Abstract
The effluent from the tannery industry contains high concentrations of organic pollutants, particularly chromium (Cr), which is a priority pollutant that harms human health, plants, animals, and affects compliance with environmental standards. This study significantly reduced tannery wastewater pollution and its toxic effects through the innovative use of an integrated treatment system with a coagulation/flocculation/settling process followed by a membrane bioreactor (MBR). Experiments were conducted to maximize the removal of pollutants by evaluating the effects of pH values, coagulant doses in the chemical treatment, and the biological treatment coupled with membrane separation within the MBR. The results indicated that optimizing the parameters achieved the highest reductions during the chemical treatment step: 97% for Cr, 63% for chemical oxygen demand (COD), and 90% for turbidity. The wastewater was then treated using the MBR system, which further improved removal efficiency to 99% for Cr, 96% for COD, and 99.8% for turbidity. These outcomes demonstrate the effectiveness of the hybrid treatment process in significantly lowering pollutant concentrations in tannery wastewater, ensuring compliance with Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) standards and the regulatory obligations under European Regulation (EU) 2020/741. This hybrid approach offers promising potential for broader industrial applications.
1. Introduction
The tannery industries are recognized as significant contributors to the production of solid, liquid, and gaseous wastes, which necessitate effective management strategies to mitigate their environmental impact [1]. The leather industries utilize a considerable amount of chemicals, comprising a broad range of substances, approximately 130 different types, including sodium salts and chromium [2]. Moreover, tannery wastewater is characterized by high concentrations of chemical oxygen demand (COD), biological oxygen demand (BOD), suspended solids, sulfides, and organic nitrogen [3]. The predominant process in leather production is chrome tanning, which constitutes about 90% of total global leather production [1]. Chromium occurs naturally in various geological formations, existing in multiple oxidation states, with trivalent chromium (Cr(III)) and hexavalent chromium (Cr(VI)) being the most prevalent in industrial contexts. While Cr(III) is relatively less toxic, Cr(VI) is soluble, highly mobile, and poses severe risks to human health, including respiratory issues, liver and kidney damage, and carcinogenic effects [4]. Only Cr(III) is employed in tanning processes, as Cr(VI) cannot induce tanning effects. However, trace amounts of Cr(VI) can be present in tannery wastewater due to the oxidation of Cr(III) under specific conditions. Tannery wastewater typically contains elevated levels of Cr, with concentrations ranging from 1500 to 3000 mg.L−1 [2]. Chromium used during the tanning process is partially absorbed by the hides (30–40%), with the remainder discharged in solid or liquid waste [2]. Given the complex composition of chromium and other pollutants, a diverse array of remediation strategies has been explored, including adsorption [5], ion exchange [6], electrochemical processes [7], coagulation/flocculation [2,8], biological treatment such as the activated sludge process [9], membrane filtration [10], and a membrane bioreactor [11].
Relying on a single approach is often insufficient for achieving regulatory limits for chromium discharge at high concentrations from treated wastewater. Therefore, hybrid or combined treatment approaches are increasingly applied to improve overall removal efficiency and meet discharge standards [12,13]. In this regard, Atallah et al. (2024) investigated the effectiveness of a hybrid electrocoagulation-ceramic membrane microfiltration/ultrafiltration process in the treatment of heavy metals like chromium from mining wastewater. Based on the findings, the EC-MF/UF hybrid process shows promise in improving throughput by eliminating the sedimentation tank requirements in traditional EC processes [14]. It is also recommended to use the coagulation/flocculation method for the pretreatment of biological units in wastewater containing high concentrations of pollutants. Concerning this matter, Costa et al. (2024) implemented a pretreatment process comprising pre-oxidation, coagulation, and flocculation (C/F) within an ultrafiltration (UF)–reverse osmosis (RO) system to facilitate arsenic removal from water [15]. The analysis revealed that pre-treatment technique utilization provides superior resistance to the treatment concerning a higher and more stable membrane permeability [15]. Coagulation, particularly when combined with membrane bioreactors (MBRs), has proven to be effective for chromium removal, though operational challenges such as coagulant usage, sludge generation, and membrane fouling remain [16]. MBR has emerged as a highly promising system for wastewater treatment. MBR technology integrates the conventional activated sludge process with membrane separation, providing a comprehensive approach to wastewater treatment [17]. The adoption of MBR technology provides significant advantages over activated sludge processes (ASPs), including the production of high-quality effluent, enabling high volumetric loading rates, and reducing hydraulic retention time (HRT). Additionally, an MBR supports prolonged solid retention times (SRTs) and simultaneous nitrification/denitrification while minimizing sludge production [18,19,20,21]. Despite these benefits, membrane fouling remains a major operational issue, reducing permeability and a shortened membrane lifespan [22,23,24]. To enhance their efficiency, MBRs are often coupled with advanced filtration processes (e.g., reverse osmosis) [25], and to eliminate membrane fouling, they are frequently paired with other techniques such as electrocoagulation [26] and coagulation [27]. Shen et al. (2020) emphasize the combination of coagulation and flocculation as a pretreatment tool for controlling the fouling of UF membranes. The findings indicate that the combined method is successfully capable of reducing fouling and enhancing the properties of flocs and the structure of the cake layer [28].
