Modeling the Effect of Soil Type Change on Irrigation Water Requirements of Sunflower and Wheat Using CROPWAT 8.0
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Area
2.2. Climate of the Research Area
2.3. Climate Data Used in the Research
2.4. Plant Data Used in the Research
2.5. Soil Data Used in the Research
2.6. CROPWAT 8.0
2.7. Method
- TAW: The total available soil water in the root zone (mm),
- : The water content at field capacity (m3 m−3),
- : The water content at wilting point (m3 m−3),
- : The rooting depth (m).
- RAW: the readily available soil water in the root zone (mm);
- p: average fraction of total available soil water (TAW) that can be depleted from the root zone before moisture stress (reduction in ET) occurs.
- ETc: Evapotranspiration (mm day−1)
- ETo: Reference evapotranspiration (mm day−1)
- kc: Plant coefficient
- IWR: Irrigation water requirement (mm day−1)
- ETc: Evapotranspiration (mm day−1)
- Peff: Effective rainfall (mm day−1)
3. Results
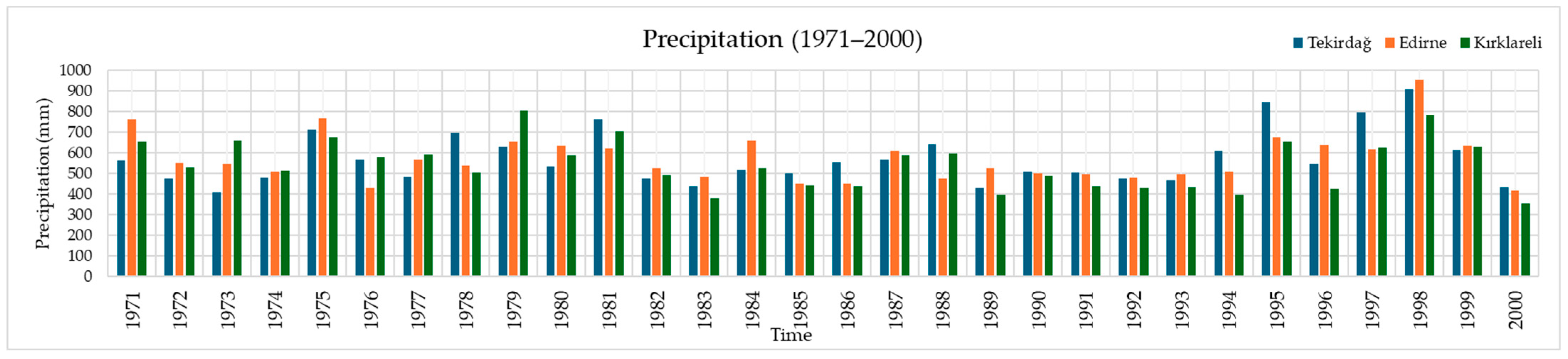
3.1. Changes in Temperature and Precipitation in Tekirdağ, Edirne, and Kırklareli Provinces During the 1971–2000 Period
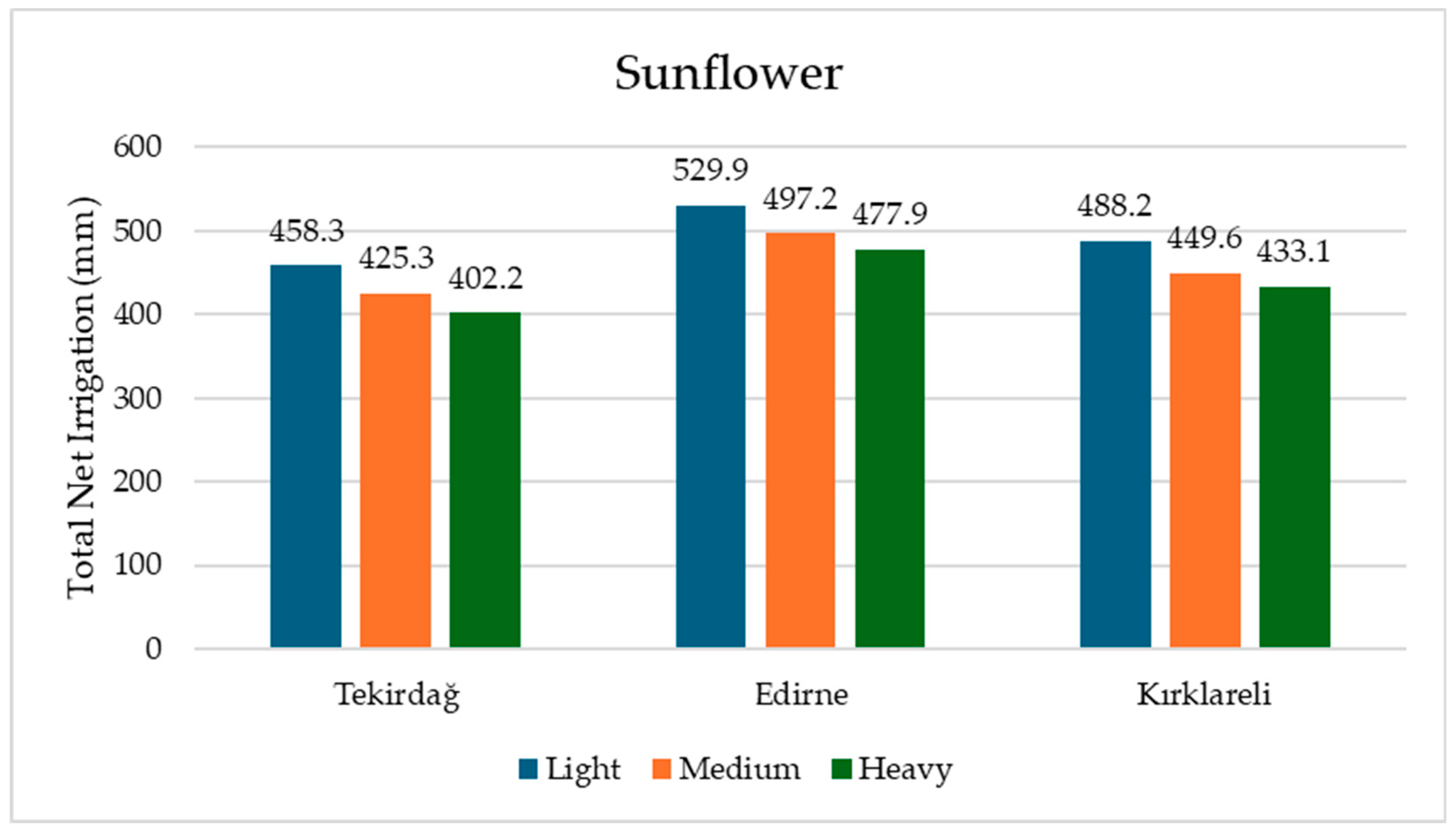
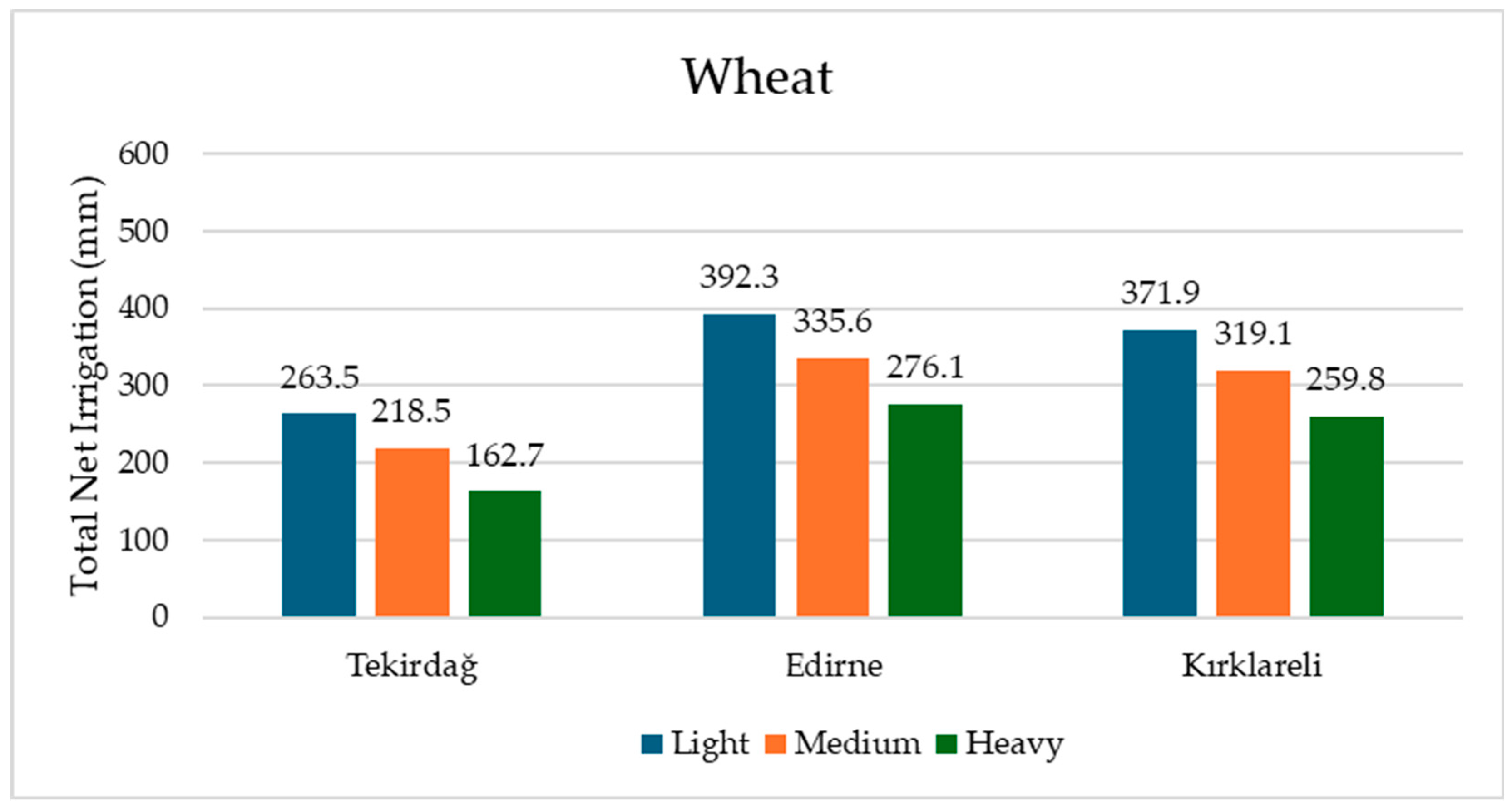
3.2. The Effects of Different Soil Textures on Total Net Irrigation Water Requirements for Sunflower and Wheat Crops in Tekirdağ, Edirne, and Kırklareli During the 1971–2000 Period
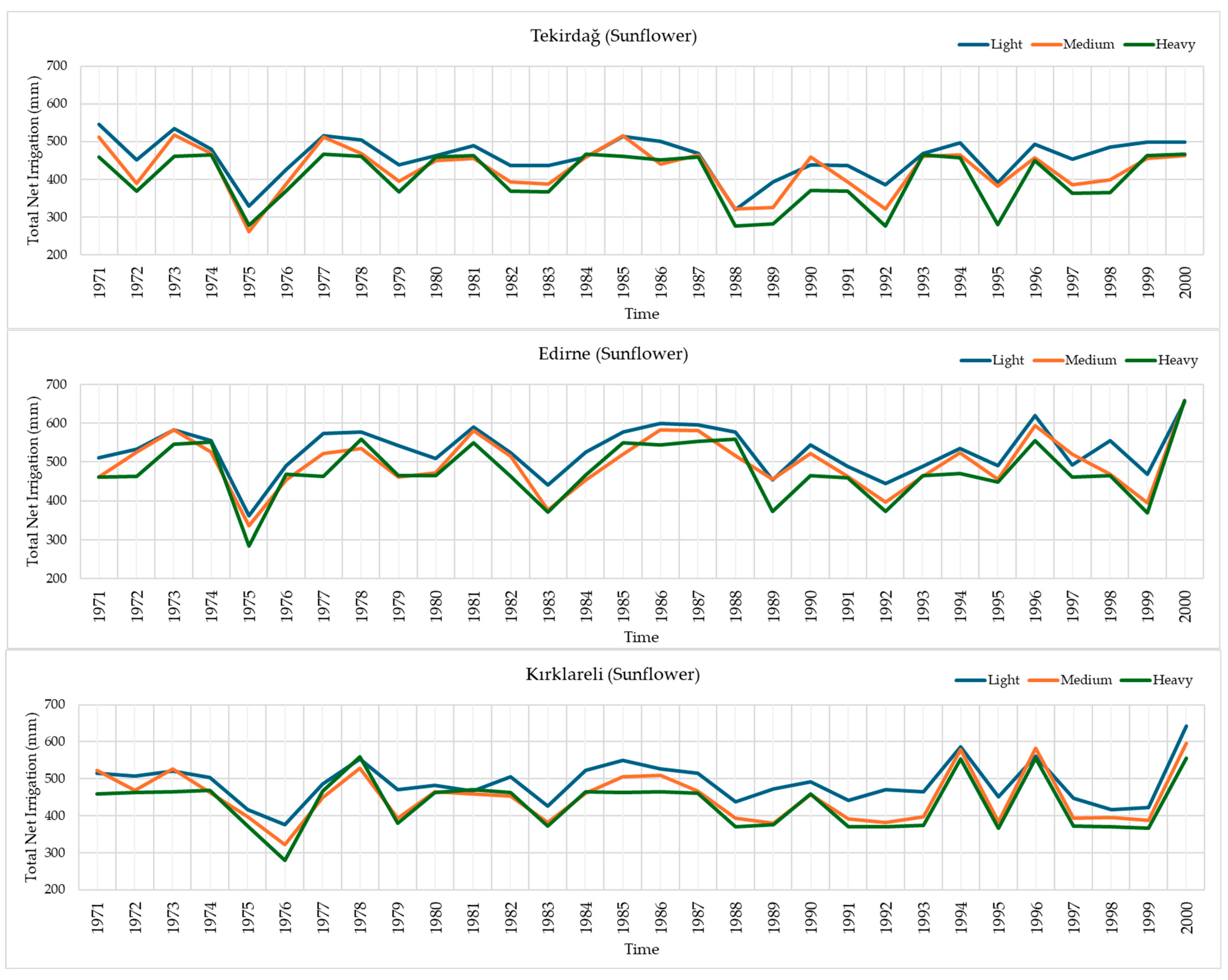
3.3. Temporal Variation of Total Net Irrigation Water Requirements for Different Soil Textures in Sunflower Across Tekirdağ, Edirne, and Kırklareli Provinces (1971–2000)
