Evaluation of Water Richness in Sandstone Aquifers Based on the CRITIC-TOPSIS Method: A Case Study of the Guojiawan Coal Mine in Fugu Mining Area, Shaanxi Province, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
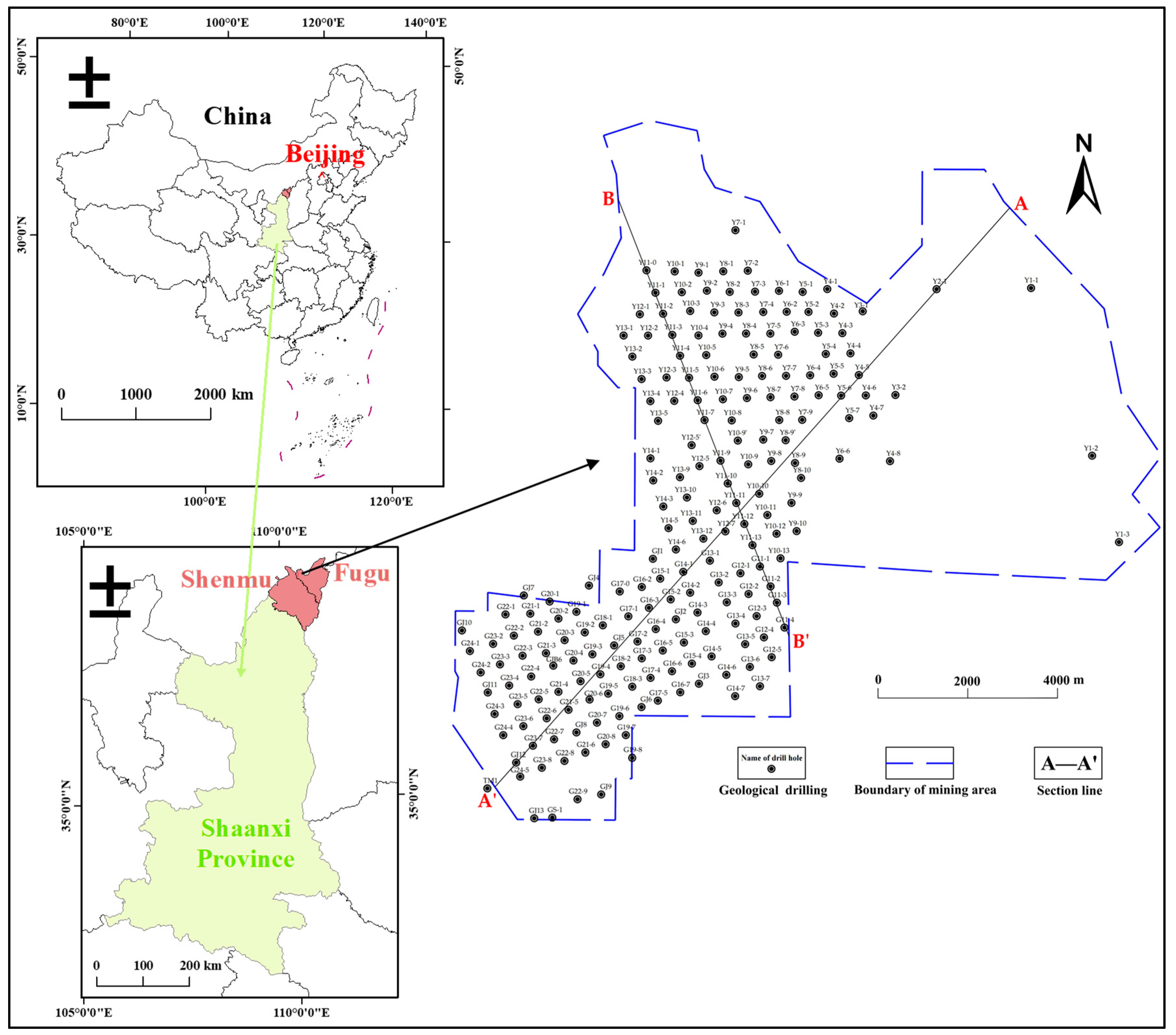
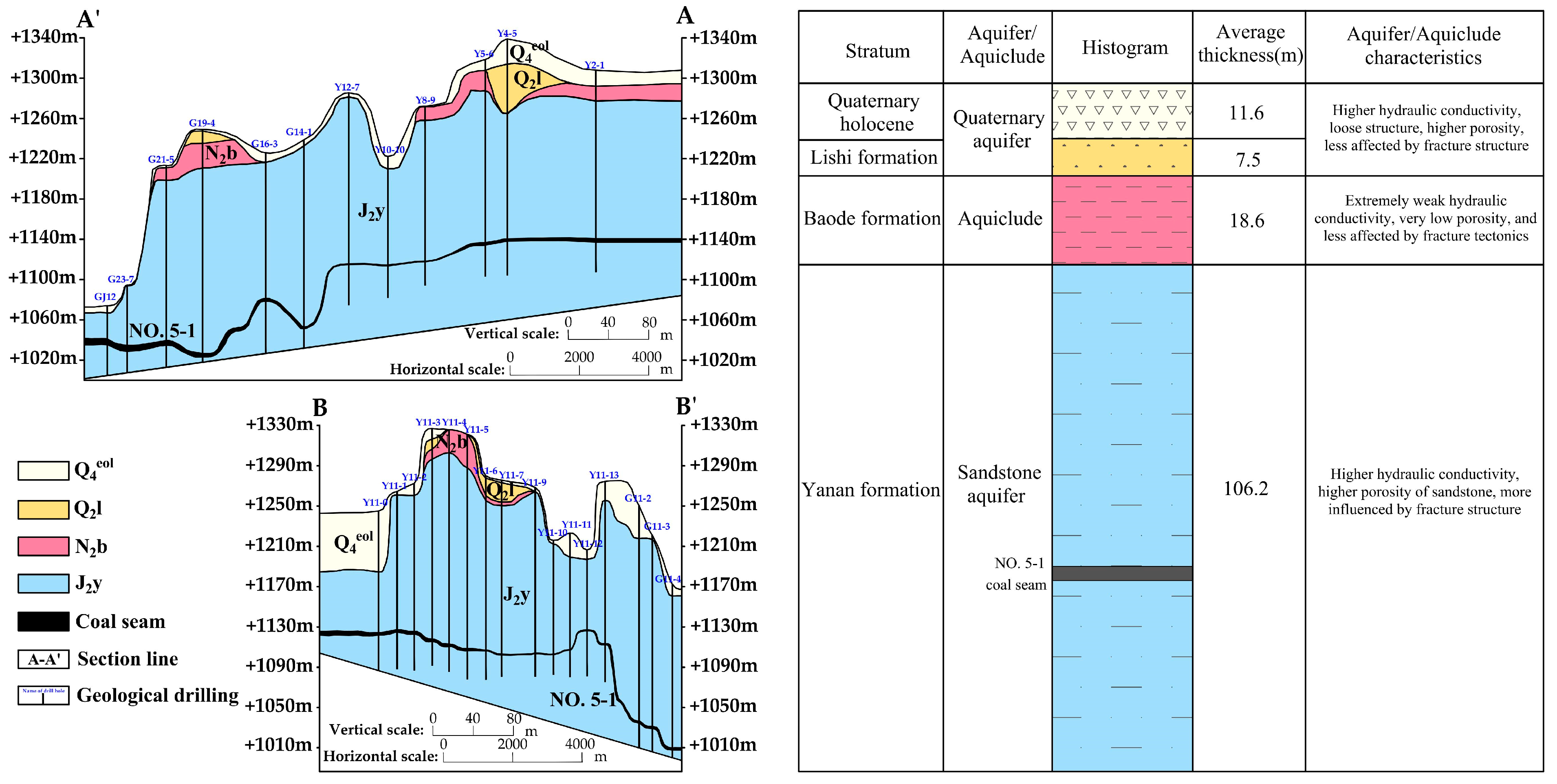
2. Overview of the Study Area
3. Evaluation Indicators
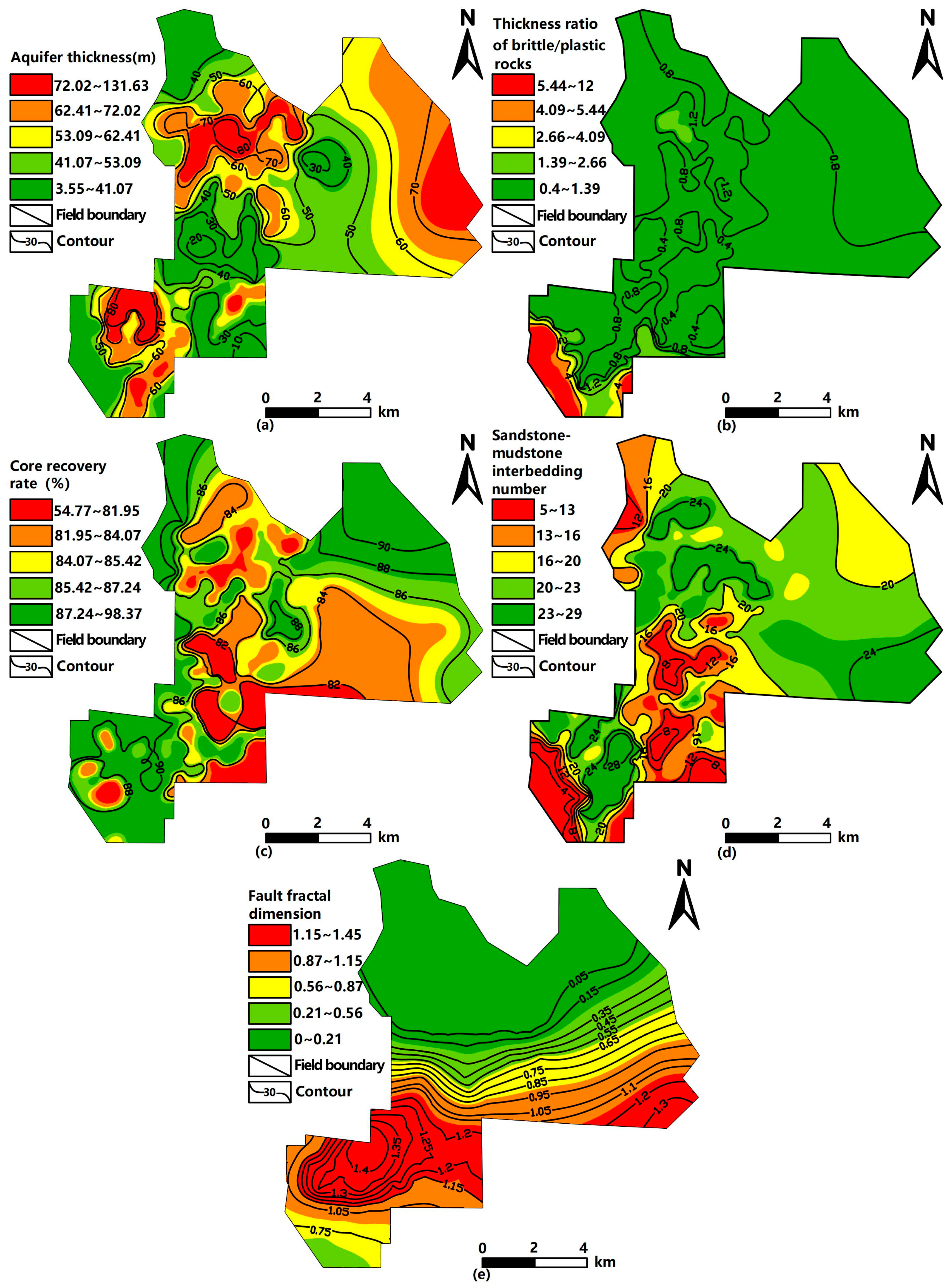
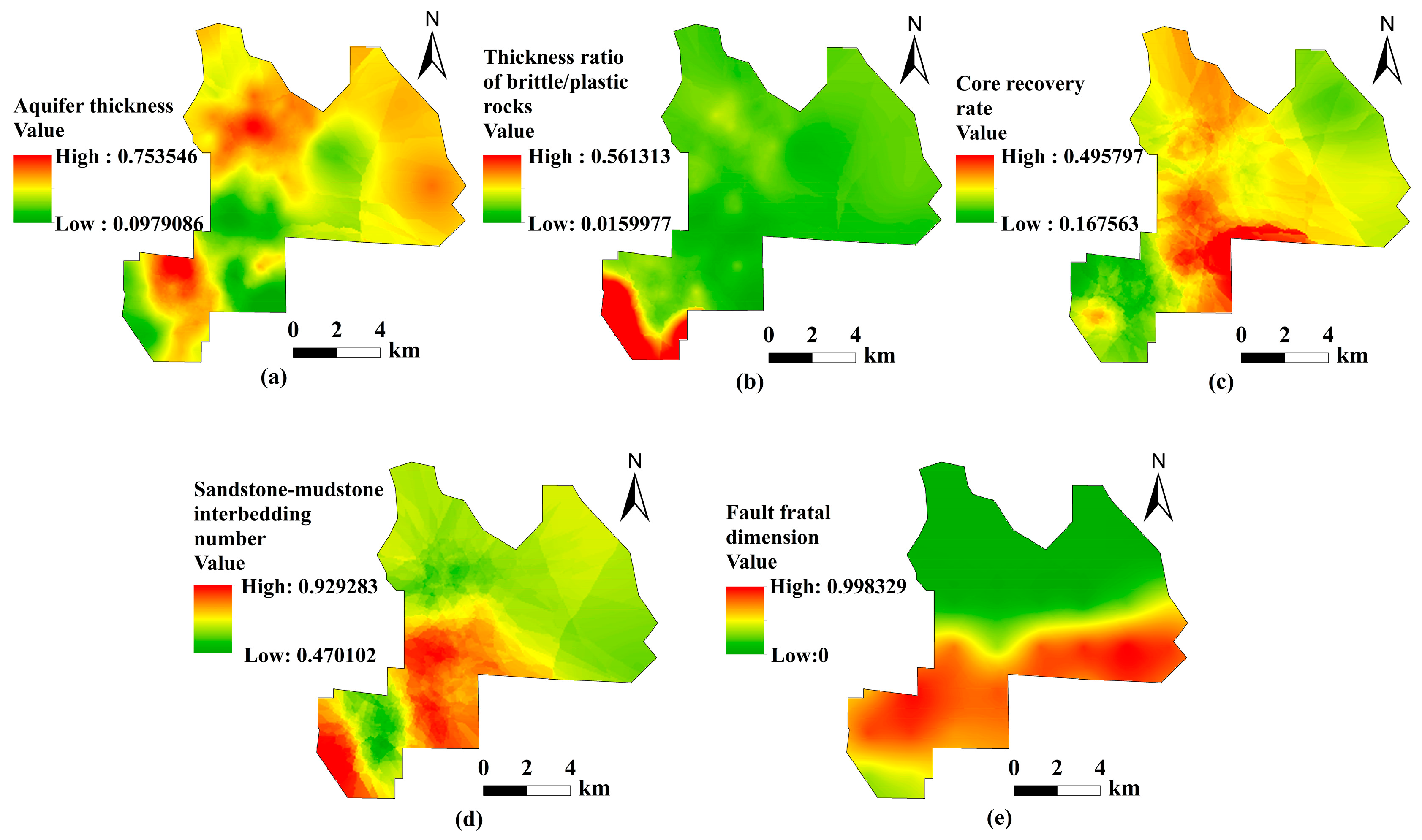
3.1. Sandstone Aquifer Thickness
3.2. Thickness Ratio of Brittle/Plastic Rocks
3.3. Core Recovery Rate
3.4. Number of Sandstone–Mudstone Interbeds
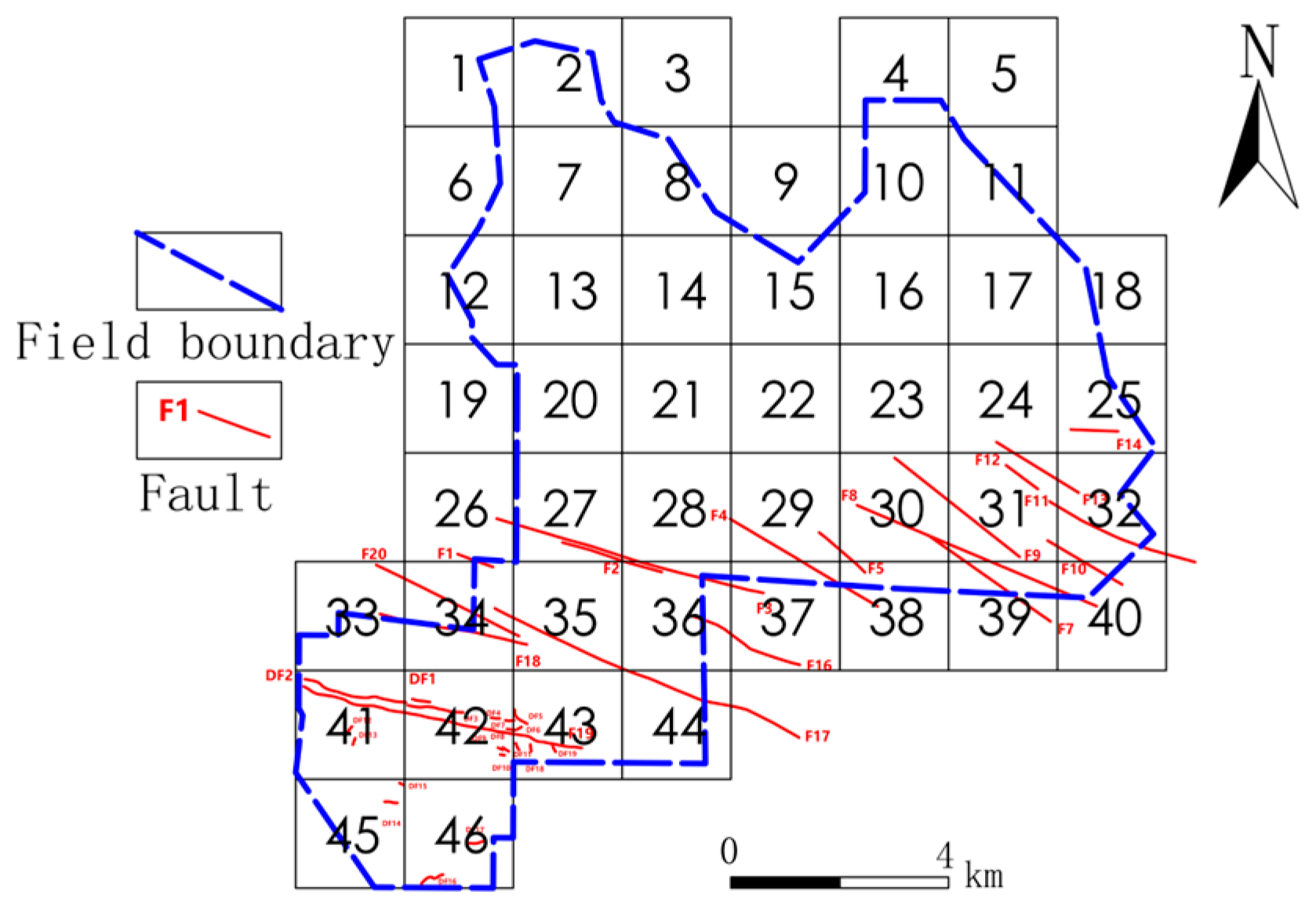
3.5. Fault Dimension
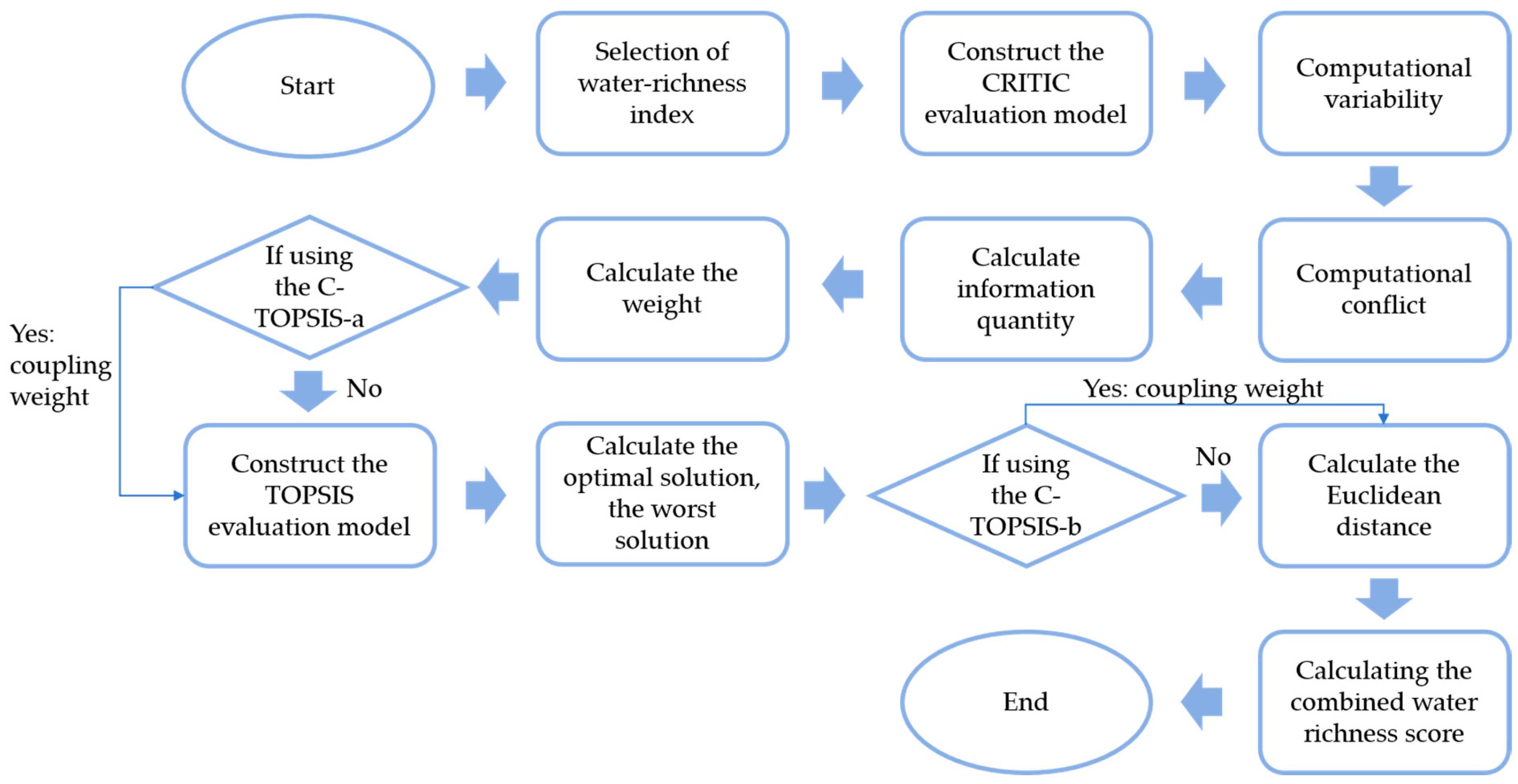
4. CRITIC-TOPSIS Model
4.1. CRITIC Objective Empowerment Method
4.2. TOPSIS Integrated Evaluation Method
4.3. CRITIC-TOPSIS Evaluation Methodology
5. Discussion of the Results
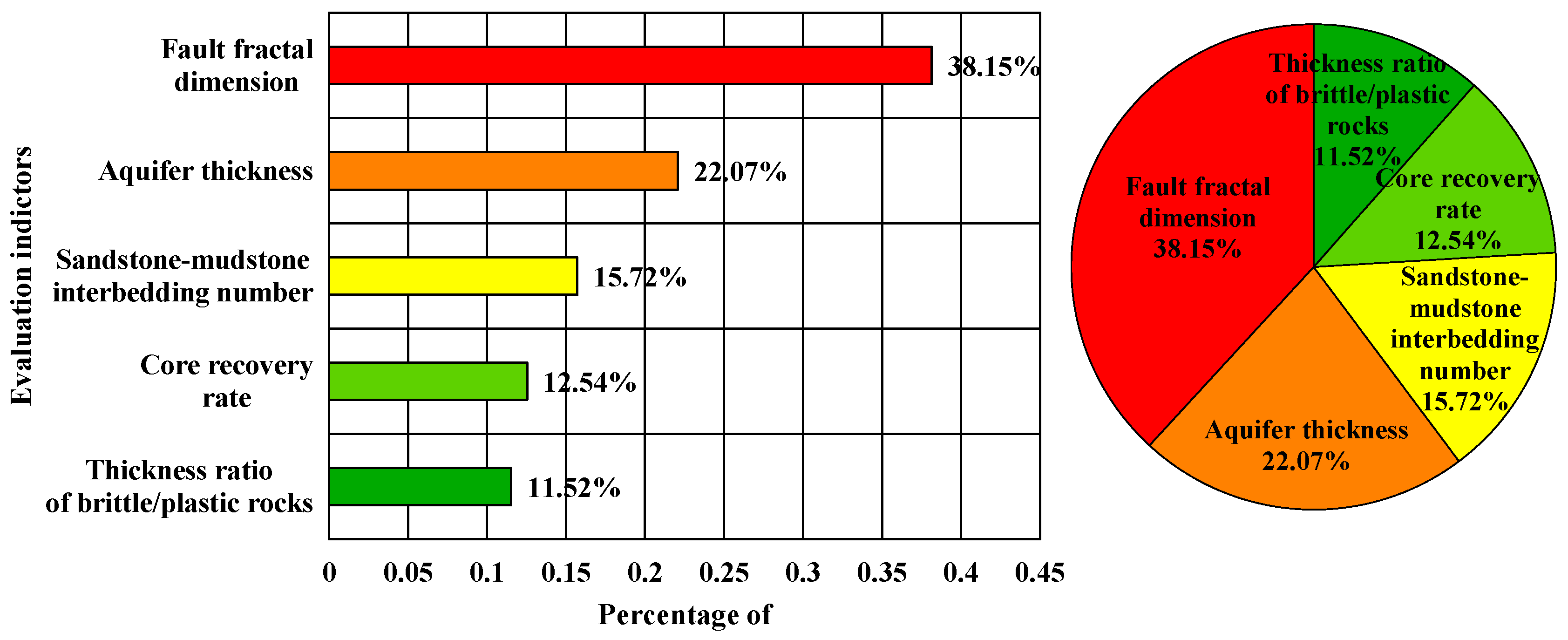
5.1. Weighting Analysis of Main Controlling Factors
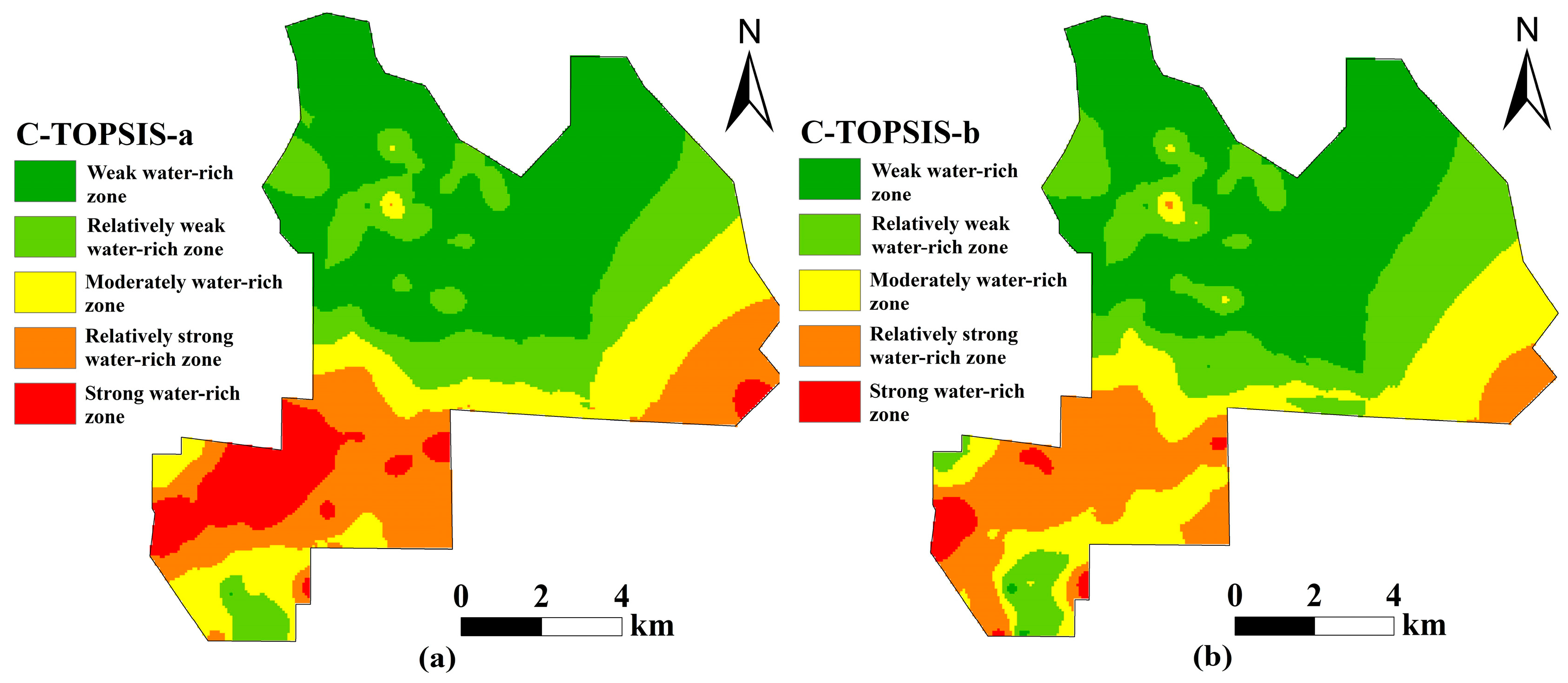
5.2. Comparison of Water Richness Evaluation Results
5.3. Validation of Evaluation Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zeng, Y.; Zhu, H.; Wu, Q.; Guo, X.; Pang, Z.; Liu, S.; Yang, W. Research status and prevention and control path of coal seam roof water disaster in China. J. China Coal Soc. 2024, 50, 1073–1099. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Ning, L.; Bi, J. Permeability evolution of coal subjected to triaxial compression based on in-situ nuclear magnetic resonance. