A New Insight into Sulfate Contamination in Over-Exploited Groundwater Areas: Integrating Multivariate and Geostatistical Techniques
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area Overview
2.2. Hydrogeological Conditions
2.3. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.3.1. Sample Collection
2.3.2. Sample Analysis and Testing
2.4. Data Analysis
2.4.1. Data Preprocessing
2.4.2. Statistical Analysis and Spatial Interpolation Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of Groundwater Quality
3.2. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of SO42− in Groundwater
3.2.1. Variations in SO42− Across Distinct Hydrogeological Units
3.2.2. Variation of SO42− with Groundwater Depth
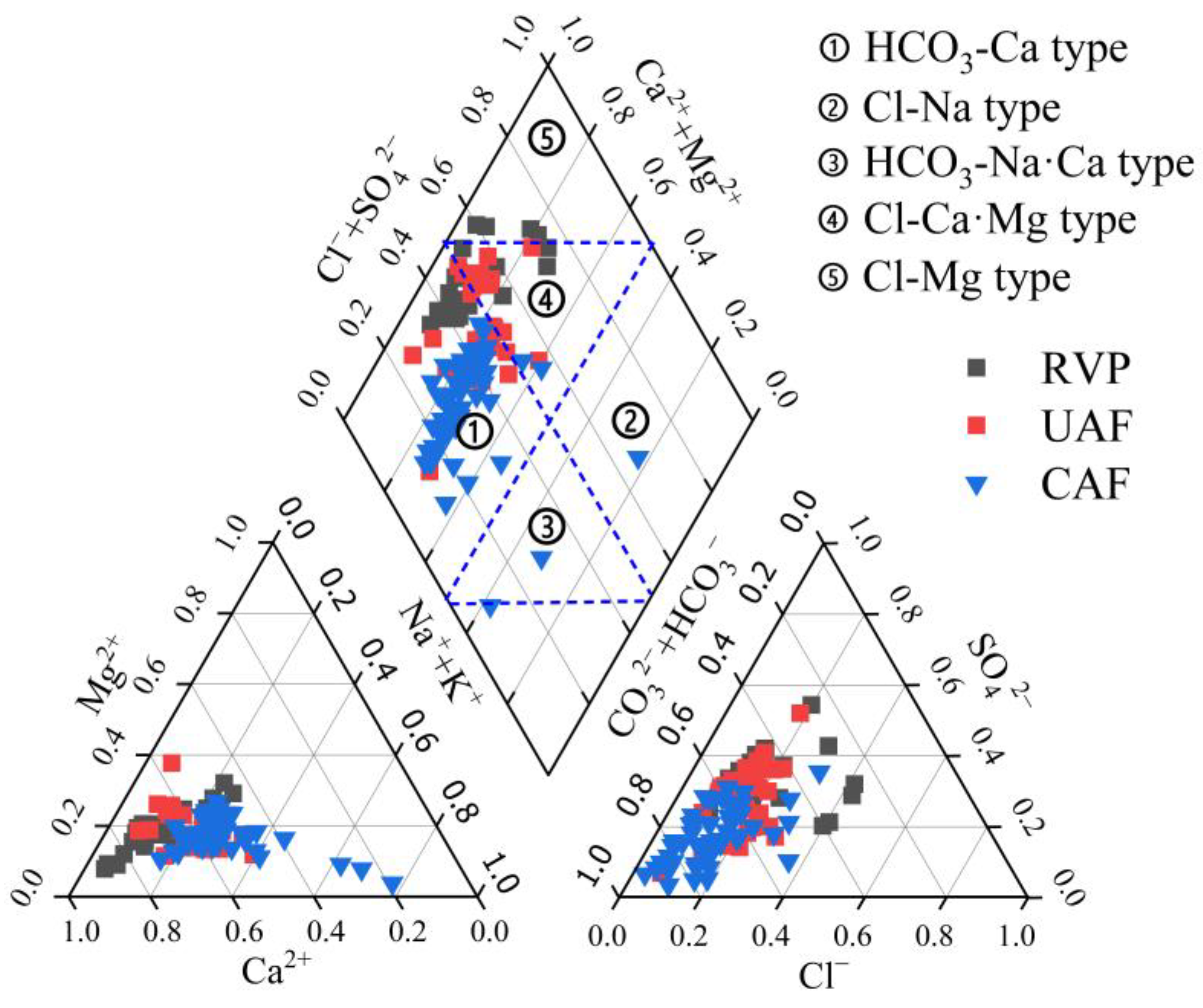
3.3. Hydrochemical Types of Groundwater
3.4. Identification of SO42− Sources in Groundwater
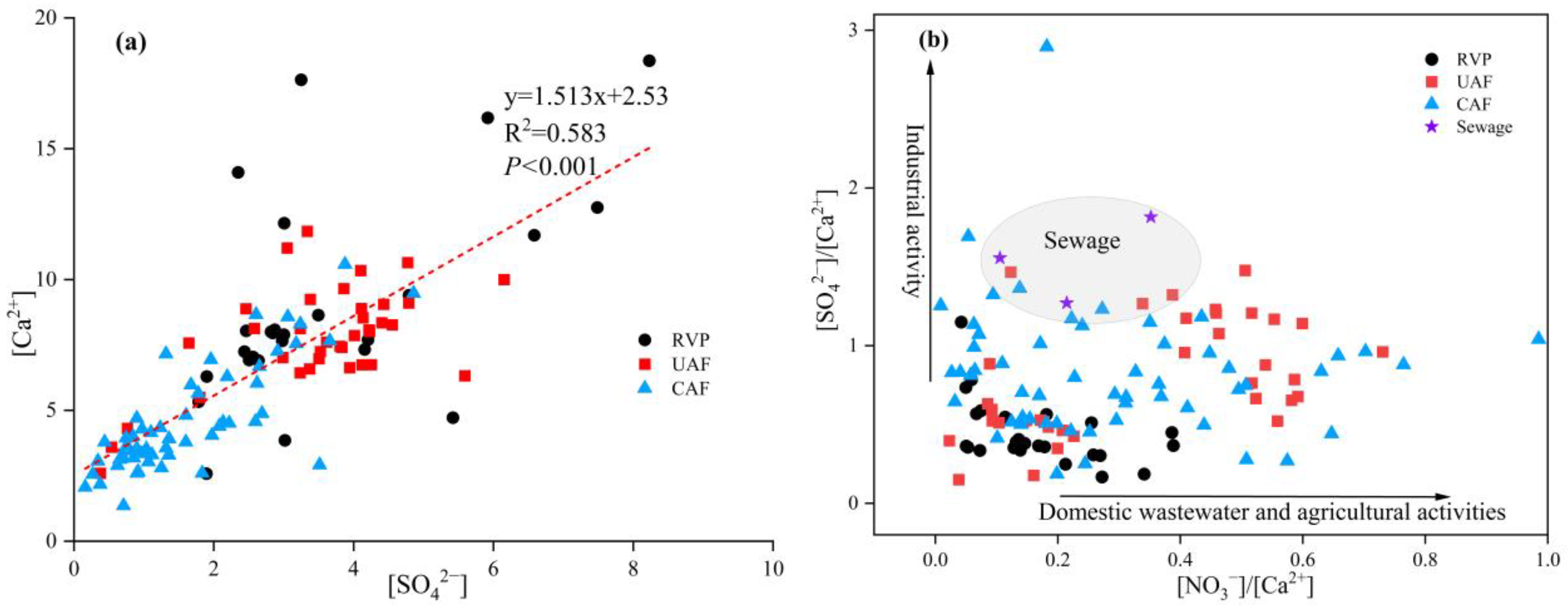
3.4.1. Identification of SO42− Sources Using Hydrochemical Methods
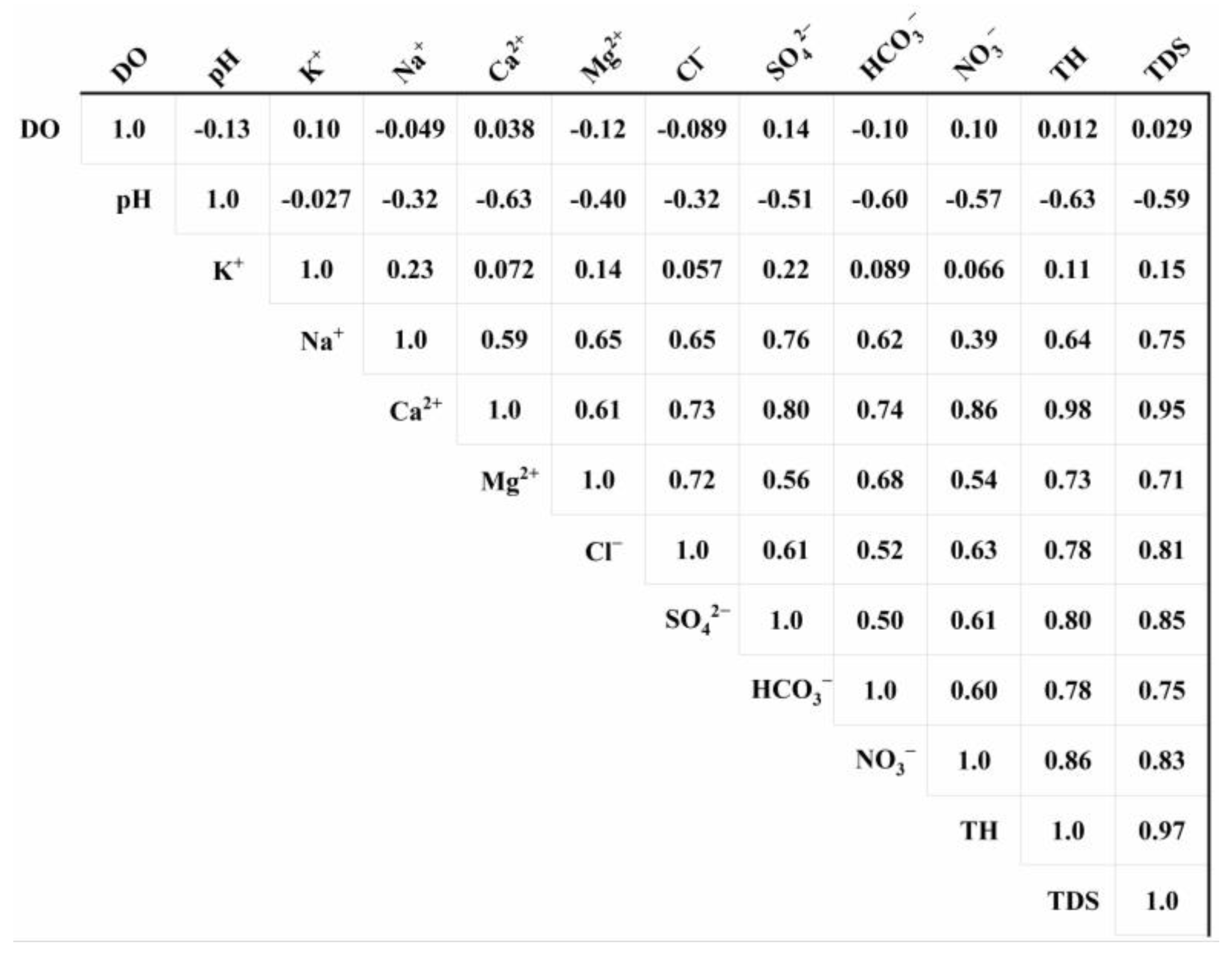
3.4.2. Identification of SO42− Sources Using Correlation Analysis
3.4.3. Identification of Sulfate Sources Using PCA
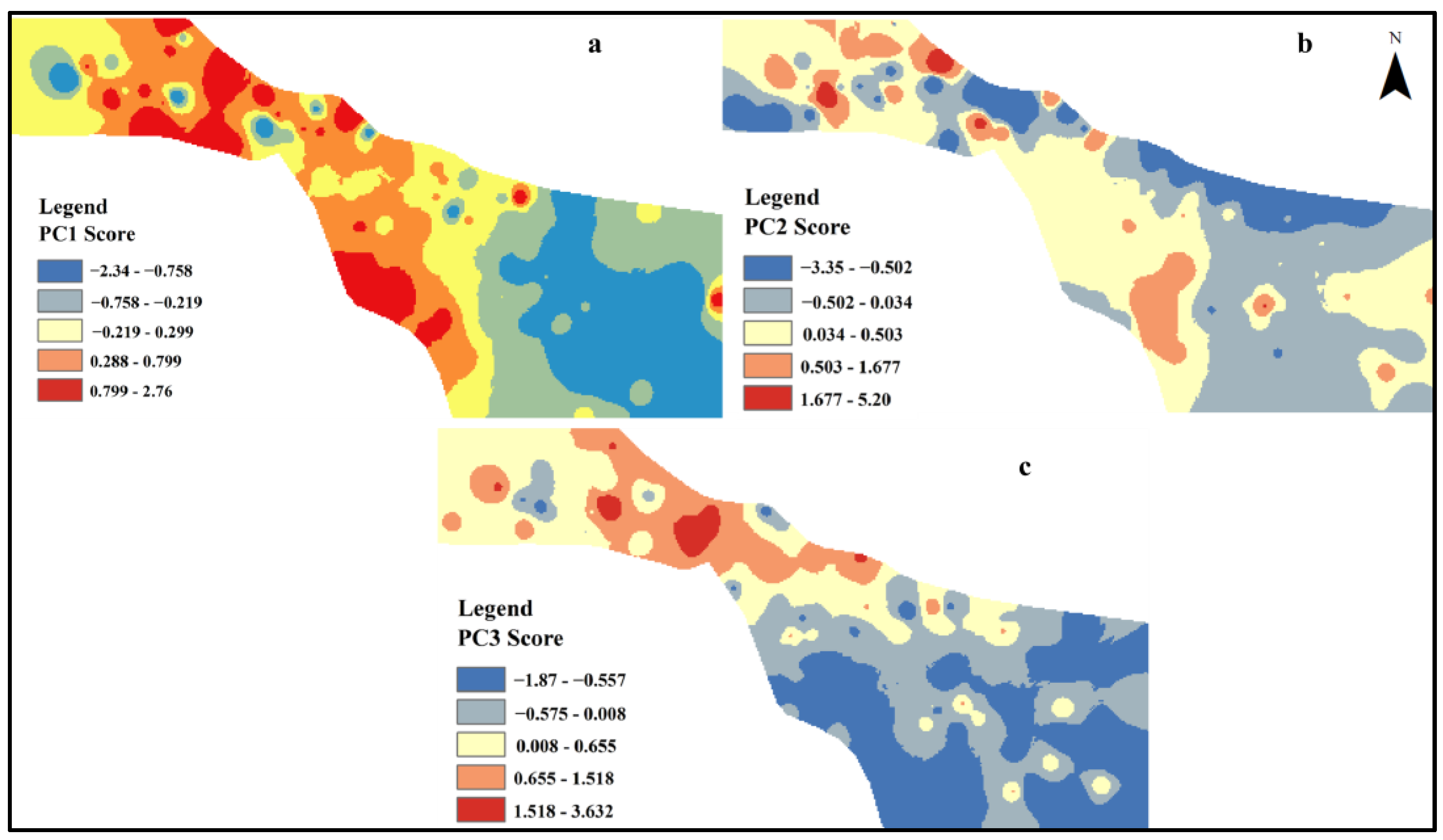
3.5. Spatial Distribution of Sulfate Sources in Groundwater
4. The Limitations of This Study
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Lu, C. Tracing sulfate origin and transformation in an area with multiple sources of pollution in northern China by using environmental isotopes and Bayesian isotope mixing model. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 115105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, R. Human health risk assessment of heavy metals in groundwater in the luan river catchment within the north China Plain. Geofluids 2020, 2020, 8391793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.; Kim, J.; Lee, J. Seasonal and spatial contributions of sulfate and trace elements in river water in mining districts: Insights from hydrogeochemical and isotopic analysis based on statistical models. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 488, 137246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yustika, R.D.; Handayani, C.O.; Dewi, T.; Yanti, D.; Dariah, A. Risk assessment for non-carcinogenic effect posed by sulfates in water on the health of residents around The Sumpur River, West Sumatra-Indonesia. Toxicol. Rep. 2025, 14, 101921. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, B.; Shi, X.; Guo, J. Interaction of sulfate-reducing bacteria and methanogenic archaea in urban sewers, leads to increased risk of proliferation of antibiotic resistance genes. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 368, 125777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Q. Research advances in identifying sulfate contamination sources of water environment by using stable isotopes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tostevin, R.; Turchyn, A.V.; Farquhar, J.; Johnston, D.T.; Eldridge, D.L.; Bishop, J.K.; McIlvin, M. Multiple sulfur isotope constraints on the modern sulfur cycle. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2014, 396, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, A.; Zhang, B. Sulfur and oxygen isotope compositions of dissolved sulfate in the Yangtze River during high water period and its sulfate source tracing. Earth Sci. 2014, 39, 1647–1654. [Google Scholar]
- Qiong, X.I.A.O.; Wen, L.I.U.; Fang, G.U.O.; Moucheng, P.A.N.; Shi, Y.U. Using δ34S-SO42−and δ15N-NO3−, δ18O-NO3− to trace the sources of sulfur and nitrate in Lihu lake undergound water, Guangxi. China Environ. Sci. 2015, 36, 2877–2886. [Google Scholar]
- Otero, N.; Soler, A. Sulphur isotopes as tracers of the influence of potash mining in groundwater salinization in the Llobregat Basin (NE Spain). Water Res. 2002, 36, 3989–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Tang, C.; Chen, J.; Song, X.F.; Li, F.D.; Sakura, Y. Spatial characteristics of water quality, stable isotopes and tritium associated with groundwater flow in the Hutuo River alluvial fan plain of the North China Plain. Hydrogeol. J. 2008, 16, 