Groundwater Potential Mapping Using Optimized Decision Tree-Based Ensemble Learning Model with Local and Global Explainability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data Used
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Inventory Map
2.3. Environmental Features
3. Materials and Methods
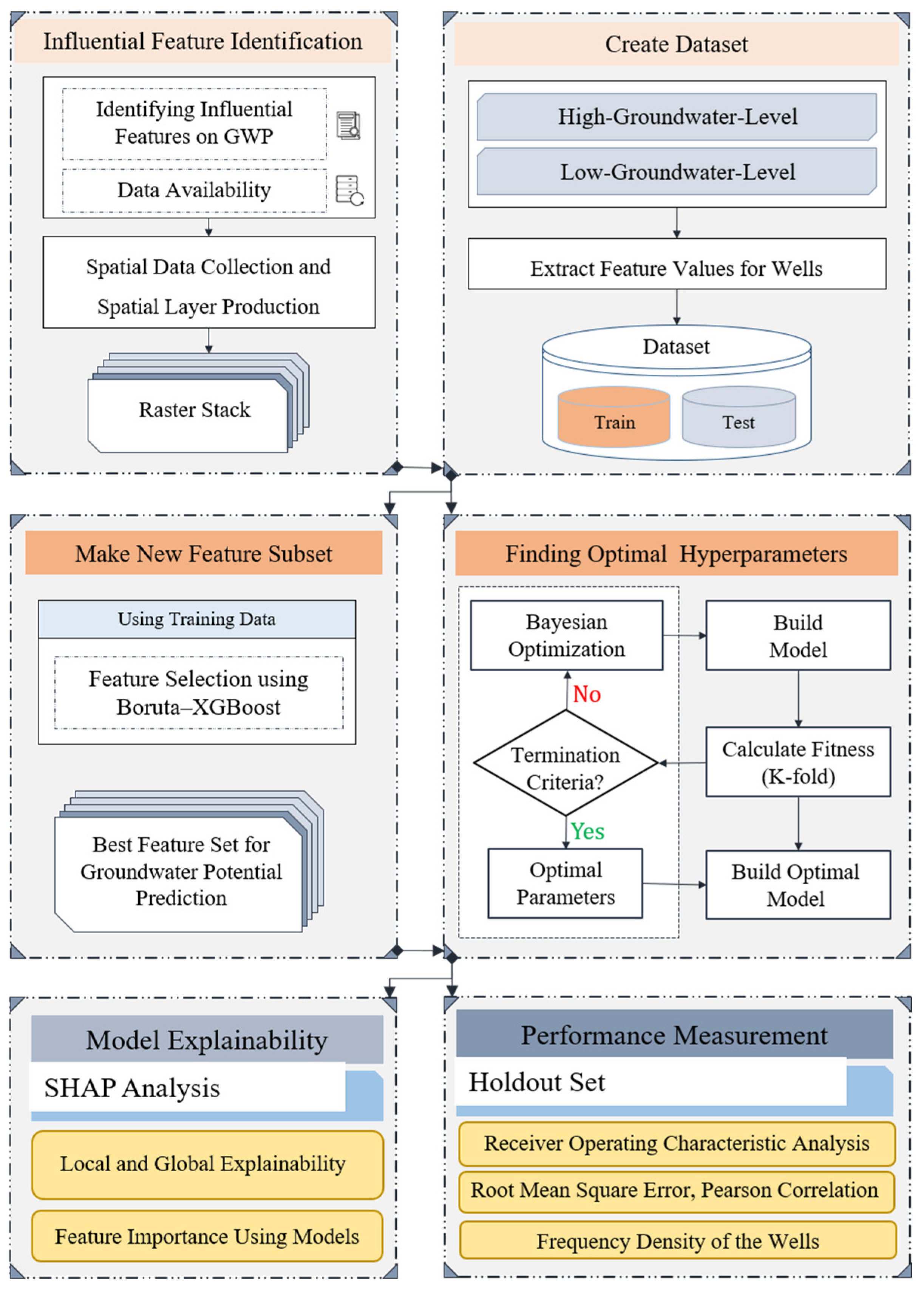
3.1. Proposed Methodology
3.2. Models
3.2.1. RFs
3.2.2. CatBoost
3.3. Validation Criteria
- Root Mean Square Error (RMSE)
- Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC)
- Accuracy
- Precision
3.4. Boruta Algorithm
3.5. Explainable Model (SHapley Additive exPlanation)
4. Results
4.1. Feature Selection
4.2. Model Development
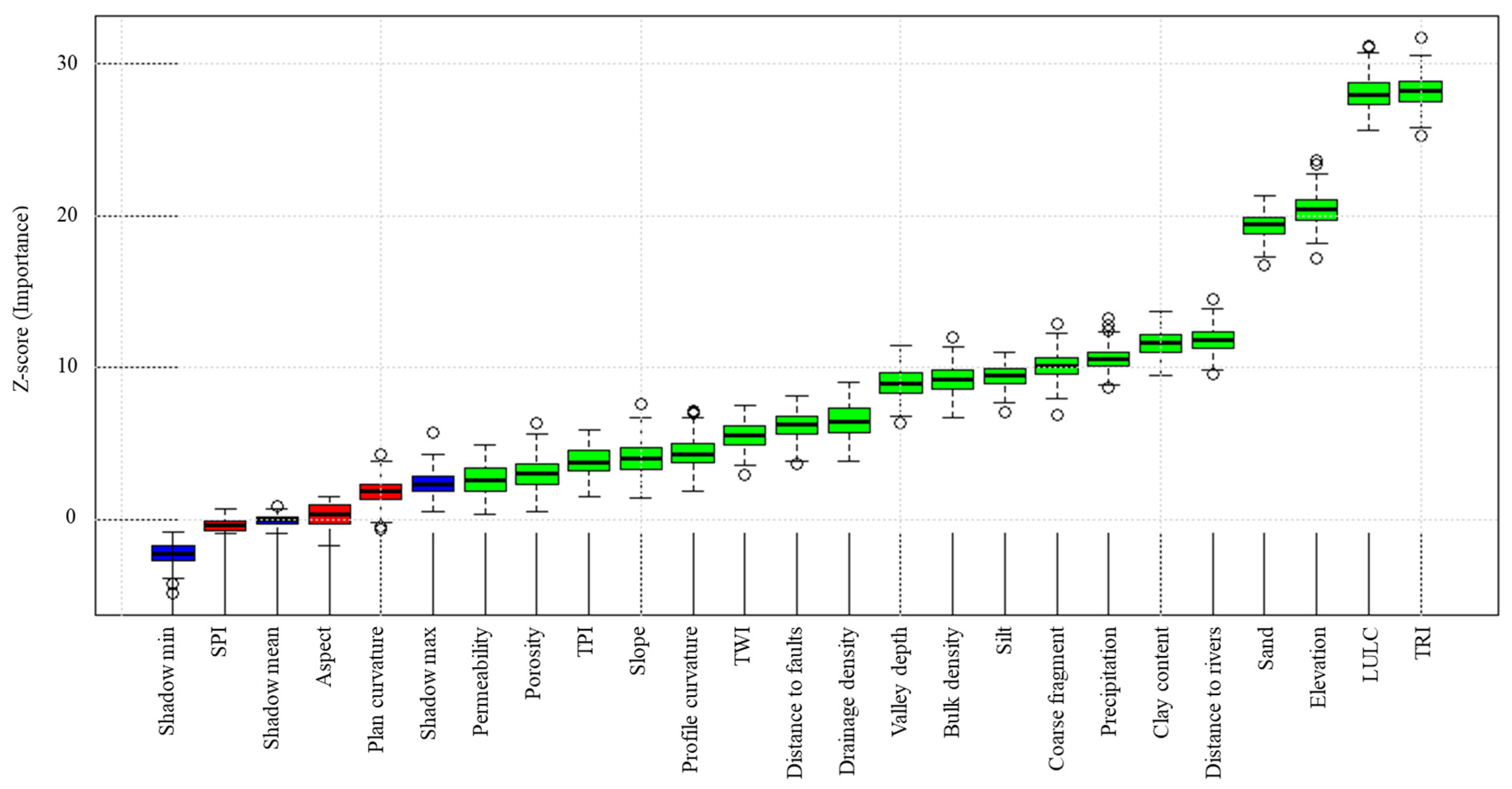
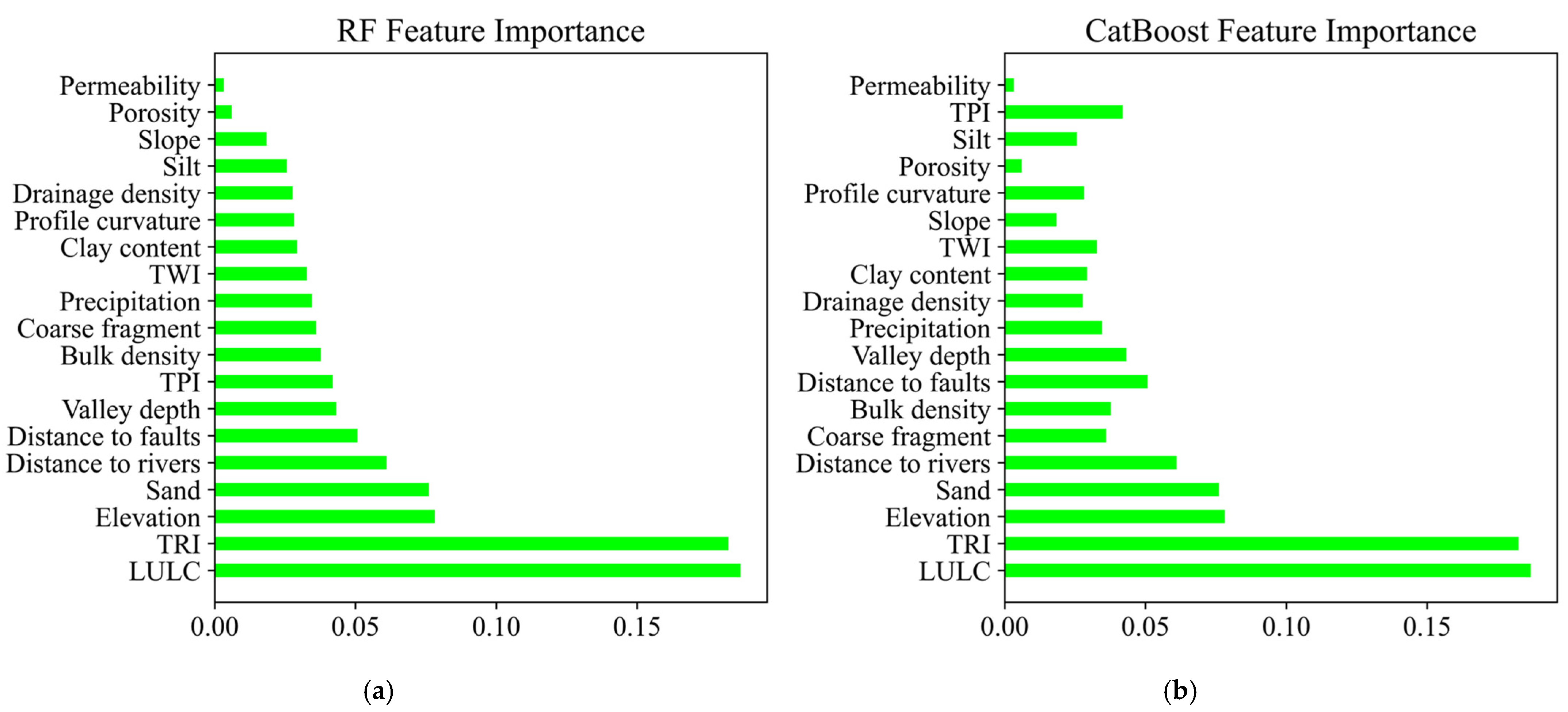
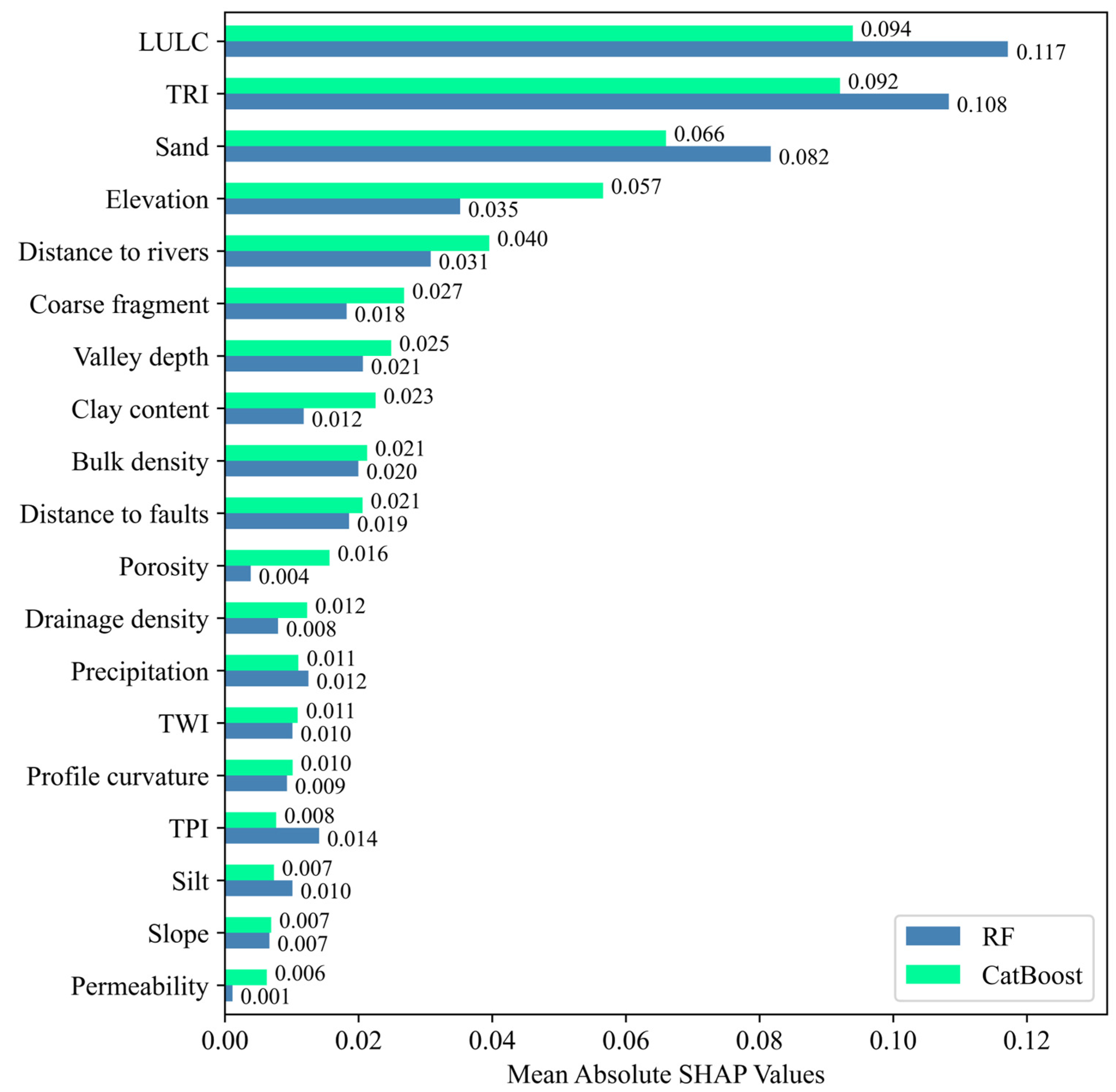
4.3. Feature Importance
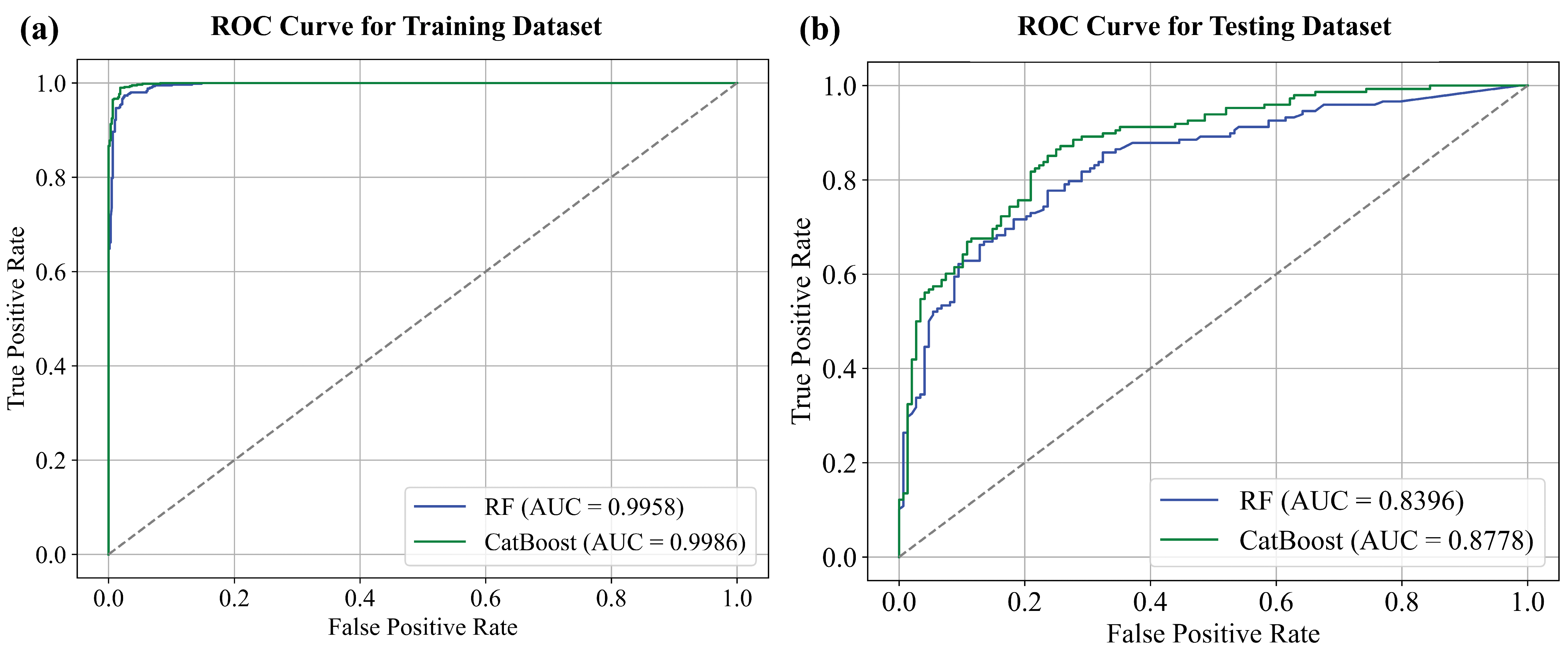
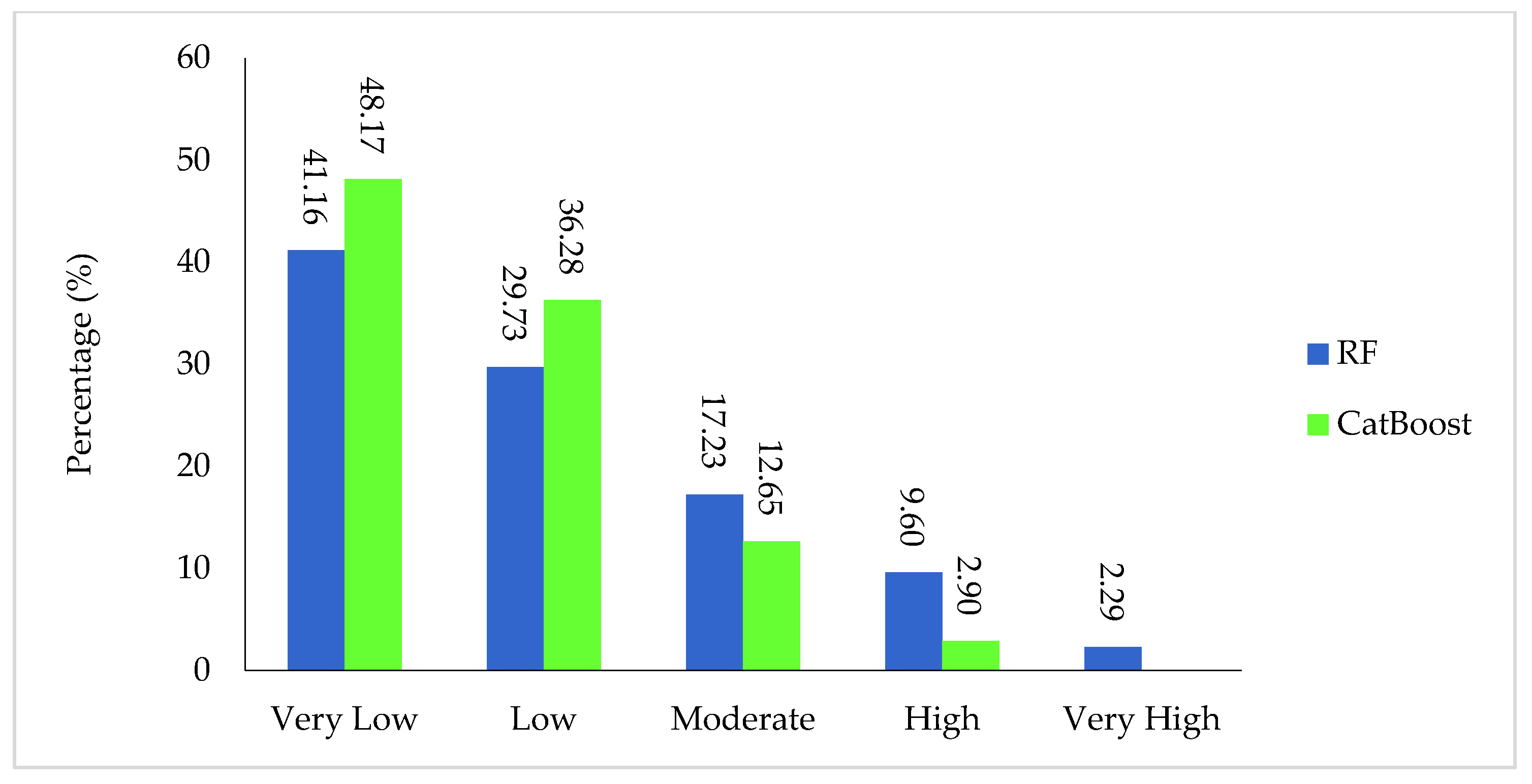
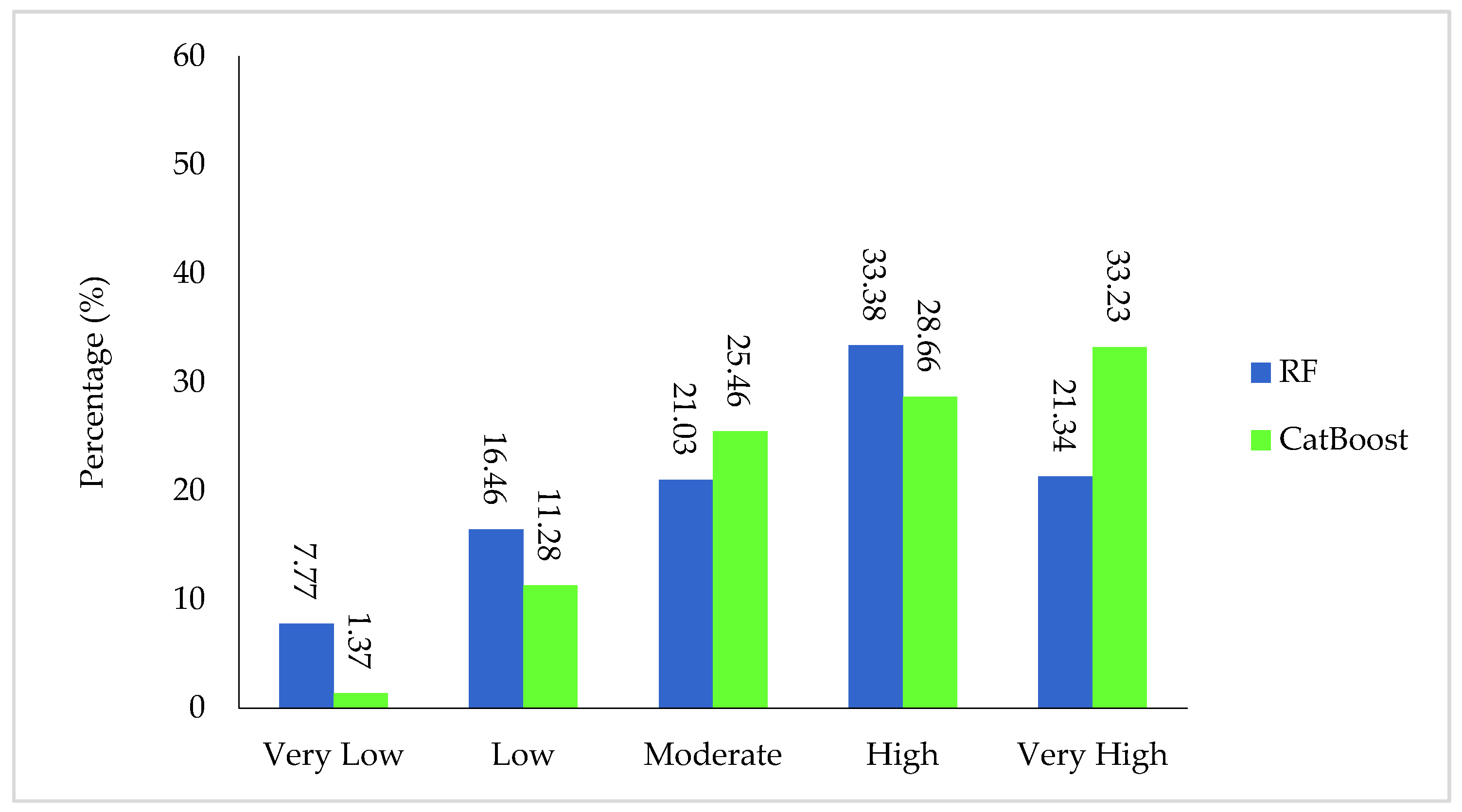
4.4. Groundwater Potential Maps
4.5. Model Interpretation
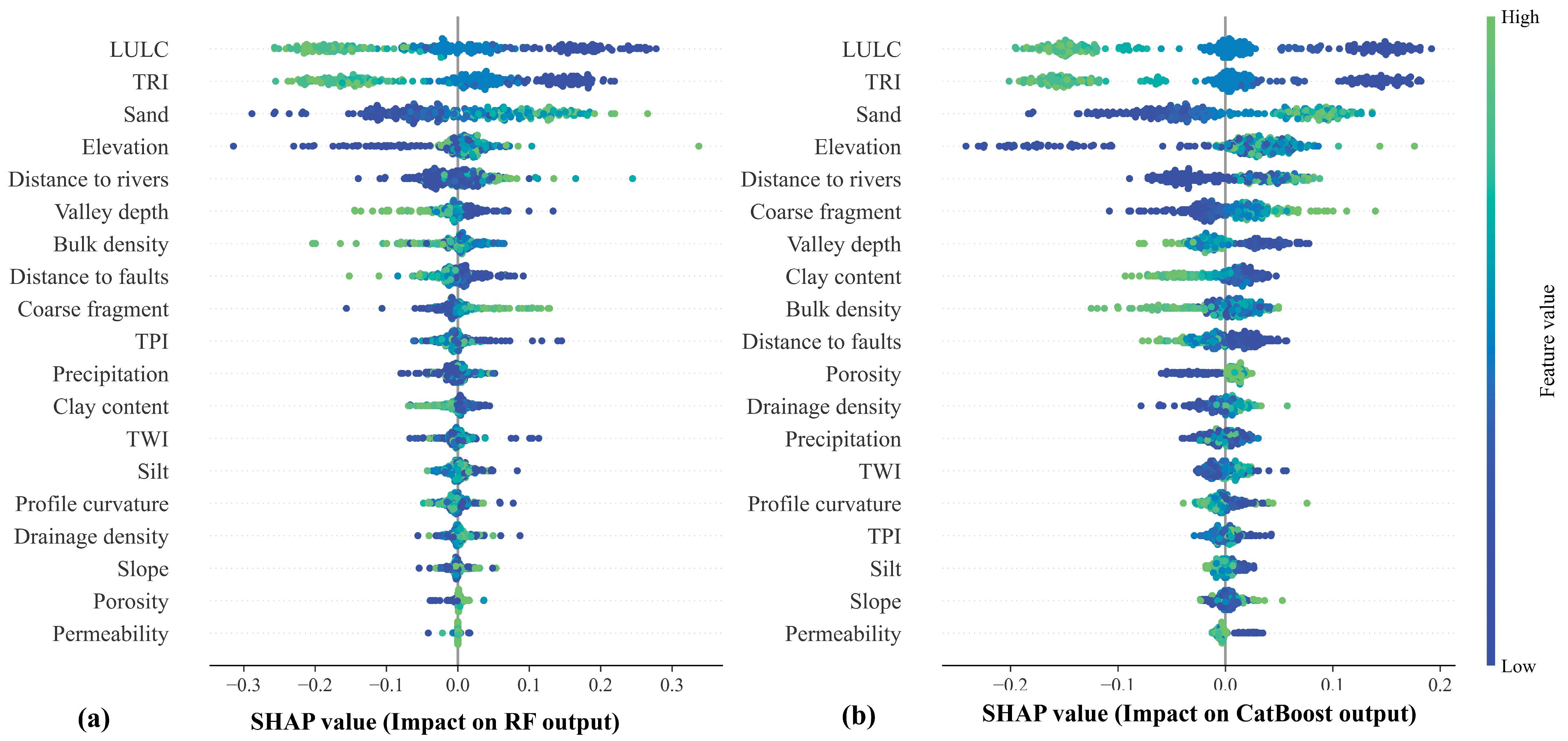
4.5.1. Global SHAP
4.5.2. Local SHAP
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UN Water (Ed.) The United Nations World Water Development Report 2022: Groundwater: Making the Invisible Visible; United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization: Paris, France, 2022; ISBN 92-3-100507-3. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz-Alcaide, S.; Martínez-Santos, P. Review: Advances in Groundwater Potential Mapping. Hydrogeol. J. 2019, 27, 2307–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleeson, T.; Befus, K.M.; Jasechko, S.; Luijendijk, E.; Cardenas, M.B. The Global Volume and Distribution of Modern Groundwater. Nat. Geosci. 2016, 9, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN Water (Ed.) Water for Prosperity and Peace; The United Nations World Water Development Report; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2024; ISBN 978-92-3-100657-9. [Google Scholar]
- Nugroho, J.T.; Lestari, A.I.; Gustiandi, B.; Sofan, P.; Prasasti, I.; Rahmi, K.I.N.; Noviar, H.; Sari, N.M.; Manalu, R.J.; Arifin, S. Groundwater Potential Mapping Using Machine Learning Approach in West Java, Indonesia. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 27, 101382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO (Ed.) Nature-Based Solutions for Water; The United Nations world water development report; Unesco: Paris, France, 2018; ISBN 978-92-3-100264-9. [Google Scholar]
- Wada, Y.; Flörke, M.; Hanasaki, N.; Eisner, S.; Fischer, G.; Tramberend, S.; Satoh, Y.; Van Vliet, M.; Yillia, P.; Ringler, C. Modeling Global Water Use for the 21st Century: The Water Futures and Solutions (WFaS) Initiative and Its Approaches. Geosci. Model. Dev. 2016, 9, 175–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, R.; Maghrebi, M.; Jessen, S.; Bateni, S.M.; Heggy, E.; Javadi, S.; Noury, M.; Pistre, S.; Abolfathi, S.; AghaKouchak, A. Decline in Iran’s Groundwater Recharge. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, A.; Saghafian, B.; Mirchi, A.; Madani, K. The Groundwater–energy–food Nexus in Iran’s Agricultural Sector: Implications for Water Security. Water 2019, 11, 1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safdari, Z. Groundwater Level Monitoring Across Iran’s Main Water Basins Using Temporal Satellite Gravity Solutions and Well Data. Ph.D. Thesis, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim, Norway, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Maghrebi, M.; Noori, R.; Bhattarai, R.; Mundher Yaseen, Z.; Tang, Q.; Al-Ansari, N.; Danandeh Mehr, A.; Karbassi, A.; Omidvar, J.; Farnoush, H. Iran’s Agriculture in the Anthropocene. Earth’s Future 2020, 8, e2020EF001547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samani, S. Analyzing the Groundwater Resources Sustainability Management Plan in Iran through Comparative Studies. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 12, 100521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safdari, Z.; Nahavandchi, H.; Joodaki, G. Estimation of Groundwater Depletion in Iran’s Catchments Using Well Data. Water 2022, 14, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh, N.N.; Thunyawatcharakul, P.; Ngu, N.H.; Chotpantarat, S. Global Review of Groundwater Potential Models in the Last Decade: Parameters, Model Techniques, and Validation. J. Hydrol. 2022, 614, 128501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, R.; Maghrebi, M.; Mirchi, A.; Tang, Q.; Bhattarai, R.; Sadegh, M.; Noury, M.; Torabi Haghighi, A.; Kløve, B.; Madani, K. Anthropogenic Depletion of Iran’s Aquifers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2024221118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, B.; Alesheikh, A.A.; Jafari, A.; Rezaie, F. Performance Evaluation of Convolutional Neural Network and Vision Transformer Models for Groundwater Potential Mapping. J. Hydrol. 2025, 654, 132840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, S.; Jain, J.; Pingale, S.M.; Khare, D. A Comprehensive Review on Mapping of Groundwater Potential Zones: Past, Present and Future Recommendations. In Emerging Technologies for Water Supply, Conservation and Management; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 109–132. [Google Scholar]
- Saranya, T.; Saravanan, S. Groundwater Potential Zone Mapping Using Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP) and GIS for Kancheepuram District, Tamilnadu, India. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2020, 6, 1105–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genjula, W.; Jothimani, M.; Gunalan, J.; Abebe, A. Applications of Statistical and AHP Models in Groundwater Potential Mapping in the Mensa River Catchment, Omo River Valley, Ethiopia. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2023, 9, 4057–4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adiat, K.; Nawawi, M.; Abdullah, K. Assessing the Accuracy of GIS-Based Elementary Multi Criteria Decision Analysis as a Spatial Prediction Tool–a Case of Predicting Potential Zones of Sustainable Groundwater Resources. J. Hydrol. 2012, 440, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, R.K.; Tripathi, G.; Đurin, B.; Šamanović, S.; Cetl, V.; Kishore, N.; Sharma, M.; Singh, S.K.; Kanga, S.; Wasim, M. Groundwater Potential Zone Mapping in the Ghaggar River Basin, North-West India, Using Integrated Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques. Water 2023, 15, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S. Unveiling Groundwater Gems: A GIS-Powered Fusion of AHP and TOPSIS for Mapping Groundwater Potential Zones. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2025, 29, 101431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, M.S.P.; Rahman, M.T.; Hassan, M.F. Mapping Groundwater Potential Zone by Robust Machine Learning Algorithms & Remote Sensing Techniques in Agriculture Dominated Area, Bangladesh. Clean. Water 2025, 3, 100064. [Google Scholar]
