Development of Flood Early Warning Framework to Predict Flood Depths in Unmeasured Cross-Sections of Small Streams in Korea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
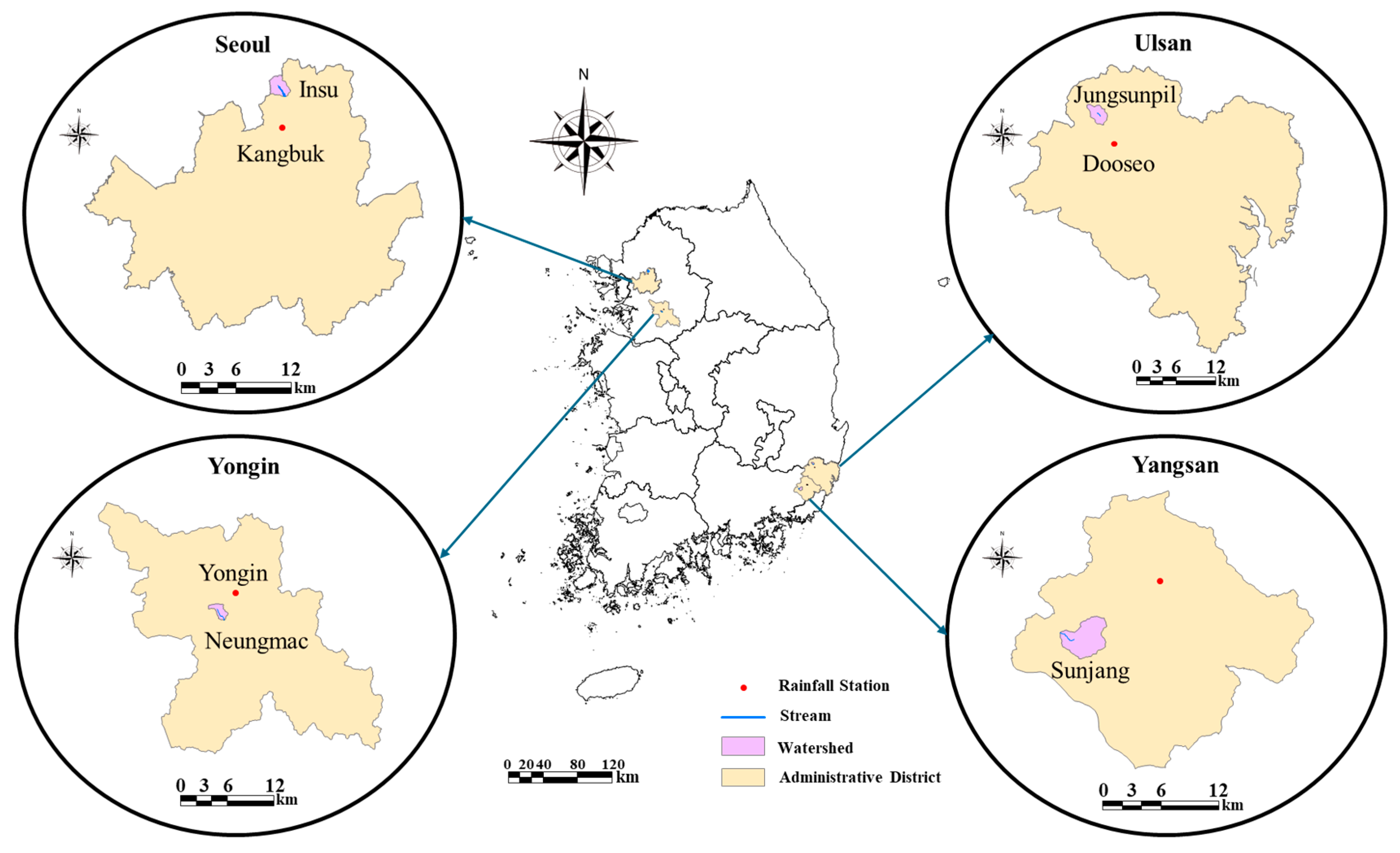
2.1. Selection of Small Streams
2.2. Selection of Weather Stations
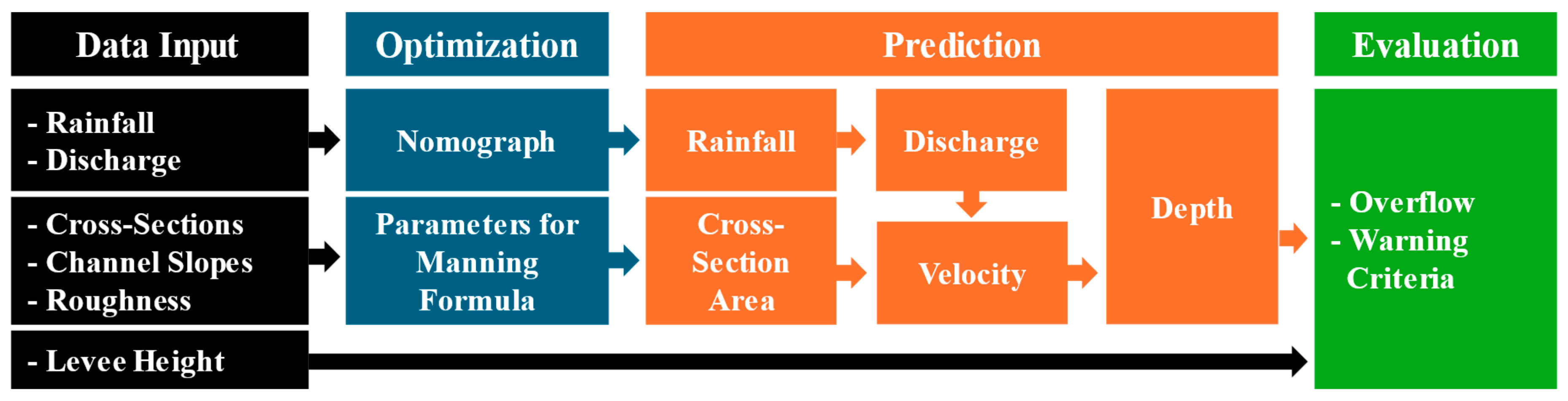
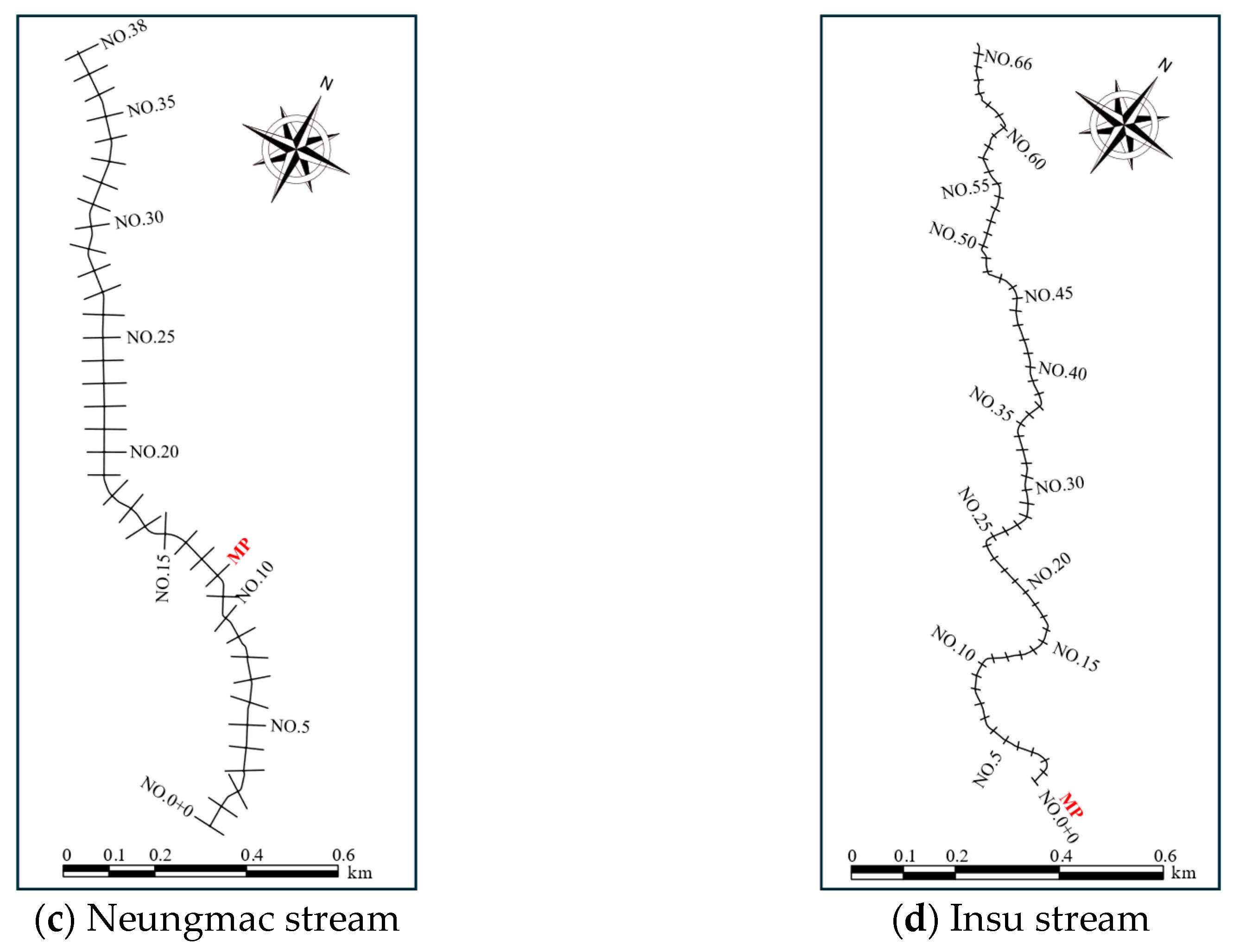
2.3. Flood Depth Prediction Method for Unmeasured Cross-Sections and Data Collection
3. The Development of the Small Stream Flood Early Warning Framework
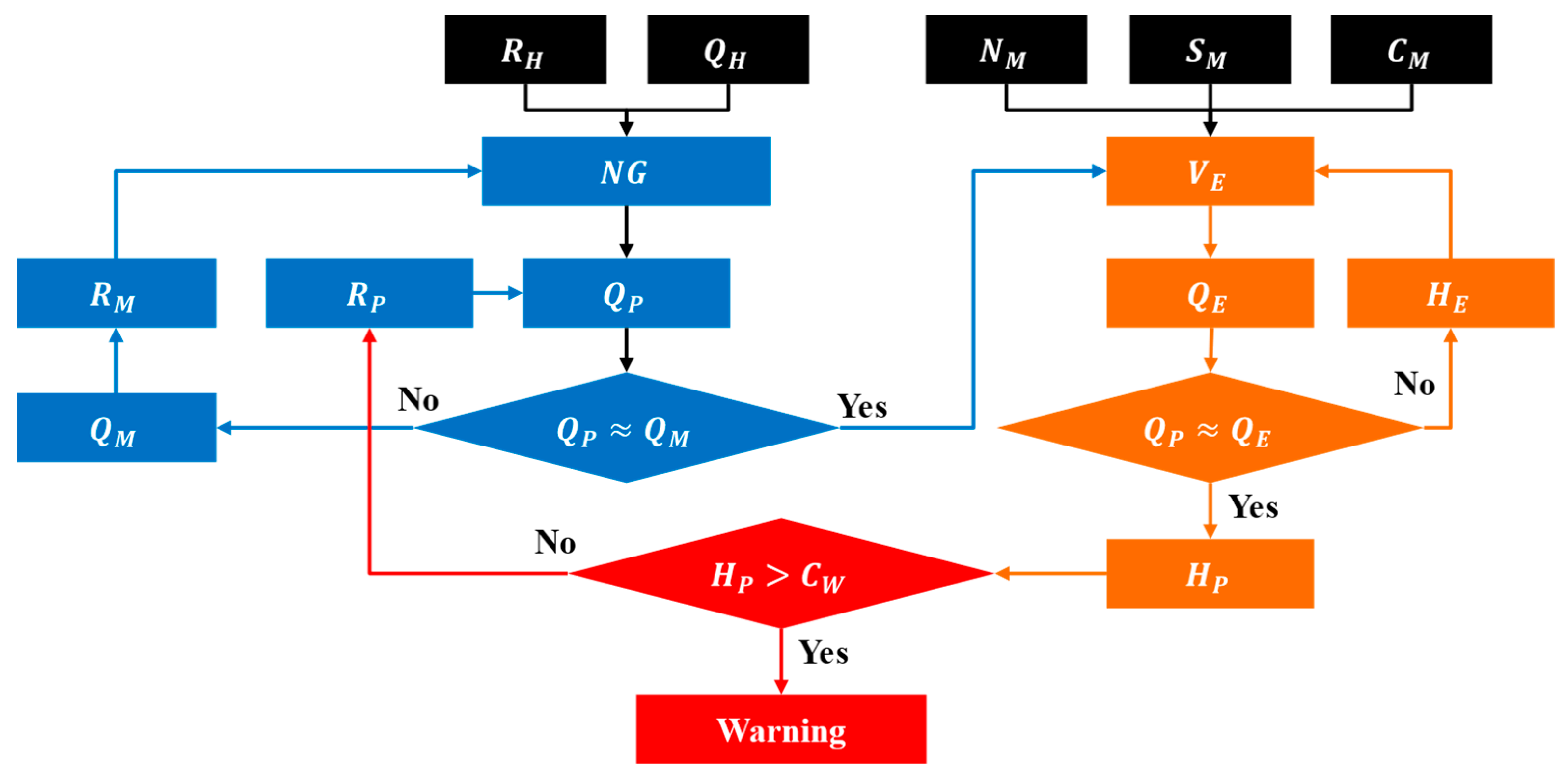
3.1. Real-Time Flood Discharge Prediction Technology
3.2. Robust Constrained Nonlinear Optimization Algorithm
3.3. Technology for Predicting Real-Time Flood Depth in Unmeasured Cross-Sections
3.4. Setting Flood Warning Criteria
4. Results and Discussion
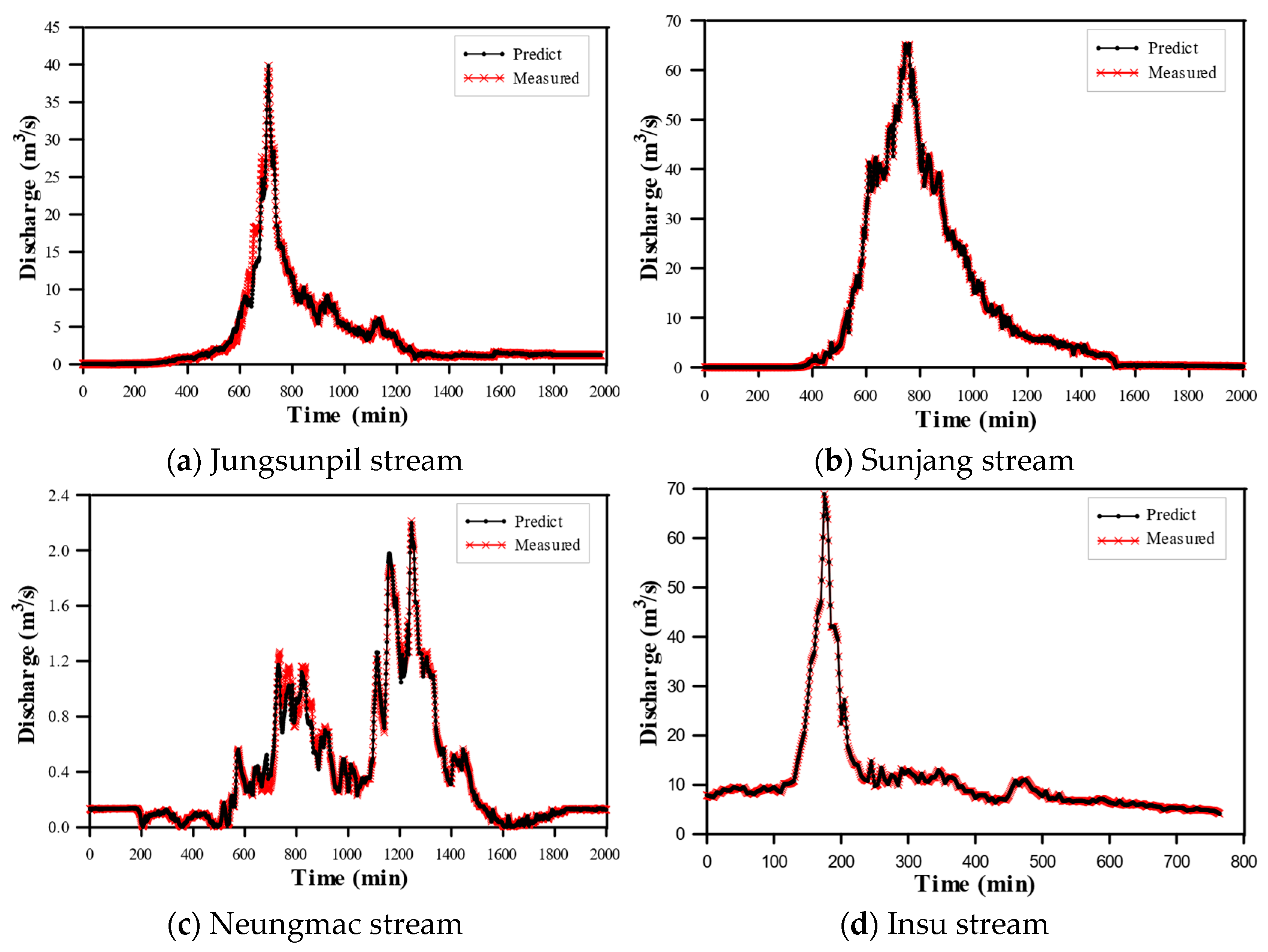
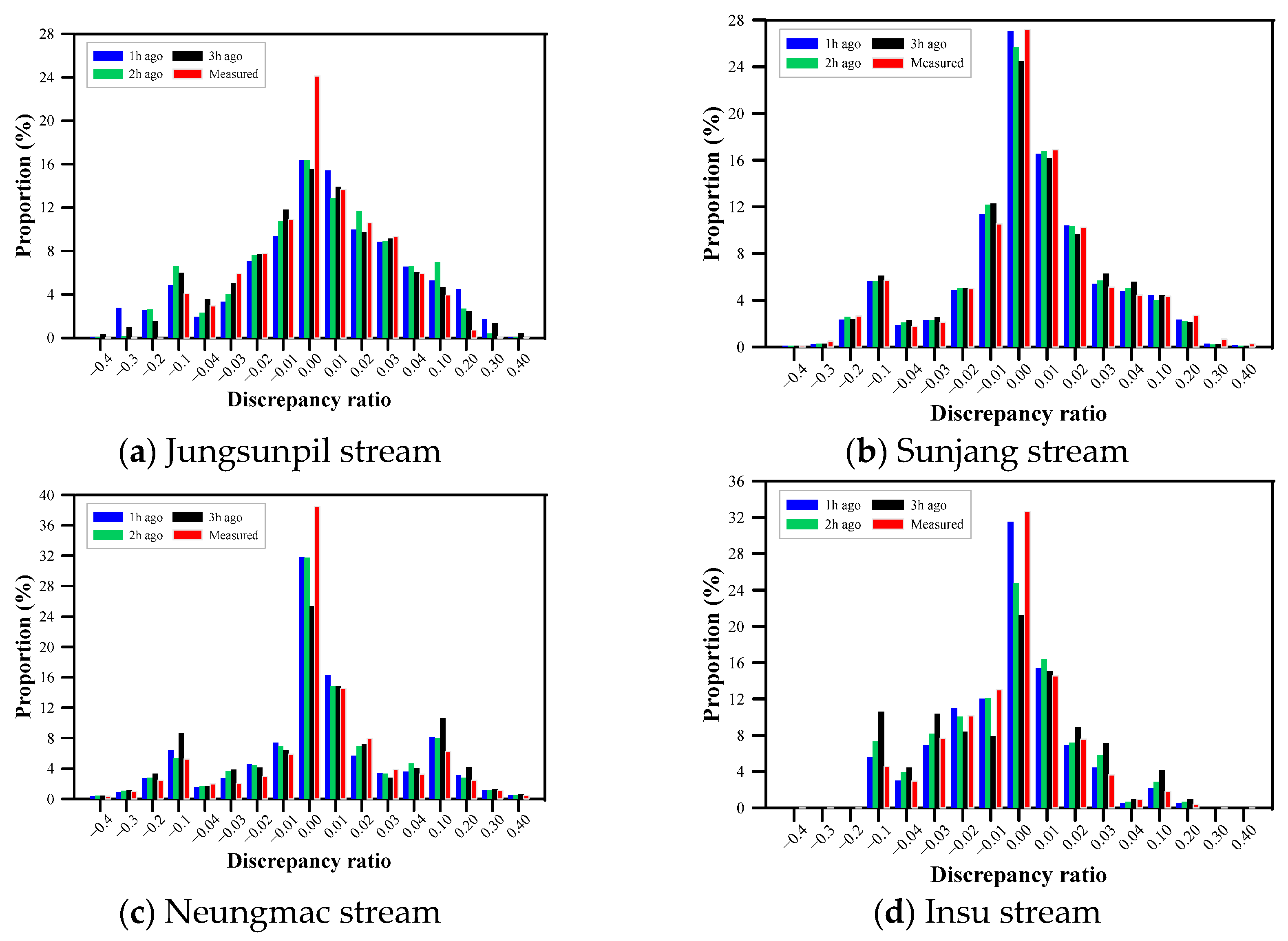
4.1. Discharge Prediction and Evaluation for Measured Small Stream Section