1003–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Miao, L.; Wang, H.; Hou, J.; Li, Y. How rapid urbanization drives deteriorating groundwater quality in a provincial capital of China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2020, 29, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Liu, C.L.; Jiang, J.M.; Pei, L.X.; Guo, J. Risk assessments of groundwater pollution in the shijiazhuang reach of the hutuo river, China. Geol. Bull. China 2008, 27, 1065–1070. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, H. Assessment of sources and transformation of nitrate in the alluvial-pluvial fan region of north China using a multi-isotope approach. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 89, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannel, P.R.; Lee, S.; Kanel, S.R.; Khan, S.P. Chemometric application in classification and assessment of monitoring locations of an urban river system. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 582, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB/T14848-2017; Standard for Groundwater Quality. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’ s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Fei, Y.; Chen, H.; Qian, Y.; Dun, Y. Investigation of quality and pollution characteristics of groundwater in the Hutuo River Alluvial Plain, North China Plain. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín del Campo, M.A.; Esteller, M.V.; Expósito, J.L.; Hirata, R. Impacts of urbanization on groundwater hydrodynamics and hydrochemistry of the Toluca Valley aquifer (Mexico). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 2979–2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, M.; Zhu, L. Groundwater quality assessment and pollution source apportionment in an intensely exploited region of northern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 16639–16650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Abdulraheem, M.I.; Li, L.; Moshood, A.Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Hu, J.D. Spatial analysis techniques for assessing groundwater vulnerability: A strategic approach to proactive conservation and mitigation strategies. Environ Earth Sci. 2024, 83, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakóbczyk-Karpierz, S.; Ślósarczyk, K. Isotopic signature of anthropogenic sources of groundwater contamination with sulfate and its application to groundwater in a heavily urbanized and industrialized area (Upper Silesia, Poland). J. Hydrol. 2022, 612, 128255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, C.H. Effect of land use and urbanization on hydrochemistry and contamination of groundwater from Taejon area, Korea. J. Hydrol. 2001, 253, 194–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Qian, H.; Ren, W.; Wang, H.; Liu, F.; Yang, F. Hydrogeochemical characterization and quality assessment of groundwater based on integrated-weight water quality index in a concentrated urban area. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 260, 121006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, R.; Wu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Xie, D.; Zhang, C. Assessing the impact of natural and anthropogenic activities on groundwater quality in coastal alluvial aquifers of the lower Liaohe River Plain, NE China. Appl. Geochem. 2013, 31, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Q. Assessment of the evolution of groundwater chemistry and its controlling factors in the Huangshui River Basin of northwestern China, using hydrochemistry and multivariate statistical techniques. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samantara, M.K.; Padhi, R.K.; Satpathy, K.K.; Sowmya, M.; Kumaran, P. Groundwater nitrate contamination and use of Cl/Br ratio for source appointment. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murgulet, D.; Tick, G.R. Understanding the sources and fate of nitrate in a highly developed aquifer system. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2013, 155, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, H.; Fu, Y.; Gao, Z.; Nan, T.; Li, Z. Spatial distribution and controlling mechanisms of high fluoride groundwater in the coastal plain of Bohai Rim, North China. J. Hydrol. 