- Prapanchan, V.; Subramani, T.; Karunanidhi, D. GIS and Fuzzy Analytical Hierarchy Process to Delineate Groundwater Potential Zones in Southern Parts of India. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 25, 101110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlAyyash, S.; Al-Fugara, A.; Shatnawi, R.; Al-Shabeeb, A.R.; Al-Adamat, R.; Al-Amoush, H. Combination of Metaheuristic Optimization Algorithms and Machine Learning Methods for Groundwater Potential Mapping. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatah, K.K.; Mustafa, Y.T.; Hassan, I.O. Groundwater Potential Mapping in Arid and Semi-Arid Regions of Kurdistan Region of Iraq: A Geoinformatics-Based Machine Learning Approach. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 27, 101337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi-Termeh, S.V.; Sadeghi-Niaraki, A.; Abba, S.I.; Ali, F.; Choi, S.-M. Enhancing Spatial Prediction of Groundwater-Prone Areas through Optimization of a Boosting Algorithm with Bio-Inspired Metaheuristic Algorithms. Appl. Water Sci. 2024, 14, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, K.; Srivastava, A.K.; Ghosh, A.; Nabik, R.; Pan, S.; Chatterjee, U.; Bisai, D.; Pal, S.C.; Zeng, W.; Ewert, F. Application of Bagging and Boosting Ensemble Machine Learning Techniques for Groundwater Potential Mapping in a Drought-Prone Agriculture Region of Eastern India. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2024, 36, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Guo, X.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, R.; Gui, X.; Hu, X.; Li, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Tan, J.; Ma, C. Spatial Prediction of Groundwater Potential by Various Novel Boosting-Based Ensemble Learning Models in Mountainous Areas. Geocarto Int. 2023, 38, 2274870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.D.; Nguyen, Q.-H.; Dang, D.K.; Nguyen, T.G.; Truong, Q.H.; Nguyen, V.H.; Bretcan, P.; Șerban, G.; Bui, Q.-T.; Petrisor, A.-I. Integrated Machine Learning and Remote Sensing for Groundwater Potential Mapping in the Mekong Delta in Vietnam. Acta Geophys. 2024, 72, 4395–4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.S.; Mitra, B.; Mahmud, K.; Rahman, S.M.; Chowdhury, S.; Rahman, M.M. An Ensemble Machine Learning Approach for Predicting Groundwater Storage for Sustainable Management of Water Resources. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2025, 29, 101417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, D.D.; Rahmati, O.; Panahi, M.; Tiefenbacher, J.; Darabi, H.; Haghizadeh, A.; Haghighi, A.T.; Nalivan, O.A.; Bui, D.T. The Effect of Sample Size on Different Machine Learning Models for Groundwater Potential Mapping in Mountain Bedrock Aquifers. Catena 2020, 187, 104421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngouokouo Tchikangoua, A.; Enyegue A Nyam, F.M.; Kouamou Njifen, S.R.; Teikeu, W.A.; Ndougsa Mbarga, T.; Perilli, N. Bivariate Statistical and Neural Network Models to Map Groundwater Potential Zones in Bafia Area (Central Cameroon). Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2025, 11, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masroor, M.; Sajjad, H.; Kumar, P.; Saha, T.K.; Rahaman, M.H.; Choudhari, P.; Kulimushi, L.C.; Pal, S.; Saito, O. Novel Ensemble Machine Learning Modeling Approach for Groundwater Potential Mapping in Parbhani District of Maharashtra, India. Water 2023, 15, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.K.; Hasan, M.M.; Mondal, I.; Akhter, J.; Roy, S.K.; Talukder, S.; Islam, A.S.; Rahman, A.; Karuppannan, S. Empowered Machine Learning Algorithm to Identify Sustainable Groundwater Potential Zone Map in Jashore District, Bangladesh. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 25, 101168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, A.; Alesheikh, A.A.; Rezaie, F.; Panahi, M.; Shahsavar, S.; Lee, M.-J.; Lee, S. Enhancing a Convolutional Neural Network Model for Land Subsidence Susceptibility Mapping Using Hybrid Meta-Heuristic Algorithms. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2023, 277, 104350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, Z.; Alesheikh, A.A.; Jafari, A.; Torktatari, S.; Sharif, M. Stacking Ensemble Technique Using Optimized Machine Learning Models with Boruta–XGBoost Feature Selection for Landslide Susceptibility Mapping: A Case of Kermanshah Province, Iran. Information 2024, 15, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahal, A.; Lombardo, L. Explainable Artificial Intelligence in Geoscience: A Glimpse into the Future of Landslide Susceptibility Modeling. Comput. Geosci. 2023, 176, 105364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Lee, S.-I. A Unified Approach to Interpreting Model Predictions. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Volume 30. Available online: https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper_files/paper/2017/file/8a20a8621978632d76c43dfd28b67767-Paper.pdf (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Ribeiro, M.T.; Singh, S.; Guestrin, C. “Why Should I Trust You?”: Explaining the Predictions of Any Classifier. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 1135–1144. [Google Scholar]
- Razavi-Termeh, S.V.; Sadeghi-Niaraki, A.; Yao, X.A.; Naqvi, R.A.; Choi, S.-M. Assessment of Noise Pollution-Prone Areas Using an Explainable Geospatial Artificial Intelligence Approach. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alesheikh, A.A.; Chatrsimab, Z.; Rezaie, F.; Lee, S.; Jafari, A.; Panahi, M. Land Subsidence Susceptibility Mapping Based on InSAR and a Hybrid Machine Learning Approach. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2024, 27, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teke, A.; Kavzoglu, T. Exploring the Decision-Making Process of Ensemble Learning Algorithms in Landslide Susceptibility Mapping: Insights from Local and Global eXplainable AI Analyses. Adv. Space Res. 2024, 74, 3765–3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhang, H.; Dahal, A.; Cheng, W.; Zhao, M.; Lombardo, L. On the Use of Explainable AI for Susceptibility Modeling: Examining the Spatial Pattern of SHAP Values. Geosci. Front. 2024, 15, 101800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, A.; Alesheikh, A.A.; Zandi, I.; Lotfata, A. Spatial Prediction of Human Brucellosis Susceptibility Using an Explainable Optimized Adaptive Neuro Fuzzy Inference System. Acta Trop. 2024, 260, 107483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrami, A.; Bahrami, M.; Haghani, E. Groundwater Quality Assessment for Potable Using WQI and GIS Technology in the South of Iran. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2024, 10, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamalimoghaddam, E.; Yazdani, S.; Salami, H.; Peykani, G. The Impact of Water Supply on Farming Systems: A Sustainability Assessment. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2019, 17, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, M.; Homaee, M.; Pereira, L.S.; Bybordi, M. Water Management Dilemma in the Agricultural Sector of Iran: A Review Focusing on Water Governance. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 288, 108480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torabi Haghighi, A.; Abou Zaki, N.; Rossi, P.M.; Noori, R.; Hekmatzadeh, A.A.; Saremi, H.; Kløve, B. Unsustainability Syndrome—From Meteorological to Agricultural Drought in Arid and Semi-Arid Regions. Water 2020, 12, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghaei, Y.; Nazari-Sharabian, M.; Afzalimehr, H.; Karakouzian, M. Hydrogeochemical Assessment of Groundwater Quality and Suitability for Drinking and Agricultural Use. The Case Study of Fars Province, Iran. Eng. Technol. Appl. Sci. Res. 2023, 13, 10797–10807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golian, M.; Saffarzadeh, A.; Katibeh, H.; Mahdad, M.; Saadat, H.; Khazaei, M.; Sametzadeh, E.; Ahmadi, A.; Sharifi Teshnizi, E.; Samadi Darafshani, M. Consequences of Groundwater Overexploitation on Land Subsidence in Fars Province of Iran and Its Mitigation Management Programme. Water Environ. J. 2021, 35, 975–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi-Termeh, S.V.; Sadeghi-Niaraki, A.; Farhangi, F.; Khiadani, M.; Pirasteh, S.; Choi, S.-M. Solving Water Scarcity Challenges in Arid Regions: A Novel Approach Employing Human-Based Meta-Heuristics and Machine Learning Algorithm for Groundwater Potential Mapping. Chemosphere 2024, 363, 142859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.T.; Ha, D.H.; Jaafari, A.; Nguyen, H.D.; Van Phong, T.; Al-Ansari, N.; Prakash, I.; Le, H.V.; Pham, B.T. Groundwater Potential Mapping Combining Artificial Neural Network and Real AdaBoost Ensemble Technique: The DakNong Province Case-Study, Vietnam. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, G. Analysis of Methods Used to Validate Remote Sensing and GIS-Based Groundwater Potential Maps in the Last Two Decades: A Review. Geosystems Geoenvironment 2024, 3, 100245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleeson, T.; Moosdorf, N.; Hartmann, J.; van Beek, L. van A Glimpse beneath Earth’s Surface: GLobal HYdrogeology MaPS (GLHYMPS) of Permeability and Porosity. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 3891–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleeson, T. GLobal HYdrogeology MaPS (GLHYMPS) of Permeability and Porosity 2018 [Dataset]. [CrossRef]
