuzzy logical control (FLC). RBC predefines extensive operational rules, enabling rapid selection of rule-compliant actions based on real-time system states [107]. FLC addresses input uncertainties and imprecisions by converting qualitative linguistic variables into quantitative control actions through structured fuzzy inference systems [108]. However, fuzzy logic control fails to holistically address the entire system and requires frequent rule modifications as devices are adjusted or expanded. Additionally, it heavily relies on historical data for rule calibration, which limits its applicability in data-scarce regions (e.g., newly developed urban areas).
Early studies predominantly utilized RBC due to its simplicity, particularly for regulating downstream water levels during major storm events [109]. With advancements in rapid real-time water quality monitoring (e.g., TSS concentration, turbidity) and controllable valves, RBC has expanded to incorporate water quality objectives [110,111]. Water resource efficiency demands have further shaped RBC development. Stormwater, as a high-quality renewable resource, aligns with goals of water supply diversification, wastewater discharge reduction, waterway pollutant load mitigation, and urban sustainability [112]. Storage basins are increasingly designed to reduce municipal drinking water demand, with control rules prioritizing non-potable stormwater reuse [113]. Altobelli et al. (2023) [114] optimized basin discharges using four control rules integrated with rainfall forecasting, enhancing stormwater utilization from rooftop and outdoor runoff. Their approach increased non-potable water reuse for toilet flushing from 32% to 90%, significantly improving supply reliability for non-drinking purposes.
Coordinated operation among storage basins enables water redistribution across drainage networks, maximizing storage utilization. Carp et al. (2013) [115] optimized control of four storage tanks with varying capacities using FLC, incorporating inflow rates, local filling levels, and downstream basin status into control logic. Barbu et al. (2016) [116] applied FLC to six basins across six subcatchments via the Benchmark Simulation Model-Sewer (BSM-Sewer), considering basin water levels, downstream conditions, and inflows. While allowing intentional basin overflows (suboptimal for individual units), this global FLC approach optimized network-wide performance, achieving better-distributed filling levels and reduced overflow volumes and pollutant loads.
To address reactive control limitations like scenario-specific calibration needs, Liang et al. (2022) [117] proposed Target Flow Control (TFC)—a calibration-free method adjusting discharge via real-time water level monitoring to maintain outflow at or below predetermined target flow rates, demonstrating broad applicability without rainfall forecasting.
In summary, RBC for storage basins is evolving toward holistic water quantity-quality management and system-wide control, though universality remains a persistent challenge.
3.2.2. Predictive Control/Model Predictive Control
Model Predictive Control (MPC) takes the current state as the initial state and determines optimal control actions for the controlled object at each time step based on model simulations of future scenarios, aiming to achieve predefined objective functions [118]. The performance of predictive control exhibits high sensitivity to the spatiotemporal heterogeneity of rainfall, which has driven intensive research on the deep integration of rainfall forecast with MPC. Sun et al. (2023) [106] integrated predicted hydrological states (rainfall and flow) with real-time control to optimize discharge from small detention tanks during storm events. Their control framework comprises three main components: real-time monitoring and hydrological forecasting, algorithm coupling and decision-making, and strategy implementation with state updating. In selected heavy rainfall events, the modified predictive RTC demonstrated 16.3–58.2% greater peak flow reduction compared to Rule-Based Control (RBC). Regarding rainfall forecast impacts on storage facilities, existing reservoir-related studies provide valuable insights for predictive control in urban drainage networks. Jia et al. (2020) [119] conducted an evaluation of 24 h rainfall forecast error impacts on flood forecasting operations in China’s Qianhe River Basin (Shaanxi Province), applying Bayesian theory to assess rainfall forecast error effects on flood forecasting operations. Through posterior probability calculations, they quantified flood risks under different forecast reliability levels. Cai et al. (2023) [120] developed a continuous precipitation forecast reliability evaluation model for China’s Meishan Reservoir, employing a generalized Bayesian model to characterize precipitation forecast uncertainty. They obtained fuzzy reliability metrics for continuous precipitation forecasts using the first-passage fuzzy probability model (FFPM), achieving increased reservoir storage capacity while maintaining flood control safety. These control paradigms offer operational references for Quasi-Dynamic Boundary (QDB) control systems, suggesting potential strategies for pre-storm emptying based on rainfall forecasts to reserve storage capacity.
Furthermore, predictive control demonstrates unique advantages in rainwater harvesting and utilization due to its anticipatory analysis of future conditions. Rainwater harvesting systems (RHS) can detain roof runoff induced by rainfall, effectively controlling peak flow and volume [121], while collecting, storing, and treating rooftop rainwater for domestic and irrigation purposes (Figure 3). Roman et al. (2017) [113] designed rainwater tanks as RHS facilities for irrigation at a recreational center in New York City, employing continuous monitoring and adaptive control (CMAC) to optimize system operation. This approach pre-releases water from tanks based on rainfall forecasts to create storage space for impending precipitation. During a decade-long simulation, the CMAC scenario captured and retained 76.6% of roof runoff annually while consuming only 11 m3 for irrigation, significantly lower than the 59 m3 required for timer-based irrigation systems. Di Chiano et al. (2023) [122] proposed a probabilistic approach accounting for rainfall and water demand stochasticity. By analyzing random processes of rainfall events, they derived analytical expressions for the cumulative distribution function of active storage capacity in detention tanks, achieving flow balance between rainfall and water demand to determine the minimum storage capacity of detention tanks.
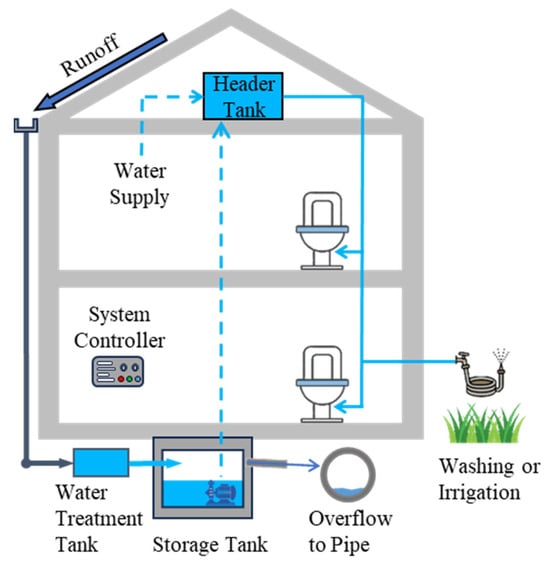
Figure 3.
Household rainwater harvesting system.