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2022, 159, 105213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Yang, G.; Guo, K.; Xu, J.; Liu, D.; Han, J.; Shi, D.; Pan, J. Predicting water flowing fracture zone height using GRA and optimized neural networks. Processes 2024, 12, 2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, P.; Li, N. Predicting the height of the hydraulic fracture zone using a convolutional neural network. Mine Water Environ. 2023, 42, 500–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Y.; Dong, Q. Quantitative prediction of water abundance in rock mass by transient electro–magnetic method with LBA—BP neural network. J. China Coal Soc. 2020, 45, 330–337. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, E.; Wu, J.; Yang, F.; Zhang, C. Evaluation of Water-richness of Weathered Bedrock Based on the WOA-SVM Discriminant Model: Take Zhangjiamao Coal Mine in Shenfu Coal Field as an Example. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2025, 25, 119–127. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, E.; Ji, Z.; Che, X.; Wang, J.; Guo, L.; Tian, S.; Yang, F. Water-richness prediction method for weathered bedrock based on the coupling of improved AHP and entropy weight method. J. Coal 2019, 44, 3164–3173. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, E.; Li, Q.; Yang, L.; Bi, M.; Li, Y.; He, Y. Prediction of Water-Richness Zoning of Weathered Bedrock Based on Whale Optimisation Algorithm and Random Forest. Water 2025, 16, 3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W. Study on the Prediction of Sudden Water Hazard in Hanglaiwan Coal Mine in Yushen Mining Area. Master’s Thesis, China University of Mining and Technology, Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, C.; Tian, Q.; Xiao, L.; Xue, X.; Zhang, R.; Xu, D.; Luo, S. Principal