Abstract
An integrated hybrid system was developed, incorporating sedimentation, anaerobic digestion, biological filtration, and a two-stage hybrid subsurface flow constructed wetland, horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland (HSSFCW) and vertical subsurface flow constructed wetland (VSSFCW), to treat rural sewage in southern Jiangsu. To optimize nitrogen and phosphorus removal, the potential of six readily accessible industrial and agricultural waste byproducts—including plastic fiber (PF), hollow brick crumbs (BC), blast furnace steel slag (BFS), a zeolite–blast furnace steel slag composite (ZBFS), zeolite (Zeo), and soil—was systematically evaluated individually as substrates in vertical subsurface flow constructed wetlands (VSSFCWs) under varying hydraulic retention times (HRTs, 0–120 h). The synergy among substrates, plants, and microbes, coupled with the effects of hydraulic retention time (HRT) on pollutant degradation performance, was clarified. Results showed BFS achieved optimal comprehensive pollutant removal efficiencies (97.1% NH4+-N, 76.6% TN, 89.7% TP, 71.0% COD) at HRT = 12 h, while zeolite excelled in NH4+-N/TP removal (99.5%/94.5%) and zeolite–BFS specializing in COD reduction (80.6%). System-wide microbial analysis revealed organic load (sludges from the sedimentation tank [ST] and anaerobic tanks [ATs]), substrate type, and rhizosphere effects critically shaped community structure, driving specialized pathways like sulfur autotrophic denitrification (Nitrospira) and iron-mediated phosphorus removal. Annual engineering validation demonstrated that the optimized strategy of “pretreatment unit for phosphorus control—vertical wetland for enhanced nitrogen removal” achieved stable effluent quality compliance with Grade 1-A standard for rural domestic sewage discharge after treatment facilities, without the addition of external carbon sources or exogenous microbial inoculants. This low-carbon operation and long-term stability position it as an alternative to energy-intensive activated sludge or membrane-based systems in resource-limited settings.
1. Introduction
With the advancement of rural revitalization strategies, rural domestic wastewater treatment has become a critical issue for improving living environments and ensuring ecological security. According to the Second National Pollution Source Census Bulletin [1], rural areas contribute nearly 40% of China’s total water pollutant emissions, with chemical oxygen demand (COD), ammonium nitrogen (NH4+-N), total nitrogen (TN), and total phosphorus (TP) accounting for 51%, 35%, 30%, and 39% of national totals, respectively. By the end of 2010, only 6% of rural areas had wastewater treatment systems [2], increasing to 19% by 2018 [3]. Non-point source pollution caused by nitrogen and phosphorus is particularly severe. Traditional centralized wastewater treatment systems are often unsuitable for widespread rural application, while constructed wetlands (CWs), with their low energy consumption, ease of maintenance, and ecological friendliness, are considered a preferred technology for decentralized wastewater treatment [4,5]. However, conventional CWs face bottlenecks such as seasonal performance fluctuations, unstable nitrogen/phosphorus removal efficiency, and high operational costs, necessitating breakthroughs in mechanism exploration, process optimization, and system management.
Existing studies indicate that pollutant removal in CWs primarily relies on synergistic interactions among substrates, plants, and microorganisms [6,7]. Substrates, serving as the system’s physical framework and reactive interface, directly influence pollutant migration and transformation through their physicochemical properties. Zeolite (Zeo) exhibits superior NH4+-N adsorption due to its high cation exchange capacity. Millar et al. (2016) demonstrated that acid/alkali-modified Australian natural zeolite (sodium hydroxide for Na+ exchange) achieves a maximum NH4+-N adsorption capacity of 20.02 mg/g at 1000 mg/L ammonium concentration, representing a ≥90.0% improvement over unmodified samples (10.07 mg/g) [8]. Blast furnace steel slag (BFS) immobilizes phosphorus via Fe3+/Ca2+-mediated coordinative precipitation, achieving TP removal rates up to 99% [9]. Composite substrates (e.g., zeolite+ blast furnace steel slag [ZBFS]) enhance simultaneous nitrogen/phosphorus removal through multi-mechanism coupling, though their efficacy is constrained by pH (4–12) [10], substrate configuration [10], and material ratios [11]. Plants regulate microenvironments through nutrient uptake, root oxygenation, and exudate secretion. For example, citric acid secreted by Canna indica roots activates Fe-P precipitation [12], and phosphate removal efficiency increases with environmental temperature, reaching 90.3% in summer [13]. Microbial functional differentiation underpins system stability: Proteobacteria and Nitrospira dominate nitrification–denitrification [14], while BFS-enriched iron-reducing bacteria (Geobacter) enhance phosphorus fixation via Fe3+/PO43− co-precipitation [15]. Recent studies reveal that sulfur autotrophic denitrifiers (Thiobacillus) can replace heterotrophic pathways under low-carbon conditions, offering new strategies for low C/N ratio wastewater treatment [16]. While bacteria drive key nutrient cycling processes as described above, fungi contribute distinct and complementary functions. Fungi play a crucial role in the bioremediation and biodegradation of organic compounds owing to their sophisticated enzymatic machinery [17]. Through mechanisms such as biodegradation, biosorption, chemical modification, and volatilization, they effectively remove diverse pollutants from soil and water [18]. In symbiotic interactions with plants, arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) epitomize this mutualism by transferring essential nutrients—most notably phosphorus (P)—from degradation products to the root systems of macrophytes via their extensive hyphal networks. This not only expands the plants’ absorptive surface area but also substantially enhances nutrient utilization efficiency, thereby promoting growth and bolstering their resilience to environmental stresses [19].
Despite mechanistic advancements, practical CW applications face multifaceted challenges [20]. Technically, traditional surface-flow CWs suffer a >20% efficiency decline in winter due to freezing [21], while vertical-flow CWs, though stable, incur high construction costs [22]. Economically, pipeline networks account for >50% of rural infrastructure costs [23], with remote villages relying on government subsidies for operation [24], leading to 40–70% facility idleness [25,26]. Managerially, the lack of professional maintenance and smart monitoring results in plant withering and substrate clogging in ~70% of CWs [27]. Recent innovations address these issues: pretreatment units (e.g., sedimentation tanks, anaerobic tanks, biofilters) combined with CWs improve resilience to water quantity/quality fluctuations [28]; cold-tolerant plants (e.g., Iris spp.) maintain winter performance [28]; hybrid CWs integrating horizontal and vertical subsurface flow configurations achieve median removal efficiencies of 75.7% COD, 72.1% NH4+-N, 63.4% TN, and 71.8% TP with minimal global warming potential [29].
However, existing studies predominantly focus on single pollutants or static conditions, lacking systematic investigation of multi-substrate synergies, microbial functional responses, and seasonal adaptation strategies [29,30,31]. Southern Jiangsu, characterized by high population density and ecological sensitivity, requires tailored optimization of parameters like hydraulic retention time (HRT) and substrate composition. This study establishes a hybrid “sedimentation tank-anaerobic tank-biofilter-two-stage subsurface flow CW” system to investigate the following: (1) physicochemical mechanisms and seasonal adaptability of nitrogen/phosphorus removal by substrates (plastic fiber, zeolite, blast furnace steel slag, etc.); (2) HRT (0–120 h) impacts on pollutant removal and optimal HRT determination; and (3) functional differentiation of rhizospheric vs. non-rhizospheric microbial communities and their environmental drivers. By integrating water quality analysis, plant nutrient uptake, and microbial community data, we aim to propose a “process-substrate-microbe” co-optimization framework, providing theoretical and practical guidance for decentralized wastewater treatment in southern Jiangsu’s rural areas.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The hybrid constructed wetlands system (HCWs) (31°32.98′ N, 120°41.87′ E) is situated at the Changshu Agro-Ecological Experimental Station of the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Xinzhuang Town, Changshu City, Jiangsu Province. Located in the Yangtze River Delta, the study area features a humid subtropical monsoon climate with an annual average temperature of 15.5 °C, ≥10 °C effective accumulated temperature of 4933.7 °C, annual precipitation of 1038 mm, sunshine duration of 2203 h, solar radiation of 4.94 × 105 J/cm2, and a frost-free period of 242 days. The station is part of the low-lying Yangcheng Lake plain at an elevation of 1.3 m (Wusong datum).