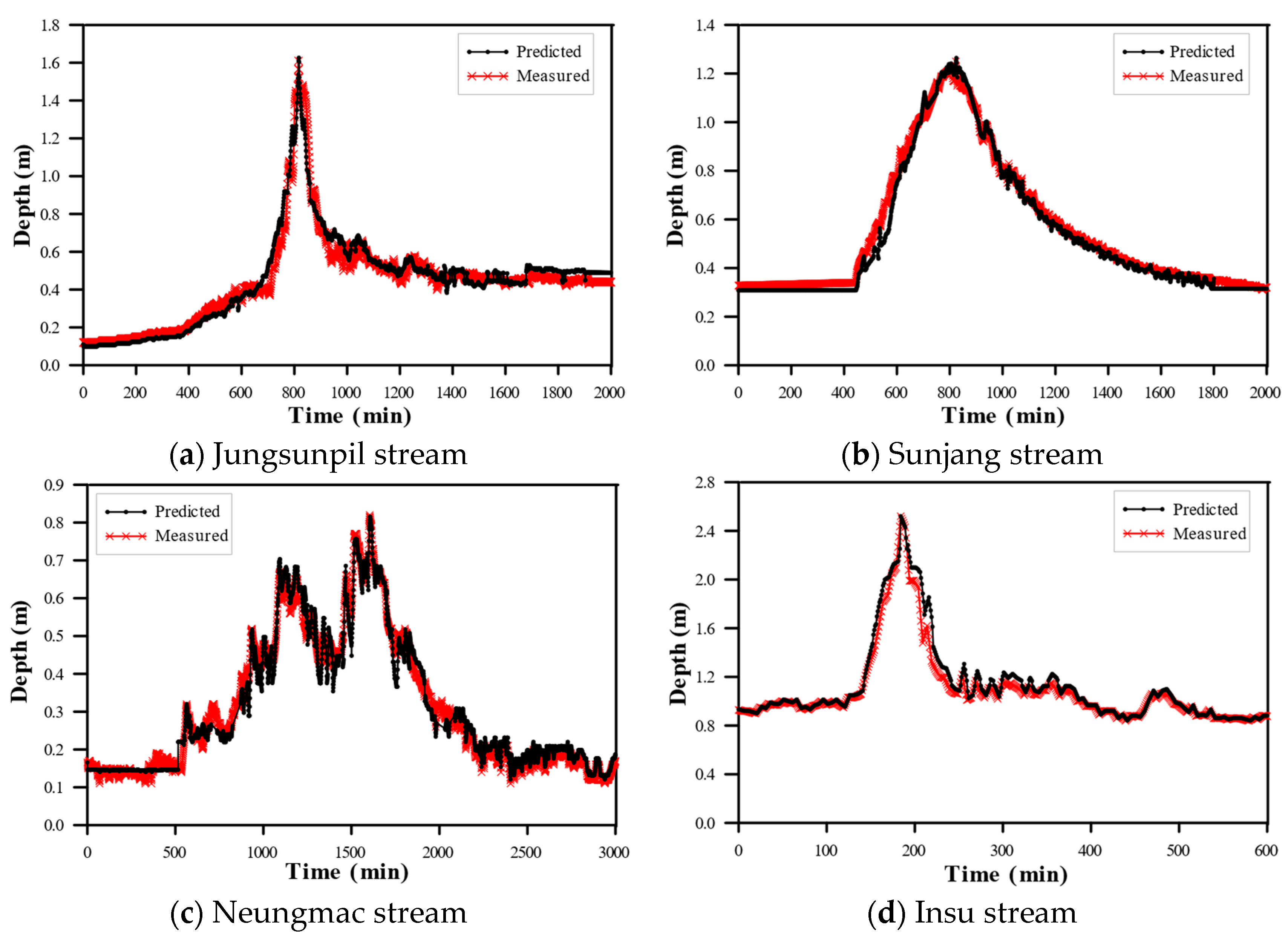
4.2. The Depth Prediction and Evaluation for Unmeasured Small Stream Sections
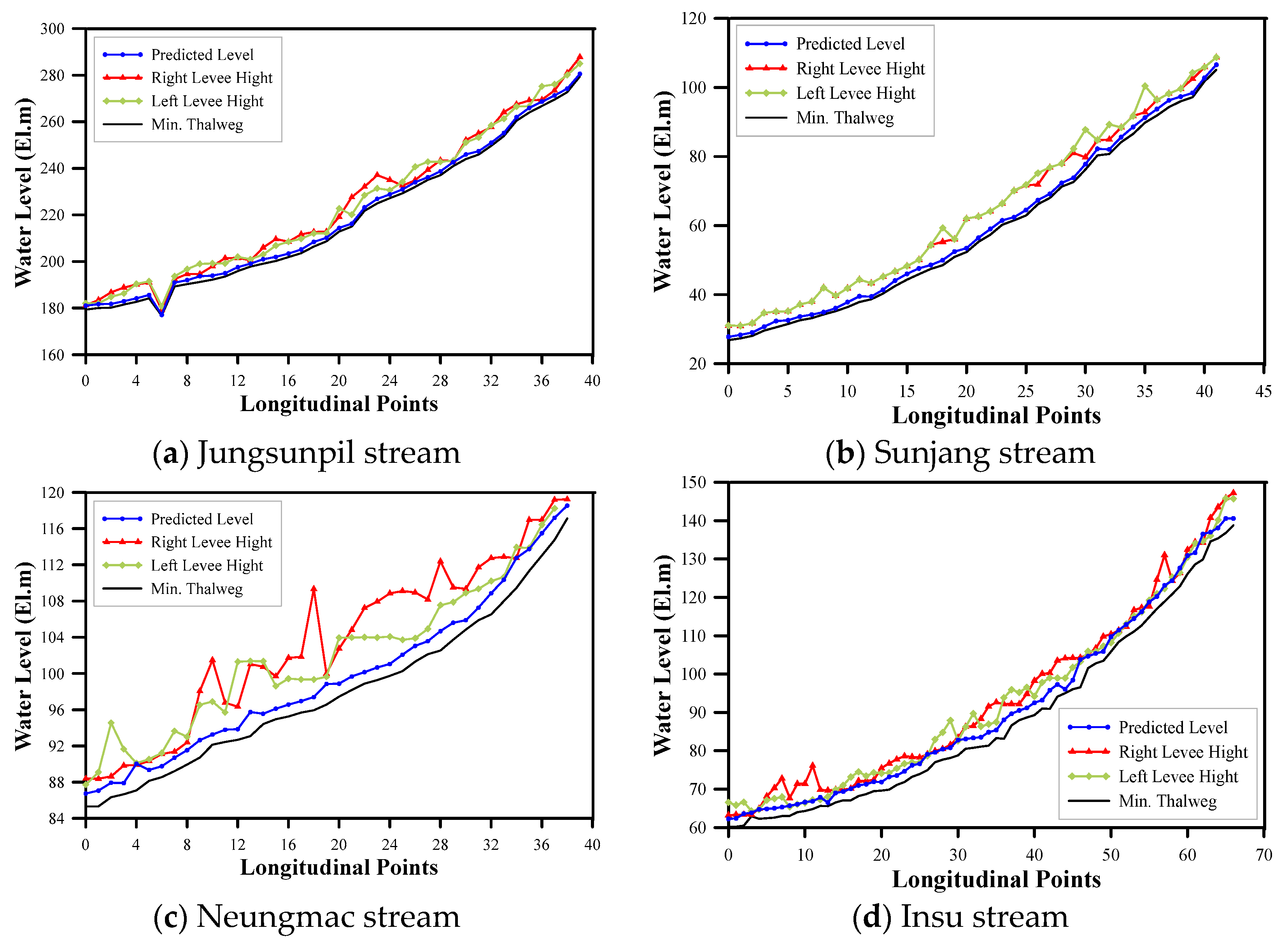
4.3. Applicability Evaluation of Depth Prediction for Unmeasured Cross-Sections
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Joint Ministries. 2023 Climate Change Report; KMA: Daejeon, Republic of Korea, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- UNDRR. Annual Report 2023; United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- MOIS. Natural Disasters Yearbook 2023; MOIS: Sejong, Republic of Korea, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, N.; Zhang, L.; Yu, H.; Gao, J.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Y.; Wan, X. Quantifying the Impact of Climate Change and Human Activities on Multiobjective Water Resource Management in the Hanjiang River Basin, China. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2025, 151, 05025001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaál, L.; Szolgay, J.; Kohnová, S.; Parajka, J.; Merz, R.; Viglione, A.; Blöschl, G. Flood timescales: Understanding the interplay of climate and catchment processes through comparative hydrology. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, w04511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomi, T.; Sidle, R.C.; Richardson, J.S. Understanding processes and downstream linkages of headwater systems: Headwaters differ from downstream reaches by their close coupling to hillslope processes, more temporal and spatial variation, and their need for different means of protection from land use. BioScience 2002, 52, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewlett, J.D. The varying source area of streamflow from upland basins. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Interdisciplinary Aspect of Watershed Management, Bozeman, MT, USA, 3–6 August 1970; ASCE: New York, NK, USA, 1970; pp. 65–83. [Google Scholar]
- Hunter, M.A.; Quinn, T.; Hayes, M.P. Low flow spatial characteristics in forested headwater channels of southwest Washington. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2005, 41, 503–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGlynn, B.L.; McDonnell, J.J.; Seibert, J.; Kendall, C. Scale effects on headwater catchment runoff timing, flow sources, and groundwater-streamflow relations. Water Resour. Res. 2004, 40, w07504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamara, J.P.; Chandler, D.; Seyfried, M.; Achet, S. Soil moisture states, lateral flow, and streamflow generation in a semi-arid, snowmelt-driven catchment. Hydrol. Process. Int. J. 2005, 19, 4023–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiting, P.J.; Bradley, J.B. A process-based classification system for headwater streams. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1993, 18, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D. Field studies of hillslope flow processes. In Hillslope