causes of water damage in mining roofs under giant thick topsoil-lilou coal mine. Appl. Water Sci. 2024, 14, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Li, F.; Niu, C.; Dai, G.; Qiao, Q.; Lin, C. Evaluation of water inrush hazard in coal seam roof based on the AHP-CRITIC composite weighted method. Energies 2022, 16, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G. Water-rich zoning and water quantity prediction of coal seam in Balasu Mine Field. Saf. Coal Mines 2024, 55, 200–207. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, Z.; Meng, F.; Lyu, W.; Li, L. Improved Method for Predicting and Evaluating Water Yield Property. Coal Technol. 2023, 42, 152–155. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, K.; Miao, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Fan, L.; Yang, L.; Ma, W.; Lu, B.; Li, C.; Chen, J.; et al. Occurrence characteristics and water abundance of Zhiluo Formation in nortnern Ordos Basin. J. China Coal Soc. 2022, 47, 3572–3598. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, W.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, Q.; Li, L. Prediction Model of Water Abundance of Weakly Cemented Sandstone Aquifer Based on Principal Component Analysis–Back Propagation Neural Network of Grey Correlation Analysis Decision Making. Water 2024, 16, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, S.; Bian, K.; Yang, H.; Chang, J. Risk assessment of water inrush based on FAHP-EWM combined weighting method. Coal Mine Saf. 2024, 55, 184–193. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Bao, K.; Hou, E.; Lu, B.; Li, Y. Evaluation of water richness of weathered bedrock aquifers based on subjective and objective combination of TOPSIS-RSR. Coal Sci. Technol. 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.; Niu, C.; Li, F.; Xiang, M.; Zhao, S. Water abundance evaluation of weathered bedrock aquifers based on FAHP and coefficient of variance method. Saf. Coal Mines 2023, 54, 143–149. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, G.; Wan, B.; Feng, L.; Zhang, R.; Jiao, J.; Hou, L.; Li, Y.; Gu, L. Water-richness evaluation of Luohe Formation aquifer above coal seam based on combination weighting method. Coal Sci. Technol. 2024, 52, 201–210. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Bi, J.; Wang, C.; Liu, P. Effect of unloading rate on the mechanical behavior and fracture Characteristics of Sandstones under complex triaxial stress conditions. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2021, 54, 4851–4866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, H. An elastic Stress-Strain relationship for porous rock under anisotropic stress conditions. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2012, 45, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, C.; Bi, J. Analysis of fractured rock permeability evolution under unloading conditions by the model of elastoplastic contact between rough surfaces. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2020, 53, 5795–5808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Liu, Y.; Bi, Y.; Sun, H.; Ning, B. Spatial-temporal heterogeneity of landscape ecological risk in Yushenfu Mining Area from 1995 to 2021. Coal Sci. Technol. 2024, 52, 270–279. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Zhu, G.; Liu, Y.; Chao, W.; Du, J.; Yang, Q.; Mi, H.; Zhang, S. Breakthrough, future challenges and countermeasures of deep coalbed methane in the eastern margin of Ordos Basin: A case study of Linxing-Shenfu block. Acta Pet. Sin. 2023, 44, 1827–1839. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Pu, Z.; Ge, Q.; Liu, J. Study on the water-richness law and zoning assessment of mine water-bearing aquifers based on sedimentary characteristics. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, M.; Shao, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, Y.; Yin, X.; Gai, G.; Han, Z.; Zhao, J. Water-richness evaluation method and application of clastic rock aquifer in mining seam roof. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 6465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Li, X. Evaluation of coal-seam roof-water richness based on improved weight method: A case study in the dananhu No. 7 coal mine, China. Water 2024, 16, 1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, G.; Qiu, M.; Zhang, W.; Shi, L. Evaluation of water richness in coal seam roof aquifer based on factor optimization and random forest method. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 24421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, P.; Xu, J. Fractal dimension calculation of fault system and discussion on its relation to the deep-source gas migration. Nat. Gas Ind. 1998, 18, 27–30+23–24. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, C.C.; Zhang, X.J. Multifractal characteristics of spatial distribution of the faults in west subsag of Bozhong Sag. Oil Drill. Prod. Technol. 