The present study addressed the research gap in existing studies that explore a hybrid solution for industrial wastewater treatment using a treatment technique incorporating coagulation, flocculation, and settling (CFS) procedures utilizing a green coagulant derived from basil seeds mucilage to enhance treatment performance with biological treatment, namely MBRs, by improving the pollutant removal and efficiency of therapy and increasing the potential for treating high loadings of contaminants. This study emphasizes the role of the MBR system in compliance with regulations applied to the facility’s operations and in developing alternative operational parameters. Similarly, the hybrid solution presented greater removal efficiencies of chromium, COD, and turbidity while reducing sludge production and membrane fouling that can leave a smaller environmental footprint on the facility, regardless of it being toxic wastewater.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tannery Wastewater
Wastewater effluent employed in this investigation was retrieved from the chrome plating operations of a leather production plant in Charmshahr, Varamin, Iran. The influent characteristics of wastewater properties for each step are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Tannery wastewater characteristics.
2.2. The Hybrid System (Coagulation/Flocculation/Settling Stage Followed by Membrane Bioreactor)
The hybrid system integrates a coagulation/flocculation/settling stage followed by a biological treatment and an MBR separation step (CFS-MBR), operating as a continuous system. The coagulation stage was optimized by using a combination of alum (Al2(SO4)3·18H2O) (Merck, Germany) and basil seed mucilage as flocculants, based on Design Expert software (Version 11.1.2.0, Stat-Ease). Following its deposition in the coagulation system, the clarified liquid was subsequently transferred to the second-stage tank, where it underwent biological treatment and membrane separation. This integrated approach is regarded as the most efficacious method for the treatment of industrial wastewater. Moreover, the membrane bioreactor (MBR) will allow it to meet U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) standards for effluent (and particularly for organic compounds).
2.2.1. Coagulation Section
Preparation of Coagulants
Basil seed mucilage (as a green chemical) and alum coagulants were selected and prepared as coagulants. Basil seeds were meticulously cleaned and finely ground. They were then dried in an oven at a temperature of 100 °C for 2 h. The powder was subsequently passed through a 210-micrometer-mesh sieve. Two grams of powder were combined with 100 mL of warm water containing 0.9 g of NaCl, and the mixture was stirred for 2 h using a magnetic stirrer. The mixture was then centrifuged for 10 min at 3400 rpm. The resulting polysaccharide exhibited high viscosity and was used as a coagulant in the treatment process [18,29].
Coagulation Studies
Coagulation experiments were performed using a jar test to study operational variables on the removal efficiency of chromium, COD, and turbidity. During the preliminary phase of treatment, the wastewater was screened through a strainer to remove solid impurities. Subsequently, the pH value of the sample was adjusted using NaOH. The primary tests were carried out in triplicate in 1 L standard beakers containing wastewater samples with 0.5 L of influent with the specified pH. Notably, the amounts of alum and basil mucilage added to the beakers were determined by the Design Expert software, showcasing the use of advanced technology in our research. The removal efficiency (R, %) of Cr, COD, and turbidity was calculated using Equation (1).
where C0 is the initial concentration (mg.L−1) and C is the final concentration (mg.L−1) of each parameter. It is important to note that each test was performed three times.
2.2.2. MBR Filtration Experiment
After optimizing the parameters for the chemical treatment stage, tannery wastewater was treated under the optimized conditions during the coagulation/flocculation/settling phase. The supernatant from this stage was then used as the influent for the biological treatment. The biological treatment process took place in a 40 L plexiglass reactor, equipped with a flat-sheet membrane module (Kubota Company, Osaka, Japan) made of polyether sulfone (PES), with a surface area of 0.11 m2 and a pore size of 0.4 µm. The membrane module was connected to a peristaltic pump to maintain a constant flow rate for stable operation. The schematic diagram of the entire system is presented in Figure 1.
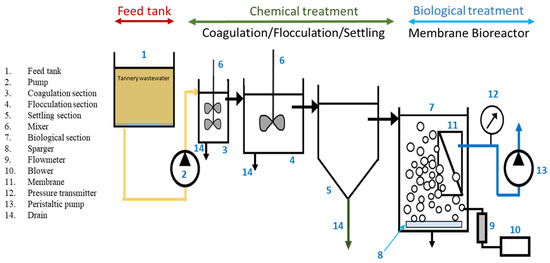
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the coagulation/flocculation/settling stage followed by a biological treatment and an MBR separation step (CFS-MBR).
The system was continuously fed at a rate of 40 L. d−1 with an organic loading rate (OLR) of 2.2 kg COD.m−3. d−1, utilizing the effluent from the chemical treatment phase, where the supernatant had settled in the tank. This process continued for 39 days at ambient temperature. The operating conditions of the MBR system are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Operating conditions of the MBR.
2.3. Analysis
2.3.1. Measurement of MLSS and MLVSS
The concentrations of Mixed Liquor Suspended Solids (MLSSs) and Mixed Liquor Volatile Suspended Solids (MLVSSs) were determined daily according to the APHA standard methods 2540 D and APHA 2540 E [30,31,32,33]. The measurements were performed using a standard laboratory filtration technique, and the results were recorded with an accuracy of ±0.01 g.L−1, based on the sensitivity of the balance used and the filtered volume (40 mL).
2.3.2. Chromium, Turbidity, and COD Measurements
Chromium concentration, chemical oxygen demand (COD), and turbidity were measured employing EPA Method 6020B, EPA Method 410.4, and EPA Method 180.1, respectively. Measurements were conducted using Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (Spectra AA-200, Varian Inc., Mulgrave, Australia), a UV-Vis spectrophotometer (Hach DR-5000, Hach Company, Loveland, CO, USA), and a turbidimeter (Hach 2100 Q, Hach Company, Loveland, CO, USA), ensuring precise analytical assessments. Detection limits were reported as ± [1–2% (Cr), 0.1 nm (COD), and 2% (turbidity)]. These methods were selected to ensure the accurate quantification of contaminants in tannery wastewater.