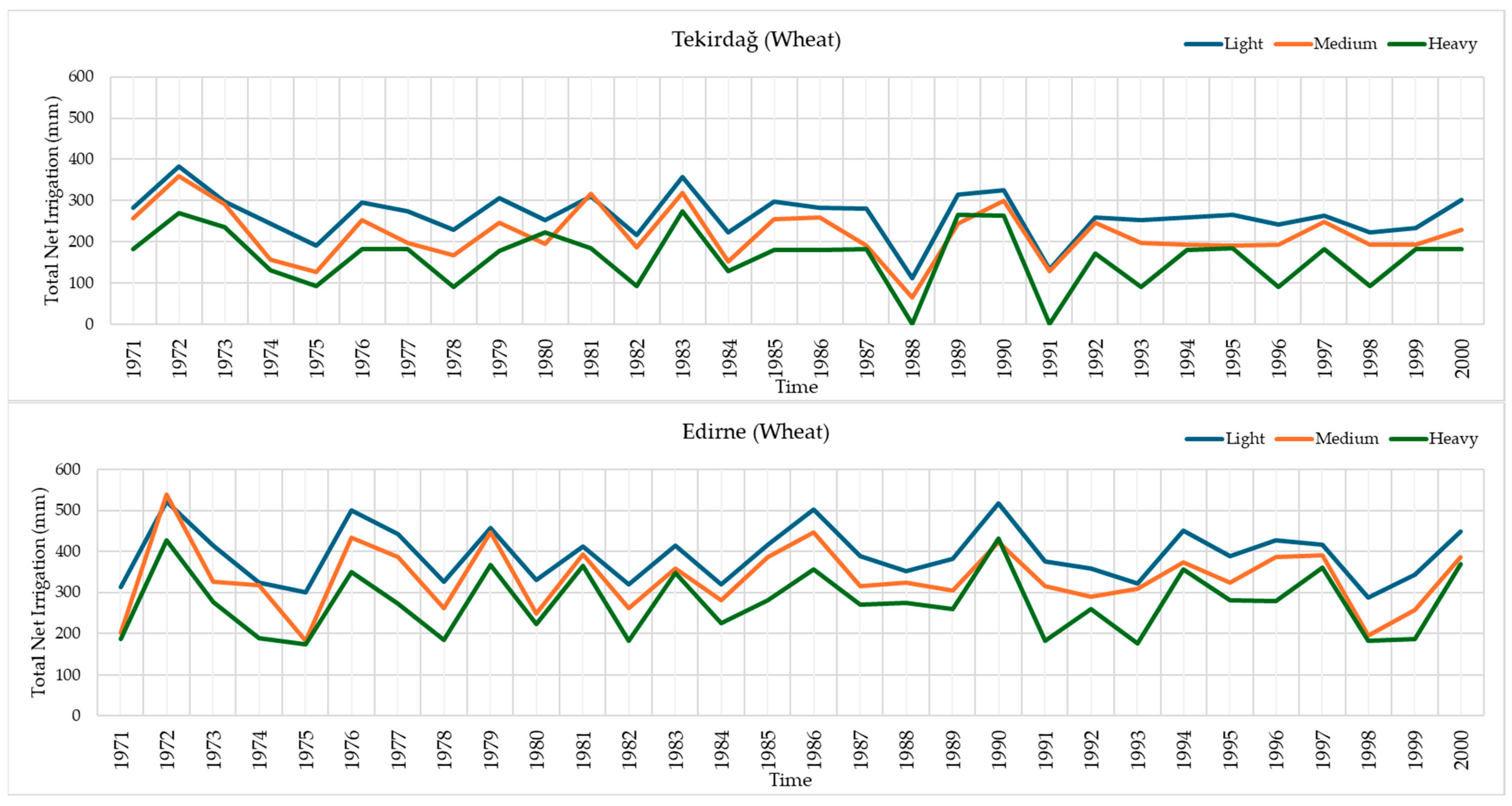
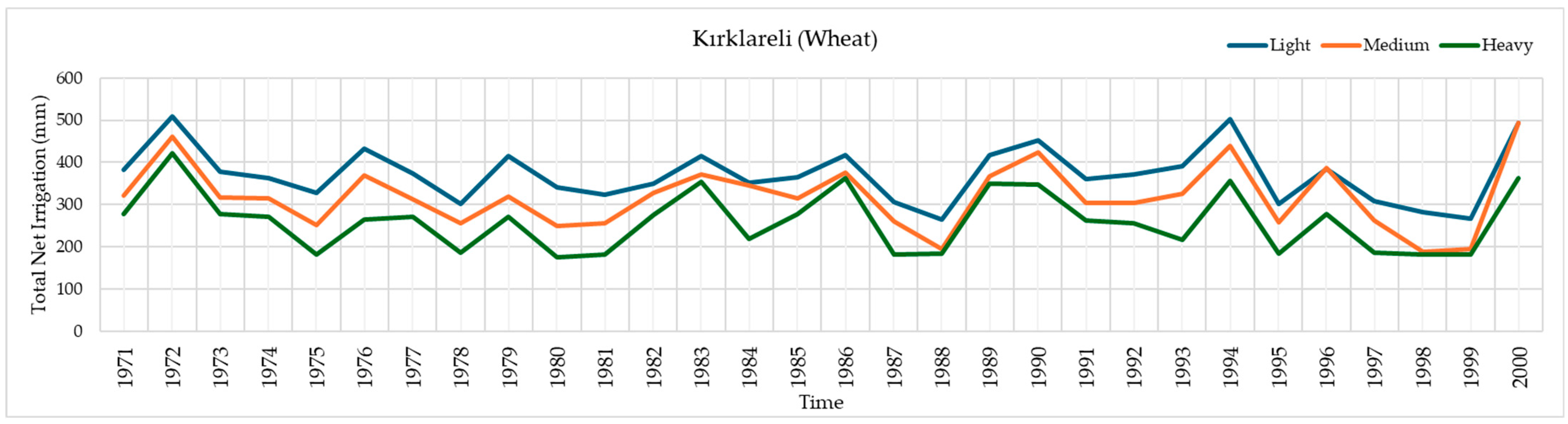
3.4. Temporal Variation of Total Net Irrigation Water Requirements for Wheat Across Different Soil Textures in Tekirdağ, Edirne, and Kırklareli Provinces (1971–2000)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- SMDA. Agricultural Research Report. South Marmara Development Agency (SMDA). Türkiye. Available online: https://www.gmka.gov.tr/dokumanlar/yayinlar/Tarim-Arastirma-Raporu.pdf (accessed on 15 November 2024).
- TDA. Edirne, Kırklareli, Tekirdağ Agriculture and Rural Development Sector. Thrace Development Agency (TDA), Türkiye. Available online: https://ka.gov.tr/en/pages/trakya-kalkinma-ajansi-tarim-ve-kirsal-kalkinma--29-467 (accessed on 24 November 2024).
- TurkStat. Crop Production Statistics. Turkish Statistical Institute. Available online: https://biruni.tuik.gov.tr/medas/?kn=92&locale=tr (accessed on 22 November 2024).
- Şen, A.S.; Deveci, H.; Konukcu, F. Modelling the adaptation of some cultural plants produced in Thrace Region to climate change. J. Tekirdag Agric. Fac. 2024, 21, 501–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Hou, H.; Wu, J.; Tian, D.; Miao, P. Irrigation schedule optimization for wheat and sunflower intercropping under water supply restrictions in Inner Mongolia, China. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeşilköy, S.; Şaylan, L. Yields and water footprints of sunflower and winter wheat under different climate projections. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 298, 126780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürkan, H. Evaluation of the Impacts of climate change on sunflower with aquacrop model. J. Tekirdag Agric. Fac. 2023, 20, 933–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deveci, H.; Konukcu, F. Modeling the effect of climate change on evapotranspiration in the Thrace Region. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, K.B. A study of climate changes impact on the quantities of water used for irrigation. J. Al-Azhar Univ. Eng. Sect. 2021, 16, 538–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessema Roba, N.; Kebede Kassa, A.; Yadeta Geleta, D. Modeling climate change impacts on crop water demand, middle Awash River basin, case study of Berehet woreda. Water Pract. Technol. 2021, 16, 864–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groh, J.; Vanderborght, J.; Pütz, T.; Vogel, H.J.; Gründling, R.; Rupp, H.; Rahmati, M.; Sommer, M.; Vereecken, H.; Gerke, H.H. Responses of soil water storage and crop water use efficiency to changing climatic conditions: A lysimeter-based space-for-time approach. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 24, 1211–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irmak, S.; Odhiambo, L.O.; Kranz, W.L.; Eisenhauer, D.E. Irrigation efficiency and uniformity, and crop water use efficiency. Biol. Syst. Eng. Pap. Publ. 2011, 451, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Soil Texture. Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations, Rome, Italy. Available online: https://www.fao.org/fishery/static/FAO_Training/FAO_Training/General/x6706e/x6706e06.htm (accessed on 10 November 2024).