2.2. Materials
The vertical subsurface flow constructed wetlands (VSSFCWs) required six types of industrial and agricultural waste byproducts as substrates: plastic fiber (PF), hollow brick crumbs (BC), blast furnace steel slag (BFS), zeolite–blast furnace steel slag composite (ZBFS), zeolite (Zeo), and local agricultural topsoil (0–20 cm). Two plant species were used: Canna indica in HSSFCW and cold-tolerant Iris spp. in VSSFCWs. Each VSSFCW unit was structured with gravel, fine sand, test substrate, and topsoil, supported by a siphon-activated wastewater distribution system to evaluate hydraulic retention times (HRTs: 0–120 h). Water quality analysis involved reagents such as salicylate, alkaline persulfate, ammonium molybdate, potassium dichromate, and others, with measurements conducted using a UV-Vis spectrophotometer and additional instruments. Soil and plant nutrient analysis required pretreatment with concentrated acids (H2SO4, HNO3, HClO4, etc.), supported by a Kjeldahl distillation unit, flame photometer, glass electrodes, and related equipment. The microbial analysis utilized the E.Z.N.A. Soil DNA Kit, PCR primers targeting the 16S rRNA V3–V4 region, and the Illumina MiSeq platform. Influent from the sedimentation tank represented typical rural domestic wastewater characteristics. Several rubber stoppers (for sealing water outlets) and three-way valves (for fluid flow control) were used, which were combined to enable sampling under specific hydraulic retention times (HRTs). Detailed configurations and operational methods for these components, along with other related consumables (e.g., reagents, sampling devices) and construction materials (e.g., pipelines, substrates), are described in Section 2.3. Specific reagent formulations and analytical methodologies can be found in Section 2.4.
2.3. System Design
The total system, initially constructed in May 2009 and reconstructed in October 2020, serves as a rural domestic wastewater treatment platform. The upgraded system integrates six functional units (Figure 1), with key components as follows.
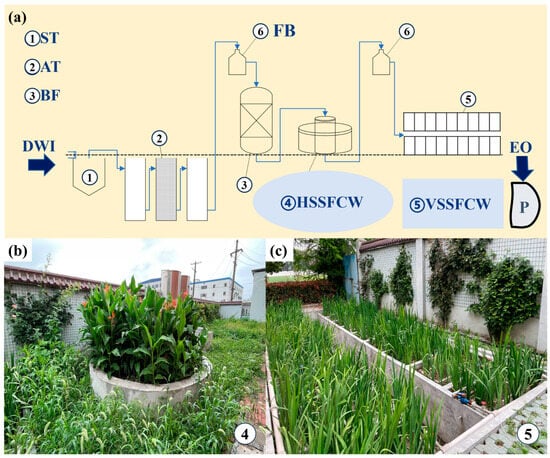
Figure 1.
Process flow and field photos of the composite treatment system for rural domestic sewage. Notes: (a) Schematic illustration of the treatment process, showing six functional units such as ① ST-sedimentation tank; ② AT-anaerobic tank; ③ BF-biological filter; ④ HSSFCW-horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland; ⑤ VSSFCW-vertical subsurface flow constructed wetland; ⑥ FB-feeding basin; DWI-domestic wastewater inflow; EO-effluent outlet; P-pond; (b) field photograph of the horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland (HSSFCW, labeled as ④ in the diagram); (c) field photograph of the vertical subsurface flow constructed wetland (VSSFCW, labeled as ⑤ in the diagram).
① Sedimentation tank (B, ST): Receives combined wastewater flows from five sources: (1) north dormitory septic tanks, (2) public restroom septic tanks, (3) staff dormitory septic tanks, (4) cafeteria wastewater, and (5) south dormitory septic tanks. The tank is sequentially equipped with parallel coarse screens (primary filtration) and fine screens (secondary filtration) for phased solid waste removal.
② Three-chamber anaerobic biofilter (C1, C2, C3, AT1-AT3): Facilitates anaerobic digestion of pretreated wastewater.
③ Tower-type biofilm filter (D, BF): Anaerobically pretreated effluent is pumped to a 110 cm elevated feed basin (2 m3). Gravity-driven aeration occurs during vertical pipe flow. At set water levels, siphon-activated distribution delivers wastewater to a 1.0 × 0.6 × 1.5 m filter unit with a 1 m media bed. Filtered water collects in a base drainage channel/storage tank before pumping to the annular HSSFCW.
④ Primary annular horizontal subsurface flow CW (E, HSSFCW): Comprising a central distribution pool (0.6 m inner diameter) and surrounding annular wetland (1.8 m outer diameter), with a total depth of 0.75 m (20 cm gravel, 10 cm fine sand, a 30 cm layer of hollow brick crumbs [BC], with isolation layers above and below, and a 15 cm soil layer). Vegetation: Canna indica. Vertical structural configuration corresponds to the vertical subsurface flow constructed wetlands (VSSFCWs, shown in Figure 2b).
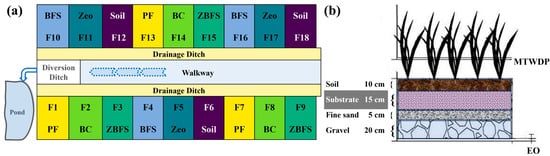
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of substrate distribution and structural design of VSSFCW. Notes: (a) Top-view illustration of units with different substrate distribution, presenting various substrates such as PF, BC, ZBFS, BFS, Zeo, and Soil, with each unit marked as F1-F18; (b) structural cross-section of each vertical subsurface flow constructed wetland—all share the identical structure, with distinctions solely in substrates. P-pond; PF-plastic fiber; BC- hollow brick crumbs; ZBFS-zeolite + blast furnace steel slag; BFS-blast furnace steel slag; Zeo-zeolite; Soil-soil; MTWDP-manifold-type water distribution pipe; EO-effluent outlet.
⑤ 18 secondary vertical subsurface flow CWs (F1-F18, VSSFCW): Divided into 6 substrate groups (triplicate units each): plastic fiber (PF), hollow brick crumbs (BC), zeolite + blast furnace steel slag (ZBFS), blast furnace steel slag (BFS), pure zeolite (Zeo), and soil (Soil). Each unit, cement-constructed and 1.5 m long and 1.0 m wide, comprises layered media: 20 cm gravel (drainage), 5 cm fine sand (filtration), 15 cm substrate (variable materials), and 10 cm topsoil (plant growth). Iris spp. were planted to enhance rhizosphere functions. The horizontal distribution of substrate groups and functional zones (e.g., walkways, drainage ditches) is shown in Figure 2a, while the vertical layer configuration (substrate, sand, gravel) is detailed in the lower panel (Figure 2b). Effluent from individual units was collected for water quality analysis.
During the performance evaluation of the constructed wetland system operating continuously across four seasons, this study focused on its resource utilization pathway for treated domestic wastewater. The effluent, meeting discharge standards after treatment, and flowing into the pond via the collection basin, was transported via dedicated pipelines to a reservoir pond at the experimental station for subsequent agricultural irrigation, achieving closed-loop management through wastewater purification and agricultural reuse.
2.4. Sampling and Analysis
2.4.1. Water Sampling and Analysis Protocol
Sampling followed DB32/3462-2020 [32] (rural wastewater standards) and GB/T 5750.2-2023 (drinking water protocols) [33]. Quarterly influent/effluent samples (100 mL) were collected under predefined HRT, stored at 4 °C, and analyzed within 72 h. Analytical methods included the following: pH: glass electrode method (GB/T 6920-1986) [34]; NH4+-N: salicylate spectrophotometry (HJ 536-2009) [35]; TN: alkaline persulfate digestion–UV spectrophotometry (HJ 636-2012) [36]; TP: ammonium molybdate spectrophotometry (GB/T 11893-1989) [37]; and COD: dichromate method (HJ 828-2017) [38].
2.4.2. Soil and Plant Analysis Protocol
Rhizosphere Soil and Plant Sampling: At harvest (spring), tools were sterilized with ethanol prior to sampling. Representative Iris spp. (VSSFCWs) and Canna indica (HSSFCW) plants of average height were selected. Whole plants, including roots, were carefully excavated, and loosely adhered soil was gently brushed off. Rhizosphere soil (10–20 cm depth) attached to roots was collected, homogenized from duplicate samples, and stored in sterile bags on dry ice for 16S rRNA sequencing (V3–V4 region, PE300 strategy) [39]. Plant samples were weighed for fresh weight, oven-dried at 105 °C for 10 min to deactivate enzymes, and further dried at 70 °C to constant weight. The dried samples were ground to <0.25 mm (60-mesh sieve, GB/T 6003.1-2022 [40]). Total nitrogen was analyzed using the Kjeldahl method with H2SO4 digestion and K2SO4/CuSO4 catalysis as specified in LY/T 1269-1999 [41]. For total phosphorus and potassium, samples underwent HNO3-HClO4 digestion, after which the same digestate was split for parallel analyses: phosphorus was quantified by molybdenum-antimony colorimetry at 700 nm following neutralization and dilution per LY/T 1271-1999 [42], while potassium was directly measured via flame photometry using the undiluted digestate in accordance with LY/T 1271-1999 [42]. For fibrous Iris spp. tissues, digestion durations were extended to ensure complete decomposition.