2.3.3. pH Measurement
The pH value was measured using a pH meter (691 pH Meter, Metrohm, Herisau, Switzerland). The pH meter was calibrated daily with standard buffer solutions (pH 4.00, 7.00, and 10.00), and the measurement accuracy was ±0.01 pH units.
2.3.4. Monitoring Transmembrane Pressure (TMP)
The transmembrane pressure (TMP), an indicator of membrane fouling, was monitored using a pressure gauge positioned between the membrane module and the peristaltic pump. TMP was recorded hourly, with an accuracy of ±2.5 mbar, and membrane cleaning was initiated when the TMP reached 250 mbar. The cleaning procedure was carried out as per the manufacturer’s recommendations and included the use of 1 molar NaOH for 6–8 h, followed by 22 g.L−1 citric acid for 1–2 h, and finally 20 mg.L−1 sodium hypochlorite for 10 min [34,35].
2.4. Statistical Modeling, Data Analysis, and Optimization
The optimized range of pH, alum, and basil mucilage concentration was determined using Design Expert software (Version 11.0.3) and a quadratic model. The range of the parameters was a pH from 6 to 10, 200 to 2000 mg of Alum·L−1, and 200 to 2000 mg of Basil.L−1. A total of 20 assays were performed for response surface modeling. The results were statistically validated using Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) to assess the significance of the model (p-value < 0.05). Optimization was carried out using the maximum ridge analysis and canonical analysis.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Performance of Coagulation/Flocculation Treatment
Second-order polynomial equations were employed to model the removal efficiencies of Cr, COD, and turbidity in tannery wastewater. The peak removal efficiencies observed were 97%, 63%, and 90% for Cr, COD, and turbidity, respectively, during the 19th trial when the coagulant dose and pH were optimized. Table 3 details chromium removal efficiency and other pollutants under different experimental conditions. The 3rd and 5th runs showed impressive chromium removal efficiencies of 90% and 92.5%, respectively, emphasizing the optimization of important parameters such as pH and coagulant concentrations for chromium reduction. The sedimentation activity plays a critical role in the overall removal process. In the coagulation and flocculation process, alum and basil mucilage also acted as coagulants to produce flocs containing suspended chromium ions and organic matter. These flocs provide the basis for sedimentation and lower concentrations of Cr and COD. The effectiveness of the sedimentation depends on the sedimentation pH and coagulant concentration, which, together with sedimentation time, affect floc formation and size. Increasing alum concentration and pH maxima are strategies to enhance sedimentation. The most effective condition for Cr removal using alum was determined to be 1510 mg.L−1 at pH 9, likely due to a more optimal coagulation environment allowing for floc formation to produce larger and more stable floc particles. While the higher doses of alum made Cr removal more efficient by improving binding with chromium ions, excessive exposures to high alum concentrations can adversely affect particle settlement if there are too many finer particles. COD removal trends were similar to Cr removal in that an elevated alum concentration also facilitated a new site for the aggregation of organic particulate matter with settling occurring during sedimentation. The interaction between alum and basil mucilage most likely facilitates floc growth to help eliminate organic pollutants. Equally, alkaline pH suits coagulation and flocculation since, from other studies, increased metal removal occurred under alkaline pH.

Table 3.
Experimental design matrix and response for chromium, COD, and turbidity removal Rates utilizing Design Expert.
The positive effect of the optimized pH level on chromium removal aligns with the findings of Lugo et al. (2021), who highlighted the importance of pH in influencing metal removal from wastewater. Their results further emphasize the critical role of pH in the coagulation and precipitation of metals during wastewater treatment, providing insight into a key factor in our process and reporting removal rates of 87% for chromium, 88% for COD, and 94% for turbidity using modified Acacia tannin (MAT) at pH 10 [13].
The interaction between the alum concentration, pH, and Cr removal rate is shown in Figure 2. The data indicate that the highest Cr removal efficiency (97%) occurred at a pH range of 9 to 10 and an alum concentration between 1100 and 1550 mg.L−1. Notably, the study found that increasing the pH level with an alum concentration of 1635 mg.L−1 was more effective for Cr removal than using a lower alum concentration.
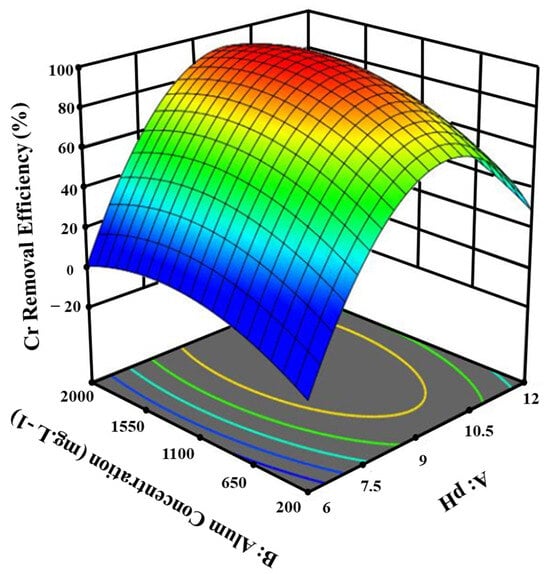
Figure 2.
The effect of pH and alum concentration on the removal efficiency of Cr from tannery wastewater.