2023, 617, 128952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, G.; Li, Y.; Wei, Z.; Lin, W.; Qin, X.; Long, X. Hydrogeochemistry of geothermal water in Huangshadong and adjacent areas of Guangdong province: Implications for water-rock interaction. Geothermics 2024, 122, 103084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, H. Spatiotemporal variation in groundwater quality and source apportionment along the ye river of north China using the PMF model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, N.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Q. Research on the features and driving factors of shallow groundwater quality in arid areas, northwest China. Water 2025, 17, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Cao, S.; Li, B. Evolution of groundwater hydrochemical characteristics and formation mechanism during groundwater recharge: A case study in the Hutuo River alluvial–pluvial fan, North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 915, 170159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, J.; Zhou, Z.; Cao, W. Tracing the source and behaviour of sulphate in karst reservoirs, using stable isotopes and Bayesian isotopic-mixing models. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 958, 177994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Gao, H.; Cui, M.; Chai, S. A multiple isotope (S, H, O and C) approach to estimate sulfate increasing mechanism of groundwater in coal mine area. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 900, 165852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Parameters | Min | Max | Mean | SD | RES (%) | Standard |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DO | 1.04 | 13.8 | 4.91 | 2.66 | 0 | — |
| pH | 6.53 | 8.47 | 7.47 | 0.356 | 0 | 6.5–8.5 |
| K+ | 0.12 | 25.9 | 2.29 | 2.57 | 0 | — |
| Na+ | 8.78 | 172 | 34.7 | 26.4 | 0 | 200 |
| Ca2+ | 27.2 | 367 | 131 | 63.8 | 0 | — |
| Mg2+ | 10.3 | 102 | 32.0 | 13.8 | 0 | — |
| Cl− | 11.9 | 379 | 71.4 | 59.7 | 1.7 | 250 |