Non-rhizosphere soil and Analysis: Non-rhizosphere soil was collected from vertical and horizontal flow wetlands using a five-point method [43] (four corners and center, 0–10 cm and 10–20 cm depths). Samples (≥300 g per depth) were homogenized, sieved to remove roots/debris, and split into two subsets: one stored on dry ice for sequencing and the other air-dried for physicochemical analysis. Sediment from pretreatment units (sedimentation tank B, anaerobic tanks C1–C3) was similarly processed. Air-dried soils were ground through 100/200-mesh sieves and analyzed for the following: pH was measured using a 1:2.5 soil/CO2-free water slurry equilibrated for 30 min with a glass electrode (LY/T 1239-1999) [44]; alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen was determined by NaOH diffusion absorption in H3BO3 followed by titration (LY/T 1228-2015) [45]; total nitrogen was quantified via the Kjeldahl method using H2SO4 digestion with K2SO4/CuSO4 catalysts (LY/T 1228-2015) [45]; total phosphorus was analyzed through acid digestion with H2SO4-HClO4 and molybdenum-antimony colorimetry (LY/T 1232-2015) [46]; Organic matter was determined by K2Cr2O7-H2SO4 oxidation in a 170 °C oil bath followed by titration (LY/T 1237-1999) [47]; available phosphorus was extracted using NaHCO3 and quantified colorimetrically (LY/T 1232-2015) [46]; and available potassium was determined by NH4OAc extraction coupled with flame photometry (LY/T 1234-2015) [40].
Quality Control: Augers were sterilized with 75% ethanol between samples. All soils were stored in sterile, labeled containers. Sequencing samples included rhizosphere soil, non-rhizosphere soil, and sludge analyzed in parallel. Protocols strictly adhered to Chinese forestry standards (LY/T series) to ensure reproducibility and cross-study comparability. This integrated protocol ensures rigorous characterization of soil–plant–microbe interactions in constructed wetlands, balancing methodological precision with ecological relevance.
2.5. Data Analysis
Performance Evaluation: The treatment capacity of the constructed wetlands (CWs) was assessed through continuous monitoring of influent flow rates and pollutant concentrations (NH4+-N, TN, TP, COD). Removal efficiency (RE) for each treatment unit were calculated using the following:
where and represent influent and effluent concentrations, respectively.
Note: When “total” was not emphasized, calculations followed this rule, with influent defined as the rural domestic sewage concentration entering a specific unit. In this study, VSSFCW was primarily used as the secondary treatment facility. Considering the system’s overall removal performance and stage-by-stage fluctuations, the research focused on the total removal efficiency—using the concentration of sedimentation tank (B, ST) sewage as the initial value. Statistical significance of intergroup differences was determined via one-way ANOVA (SPSS 26.0, α = 0.05), and results were visualized using the ggplot2package (version 3.5.1) in R version 4.3.3, implemented through the RStudio 2024.07.0+735 integrated development environment.
Statistical significance of intergroup differences was determined through one-way ANOVA (SPSS 26.0, α = 0.05), with results visualized using ggplot2 in R Studio.
Gene Amplicon Sequencing: Sample pretreatment strictly followed molecular biology protocols: Frozen specimens transported under low-temperature conditions were thawed on ice, subjected to centrifugation at 3000× g for 5 min to remove impurities, thoroughly homogenized using a vortex mixer, and assessed for nucleic acid quality with a Nanodrop spectrophotometer. High-purity DNA templates (30 ng) were quantitatively selected for downstream analyses. DNA extracts from soil samples and sludges underwent 16S rDNA amplification targeting the V3–V4 hypervariable region (338F/806R primers) under standardized PCR conditions: initial denaturation at 94 °C (5 min), 30 cycles of 94 °C (30 s), 50 °C (30 s), and 72 °C (60 s), followed by final extension at 72 °C (7 min). Amplification products were verified through 1% agarose gel electrophoresis (constant voltage electrophoresis at 170 V for 30 min) using D2000 DNA Marker as reference, confirming successful amplification of target fragments and ensuring V3-V4 region specificity met high-throughput sequencing requirements. Core microbiome identification and taxonomic classification were performed using QIIME v1.8.0, considering operational taxonomic units (OTUs) present in ≥95% of samples.
Ecological Diversity Analysis: Alpha diversity indices (Chao1 richness, Shannon diversity) were computed in QIIME after rarefaction normalization. Beta diversity patterns were visualized through principal coordinates analysis (PCoA) based on Bray–Curtis dissimilarity matrices, with the first three axes explaining 47.12% cumulative variance, PERMANOVA revealed statistically significant differences (pseudo-F = 1.8912, p = 0.001; 999 permutations). LEfSe biomarker discovery, combining Kruskal–Wallis testing (p < 0.05) with Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA score > 3.0), was performed using Python version 2.7.16.
Environmental Drivers Assessment: Mantel tests evaluated spatial correlations between microbial communities (Bray–Curtis distances) and environmental parameters (Euclidean distances). Statistical significance was determined through 999 permutations, with p < 0.05 indicating meaningful associations.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Annual System Performance and Pollution Load
Seasonal variations in pollutant loads and water inflow volumes of the rural domestic wastewater treatment system are summarized (Table 1).

Table 1.
Seasonal and annual pollutant loads (NH4+-N, TN, TP, COD) and water inflow volumes of the rural domestic wastewater treatment system
The system processed 293.91 m3 of wastewater annually, with a distinct single-peak seasonal distribution: spring accounted for 55.7% (163.81 m3) of the total inflow, while winter contributed only 1.4% (4.13 m3) (Table 1). Annual pollutant loads ranked as COD (63.69 kg) > TN (11.12 kg) > NH4+-N (8.04 kg) > TP (0.65 kg). Spring dominated pollutant contributions, responsible for 89.7% of COD (57.15 kg), 82.4% of TN (9.16 kg), 79.7% of NH4+-N (6.41 kg), and 90.8% of TP (0.59 kg). In contrast, summer and winter loads were notably lower: summer COD (5.94 kg) represented only 10.4% of spring levels, and winter TP (0.01 kg) reached the annual minimum. Pollutant inputs originated solely from domestic wastewater, unaffected by organic fertilizer storage or agricultural activities. The spring surge was attributed to intensified personnel activities at the experimental station, including increased detergent-rich laundry water, kitchen waste, and sanitary wastewater, which contributed organic matter and urea-derived nitrogen [48]. Winter performance was hindered by dual inhibitory mechanisms: suppressed microbial activity reduced NH4+-N conversion efficiency, while diminished plant uptake and low inflow dilution exacerbated NH4+-N retention [49]. Additionally, compensatory personnel mobility following severe pandemic restrictions in the previous winter contributed to abnormal spring peaks.
3.2. Pollutant Removal Capacity Across Treatment Units
Pollutant load variations across treatment nodes demonstrated significant removal efficiency by the pretreatment units (ATs, BF, and HSSFCWs) (Figure 3). Although NH4+-N and TP loads temporarily increased by 0.1–12.6% at the anaerobic tanks (C1–C3) due to influent concentration fluctuations, subsequent microbial degradation in biofilters, physical filtration, and substrate–plant–microbe synergies in HSSFCWs reduced final effluent loads by 50–80% compared to sedimentation tank influent. The rough surface of BCs facilitated biofilm formation, enriching nitrifying bacteria (e.g., Nitrospira), whose metabolic activity is critical for ammonia oxidation. The high cation exchange capacity (CEC) of Fe₂O₃-rich BCs allows selective, reversible exchange with competing cations, with NH4+ favored due to its ionic radius and charge density, consistent with pseudo-second-order kinetic models observed in similar iron-modified systems [50,51]. Concurrently, shear aeration in HSSFCWs enhances dissolved oxygen (DO) levels, creating an optimal aerobic environment that accelerates the nitrification process carried out by these bacteria. This synergy between ion exchange on BC and oxygen-driven microbial activity achieves 99.1% NH4+-N removal in autumn. For TP removal, Fe3+ in BC coordinates with PO43− to form stable precipitates, while organic acids from Canna roots promote Fe-P complexation. Biofilm-mediated phosphorus immobilization further enhances TP removal, culminating in 82.1% autumn efficiency.
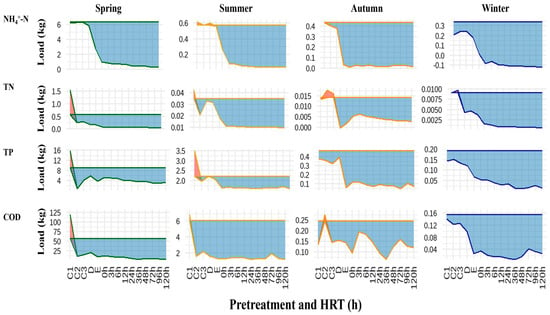
Figure 3.
Seasonal variation of NH4+-N, TN, TP, and COD loads in the integrated treatment system under different HRTs. Notes: Substrate-averaged values; initial load referenced to sedimentation tank influent (Node B). Process nodes: B (sedimentation tank) → C1–C3 (anaerobic tank) → D (biofilm filter) → E (HSSFCW) → F1–F18 (VSSFCWs); all subsequent annotations adhere to the same labeling convention.
Overall, the pretreatment unit removed 70–80% of pollutant loads, while VSSFCWs accomplished the remaining 20–30% through advanced polishing. Although NH4+-N, TP, and COD were nearly compliant after pretreatment, VSSFCWs (particularly substrate selection) proved critical for TN compliance and ensured stable compliance with discharge standards for all parameters.
