Study on the Pollution Mechanism and Driving Factors of Groundwater Quality in Typical Industrial Areas of China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Geology and Hydrogeology
2.3. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.4. Data Analysis Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Groundwater Chemical Composition Characteristics
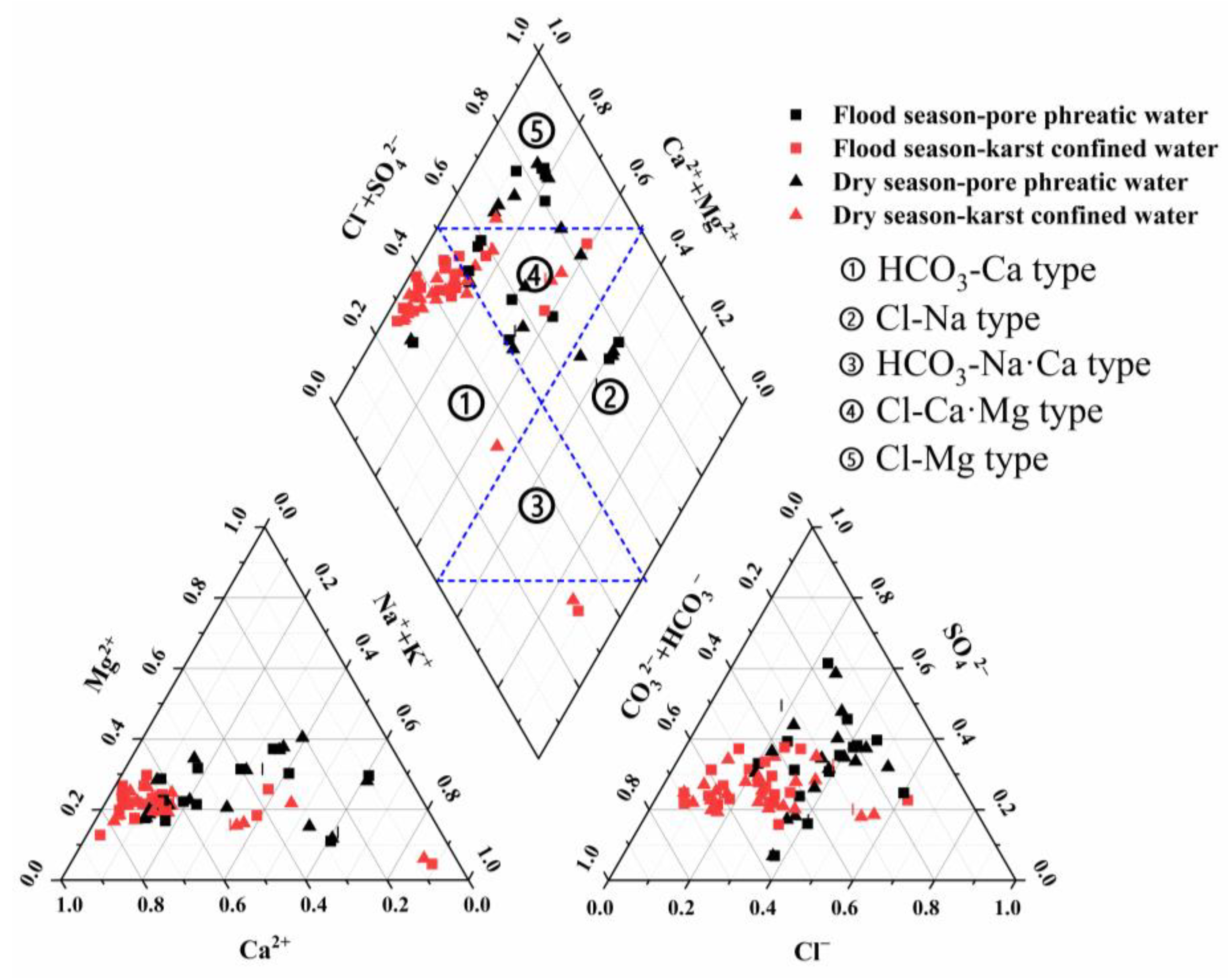
3.2. Analysis of Groundwater Chemical Types
3.3. Control Factors and Sources of Groundwater Ions
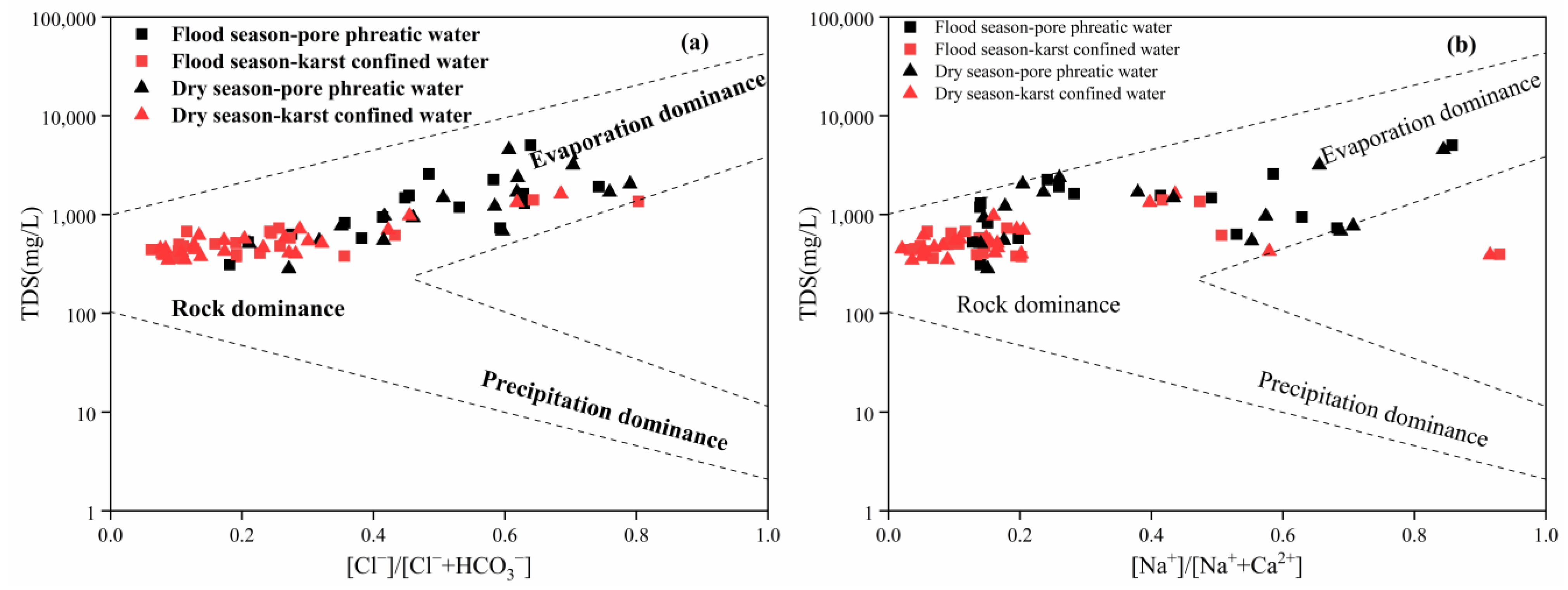
3.3.1. Analysis of Control Factors Based on Gibbs Diagrams
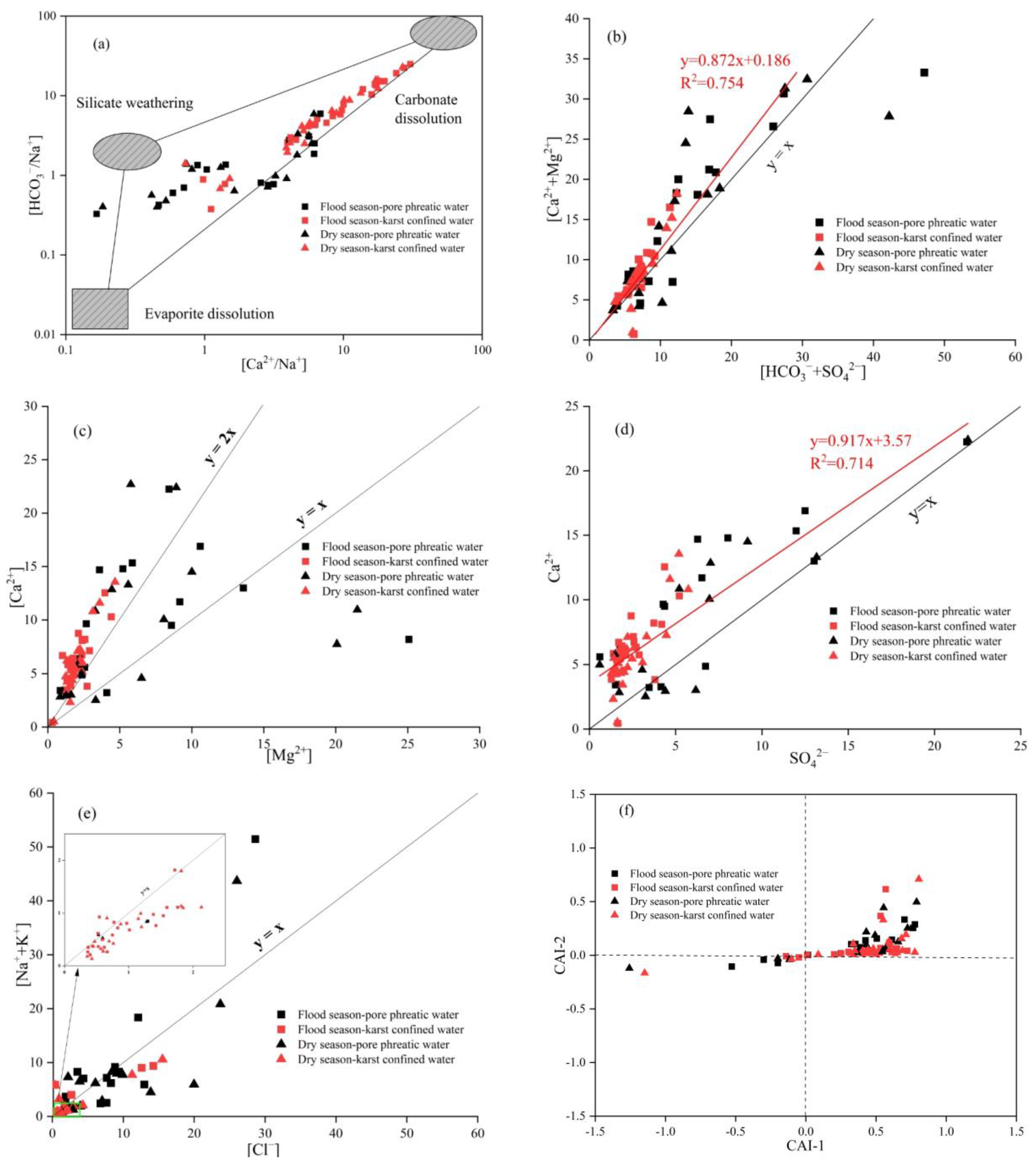
3.3.2. Identifying the Sources of Hydrochemical Parameters
3.4. Impact of Human Activities
3.5. Identification of the Main Factors Controlling Groundwater Quality
3.5.1. Primary Factors Influencing Groundwater Quality During the Flood Season
3.5.2. Primary Factors Influencing Groundwater Quality During the Dry Season
4. Limitations of This Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Velis, M.; Conti, K.I.; Biermann, F. Groundwater and human development: Synergies and trade-offs within the context of the sustainable development goals. Sustain. Sci. 2017, 12, 1007–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Miao, L.; Wang, H.; Hou, J.; Li, Y. How Rapid Urbanization Drives Deteriorating Groundwater Quality in a Provincial Capital of