| SO42− | 12.9 | 395 | 127 | 77.2 | 5.1 | 250 |
| HCO3− | 109 | 565 | 296 | 72.6 | 0 | — |
| NO3− | 0.24 | 440 | 61.8 | 70.2 | 22.0 | 88.6 |
| TH | 115 | 1339 | 458 | 198 | 50.0 | 450 |
| TDS | 174 | 2091 | 628 | 292 | 8.5 | 1000 |
| Parameters | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| TH | 0.825 | 0.529 | −0.024 |
| NO3− | 0.820 | 0.224 | 0.178 |
| Ca2+ | 0.814 | 0.470 | 0.064 |
| pH | −0.814 | 0.157 | 0.070 |
| HCO3− | 0.751 | 0.225 | −0.305 |
| TDS | 0.739 | 0.652 | 0.009 |
| Mg2+ | 0.589 | 0.522 | −0.264 |
| K+ | −0.112 | 0.781 | 0.044 |
| Na+ | 0.359 | 0.769 | −0.065 |
| Cl− | 0.523 | 0.688 | −0.138 |
| SO42− | 0.592 | 0.595 | 0.222 |
| DO | −0.009 | −0.006 | 0.940 |
| Eigenvalue | 6.98 | 1.30 | 1.14 |
| Contribution Rate (%) | 58.2 | 10.8 | 9.46 |
| Cumulative Contribution Rate (%) | 58.2 | 69.0 | 78.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Wang, Q.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q. A New Insight into Sulfate Contamination in Over-Exploited Groundwater Areas: Integrating Multivariate and Geostatistical Techniques. Water 2025, 17, 1530. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101530
Wang L, Wang Q, Li W, Liu Y, Zhang Q. A New Insight into Sulfate Contamination in Over-Exploited Groundwater Areas: Integrating Multivariate and Geostatistical Techniques. Water. 2025; 17(10):1530. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101530
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Li, Qi Wang, Wenchang Li, Yifeng Liu, and Qianqian Zhang. 2025. "A New Insight into Sulfate Contamination in Over-Exploited Groundwater Areas: Integrating Multivariate and Geostatistical Techniques" Water 17, no. 10: 1530. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101530
APA StyleWang, L., Wang, Q., Li, W., Liu, Y., & Zhang, Q. (2025). A New Insight into Sulfate Contamination in Over-Exploited Groundwater Areas: Integrating Multivariate and Geostatistical Techniques. Water, 17(10), 1530. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101530