Furthermore, as revealed in Table 3, increasing the alum concentration to 1635.1 mg.L−1 was more effective when the pH was around 9, compared to when it was either lower or higher. These results align with previous studies that noted reduced coagulant activity in acidic conditions due to the influence of the coagulant’s surface charge [36]. The effectiveness of alum at higher pH values for Cr removal is also consistent with the findings of Arukula et al. (2018), who demonstrated that 70–80% of Cr(VI) was removed under alkaline conditions, while lower coagulant activity was observed at an acidic pH. This could be due to competition between protons and metal ions for common binding sites under acidic conditions [37].
In contrast, Ogunfowokan et al. (2007) reported a significant 96.2% Cr removal rate using 10 mg.L−1 alum at pH 7.5 for wastewater from battery industries. In the current study, with an initial Cr concentration of 2860 mg.L−1, the removal efficiency reached 97% at pH 9.1 [38]. The wastewater characteristics in both studies were different, which likely accounts for the discrepancies in performance. The initial Cr concentration in the current study was substantially higher, yet the removal efficiency was nearly the same, demonstrating the robustness of the optimized coagulation process under the conditions tested.
Figure 3 shows that pH changes have a more significant effect on chromium removal than basil seed extract concentration. Additionally, an increase in the coagulant dose led to an increase in the removal rate; however, further increases in the dose did not yield higher removal rates due to the potential disruption of the particle settlement process [38].
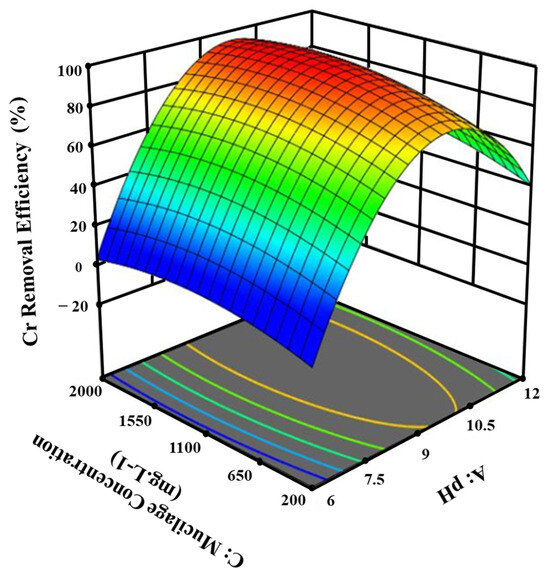
Figure 3.
The effect of pH and mucilage concentration on the removal efficiency of Cr from tannery wastewater.
As illustrated in Figure 4, while alum concentrations were between 1100 and 1550 mg.L−1, the impact of basil mucilage concentration on chromium removal exhibited more significance. In contrast, when alum concentrations exceeded or fell below this range, the effect of changes in basil mucilage concentration on chromium removal became less significant.
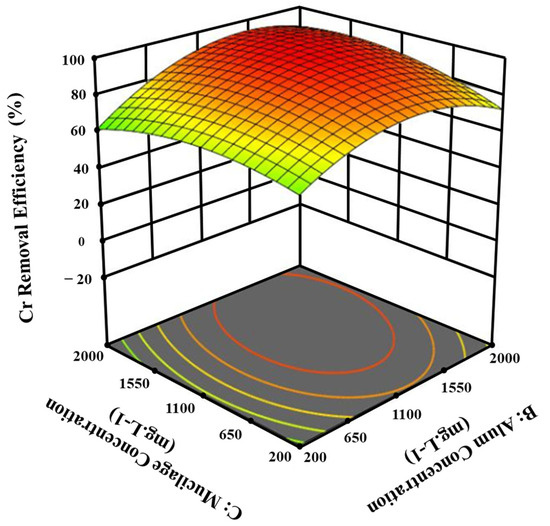
Figure 4.
The effect of alum concentration and mucilage concentration on the removal of chromium from tannery wastewater.
Increasing the alum concentration beyond this point significantly enhances the efficiency of Cr removal at the optimal basil mucilage concentration. This improvement can be attributed to the synergistic interaction between basil mucilage and alum, which likely creates additional binding sites for chromium ions. The optimized balance of these components ensures maximum removal efficiency while maintaining stability within the treatment system. The results underscore carefully adjusting the alum concentration to improve the process significantly.
3.2. Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) Treatment
The bioreactor influent comes from the coagulation/flocculation/settling (CFS) stage, which has been optimized by Design Expert software (Table 3). Second-order polynomial equations were used to model the removal efficiencies of Cr, COD, and turbidity. The highest removal rates (97% for chromium, 63% for COD, and 90% for turbidity) were observed during the 19th trial, when both coagulant dosage and pH were optimized. The positive effect of the optimized pH level on chromium removal aligns with the findings of Lugo et al. (2020), who highlighted the importance of pH in influencing metal removal from wastewater. Their results further emphasize the critical role of pH in the coagulation and precipitation of metals during wastewater treatment [13]. After treating the influent of tannery wastewater in the CFS stage, the effluent from this stage is sent to the bioreactor.
3.2.1. MLSS and MLVSS Variation in MBR
Figure 5 demonstrates a progressive increase in biomass concentration (MLSS and MLVSS) over the 35-day operational period. The absence of activated sludge extraction in the system, coupled with an infinite sludge retention time (SRT), allowed for the uninterrupted accumulation of solids. This behavior reflects the system’s adaptation and stabilization, as microbial activity steadily increased [39]. MLSS consistently exceeded MLVSS concentrations throughout the timeframe, which aligns with the fundamental distinction between the two parameters. While MLSS encompasses the total suspended solids, including both organic and inorganic fractions, MLVSS is restricted to the organic volatile portion. The observed disparity highlights the contribution of inorganic materials in the treatment system and provides critical insight into biomass dynamics. Moreover, these trends underline the system’s operational efficiency and its capacity to support high amounts of microbial activity, a key factor in effective organic matter degradation and heavy metal removal. Malik et al. (2021) observed in the aerobic granular sludge system that increasing MLSS concentrations led to the improved removal of COD, TSS, and oil/grease from textile wastewater, which is indicative of healthy system performance and aligns with expectations in wastewater treatment studies [40].