3.3. Research on Total Pollutant Removal Efficiency in VSSFCWs
The pollutant removal efficiency of the total system is closely linked to the physicochemical properties of substrate materials in VSSFCWs, which directly determine long-term operational performance [52]. To address the resource utilization needs of rural industrial/agricultural byproducts, this study evaluated six substrates: plastic fiber (PF), hollow brick crumbs (BC), zeolite–blast furnace steel slag composite (ZBFS), blast furnace steel slag (BFS), zeolite (Zeo), and soil (Soil), all recognized for their potential in high-efficiency CW systems [53]. Ten HRTs (0, 3, 6, 12, 24, 36, 48, 72, 96, and 120 h) were tested to assess combined substrate–HRT effects on pollutant removal.
3.3.1. Influence of HRT on Pollutant Removal Efficiency
HRT, as a core operational parameter, regulates wastewater–substrate contact duration and microbial metabolic cycles, influencing nitrogen and phosphorus removal [54]. The influent pH of rural wastewater averaged 7.4, while effluent pH stabilized at 8.2–8.5 across substrates. ZBFS and BFS substrates exhibited the highest pH (~8.5). Except for seasonal COD fluctuations in autumn and winter, NH4+-N, TN, and TP removal rates increased with HRT (0–120 h), reaching 80–100% for NH4+-N and TP and 60–90% for TN and COD at HRT = 120 h (Figure 4). Compliance assessment against the Grade 1-A discharge standards of DB32/3462-2020: Water Pollutant Emission Standards for Rural Domestic Sewage Treatment Facilities (NH4+-N < 8 mg/L; TN < 20 mg/L; TP < 1 mg/L; COD < 60 mg/L) [32] revealed that TP and COD achieved the highest compliance rates, whereas TN removal—constrained by substrate properties and HRT—emerged as the system’s limiting factor.
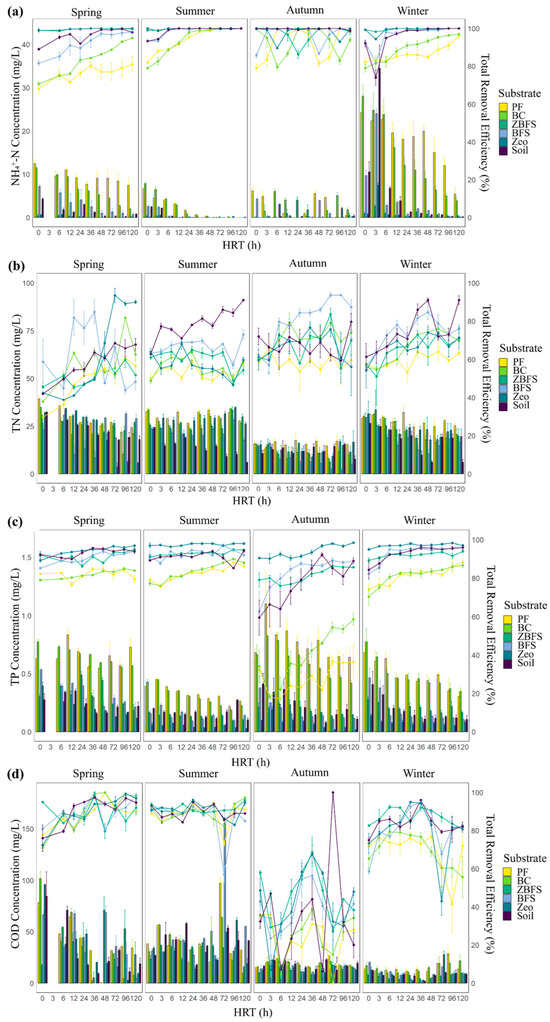
Figure 4.
Influence of hydraulic retention time (HRT) and substrates on pollutant concentration (bar chart) and system total removal efficiency (line chart) across seasons. Notes: Each subplot shows the concentration and removal efficiency of the corresponding pollutant under six substrates (PF, BC, ZBFS, BFS, Zeo, and Soil) across spring, summer, autumn, and winter at varying HRTs. (a) Ammonium nitrogen (NH4+-N); (b) total phosphorus (TP); (c) chemical oxygen demand (COD); (d) total nitrogen (TN).
3.3.2. Substrate-Specific Removal Dynamics
As shown in Figure 5, statistical analysis (one-way ANOVA, p < 0.05) revealed that the system with VSSFCWs with BFS as the substrate operating at a 12 h HRT significantly purified the influent and consistently maintained TN effluent concentrations below 20 mg/L, achieving full compliance with the Grade 1-A discharge standards, likely due to Fe2+-mediated chemical reduction and porous structure adsorption under low C/N conditions [55]. When TN was not limiting (e.g., NH4+-N/TP/COD-dominated influent), Zeo achieved >98% NH4+-N and >90% TP removal annually at HRT = 12 h, with ~90% COD removal even under spring high-load conditions. ZBFS outperformed BFS only when COD was limiting, showing 48% autumn COD removal and 66% winter removal, highlighting physical adsorption dominance in cold periods [56].
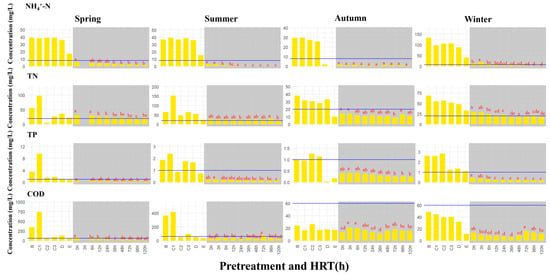
Figure 5.
BFS in VSSFCWs optimizes system effluent compliance. Notes: The horizontal line represents the Grade 1-A discharge standards. Lowercase letters above the bars indicate significant intergroup differences (p < 0.05, n = 3) determined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s HSD post hoc test.
3.3.3. Plant Nutrient Characteristics
In HSSFCW treating high-load rural domestic wastewater, Canna facilitates organic pollutant degradation through substantial biomass accumulation, while Iris spp.—a cold-tolerant species with ecological landscaping value—further enhances nitrogen and phosphorus removal efficiency via rhizosphere-mediated microbial processes in VSSFCWs. Collectively, these two plant species establish a sequential remediation cascade within the total engineered wetland systems. The comparative analysis of plant nutrients is visualized through boxplots (Figure 6), with detailed statistical annotations indicating intergroup differences.
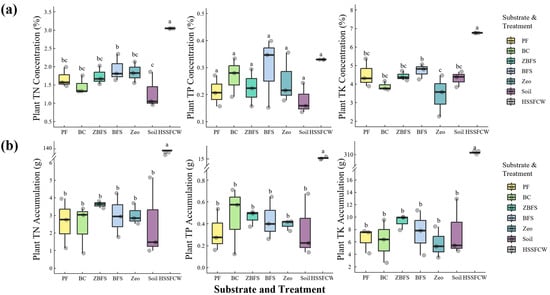
Figure 6.
Boxplots of plant nutrient concentrations and accumulation capacities under different substrates and treatments. (a) Total nitrogen (TN), phosphorus (TP), and potassium (TK) concentrations; (b) Corresponding nutrient accumulation capacities. Lowercase letters above boxes denote significant intergroup differences (p < 0.05, n = 3) determined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s HSD post hoc test. The VSSFCW was planted with Iris spp. and tested with six substrates, including PF and BC and others, while the HSSFCW was planted with Canna indica and used BC as the substrate.
Notably, while this study focuses on bacterial contributions to nutrient cycling and pollutant removal, fungal–bacterial interactions likely modulate system performance through niche differentiation and the degradation of recalcitrant carbon. Fungi, particularly saprophytic and mycorrhizal taxa, may secrete extracellular enzymes (e.g., laccases and cellulases) to decompose complex organic matter that is resistant to bacterial degradation [57]. This process subsequently releases bioavailable carbon, which can fuel bacterial denitrification or facilitate phosphorus solubilization. Such synergistic interactions can create microhabitat heterogeneity—establishing gradients of oxygen and substrates—that promote complementary metabolic pathways, with bacteria specializing in inorganic nitrogen and phosphorus transformations while fungi drive the turnover of recalcitrant organic carbon [58,59].
Differences in TN, TP, and TK concentration between Canna and Iris were driven by plant physiology–substrate interactions. Canna exhibited higher TN due to enhanced root-mediated nitrogen assimilation (e.g., nitrate reductase activity) [60]. BFS-grown Iris showed higher TN concentration than soil-grown plants, likely due to alkaline-induced organic nitrogen mineralization [61] and porous structure-enhanced nitrification. No significant TP variation (p = 0.052) reflected Fe-P/Ca-P precipitation and comparable organic acid (e.g., citric acid) secretion across plants [62]. Canna accumulated higher TK than BFS-grown Iris, driven by biomass demand, while Zeo-substrate Iris had the lowest TK due to zeolite’s K+ adsorption [63].