- Wankmüller, F.J.P.; Delval, L.; Lehmann, P.; Baur, M.J.; Wolf, S.; Or, D.; Javaux, M.; Carminati, A. Soil Texture Controls the Relative Importance of Vapor Pressure Deficit and Soil Moisture for Ecosystem Water Limitation Globally. In Proceedings of the European Geosciences Union General Assembly 2024 (EGU24), Vienna, Austria, 14–19 April 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busschaert, L.; de Roos, S.; Thiery, W.; Raes, D.; De Lannoy, G.J.M. Net irrigation requirement under different climate scenarios using AquaCrop over Europe. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 26, 3731–3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakanoğulları, F.; Bahar, E.; Kıvrak, C.; Gür, M. Assessment of Meteorological and Agricultural Drought Analysis in Kırklareli province. Tekirdağ Ziraat Fakültesi Derg. 2022, 19, 756–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deveci, H.; Önler, B.; Erdem, T. Modeling the effects of climate change on the irrigation water requirements of wheat and canola in the TR21 Thrace Region using CROPWAT 8.0. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2025, 9, 1563048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neamah, I.F. The effects of soil texture on irrigation schedule. Int. J. Civ. Eng. Constr. 2024, 3, 35–43. [Google Scholar]
- Niţu, O.A.; Muşat, M.; Ivan, E.Ș.; Burtan, L.; Anghel, A. The determination of the most optimal methods for the irrigation of crops on different soil types. Ann. Univ. Craiova-Agric. Mont. Cadastre Ser. 2024, 53, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deveci, H.; Konukcu, F. Prediction of climate change and its impact on water resources and crop yileds in Ergene River Basin. In Integrated Land-Use Management Modelling of Black Sea Estuaries (ILMM-BSE) Project: Ergene River Basin, 1st ed.; Konukcu, F., Ed.; Soil Offset: Tekirdağ, Türkiye, 2016; pp. 269–290. [Google Scholar]
- Hanedar, A.; Ferat, Ç.; Erdem, G.; Konukcu, F.; Altürk, B.; Albut, S. TR21 Region Climate Assessment: Current Situation and Projections. In Effects of Climate Change and Adaptation Strategies in TR21 Thrace Region, 1st ed.; Konukcu, F., Albut, S., Altürk, B., Eds.; Tekirdağ Namık Kemal University: Tekirdağ, Türkiye, 2019; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- TDA. TR21 Thrace Regional Plan Tekirdağ, Edirne, Kırklareli 2010. Thrace Development Agency (TDA), Türkiye. Available online: https://www.trakyaka.org.tr/upload/Node/33265/xfiles/tr21_trakya_2010-2013.pdf (accessed on 24 November 2024).
- Özşahin, E.; Öztürk, M. The effect of sea level rise caused by climate change for TR21 Thrace Region (Türkiye). In Proceedings of the Akdeniz 9th International Conference on Applied Sciences, Adana, Türkiye, 1–2 April 2023; pp. 226–234. [Google Scholar]
- Gürbüz, M.A.; Kayalı, E.; Bahar, E.; Öz, T.A.; Kurşun, İ. Composing the database of Thrace soils and some soil characteristics. J. Soil. Sci. Plant Nutr. 2019, 7, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TSMS. Location of Meteorological Stations, Tekirdağ, Edirne, Kırklareli. Turkish State Meteorological Service (TSMS). Available online: https://www.mgm.gov.tr/kurumsal/istasyonlarimiz.aspx (accessed on 23 July 2024).
- Asan, A.; Yarcı, C. Botanical tours in Thrace. Ecol. Environ. J. 1993, 2, 26–30. [Google Scholar]
- TSMS. Long-term Monthly Averages Climate Data, Tekirdağ. Turkish State Meteorological Service (TSMS). Available online: https://www.mgm.gov.tr/veridegerlendirme/il-ve-ilceler-istatistik.aspx?m=TEKIRDAG (accessed on 15 May 2024).
- TSMS. Long-term Monthly Averages Climate Data, Edirne. Turkish State Meteorological Service (TSMS). Available online: https://www.mgm.gov.tr/veridegerlendirme/il-ve-ilceler-istatistik.aspx?m=EDIRNE (accessed on 15 May 2024).
- TSMS. Long-term Monthly Averages Climate Data, Kırklareli. Turkish State Meteorological Service (TSMS). Available online: https://www.mgm.gov.tr/veridegerlendirme/il-ve-ilceler-istatistik.aspx?m=KIRKLARELI (accessed on 15 May 2024).
- RTMAFGDARP. Plant Water Consumption of Irrigated Plants in Türkiye, Republic of Türkiye Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry General Directorate of Agricultural Research and Policies (RTMAFGDARP), Ankara, Türkiye. Available online: https://www.tarimorman.gov.tr/TAGEM/Belgeler/yayin/Tu%CC%88rkiyede%20Sulanan%20Bitkilerin%20Bitki%20Su%20Tu%CC%88ketimleri.pdf (accessed on 22 December 2023).
- FAO. Wheat. Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations, Rome, Italy. Available online: https://www.fao.org/land-water/databases-and-software/crop-information/wheat/en/ (accessed on 12 July 2024).
- Steduto, P.; Hsiao, T.C.; Fereres, E.; Raes, D. Crop Yield Response to Water; FAO Rome: Rome, Italy, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Sunflower. Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations, Rome, Italy. Available online: https://www.fao.org/land-water/databases-and-software/crop-information/sunflower/en/ (accessed on 14 July 2024).
- Erdem, T. Evapotranspiration of sunflower for Tekirdağ conditions. J. Agric. Sci. 2001, 7, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. CROPWAT. Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations, Rome, Italy. Available online: https://www.fao.org/land-water/databases-and-software/cropwat/en/ (accessed on 19 August 2024).
- Smith, M.; CROPWAT. A computer program for irrigation planning and management. In FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper No. 46; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Aydın-Kandemir, F.; Yıldız, D. Assessment of crop water requirements by using cropwat for sustainable water resources management in agriculture (Akhisar-Manisa, Turkey). Int. J. Water Manag. Dipl. 2022, 1, 5–20. [Google Scholar]
- El-Shafei, A.A.; Mattar, M.A. Irrigation Scheduling and Production of Wheat with Different Water Quantities in Surface and Drip Irrigation: Field Experiments and Modelling Using CROPWAT and SALTMED. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewaid, S.H.; Abed, S.A.; Al-Ansari, N. Crop water requirements and irrigation schedules for some major crops in Southern Iraq. Water 2019, 11, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GDM. Climate Change Projections for Türkiye with New Scenarios. General Directorate of Meteorology (GDM). Available online: https://www.mgm.gov.tr/files/iklim/iklim_degisikligi_projeksiyonlari.pdf (accessed on 21 April 2025).
- GDWM. Impact of Climate Change on Water Resources Project Project Final Report. General Directorate of Water Management (GDWM). Available online: https://www.tarimorman.gov.tr/SYGM/Belgeler/iklim%20de%C4%9Fi%C5%9Fikli%C4%9Finin%20su%20kaynaklar%C4%B1na%20etkisi/Iklim_NihaiRapor.pdf (accessed on 12 February 2023).