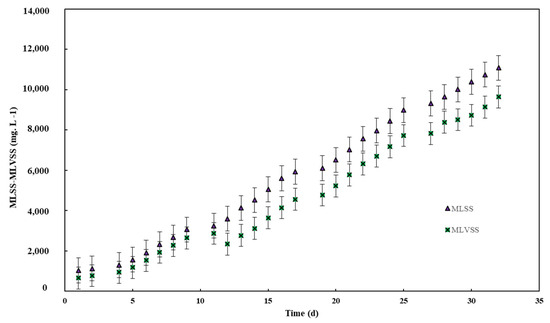
Figure 5.
MLSS and MLVSS concentration vs. time.
3.2.2. COD Removal
Figure 6 shows the COD removal efficiency vs. time in the MBR system. Figure 6 shows a latent phase of 12 days, during which COD removal remained constant (between 10 and 20%). During the adaptation phase, microorganisms in the activated sludge adapted to the tannery wastewater, and the microorganisms that would eliminate more COD dominated the system. This adaptation phase aligns with the findings of Izadi et al. (2019), where the microbial community in the MBR adapted to the effluent contaminants after a stabilization period, resulting in an increase in overall COD removal efficiency [18]. After 12 days, the biological efficiency increased steadily, eventually plateauing at an overall efficiency of 95%. The biomass adapted to the effluent in a relatively short period (28 days), with COD removal efficiency improving steadily, reflecting robust microbial activity and the effective degradation of organic matter. This is further supported by the growth of MLVSS during continuous operation, facilitated by the total retention of biomass by the membrane (no sludge withdraw). The COD removal rate through the membrane remained stable at around 20%, while the overall removal rate gradually increased, ultimately reaching 95% after 28 days. This result complies with the European standard for Class D (<125 mg COD.L−1). The presence of chromium likely adds complexity to the COD removal process, but it did not appear to be toxic to the microorganisms.
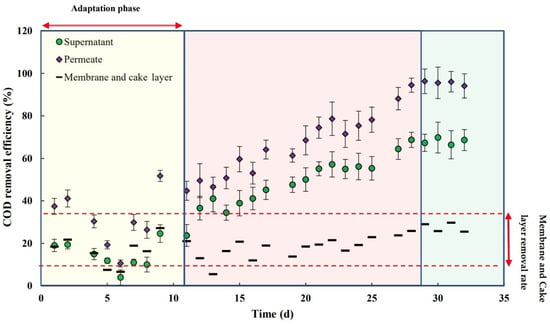
Figure 6.
COD removal efficiency (supernatant, permeate, membrane, and cake layer) vs. time.
The observed conversion yield after the stabilization phase (28 days) was approximately 0.12 gSS produced per g of COD removed. This low conversion rate can be attributed to the soluble nature of the COD. Furthermore, data variability patterns, demonstrated by error bars in the figure, could be affected by wastewater fluctuations or operational factors. Moreover, it is reasonable to theorize that the COD removal rate would remain stable around 95% if the experiments were extended beyond 32–33 days, assuming that operational conditions (e.g., temperature, pH, and feed composition) remain constant. This behavior aligns with studies such as that of Izadi et al. (2019), where long-term microbial activity maintained consistent removal rates of pollutants after an adaptation phase [18]. Furthermore, the membrane bioreactor (MBR) demonstrates its capacity to achieve effluent standards set by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), particularly for organic compounds. This performance aligns with broader environmental goals for effective wastewater treatment.
3.2.3. Turbidity Removal
As shown in Figure 7, the turbidity evaluation over time for the permeate, supernatant, and membrane demonstrates consistent and reliable performance, achieving an average turbidity removal of 98.8%, well below the European threshold of 5 NTU. The membrane system is particularly significant, as it highlights the crucial role of filtration in separating suspended particles, thereby optimizing the biological filtration process. The membrane system and the cake layer formed on its surface contributed significantly to turbidity control, accounting for 30% of the total removal efficiency. The biological phase was responsible for 68% of the turbidity elimination, emphasizing its critical role. These findings align with the results reported by Mlaik et al. (2012), where membrane bioreactor (MBR) systems exhibited exceptional turbidity removal efficiency, achieving rates of up to 98% when treating unhairing wastewater. The results underscore the effectiveness of combining coagulation/flocculation/settling with membrane filtration as a robust strategy for managing complex waste streams [41].
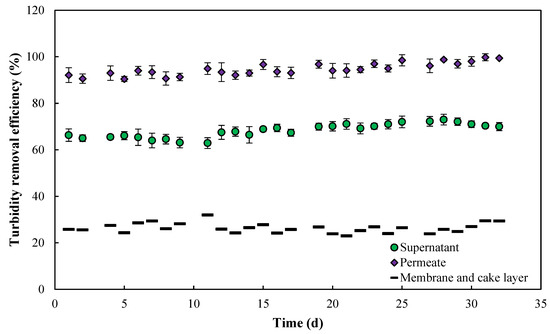
Figure 7.
Turbidity removal efficiency (supernatant, permeate, membrane, and cake layer) vs. time.