Model Predictive Control (MPC) often requires optimization algorithms to achieve operational objectives. Yazdi (2019) [11] integrated differential evolution (DE) with SWMM to determine optimal gate openings at different water levels for detention tank control, aiming to minimize flood overflow in drainage networks during extreme rainfall events. Di Matteo et al. (2019) [123] employed NSGA-II for global optimization of multiple stormwater tank controls, regulating gate discharges under varying rainfall patterns and tank sizes to stagger flood peak timings across different sub-catchments, thereby reducing the system’s overall peak flow.
Beyond conventional optimization algorithms, researchers have incorporated machine learning into MPC frameworks. Mullapudi et al. (2020) [124] implemented deep neural networks (DNNs) to enable controllers to learn optimal control strategies through system interactions. By constructing a simulated environment with 11 interconnected stormwater basins and designing reward functions, they trained controllers to regulate stormwater flow and maintain water levels across diverse rainfall events. The reinforcement learning agent for single-basin control converged to stable reward values after 3500 training episodes, achieving smooth control of water levels and flows. In multi-basin control scenarios, batch-normalized neural network-based RL agents demonstrated enhanced training stability and superior reward values. Despite deep reinforcement learning (DRL) representing an advanced methodology, the adaptability of its open-loop logic in drainage systems requires further investigation [125].
The introduction of complex models and excessive optimization algorithms in predictive control increases computational workload, limiting their real-time control applicability. Recent studies have adopted model simplification approaches to enhance computational efficiency without compromising control effectiveness. Vasiliev et al. (2024) [126] simplified a sewer network model containing seven detention tanks by considering only hydraulic phenomena while excluding pollutant transport and storage. They employed Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) to control detention tank inlet/outlet gates through predictive inflow optimization over a future time horizon. This approach achieved over 50% average reduction in pollutant loads during overflow events while reducing simulation time from 30 s to approximately 3 s. However, the simplified model’s reliability and comprehensiveness remain subjects requiring critical evaluation.
3.2.3. Integration of Reactive and Predictive Control Frameworks
Reactive control eliminates the need for complex mathematical algorithms or inaccessible rainfall data, utilizing empirically derived rules that prove more practical in storm control. Conversely, predictive control enables anticipatory decision-making. Combining their respective strengths allows the development of comprehensive control strategies bridging historical experience and future projections. Some studies have implemented relatively mechanistic integrations of these approaches. Meneses et al. (2018) [127] applied both predefined Rule-Based Control (RBC) and Model Predictive Control (MPC) with dynamic overflow risk assessment to a Danish catchment using MIKE URBAN. Both methods achieved up to 21% reduction in storage volume, with comparable performance in storage optimization and combined sewer overflow (CSO) reduction between RBC and MPC strategies, potentially attributable to regional specificities.
Other research has achieved more synergistic integration of both control paradigms. Shishegar et al. (2019) [128] implemented a rolling horizon strategy for stormwater basin management in Canada, embedding optimization models within reactive control frameworks. This approach dynamically schedules future outflows at each timestep by integrating forecasted and real-time data, employing linear programming to minimize peak flows and maximize detention time. Under climate change scenarios, the system achieved 76% average peak flow reduction with decreased outflow fluctuations. Bilodeau et al. (2018) [129] developed a hybrid RBC-MPC strategy for a Canadian detention tank, where reactive control passively empties the tank at high water levels while predictive control proactively adjusts levels based on rainfall forecasts to ensure sufficient storage capacity. Simulations demonstrated a 36 h average retention time, enhancing total suspended solids (TSS) removal efficiency. Sun et al. (2024) [125] achieved deep integration of fuzzy logic control (FLC) with rainfall forecasting through their predictive fuzzy logic and rule-based control approach (PFL-RBC). By converting rainfall process forecasts into rainfall depth predictions categorized into nine levels, they incorporated precipitation forecasts into fuzzy logic control. Genetic algorithms (GA) optimized membership functions based on predefined fuzzy rules for continuous stormwater tank control. Across the simulation scenarios, PFL-RBC outperformed conventional RBC, achieving 7% average runoff reduction in continuous simulations (20% for large-capacity tanks), alongside significant improvements in retention time and reuse volumes, while maintaining robustness against rainfall forecast errors and measurement noise.
The fusion of these control methodologies remains exploratory, with future research expected to focus on integrating reactive control’s empirical simplicity with predictive control’s anticipatory capabilities.
4. Future Research
4.1. Computational Efficiency Enhancement
Within RTC frameworks, the rolling time-step optimization mechanism of MPC necessitates numerical solutions for constrained optimization problems at each step to generate optimal control commands for FCD (Flow Control Devices). Shorter time steps correlate positively with enhanced control precision, requiring further improvements in computational efficiency.
Strategic neglect of secondary components can accelerate operational speed without compromising primary operational conclusions. Some studies streamline model redundancies to concentrate computational resources on core objectives. Mannina and Viviani (2010) [130] developed a simplified conceptual model retaining only hydrological, hydraulic, and solid transport modules. Ryu et al. (2017) [87] replaced complex Saint–Venant equations with discrete-time dynamic formulations and first-order linear approximations, ensuring model accuracy through parameter calibration. Dastgir et al. (2024) [131] constructed a hybrid graph–hydrodynamic model using network topology and graph measures to simulate pipe network structures and hydraulic characteristics. These simplifications maintain simulation fidelity while improving computational performance.
Alternative approaches employ strategies akin to Attention Mechanism [132] or Level of Detail [133], directing limited computational resources to dynamically critical model components. Hu et al. (2018) [134] developed an adaptive unstructured mesh-based control-volume finite-element flood model that dynamically adjusts spatial-temporal mesh resolution according to hydrodynamic features (e.g., wetting/drying fronts, flow along flooding paths). This methodology employs fine meshes only in high-priority zones and coarse meshes elsewhere, achieving 20–84% computational time reduction without compromising accuracy. Li et al. (2024) [135] proposed a high-efficiency algorithm utilizing DEM to partition urban areas into hydrologic units, replacing full-domain shallow water equations with unit hydrograph methods for runoff simulation. Computational granularity is dynamically adjusted in critical zones (e.g., depressions, building peripheries), minimizing resource consumption in non-flooded areas. Such attention-inspired approaches significantly conserve computational power in non-critical regions.
Future research should focus on computational advancements through both model optimization and algorithm refinement, as more accurate and efficient computations are critical for enhancing model precision.
4.2. Hybrid Green–Blue–Grey Infrastructures
Green Infrastructure (GI) can achieve resilience enhancement effects comparable to Grey Infrastructure (GREI) at lower costs [136]. However, in space-constrained urban environments, GI demonstrates limited effectiveness in runoff and water quality control, exhibiting pronounced diminishing marginal returns [137]. Some researchers propose hybrid GI-GREI systems for “smart city” development [138].