Canna in HSSFCW showed significantly higher TN, TP, and TK accumulation (e.g., TN = 139.83 g) than Iris in VSSFCWs, indicating passive nutrient uptake from high-load influent. BFS-grown Iris TN (3.00 g) exceeded soil-grown plants (2.55 g) by 17.6%, linked to alkaline-enhanced ammonium release [64]. TP homogeneity (0.33–0.47 g) reflected dynamic Fe3+/Ca2+-P precipitation and organic acid-mediated solubilization. TK distribution highlighted substrate-specific K+ dynamics: zeolite’s K+ adsorption reduced bioavailability (TK = 5.76 g), while ZBFS synergized slag-derived slow-release potassium and zeolite’s ion buffering (TK = 9.30 g), offering insights for substrate optimization.
3.4. Microbial Community Characteristics of System
Microbial communities are critical drivers of pollutant transformation and removal in rural domestic sewage treatment systems. In this study, microbial communities were systematically investigated across all functional units of the HCW system, including sludges from the ST and AT1–AT3, as well as rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere soils in both HSSFCW and VSSFCW. To profile the structural and functional roles of microbial communities in pollutant removal and system efficiency, related analyses of community composition, diversity, and environmental linkages were conducted.
3.4.1. Analysis of OTU Distribution Patterns
Analysis using a Venn diagram and petal plot revealed the shared and unique characteristics of microbial operational taxonomic units (OTUs) across different samples/groups in the system (Figure 7).
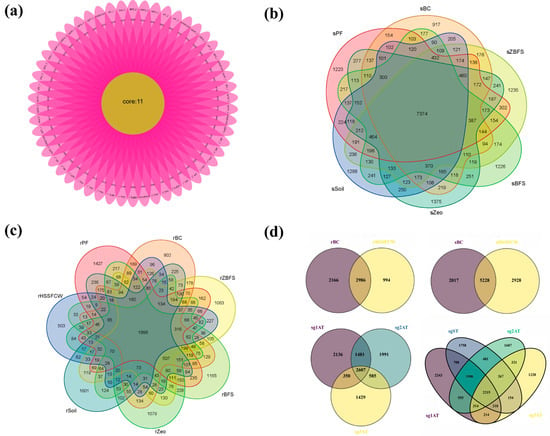
Figure 7.
Petal plot and Venn diagram. Notes: (a) Petal plot: Each petal represents a sample. The central number denotes OTUs shared by all samples, while numbers on individual petals indicate unique OTUs specific to each sample; (b–d) Venn diagram: Different colors represent distinct groups. Overlapping areas between colored circles show shared OTUs, and non-overlapping sections display unique OTUs for each circle. Venn diagrams can only visualize 2–7 circles. Annotations: r indicates sampling in rhizosphere soil, s represents sampling in non-rhizosphere soil, and sg denotes sediment sampling. HSSFCW stands for horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland. Substrate designations (like PF, BC) represent soil samples collected from different units in vertical subsurface flow constructed wetlands. ST represents the sedimentation tank, while 1AT–3AT indicates three-compartment anaerobic tanks. All subsequent annotations adhere to the same labeling convention.
All samples shared 11 core OTUs (Figure 7a), while the non-rhizosphere soils from six treatment groups of VSSFCWs (PF, BC, ZBFS, BFS, Zeo, Soil) collectively contained 7374 OTUs (Figure 7b), as the highest multi-group overlap, accounting for 49.59–53.72% of the total OTUs per group. Among them, the PF group exhibited the highest total OTU count (with the lowest proportion of unique OTUs), whereas the BC group had the lowest total OTU count (with the highest proportion of unique OTUs). The Zeo group contained the most unique OTUs (1375), while the BC group had the fewest (917). Including horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands (HSSFCWs) in rhizosphere comparisons reduced OTU overlap to 1996 (Figure 7c), as the lowest multi-group overlap attributed to plant species-specific rhizosphere effects. Additional Venn diagram results are shown (Figure 7d).
3.4.2. Core Microbiome and Functional Taxa
Functionally relevant microbial groups closely associated with nitrogen and phosphorus removal were identified through this analysis. The top 20 most relative abundant bacterial phyla and genera are visualized (Figure 8). During the study, phyla with detection frequencies exceeding 1% were classified as dominant bacterial phyla.
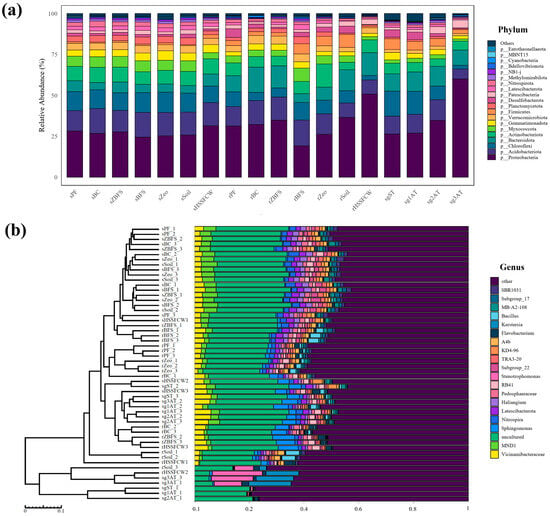
Figure 8.
Microbial community composition at phylum and genus levels in the system. (a) Relative abundance of bacterial phyla in different samples; (b) levels bar tree plot of microbial community composition at the genus level. The plot integrates hierarchical clustering and relative abundance visualization, presenting the composition of microbial genera and their clustering relationships.
Sixteen dominant bacterial phyla were identified in the CW microbial community analysis, including Proteobacteria, Acidobacteriota, Chloroflexi, and others (Figure 8a). Additionally, less abundant phyla (relative abundance <1%), such as Entotheonellaeota and Cyanobacteria, were detected. These phyla may exert significant impacts on system functionality through specialized metabolic traits. For instance, Cyanobacteria may contribute to carbon and nitrogen cycling via oxygenic photosynthesis and nitrogen fixation, while Entotheonellaeota’s potential for secondary metabolite biosynthesis warrants further exploration.
At the genus level, 20 major taxa were identified, including environmentally adaptive groups such as Bacillus and Sphingomonas, alongside unclassified taxa (g__uncultured) (Figure 8b). Bacillus exhibits strong stress resistance and organic matter decomposition capabilities across diverse environmental conditions, whereas Sphingomonas plays a critical role in degrading organic pollutants.
Species-level analysis revealed 13 primary taxonomic units, with uncultured groups dominating (7/13), such as s__uncultured_gamma (γ-proteobacteria) and s__uncultured_Bacteroidetes. These groups may possess unique metabolic and ecological roles. Notably, the detection of functional taxa like Nitrospira (nitrification) and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia (nitrogen metabolism) suggests active nitrogen transformation processes within the system. Nitrospira is pivotal in nitrification, converting ammonium nitrogen (NH4+-N) to nitrate (NO₃−-N), while S. maltophilia participates in nitrogen assimilation and transformation pathways.
3.4.3. Alpha Diversity and Environmental Responses
Statistical analysis of Alpha diversity indices revealed significant differences in species richness, evenness, and phylogenetic diversity among samples (Figure 9).
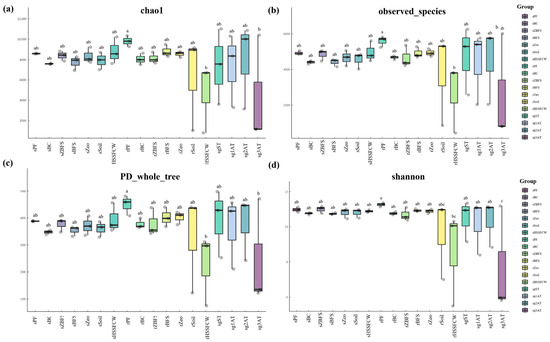
Figure 9.
Alpha diversity indices of microbial communities. Notes: (a) Chao1 richness estimator; (b) observed species; (c) phylogenetic diversity; (d) Shannon diversity index. Lowercase letters above boxes denote significant intergroup differences (p < 0.05, n = 3) determined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s HSD post hoc test.
Sequencing coverage across microbial samples ranged from 0.87 to 0.90, indicating the high reliability of the sequencing results. The sg3AT group exhibited exceptionally high coverage (0.99), suggesting a low-complexity microbial community where nearly all detectable species were captured. Phylogenetic diversity, assessed via the PD Whole Tree index, showed high evolutionary complexity in most samples. However, sg3AT displayed significantly lower PD Whole Tree values, reflecting simplified evolutionary lineages and weak phylogenetic associations among populations.
Shannon index results demonstrated relatively uniform species distribution and high diversity in most samples (indices > 10). In contrast, sg3AT showed markedly lower Shannon indices, indicating extremely low species evenness and diversity. This was further corroborated by Simpson indices approaching 1.00, confirming low species diversity in sg3AT. These findings suggest a structurally simplistic and unevenly distributed microbial community in sg3AT. Significance analysis revealed that rHSSFCW and sg3AT groups exhibited universally low Alpha diversity metrics, likely due to environmental stressors or adverse conditions. Conversely, other groups (e.g., rPF) displayed higher species richness, evenness, and phylogenetic complexity, with the rPF group’s Shannon index significantly exceeding those of sg3AT and rHSSFCW (p < 0.05), indicating a stable and diverse ecological community.