3.2.4. Cr Removal Performance
Figure 8 illustrates the chromium removal efficiency across the supernatant, permeate, and membrane over a specific operational timeframe. The data show that the biological chromium removal process had negligible activity during the latent phase, with little change in the removal efficiency. The results reveal that the biological chromium removal process remained largely stagnant, with no notable variations observed in removal efficiency during the latent phase. This emphasizes the initial stabilization period before the system achieves optimized performance. However, as with COD, Cr removal gradually increased over time from day 13 to day 28, reaching a constant global efficiency of 98% by day 28. The elevated MLSS values exert a substantial influence on the removal of chromium, as a greater number of metal ions become attached to sludge flocs, thereby impeding their escape with the final effluent. The proliferation and adaptation of the biological sludge within the reactor resulted in enhanced Cr removal, a phenomenon analogous to the trend observed for COD [42]. These findings are consistent with those of Ji et al. (2020), where biological systems in MBRs showed increased heavy metal removal after an adaptation period, particularly for metals like chromium, which is known to be toxic to microorganisms initially [11].
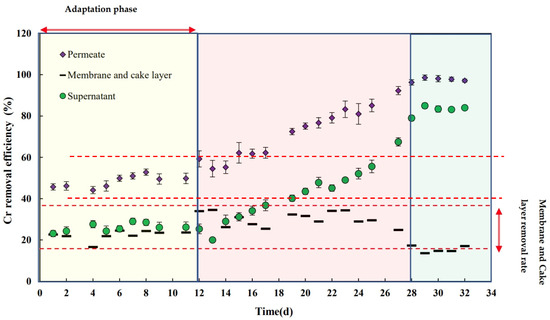
Figure 8.
Cr removal efficiency vs. time (for supernatant, permeate, membrane, and cake layer).
Unlike the initial phase of the experiment, the results indicate a gradual increase in Cr removal. While membrane removal was initially comparable to biological removal (20% each), biological removal became five times more effective than membrane removal, resulting in an average chromium concentration of 2.4 mg.L−1. In the supernatant of a system without a membrane (conventional activated sludge), this concentration would have been around 19 mg.L−1. This finding aligns with the conclusions of Malamis et al. (2009), who posited that the MBR system is anticipated to demonstrate superior performance in comparison to an AS system. This expectation is rooted in the hypothesis that the metal ions that are associated with colloidal matter or with diminutive sludge flocs are efficiently retained by the membrane within the reactor [42].
Hence, the adaptation stage was critical for chromium removal efficiency. Activated sludge microorganisms underwent physiological and metabolic adaptations to survive in tannery wastewater, showing selective enrichment in chromium-resistant microbial populations during the adaption stage. These populations developed special enzymatic mechanisms, such as chromate reductase activity, supportive environmental conditions, and greater close-contact within the system to overcome chromium concentration [43,44]. Also, biomass accumulation within the MBR system strengthened microbial activity and promoted diversification and, subsequently, homogeneity in chromium removal. Collectively, these mechanisms greatly improved chromium removal during the period of adaptation and reduced the chromium concentration significantly.
4. Conclusions
This research successfully demonstrated the effectiveness of a hybrid treatment process, combining coagulation/flocculation/settling with a membrane bioreactor (MBR), for the treatment of tannery wastewater. The optimized chemical treatment achieved significant reductions, including 97% for Cr, 63% for chemical oxygen demand (COD), and 90% for turbidity. The biological phase of the MBR system further enhanced efficiency and adaptability. The MBR system exhibited impressive performance, achieving a 99.8% removal of turbidity, a 96% removal of COD, and a 99% removal of Cr. No toxic effects were detected, even at high Cr concentrations and loads, and the conversion yield remained low, indicating an environmentally sustainable approach. By reducing Cr concentration from approximately 2860 ppm to below 2 ppm, the process significantly minimizes the environmental impact and health risks, in line with European standards (Regulation (EU) 2020/741), enabling potential wastewater reuse. Future studies should focus on optimizing operational parameters to reduce latency and enhance system performance, and explore the recovery of chromium from sludge to enhance the sustainability of the process.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.P.S., M.H. and S.B.; data curation, M.G., M.M. and M.B.; formal analysis, M.G., M.M. and M.B.; investigation, M.G., M.M., H.S., M.K. and M.B.; methodology, M.G., M.M. and M.B.; project administration, F.P.S. and S.B.; supervision, F.P.S. and S.B.; Co-supervision, O.T., A.H. and M.H.; visualization, M.G., M.M., H.S. and M.B.; writing—original draft, M.K., H.S., M.H., G.L. and F.P.S.; writing—review and editing, M.K., H.S., M.H., G.L. and F.P.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data of this research are available to everyone. Those who are interested can acquire the data by sending an email to farshid.pajoumshariati@umontpellier.fr.