China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2020, 29, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picetti, R.; Deeney, M.; Pastorino, S.; Miller, M.R.; Shah, A.; Leon, D.A.; Dangour, A.D.; Green, R. Nitrate and nitrite contamination in drinking water and cancer risk: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Environ. Res. 2022, 210, 112988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Backer, L.C. Assessing the acute gastrointestinal effects of ingesting naturally occurring, high levels of sulfate in drinking water. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2000, 37, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teklearegay, T.; Atlabachew, A.; Abebe, A.; Jothimani, M. Comprehensive hydrogeochemical and statistical assessment of groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation in the Demie River catchment, Southern Ethiopia. SN Appl. Sci. 2025, 7, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Duan, L.; Shi, Z.; Liang, X.; Lv, S.; Wang, G.; Yu, R. Hydrochemical assessments and driving forces of groundwater quality and potential health risks of sulfate in a coalfield, northern Ordos Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 835, 155519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewusi, A.; Sunkari, E.D.; Seidu, J.; Coffie-Anum, E. Hydrogeochemical characteristics, sources and human health risk assessment of heavy metal dispersion in the mine pit water-surface water-groundwater system in the largest manganese mine in ghana. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 26, 102312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Xie, Y.; Su, J.; Lu, S. Assessment of groundwater quality of unconfined aquifers in an urbanized area using the water quality index method. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 64870–64883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, T.L.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.W. Temporal and spatial variations hydrochemical components and driving factors in Baiyangdian lake in the northern plain of China. J. Groundw. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.S.; Wang, G.; Xia, J.; Chen, J. Quantification of effects of climate variations and human activities on runoff by a monthly water balance model: A case study of the Chaobai River basin in northern China. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Y.K.; Zhao, Y. Evaluation on quality and health risk of groundwater in a highly urbanized watershed, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 27136–27154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB/T14848-2017; Standard for Groundwater Quality. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’ s Republic of China. Ministry of Natural Resources of the People’s Republic of China (MNRPRC): Beijing, China, 2017.
