Transboundary Urban Basin Analysis Using GIS and RST for Water Sustainability in Arid Regions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
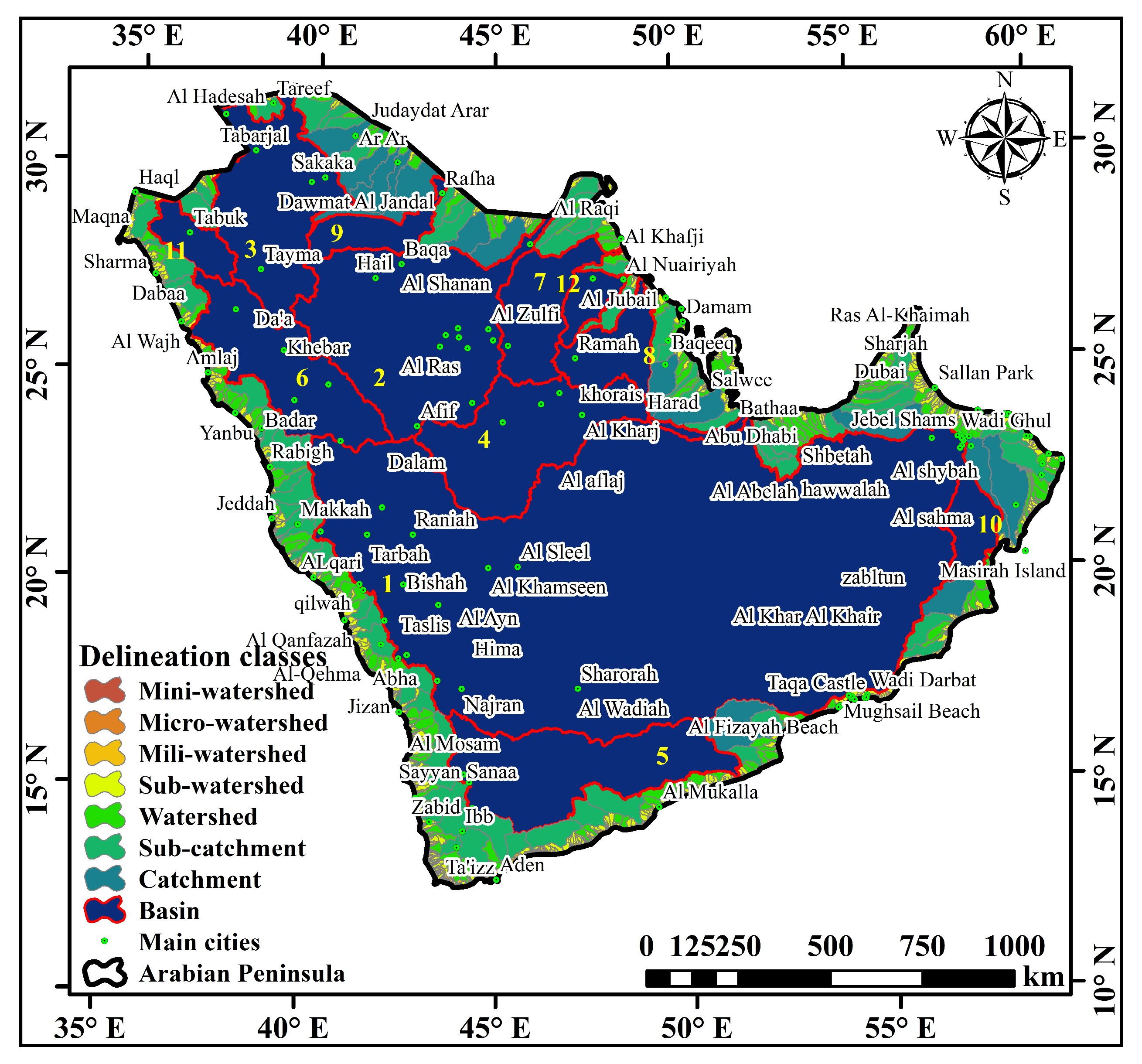
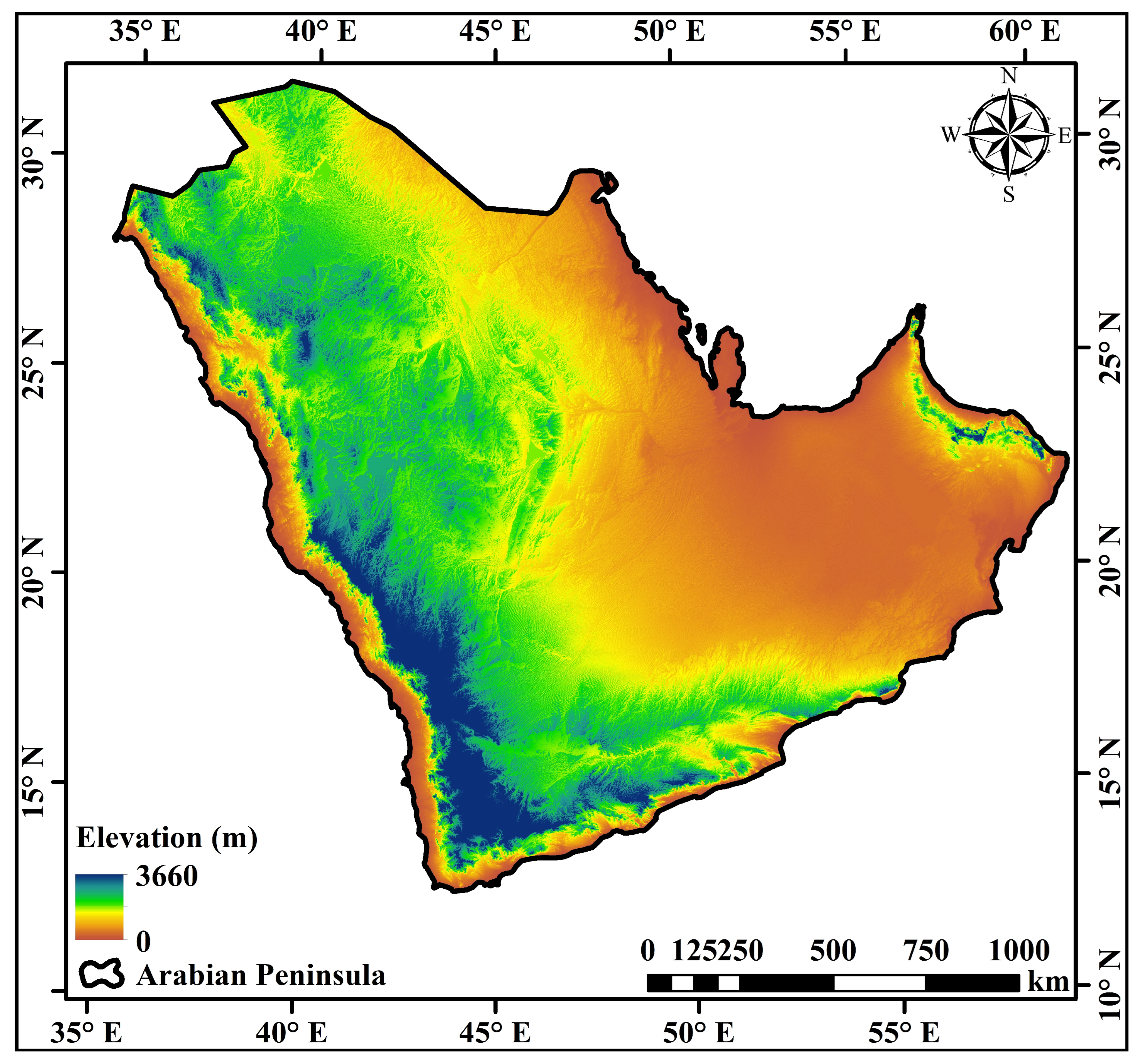
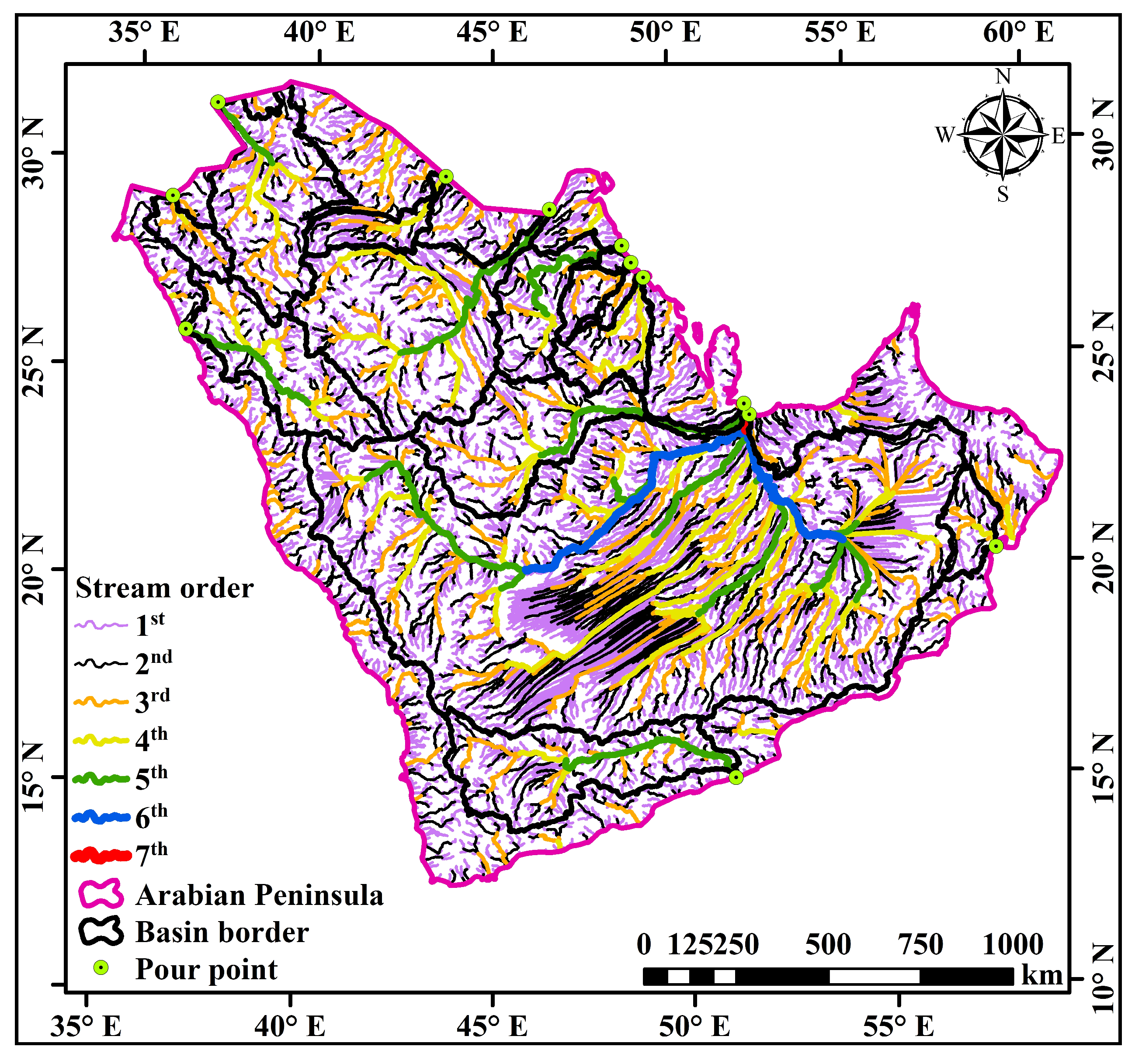
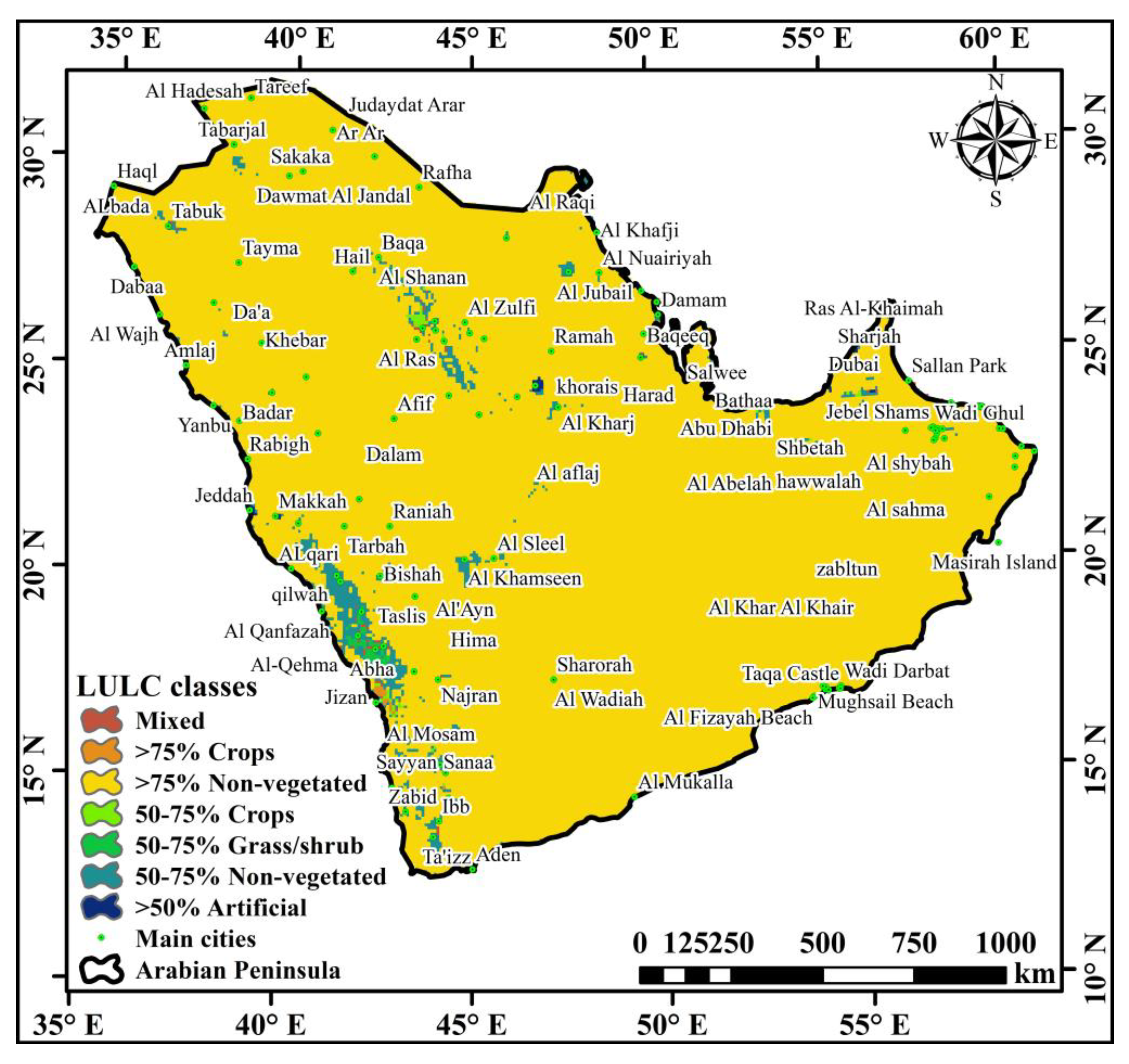
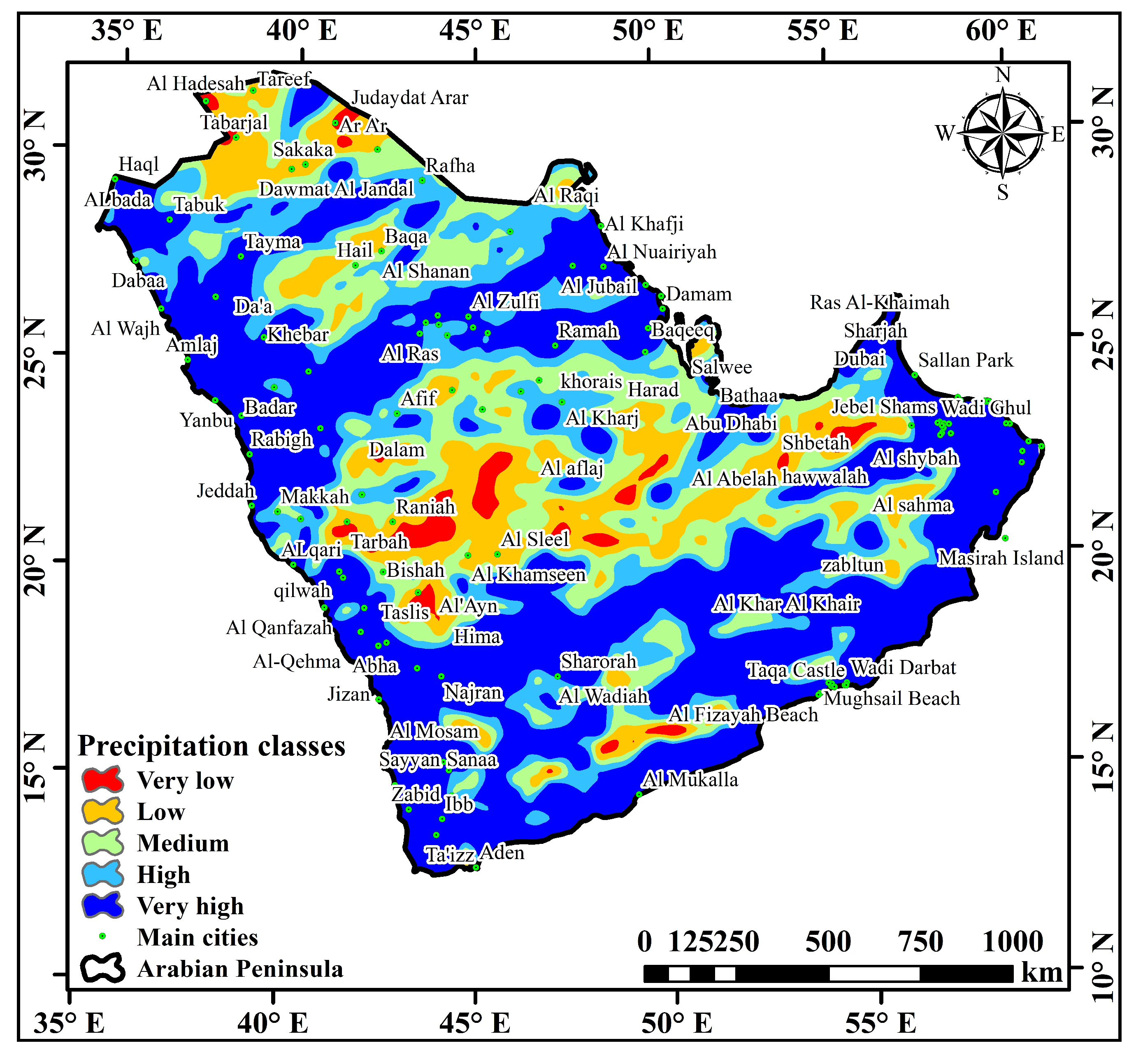
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Morphometric Parameters Analysis
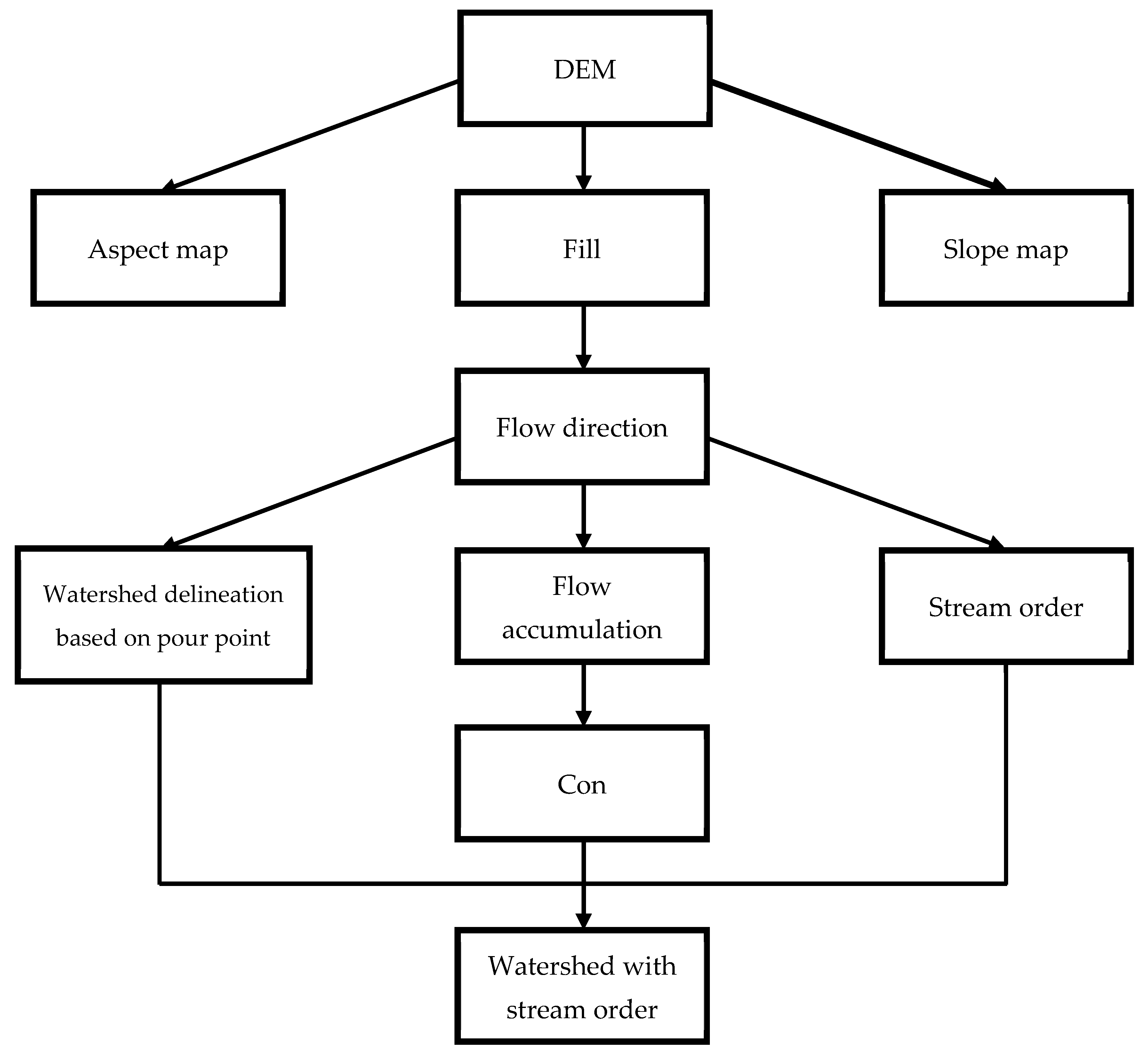
2.2.1. Data Collection and Sources
2.2.2. Morphometric Parameter Classification and Calculation
3. Results and Discussion
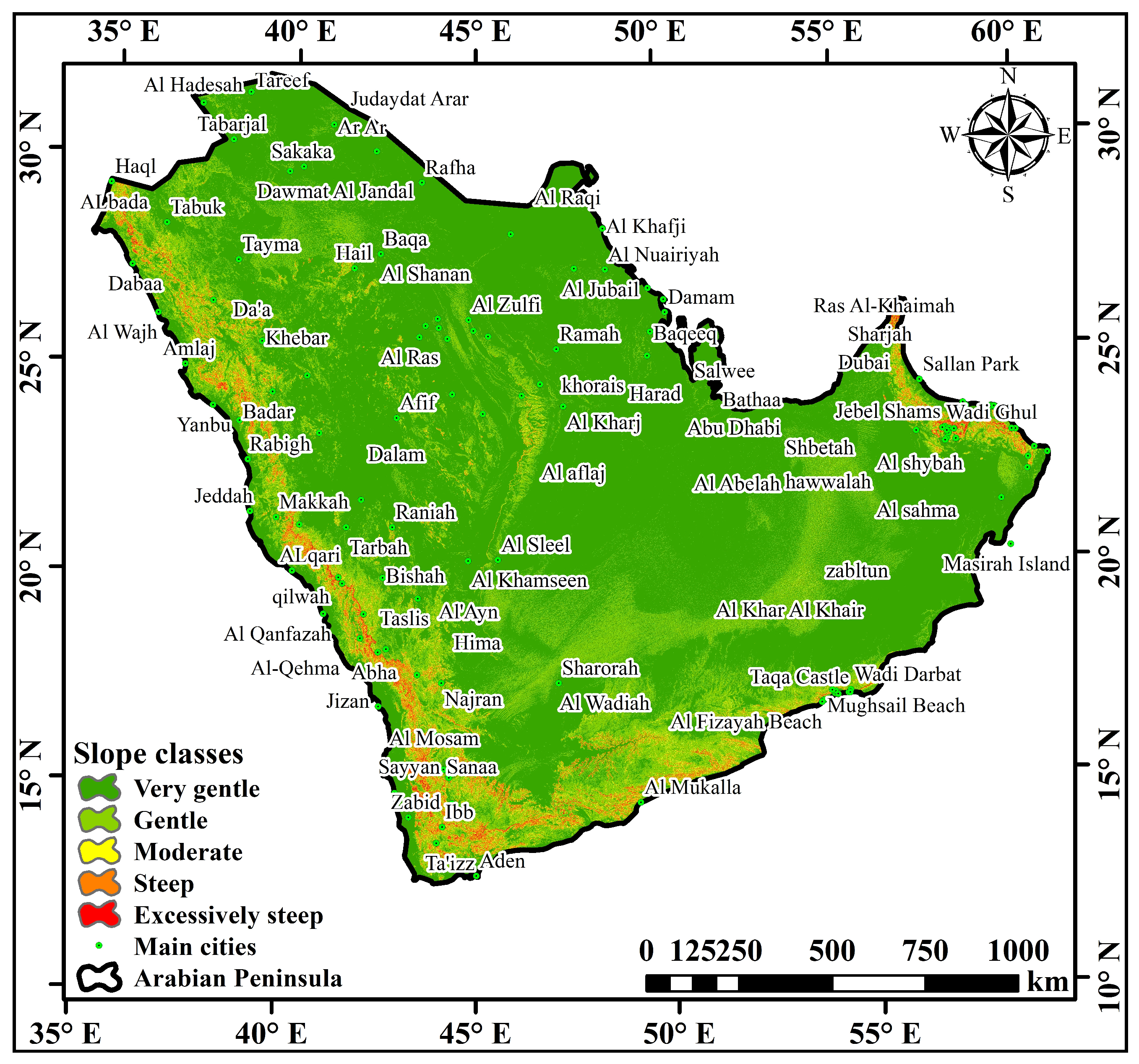
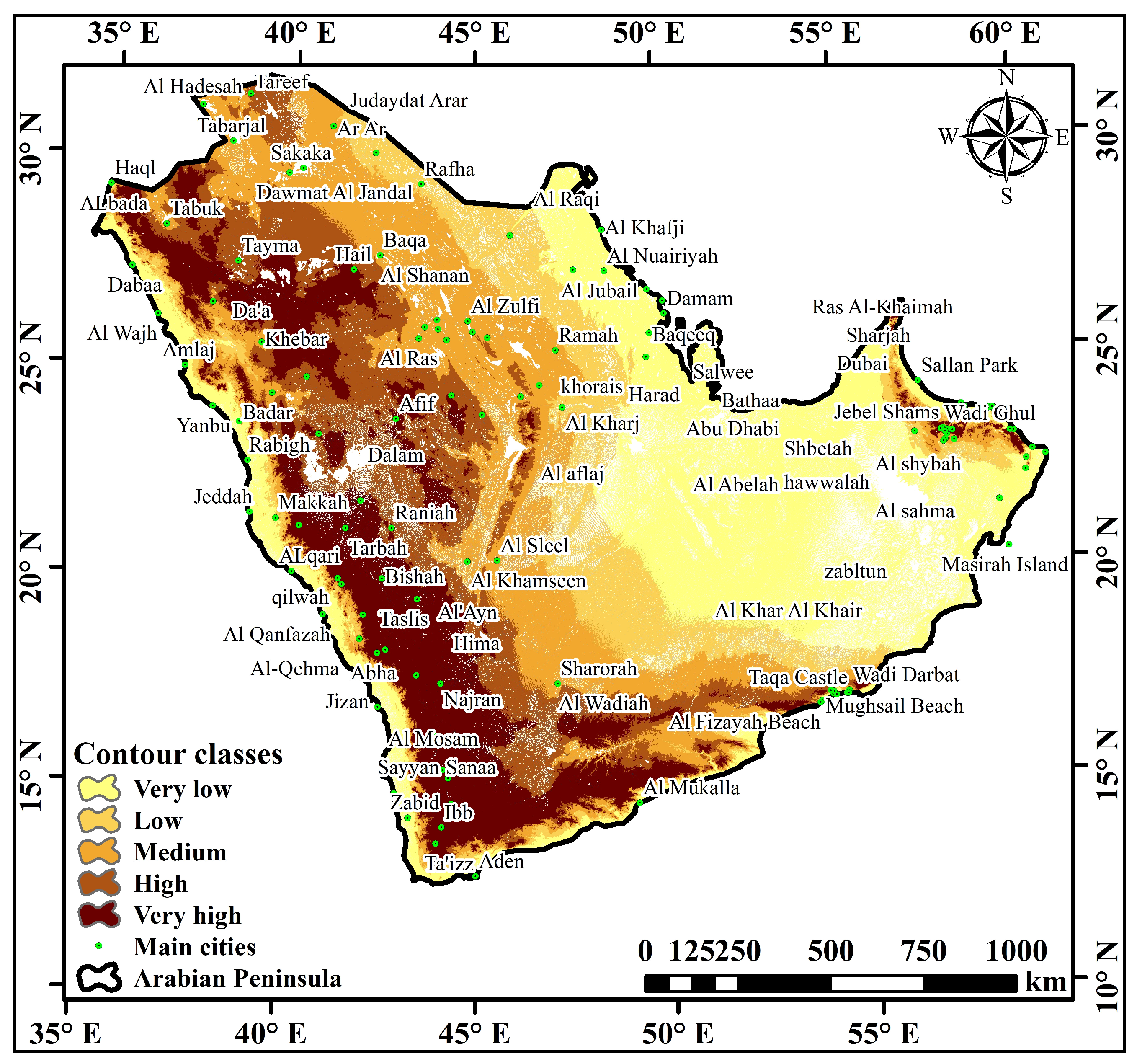
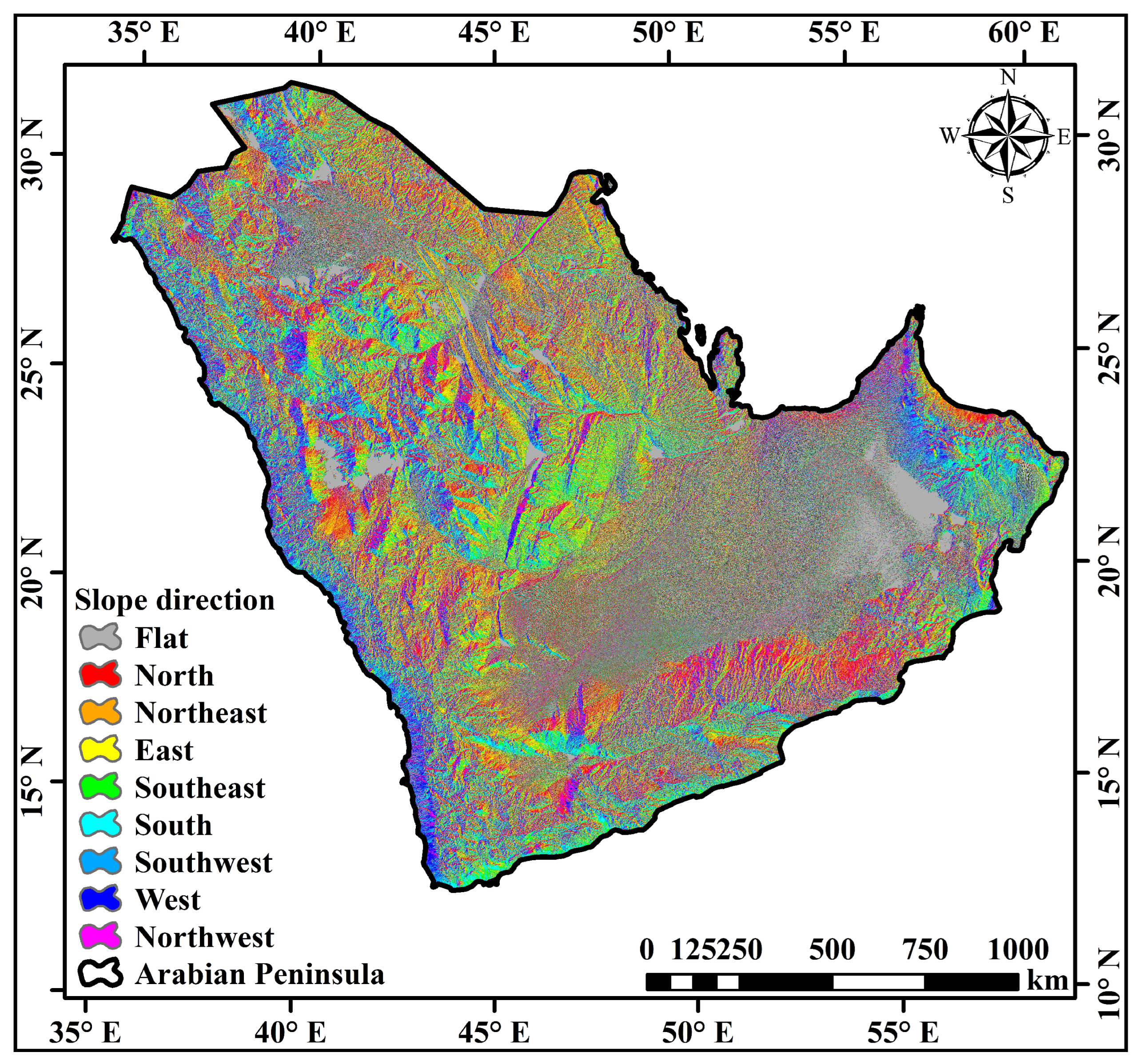
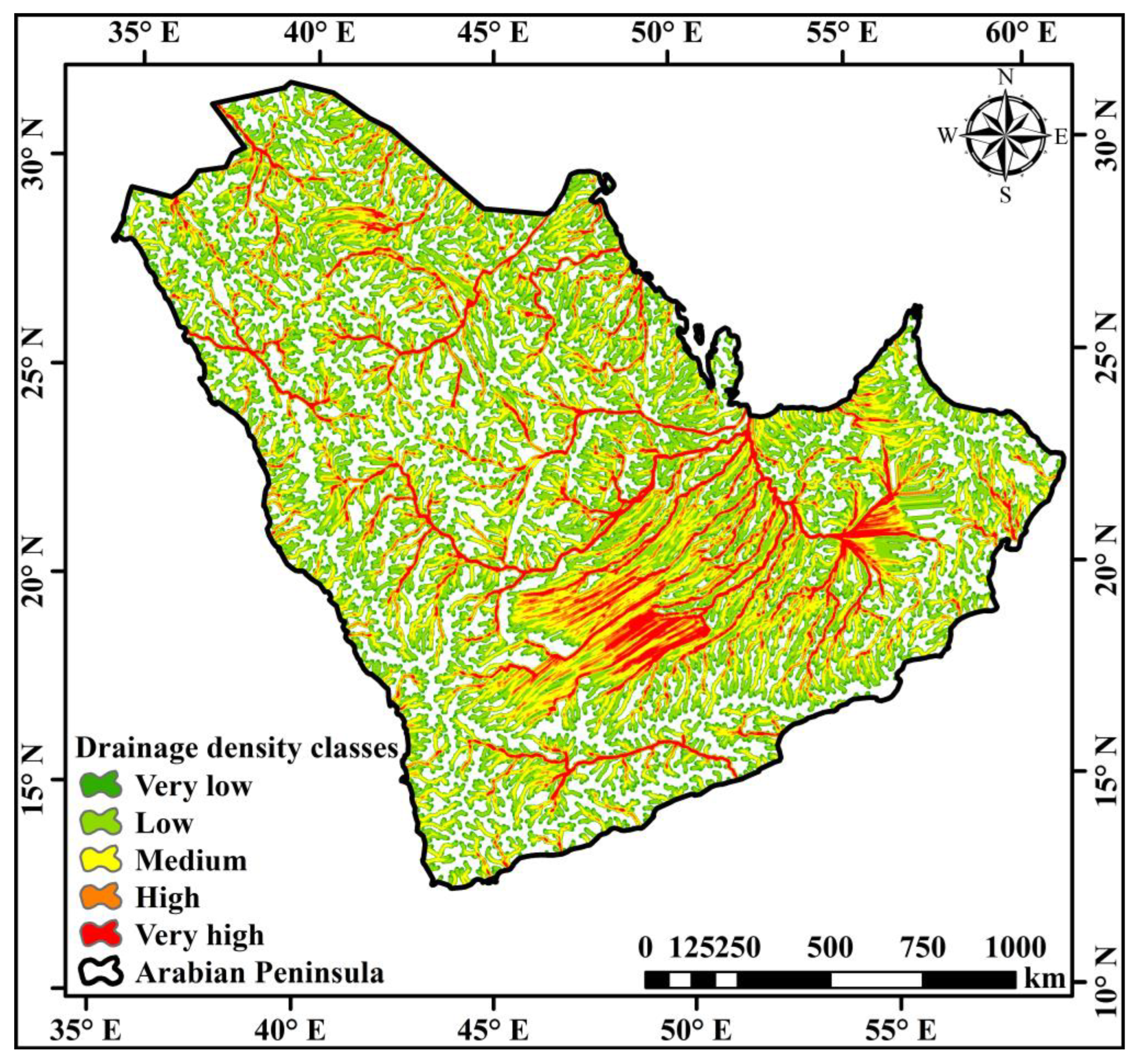
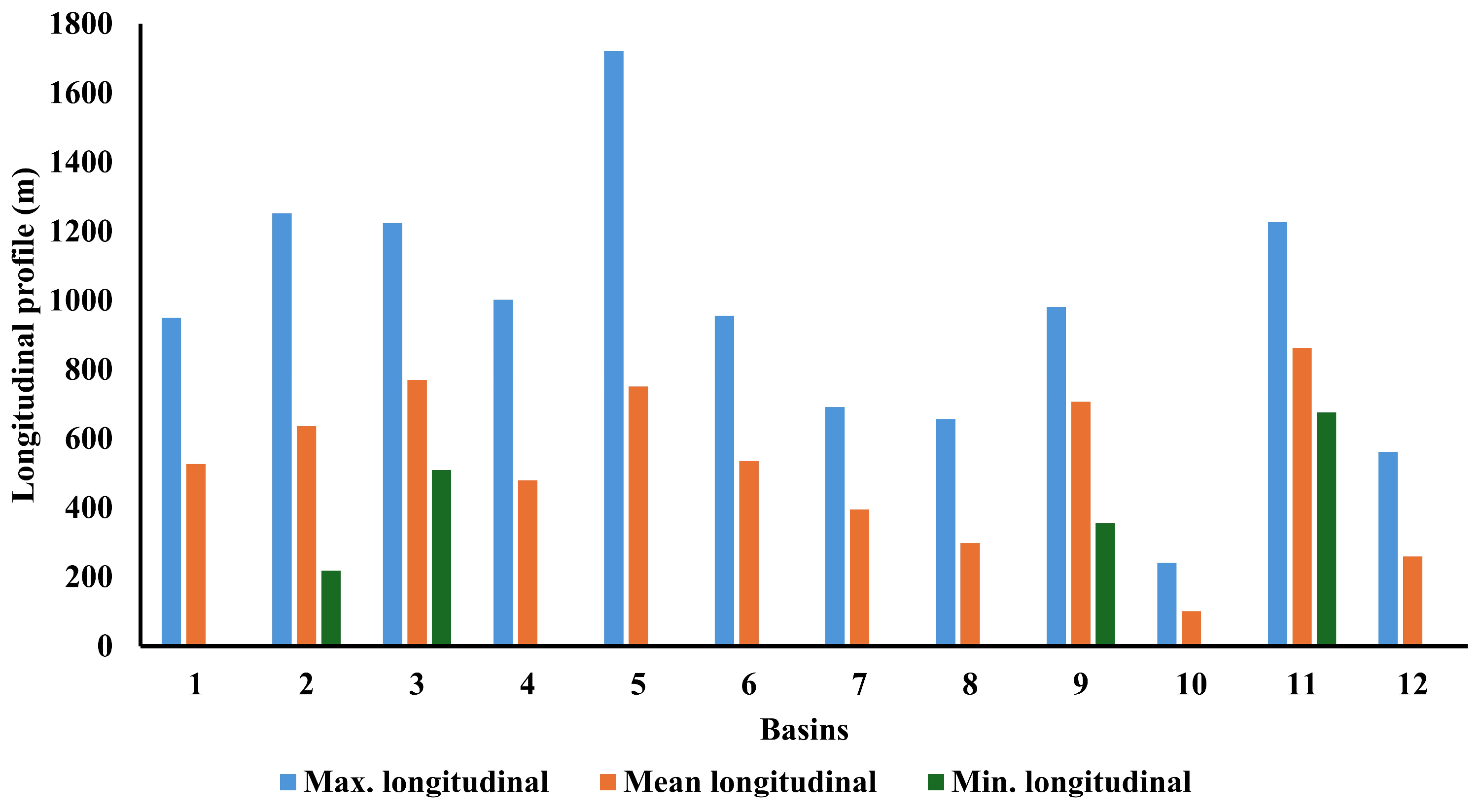
3.1. Linear Morphometric Parameters
3.2. Areal Morphometric Parameters
3.3. Relief Morphometric Parameters
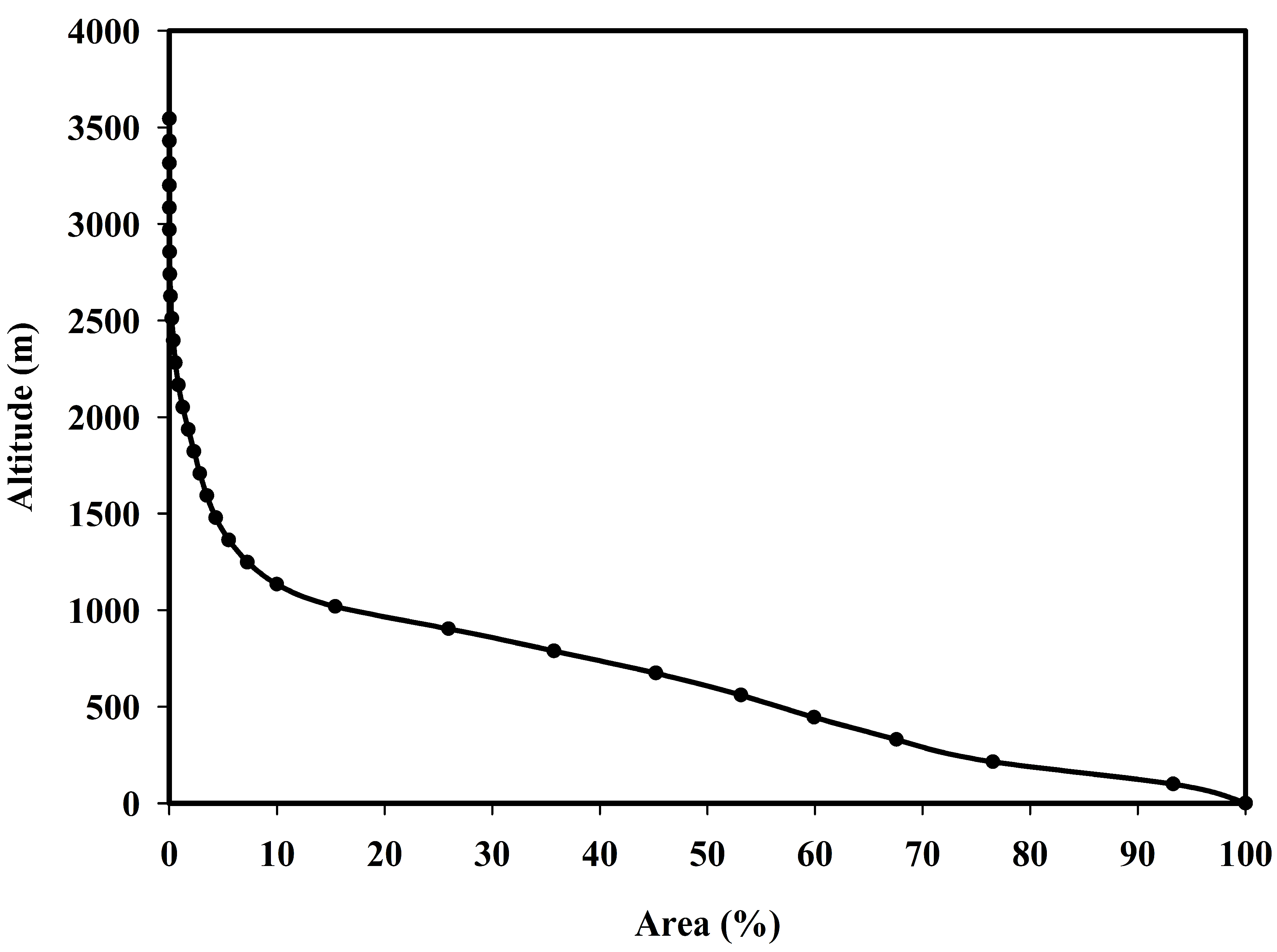
3.4. Hypsometric Analysis
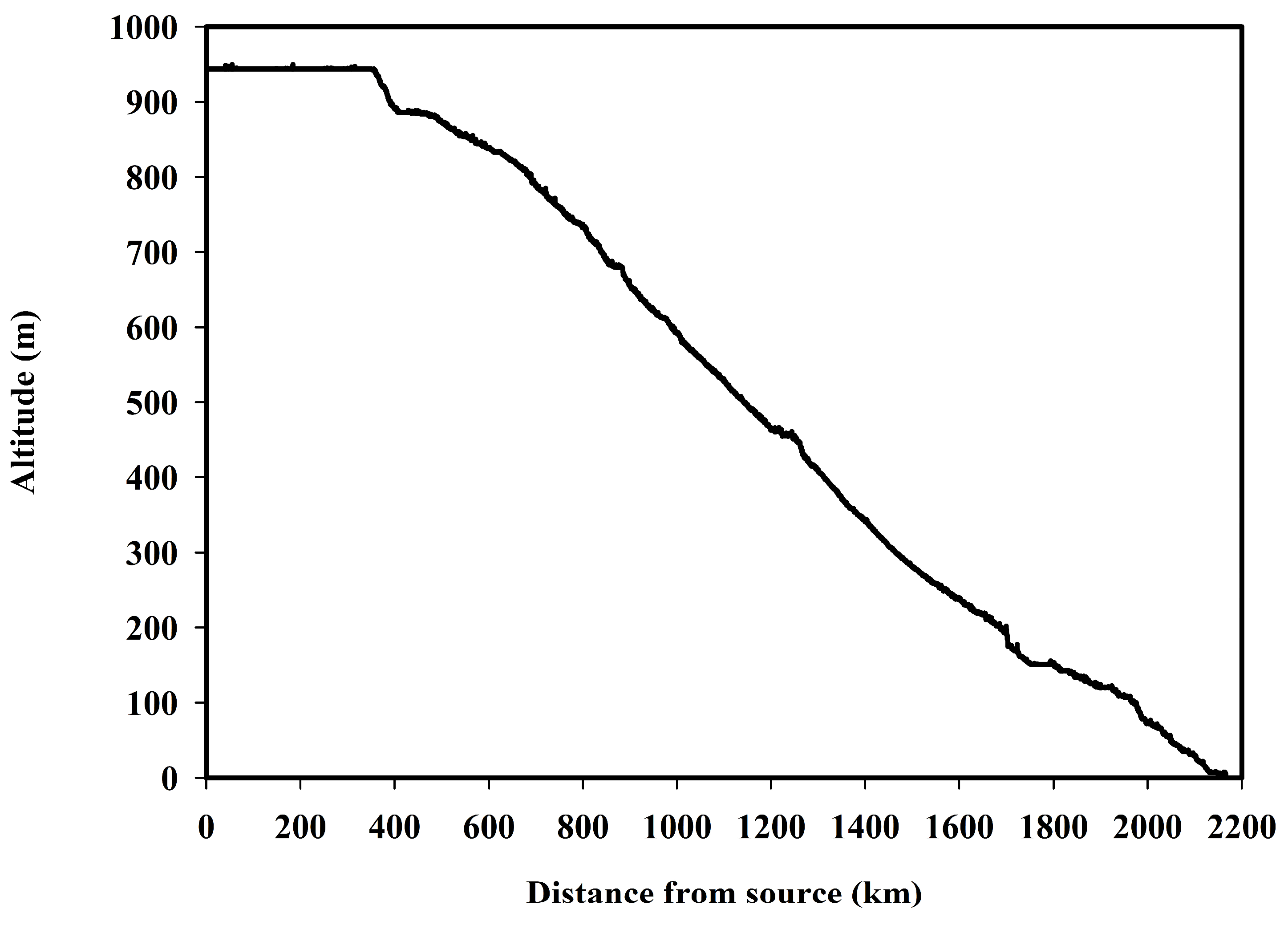
3.5. Slope and Basin Profile
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mosa, M.; Radwan, F.; Al-Ghobari, H.; Fouli, H.; Alazba, A.A. Impact of varied fog collector designs on fog and rainwater harvesting under fluctuating wind speed and direction. Earth Sci. Inform. 2023, 17, 617–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boretti, A.; Rosa, L. Reassessing the projections of the world water development report. NPJ Clean Water 2019, 2, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radwan, F.; Alazba, A.A. Suitable sites identification for potential rainwater harvesting (PRWH) using a multi-criteria decision support system (MCDSS). Acta Geophys. 2023, 71, 449–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzeldin, M.; Alazba, A.A.; Alrdyan, N.; Radwan, F. Rationalizing Irrigation Water Consumption in Arid Climates Based on Multicomponent Landscape Coefficient Approach. Earth Syst. Environ. 2024, 9, 277–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radwan, F.; Alazba, A.A.; Alotaibi, M.; Mossad, A. Site suitability analysis for desalination plants based on the complementarity of GIS, RST, MCE, and spatial AHP in arid and semiarid regions. Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change and Land: An IPCC Special Report on Climate Change, Desertification, Land Degradation, Sustainable Land Management, Food Security, and Greenhouse Gas Fluxes in Terrestrial Ecosystems. In Climate Change and Land; Shukla, P.R., Skea, J., Buendia, E.C., Masson-Delmotte, V., Pörtner, H.O., Roberts, D., Zhai, P., Slade, R., Connors, S., et al., Eds.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Radwan, F.; Alazba, A.A.; Mossad, A. Flood risk assessment and mapping using AHP in arid and semiarid regions. Acta Geophys. 2019, 67, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radwan, F.; Alazba, A.A.; Mossad, A. Estimating potential direct runoff for ungauged urban watersheds based on RST and GIS. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altinbilek, D.; Hatipoglu, M.A. Water Resources Development. In Water Resources of Turkey; Harmancioglu, N.B., Altinbilek, D., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 61–84. [Google Scholar]
- UN. The Sustainable Development Goals Report 2022. 2022. Available online: https://unstats.un.org/sdgs/report/2022/ (accessed on 23 April 2025).
