Hydrogeochemical and Geospatial Insights into Groundwater Contamination: Fluoride and Nitrate Risks in Western Odisha, India
Abstract
1. Introduction
- To analyze the spatial variation in fluoride and nitrate concentrations in groundwater across the Boudh district.
- To investigate the geological and anthropogenic factors influencing groundwater contamination.
- To conduct a health risk assessment using hazard quotient (HQ) and total hazard index (HI) for different age groups.
- To employ remote sensing (RS) and GIS techniques for groundwater quality mapping and contamination hotspot identification.
- To propose sustainable groundwater management and mitigation strategies for the region’s safe drinking water supply.
2. Materials and Methods
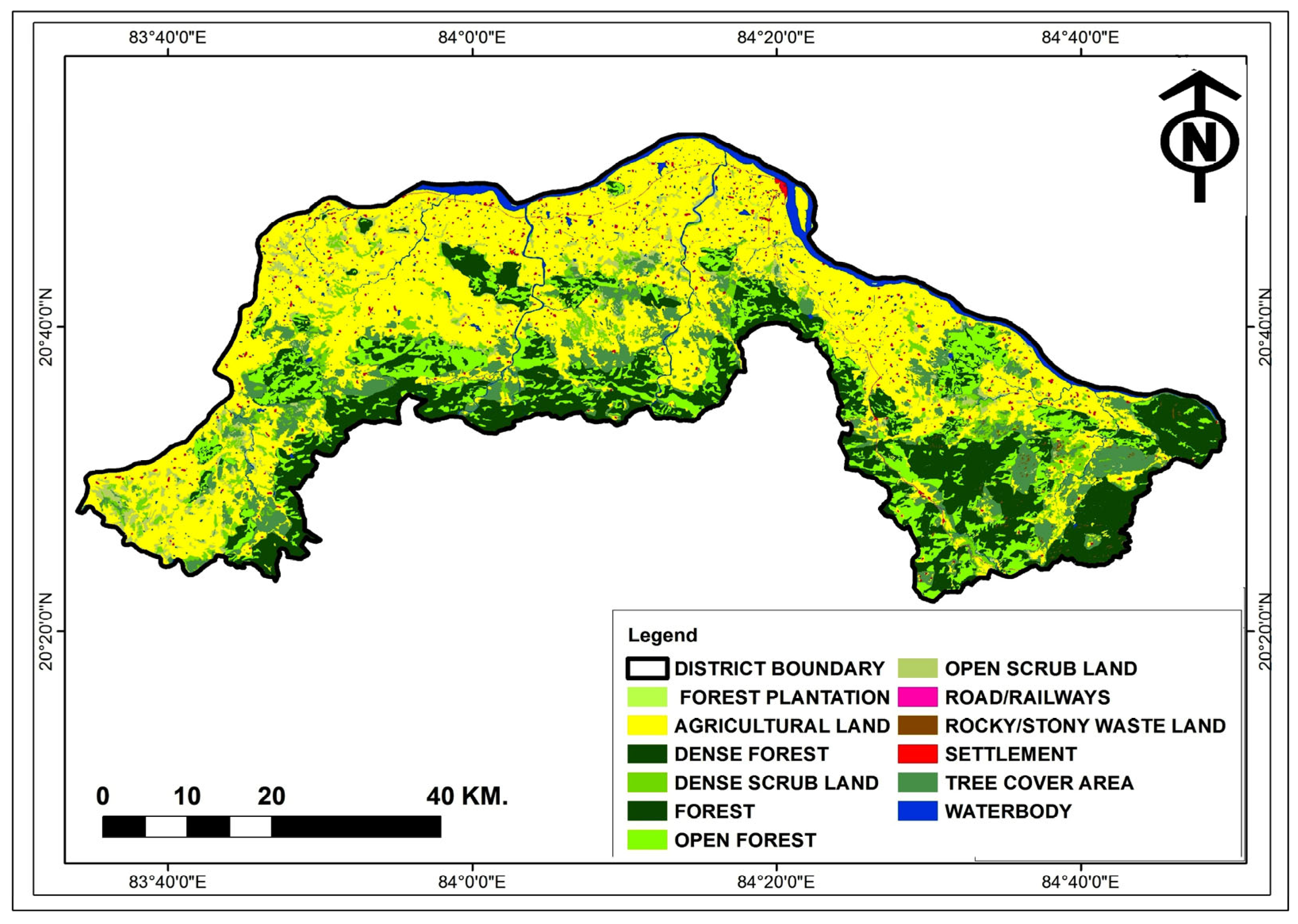
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Methodology
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical Characteristics of Groundwater
3.2. Water Quality Concerns
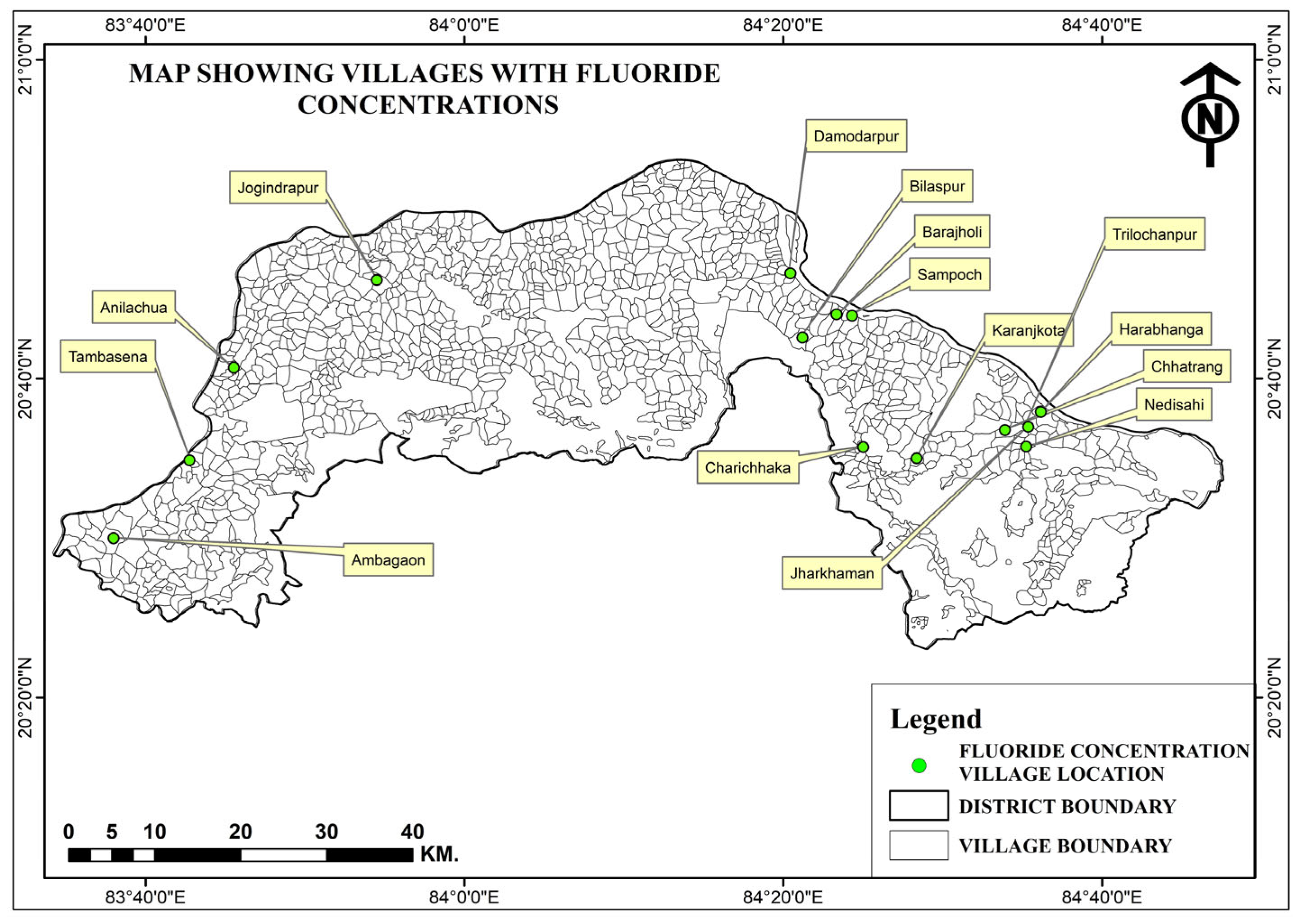
3.3. Spatial Distribution of Nitrate and Fluoride
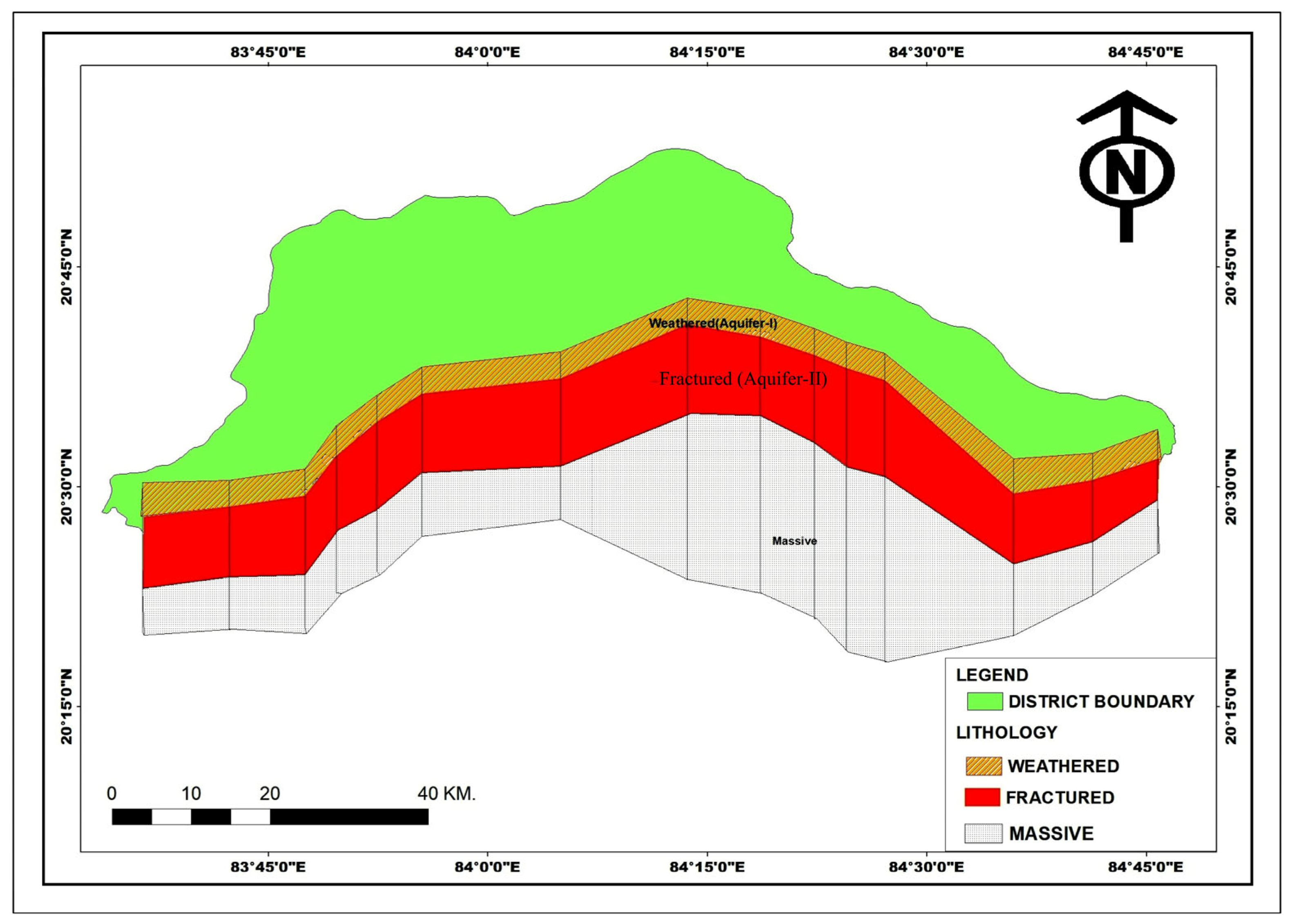
3.4. Geological Investigation
3.5. XRD Analysis
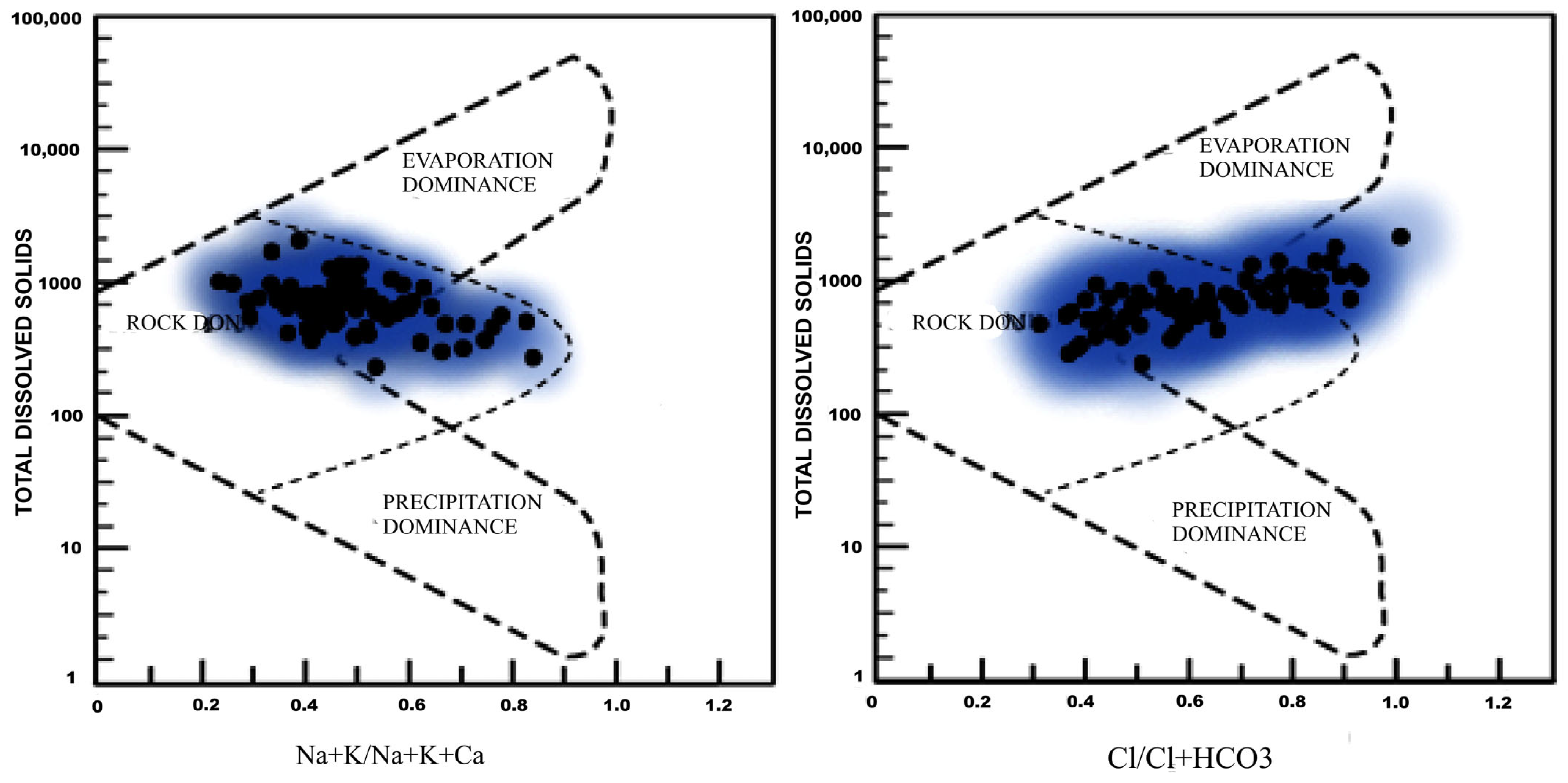
3.6. Hydrogeochemistry
3.6.1. Genesis of Groundwater Chemistry
3.6.2. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
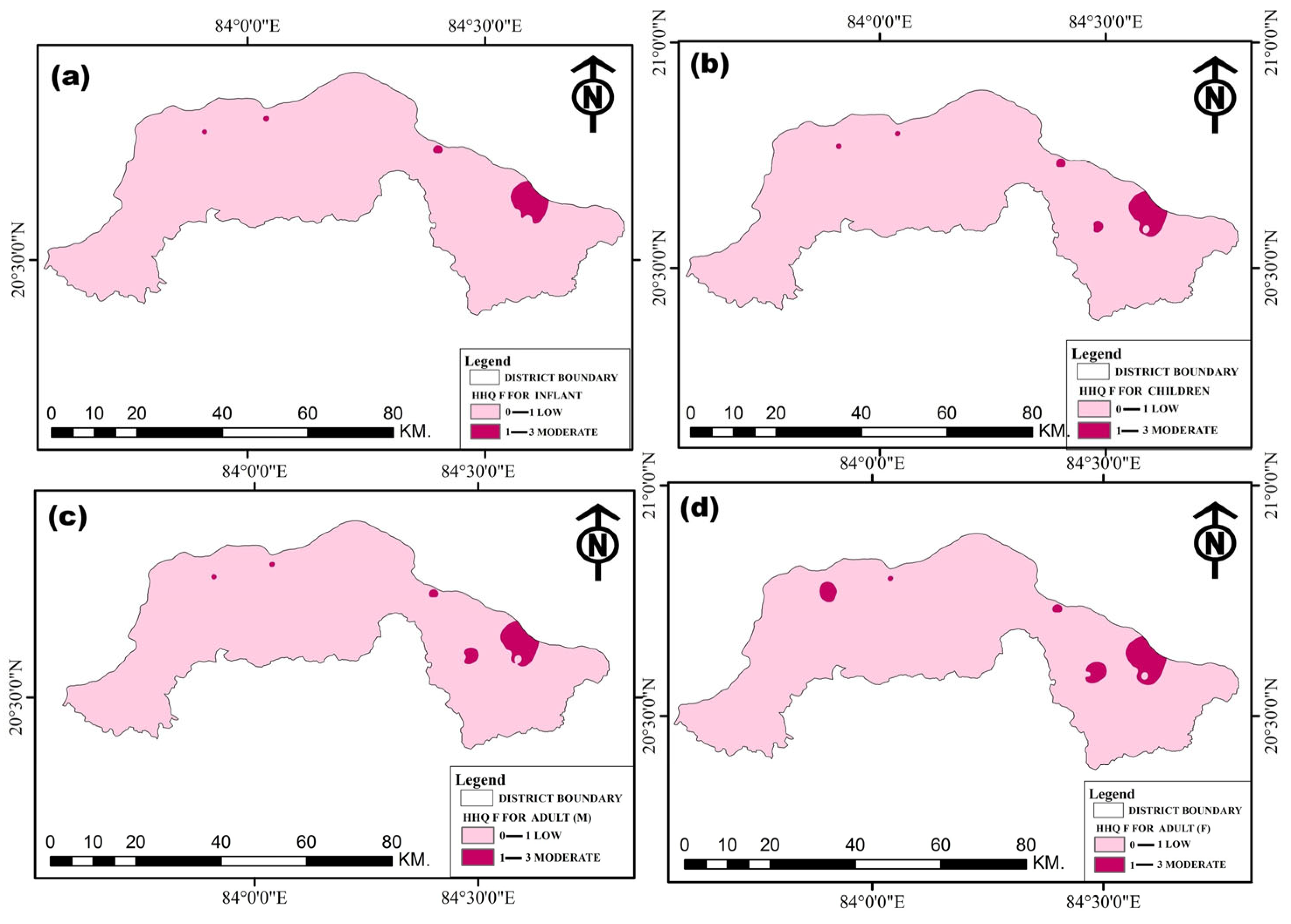
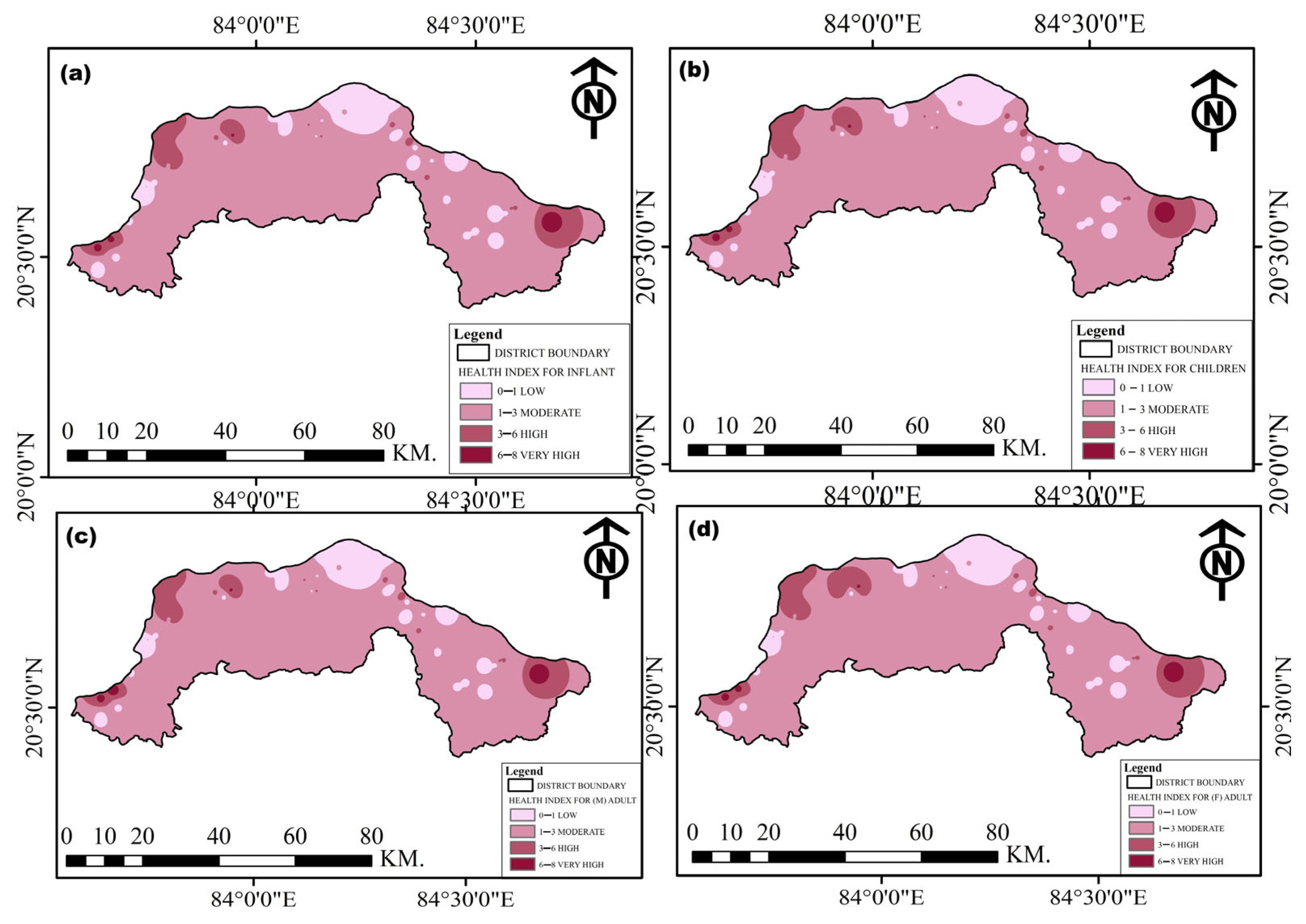
3.6.3. Non-Carcinogenic Human Health Risks
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meneses, Y.E.; Stratton, J.; Flores, R.A. Water Reconditioning and Reuse in the Food Processing Industry: Current Situation and Challenges. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 61, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyena, A.P.; Sam, K. The Blue Revolution: Sustainable Water Management for a Thirsty World. Discov. Sustain. 2025, 6, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fróna, D.; Szenderák, J.; Harangi-Rákos, M. The challenge of feeding the world. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, S.; Taloor, A.K.; Dhal, L.; Sahoo, S.; Al-Ansari, N. Impact of climate change on groundwater hydrology: A comprehensive review and current status of the Indian hydrogeology. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrard, N.; Foster, T.; Willetts, J. Groundwater as a Source of Drinking Water in Southeast Asia and the Pacific: A Multi-Country Review of Current Reliance and Resource Concerns. Water 2019, 11, 1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, F.F.; Gonzalo, J.A. Falling Birth Rates and World Population Projections: A Quantitative Discussion (1950–2050). In World Population; DESA: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 117–142. [Google Scholar]
- Ingrao, C.; Strippoli, R.; Lagioia, G.; Huisingh, D. Water scarcity in agriculture: An overview of causes, impacts and approaches for reducing the risks. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishaque, W.; Mukhtar, M.; Tanvir, R. Pakistan’s water resource management: Ensuring water security for sustainable development. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1096747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayre, S.S.; Taraz, V. Groundwater depletion in India: Social losses from costly well deepening. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2019, 93, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plessis, A.D. Persistent degradation: Global water quality challenges and required actions. One Earth 2022, 5, 129–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekar, A.; Valliammai, A.; Nagarajan, M.; Sivakumar, S.D.; Baskar, M.; Sujitha, E. Conjunctive use in water resource management: Current trends and future directions. Water Supply 2024, 24, 3881–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yosra, A.; Matteo, G.; Kaouther, N.; Rihab, H.; Younes, H. Assessment of a Groundwater Potential Zone Using Geospatial Artificial Intelligence (Geo-AI), Remote Sensing (RS), and GIS Tools in Majerda Transboundary Basin (North Africa). Water 2025, 17, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, D.; Sing, D.; Sahu, P.C. Geospatial analysis of groundwater potential zones using GIS-based multi-criteria decision-making AHP approach. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2024, 10, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elewa, H.H.; Nosair, A.M.; Ibrahim, A.; Zelenakova, M.; Pietrucha-Urbanik, K.; Habib, H.M.; Moneam, N.A.A.; Ragab, R.M.; Ramadan, E.M. Use of remote sensing, spatial and geophysical modeling, and real recharging capabilities to identify suitable areas for groundwater exploitation in dry coastal areas. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 363, 121243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidya, K.; Manoharan, A.; Suchitra, B.; Shyni, M. Combination of remote sensing, GIS, AHP techniques and geophysical data to delineate groundwater potential zones in the Shiriya River Basin, South India. Geosystems Geoenvironment 2024, 3, 100294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopher, S.; Mariner, K. Collaborative Groundwater Modeling: Open-Source, Cloud- Based, Applied Science at a Small-Island Water Utility Scale. Environ. Model. Softw. 2020, 127, 104693. [Google Scholar]
- Obura, D.; Nabifo, V.; Apiny, I.; Akamushaba, O.; Dadebo, D. Application of a decision support system for monitoring and maintenance management of water valley tank facilities: A technological transformation toward sector sustainability. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 25, 101109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abba, S.; Egbueri, J.C.; Benaafi, M.; Usman, J.; Usman, A.; Aljundi, I.H. Fluoride and nitrate enrichment in coastal aquifers of the Eastern Province, Saudi Arabia: The influencing factors, toxicity, and human health risks. Chemosphere 2023, 336, 139083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunkari, E.D.; Ambushe, A.A. Groundwater fluoride contamination, sources, hotspots, health hazards, and sustainable containment measures: A systematic review of the Ghanaian context. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 27, 101352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narsimha, A.; Tiwari, A.K. Fluoride contamination in groundwater and its impact on human health: A case study. Curr. Dir. Water Scarcity Res. 2022, 5, 341–354. [Google Scholar]