2018, 40, 14–16. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Liu, G.; Zhou, Q.; Zhao, G. Application of fractal theory in the study of the relationship between fracture and mineral. J. Hefei Univ. Technol. 2016, 39, 701–706. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, Z.; Wu, M.; Song, Z.; Zhao, T.; Du, G. Comprehensive evaluation of power quality on CRITIC-TOPSIS method. Electr. Mach. Control 2020, 24, 137–144. [Google Scholar]


| Serial Number | Drill Hole Number | Aquifer Thickness (m) | Thickness Ratio of Brittle/Plastic Rocks | Core Take Rate (%) | Number of Sandstone–Mudstone Interbeds | Fault Dimension |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | G11-1 | 21.43 | 0.14 | 73.02 | 12 | 1.10 |
| 2 | G11-2 | 26.95 | 0.18 | 73.41 | 14 | 1.20 |
| 3 | G11-3 | 90.75 | 1.01 | 54.77 | 7 | 1.25 |
| 4 | G11-4 | 42.07 | 0.60 | 89.25 | 18 | 1.25 |
| 5 | G12-1 | 33.40 | 0.21 | 89.74 | 25 | 1.15 |
| 6 | G12-2 | 64.06 | 0.41 | 83.05 | 12 | 1.20 |
| 7 | G12-3 | 61.92 | 0.44 | 79.89 | 24 | 1.25 |
| 8 | G12-4 | 19.07 | 0.19 | 86.64 | 20 | 1.20 |
| 9 | G12-5 | 36.52 | 0.33 | 74.76 | 19 | 1.20 |
| 10 | G13-1 | 28.71 | 0.25 | 81.89 | 8 | 1.15 |
| 11 | G13-2 | 44.64 | 0.31 | 89.59 | 25 | 1.20 |
| 12 | G13-3 | 34.93 | 0.31 | 82.81 | 11 | 1.20 |
| 13 | G13-4 | 107.07 | 2.28 | 82.03 | 12 | 1.20 |
| 14 | G13-5 | 55.10 | 0.38 | 88.80 | 22 | 1.20 |
| 15 | G13-6 | 16.17 | 0.31 | 85.90 | 10 | 1.15 |
| 17 | G14-1 | 46.50 | 0.36 | 74.20 | 21 | 1.25 |
| 18 | G14-2 | 58.90 | 0.44 | 71.72 | 11 | 1.25 |
| 19 | G14-3 | 16.41 | 0.13 | 76.29 | 11 | 1.25 |
| 20 | G14-4 | 20.30 | 0.16 | 73.49 | 7 | 1.25 |
| … | … | … | … | … | … | … |