- Gorgoglione, A.; Crisci, M.; Kayser, R.H.; Chreties, C.; Collischonn, W. A New Scenario-Based Framework for Conflict Resolution in Water Allocation in Transboundary Watersheds. Water 2019, 11, 1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zittis, G.; Almazroui, M.; Alpert, P.; Ciais, P.; Cramer, W.; Dahdal, Y.; Fnais, M.; Francis, D.; Hadjinicolaou, P.; Howari, F. Climate change and weather extremes in the Eastern Mediterranean and Middle East. Rev. Geophys. 2022, 60, e2021RG000762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfa, A.; Ayyoubzadeh, S.A.; Shafizadeh-Moghadam, H.; Mianabadi, H. Transboundary hydropolitical conflicts and their impact on river morphology and environmental degradation in the Hirmand Basin, West Asia. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoudy, M.; Al-Saidi, M.; Al Manji, A.; Ayoub, J.; Bateh, F.; Dajani, M.; El Sheikh, R.; El Musa, S.; Mahmoud, M.; Shuker, Z. Troubled Waters in Conflict and a Changing Climate: Transboundary Basins Across the Middle East and North Africa; Carnegie Endowment for International Peace: Washington, DC, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulrazzak, M.J.; Oikonomou, P.D.; Grigg, N.S. Transboundary groundwater cooperation among countries of the Arabian Peninsula. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2020, 146, 05019023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolokytha, E.; Malamataris, D. Integrated water management approach for adaptation to climate change in highly water stressed basins. Water Resour. Manag. 2020, 34, 1173–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajadi, P.; Singh, A.; Mukherjee, S.; Sang, Y.-F.; Chapi, K.; Salari, M. Drainage network extraction and morphometric analysis in an Iranian basin using integrating factor analysis and geospatial techniques. Geocarto Int. 2022, 37, 896–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erosemiah, D.; Viji, R. Study on drainage network pattern and morphometric analysis by using hydrology support algorithm. J. Geol. Soc. India 2023, 99, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radwan, F.; Alazba, A. Integrated Hydrologic Study of the Arid and Semi-arid Regions using RST and GIS in the Riyadh Metropolitan Area, Saudi Arabia. J. Geol. Soc. India 2021, 97, 539–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radwan, F.; Alazba, A.; Mossad, A. Analyzing urban watersheds morphometric in arid and semiarid regions using the complementarity of RST and GIS. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu El-Magd, S.A.; Orabi, H.O.; Ali, S.A.; Parvin, F.; Pham, Q.B. An integrated approach for evaluating the flash flood risk and potential erosion using the hydrologic indices and morpho-tectonic parameters. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radwan, F.; Alazba, A.; Mossad, A. Watershed morphometric analysis of Wadi Baish Dam catchment area using integrated GIS-based approach. Arab. J. Geosci. 2017, 10, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portuguez-Maurtua, M.; Arumi, J.L.; Stehr, A.; Lagos, O.; Chávarri-Velarde, E.; Rivera-Ruiz, D. Mapping of Areas Vulnerable to Flash Floods by Means of Morphometric Analysis with Weighting Criteria Applied. Water 2023, 15, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutradhar, S.; Mondal, P. Prioritization of watersheds based on morphometric assessment in relation to flood management: A case study of Ajay river basin, Eastern India. Watershed Ecol. Environ. 2023, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogale, A. Morphometric analysis of a drainage basin using geographical information system in Gilgel Abay watershed, Lake Tana Basin, upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Appl. Water Sci. 2021, 11, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, R.N.; Kushwaha, V.K. Watershed prioritization based on morphometric parameters and PCA technique: A case study of deonar river sub basin, sidhi area, Madhya Pradesh, India. J. Geol. Soc. India 2021, 97, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radwan, F.; Alazba, A.A.; Mossad, A. Analyzing the geomorphometric characteristics of semiarid urban watersheds based on an integrated GIS-based approach. Mod. Earth Syst. Environ. 