Environmental impacts on microbial diversity were pronounced in sg3AT, which showed significant reductions in species richness and phylogenetic diversity. The Shannon and Simpson indices further highlighted highly uneven species distribution and minimal overall diversity in this group. Despite near-complete sequencing coverage, the ecological simplicity of sg3AT likely stems from its unique chemical conditions and environmental pressures. By its very nature, sludge (a mixture of water and sediment) inherently exhibits higher mobility than soil, rendering microbial colonization inherently challenging. Compared to the first two anaerobic chambers, the third chamber—as the final unit in the anaerobic train—experiences greater hydraulic instability and microbial washout, with effluent microbes subsequently feeding into the downstream biofilter.
As a non-porous material, PF provides a smooth and stable surface structure that reduces water loss and creates a stable microenvironment for microbial communities. Simultaneously, PF facilitates the accumulation of organic matter from domestic wastewater, shielding soil microbial populations from external fluctuations and promoting microbial growth and proliferation [65]. These properties likely explain PF’s role in fostering stable and diverse ecological communities within the wetland system.
3.4.4. Beta Diversity and Environmental Drivers
Beta diversity was quantified using Bray–Curtis dissimilarity matrices and visualized through principal coordinates analysis (PCoA) (Figure 10). The first three principal coordinate axes cumulatively accounted for 47.12% of the total community variation, with individual contributions of 26.92% (PC1), 12.21% (PC2), and 7.99% (PC3).
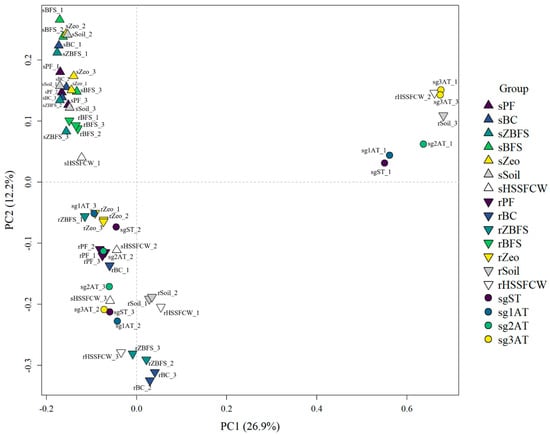
Figure 10.
PCoA based on the Bray–Curtis distance matrix derived from OTU data. Notes: Gray dashed lines indicate the origin (x = 0, y = 0) of the principal coordinates, dividing the plot into quadrants for comparative interpretation of sample clusters. Points with distinct colors/shapes represent different sample groups; axis scales reflect relative distances without physical units. PC1 and PC2 denote putative environmental drivers underlying microbial community divergence between groups.
The synergistic effects of rhizosphere influence and substrate type shaped microbial community divergence. For example, the rPF exhibited spatial separation from the sPF as a result, indicating that Iris root exudates (e.g., carbon sources and growth factors) regulated microbial composition [66]. Concurrently, the hydrophobic organic structure and surface charge characteristics of plastic fiber enhanced nutrient adsorption, favoring the enrichment of functional microbes [65]. Contrasts between sZeo and rZeo groups further validated plant–substrate interactions: root-secreted organic acids likely dissolved zeolite minerals, releasing trace elements (e.g., Fe3+, Zn2+) that selectively stimulated metabolic activity in specific taxa, resulting in axis shift in rZeo.
Environmental stress gradients significantly filtered microbial community assembly [67]. The low-load sg3AT clustered positively on the V3-axis, contrasting with the negative distribution of high/moderate-load groups (sg1AT, sg2AT). This pattern reflects reduced substrate competition under low organic loads, favoring oligotrophic K-strategists (e.g., Nitrosomonas), while high-load conditions suppressed r-strategists (e.g., methanogens) via substrate inhibition. Notably, an anomalously high V1 value (0.66) in the rHSSFCW may correlate with dissolved oxygen gradients stemming from spatial heterogeneity within the HSSFCW, particularly localized aeration unevenness far from the effluent zone, which promotes facultative anaerobes (e.g., Desulfovibrionaceae) through metabolic flexibility.
Substrate physicochemical properties exerted conditional regulatory effects. sZBFS, sBFS clustered on the V1-axis, overlapping with soil, suggesting alkaline conditions in slag inhibited acidophilic taxa and weakened substrate specificity. Conversely, the extreme V1 deviation (0.68) in rSoil_3 may stem from heterotroph proliferation (e.g., Bacillus) due to soil aggregate disruption [68], necessitating validation via phospholipid fatty acid (PLFA) analysis.
3.4.5. Taxonomic Biomarker Identification by LEfSe
Functional specialization of microbial communities under organic loading gradients was rigorously validated through LEfSe analysis (Linear Discriminant Analysis Effect Size, LDA score > 3.0, p < 0.05 with FDR correction), revealing statistically significant biomarkers and their metabolic roles (results detailed in Supplementary Materials).
LDA analysis (result shown in Supplementary Materials) identified Thiobacillus as the key biomarker in the sgST, where sulfur autotrophic denitrification (SAD) likely dominated nitrogen–sulfur co-transformation. Additionally, Dechloromonas coupled denitrification with polyphosphate metabolism via endogenous polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) storage, while Fe2+ released from steel slag substrates enhanced phosphorus removal through chemical precipitation, forming a unique bio-chemical synergistic phosphorus removal mechanism. In the high organic load environment (sg1AT), Longilinea (Anaerolineaceae; LDA = 3.65, (p < 0.01)) emerged as a critical biomarker, potentially driving nitrogen and phosphorus release through organic matter degradation. Concurrently, sulfate-reducing bacteria (Desulfobulbus) activated the SAD pathway, bypassing traditional denitrification routes [69]. However, anaerobic conditions in this environment likely suppressed polyphosphate-accumulating organisms (PAOs), necessitating process optimization to improve phosphorus removal [70].
The medium organic load group (sg2AT) demonstrated efficient carbon–nitrogen coupling: strict anaerobes (Paludibacter) generated volatile fatty acids (VFAs) via fermentation, supplying carbon to denitrifiers (Paracoccus) and establishing a “fermentation-denitrification” metabolic chain. This interaction optimized denitrification efficiency under moderate C/N ratios. The low organic load group (sg3AT) was dominated by Proteobacteria members (Xanthomonadales, Rhodobacterales) and Comamonadaceae genera (Variovorax, Acidovorax). Among these, Acinetobacter utilized VFAs for anaerobic phosphorus release and aerobic uptake, synergizing with denitrifiers to optimize dual nitrogen–phosphorus removal pathways [71].
Rhizosphere microbial communities were markedly influenced by plant–substrate interactions. For instance, Flavobacterium (LDA = 3.91, p < 0.05) in Canna rhizosphere (rHSSFCW) was linked to root exudate-driven phosphorus solubilization [72]. Oxygen gradients from root aeration spatially segregated nitrification–denitrification processes. In rBC, Bacteroidia secreted lignin-degrading enzymes (e.g., laccase, peroxidase), breaking down plant residues (lignin/cellulose) to release carbon for denitrifiers. Simultaneously, comammox Nitrospira (Nitrospiraceae) mediated complete ammonia oxidation to nitrate, supplying substrates for subsequent denitrification [73]. In rBFS, Geobacter (Desulfuromonadales) released adsorbed phosphorus via Fe3+ reduction while coupling acetate oxidation to iron reduction. Predatory Myxococcales further stabilized community structure, highlighting substrate chemistry-directed microbial regulation [74].
Non-rhizosphere soil microbial communities were primarily shaped by substrate physicochemical properties. Porous sBC promoted oxygen diffusion, favoring nitrifier dominance. Conversely, sPF enriched DAMO (denitrifying anaerobic methane oxidation) bacteria (Methylomirabilota phylum, NC10), which utilized CH4 as an electron donor for anaerobic denitrification [75]. However, glycogen-accumulating organisms (Defluviicoccus, GAOs) in this environment likely competed with PAOs for carbon, impairing phosphorus removal [76].
Notably, sulfur metabolism dominance in high-load anaerobic tanks (AT1) and iron cycling in rhizosphere environments revealed complementary phosphorus removal pathways: microbial reduction-driven release versus chemical adsorption–fixation.
3.4.6. Identification of Environmental Drivers via Mantel Test
To identify key environmental drivers shaping microbial community structure, Mantel tests were conducted to quantify associations between the top 20 dominant bacterial species (grouped by phylum-level taxonomy) in non-rhizosphere soil and environmental parameters (plant nutrients, soil nutrients, pH, etc.) (Figure 11).