Hydrology; Kirkby, M.J., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NK, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Woods, R.; Sivapalan, M.; Duncan, M. Investigating the representative elementary area concept: An approach based on field data. Hydrol. Process. 1995, 9, 291–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeau, T.L.; Rains, M.C. Hydrological connectivity between headwater streams and downstream waters: How science can inform policy 1. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2007, 43, 118–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J.S.; Sivapalan, M.; Snell, J.D. On the relative roles of hillslope processes, channel routing, and network geomorphology in the hydrologic response of natural catchments. Water Resour. Res. 1995, 31, 3089–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pingel, N.; Jones, C.; Ford, D. Estimating forecast lead time. Nat. Hazards Rev. 2005, 6, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieux, B.E. Distributed Hydrologic Modeling Using GIS. In Distributed Hydrologic Modeling Using GIS; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Cheong, T.; Joo, J.; Byun, H. Advancement of Automatic Discharge Measurement Technology to Enhance Disaster-Safety Codes Forsmall Stream; NDMIPR (ER)-2019-06-01; National Disaster Management Institute: Ulsan, Republic of Korea, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Cheong, T.S.; Kim, S.; Koo, K.M. Development of measured hydrodynamic information-based flood early warning system for small streams. Water Res. 2024, 263, 122159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Meteorological Organization. Manual on Stream Gauging, Vol. I: Fieldwork Vol. II: Computation of Discharge; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010; Volume WMO-No. 1044. [Google Scholar]
- ISO Standard No. 9196:1992; Liquid Flow Measurement in Open Channels—Flow Measurements Under Ice Conditions. American National Standards Institute: New York, NK, USA, 1992.