Acknowledgments
The author would like to thank Alireza Satchi, Mahsa Keyvan Hossieni, Helia Abdolahzadeh, Mohammad Reza Mosaddeghi, and Soroush Azizi for their help during this project. The manuscript was entirely written by the authors without the use of AI tools for content creation. However, to ensure the manuscript reflects the quality and fluency of native English, we utilized an AI-based tool solely for language enhancement and grammar correction. The tool was employed to improve the manuscript’s language without affecting the original content or structure.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Hashem, A.; Mim, M.W.; Noshin, N.; Maoya, M. Chromium Adsorption Capacity from Tannery Wastewater on Thermally Activated Adsorbent Derived from Kitchen Waste Biomass. Clean. Water 2024, 1, 100001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawalha, H.; Alsharabaty, R.; Sarsour, S.; Al-Jabari, M. Wastewater from Leather Tanning and Processing in Palestine: Characterization and Management Aspects. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 251, 109596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, R.A.; Cerutti, S.; Gásquez, J.A.; Olsina, R.A.; Martinez, L.D. Preconcentration and Speciation of Chromium in Drinking Water Samples by Coupling of On-Line Sorption on Activated Carbon to ETAAS Determination. Talanta 2006, 68, 1065–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, C.M.; Keçili, R. Modern Environmental Analysis Techniques for Pollutants; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Daneshvar, N.; Salari, D.; Aber, S. Chromium Adsorption and Cr(VI) Reduction to Trivalent Chromium in Aqueous Solutions by Soya Cake. J. Hazard. Mater. 2002, 94, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Z.; Zhang, G.; Du, H.; Zhu, J.; Li, J. Preparation and Application of BiOBr-Bi2S3 Heterojunctions for Efficient Photocatalytic Removal of Cr(VI). J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 407, 124394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Kang, D.; Chen, Z.; Zhan, J.; Wu, X. Removal of Chromium Using Electrochemical Approaches: A Review. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2018, 13, 1250–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolkou, A.K.; Trikalioti, S.; Makrogianni, O.; Xanthopoulou, M.; Deliyanni, E.A.; Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Kyzas, G.Z. Chromium(VI) Removal from Water by Lanthanum Hybrid Modified Activated Carbon Produced from Coconut Shells. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamais, D.; Noutsopoulos, C.; Kavallari, I.; Nyktari, E.; Kaldis, A.; Panousi, E.; Nikitopoulos, G.; Antoniou, K.; Nasioka, M. Biological Groundwater Treatment for Chromium Removal at Low Hexavalent Chromium Concentrations. Chemosphere 2016, 152, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imdad, S.; Dohare, R.K.; Agarwal, M.; Srivastava, A. Efficient Removal of Cr (VI) from Wastewater Using Recycled Polymer-Based Supported Ionic Liquid Membrane Technology. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 327, 124908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Kulshreshtha, S.; Kakade, A.; Majeed, S.; Li, X.; Liu, P. Bioaugmentation of Membrane Bioreactor with Aeromonas Hydrophila LZ-MG14 for Enhanced Malachite Green and Hexavalent Chromium Removal in Textile Wastewater. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2020, 150, 104939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghangrekar, M.M.; Sathe, S.M.; Chakraborty, I. Situ Bioremediation Techniques for the Removal of Emerging Contaminants and Heavy Metals Using Hybrid Microbial Electrochemical Technologies. In Emerging Technologies in Environmental Bioremediation; Shah, M.P., Couto, S.R., Şengör, S.S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 233–255. [Google Scholar]
- Lugo, L.; Martín, A.; Diaz, J.; Pérez-Flórez, A.; Celis, C. Implementation of Modified Acacia Tannin by Mannich Reaction for Removal of Heavy Metals (Cu, Cr and Hg). Water 2020, 12, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atallah, C.; Mosadeghsedghi, S.; Dashtban Kenari, S.L.; Hudder, M.; Morin, L.; Volchek, K.; Mortazavi, S.; Ben Salah, I. Removal of Heavy Metals from Mine Water Using a Hybrid Electrocoagulation-Ceramic Membrane Filtration Process. Desalination Water Treat. 2024, 320, 100730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, F.C.R.; Moreira, V.R.; Guimarães, R.N.; Moser, P.B.; Santos, L.V.S.; De Paula, E.C.; Amaral, M.C.S. Pre-Oxidation and Coagulation-Flocculation as a Pretreatment to UF-RO Applied for Surface Water Treatment and Arsenic Removal. Desalination 2024, 586, 117855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteki, S.; Karsaz, M.; Ghofrani, B.; Yegani, R.; Majidi, S. Combination of Membrane Bioreactor with Chemical Coagulation for the Treatment of Real Pharmaceutical Wastewater: Comparison of Simultaneous and Consecutive Pre-Treatment of Coagulation on MBR Performance. J. Water Process. Eng. 2024, 60, 105108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyvan Hosseini, M.; Liu, L.; Keyvan Hosseini, P.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Lee, K.; Miao, J.; Chen, B. Review of Hollow Fiber (HF) Membrane Filtration Technology for the Treatment of Oily Wastewater: Applications and Challenges. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadi, A.; Hosseini, M.; Darzi, G.N.; Bidhendi, G.N.; Shariati, F.P. Performance of an Integrated Fixed Bed Membrane Bioreactor (FBMBR) Applied to Pollutant Removal from Paper-Recycling Wastewater. Water Resour. Ind. 2019, 21, 100111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorhemen, O.T.; Hamza, R.A.; Tay, J.H. Membrane Bioreactor (Mbr) Technology for Wastewater Treatment and Reclamation: Membrane Fouling. Membranes 2016, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, L.; Vinardell, S.; Charreton, J.; Heran, M.; Lesage, G. Assessing the Impact of Granular Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactor 1 Intensification on Treatment Performance, Membrane Fouling and 2 Economic Balance. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannina, G.; Alliet, M.; Brepols, C.; Comas, J.; Heran, M.; Robles, A.; Rodriguez-Roda, I.; Ruano, M.V.; Garcia, V.S.; Smets, I.; et al. Optimization of MBRs through Integrated Modelling: A State of the Art. J. Env. Manag. 2024, 370, 122720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keerthi; Vinduja, V.; Balasubramanian, N. Electrocoagulation-Integrated Hybrid Membrane Processes for the Treatment of Tannery Wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2013, 20, 7441–7449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarup, R.; Behl, K.; Joshi, M.; Nigam, S. Heavy Metal Removal by Cyanobacteria. In New Trends in Removal of Heavy Metals from Industrial Wastewater; Shah, M.P., Couto, S.R., Kumar, V., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 441–466. [Google Scholar]