| 195 | Y11-3 | 89.63 | 1.14 | 88.08 | 29 | 0.00 |
| 196 | Y11-4 | 79.07 | 0.76 | 81.25 | 18 | 0.00 |
| 197 | Y11-5 | 70.56 | 0.69 | 93.75 | 20 | 0.00 |
| 198 | Y11-6 | 58.94 | 0.72 | 81.32 | 24 | 0.00 |
| 199 | Y11-7 | 34.45 | 0.59 | 87.65 | 17 | 0.05 |
| 200 | Y12-1 | 86.40 | 1.08 | 87.70 | 18 | 0.00 |
| 201 | Y12-2 | 60.43 | 0.62 | 83.98 | 30 | 0.00 |
| 202 | Y12-3 | 94.50 | 1.27 | 79.35 | 35 | 0.00 |
| 203 | Y12-4 | 68.51 | 0.98 | 88.36 | 22 | 0.00 |
| 204 | Y12-5 | 41.26 | 0.55 | 84.04 | 18 | 0.55 |
| 205 | Y13-1 | 68.71 | 0.73 | 89.28 | 22 | 0.00 |
| 206 | Y13-2 | 27.62 | 1.01 | 91.07 | 10 | 0.00 |
| 207 | Y13-3 | 48.49 | 0.43 | 83.37 | 20 | 0.00 |
| 208 | Y13-4 | 79.99 | 1.08 | 86.72 | 31 | 0.00 |
| 209 | Y13-5 | 70.14 | 1.20 | 83.19 | 34 | 0.10 |
| 210 | Y14-1 | 66.15 | 1.66 | 92.40 | 19 | 0.50 |
| 211 | GS-1 | 67.56 | 1.32 | 87.71 | 22 | 0.50 |
| 212 | Y11-0 | 31.75 | 1.18 | 90.01 | 9 | 0.00 |
| Grid Number | DS | R2 | Grid Number | DS | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | 0.7551 | 0.9884 | 36 | 1.2721 | 0.9597 |
| 26 | 0.834 | 0.9902 | 37 | 1.317 | 0.9608 |
| 27 | 1.17 | 0.9974 | 39 | 1.3485 | 0.9965 |
| 29 | 1.2686 | 0.9927 | 40 | 1.0832 | 0.9937 |
| 30 | 1.4066 | 0.9713 | 41 | 1.3432 | 0.9668 |
| 31 | 1.5561 | 0.9878 | 42 | 1.3732 | 0.9974 |
| 32 | 1.3925 | 0.9955 | 43 | 1.0793 | 0.959 |
| 33 | 0.9422 | 0.9975 | 44 | 1.1288 | 0.9968 |
| 34 | 1.5214 | 0.9836 | 46 | 0.6585 | 0.9608 |
| 35 | 1.2686 | 0.9927 |
| Evaluation Methods | CRITIC | TOPSIS | C-TOPSIS-a | C-TOPSIS-b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRITIC | 1 | 0.681615876 | 0.95142371 | 0.872978244 |