Synergistic benefits of GI-GREI integration in water quantity management, quality improvement, and cost efficiency have been systematically evaluated. Xu et al. (2019) [139] assessed coupled grey-green infrastructure benefits through Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) and lifecycle cost analysis, demonstrating up to 94% lifecycle cost savings compared to conventional GREI. Jin et al. (2020) [140] designed a hybrid system combining storage tanks with wetlands to synergistically remove COD, TN, and TP, thereby reducing impacts on WWTPs. Cavadini et al. (2024) [141] quantitatively investigated CSO reduction effectiveness and cost–benefit ratios across different Blue–Green Infrastructure (BGI) combinations and implementation rates. M. Wang et al. (2021) [142] demonstrated that grey–green coupled solutions in high-density catchments yield lower lifecycle costs than traditional GREI while exhibiting enhanced operational resilience during system failures. These integrated measures show significant advantages in pipe diameter optimization, burial depth reduction, storage capacity enhancement, and environmental sustainability [143]. Sun et al. (2024) [144] integrated Green Infrastructure (GI) with Grey Infrastructure (GREI) in historical and cultural areas using Genetic Algorithms (GA) and multi-objective optimization, enhancing the region’s flood resistance and resilience. Compared to standalone GREI, the coupled GI-GREI solution achieved 29.0% and 29.6% cost savings and reduced surface overflow by up to 22.6% under system failure scenarios.
However, GI-GREI coupling faces limitations: its control performance degrades under extreme storm events [142,144] and implementation is hindered by limited urban land availability [145]. Future research directions include multi-objective optimization of coupled solutions to identify optimal trade-offs between economic and functional benefits, exploring region-specific cost or area allocation ratios for GREI and GI tailored to local urban characteristics, and quantifying stakeholder preferences (e.g., policymakers and residents) toward GI-GREI development and urban flood risk reduction strategies. Optimized design and dynamic synergy research for grey-green hybrid systems will constitute core directions for urban water system resilience improvement. This paradigm shift will advance urban stormwater management from static “infrastructure superposition” to dynamic “system symbiosis”, providing more resilient solutions to address dual challenges of extreme climate events and urban expansion.
4.3. Deep Learing
Deep learning enables automatic acquisition of hierarchical feature representations through multiple layers of nonlinear modules, eliminating reliance on manually designed feature extractors [146], while being capable of processing extensive monitoring and rainfall data within drainage systems.
Deep learning demonstrates applicability across multiple domains of UDS, including prediction, flood assessment, and Real-Time Control (RTC) [147]. Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)-based models coupled with remote sensing imagery achieve over 90% accuracy in disaster assessment during flood events [148], while facilitating tool-generated 3D flood dynamic models. Through learning complex patterns from historical flood data, Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks enable predictions of flood event timing and magnitude, supporting managerial flood risk evaluations [149]. At the RTC level, Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) learns optimal control strategies via environmental interactions, adapts to varying rainfall conditions and system states, and exhibits lower computational demands with enhanced adaptability compared to reactive and predictive control methods [150].
Deep learning applications in urban drainage systems are progressively transitioning to practical deployment, promising to overcome limitations of conventional approaches and drive the evolution toward intelligent, self-adaptive urban drainage management systems.
5. Conclusions
This paper introduces and briefly discusses adjustable stormwater management facilities within Urban Drainage Systems (UDS), focusing on drainage networks, ancillary Flow Control Devices (FCDs), and Quasi-Detention Basins (QDBs), bridging Green Infrastructure (GI) and Grey Infrastructure (GREI). It further reviews design methodologies and control strategies for drainage networks and QDBs.
As the core component of UDS, drainage network design optimization and resilience enhancement constitute critical measures against extreme climate events. Graph theory-driven topological design (e.g., loop-cutting algorithms and random walk generation) and decentralized layout strategies have significantly improved network redundancy and residual space utilization, effectively mitigating urban flooding risks. Concurrently, intelligent flow control device technologies—including real-time control and distributed gate strategies—optimize overflow management and wastewater treatment plant load balancing through dynamic regulation of network storage-discharge capacities. However, studies on pump control predominantly focus on energy optimization, with insufficient attention to dynamic responses to stormwater and sewage inflow patterns. The optimization process often neglects sewer storage capacity, and limited studies evaluate the inherent storage potential of drainage networks.
QDBs demonstrate spatial adaptability and functional flexibility by integrating conventional grey infrastructure with Low Impact Development (LID) techniques (e.g., rainwater tanks and bioretention cells). Multi-objective optimization algorithms (e.g., Particle Swarm Optimization and Harmony Search) enable coordinated design of detention basin locations and volumes to address dual objectives of flow regulation and pollution control. Hybrid control strategies combining reactive methods (e.g., fuzzy logic control) and predictive approaches (e.g., Model Predictive Control) enhance dynamic response capabilities, achieving concurrent peak flow reduction and pollutant removal. In QDB-related multi-objective control research, most treat water quality improvement as a secondary outcome of detention design, while only a few explicitly target pollutant load reduction. In terms of control strategies, Rule-Based Control (RBC) relies on manually defined rules with poor generalizability, and Model Predictive Control (MPC) remains impractical for real-world applications due to time step constraints.
Coordinated management of drainage networks and QDBs represents a pivotal pathway for enhancing urban stormwater system resilience. Future research should prioritize computational strategy refinement, grey–green infrastructure hybridization, and deep integration of intelligent control frameworks to advance UDS resilience in evolving urban environments.
Author Contributions
W.Q. and J.X.: Investigation, data analysis, validation, writing—original draft. G.F.: Investigation, data analysis, validation, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing, funding acquisition. Y.L., K.-Q.X., Y.H., D.Z., S.C. and Y.P.: Validation, writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Science and Technology Project of Fujian Province in China (No. 2021Y3002) and the Fujian Provincial Environmental Protection Science and Technology Program (No. 2023R019).