- Keyvan Hosseini, M.; Keyvan Hosseini, P.; Helchi, S.; Pajoum Shariati, F. The comparison between two methods of membrane cleaning to control membrane fouling in a hybrid membrane photobioreactor (HMPBR). Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2023, 53, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Domínguez, A.; Rivera-Huerta, M.L.; Pérez-Castrejón, S.; Garrido-Hoyos, S.E.; Villegas-Mendoza, I.E.; Gelover-Santiago, S.L.; Drogui, P.; Buelna, G. Chromium Removal from Drinking Water by Redox-Assisted Coagulation: Chemical versus Electrocoagulation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 200, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; Hering, J.G. Removal of Chromium(VI) from Drinking Water by Redox-Assisted Coagulation with Iron(II). J. Water Supply: Res. Technol.—AQUA 2003, 52, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, T.; Stephenson, T. Effects of Chemical Addition on Aerobic Biological Treatment of Municipal Wastewater. Environ. Technol. 1998, 19, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Gao, B.; Guo, K.; Yue, Q. Characterization and Influence of Floc under Different Coagulation Systems on Ultrafiltration Membrane Fouling. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosaddeghi, M.R.; Pajoum Shariati, F.; Vaziri Yazdi, S.A.; Nabi Bidhendi, G. Application of Response Surface Methodology (RSM) for Optimizing Coagulation Process of Paper Recycling Wastewater Using Ocimum basilicum. Environ. Technol. 2020, 41, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dell, J.W. Method 180.1, Revision 2.0: The Determination of Turbidity by Nephelometry. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), Environmental Monitoring Systems Laboratory, Office of Research and Development, Cincinnati, Ohio, August 1993. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/ (accessed on 1 August 1993).
- Kumar, K.; Singh, G.K.; Dastidar, M.G.; Sreekrishnan, T.R. Effect of Mixed Liquor Volatile Suspended Solids (MLVSS) and Hydraulic Retention Time (HRT) on the Performance of Activated Sludge Process during the Biotreatment of Real Textile Wastewater. Water Resour. Ind. 2014, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), Method 6020A, Revision 1: Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry. EPA SW-846, Office of Solid Waste, February 2007. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/ (accessed on 1 January 1998).
- O’Dell, J.W. Method 410.4, Revision 2.0: The Determination of Chemical Oxygen Demand by Semi-Automated Colorimetry. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), Environmental Monitoring Systems Laboratory, Office of Research and Development, Cincinnati, Ohio, August 1993. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/ (accessed on 1 August 1993).
- Chatzikonstantinou, K.; Tzamtzis, N.; Pappa, A.; Liodakis, S. Membrane Fouling Control Using High-Frequency Power Vibration, in an SMBR Pilot System—Preliminary Studies. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 11550–11560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugarte, P.; Ramo, A.; Quílez, J.; Bordes, M.d.C.; Mestre, S.; Sánchez, E.; Peña, J.Á.; Menéndez, M. Low-Cost Ceramic Membrane Bioreactor: Effect of Backwashing, Relaxation and Aeration on Fouling. Protozoa and Bacteria Removal. Chemosphere 2022, 306, 135587. [Google Scholar]
- Bhagawan, D.; Poodari, S.; Pothuraju, T.; Srinivasulu, D.; Shankaraiah, G.; Yamuna Rani, M.; Himabindu, V.; Vidyavathi, S. Effect of Operational Parameters on Heavy Metal Removal by Electrocoagulation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2014, 21, 14166–14173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arukula, D.; Prem, P.; Tanwi, P.; Hariraj, S.; Vijay, L.M.; Brijesh, K.M. Treatment of Tannery Wastewater Using Aluminium Formate: Influence of the Formate over Sulphate-Based Coagulant. Glob. NEST J. 2018, 20, 458–464. [Google Scholar]
- Ogunfowokan, A.O.; Durosinmi, L.M.; Oyekunle, J.A.O.; Ogunkunle, O.A.; Igbafe, I.T. Removal of Heavy Metals from Industrial Wastewaters Using Local Alum and Other Conventional Coagulants—A Comparative Study. J. Appl. Sci 2007, 7, 1416–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chuan, C.H.; Zhou, J.; Fane, A.G. Effect of sludge retention time on membrane bio-fouling intensity in a submerged membrane bioreactor. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2006, 41, 1313–1329. [Google Scholar]
- Malik, A.; Hussain, M.; Uddin, F.; Raza, W.; Hussain, S.; Habiba, U.E.; Malik, T.; Ajmal, Z. Investigation of textile dyeing effluent using activated sludge system to assess the removal efficiency. Water Environ. Res. 2021, 93, 2931–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlaik, N.; Bouzid, J.; Belbahri, L.; Woodward, S.; Mechichi, T. Combined Biological Processing and Microfiltration in the Treatment of Unhairing Wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2012, 19, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malamis, S.; Katsou, E.; Chazilias, D.; Loizidou, M. Investigation of Cr(III) Removal from Wastewater with the Use of MBR Combined with Low-Cost Additives. J. Memb. Sci. 2009, 333, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayani, M.; Shetty, K.V. Chromium-resistant bacteria and their environmental condition for hexavalent chromium removal: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 43, 955–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kookhaee, F.; Bafroee, A.S.; Jabalameli, L. Isolation and characterization of chromium (VI) tolerant bacteria from tannery effluents. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2022, 20, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).