2020, 6, 1913–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Karan, K.; Singh, S.K.; Chauhan, P.; Berndtsson, R. Fusing morphometric characteristics with extreme precipitation indices for identifying the most vulnerable sub-basin at risk of flooding. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2023, 50, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, M.; Gope, D. Hydro-morphometric characterization and prioritization of sub-watersheds for land and water resource management using fuzzy analytical hierarchical process (FAHP): A case study of upper Rihand watershed of Chhattisgarh State, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2021, 11, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahala, A. The significance of morphometric analysis to understand the hydrological and morphological characteristics in two different morpho-climatic settings. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaber, S.M.; Abu-Allaban, M.M.; Sengupta, R. Spatial and temporal patterns of indicators of climate change and variability in the Arab world in the past four decades. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 15145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadry, B.N.; Abdel Maksoud, K.M.; Zahabnazouri, S. Geotourism Development in the Middle East: A Comparative Study of Iran, Saudi Arabia, Oman and Jordan. In Tourism Planning and Development in the Middle East; CABI GB: Carson, CA, USA, 2022; pp. 126–141. [Google Scholar]
- Alsharhan, A.S.; Kendall, C.G.S.C. Paleozoic sequence stratigraphy, depositional systems, and hydrocarbon habitats across the Arabian plate. AAPG Bull. 2021, 105, 1149–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valjarević, A.; Algarni, S.; Morar, C.; Grama, V.; Stupariu, M.; Tiba, A.; Lukić, T. The coastal fog and ecological balance for plants in the Jizan region, Saudi Arabia. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 30, 103494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almazroui, M.; Nazrul Islam, M.; Athar, H.; Jones, P.; Rahman, M.A. Recent climate change in the Arabian Peninsula: Annual rainfall and temperature analysis of Saudi Arabia for 1978–2009. Int. J. Climatol. 2012, 32, 953–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sakkaf, A.S.; Jiahua, Z.; Fengmei, Y.; Hamed, M.M.; Simbi, C.H.; Ahmed, A.; Shahid, S. Assessing exposure to climate extremes over the Arabian Peninsula using ERA5 reanalysis data: Spatial distribution and temporal trends. Atmos. Res. 2024, 300, 107224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagami, Y.; Tatebe, H.; Kataoka, T.; Suzuki, T.; Watanabe, M. Impacts of oceanic mesoscale structures on sea surface temperature in the Arabian Sea and Indian summer monsoon revealed by climate model simulations. J. Clim. 2023, 36, 5477–5490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almazroui, M. Changes in temperature trends and extremes over Saudi Arabia for the period 1978–2019. Adv. Meteorol. 2020, 2020, 8828421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patlakas, P.; Stathopoulos, C.; Flocas, H.; Bartsotas, N.S.; Kallos, G. Precipitation climatology for the arid region of the Arabian Peninsula—Variability, trends and extremes. Climate 2021, 9, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharath, A.; Kumar, K.K.; Maddamsetty, R.; Manjunatha, M.; Tangadagi, R.B.; Preethi, S. Drainage morphometry based sub-watershed prioritization of Kalinadi basin using geospatial technology. Environ. Chall. 2021, 5, 100277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, P.; Kumar, P.; Vishwakarma, D.K.; Ashok, A.; Elbeltagi, A.; Gupta, S.; Kuriqi, A. Watershed prioritization using morphometric analysis by MCDM approaches. Ecol. Inform. 2022, 70, 101763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, R.E. Drainage-basin characteristics. Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1932, 13, 350–361. [Google Scholar]