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Jiankun Xie and Yiyuan Lin were employed by the company Fujian Academy of Building Research Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| Abbreviations | Description |
| AHP | Analytic Hierarchy Process |
| ANN | Artificial Neural Network |
| BMP | Best Management Practices |
| CSO | Combined Sewer Overflow |
| CSS | Combined Sewer System |
| DEM | Digital Elevation Model |
| DP | Dynamic Programming |
| DTM | Digital Terrain Model |
| FLC | Fuzzy Logic Control |
| GA | Genetic Algorithm |
| GI | Green Infrastructure |
| GBI | Green–Blue Infrastructure |
| GreyI | Grey Infrastructure |
| HGBGI | Hybrid Green–Blue–Grey Infrastructure |
| HSA | Harmony Search Algorithm |
| LASSO | The Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator |
| LID | Low Impact Development |
| LSTM | Long-Short Term Memory |
| MIP | Mixed-Integer Programming |
| MOPSO | Multiple Objective Particle Swarm Optimization |
| PSO | Particle Swarm Optimization |
| QDB | Quasi-Detention Basin |
| RBC | Rule-Based Control |
| RNN | Recurrent Neural Network |
| RTC | Real-time Control |
| SSO | Sanitation Sewer Overflow |
| SUDS | Sustainable Urban Drainage Systems |
| SWMM | Storm Water Management Model |
| TSS | Total Soluble Solid |
| UDS | Urban Drainage System |
| WSUD | Water Sensitive Urban Design |
| WWTP | Wastewater Treatment Plant |
References
- Zhang, W.; Zhou, T.; Wu, P. Anthropogenic Amplification of Precipitation Variability over the Past Century. Science 2024, 385, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajagopalan, S.; Duraisekaran, E.; Mathivanan, M.; Ravikumar, G. Assessing the Impact of Urbanisation on the Hydrology of Tank (Detention Reservoirs) at City, Sub-Basin and Micro-Watershed Scale. Environ. Dev. 2024, 49, 100964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tradowsky, J.S.; Philip, S.Y.; Kreienkamp, F.; Kew, S.F.; Lorenz, P.; Arrighi, J.; Bettmann, T.; Caluwaerts, S.; Chan, S.C.; De Cruz, L.; et al. Attribution of the Heavy Rainfall Events Leading to Severe Flooding in Western Europe during July 2021. Clim. Chang. 2023, 176, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Ren, H.; Qin, J.; Wang, M.; Shi, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, R.; Hu, Y. Analysis of Pollutant Dispersion Patterns in Rivers under Different Rainfall Based on an Integrated Water-Land Model. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 354, 120314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arden, S.; Ma, X.C.; Brown, M. An Ecohydrologic Model for a Shallow Groundwater Urban Environment. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 70, 1789–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, T.D.; Shuster, W.; Hunt, W.F.; Ashley, R.; Butler, D.; Arthur, S.; Trowsdale, S.; Barraud, S.; Semadeni-Davies, A.; Bertrand-Krajewski, J.-L.; et al. SUDS, LID, BMPs, WSUD and More—The Evolution and Application of Terminology Surrounding Urban Drainage. Urban Water J. 2015, 12, 525–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y. Evapotranspiration from Green Infrastructure: Benefit, Measurement, and Simulation; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kourtis, I.M.; Tsihrintzis, V.A.; Baltas, E. A Robust Approach for Comparing Conventional and Sustainable Flood Mitigation Measures in Urban Basins. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 269, 110822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreeja, P.; Gupta, K. An Alternate Approach for Transient Flow Modeling in Urban Drainage Systems. Water Resour. Manag. 2007, 21, 1225–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, W.; Wang, L.; Li, L.; Xu, B. The Scenario Simulations and Several Problems of the Sponge City Construction in Semi-Arid Loess Region, Northwest China. Landsc. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 18, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdi, J. Optimal Operation of Urban Storm Detention Ponds for Flood Management. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 33, 2109–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.; Long, Y.; Wang, Y. Choosing the LID for Urban Storm Management in the South of Taiyuan Basin by Comparing the Storm Water Reduction Efficiency. Water 2019, 11, 2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tansar, H.; Li, F.; Zheng, F.; Duan, H.-F. A Critical Review on Optimization and Implementation of Green-Grey Infrastructures for Sustainable Urban Stormwater Management. AQUA Water Infrastruct. Ecosyst. Soc. 2024, 73, 1135–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muttil, N.; Nasrin, T.; Sharma, A.K. Impacts of Extreme Rainfalls on Sewer Overflows and WSUD-Based Mitigation Strategies: A Review. Water 2023, 15, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckart, K.; McPhee, Z.; Bolisetti, T. Performance and Implementation of Low Impact Development—A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607–608, 413–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngamalieu-Nengoue, U.A.; Martínez-Solano, F.J.; Iglesias-Rey, P.L.; Mora-Meliá, D. Multi-Objective Optimization for Urban Drainage or Sewer Networks Rehabilitation through Pipes Substitution and Storage Tanks Installation. Water 2019, 11, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Ding, W. Vulnerability Analysis of Urban Drainage Systems: Tree vs. Loop Networks. Sustainability 2017, 9, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeini, R.; Afshar, M.H. Arc Based Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm for Optimal Design of Gravitational Sewer Networks. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2017, 8, 207–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeini, R.; Afshar, M.H. Constrained Ant Colony Optimisation Algorithm for the Layout and Size Optimisation of Sanitary Sewer Networks. Urban Water J. 2013, 10, 154–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque, N.; Duque, D.; Aguilar, A.; Saldarriaga, J. Sewer Network Layout Selection and Hydraulic Design Using a Mathematical Optimization Framework. Water 2020, 12, 3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, N.J.; Kuller, M.; Yasmin, T.; Castonguay, A.C.; Copa, V.; Duncan-Horner, E.; Gimelli, F.M.; Jamali, B.; Nielsen, J.S.; Ng, K.; et al. Towards Water Sensitive Cities in Asia: An Interdisciplinary Journey. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 1150–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poustie, M.S.; Deletic, A.; Brown, R.R.; Wong, T.; De Haan, F.J.; Skinner, R. Sustainable Urban Water Futures in Developing Countries: The Centralised, Decentralised or Hybrid Dilemma. Urban Water J. 2015, 12, 543–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque, N.; Scholten, L.; Maurer, M. Exploring Transitions of Sewer Wastewater Infrastructure towards Decentralisation Using the Modular Model TURN-Sewers. Water Res. 2024, 257, 121640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes-Silva, J.D.; Bangura, E.; Helm, B.; Benisch, J.; Krebs, P. The Role of Sewer Network Structure on the Occurrence and Magnitude of Combined Sewer Overflows (CSOs). Water 2020, 12, 2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhshipour, A.E.; Bakhshizadeh, M.; Dittmer, U.; Haghighi, A.; Nowak, W. Hanging Gardens Algorithm to Generate Decentralized Layouts for the Optimization of Urban Drainage Systems. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2019, 145, 4019034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Liu, S.; Li, M.