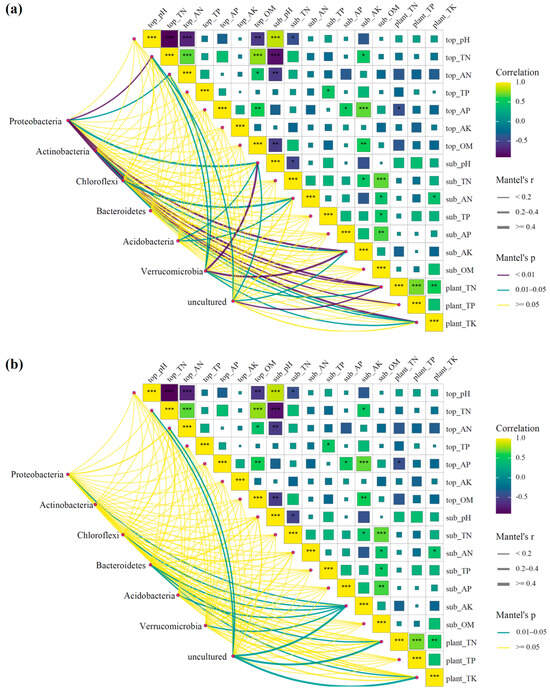
Figure 11.
Mantel test analysis of microbial communities and environmental factors. Notes: (a) Microbes in non-rhizosphere soil of HSSFCW and VSSFCW; (b) microbes in rhizosphere soil of HSSFCW and VSSFCW. Mantel’s r, which measures the correlation strength between microbial community structure (Bray–Curtis distance) and environmental matrices (Euclidean distance), and Mantel’s p, which indicates the statistical significance of the observed correlations. Visualization details include the following: for the right-side environmental factor pairwise correlations, these stem from Spearman’s analysis, depicted via a yellow-to-purple gradient (yellow for positive correlations, r > 0; purple for negative correlations, r < 0), with asterisks [*** (p < 0.001), ** (p < 0.01), * (p < 0.05), Spearman’s analysis] within dashed boxes to denote significance levels. The left network presents phylum-grouped species–environment linkages, distinguishing significant correlations (0.01 ≤ p < 0.05) from non-significant ones (p ≥ 0.05), with line thickness reflecting correlation magnitude. The prefix “top-” denotes “Topsoil”, “sub-” signifies “Subsoil”, and “plant-” represents “Plant”. For suffixes, “pH” refers to pH value; “TN” is total nitrogen; “AN” is alkali hydrolyzable nitrogen; “TP” means total phosphorus; “AP” indicates available phosphorus; “AK” stands for available potassium; “OM” represents organic matter; “TK” denotes total potassium. Soil samples reflect the elemental content of the corresponding soil layer, while plant samples indicate the index content of plants.
Microbial community–environment interactions demonstrated differentiation between rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere compartments. In non-rhizosphere soils, Proteobacteria showed significant positive correlations with subsurface available potassium (sub_AK, r = 0.57, p < 0.01), plant total nitrogen (plant_TN, r = 0.53, p < 0.01), and plant total potassium (plant_TK, r = 0.58, p < 0.01), likely due to their central roles in nitrogen cycling and organic matter degradation. For example, Pseudomonas (a genus in the phylum Proteobacteria) participates in soil nitrogen metabolism via nitrate reduction, while elevated sub_AK may enhance enzyme activation. In contrast, Actinobacteria displayed weaker correlations with plant_TN (r = 0.32, p < 0.01) and plant_TP (r = 0.25, p < 0.01), reflecting their preference for decomposing complex organics (e.g., lignin), a trait linked to plant phenolic secretion in maize rhizosphere studies. Notably, Chloroflexi and Verrucomicrobia were significantly associated with subsurface available nitrogen (sub_AN, r = 0.47, p < 0.05) and pH (sub_pH, r = 0.49, p < 0.01), respectively, suggesting potential roles in anaerobic ammonium oxidation and intracellular proton gradient regulation under pH fluctuations.
Rhizosphere microbial dynamics were predominantly plant-driven. Uncultured taxa exhibited stronger correlations with sub_AK (r = 0.48) and plant nutrients (plant_TK/TN, r = 0.42–0.43) in the rhizosphere than in non-rhizosphere soils (p < 0.05), indicating root exudate-mediated activation of specific functional taxa. This aligns with the “amplification-selection” model, where plants selectively enrich microbes with nutrient-transforming capabilities via root exudates (e.g., organic acids, sugars). For instance, Bacteroidetes showed weaker rhizosphere correlation with sub_AK (r = 0.37, p < 0.05) compared to non-rhizosphere Proteobacteria (r = 0.57, p < 0.01), likely due to their reliance on direct exudate utilization over soil-inherent potassium pools. Additionally, Acidobacteria weakly correlated with sub_pH (r = 0.31, p < 0.05), yet their slight abundance increase under higher pH contradicts their known acidophilic preference. This paradox may arise from enhanced organic matter mineralization at elevated pH, providing compensatory carbon sources for Acidobacteria. Furthermore, rhizosphere pH fluctuations might impair Acidobacteria competitiveness by altering iron bioavailability. For example, reduced iron accessibility at higher pH could limit iron acquisition unless offset by efficient siderophore synthesis, necessitating functional gene analysis (e.g., sid genes) for validation.
Ecological contrasts between rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere communities underscore the importance of plant–microbe interactions. Non-rhizosphere microbes were primarily regulated by subsurface physicochemical factors (sub_AK, sub_pH), reflecting dependence on stable environmental variables. In contrast, rhizosphere communities responded more dynamically to plant nutrient fluxes. For example, the strong correlation between Proteobacteria and plant_TN in non-rhizosphere soils (r = 0.58, p < 0.01) diminished in the rhizosphere, suggesting rhizosphere taxa may substitute soil nitrogen sources with root-exuded amino acids. Future studies should integrate metagenomics to resolve uncultured taxa functions and validate whether subsurface potassium gradients drive microbial succession via ATPase activity modulation.
This study uniquely explores wetland soil microbial dynamics by contrasting rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere communities across surface/subsurface layers via long-term field observations—an understudied dimension. It reveals distinct drivers: deep non-rhizosphere microbes are governed by stable physicochemical factors, while surface rhizosphere communities show plant-driven specialization following a root exudate-mediated “amplification-selection” model. This perspective uncovers novel synergies between industrial substrates (e.g., steel slag) and microbial groups (e.g., nitrifiers), differentiating the system from conventional wetlands. By linking subsurface chemistry with rhizosphere interactions, it provides a mechanistic framework for wetland optimization, integrating matrix properties and plant–microbe feedback to enhance resilience.
4. Conclusions
The integrated “sedimentation tank-anaerobic tank-biofilter-two-stage subsurface flow constructed wetland” system developed in this study achieved efficient purification of rural domestic wastewater in southern Jiangsu, with effluent consistently meeting China’s Grade 1-A standards (DB32/3462-2020) year-round, providing an innovative solution for decentralized wastewater treatment. Key conclusions are as follows:
1. Process Synergy and Substrate Optimization Mechanisms: Using Iris as the wetland plant, without external carbon supplementation, the system achieved optimal performance at HRT = 12 h with industrial waste BFS as the substrate, yielding annual average removal rates of 97.1% for NH4+-N, 76.6% for TN, 89.7% for TP, and 71.0% for COD. Substrate screening revealed zeolite’s superior specificity for NH4+-N (99.5%) and TP (94.5%) adsorption, while the zeolite + BFS combination maximized COD removal (80.6%) through multi-mechanistic coupling, confirming synergistic effects of composite substrates in targeted pollutant removal;
2. Microbial Community Profiling: System-scale microbial community analysis was conducted. Substrate type and rhizosphere effects significantly shaped microbial community structure and function. Plastic fiber (PF) substrates maintained high microbial diversity due to stable microenvironments. LEfSe analysis identified key biomarkers whose distributions correlated likely with pollutant removal pathways. Community differentiation was jointly driven by environmental factors and plant activity: non-rhizosphere taxa (e.g., Proteobacteria) were regulated by subsurface available potassium (sub_AK) and pH, while rhizosphere communities exhibited functional specialization dependent on root exudates. Low organic loads enriched oligotrophic nitrogen/phosphorus-metabolizing taxa, whereas high loads suppressed PAO activity. Plant–substrate interactions (e.g., carbon release, mineral dissolution) directionally modulated microbial functions, such as root exudate-enhanced denitrifier enrichment in zeolite substrates. These findings clarify microbial assembly rules in CWs, offering theoretical guidance for optimizing nitrogen/phosphorus removal;
3. Engineering Validation and Adaptability: The “pretreatment unit for phosphorus control—vertical wetland for enhanced nitrogen removal” strategy ensured 100% compliance with discharge standards year-round, validating system reliability and environmental adaptability.