- Horton, R.E. Erosional development of streams and their drainage basins; hydrophysical approach to quantitative morphology. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1945, 56, 275–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strahler, A.N. Dynamic basis of geomorphology. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1952, 63, 923–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, V.C. A Quantitative Geomorphic Study of Drainage Basin Characteristics in the Clinch Mountain Area Virginia and Tennessee; Columbia University: New York, NY, USA, 1953. [Google Scholar]
- Schumm, S.A. Evolution of drainage systems and slopes in badlands at perth amboy, New Jersey. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1956, 67, 597–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strahler, A.N. Quantitative Geomorphology of Drainage Basin and Channel Networks. In Handbook of Applied Hydrology; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Pande, C.; Moharir, K.; Pande, R. Assessment of morphometric and hypsometric study for watershed development using spatial technology—A case study of Wardha river basin in Maharashtra, India. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2021, 19, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guth, P.L.; Van Niekerk, A.; Grohmann, C.H.; Muller, J.-P.; Hawker, L.; Florinsky, I.V.; Gesch, D.; Reuter, H.I.; Herrera-Cruz, V.; Riazanoff, S. Digital elevation models: Terminology and definitions. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavoiance, I. Morphometry of Drainage Basins (Developments in Water Science); Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1985; Volume 20, pp. 104–105. [Google Scholar]
- Melton, M.A. An Analysis of the Relations Among Elements of Climate, Surface Properties, and Geomorphology; Columbia University: New York, NY, USA, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- Pike, R.J.; Wilson, S.E. Elevation-relief ratio, hypsometric integral, and geomorphic area-altitude analysis. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1971, 82, 1079–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreedevi, P.; Subrahmanyam, K.; Ahmed, S. The significance of morphometric analysis for obtaining groundwater potential zones in a structurally controlled terrain. Environ. Geol. 2005, 47, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.P. Elementary Hydrology; Prentice Hall of India Private Limited: New Delhi, India, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Chelladurai, V.; BharaniPriya, A.; Mullaivasanthan, M. Groundwater Level Analysis of Sathyamangalam Region, Tamil Nadu, India Using GIS. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2023, 1258, 012005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasi, V.; Pinninti, R.; Landa, S.R.; Rathinasamy, M.; Sangamreddi, C.; Kuppili, R.R.; Dandu Radha, P.R. Comparison of different digital elevation models for drainage morphometric parameters: A case study from South India. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taib, H.; Hadji, R.; Hamed, Y. Erosion patterns, drainage dynamics, and their environmental implications: A case study of the hammamet basin using advanced geospatial and morphometric analysis. J. Umm Al-Qura Univ. Appl. Sci. 2023, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, A.; Gupta, N.C.; Dey, B. Morphometric Analysis of Gandak River Drainage Basin Using Geographic Information System (GIS) And SRTM-DEM. Geology 2022, 4, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, S. Morphometric analysis of a drainage basin: A study of Ghatganga River, Bajhang District, Nepal. Geogr. Base 2020, 7, 127–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Y.A.; ElKashouty, M. Watershed prioritization and hydro-morphometric analysis for the potential development of Tabuk Basin, Saudi Arabia using multivariate statistical analysis and coupled RS-GIS approach. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivhare, V.; Gupta, C.; Mallick, J.; Singh, C.K. Geospatial modelling for sub-watershed prioritization in Western Himalayan Basin using morphometric parameters. Nat. Hazards 2022, 110, 545–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongare, C.U.; Deota, B.S.; Deshpande, R.D. High resolution morphometric studies with special reference to hydrological setup of Khapri watershed, Dangs district, Gujarat, Western India. Geocarto Int. 2022, 37, 3697–3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hema, H.; Vittala, S.; Govindaiah, S. Quantitative morphometric infer in the hard rock Terrain based on SRTM-DEM and GIS-Chintamani Watershed, Chikkaballapur District, Karnataka, India. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 7, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeidat, M.; Awawdeh, M.; Al-Hantouli, F. Morphometric analysis and prioritisation of watersheds for flood risk management in Wadi Easal Basin (WEB), Jordan, using geospatial technologies. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2021, 14, e12711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kant, C.; Kumar, G.; Meena, R.S. Modeling morphometric and geomorphological parameters of mountainous river basin for water resource management using remote sensing and GIS approach. Mod. Earth Syst. Environ. 2023, 9, 2151–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganie, P.A.; Posti, R.; Bharti, V.S.; Sehgal, V.K.; Sarma, D.; Pandey, P.K. Striking a balance between conservation and development: A geospatial approach to watershed prioritisation in the Himalayan Basin. Conservation 2023, 3, 460–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimple, D.; Rajput, J.; Al-Ansari, N.; Elbeltagi, A.; Zerouali, B.; Santos, C.A.G. Determining the hydrological behaviour of catchment based on quantitative morphometric analysis in the hard rock area of Nand Samand Catchment, Rajasthan, India. Hydrology 2022, 9, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukristiyanti, S.; Maria, R.; Lestiana, H. Watershed-based morphometric analysis: A review. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 118, 012028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekar, P.R.; Mathew, A. Morphometric Analysis of Watersheds: A Comprehensive Review of Data Sources, Quality, and Geospatial Techniques. Watershed Ecol. Environ. 2024, 6, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pareta, K.; Pareta, U. Quantitative morphometric analysis of a watershed of Yamuna basin, India using ASTER (DEM) data and GIS. Int. J. Geomat. Geosci. 2011, 2, 248. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, S.; Iqbal, M.; Waseem, M.; Abbas, A.; Masood, M.; Nabi, G.; Tariq, M.A.U.R.; Sadam, M. Potential Sites for Rainwater Harvesting Focusing on the Sustainable Development Goals Using Remote Sensing and Geographical Information System. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrashekar, H.; Lokesh, K.; Sameena, M.; Roopa, J.; Ranganna, G. Coastal and Ocean Engineering (Mangalore). In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Water Resources and Environment, Beijing, China, 25–28 July 2015; pp. 1345–1353. [Google Scholar]