- Demir, İ.; Kılıç, G.; Coşkun, M.; Sümer, U.M. Changes and Trends Observed in Maximum, Minimum and Average Air Temperatures and Precipitation Series in Türkiye. In Proceedings of the TMMOB Climate Change Symposium, Ankara, Türkiye, 13–14 March 2008; pp. 69–84. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration-Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements-FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56; Fao: Rome, Italy, 1998; Volume 300, p. D05109. [Google Scholar]
- Rolle, M.; Tamea, S.; Claps, P.; Poggi, D. Climate-driven local assessment of future irrigation requirements and available water resources in North-West Italy. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts, Vienna, Austria, 1 May 2023; p. EGU–14197. [Google Scholar]
- Debaeke, P.; Casadebaig, P.; Flénet, F.; Langlade, N. Sunflower crop and climate change: Vulnerability, adaptation, and mitigation potential from case-studies in Europe. OCL-Oilseeds Fats Crops Lipids 2017, 24, D102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, H.; Ali, N.; Iqbal, M.M.; Khan, A.M. Vulnerability and adaptability of wheat production in different climatic zones of Pakistan under climate change scenarios. Clim. Change 2009, 94, 123–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fader, M.; Shi, S.; von Bloh, W.; Bondeau, A.; Cramer, W. Mediterranean irrigation under climate change: More efficient irrigation needed to compensate for increases in irrigation water requirements. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 953–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, A.; Garrote, L. Adaptation strategies for agricultural water management under climate change in Europe. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 155, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.B. Resilience in agriculture through crop diversification: Adaptive management for environmental change. BioScience 2011, 61, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moniruzzaman, S. Crop choice as climate change adaptation: Evidence from Bangladesh. Ecol. Econ. 2015, 118, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, J.; Khanna, R. More crop per drop: Ways to increase water use efficiency for crop production: A review. Int. J. Chem. Stud. 2018, 6, 3573–3578. [Google Scholar]
- Shareef, T.M.E.; Ma, Z.; Zhao, B. Essentials of Drip Irrigation System for Saving Water and Nutrients to Plant Roots: As a Guide for Growers. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2019, 11, 1129–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinz, M.; Turek, M.E.; Holzkämper, A.; Schaefli, B.; Raible, C. Exploring the possibilities to reduce irrigation demands through adaptations in soil and crop management. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly 2024, Vienna, Austria, 14–19 April 2024; p. EGU24–2081. [Google Scholar]
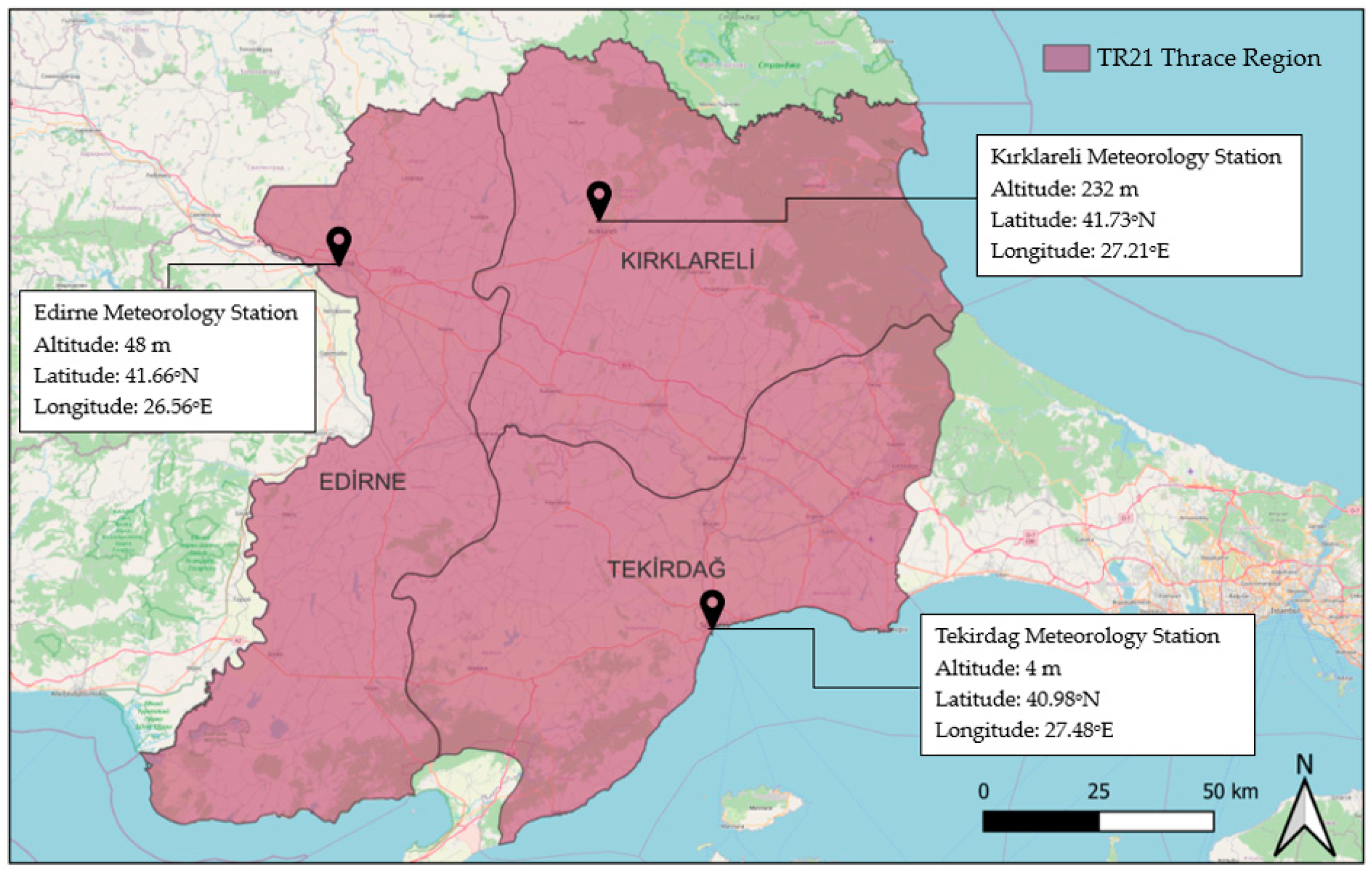
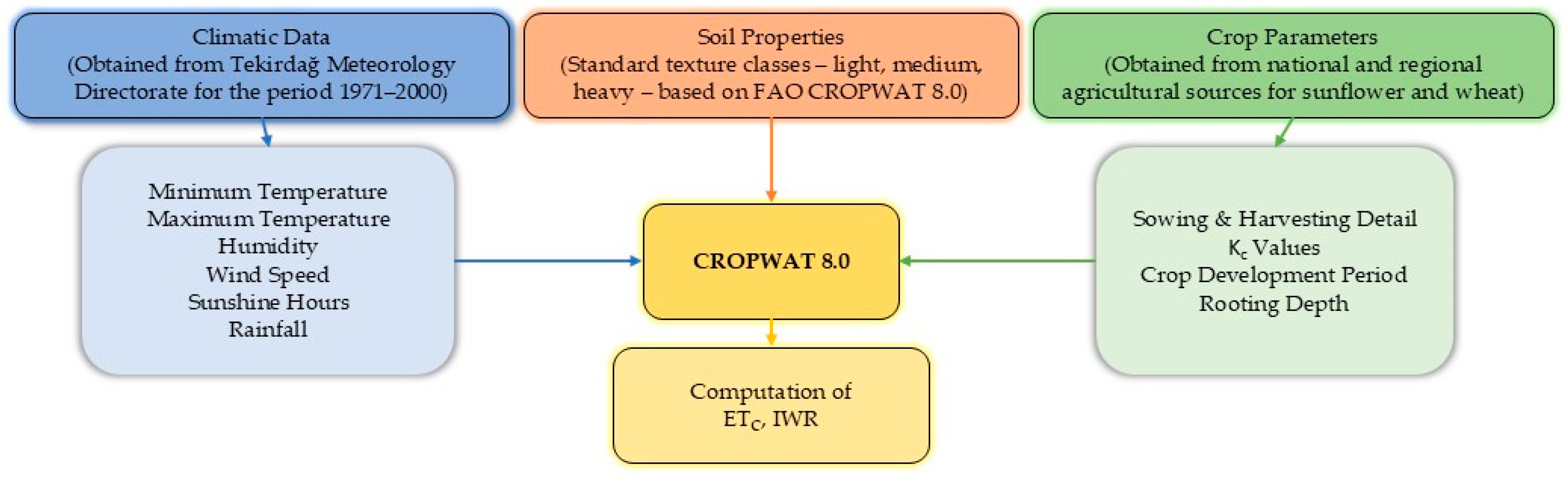
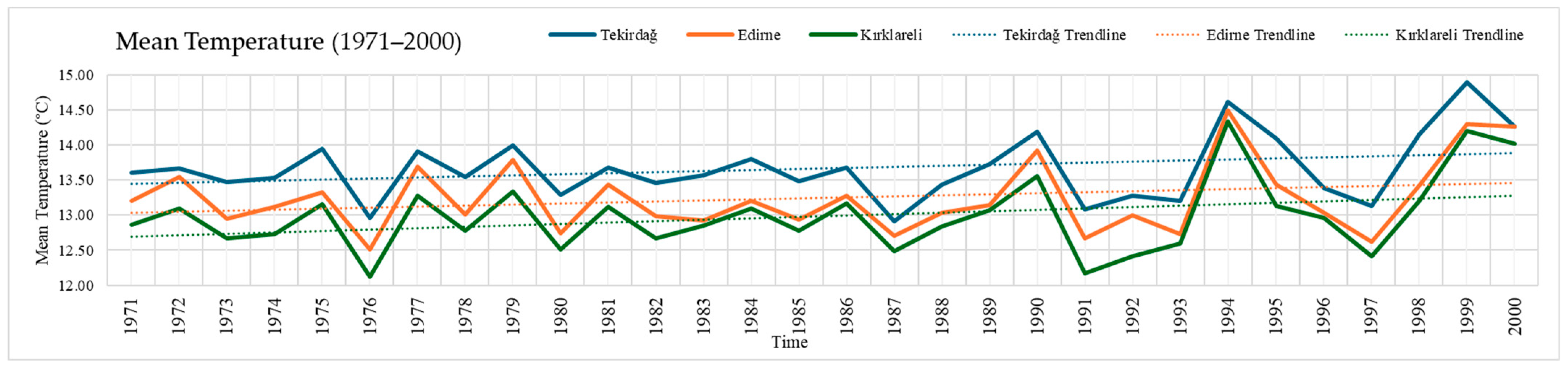
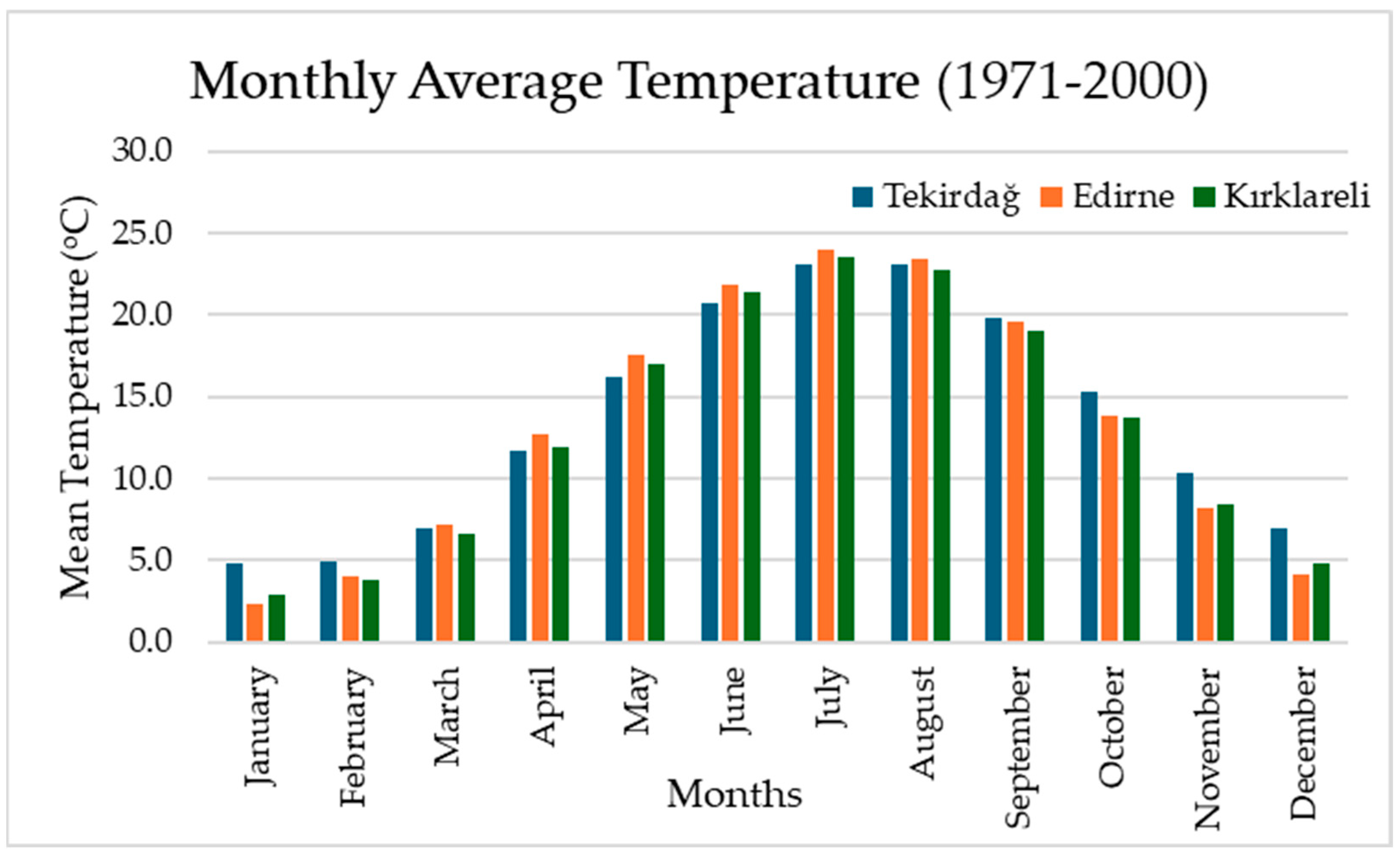