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Hao, X.; Cui, J. Topological Analysis and Application of Urban Drainage Network. Water 2022, 14, 3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, D.; Korving, H.; Clemens-Meyer, F. A Topological Characterisation of Looped Drainage Networks. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2024, 20, 1563–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighi, A. Loop-by-Loop Cutting Algorithm to Generate Layouts for Urban Drainage Systems. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2013, 139, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Dong, X.; Zeng, S. Exploring the Structural Factors of Resilience in Urban Drainage Systems: A Large-Scale Stochastic Computational Experiment. Water Res. 2021, 188, 116475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesarkazzazi, S.; Bakhshipour, A.E.; Hajibabaei, M.; Dittmer, U.; Haghighi, A.; Sitzenfrei, R. Battle of Centralized and Decentralized Urban Stormwater Networks: From Redundancy Perspective. Water Res. 2022, 222, 118910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesarkazzazi, S.; Hajibabaei, M.; Bakhshipour, A.E.; Dittmer, U.; Haghighi, A.; Sitzenfrei, R. Generation of Optimal (de) Centralized Layouts for Urban Drainage Systems: A Graph-Theory-Based Combinatorial Multi-Objective Optimization Framework. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 81, 103827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möderl, M.; Butler, D.; Rauch, W. A Stochastic Approach for Automatic Generation of Urban Drainage Systems. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 59, 1137–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, D.; Ward, S.; Sweetapple, C.; Astaraie-Imani, M.; Diao, K.; Farmani, R.; Fu, G. Reliable, Resilient and Sustainable Water Management: The Safe & SuRe Approach. Glob. Chall. 2017, 1, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Chen, W.; Huang, G. Assessing Urban Pluvial Flood Resilience Based on a Novel Grid-Based Quantification Method That Considers Human Risk Perceptions. J. Hydrol. 2021, 601, 126601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behzadian, K.; Kapelan, Z.; Morley, M.S. Resilience-Based Performance Assessment of Water-Recycling Schemes in Urban Water Systems. Procedia Eng. 2014, 89, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Fu, G.; Farmani, R.; Sweetapple, C.; Butler, D. Topological Attributes of Network Resilience: A Study in Water Distribution Systems. Water Res. 2018, 143, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadiun, S.; Yazdi, J.; Salehi Neyshabouri, S.A.A.; Sadiq, R. Development of a Stochastic Framework to Design/Rehabilitate Urban Stormwater Drainage Systems Based on a Resilient Approach. Urban Water J. 2018, 15, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweetapple, C.; Fu, G.; Farmani, R.; Butler, D. General Resilience: Conceptual Formulation and Quantitative Assessment for Intervention Development in the Urban Wastewater System. Water Res. 2022, 211, 118108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, L. Enhancing Urban Flood Resilience—A Case Study for Policy Implementation. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Water Manag. 2016, 169, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Tan, Q.; Zhu, S. Characteristics of Combined Sewer Overflows in Shanghai and Selection of Drainage Systems. Water Environ. J. 2010, 24, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Huang, G. Integrating Resilience into an Urban Flood Risk Assessment Framework: A Case Study of the Minzhi Region, Shenzhen City. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2023, 37, 1183–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tscheikner-Gratl, F.; Caradot, N.; Cherqui, F.; Leitão, J.P.; Ahmadi, M.; Langeveld, J.G.; Le Gat, Y.; Scholten, L.; Roghani, B.; Rodríguez, J.P.; et al. Sewer Asset Management—State of the Art and Research Needs. Urban Water J. 2019, 16, 662–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J. Remotely Controlled Sewers. Procedia Eng. 2014, 70, 1084–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Garofalo, G.; Giordano, A.; Piro, P.; Spezzano, G.; Vinci, A. A Distributed Real-Time Approach for Mitigating CSO and Flooding in Urban Drainage Systems. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2017, 78, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darsono, S.; Labadie, J.W. Neural-Optimal Control Algorithm for Real-Time Regulation of in-Line Storage in Combined Sewer Systems. Environ. Model. Softw. 2007, 22, 1349–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph-Duran, B.; Ocampo-Martinez, C.; Cembrano, G. Output-Feedback Control of Combined Sewer Networks through Receding Horizon Control with Moving Horizon Estimation. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 8129–8145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sharma, K.; Li, W.; Yuan, Z. Swift Hydraulic Models for Real-Time Control Applications in Sewer Networks. Water Res. 2022, 213, 118141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Martinez, N.; Lindholm, G.; Ratnaweera, H. Manage Sewer In-Line Storage Control Using Hydraulic Model and Recurrent Neural Network. Water Resour. Manag. 2018, 32, 2079–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sufi Karimi, H.; Natarajan, B.; Ramsey, C.L.; Henson, J.; Tedder, J.L.; Kemper, E. Comparison of Learning-Based Wastewater Flow Prediction Methodologies for Smart Sewer Management. J. Hydrol. 2019, 577, 123977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmitessa, R.; Mikkelsen, P.S.; Borup, M.; Law, A.W.K. Soft Sensing of Water Depth in Combined Sewers Using LSTM Neural Networks with Missing Observations. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2021, 38, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Xu, G.; Ding, Y.; Zeng, S.; You, L.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, H. Online Storage Technology of the Separate Sewage System: Demonstration Study in a Typical Plain River Network City. Water 2022, 14, 3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathnayake, U. Static Optimal Control of Combined Sewer Networks under Enhanced Cost Functions to Minimize the Adverse Environmental Effects. ISH J. Hydraul. Eng. 2021, 27, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fecarotta, O.; Cimorelli, L. Optimal Scheduling and Control of a Sewer Pump under Stochastic Inflow Pattern. Urban Water J. 2021, 18, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Yu, Z.; Yin, H.; Xu, Z. Abatement of Sewer Overflow Pollution Based on Distributed Optimal Control Approach. ACS EST Water 2024, 4, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggaber, T.P.; Talley, J.W.; Montestruque, L.A. Using Embedded Sensor Networks to Monitor, Control, and Reduce CSO Events: A Pilot Study. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2007, 24, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathnayake, U.; Anwar, A.H.M.F. Dynamic Control of Urban Sewer Systems to Reduce Combined Sewer Overflows and Their Adverse Impacts. J. Hydrol. 2019, 579, 124150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Liu, P.; Cheng, L.; Liu, W.; Cheng, Q.; Zhou, C. Optimization of In-Pipe Storage Capacity Use in Urban Drainage Systems with Improved DP Considering the Time Lag of Flow Routing. Water Res. 2022, 227, 119350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroll, S.; Weemaes, M.; Van Impe, J.; Willems, P. A Methodology for the Design of RTC Strategies for Combined Sewer Networks. Water 2018, 10, 1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitão, J.P.; Carbajal, J.P.; Rieckermann, J.; Simões, N.E.; Sá Marques, A.; de Sousa, L.M. Identifying the Best Locations to Install Flow Control Devices in Sewer Networks to Enable In-Sewer Storage. J. Hydrol. 