- Mester, T.; Szabó, G.; Kiss, E.; Balla, D. Long-term spatiotemporal changes in nitrate contamination of municipal groundwater resources after sewerage network construction in the Hungarian Great Plain. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 61114–61137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Craswell, E. Fertilizers and nitrate pollution of surface and ground water: An increasingly pervasive global problem. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abascal, E.; Gómez-Coma, L.; Ortiz, I.; Ortiz, A. Global diagnosis of nitrate pollution in groundwater and review of removal technologies. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 810, 152233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, W.; Chen, K.; Jiang, J. Microbial dehalogenation mechanisms and prospects of bioremediation of persistent halogenated organic contaminants. In Water Security: Big Data-Driven Risk Identification, Assessment and Control of Emerging Contaminants; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 337–350. [Google Scholar]
- Su, H.; Li, H.; Chen, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, S. Source identification and potential health risks of fluoride and nitrate in groundwater of a typical alluvial plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.; Subba Rao, N.; Sahoo, H.; Sakram, G. Nitrate contamination in groundwater and its health implications in a semi-urban region of Titrol block, Jagatsinghpur district, Odisha, India. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2023, 132, 103424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaji, E.; Sarath, K.; Santosh, M.; Krishnaprasad, P.; Arya, B.; Babu, M.S. Fluoride contamination in groundwater: A global review of the status, processes, challenges, and remedial measures. Geosci. Front. 2024, 15, 101734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.; Singh, G.; Jadeja, R. Fluoride Contamination in Groundwater, Impacts, and Their Potential Remediation Techniques. In Groundwater Geochemistry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 22–41. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, S.; Fakhri, Y.; Golbini, M.; Thakur, S.K.; Alinejad, A.; Parseh, I.; Shekhar, S.; Bhattacharya, P. Concentration of fluoride in groundwater of India: A systematic review, meta-analysis and risk assessment. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 9, 100224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha Pawan, K.; Tripathi, P. Arsenic and fluoride contamination in groundwater: A review of global scenarios with special reference to India. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 13, 100576. [Google Scholar]
- Kashyap, C.A.; Ghosh, A.; Singh, S.; Ali, S.; Singh, H.K.; Chandrasekhar, T.; Chandrasekharam, D. Distribution, genesis and geochemical modeling of fluoride in the water of tribal area of Bijapur district, Chhattisgarh, central India. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 11, 100403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keesari, T.; Pant, D.; Roy, A.; Sinha, U.K.; Jaryal, A.; Singh, M.; Jain, S.K. Fluoride Geochemistry and Exposure Risk Through Groundwater Sources in Northeastern Parts of Rajasthan, India. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 80, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadpour, A.; Gharehchahi, E.; Gharaghani, M.A.; Shahsavani, E.; Golaki, M.; Berndtsson, R.; Khaneghah, A.M.; Hashemi, H.; Abolfathi, S. Assessment of drinking water quality and identifying pollution sources in a chromite mining region. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 136050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, R.; Nasim, I.; Irfan, A.; Islam, A.; Naeem, A.; Ghani, N.; Irshad, M.A.; Latif, M.; Nisa, B.U.; Ullah, R. Water Quality Index and Human Health Risk Assessment of Drinking Water in Selected Urban Areas of a Mega City. Toxics 2023, 11, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kom, K.P.; Gurugnanam, B.; Bairavi, S. Non-carcinogenic health risk assessment of nitrate and fluoride contamination in the groundwater of Noyyal basin, India. Geod. Geodyn. 