- Makhamreh, Z.; Al-Hawary, M.; Odeh, S. Assessment of morphometric characteristics of Wadi Al-Shumar catchment in Jordan. Open J. Geol. 2020, 10, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqsoom, A.; Aslam, B.; Khalid, N.; Ullah, F.; Anysz, H.; Almaliki, A.H.; Almaliki, A.A.; Hussein, E.E. Delineating groundwater recharge potential through remote sensing and geographical information systems. Water 2022, 14, 1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, B.; Alsalman, A. Identifying Soil Erosion-Prone Areas in the Wadi Haly Catchment, Saudi Arabia Using Morphometric Analysis and Watershed Features. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 10854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzougagh, B.; Meshram, S.G.; Dridri, A.; Boudad, L.; Baamar, B.; Sadkaoui, D.; Khedher, K.M. Identification of critical watershed at risk of soil erosion using morphometric and geographic information system analysis. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tukura, N.G.; Akalu, M.M.; Hussein, M.; Befekadu, A. Morphometric analysis and sub-watershed prioritization of Welmal watershed, Ganale-Dawa River Basin, Ethiopia: Implications for sediment erosion. J. Sediment. Environ. 2021, 6, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Cui, P.; Regmi, A.D.; Hu, S.; Zhang, Y.; He, Y. Landslide distribution and size versus relative relief (Shaanxi Province, China). Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2018, 77, 1331–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhunia, G.S.; Samanta, S.; Pal, B. Quantitative analysis of relief characteristics using space technology. Int. J. Phys. Soc. Sci. 2012, 2, 350–365. [Google Scholar]
- Pareta, K.; Pareta, U. Quantitative geomorphological analysis of a watershed of Ravi River basin, HP India. Int. J. Remote Sens. GIS 2012, 1, 47–62. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. World Reference Base for Soil Resources, 2006: A Framework for International Classification, Correlation, and Communication; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2006; Volume 103. [Google Scholar]
- López-Ramos, A.; Medrano-Barboza, J.P.; Martínez-Acosta, L.; Acuña, G.J.; Remolina López, J.F.; López-Lambraño, A.A. Assessment of morphometric parameters as the basis for hydrological inferences in water resource management: A case study from the sinú river basin in Colombia. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2022, 11, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, B.; Nagaraju, M.; Sahu, N.; Nasre, R.; Mohekar, D.; Srivastava, R.; Singh, S. Morphometric analysis for planning soil and water conservation measures using geospatial technique. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2019, 8, 2719–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godif, G.; Manjunatha, B. Prioritizing sub-watersheds for soil and water conservation via morphometric analysis and the weighted sum approach: A case study of the Geba river basin in Tigray, Ethiopia. Heliyon 2022, 8, e12261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaewdum, N.; Chotpantarat, S. Mapping potential zones for groundwater recharge using a GIS technique in the lower Khwae Hanuman Sub-Basin Area, Prachin Buri Province, Thailand. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 717313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakthivel, R.; Jawahar Raj, N.; Sivasankar, V.; Akhila, P.; Omine, K. Geo-spatial technique-based approach on drainage morphometric analysis at Kalrayan Hills, Tamil Nadu, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosh Bin Ghomash, S.; Bachmann, D.; Caviedes-Voullième, D.; Hinz, C. Impact of rainfall movement on flash flood response: A synthetic study of a semi-arid mountainous catchment. Water 2022, 14, 1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaihani, M.; Alharbi, R. Mapping of Soil Erosion Vulnerability in Wadi Bin Abdullah, Saudi Arabia through RUSLE and Remote Sensing. Water 2024, 16, 2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, B.; Alsalman, A. Morphometric and Soil Erosion Characterization Based on Geospatial Analysis and Drainage Basin Prioritization of the Rabigh Area Along the Eastern Red Sea Coastal Plain, Saudi Arabia. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Hierarchical rank | Strahler [47] | ||