2018, 556, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, D.F.; Simões, N.E.; de Sousa, L.M.; Maluf, L.; Sá Marques, A.; Leitão, J.P. Generalizing Multi-Reward Functions Aimed at Identifying the Best Locations to Install Flow Control Devices in Sewer Systems. Urban Water J. 2019, 16, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eulogi, M.; Ostojin, S.; Skipworth, P.; Shucksmith, J.D.; Schellart, A. Hydraulic Optimisation of Multiple Flow Control Locations for the Design of Local Real Time Control Systems. Urban Water J. 2021, 18, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eulogi, M.; Ostojin, S.; Skipworth, P.; Kroll, S.; Shucksmith, J.D.; Schellart, A. Optimal Positioning of RTC Actuators and SuDS for Sewer Overflow Mitigation in Urban Drainage Systems. Water 2022, 14, 3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Leitão, J.P.; Wani, O. Is Flow Control in a Space-Constrained Drainage Network Effective? A Performance Assessment for Combined Sewer Overflow Reduction. Environ. Res. 2021, 202, 111688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalili, H.; Chevalier, L.; Nicklow, J.W. Optimization of Real-Time Control Approach: Number, Placement, and Proportional–Integral–Derivative Control Rules of Flow Control Devices in Distributed Flood Routing. Water 2024, 16, 3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, J.P.; McIntyre, N.; Díaz-Granados, M.; Quijano, J.P.; Maksimović, Č. Monitoring and Modelling to Support Wastewater System Management in Developing Mega-Cities. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 445–446, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heusch, S.; Hanss, H.; Ostrowski, M.; Rosen, R.; Sohr, A. Optimal Control of Sewer Networks Problem Description. In Mathematical Optimization of Water Networks; Martin, A., Klamroth, K., Lang, J., Leugering, G., Morsi, A., Oberlack, M., Ostrowski, M., Rosen, R., Eds.; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2012; pp. 69–82. ISBN 978-3-0348-0436-3. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Qin, H.; Zheng, Y.; Fu, G. Spatial Variations of Pollutants from Sewer Interception System Overflow. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 233, 748–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starzec, M.; Dziopak, J.; Słyś, D. An Analysis of Stormwater Management Variants in Urban Catchments. Resources 2020, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, F.; Mehmood, R.; Katib, I.; Albeshri, A. Analysis of Eight Data Mining Algorithms for Smarter Internet of Things (IoT). Procedia Comput. Sci. 2016, 98, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Li, D.; Xi, Y.; Cen, L. Energy-Saving Optimization of Urban Drainage System Based on Pump Performance. In Proceedings of the 27th Chinese Control and Decision Conference (2015 CCDC), Qingdao, China, 23–25 May 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 308–313. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, Y.K.; Kwon, S.H.; Lee, E.H.; Kim, J.H. Development of Optimal Pump Operation Method for Urban Drainage Systems. In Proceedings of the Advances in Harmony Search, Soft Computing and Applications; Kim, J.H., Geem, Z.W., Jung, D., Yoo, D.G., Yadav, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 63–69. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Kusiak, A.; Zeng, Y.; Wei, X. Modeling and Optimization of a Wastewater Pumping System with Data-Mining Methods. Appl. Energy 2016, 164, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fecarotta, O.; Carravetta, A.; Morani, M.C.; Padulano, R. Optimal Pump Scheduling for Urban Drainage under Variable Flow Conditions. Resources 2018, 7, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimorelli, L.; D’Aniello, A.; Cozzolino, L. Boosting Genetic Algorithm Performance in Pump Scheduling Problems with a Novel Decision-Variable Representation. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2020, 146, 4020023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, M.; Garofalo, G.; Piro, P. Decentralized Real Time Control in Combined Sewer System by Using Smart Objects. Procedia Eng. 2014, 89, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Newhart, K.B.; Holloway, R.W.; Hering, A.S.; Cath, T.Y. Data-Driven Performance Analyses of Wastewater Treatment Plants: A Review. Water Res. 2019, 157, 498–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorelli, D.; Schutz, G. Real-Time Control of a Sewer Network Using a Multi-Goal Objective Function. In Proceedings of the 2009 17th Mediterranean Conference on Control and Automation, Thessaloniki, Greece, 24–26 June 2009; pp. 676–681. [Google Scholar]
- Ryu, J.; Lee, J.; Oh, J. Examination of the Storage Function of Intercepting Sewers Using Long-Term Flow Monitoring Data. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 54, 1299–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroll, S.; Dirckx, G.; Donckels, B.M.R.; Van Dorpe, M.; Weemaes, M.; Willems, P. Modelling Real-Time Control of WWTP Influent Flow under Data Scarcity. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 73, 1637–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakson, G.; Zawilski, M.; Brzezińska, A. Analysis of Combined Sewer Flow Storage Scenarios Prior to Wastewater Treatment Plant. Ecol. Chem. Eng. S 2018, 25, 619–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langeveld, J.; Van Daal, P.; Schilperoort, R.; Nopens, I.; Flameling, T.; Weijers, S. Empirical Sewer Water Quality Model for Generating Influent Data for WWTP Modelling. Water 2017, 9, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Pan, Z.; Chen, Y.; Tan, Z.; Zhang, J. Influent Quality and Quantity Predictionin Wastewater Treatment Plant: ModelConstruction and Evaluation. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2021, 30, 4267–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Vanrolleghem, P.A. An Essential Tool for WRRF Modelling: A Realistic and Complete Influent Generator for Flow Rate and Water Quality Based on Data-Driven Methods. Water Sci. Technol. 2022, 85, 2722–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Vanrolleghem, P.A. An Influent Generator for WRRF Design and Operation Based on a Recurrent Neural Network with Multi-Objective Optimization Using a Genetic Algorithm. Water Sci. Technol. 2022, 85, 1444–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, M.C.; Zeferino, J.A.; Simões, N.E.; Saldarriaga, J.G. Optimal Location and Sizing of Storage Units in a Drainage System. Environ. Model. Softw. 2016, 83, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, H.; Ryu, J.; Oh, J.; Kim, T.-H. Optimal Design of Multi-Storage Network for Combined Sewer Overflow Management Using a Diversity-Guided, Cyclic-Networking Particle Swarm Optimizer—A Case Study in the Gunja Subcatchment Area, Korea. Expert Syst. Appl. 2015, 42, 6966–6975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.; Baek, H.; Lee, G.; Kim, T.-H.; Oh, J. Optimal Planning of Decentralised Storage Tanks to Reduce Combined Sewer Overflow Spills Using Particle Swarm Optimisation. Urban Water J. 2017, 14, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, T.T.; Yazdi, J.; Mousavi, S.J.; Kim, J.H. Linear System Theory-Based Optimization of Detention Basin’s Location and Size at Watershed Scale. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2016, 21, 6016013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Li, M.; Sweetapple, C. A New Framework for Distributed Storage Tanks Placement Based on a Resilience Characteristic Metric and Reduced Modelling. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 342, 118098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Melching, C.S. Experimental Evaluation of the Effect of Storm Movement on Peak Discharge. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2015, 30, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starzec, M.; Dziopak, J.; Słyś, D.; Pochwat, K.; Kordana, S. Dimensioning of Required Volumes of Interconnected Detention Tanks Taking into Account the Direction and Speed of Rain Movement. Water 2018, 10, 1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Tan, Y. Overview on Failures of Urban Underground Infrastructures in Complex Geological Conditions due to Heavy Rainfall in China during 1994–2018. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 76, 103509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelodun, B.; Odey, G.; Lee, S.; Choi, K.S. Investigating the Causal Impacts Relationship between Economic Flood Damage and Extreme Precipitation Indices Based on ARDL-ECM Framework: A Case Study of Chungcheong Region in South Korea. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 95, 104606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.H.; Kim, J.H. Development of a Reliability Index Considering Flood Damage for Urban Drainage Systems. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2019, 23, 1872–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, B.; Bach, P.M.; Deletic, A. Rainwater Harvesting for Urban Flood Management—An Integrated Modelling Framework. Water Res. 2020, 171, 115372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Lee, E.H.; Joo, J.G.; Kim, J.H. Determining Optimal Locations for Rainwater Storage Sites with the Goal of Reducing Urban Inundation Damage Costs. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2017, 21, 2488–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, C.; Han, Q.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Xiao, Y. Coupling Simulation of Pipeline Nodes—Storage Tank Linkage in Urban High-Density Built-up Areas Using Optimization Model. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 357, 120850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Sun, Y.; Sweetapple, C. Optimization of Storage Tank Locations in an Urban Stormwater Drainage System Using a Two-Stage Approach. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 204, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Lu, L.; Huang, X.; Shangguan, H.; Wei, Z. An Optimal Design Strategy of Decentralized Storage Tank Locations for Multi-Objective Control of Initial Rainwater Quality. Water Supply 2020, 20, 2069–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermoso, M.; García-Ruiz, M.J.; Osorio, F. Efficiency of Flood Control Measures in a Sewer System Located in the Mediterranean Basin. Water 2018, 10, 1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Hua, W.; Xiong, L.; He, Z. Novel Design of Volume of Detention Tanks Assisted by a Multi-Source Pollution Overflow Model towards Pollution Control in Urban Drainage Basins. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 12781–12791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J. A Data-Driven Improved Fuzzy Logic Control Optimization-Simulation Tool for Reducing Flooding Volume at Downstream Urban Drainage Systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 732, 138931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, Z.K.; Hodges, C.C.; Dymond, R.L. Simulation and Assessment of Long-Term Stormwater Basin Performance under Real-Time Control Retrofits. Urban Water J. 2020, 17, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishegar, S.; Duchesne, S.; Pelletier, G. Optimization Methods Applied to Stormwater Management Problems: A Review. Urban Water J. 2018, 15, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.D.; Fletcher, T.D.; Burns, M.J.; Cherqui, F. Real Time Control of Rainwater Harvesting Systems: The Benefits of Increasing Rainfall Forecast Window. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2020WR027856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Xia, J.; She, D.; Guo, Q.; Su, Y.; Wang, W. Integrated Intra-Storm Predictive Analysis and Real-Time Control for Urban Stormwater Storage to Reduce Flooding Risk in Cities. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 92, 104506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, L.; Barreiro-Gomez, J.; Escobar, E.; Téllez, D.; Quijano, N.; Ocampo-Martinez, C. Modeling and Real-Time Control of Urban Drainage Systems: A Review. Adv. Water Resour. 2015, 85, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mounce, S.R.; Shepherd, W.; Ostojin, S.; Abdel-Aal, M.; Schellart, A.N.A.; Shucksmith, J.D.; Tait, S.J. Optimisation of a Fuzzy Logic-Based Local Real-Time Control System for Mitigation of Sewer Flooding Using Genetic Algorithms. J. Hydroinformatics 2020, 22, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zug, M.; Faure, D.; De Belly, B.; Phan, L. Use of Real Time Control Modelling on the Urban Sewage System of Nancy. Water Sci. Technol. 2001, 44, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akin, A.A.; Hathaway, J.M.; Khojandi, A. Turbidity Informed Real-Time Control of a Dry Extended Detention Basin: A Case Study. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2022, 8, 2040–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharior, S.; McDonald, W.; Parolari, A.J. Improved Reliability of Stormwater Detention Basin Performance through Water Quality Data-Informed Real-Time Control. J. Hydrol. 2019, 573, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, C.; Kenway, S.; Hassall, M.; Yuan, Z. Expert Opinion on Risks to the Long-Term Viability of Residential Recycled Water Schemes: An Australian Study. Water Res. 2017, 120, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Roman, D.; Braga, A.; Shetty, N.; Culligan, P. Design and Modeling of an Adaptively Controlled Rainwater Harvesting System. Water 2017, 9, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altobelli, M.; Evangelisti, M.; Maglionico, M. Multi-Objective Performance of Detention Basins and Rainwater Harvesting Systems Using Real-Time Controls with Rainfall Forecasts. Water 2023, 16, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carp, D.; Barbu, M.; Mînzu, V. Network Discharge Control Using a Fuzzy Logic Approach. In Proceedings of the 2013 4th International Symposium on Electrical and Electronics Engineering (ISEEE), Galati, Romania, 11–13 October 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Barbu, M.; Vilanova, R.; Santin, I. Fuzzy Control Applied on a Benchmark Simulation Model for Sewer Networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 20th International Conference on System Theory, Control and Computing (ICSTCC), Sinaia, Romania, 13–15 October 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 180–185. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, R.; Maier, H.R.; Thyer, M.A.; Dandy, G.C.; Tan, Y.; Chhay, M.; Sau, T.; Lam, V. Calibration-Free Approach to Reactive Real-Time Control of Stormwater Storages. J. Hydrol. 2022, 614, 128559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Bartos, M. Model Predictive Control of Stormwater Basins Coupled with Real-Time Data Assimilation Enhances Flood and Pollution Control under Uncertainty. Water Res. 2023, 235, 119825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Z.; Guan, Z.; Liu, Z.; Yang, D. Influence of Short-Term Rainfall Forecast Error on Flood Forecast Operation: A Risk Assessment Based on Bayesian Theory. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2020, 26, 2447–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Shen, X.; Wen, J.; Wang, H.; Zhou, X. Evaluating and Modeling the Reliability of Continuous No-Rain Forecast from TIGGE Based on the First-Passage Problem and Fuzzy Mathematics. J. Hydrometeorol. 2023, 26, 1119–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freni, G.; Liuzzo, L. Effectiveness of Rainwater Harvesting Systems for Flood Reduction in Residential Urban Areas. Water 2019, 11, 1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Chiano, M.G.; Marchioni, M.; Raimondi, A.; Sanfilippo, U.; Becciu, G. Probabilistic Approach to Tank Design in Rainwater Harvesting Systems. Hydrology 2023, 10, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Matteo, M.; Liang, R.; Maier, H.R.; Thyer, M.A.; Simpson, A.R.; Dandy, G.C.; Ernst, B. Controlling Rainwater Storage as a System: An Opportunity to Reduce Urban Flood Peaks for Rare, Long Duration Storms. Environ. Model. Softw. 2019, 111, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullapudi, A.; Lewis, M.J.; Gruden, C.L.; Kerkez, B. Deep Reinforcement Learning for the Real Time Control of Stormwater Systems. Adv. Water Resour. 2020, 140, 103600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Xia, J.; She, D.; Ding, W.; Jiang, J.; Liu, B.; Zhao, F. A Predictive Fuzzy Logic and Rule-Based Control Approach for Practical Real-Time Operation of Urban Stormwater Storage System. Water Res. 2024, 266, 122437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiliev, I.; Luca, L.; Barbu, M.; Vilanova, R.; Caraman, S. Reducing the Environmental Impact of Sewer Network Overflows Using Model Predictive Control Strategy. Water Resour. Res. 2024, 60, e2023WR035448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneses, E.J.; Gaussens, M.; Jakobsen, C.; Mikkelsen, P.S.; Grum, M.; Vezzaro, L. Coordinating Rule-Based and System-Wide Model Predictive Control Strategies to Reduce Storage Expansion of Combined Urban Drainage Systems: The Case Study of Lundtofte, Denmark. Water 2018, 10, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishegar, S.; Duchesne, S.; Pelletier, G. An Integrated Optimization and Rule-Based Approach for Predictive Real Time Control of Urban Stormwater Management Systems. J. Hydrol. 2019, 577, 124000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilodeau, K.; Pelletier, G.; Duchesne, S. Real-Time Control of Stormwater Detention Basins as an Adaptation Measure in Mid-Size Cities. Urban Water J. 2018, 15, 858–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannina, G.; Viviani, G. An Urban Drainage Stormwater Quality Model: Model Development and Uncertainty Quantification. J. Hydrol. 2010, 381, 248–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastgir, A.; Satish, R.; Hajibabaei, M.; Oberascher, M.; Sitzenfrei, R. Modeling Multiple-Pipe Failures in Stormwater Networks Using Graph Theory. J. Hydroinformatics 2024, 26, 3027–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention Is All You Need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30 (nips 2017); Guyon, I., Luxburg, U.V., Bengio, S., Wallach, H., Fergus, R., Vishwanathan, S., Garnett, R., Eds.; Neural Information Processing Systems (nips): La Jolla, CA, USA, 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, P.; Zhu, F.; Li, P.; Kim, J.; Sheng, B.; Mao, L. Hierarchical Rendering System Based on Viewpoint Prediction in Virtual Reality. In Proceedings of the Advances in Computer Graphics; Magnenat-Thalmann, N., Stephanidis, C., Wu, E., Thalmann, D., Sheng, B., Kim, J., Papagiannakis, G., Gavrilova, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 24–32. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, R.; Fang, F.; Salinas, P.; Pain, C.C. Unstructured Mesh Adaptivity for Urban Flooding Modelling. J. Hydrol. 2018, 560, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Y.; Zheng, S.; Chen, G.; Zhao, P.; Wang, C. High Efficiency Integrated Urban Flood Inundation Simulation Based on the Urban Hydrologic Unit. J. Hydrol. 2024, 630, 130724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Guo, H.; Zeng, S. Enhancing Future Resilience in Urban Drainage System: Green versus Grey Infrastructure. Water Res. 2017, 124, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Liu, L.; Tao, S. Determination of the Cost-Benefit Efficient Interval for Sponge City Construction by a Multi-Objective Optimization Model. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 10, 1072505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, N.S.V.; Borup, M.; Madsen, H.; Mark, O.; Arnbjerg-Nielsen, K.; Mikkelsen, P.S. Integrated Stormwater Inflow Control for Sewers and Green Structures in Urban Landscapes. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Tang, T.; Jia, H.; Xu, M.; Xu, T.; Liu, Z.; Long, Y.; Zhang, R. Benefits of Coupled Green and Grey Infrastructure Systems: Evidence Based on Analytic Hierarchy Process and Life Cycle Costing. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 151, 104478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Wu, W.; Li, J.; Yang, F.; Zhou, B. Simulation and Engineering Demonstration of the Advanced Treatment of Rainy Overflow Wastewater Using a Combined System of Storage Tank-wastewater Treatment Plant-wetland. Water Environ. Res. 2020, 92, 1057–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavadini, G.B.; Rodriguez, M.; Cook, L.M. Connecting Blue-Green Infrastructure Elements to Reduce Combined Sewer Overflows. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 365, 121465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zheng, Y.; Li, S.; Tan, S.K. Life-Cycle Cost Analysis and Resilience Consideration for Coupled Grey Infrastructure and Low-Impact Development Practices. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 75, 103358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhshipour, A.E.; Dittmer, U.; Haghighi, A.; Nowak, W. Hybrid Green-Blue-Gray Decentralized Urban Drainage Systems Design, a Simulation-Optimization Framework. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 249, 109364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Rao, Q.; Xiong, Z.; Liu, M.; Liu, Y.; Fan, C.; Li, J.; Tan, S.K.; Wang, M.; Zhang, D. Optimized Resilience Coupled with Cost-Effectiveness for Grey and Green Infrastructure: A Case Study in a Historical and Cultural Area, Guangzhou, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 167, 112684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Yi, W.; Yuan, P.; Song, Y. Optimization and Trade-off Framework for Coupled Green-Grey Infrastructure Considering Environmental Performance. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 329, 117041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep Learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Jin, Y.; Sun, S.; Yuan, Z.; Butler, D. The Role of Deep Learning in Urban Water Management: A Critical Review. Water Res. 2022, 223, 118973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, U.; Perez, P.; Li, W.; Barthelemy, J. How Computer Vision Can Facilitate Flood Management: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2021, 53, 102030–102047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Zhou, Q.; Guo, J.; Guo, S.; Wang, L. Deep Learning with Long Short-Term Memory Neural Networks Combining Wavelet Transform and Principal Component Analysis for Daily Urban Water Demand Forecasting. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 171, 114571–114584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Fu, G.; Xin, K.; Zhang, Z.; Liao, Z. Improving the Interpretability of Deep Reinforcement Learning in Urban Drainage System Operation. Water Res. 2024, 249, 120912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).