| Location | Cereals and Other Plant Products | Vegetable Gardens | Fruit, Beverage, and Spice Plants | Ornamental Plants | Total | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ha | % | ha | % | ha | % | ha | % | ha | % | |
| Tekirdağ | 401,206 | 96.6 | 2387 | 0.6 | 11,738 | 2.8 | 15 | 0.0 | 415,346 | 100 |
| Edirne | 335,707 | 97.2 | 3843 | 1.1 | 5729 | 1.7 | 185 | 0.1 | 345,463 | 100 |
| Kırklareli | 244,706 | 98.1 | 1405 | 0.6 | 3395 | 1.4 | 0 | 0.0 | 249,506 | 100 |
| TR21 Thrace Region | 981,618 | 97.2 | 7635 | 0.8 | 20,862 | 2.1 | 200 | 0.0 | 1,010,314 | 100 |
| Türkiye | 19,558,942 | 81.6 | 712,264 | 3.0 | 3,694,256 | 15.4 | 5769 | 0.0 | 23,971,231 | 100 |
| Planting Areas and Production Quantities | Plants | Tekirdağ | Edirne | Kırklareli | TR21 Thrace Region | Türkiye |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Planted Areas (ha) | Wheat | 195,973 | 135,181 | 114,097 | 445,251 | 5,569,254 |
| (3.5%) | (2.4%) | (2.0%) | (8.0%) | (100%) | ||
| Sunflower | 174,615 | 129,420 | 97,730 | 401,765 | 864,668 | |
| (20.2%) | (15.0%) | (11.3%) | (46.5%) | (100%) | ||
| Paddy | 1057 | 44,553 | 1511 | 41,721 | 112,120 | |
| (0.9%) | (39.7%) | (1.3%) | (37.2%) | (100%) | ||
| Barley | 14,130 | 6572 | 7137 | 27,839 | 3,170,272 | |
| (0.4%) | (0.2%) | (0.2%) | (0.9%) | (100%) | ||
| Maize (Silage) | 4765 | 7025 | 8299 | 20,088 | 524,861 | |
| (0.9%) | (1.3%) | (1.6%) | (3.8%) | (100%) | ||
| Production Quantities (tons) | Wheat | 687,601 | 724,119 | 431,530 | 1,843,250 | 17,700,000 |
| (3.9%) | (4.1%) | (2.4%) | (10.4%) | (100%) | ||
| Maize (Silage) | 201,937 | 378,148 | 396,695 | 976,780 | 28,653,531 | |
| (0.7%) | (1.3%) | (1.4%) | (3.4%) | (100%) | ||
| Sunflower | 201,200 | 257,651 | 190,308 | 649,159 | 1,960,000 | |
| (10.3%) | (13.1%) | (9.7%) | (33.1%) | (100%) | ||
| Paddy | 8101 | 367,352 | 14,547 | 390,000 | 900,000 | |
| (0.9%) | (40.8%) | (1.6%) | (43.3%) | (100%) | ||
| Sugar beet | 49,394 | 94,336 | 86,001 | 229,731 | 25,250,213 | |
| (0.2%) | (0.4%) | (0.3%) | (0.9%) | (100%) |
| Climate Parameters | Location | January | February | March | April | May | June | July | August | September | October | November | December | Avg./Tot. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Avg. Mean Temperature (°C) | Tekirdağ | 4.9 | 5.5 | 7.3 | 11.7 | 16.7 | 21.1 | 23.7 | 23.9 | 20.3 | 15.7 | 11.3 | 7.3 | 14.1 |
| Edirne | 2.7 | 4.4 | 7.6 | 12.8 | 18.0 | 22.2 | 24.7 | 24.5 | 20.1 | 14.5 | 9.2 | 4.6 | 13.8 | |
| Kırklareli | 2.9 | 4.1 | 6.9 | 12.0 | 17.1 | 21.4 | 23.8 | 23.6 | 19.4 | 14.1 | 9.3 | 5.1 | 13.3 | |
| Avg. Max. Temperature (°C) | Tekirdağ | 8.1 | 9.0 | 11.0 | 15.7 | 20.6 | 25.3 | 28.1 | 28.3 | 24.5 | 19.5 | 14.8 | 10.5 | 18.0 |
| Edirne | 6.7 | 9.4 | 13.4 | 19.3 | 24.8 | 29.2 | 32.0 | 32.0 | 27.4 | 20.8 | 14.2 | 8.6 | 19.8 | |
| Kırklareli | 6.9 | 8.6 | 12.2 | 17.9 | 23.5 | 28.0 | 30.7 | 30.7 | 26.2 | 20.0 | 13.9 | 8.8 | 19.0 | |
| Avg. Min. Temperature (°C) | Tekirdağ | 2.0 | 2.5 | 4.1 | 8.1 | 12.7 | 16.7 | 19.1 | 19.4 | 16.2 | 12.1 | 8.2 | 4.4 | 10.5 |
| Edirne | −0.5 | 0.5 | 2.9 | 7.1 | 11.7 | 15.5 | 17.4 | 17.3 | 13.5 | 9.3 | 5.3 | 1.4 | 8.5 | |