| (Nu) | Nu = Rb(k–u) where Rb = bifurcation ratio; k = highest order of the basin; u = basin order | Horton [43] | |
| (Lu) | Length of the stream (km) | Horton [43] | |
| (Lsm) | Lsm = Lu/Nu where Lu = total stream length of order u (km) Nu = total number of stream segments of order u | Strahler [47] | |
| (RL) | RL = Lsmu/(Lsmu − 1) where Lsmu = mean stream length of order u; Lsmu − 1 = mean stream length of its next lower order | Horton [43] | |
| (Rb) | Rb = Nu/(Nu +1) where Nu = total number of stream segments of the order u Nu + 1 = number of segments of the next higher order | Schumm [46] | |
| (Rbm) | Rbm = average of bifurcation ratios of all orders | Strahler [47] | |
| (Lg) | Lg = 1/(2 × Dd) (km) where Lg = length of overland flow and Dd = drainage density | Horton [43] | |
| (Lb) | The longest dimension of the basin which parallels to the principal drainage (km) | Schumm [46] | |
| Total length of outer boundary of drainage basin (km) | Schumm [46] | ||
| Area of the basin (km2) | Strahler [47] | ||
| (Rf) | Rf = A/Lb2 where A = basin area (km2); Lb2 = square of basin length | Horton [42] | |
| (Re) | Re = 2√(A/π)/Lb where A= area of the basin (km2); Lb = basin length (km) | Schumm [46] | |
| (Rc) | Rc = 4πA/P2 where A = basin area (km2); P2 = square of basin perimeter | Miller [45] | |
| (Dd) | Dd = L/A (km/km2) where L = total length of stream segments of a basin (km) A = basin area (km2) | Horton [42] | |
| (Fs) | Fs = Nu/A where Nu = total number of stream segments of all orders A = basin area (km2) | Horton [42] | |
| (Dt) | Dt = Nu/P where Nu = total number of stream segments of all orders P = basin perimeter (km) | Horton [43] | |
| (If) | If = Dd × Fs where Dd = drainage density, Fs = stream frequency | Zavoiance [50] | |
| The highest elevation at the source of the basin | GIS platform | ||
| Minimum relief (z) | The lowest elevation at the mouth of the basin | GIS platform | |
| Mean relief (Ź) | Statistical analysis | Statistical analysis | |
| Total relief (H) | H = Z − z | Strahler [44] | |
| Relative relief (R) | R = H/P where H = Total basin relief P = perimeter of the basin | Melton [51] | |
| Relief ratio (Rh) | Rh = H/Lb where H = Total basin relief Lb = maximum basin length | Schumm [46] | |
| Hypsometric integral (HI) | (Ź − z)/(Z − z) | Pike and Wilson [52] | |
| Gradient ratio (Rg) | Rg = (Z − z)/Lb where Z = elevation at source z = elevation at mouth Lb = length of main stream | Sreedevi, Subrahmanyam [53] |
| Category | Size (km2) | Count |
|---|---|---|
| Basin | >20,000 | 12 |
| Catchment | >10,000–20,000 | 14 |
| Sub-catchment | >2000–10,000 | 76 |
| Watershed | >500–2000 | 164 |
| Sub-watershed | >100–500 | 372 |
| Mili-watershed | >10–100 | 1321 |
| Micro-watershed | 5–10 | 783 |
| Mini-watershed | <5 | 61,761 |
| Basin. No. * | Stream Order | Stream Number | Total Stream Length (km) | Mainstream Length (km) | Mean Bifurcation Ratio | Length of Over Land Flow (km) | Shared Countries |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7 | 2714 | 141,096 | 54 | 3.7 | 4.5 | KSA, Oman, Yemen, UAE |
| 2 | 5 | 570 | 19,689 | 890 | 4.8 | 7.0 | KSA, Kuwait |
| 3 | 5 | 362 | 12,180 | 292 | 4.2 | 7.0 | KSA |
| 4 | 5 | 324 | 11,092 | 899 | 4.1 | 7.2 | KSA, UAE |
| 5 | 5 | 352 | 11,127 | 731 | 4.1 | 6.7 | Yemen |
| 6 | 5 | 300 | 8189 | 590 | 3.9 | 8.0 | KSA |