2022, 13, 619–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, T.G.; El-Sorogy, A.S. Article Health Risk Assessment of Nitrate and Fluoride in the Groundwater of Central Saudi Arabia. Water 2023, 15, 2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sun, C.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, S.; Lin, R.; Wang, Y. Groundwater Quality and Associated Human Health Risk in a Typical Basin of the Eastern Chinese Loess Plateau. Water 2022, 14, 1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Liu, F.; Chen, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Xu, Y.; Jiao, J.; El-Wardany, R.M. Arsenic and fluoride co-enrichment of groundwater in the loess areas and associated human health risks: A case study of Dali County in the Guanzhong Basin. China Geol. 2024, 7, 445–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Kang, W.; Li, Y.; Li, Z. Fluoride and nitrate contamination of groundwater in the Loess Plateau, China: Sources and related human health risks. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 286, 117287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djahed, B.; Kermani, M.; Farzadkia, M.; Taghavi, M.; Norzaee, S. Exposure to heavy metal contamination and probabilistic health risk assessment using Monte Carlo simulation: A study in the Southeast Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2020, 18, 1217–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasnia, A.; Radfard, M.; Mahvi, A.H.; Nabizadeh, R.; Yousefi, M.; Soleimani, H.; Alimohammadi, M. Groundwater quality assessment for irrigation purposes based on irrigation water quality index and its zoning with GIS in the villages of Chabahar, Sistan and Baluchistan, Iran. Data Brief 2018, 19, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogara, E.; Gyampo, M.; Shaibu, A. Evaluation of the Groundwater Quality and the Associated Potential Health Risks for Human Consumption in the Tolon District, Ghana. 2025. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=5077839 (accessed on 14 February 2025).