- Jaafarzadeh, M.S.; Tahmasebipour, N.; Haghizadeh, A.; Pourghasemi, H.R.; Rouhani, H. Groundwater Recharge Potential Zonation Using an Ensemble of Machine Learning and Bivariate Statistical Models. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebege, E.G.; Birara, Z.M.; Takele, S.G.; Jothimani, M. Geospatial Mapping and Multi-Criteria Analysis of Groundwater Potential in Libo Kemkem Watershed, Upper Blue Nile River Basin, Ethiopia. Sci. Afr. 2025, 27, e02549. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, M.M.C.; Ferolin, T.P. Groundwater Resource Exploration and Mapping Methods: A Review. J. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2023, 19, 140–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmassebipoor, N.; Rahmati, O.; Noormohamadi, F.; Lee, S. Spatial Analysis of Groundwater Potential Using Weights-of-Evidence and Evidential Belief Function Models and Remote Sensing. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjmel, K.; Amraoui, F.; Boutaleb, S.; Ouchchen, M.; Tahiri, A.; Touab, A. Mapping of Groundwater Potential Zones in Crystalline Terrain Using Remote Sensing, GIS Techniques, and Multicriteria Data Analysis (Case of the Ighrem Region, Western Anti-Atlas, Morocco). Water 2020, 12, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokarram, M.; Roshan, G.; Negahban, S. Landform Classification Using Topography Position Index (Case Study: Salt Dome of Korsia-Darab Plain, Iran). Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2015, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldırım, Ü. Identification of Groundwater Potential Zones Using GIS and Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Techniques: A Case Study Upper Coruh River Basin (NE Turkey). ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Sherbini, R.A.; Ghazala, H.H.; Ahmed, M.A.; Ibraheem, I.M.; Al Ajmi, H.F.; Genedi, M.A. Mapping Groundwater Potential Zones in the Widyan Basin, Al Qassim, KSA: Analytical Hierarchy Process-Based Analysis Using Senti-Nel-2, ASTER-DEM, and Conven-Tional Data. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wang, Z.; Wang, G.; Ning, Z.; Lian, B.; Li, S.; Tsangaratos, P.; Ilia, I.; Xue, W. Optimizing Rotation Forest-Based Decision Tree Algorithms for Groundwater Potential Mapping. Water 2023, 15, 2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, S.J.; DeGloria, S.D.; Elliot, R. Index That Quantifies Topographic Heterogeneity. Intermt. J. Sci. 1999, 5, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Affum, A.O.; Kwaansa-Ansah, E.E.; Osae, S.D. Estimating Groundwater Geogenic Arsenic Contamination and the Affected Population of River Basins Underlain Mostly with Crystalline Rocks in Ghana. Environ. Chall. 2024, 15, 100898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati, O.; Nazari Samani, A.; Mahdavi, M.; Pourghasemi, H.R.; Zeinivand, H. Groundwater Potential Mapping at Kurdistan Region of Iran Using Analytic Hierarchy Process and GIS. Arab. J. Geosci. 2015, 8, 7059–7071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Ma, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wu, W.; Xu, Z.; Xue, J. Identifying Groundwater Potential Zones in a Typical Irrigation District Using the Geospatial Technique and Analytic Hierarchy Process. Geocarto Int. 2025, 40, 2453025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taibou, A.; Jounaid, H.; Moustadraf, J.; Amraoui, F. Assessment of Groundwater Potential in the Khenifra-Azrou Basin, Central Massif, Morocco Using Frequency Ratio and Shannon’s Entropy Approaches. Sci. Afr. 2025, 27, e02616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Singh, P.; Asthana, H.; Yadav, B.; Mukherjee, S. Groundwater Potential Zone Mapping of Middle Andaman Using Multi-Criteria Decision-Making and Support Vector Machine. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 26, 101191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.G.; Phan, K.A.; Huynh, T.H.N. Application of Integrated-Weight Water Quality Index in Groundwater Quality Evaluation. Civ. Eng. J. 2022, 8, 2661–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanuzzaman, M.; Mandal, M.H.; Hasnine, M.; Shit, P.K. Groundwater Potential Mapping Using Multi-Criteria Decision, Bivariate Statistic and Machine Learning Algorithms: Evidence from Chota Nagpur Plateau, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi-Termeh, S.V.; Pourzangbar, A.; Sadeghi-Niaraki, A.; Franca, M.J.; Choi, S.-M. Metaheuristic-Driven Enhancement of Categorical Boosting Algorithm for Flood-Prone Areas Mapping. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2025, 136, 104357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi-Termeh, S.V.; Sadeghi-Niaraki, A.; Jelokhani-Niaraki, M.; Choi, S.-M. Exploring Multi-Pollution Variability in the Urban Environment: Geospatial AI-Driven Modeling of Air and Noise. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2024, 17, 2378819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokhorenkova, L.; Gusev, G.; Vorobev, A.; Dorogush, A.V.; Gulin, A. CatBoost: Unbiased Boosting with Categorical Features. 2017. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.09516. [Google Scholar]
- Bairami, M.; Khajavi, H.; Rastgoo, A. Assessing Groundwater Behavior and Future Trends in the Ardabil Aquifer: A Comparative Study of Groundwater Modeling System and Categorical Gradient Boosting Hybrid Model. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2024, 255, 124728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Chen, Y.; Chen, H. An Interpretable CatBoost Model Guided by Spectral Morphological Features for the Inversion of Coastal Water Quality Parameters. Water 2024, 16, 3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kursa, M.B.; Jankowski, A.; Rudnicki, W.R. Boruta—A System for Feature Selection. Fundam. Informaticae 2010, 101, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandi, I.; Jafari, A.; Lotfata, A. Enhancing PM 2.5 Air Pollution Prediction Performance by Optimizing the Echo State Network (ESN) Deep Learning Model Using New Metaheuristic Algorithms. Urban. Sci. 2025, 9, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.T.; Singh, S.; Guestrin, C. A Scalable Tree Boosting System. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM Sigkdd International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, X.; Chen, F.; Xia, Z.; Zhuang, L.; Jiao, K.; Peng, Z.; Wang, B.; Bucknall, R.; Yearwood, K.; Hou, Z. A Novel Feature Susceptibility Approach for a PEMFC Control System Based on an Improved XGBoost-Boruta Algorithm. Energy AI 2023, 12, 100229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Erion, G.; Chen, H.; DeGrave, A.; Prutkin, J.M.; Nair, B.; Katz, R.; Himmelfarb, J.; Bansal, N.; Lee, S.-I. Explainable AI for Trees: From Local Explanations to Global Understanding. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.04610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolpert, D.H.; Macready, W.G. No free lunch theorems for optimization. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 1997, 1, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

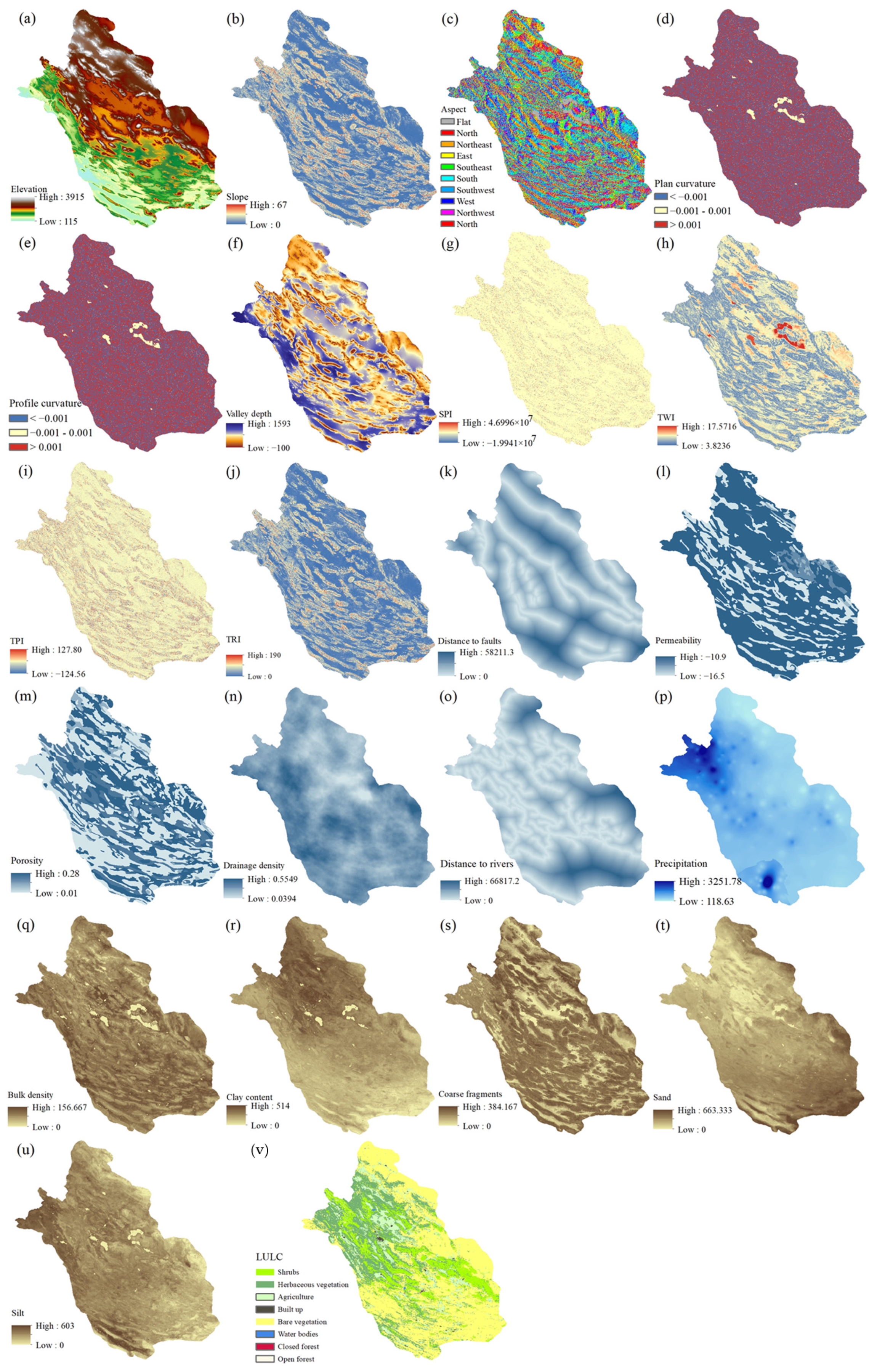