| TOPSIS | 0.681615876 | 1 | 0.771228086 | 0.931244354 |
| C-TOPSIS-a | 0.95142371 | 0.771228086 | 1 | 0.949398919 |
| C-TOPSIS-b | 0.872978244 | 0.931244354 | 0.949398919 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niu, C.; Jia, X.; Xiao, L.; Dong, L.; Qiao, H.; Huang, F.; Liu, X.; Luo, S.; Qian, W. Evaluation of Water Richness in Sandstone Aquifers Based on the CRITIC-TOPSIS Method: A Case Study of the Guojiawan Coal Mine in Fugu Mining Area, Shaanxi Province, China. Water 2025, 17, 1424. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101424
Niu C, Jia X, Xiao L, Dong L, Qiao H, Huang F, Liu X, Luo S, Qian W. Evaluation of Water Richness in Sandstone Aquifers Based on the CRITIC-TOPSIS Method: A Case Study of the Guojiawan Coal Mine in Fugu Mining Area, Shaanxi Province, China. Water. 2025; 17(10):1424. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101424
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiu, Chao, Xiangqun Jia, Lele Xiao, Lei Dong, Hui Qiao, Fujing Huang, Xiping Liu, Shoutao Luo, and Wanxue Qian. 2025. "Evaluation of Water Richness in Sandstone Aquifers Based on the CRITIC-TOPSIS Method: A Case Study of the Guojiawan Coal Mine in Fugu Mining Area, Shaanxi Province, China" Water 17, no. 10: 1424. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101424
APA StyleNiu, C., Jia, X., Xiao, L., Dong, L., Qiao, H., Huang, F., Liu, X., Luo, S., & Qian, W. (2025). Evaluation of Water Richness in Sandstone Aquifers Based on the CRITIC-TOPSIS Method: A Case Study of the Guojiawan Coal Mine in Fugu Mining Area, Shaanxi Province, China. Water, 17(10), 1424. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101424