- Carrigan, P.H. Calibration of US Geological Survey Rainfall-Runoff Model for Peak Flow Synthesis Natural Basins; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1973.
- Dawdy, D.R.; Lichty, R.W.; Bergmann, J.M. A Rainfall-Runoff Simulation Model for Estimation of Flood Peaks for Small Drainage Basins; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1972.
- Lichty, R.W.; Liscum, F. A Rainfall-Runoff Modeling Procedure for Improving Estimates of T-Year (Annual) Floods for Small Drainage Basins; Department of the Interior, Geological Survey: Golden, CO, USA, 1978.
- Park, H.G.; Choi, H.I.; Jee, H.K. Flood forecasting by using distributed models with ensemble Kalman filter. In Proceedings of the Korea Water Resources Association Conference, Pyeongchang, Republic of Korea, 21 May 2009; pp. 27–31. [Google Scholar]
- Cheong, T.S.; Choi, C.; Ye, S.J.; Shin, J.; Kim, S.; Koo, K.M. Development of flood early warning frameworks for small streams in Korea. Water 2023, 15, 1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedient, P.B.; Hoblit, B.C.; Gladwell, D.C.; Vieux, B.E. NEXRAD radar for flood prediction in Houston. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2000, 5, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedient, P.B.; Holder, A.; Benavides, J.A.; Vieux, B.E. Radar-based flood warning system applied to tropical storm Allison. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2003, 8, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoblit, B.C.; Vieux, B.E.; Holder, A.W.; Bedient, P.B. Predicting with Precision. Civ. Eng. Mag. (ASCE) 1999, 69, 40–43. [Google Scholar]
- MSIT. Demonstration of a Standalone Flood Forecasting and Warning System Using AI-Based Flood Prediction Algorithm; Ministry of Science and ICT: Sejong, Republic of Korea, 2019.
- Casati, B.; Wilson, L.; Stephenson, D.; Nurmi, P.; Ghelli, A.; Pocernich, M.; Damrath, U.; Ebert, E.; Brown, B.; Mason, S. Forecast verification: Current status and future directions. Meteorol. Appl. A J. Forecast. Pract. Appl. Train. Tech. Model. 2008, 15, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, E.; McBride, J. Verification of precipitation in weather systems: Determination of systematic errors. J. Hydrol. 2000, 239, 179–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.T.; Seo, K.A.; Hur, S.C. Flood forecasting and warning system using real-time hydrologic observed data from the Jungnang stream basin. J. Korea Water Resour. Assoc. 2010, 43, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, D.H.; Shim, J.B.; Yoon, S.S. Development and assessment of flow nomograph for the real-time flood forecasting in Cheonggye stream. J. Korea Water Resour. Assoc. 2012, 45, 1107–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, C.H.; Kim, H.J. Development of flood runoff characteristics nomograph for small catchment using R-programming. In Proceedings of the Korea Water Resources Association Conference, Goseong, Republic of Korea, 28 May 2015; p. 590. [Google Scholar]
- USGS. Flood Frequency and Storm Runoff of Urban Areas of Memphis and Shelby County, Tennessee; USGS: Reston, VA, USA, 1984; p. 110.
- Hill, A.V. The possible effects of the aggregation of the molecules of hemoglobin on its dissociation curves. J. Physiol. 1910, 40, iv–vii. [Google Scholar]
- Leow, M.K.S. Configuration of the hemoglobin oxygen dissociation curve demystified: A basic mathematical proof for medical and biological sciences undergraduates. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 2007, 31, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draper, N.R.; Smith, H. Applied Regression Analysis; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998; Volume 326. [Google Scholar]
- Gallant. Nonlinear regression. Am. Stat. 1975, 29, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, S.J. Confidence intervals for nonlinear regression: A basic program. Behav. Res. Methods Instrum. 1978, 10, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, P.J.; Elvezio, M.R. Robust Statistics; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Holland, P.W.; Welsch, R.E. Robust regression using iteratively reweighted least-squares. Commun. Stat. Theory Methods 1977, 6, 813–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfieri, L.; Zsoter, E.; Harrigan, S.; Hirpa, F.A.; Lavaysse, C.; Prudhomme, C.; Salamon, P. Range-dependent thresholds for global flood early warning. J. Hydrol. X 2019, 4, 100034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber de Melo, W.; Iglesias, I.; Pinho, J. Early warning system for floods at estuarine areas: Combining artificial intelligence with process-based models. Nat. Hazards 2024, 121, 4615–4638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; Chai, F.; Zang, W.; Zhang, H.; Hao, X.; Xu, H. A Two-Level Early Warning System on Urban Floods Caused by Rainstorm. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, W.R.; Mill, H.; Crabbe, A.D. Sediment Transport: An Appraisal of Available Methods: Volume 1: Summary of Existing Theories: Volume 2: Performance of Theoretical Methods When Applied to Flume and Field Data; Hydraulics Research Station: Wad Madani, Sudan, 1972. [Google Scholar]