| Statistics | Value (m) | Statistics | Value (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum | 0.30 | Standard Deviation | 28.46 |
| Maximum | 175.15 | Median | 26.50 |
| Mean | 34.31 |
| Parameter | Data Source | Resolution/Scale |
|---|---|---|
| Elevation (m) | SRTM DEM | 30 m |
| Slope (degree) | ||
| Aspect | ||
| Plan curvature | ||
| Profile curvature | ||
| TPI | ||
| TWI | ||
| TRI | ||
| Valley depth (m) | ||
| SPI | ||
| Sand (g/kg) | International Soil Reference and Information Centre (ISRIC; Soilgrids.org) | 250 m |
| Silt (g/kg) | ||
| Clay content (g/kg) | ||
| Bulk density (cg/cm3) | ||
| Coarse fragment (cm3/dm3) | ||
| Permeability (m2) | Global Hydrogeology Maps (GLHYMPSs) | 1:100,000 |
| Porosity | ||
| Distance to faults (m) | Geological survey and mineral exploration of Iran (GSI) | 1:100,000 |
| Distance to rivers (m) | ||
| Drainage density | ||
| LULC | Copernicus Global Land Service (CGLS) | 10 m |
| Precipitation (mm/year) | Iran Meteorological Organization (irimo.ir) | 216 precipitation stations |
| Model | Hyperparameter | Type | Range | Optimized Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RF | Number of trees | Integer | 10 to 500 | 10 |
| Depth of trees | Integer | 1 to 20 | 10 | |
| Minimum samples to split a node | Integer | 2 to 20 | 2 | |
| Minimum samples at a leaf node | Integer | 1 to 20 | 1 | |
| Maximum features | String | [“sqrt”, “log2”, none] | None | |
| CatBoost | Number of iterations | Integer | 10 to 1000 | 500 |
| Learning rate | Float | 0.01 to 0.2 | 0.026 | |
| Depth | Integer | 1 to 10 | 8 | |
| L2 regularization | Float | 1 to 9 | 8.258 | |
| Random strength | Float | 0.1 to 2.0 | 0.445 | |
| Early stopping | Integer | 10 to 100 | 50 |
| Training | RMSE | AUC | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | Precision |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RF | 0.2029 | 0.9957 | 0.9741 | 0.9748 | 0.9733 | 0.9732 |
| CatBoost | 0.2069 | 0.9986 | 0.9855 | 0.9815 | 0.9900 | 0.9898 |
| Testing | RMSE | AUC | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | Precision |
| RF | 0.4072 | 0.8396 | 0.7703 | 0.7635 | 0.7770 | 0.7740 |
| CatBoost | 0.3779 | 0.8778 | 0.8074 | 0.7500 | 0.8449 | 0.8473 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hosseini, F.S.; Jafari, A.; Zandi, I.; Alesheikh, A.A.; Rezaie, F. Groundwater Potential Mapping Using Optimized Decision Tree-Based Ensemble Learning Model with Local and Global Explainability. Water 2025, 17, 1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101520
Hosseini FS, Jafari A, Zandi I, Alesheikh AA, Rezaie F. Groundwater Potential Mapping Using Optimized Decision Tree-Based Ensemble Learning Model with Local and Global Explainability. Water. 2025; 17(10):1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101520
Chicago/Turabian StyleHosseini, Fatemeh Sadat, Ali Jafari, Iman Zandi, Ali Asghar Alesheikh, and Fatemeh Rezaie. 2025. "Groundwater Potential Mapping Using Optimized Decision Tree-Based Ensemble Learning Model with Local and Global Explainability" Water 17, no. 10: 1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101520
APA StyleHosseini, F. S., Jafari, A., Zandi, I., Alesheikh, A. A., & Rezaie, F. (2025). Groundwater Potential Mapping Using Optimized Decision Tree-Based Ensemble Learning Model with Local and Global Explainability. Water, 17(10), 1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101520