| Kırklareli | 0.1 | 1.0 | 3.0 | 7.1 | 11.6 | 15.6 | 17.8 | 17.8 | 14.1 | 9.8 | 5.9 | 2.3 | 8.8 | |
| Avg. Daily Sunshine (hour) | Tekirdağ | 2.8 | 3.4 | 4.2 | 6.0 | 7.4 | 8.5 | 9.4 | 8.4 | 6.8 | 4.9 | 3.2 | 2.5 | 5.6 |
| Edirne | 2.4 | 3.6 | 4.5 | 6.2 | 8.0 | 9.2 | 10.3 | 9.8 | 7.5 | 5.2 | 3.2 | 2.2 | 6.0 | |
| Kırklareli | 2.0 | 2.5 | 3.6 | 4.7 | 6.3 | 6.8 | 7.5 | 7.5 | 5.5 | 3.8 | 2.7 | 1.8 | 4.6 | |
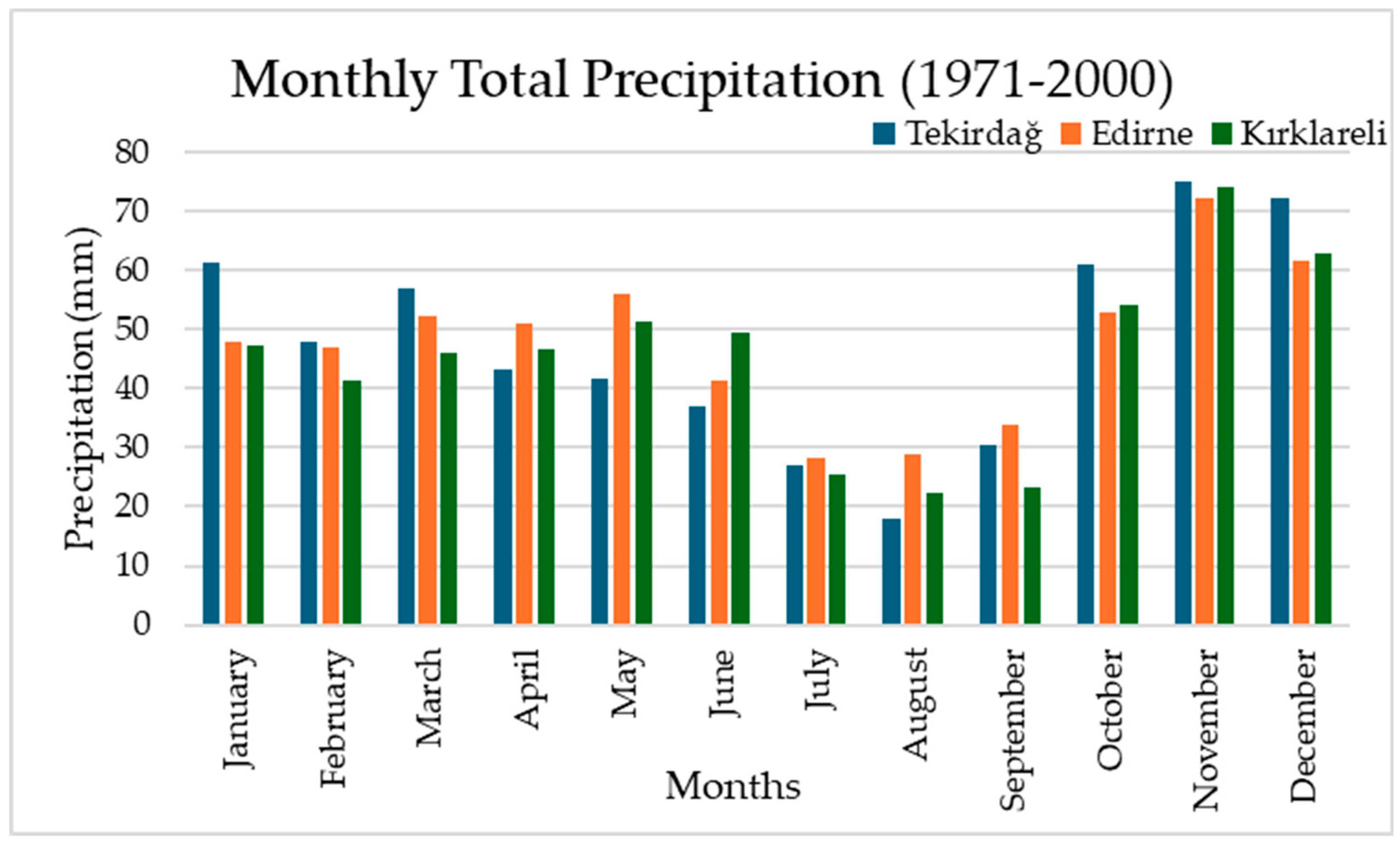
| Precipitation (mm) | Tekirdağ | 68.0 | 54.5 | 53.4 | 42.1 | 37.2 | 38.3 | 23.8 | 15.5 | 32.7 | 60.2 | 74.3 | 80.0 | 580.0 |
| Edirne | 65.0 | 52.2 | 50.1 | 48.7 | 52.4 | 47.1 | 31.7 | 23.3 | 35.9 | 56.7 | 67.3 | 70.6 | 601.0 | |
| Kırklareli | 65.0 | 51.3 | 48.7 | 45.4 | 49.3 | 52.6 | 27.8 | 21.5 | 32.8 | 51.5 | 66.7 | 71.1 | 583.7 |
| Crop | Crop Parameters | Tekirdağ | Edirne | Kırklareli | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wheat | Crop Development Period (days) | Initial | 30 | 30 | 30 | [30] |
| Development | 146 | 170 | 170 | [30] | ||
| Mid-Season | 47 | 40 | 40 | [30] | ||
| Late-Season | 30 | 30 | 30 | [30] | ||
| Crop Coefficient (Kc) | Initial | 0.62 | 0.61 | 0.56 | [30] | |
| Mid-Season | 1.09 | 1.12 | 1.12 | [30] | ||
| Late-Season | 0.20 | 0.23 | 0.23 | [30] | ||
| Rooting Depth (m) | Initial | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | [31] | |
| Late-Season | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0.90 | [31] | ||
| Sowing Date | 15 October | 15 October | 15 October | [30] | ||
| Vegetation Duration (days) | 252 | 270 | 270 | [30] | ||
| Critical Depletion (Fraction) | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | [32] | ||
| Yield Response Factor | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | [32] | ||
| Sunflower | Crop Development Period (days) | Initial | 25 | 25 | 25 | [30] |
| Development | 30 | 30 | 30 | [30] | ||
| Mid-Season | 60 | 60 | 60 | [30] | ||
| Late-Season | 30 | 30 | 30 | [30] | ||
| Crop Coefficient (Kc) | Initial | 0.40 | 0.38 | 0.36 | [30] | |
| Mid-Season | 1.11 | 1.14 | 1.12 | [30] | ||
| Late-Season | 1.31 | 0.34 | 0.32 | [30] | ||
| Rooting Depth (m) | Initial | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | [33] | |
| Late-Season | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0.90 | [34] | ||
| Sowing Date | 15 April | 15 April | 15 April | [30] | ||
| Vegetation Duration (days) | 145 | 145 | 145 | [30] | ||
| Critical Depletion (Fraction) | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | [32] | ||
| Yield Response Factor | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | [32] | ||
| Soil Parameters | Soil Types | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Light (Sand) | Medium (Loam) | Heavy (Clay) | |
| Total available soil moisture (mm m−1) | 60.0 | 140.0 | 200.0 |
| Maximum rain infiltration rate (mm day−1) | 40 | 80 | 160 |
| Maximum rooting depth (cm) | 900 | 900 | 900 |
| Initial soil moisture depletion (%) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Initial available soil moisture (mm m−1) | 60.0 | 140.0 | 200.0 |