- Li, S.L.; Liu, C.Q.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Chetelat, B.; Wang, B.; Wang, F. Assessment of the sources of nitrate in the Changjiang River, China using a nitrogen and oxygen isotopic approach. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1573–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Xiong, X.; Wu, T.; Hu, R.; Chen, Y.F.; Yang, Z. Pore-scale study of particle transport and clogging mechanisms in a porous micromodel. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 362, 131929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanale, C.; Losacco, D.; Triozzi, M.; Massarelli, C.; Uricchio, V.F. An Overall Perspective for the Study of Emerging Contaminants in Karst Aquifers. Resources 2022, 11, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Z.; Carroll, K.C.; Brusseau, M.L. Characterization and quantification of groundwater sulfate sources at a mining site in an arid climate: The Monument Valley site in Arizona, USA. J. Hydrol. 2013, 504, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.B.; Long, W.; Jie, Z.; Zhai, T.L. Hydrochemical variation characteristics and driving factors of surface water in arid Areas—A case study of Beichuan River in Northwest China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1493390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andres, M.; Paul, S. Groundwater chemistry and the gibbs diagram. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 97, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Sun, B.; Zhang, S.; Li, G.; Tian, Z.; Guo, Z. Ion sources and seasonal recharge characteristics of groundwater around Dali lake in semi-arid region of inner Mongolia plateau, China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2025, 269, 107612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Dong, S.; Wang, H.; Yang, J.; Huang, H.; Dong, X.; Yu, B. Hydrogeochemical processes and groundwater quality assessment for different aquifers in the Caojiatan coal mine of Ordos Basin, northwestern China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, C.; Xiang, W.; Zhang, S. Evaluation of the hydrochemical evolution characteristics and renewable capacity of deep fresh groundwater in the Hangzhou bay new zone, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Liu, G.; Zou, Y.; Li, X.; Ji, M.; Li, D. Coupled action of rock weathering and aquatic photosynthesis: Influence of the biological carbon pump effect on the sources and deposition of organic matter in Ngoring Lake, Qinghai–Tibet Plateau, China. Catena 2021, 203, 105370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Shao, J.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Q. Groundwater circulation and hydrogeochemical evolution in Nomhon of Qaidam basin, northwest China. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 126, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, R.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y. Hydrochemical variations and driving mechanisms in a large linked river-irrigation-lake system. Environ. Res. 2023, 225, 115596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billong, P.T.N.; Feumba, R.; Ndjigui, P.D. Hydrogeochemical appraisal of groundwater quality in Ngoua watershed (Douala-Cameroon): Implication for domestic purposes. Sci. Afr. 2023, 22, e01910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, N.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Q. Research on the Features and Driving Factors of Shallow Groundwater Quality in Arid Areas, Northwest China. Water 2025, 17, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Hu, A.; Gad, M.; Adyari, B.; Qin, D.; Zhang, L. Domestic wastewater causes nitrate pollution in an agricultural watershed, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 823, 153680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugulothu, S.; Subbarao, N.; Das, R.; Dhakate, R. Geochemical evaluation of groundwater and suitability of groundwater quality for irrigation purpose in an agricultural region of south India. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, H. Assessment of sources and transformation of nitrate in the alluvial-pluvial fan region of north China using a multi-isotope approach. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 89, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hou, K.; Qian, H.; Gao, Y.; Fang, Y.; Tang, S.; Zhang, Q. Natural-human driving factors of groundwater salinization in a long-term irrigation area. Environ. Res. 2023, 220, 115178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Liang, X.; Xiao, C.; Wang, Z. Analysis and assessment of confined and phreatic water quality using a rough set theory method in Jilin City, China. Water Sci. Technol. Water Sup. 2015, 15, 773–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. Hydrochemical characteristics, controlling factors and groundwater sources of Zaozigou gold mine. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, R.; Fu, B.; Mao, K.; Chen, A.; Zhang, D. Identification of the sources and fate of NO3−-N in shallow groundwater around a plateau lake in southwest China using NO3− isotopes (δ15N and δ18O) and a Bayesian model. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 270, 110897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Li, X.-D.; Zhao, Z.-Q.; Liu, C.-Q. Using dual isotopic data to track the sources and behaviors of dissolved sulfate in the western North China Plain. Appl. Geochem. 2015, 52, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Liu, L.; Xu, W.; Li, Y.; Ruan, Q.; Cao, W. Multiple stable isotopic approaches for tracing nitrate contamination sources: Implications for nitrogen management in complex watersheds. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2024, 269, 115822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, M.; Dai, Z.; Hussain, S.; Tariq, M.; Danish, S.; Khan, I.U. The soil pH and heavy metals revealed their impact on soil microbial community. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 321, 115770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juahir, H.; Zain, S.M.; Yusoff, M.K.; Hanidza, T.T.; Armi, A.M.; Toriman, M.E. Spatial water quality assessment of Langat River basin (Malaysia) using environmetric techniques. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 173, 625–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Liu, L.; Zhai, T.; Zhang, X. Multiple isotopes reveal the driving mechanism of high NO3− level and key processes of nitrogen cycling in the lower reaches of Yellow River. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 138, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Zhao, L.; Eastoe, C.J.; Wang, N.; Dong, X. An isotope study of the Shule River Basin, Northwest China: Sources and groundwater residence time, sulfate sources and climate change. J. Hydrol. 2022, 612, 128043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameters | Range/(mg·L−1) | Average/(mg·L−1) | Exceedance Rate/% | Standard | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flood Season | Dry Season | Flood Season | Dry Season | Flood Season | Dry Season | ||||||||
| PW | KW | PW | KW | PW | KW | PW | KW | PW | KW | PW | KW | ||
| pH | 7.55–8.19 | 7.74–8.19 | 7.11–8.03 | 7.44–8.29 | 7.86 | 8.01 | 7.66 | 7.85 | 0.00 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6.50–8.50 |
| K+ | 0.720–86.2 | 0.430–4.92 | 0.266–66.2 | 0.465–4.61 | 6.95 | 1.83 | 5.78 | 1.67 | – | – | – | – | – |
| Na+ | 12.8–1133 | 4.40–213 | 11.6–966 | 2.64–241 | 181 | 40.2 | 175 | 40.8 | 17.7 | 8.70 | 11.8 | 4.36 | 200 |