| 7 | 5 | 159 | 5852 | 616 | 3.4 | 6.8 | KSA, Kuwait |
| 8 | 5 | 123 | 4415 | 39 | 3.2 | 6.3 | KSA |
| 9 | 4 | 89 | 4358 | 357 | 4.2 | 4.9 | KSA |
| 10 | 4 | 69 | 2481 | 137 | 3.7 | 6.6 | Oman |
| 11 | 4 | 84 | 2334 | 105 | 4.0 | 6.9 | KSA |
| 12 | 4 | 53 | 1895 | 69 | 3.7 | 6.5 | KSA |
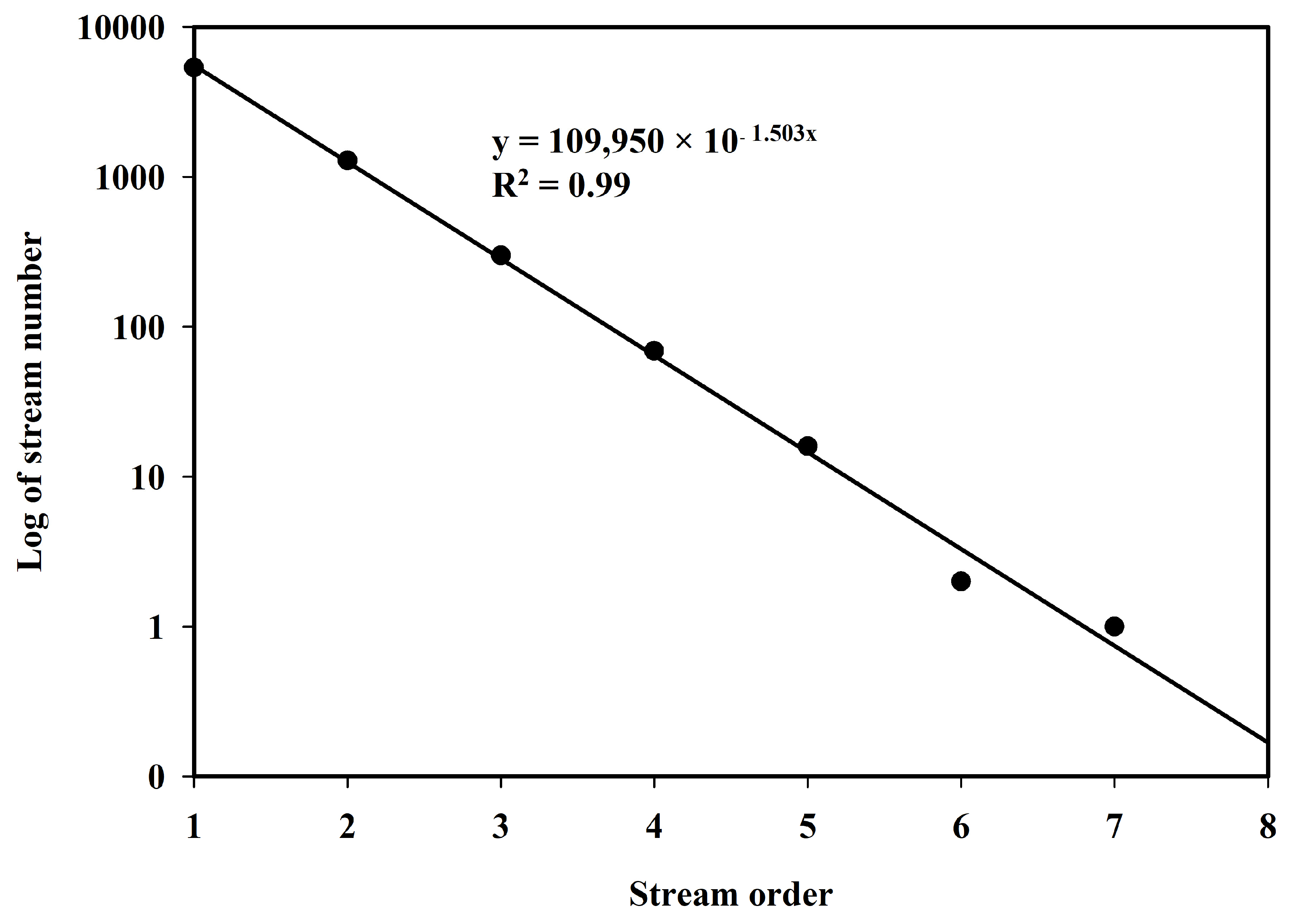
| Stream Order | Stream Number | Min. Stream Number 1 | Max. Stream Number 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5366 | 40 | 2045 |
| 2 | 1286 | 10 | 502 |
| 3 | 300 | 2 | 120 |
| 4 | 69 | 1 | 35 |
| 5 | 16 | 1 | 9 |
| 6 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 7 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
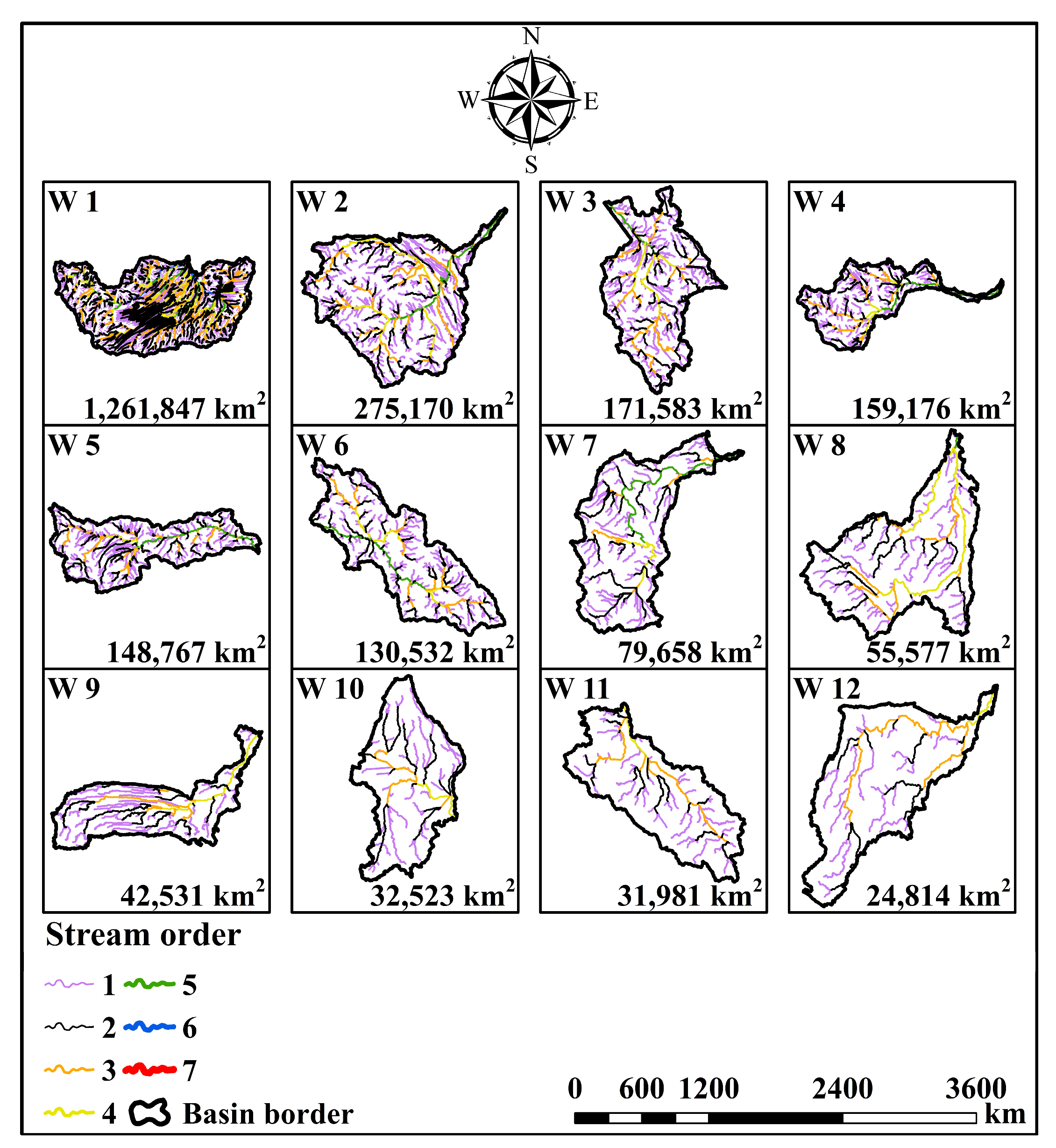
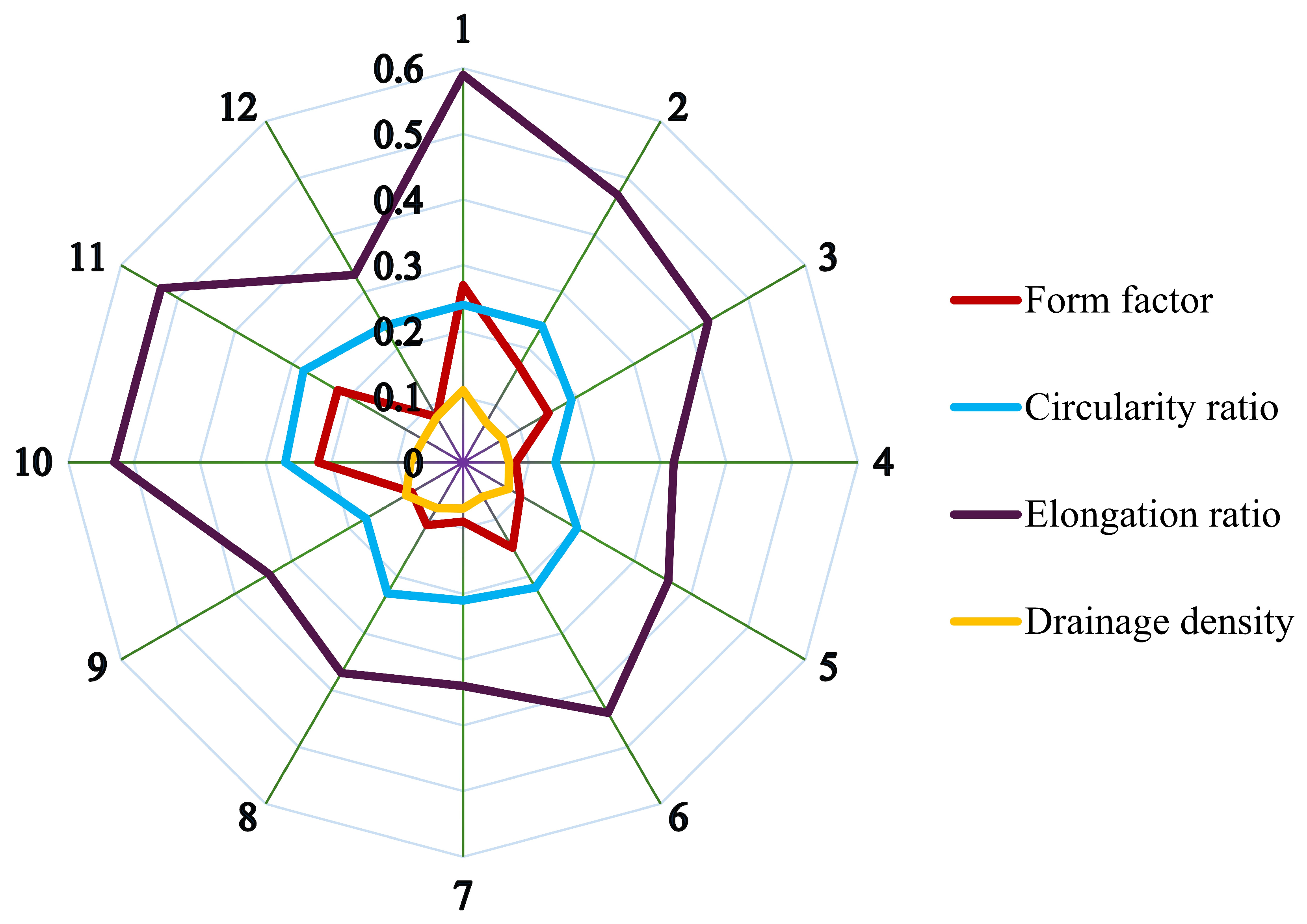
| Basin No. * | Basin Length (km) | Perimeter (km) | Area (km2) | Stream Frequency | Drainage Texture |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2167 | 8101 | 1,261,847 | 0.002 | 0.34 |
| 2 | 1269 | 3815 | 275,170 | 0.002 | 0.15 |
| 3 | 1077 | 3332 | 171,583 | 0.002 | 0.11 |
| 4 | 1422 | 3775 | 159,176 | 0.002 | 0.09 |
| 5 | 1208 | 3028 | 148,767 | 0.002 | 0.12 |
| 6 | 932 | 2761 | 130,532 | 0.002 | 0.11 |
| 7 | 938 | 2190 | 79,658 | 0.002 | 0.07 |
| 8 | 712 | 1751 | 55,577 | 0.002 | 0.07 |
| 9 | 690 | 1792 | 42,531 | 0.002 | 0.05 |
| 10 | 386 | 1226 | 32,523 | 0.002 | 0.06 |
| 11 | 383 | 1190 | 31,981 | 0.003 | 0.07 |
| 12 | 545 | 1149 | 24,814 | 0.002 | 0.05 |
| Basin No. * | Minimum Relief (m) | Mean Relief (m) | Maximum Relief (m) | Total Relief (m) | Relief Ratio | Relative Relief (m) | Dissection Index | Hypsometric Integral | Gradient Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 574 | 950 | 950 | 0.000 | 0.01 | 1.0 | 0.60 | 0.018 |
| 2 | 218 | 850 | 1252 | 1034 | 0.001 | 0.03 | 0.8 | 0.61 | 0.001 |
| 3 | 509 | 833 | 1224 | 715 | 0.001 | 0.02 | 0.6 | 0.45 | 0.002 |
| 4 | 0 | 725 | 1002 | 1002 | 0.001 | 0.03 | 1.0 | 0.72 | 0.001 |
| 5 | 0 | 1233 | 1721 | 1721 | 0.001 | 0.06 | 1.0 | 0.72 | 0.002 |
| 6 | 0 | 890 | 956 | 956 | 0.001 | 0.04 | 1.0 | 0.93 | 0.002 |
| 7 | 0 | 504 | 692 | 692 | 0.001 | 0.03 | 1.0 | 0.73 | 0.001 |
| 8 | 1 | 364 | 657 | 656 | 0.001 | 0.04 | 1.0 | 0.55 | 0.017 |
| 9 | 355 | 758 | 981 | 626 | 0.001 | 0.04 | 0.6 | 0.64 | 0.002 |
| 10 | 0 | 127 | 241 | 241 | 0.001 | 0.02 | 1.0 | 0.53 | 0.002 |
| 11 | 676 | 1043 | 1227 | 551 | 0.001 | 0.05 | 0.5 | 0.67 | 0.005 |
| 12 | 2 | 300 | 562 | 560 | 0.001 | 0.05 | 1.0 | 0.53 | 0.008 |
| Old | 30 |
| Mature | 30–60 |
| Youth | 60–80 |
| Middle | 80–100 |
| Initial | 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alazba, A.A.; Mosad, A.; Geli, H.M.E.; El-Shafei, A.; Ezzeldin, M.; Alrdyan, N.; Radwan, F. Transboundary Urban Basin Analysis Using GIS and RST for Water Sustainability in Arid Regions. Water 2025, 17, 1463. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101463
Alazba AA, Mosad A, Geli HME, El-Shafei A, Ezzeldin M, Alrdyan N, Radwan F. Transboundary Urban Basin Analysis Using GIS and RST for Water Sustainability in Arid Regions. Water. 2025; 17(10):1463. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101463
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlazba, A A, Amr Mosad, Hatim M. E. Geli, Ahmed El-Shafei, Mahmoud Ezzeldin, Nasser Alrdyan, and Farid Radwan. 2025. "Transboundary Urban Basin Analysis Using GIS and RST for Water Sustainability in Arid Regions" Water 17, no. 10: 1463. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101463
APA StyleAlazba, A. A., Mosad, A., Geli, H. M. E., El-Shafei, A., Ezzeldin, M., Alrdyan, N., & Radwan, F. (2025). Transboundary Urban Basin Analysis Using GIS and RST for Water Sustainability in Arid Regions. Water, 17(10), 1463. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101463