| Soil Texture Change Situation | Total Net Irrigation Requirement (mm) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sunflower | Wheat | |||||||
| Tekirdağ | Edirne | Kırklareli | Average | Tekirdağ | Edirne | Kırklareli | Average | |
| Light | 458.3 | 529.9 | 488.2 | 492.1 | 263.5 | 392.3 | 371.9 | 342.5 |
| Medium | 425.3 | 497.2 | 449.6 | 457.4 | 218.5 | 335.6 | 319.1 | 291.0 |
| Heavy | 402.2 | 477.9 | 433.1 | 437.7 | 162.7 | 276.1 | 259.8 | 232.9 |
| Average | 428.6 | 501.7 | 456.9 | 214.9 | 334.6 | 316.9 | ||
| Total Net Irrigation Change (%) | ||||||||
| Ligth to Medium | −7.2 | −6.2 | −7.9 | −7.1 | −17.1 | −14.5 | −14.2 | −15.0 |
| Medium to Heavy | −5.4 | −3.9 | −3.7 | −4.3 | −25.5 | −17.7 | −18.6 | −20.0 |
| Light to Heavy | −12.2 | −9.8 | −11.3 | −11.1 | −38.2 | −29.6 | −30.1 | −32.0 |
| Soil Texture | Total Net Irrigation Requirement (mm) for Sunflower | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tekirdağ | Edirne | Kırklareli | |||||||
| Min. (Year) | Max. (Year) | Average | Min. (Year) | Max. (Year) | Average | Min. (Year) | Max. (Year) | Average | |
| Light | 319.4 (1988) | 546.5 (1971) | 458.3 | 360.9 (1975) | 653.9 (2000) | 529.9 | 375.4 (1976) | 642.6 (2000) | 488.2 |
| Medium | 261.9 (1975) | 517.0 (1973) | 425.3 | 335.9 (1975) | 658.3 (2000) | 497.2 | 322.3 (1976) | 595.8 (2000) | 449.6 |
| Heavy | 275.4 (1992) | 467.4 (1984) | 402.2 | 283.5 (1975) | 657.8 (2000) | 477.9 | 279.5 (1976) | 558.6 (1978) | 433.1 |
| Soil Texture | Total Net Irrigation Requirement (mm) for Wheat | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tekirdağ | Edirne | Kırklareli | |||||||
| Min. (Year) | Max. (Year) | Average | Min. (Year) | Max. (Year) | Average | Min. (Year) | Max. (Year) | Average | |
| Light | 111.4 (1988) | 383.8 (1972) | 263.5 | 286.7 (1998) | 520.8 (1972) | 392.3 | 264.4 (1988) | 508.8 (1972) | 371.9 |
| Medium | 65.7 (1988) | 359.1 (1972) | 218.5 | 183.4 (1975) | 538.3 (1972) | 335.6 | 189.2 (1988) | 492.9 (2000) | 319.1 |
| Heavy | 0.0 (1988) | 273.9 (1983) | 162.7 | 174.3 (1975) | 432.1 (1990) | 276.1 | 175.0 (1980) | 422.0 (1972) | 259.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deveci, H.; Önler, B.; Erdem, T. Modeling the Effect of Soil Type Change on Irrigation Water Requirements of Sunflower and Wheat Using CROPWAT 8.0. Water 2025, 17, 1437. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101437
Deveci H, Önler B, Erdem T. Modeling the Effect of Soil Type Change on Irrigation Water Requirements of Sunflower and Wheat Using CROPWAT 8.0. Water. 2025; 17(10):1437. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101437
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeveci, Huzur, Buse Önler, and Tolga Erdem. 2025. "Modeling the Effect of Soil Type Change on Irrigation Water Requirements of Sunflower and Wheat Using CROPWAT 8.0" Water 17, no. 10: 1437. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101437
APA StyleDeveci, H., Önler, B., & Erdem, T. (2025). Modeling the Effect of Soil Type Change on Irrigation Water Requirements of Sunflower and Wheat Using CROPWAT 8.0. Water, 17(10), 1437. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101437