| Ca2+ | 64.5–445 | 8.75–251 | 50.4–454 | 10.4–271 | 201 | 120 | 192 | 116 | – | – | – | – | – |
| Mg2+ | 10.3–301 | 3.63–52.8 | 10.3–258 | 4.90–56.0 | 76.7 | 23.8 | 76.7 | 23.4 | – | – | – | – | – |
| Fe3+ | 0.040–0.650 | 0.040–0.280 | 0.040–0.250 | 0.040–0.240 | 0.198 | 0.088 | 0.131 | 0.077 | 17.7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.3 |
| Cl− | 18.8–1016 | 12.9–505 | 21.11–924 | 12.6–551 | 253 | 72 | 302 | 75.2 | 47.1 | 4.35 | 41.2 | 4.35 | 250 |
| SO42− | 28.8–1488 | 60.9–250 | 28.5–1215 | 61.0–275 | 400 | 115 | 408 | 113 | 52.9 | 4.35 | 52.9 | 4.35 | 250 |
| HCO3− | 146–986 | 140–426 | 97.4–1031 | 103–435 | 400 | 265 | 363 | 272 | – | – | – | – | – |
| NO3− | 4.65–346 | 1.01–128 | 3.93–431 | 0.016–139 | 83.4 | 43.4 | 75.5 | 47.8 | 29.4 | 8.70 | 11.8 | 17.4 | 88.6 |
| COD | 0.96–1.98 | 0.95–2.3 | 0.600–4.30 | 0.300–3.90 | 1.54 | 1.57 | 1.84 | 1.09 | 0 | 0 | 5.88 | 4.35 | 3.00 |
| TDS | 310–5042 | 362–1408 | 282–4528 | 345–1616 | 1422 | 565 | 1431 | 571 | 52.9 | 8.70 | 47.1 | 8.70 | 1000 |
| Parameters | Pore Phreatic Water | Karst Confined Water | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | PC1 | PC2 | |
| Na+ | 0.980 | 0.055 | 0.953 | 0.207 |
| Mg2+ | 0.922 | 0.341 | 0.875 | −0.228 |
| Fe3+ | 0.919 | 0.281 | 0.960 | −0.081 |
| TDS | 0.913 | 0.388 | 0.993 | −0.013 |
| K+ | 0.913 | −0.109 | 0.445 | 0.696 |
| Cl− | 0.901 | 0.372 | 0.926 | 0.282 |
| NO3− | 0.865 | 0.143 | −0.023 | −0.763 |
| SO42− | 0.843 | 0.274 | 0.690 | −0.581 |
| HCO3− | 0.811 | 0.449 | 0.854 | 0.183 |
| COD | 0.442 | 0.054 | −0.217 | 0.672 |
| Ca2+ | 0.132 | 0.896 | 0.852 | −0.186 |
| pH | −0.138 | −0.782 | −0.681 | 0.233 |
| Eigenvalue | 8.27 | 1.43 | 7.09 | 2.15 |
| Contribution Rate (%) | 62.3 | 18.5 | 59.0 | 18.0 |
| Cumulative Contribution Rate (%) | 62.3 | 80.8 | 59.0 | 77.0 |
| Parameters | Pore Phreatic Water | Karst Confined Water | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | |
| K+ | 0.951 | 0.021 | 0.253 | 0.150 | 0.909 |
| Na+ | 0.918 | 0.324 | 0.725 | 0.530 | 0.353 |
| NO3− | 0.892 | 0.081 | 0.068 | −0.896 | −0.112 |
| HCO3− | 0.882 | 0.288 | 0.723 | 0.553 | −0.152 |
| TDS | 0.747 | 0.659 | 0.912 | 0.240 | 0.310 |
| Mg2+ | 0.690 | 0.640 | 0.807 | 0.466 | −0.205 |
| COD | 0.305 | 0.261 | 0.518 | 0.568 | 0.294 |
| Ca2+ | −0.068 | 0.874 | 0.847 | −0.072 | 0.398 |
| pH | −0.105 | −0.801 | −0.778 | −0.069 | −0.192 |
| Fe3+ | 0.540 | 0.763 | 0.761 | 0.317 | 0.456 |
| Cl− | 0.601 | 0.760 | 0.801 | 0.385 | 0.410 |
| SO42− | 0.631 | 0.691 | 0.852 | −0.050 | 0.232 |
| Eigenvalue | 7.90 | 1.77 | 7.86 | 1.35 | 1.01 |
| Contribution Rate (%) | 46.0 | 34.6 | 51.1 | 19.5 | 14.6 |
| Cumulative Contribution Rate (%) | 46.0 | 80.6 | 51.1 | 70.6 | 85.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, D. Study on the Pollution Mechanism and Driving Factors of Groundwater Quality in Typical Industrial Areas of China. Water 2025, 17, 1420. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101420
Wang L, Wang Q, Zheng D. Study on the Pollution Mechanism and Driving Factors of Groundwater Quality in Typical Industrial Areas of China. Water. 2025; 17(10):1420. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101420
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Li, Qi Wang, and Dechao Zheng. 2025. "Study on the Pollution Mechanism and Driving Factors of Groundwater Quality in Typical Industrial Areas of China" Water 17, no. 10: 1420. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101420
APA StyleWang, L., Wang, Q., & Zheng, D. (2025). Study on the Pollution Mechanism and Driving Factors of Groundwater Quality in Typical Industrial Areas of China. Water, 17(10), 1420. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101420