| Small Stream | Latitude | Longitude | (km2) | (km) | (km) | (m) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jungsunpil | 35.65.17 N | 129.13.17 W | 5.09 | 1.60 | 0.50 | 0.096 | 3.18 | 14.00 | 0.066 |
| Sunjang | 35.24.04 N | 128.55.49 W | 13.63 | 2.17 | 0.34 | 0.093 | 2.14 | 33.50 | 0.130 |
| Neungmac | 37.24.31 N | 127.16.81 W | 2.41 | 0.78 | 0.25 | 0.054 | 3.09 | 9.450 | 0.190 |
| Insu | 37.40.20 N | 127.00.20 W | 3.66 | 1.17 | 0.38 | 0.025 | 3.12 | 17.06 | 0.225 |
| Small Stream | AWS | Latitude | Longitude | () | () | () | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jungsunpil | Dooseo | 35.62.03 N | 129.14.35 W | 123 | 4.23 | 1274 | 1991 |
| Sunjang | Yangsan | 35.30.74 N | 129.02.01 W | 6.29 | 9.86 | 1588 | 2008 |
| Neungmac | Yongin | 37.27.01 N | 127.22.18 W | 83.0 | 5.83 | 1293 | 2005 |
| Insu | Kangbuk | 37.73.50 N | 127.07.50 W | 72.0 | 10.4 | 1544 | 2001 |
| Use Type | Small Stream | R () | H () | Q () | HL () | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Max | Mean | Max | Mean | Max | Min | Max | ||
| Development (2016~2021) | Jungsunpil | 0.16 | 80.0 | 0.24 | 1.98 | 0.83 | 28.78 | 1.87 | 12.58 |
| Sunjang | 0.19 | 95.8 | 0.40 | 2.45 | 1.32 | 210.3 | 2.98 | 9.67 | |
| Neungmac | 0.15 | 55.5 | 0.18 | 1.65 | 0.15 | 14.13 | 2.15 | 15.17 | |
| Insu | 0.17 | 51.5 | 0.23 | 1.39 | 0.09 | 21.39 | 1.38 | 12.10 | |
| Evaluation (2022) | Jungsunpil | 0.16 | 84.8 | 0.11 | 1.61 | 0.08 | 35.93 | 1.87 | 12.58 |
| Sunjang | 0.17 | 59.3 | 0.20 | 1.64 | 0.85 | 65.19 | 2.98 | 9.67 | |
| Neungmac | 0.17 | 56.7 | 0.14 | 1.74 | 0.14 | 14.41 | 2.15 | 15.17 | |
| Insu | 0.30 | 62.5 | 0.21 | 2.52 | 0.24 | 68.88 | 1.38 | 12.10 | |
| Small Stream | Optimum Parameters | Coefficient of Determination () | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jungsunpil | 49.286 | 1.5220 | 15.808 | 1.8832 | 0.98 |
| Sunjang | 316.28 | 7.6866 | 44.553 | 2.8078 | 0.99 |
| Neungmac | 288.92 | 1.0491 | 86.824 | 4.2870 | 0.99 |
| Insu | 60.758 | 1.8662 | 62.927 | 3.3865 | 0.99 |
| Small Stream | RMSE () | Maximum Error | Minimum Error | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jungsunpil | 2.5 | 3.1 | 3.3 | −38.1 | −43.2 | −36.0 | −1.73 | −2.46 | −2.77 |
| Sunjang | 2.0 | 2.1 | 3.3 | −13.8 | −9.98 | 7.48 | −1.76 | −1.86 | −1.48 |
| Neungmac | 1.3 | 1.7 | 2.0 | −0.24 | −1.08 | 0.38 | −0.50 | −1.08 | −0.83 |
| Insu | 1.9 | 1.9 | 2.2 | 32.1 | 13.6 | −18.7 | −0.16 | −1.64 | −3.27 |
| Mean | 1.9 | 2.2 | 2.7 | −5.01 | −10.2 | −11.7 | −1.04 | −1.76 | −2.08 |
| Small Stream | Accuracy | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jungsunpil | 67.08 | 58.24 | 59.37 | 58.85 |
| Sunjang | 69.87 | 70.25 | 70.06 | 67.76 |
| Neungmac | 69.89 | 65.84 | 64.95 | 57.91 |
| Insu | 77.97 | 76.86 | 70.60 | 61.48 |
| Mean | 71.20 | 67.80 | 66.25 | 61.50 |
| Small Stream | RMSE | Coefficient of Determination |
|---|---|---|
| Jungsunpil | 0.042 | 0.98 |
| Sunjang | 0.024 | 0.99 |
| Neungmac | 0.023 | 0.99 |
| Insu | 0.056 | 0.97 |
| Mean | 0.031 | 0.98 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheong, T.-S.; Kim, S.; Koo, K.-M. Development of Flood Early Warning Framework to Predict Flood Depths in Unmeasured Cross-Sections of Small Streams in Korea. Water 2025, 17, 1467. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101467
Cheong T-S, Kim S, Koo K-M. Development of Flood Early Warning Framework to Predict Flood Depths in Unmeasured Cross-Sections of Small Streams in Korea. Water. 2025; 17(10):1467. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101467
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheong, Tae-Sung, Seojun Kim, and Kang-Min Koo. 2025. "Development of Flood Early Warning Framework to Predict Flood Depths in Unmeasured Cross-Sections of Small Streams in Korea" Water 17, no. 10: 1467. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101467
APA StyleCheong, T.-S., Kim, S., & Koo, K.-M. (2025). Development of Flood Early Warning Framework to Predict Flood Depths in Unmeasured Cross-Sections of Small Streams in Korea. Water, 17(10), 1467. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101467