- Balamurugan, P.; Kumar, P.; Shankar, K.; Nagavinothini, R.; Vijayasurya, K. Non-Carcinogenic Risk Assessment of Groundwater in Southern Part of Salem District in Tamilnadu, India. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2020, 65, 4697–4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, G.; Tirth, V.; Arora, S.; Algahtani, A.; Kafeel, M.; Alqarni, A.H.; Saluja, P.; Vij, H.; Bavabeedu, S.S.; Tirth, A. Effect of Fluoride Concentration in Drinking Water on Dental Fluorosis in Southwest Saudi Arabia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arahman, N.; Mulyati, S.; Lubis, M.R.; Takagi, R.; Matsuyama, H. The removal of fluoride from water based on applied current and membrane types in electrodialyis. J. Fluor. Chem. 2016, 191, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunanidhi, D.; Aravinthasamy, P.; Roy, P.D.; Praveenkumar, R.M.; Prasanth, K.; Selvapraveen, S.; Thowbeekrahman, A.; Subramani, T.; Srinivasamoorthy, K. Evaluation of non-carcinogenic risks due to fluoride and nitrate contaminations in a groundwater of an urban part (Coimbatore region) of south India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narsimha, A.; Qian, H. Groundwater quality evaluation using water quality index (WQI) for drinking purposes and human health risk (HHR) assessment in an agricultural region of Nanganur, south India. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 176, 153–161. [Google Scholar]
- Saurabh, S.; Saxena, A. Groundwater quality and associated human health risk assessment in parts of Raebareli district, Uttar Pradesh, India. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 10, 100366. [Google Scholar]
- Arun, P.; Singh, A. Evaluation of potential human health risks arising from nitrate and fluoride in the groundwater of Aurangabad, Bihar using GIS and chemometric analysis. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 46, 268. [Google Scholar]
- Khadse Rushikesh, P.; Chaurasia, H. Nutrition status and inequality among children in different geographical regions of Maharashtra, India. Clin. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2020, 8, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouassi, K.J.; Lachassagne, P.; Mangoua, O.M.; Sombo, A.P.; Dibi, B. Identifying the origin of springs in weathered-fractured crystalline aquifers using a hydrogeophysical approach. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 12977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, P.R.; Akhtar, M.S.; Thakur, R.R.; Chattopadhyay, P.; Kar, B.; Bera, D.K.; Chand, S.; Shahid, M.K. Exploring Seasonal Changes in Coastal Water Quality: Multivariate Analysis in Odisha and West Bengal Coast of India. Water 2024, 16, 2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Kang, H.; Tao, W.; Li, H.; He, D.; Ma, L.; Tang, H.; Wu, S.; Yang, K.; Li, X. A spatial distribution–Principal component analysis (SD-PCA) model to assess pollution of heavy metals in soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 859, 160112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Jayakumar, R.; Salih, A. Groundwater Dynamics in Hard Rock Aquifers: Sustainable Management and Optimal Monitoring Network Design; Springer Science Business Media: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Barad, S.; Mishra, P.; Sahu, P.C.; Sarkar, T.; Amin, M.F.; Choudhury, T.; Edinur, H.A.; Kari, Z.A.; Nandi, D.; Pati, S. Comparative approach of decision tree and CWQI analysis for classification of groundwater with a special reference to fluoride ion in drought-prone Boudh district of Odisha, India. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 7, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.; Islam, F.; Tariq, A.; Islam, I.U.; Brian, J.D.; Bibi, T.; Ahmad, W.; Waseem, L.A.; Karuppannan, S.; Al-Ahmadi, S. Groundwater potential zone mapping using GIS and Remote Sensing based models for sustainable groundwater management. Geocarto Int. 2024, 39, 2306275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetrimurugan, E.; Brindha, K.; Elango, L.; Ndwandwe, O.M. Human exposure risk to heavy metals through groundwater used for drinking in an intensively irrigated river delta. Appl. Water Sci. 2016, 7, 3267–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong-Ng, W.; McMurdie, H.; Hubbard, C.; Mighell, A. JCPDS-ICDD Research Associateship (cooperative program with NBS/NIST). J. Res. Natl. Inst. Stand. Technol. 2001, 106, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.S.; Mostafa, M.G. Evaluation of Hydrogeochemical Processes in Groundwater Using Geochemical and Geostatistical Approaches in the Upper Bengal Basin. Geofluids 2022, 2022, 9591717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, U.; Faheem, H.; Jiang, Z.; Wajid, M.; Younas, M.; Zhang, B. Integrating a GIS-Based Multi-Influence Factors Model with Hydro-Geophysical Exploration for Groundwater Potential and Hydrogeological Assessment: A Case Study in the Karak Watershed, Northern Pakistan. Water 2021, 13, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, N.A.; Dinakar, A.; Kumari, B. Appraisal of vulnerable zones of non-cancer-causing health risks associated with exposure of nitrate and fluoride in groundwater from a rural part of India. Environ. Res. 2021, 202, 111674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narsimha, A.; Qian, H. Evaluation of non-carcinogenic causing health risks (NCHR) associated with exposure of fluoride and nitrate contaminated groundwater from a semi-arid region of south India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 81370–81385. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, C.; Assunção, R.; Sequeira, D.; Esteves, F.; Valdiglesias, V.; Laffon, B.; Teixeira, J.P.; Madureira, J. From trihalomethanes chronic daily intake through multiple exposure routes to cancer and non-cancer health risk assessment: Evidence from public Portuguese indoor swimming pools facilities using a probabilistic approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 818, 151790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bus, J.S.; Banton, M.I.; Faber, W.D.; Kirman, C.R.; McGregor, D.B.; Pourreau, D.B. Human health screening level risk assessments of tertiary-butyl acetate (TBAC): Calculated acute and chronic reference concentration (RfC) and hazard quotient (HQ) values based on toxicity and exposure scenario evaluations. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2015, 45, 142–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotruvo, J.A.; Spagnuolo, F.; Cristiani, E. Letters to the Editor. Am. Water Work. Assoc. 2017, 109, 12–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 1983 IS10500; Indian Standard Specification for Drinking Water. Indian Standards Institution: New Delh, India, 1983.
- Abanyie, S.K.; Apea, O.B.; Abagale, S.A.; Amuah, E.E.; Sunkari, E.D. Sources and factors influencing groundwater quality and associated health implications: A review. Emerg. Contam. 2023, 9, 100207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaziz, S.; Gad, M.I.; El Tahan, A.H. Groundwater quality index based on PCA: Wadi El-Natrun, Egypt. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2020, 172, 103964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, R.J. Mechanisms Controlling World Water chemistry. Science 1970, 170, 1088–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.C.; Shashank Shekhar, S.S.; Nathawat, M.S. Evaluation of fluoride contamination in groundwater sources in Palamu district, Jharkhand, India. J. Appl. Sci. 2012, 12, 882–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, B.L.; Banjare, G.R.; Ramteke, S.; Patel, K.S.; Matini, L. Fluoride contamination of groundwater and toxicities in dongargaon block, Chhattisgarh, India. Expo. Health 2017, 9, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.K.; Bhargav, J.S.; KUMAR, Y.S. Nitrate contamination in shallow aquifers of Orissa. In Management of Industrial Effluent and Wastes; Swamy, Y.V., Das, S.N., Parida, K.M., Misra, V.N., Eds.; Allied Publishers Pvt. Ltd.: Mumbai, India, 2002; pp. 25–38. [Google Scholar]
- Government of India. National Water Policy 2012. Ministry of Water Resources, River Development and Ganga Rejuvenation. 2012. Available online: https://nwm.gov.in/sites/default/files/national%20water%20policy%202012_0.pdf (accessed on 18 March 2025).
- Mester, T.; Szabó, G.; Sajtos, Z.; Baranyai, E.; Kiss, E.; Balla, D. Assessment of Groundwater Decontamination Processes around a Dismantled Septic Tank Using GIS and Statistical Analysis. Water 2023, 15, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Name of Unit | Rigaku Created Ultima IV with a Graphite Monochromator, Automated Slit, and Receiving Slit. |
|---|---|
| Target used | Cu Kα |
| Scanning rate | 1°/min |
| Tube voltage | 30 Kv |
| Current | 40 Ma |
| Range | 2 × 103 cps |
| Parameter | Desirable | Permissible | Range | Inference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 6.5 | 8.5 | 7.28–8.5 | Slightly alkaline, it affects solubility. |
| Turbidity | 1 | 5 | 0.27–11.00 NTU | High values indicate suspended particles. |
| Sodium (Na) | 50 | 200 | 39–207.5 mg/L | Higher levels may impact taste and BP. |
| Potassium (K) | 10 | 12 | 1.3–13.15 mg/L | Possible agricultural/industrial contamination. |
| Calcium (Ca) | 30 | 200 | 16.5–285.6 mg/L | Contributes to hardness and causes scaling. |
| Magnesium (Mg) | 30 | 120 | 2.2–140.34 mg/L | This leads to hardness and affects taste. |
| Chloride (Cl) | 250 | 1000 | 15–915 mg/L | High values may indicate saline intrusion. |
| Sulfate (SO4) | 200 | 300 | 1.04–152.03 mg/L | Excess may cause laxative effects. |
| Iron (Fe) | - | 1 | 0.18–2.25 mg/L | A total of 11.2% of samples exceed the permissible limit, affecting taste and staining. |
| Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) | 500 | 1000 | 240–2143 mg/L | A total of 20% of samples are brackish, affecting potability. |
| Total Hardness (TH) | 200 | 600 | 50–1291 mg/L | A total of 50% of samples are very hard, requiring treatment. |
| Total Alkalinity | 200 | 600 | 285–607 mg/L | Indicates the buffering capacity of water. |
| Bicarbonate (HCO3−) | 100 | 250 | 115.5–608.5 mg/L | High levels in 50% of samples, affecting hardness. |
| Carbonate (CO32−) | 100 | 250 | 0–171.5 mg/L | Influences alkalinity and water hardness. |
| NO3 (mg/L) | 45 | 45 | 1.57–203.51 mg/L | A total of 16% of samples in the high-risk category are linked to agricultural fertilizers and waste oxidation. |
| F (mg/L) | 1 | 1.5 | 0.14–4.6 mg/L | Exceeds WHO limit (1.5 mg/L) in some samples; causes fluorosis at high levels. |
| Parameter | Range | Inference |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrate (NO3−) | 1.57–203.51 mg/L | A total of 16% of samples in the high-risk category are linked to agricultural fertilizers and waste oxidation. |
| Fluoride (F−) | 0.14–4.6 mg/L | Exceeds WHO limit (1.5 mg/L) in some samples; causes fluorosis at high levels. |
| Fluoride (F−) Concentration (mg/L) | Percentage of Samples (%) |
|---|---|
| <0.5 ppm (not desirable) | 35.36 |
| 0.5–1.5 ppm (permissible) | 36.58 |
| >1.5 ppm (above permissible) | 28.04 |
| Age Group | HQ (Fluoride) | HQ (Nitrate) | Total HI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Infants | 0.01–2.56 | 0.04–5.71 | 0.14–8.27 |
| Children | 0.12–2.96 | 0.05–6.61 | 0.17–9.57 |
| Male Adults | 0.08–2.19 | 0.03–2.89 | 0.12–7.08 |
| Female Adults | 0.08–2.07 | 0.03–4.62 | 0.11–6.69 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barad, S.; Thakur, R.R.; Nandi, D.; Bera, D.K.; Sahu, P.C.; Mishra, P.; Samal, K.P.; Ðurin, B. Hydrogeochemical and Geospatial Insights into Groundwater Contamination: Fluoride and Nitrate Risks in Western Odisha, India. Water 2025, 17, 1514. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101514
Barad S, Thakur RR, Nandi D, Bera DK, Sahu PC, Mishra P, Samal KP, Ðurin B. Hydrogeochemical and Geospatial Insights into Groundwater Contamination: Fluoride and Nitrate Risks in Western Odisha, India. Water. 2025; 17(10):1514. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101514
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarad, Subhasmita, Rakesh Ranjan Thakur, Debabrata Nandi, Dillip Kumar Bera, Pramod Chandra Sahu, Priyanka Mishra, Kshyana Prava Samal, and Bojan Ðurin. 2025. "Hydrogeochemical and Geospatial Insights into Groundwater Contamination: Fluoride and Nitrate Risks in Western Odisha, India" Water 17, no. 10: 1514. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101514
APA StyleBarad, S., Thakur, R. R., Nandi, D., Bera, D. K., Sahu, P. C., Mishra, P., Samal, K. P., & Ðurin, B. (2025). Hydrogeochemical and Geospatial Insights into Groundwater Contamination: Fluoride and Nitrate Risks in Western Odisha, India. Water, 17(10), 1514. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101514