The system’s “pretreatment for phosphorus control—vertical wetland for nitrogen polishing” framework not only reduced operational complexity but also utilized rural industrial byproducts (e.g., steel slag, brick crumbs) as substrates, enhancing scalability. By integrating natural biogeochemical processes with engineered configurations, this technology provides a practical, low-maintenance solution for decentralized rural sewage treatment, particularly suited for regions lacking technical expertise for chemical/biological supplementation. While this study advances our understanding of bacterial communities in wetland systems, the critical roles of fungi—including their contributions to organic matter degradation, plant–microbe symbiosis, and synergistic interactions with bacteria in nutrient cycling—remain underrepresented. Future research could explicitly investigate fungal communities and their functional synergies with bacteria, leveraging holistic microbial profiling to decode the combined mechanisms driving wetland purification and resilience. Although this study validates the system’s efficiency in removing nitrogen, phosphorus, and organic pollutants, future research should incorporate heavy metal analysis in both substrates and effluent. This will ensure compliance with agricultural irrigation standards and further validate the long-term ecological safety of wastewater reuse in rural settings. In a word, this study provides practical foundations for process optimization and microbial regulation in decentralized rural wastewater treatment, promoting resource utilization of industrial/agricultural byproducts and supporting rural ecological security.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w17101421/s1, LDA distribution bar plot of biomarkers identified through LEfSe analysis. Notes: The bar plot displays taxa with significant differences (biomarkers) across groups, filtered by an LDA score threshold (>3.0). Bar lengths represent the effect size of each biomarker, reflecting its discriminative power in distinguishing group-specific microbial features. Taxonomic classifications (phylum to genus) are color-coded for visualization. Symbol and substrate annotations: r: Rhizosphere soil sampling; s: Non-rhizosphere soil sampling; sg: Sediment sampling. HSSFCW: Horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland. Substrate codes (PF, BC, etc.) denote materials from vertical subsurface flow wetland units. ST: Sedimentation tank; 1AT–3AT: Three-compartment anaerobic tanks. All annotations follow the labeling conventions established in Figure 10.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.Z. and Q.L.; methodology, G.Z. and Q.L.; validation, D.W.; formal analysis, J.W. and G.Z.; investigation, J.W., Y.Z. (Yuting Zhao), L.W., and Y.Z. (Yunwen Zheng); resources, G.Z. and Q.L.; data curation, J.W.; writing—original draft preparation, J.W.; writing—review and editing, J.W., G.Z., and Q.L.; visualization, J.W.; supervision, D.W. and Q.L.; project administration, G.Z. and Q.L.; funding acquisition, G.Z. and Q.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors appreciate the funding supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2021YFD1700805-04).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article and Supplementary Materials. Further inquiries can be directed to the authors.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank the editors for their efficient coordination and careful guidance throughout the publication process. We are also grateful to the reviewers for their insightful critiques, particularly regarding experimental methodology and conceptual development, which have improved the manuscript. Their expertise has guided us in identifying and addressing the limitations of this work, while inspiring us to advance our research in the future.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ministry of Ecology Environment of the People’s Republic of China; National Bureau of Statistics; Ministry of Agriculture Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China. Bulletin of the Second National Pollution Source Census. 2020; [2020] No. 33. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/xxgk2018/xxgk/xxgk01/202006/t20200610_783547.html (accessed on 16 April 2025).
- Guo, X.; Liu, Z.; Chen, M.; Liu, J.; Yang, M. Decentralized wastewater treatment technologies and management in Chinese villages. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2014, 8, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- General Office of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China; General Office of the State Council of the People’s Republic of China. Three-Year Action Plan for Rural Living Environment Improvement. 2018; [2018] No. 5. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/2018-02/05/content_5264056.htm (accessed on 16 April 2025).
- Rai, U.N.; Tripathi, R.D.; Singh, N.K.; Upadhyay, A.K.; Dwivedi, S.; Shukla, M.K.; Mallick, S.; Singh, S.N.; Nautiyal, C.S. Constructed wetland as an ecotechnological tool for pollution treatment for conservation of Ganga river. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 148, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, J.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Hu, Z.; Liang, S.; Fan, J.; Liu, H. A review on the sustainability of constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment: Design and operation. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 175, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, X.C.; Zheng, Y.; Dzakpasu, M. Removal of pharmaceutical active compounds in wastewater by constructed wetlands: Performance and mechanisms. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 325, 116478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, R.; Zhang, J.; Lu, S.; Guo, Z.; Hu, Z.; Wang, T.; Dai, P.; Wu, H. Exploring simultaneous elimination of dimethyl phthalate and nitrogen by a novel constructed wetlands coupled with dielectric barrier discharge plasma. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 452, 139666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, G.J.; Winnett, A.; Thompson, T.; Couperthwaite, S.J. Equilibrium studies of ammonium exchange with Australian natural zeolites. J. Water Process Eng. 2016, 9, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, I.; Molle, P.; Sáenz de Miera, L.E.; Ansola, G. Basic Oxygen Furnace steel slag aggregates for phosphorus treatment. Evaluation of its potential use as a substrate in constructed wetlands. Water Res. 2016, 89, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Jiang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Sun, D.J. Impact of steel slag on the ammonium adsorption by zeolite and a new configuration of zeolite-steel slag substrate for constructed wetlands. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Lu, L.; Tong, L.; Li, P.; Du, W.; Zhu, Y. Phosphate and Ammonia Nitrogen Removal from Swine Wastewater Using Steel Slag and Zeolite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 32, 32–35. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Yang, F.-J.; Zhou, Y.-L.; Li, Y.-Y.; Liu, H. Optimization and mechanism of phosphorus removal in plant-biofilm oxidation ditches: Plant uptake, iron plaque adsorption, and rhizosphere regulation. Ecol. Eng. 2023, 191, 106950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, N.; Yadav, S.; Pipil, H.H. Phosphate removal from urban stormwater runoff using Canna lily and Cyperus alternifolius-based bioretention system. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2024, 10, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yao, X.; Wang, J.; Zheng, P.; Xi, C.; Hu, B. Dominance of comammox Nitrospira in soil nitrification. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; An, J.; Wan, Y.; Du, Q.; Wang, X.; Cheng, X.; Li, N. Phosphorus Competition in Bioinduced Vivianite Recovery from Wastewater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 13863–13870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Aquino, A.; Kalinainen, N.; Auvinen, H.; Andreottola, G.; Puhakka, J.A.; Palmroth, M.R.T. Effects of inorganic ions on autotrophic denitrification by Thiobacillus denitrificans and on heterotrophic denitrification by an enrichment culture. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 901, 165940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharitonov, S.; Shchegolkova, N.; Alexandrova, A.; Saynchuk, A.; Michel, P.; Maciejewski, K.; Gautier, M.; Gourdon, R.; Semenov, M.; Krasnov, G. Taxonomic Diversity of Fungi and Bacteria in Azoé-NP® Vertical Flow Constructed Wetlands. Water 2022, 14, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Vishwakarma, S.; Srivastava, A. Bioremediation of direct blue 14 and extracellular ligninolytic enzyme production by white rot fungi: Pleurotus spp. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 180156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesacasa, L.; Cabral, F.S.; Fochi, D.A.T.; Oliveira, W.d.S.; Oliveira, F.; Kersting, M.; Colares, G.S.; Rodriguez, A.L.; Lutterbeck, C.A.; Konrad, O.; et al. Constructed Wetlands and the role of the fungal community for wastewater treatment: A review. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuamah, L.A.; Li, Y.; Pu, Y.; Nwankwegu, A.S.; Haikuo, Z.; Norgbey, E.; Banahene, P.; Bofah-Buoh, R. Constructed wetlands, status, progress, and challenges. The need for critical operational reassessment for a cleaner productive ecosystem. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 269, 122340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Sun, Y.; Li, L.; Shao, X.; Yu, D.; Liu, Q.; Liu, H.; Han, L. Study on Winter Operation Process of the Surface Flow Constructed Wetland in Tianjin Area. Meteorol. Environ. Res. 2013, 4, 43. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Guo, F.; Wu, F.; Bryan, B.A. Costs and benefits of constructed wetlands for meeting new water quality standards from China’s wastewater treatment plants. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 199, 107248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, P.; Ajudiya, B.; Yadav, S. Water Distribution Network Design and Cost Analysis: A Case Study; GK Bharad Institute of Engineering: Rajkot, India, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.; Yue, X. Challenges facing the management of wastewater treatment systems in Chinese rural areas. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 84, 1518–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Jin, F.; Zhou, B. Performance analysis and evaluation of the 146 rural decentralized wastewater treatment facilities surrounding the Erhai Lake. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 315, 128159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Xu, D.; Wu, W.; Zhang, P.; Liu, L. Current Situation and Development Trend of Domestic Sewage Treatment in China’s Rural Areas. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 12, 8. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Wang, R.; Lin, J.; Zhang, G.; Chen, Z.; Li, L.; Shi, Q. Study on physical clogging process and practical application of horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wu, J.; Zhong, F.; Yu, S.; Chen, K.; Zeng, X.; Duan, D.; Cheng, S. Mechanism of Iris sibirica and aeration combination on promoting the water purification performance of constructed wetland under low temperature. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 19715–19724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Wang, R.; Yan, P.; Wu, S.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, C.; Hu, Z.; Zhuang, L.; Guo, Z.; et al. Constructed wetlands for pollution control. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 218–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, M.; Liu, F.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Xiao, R.; Wu, J. Seasonality distribution of the abundance and activity of nitrification and denitrification microorganisms in sediments of surface flow constructed wetlands planted with Myriophyllum elatinoides during swine wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 248, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.E.; Bin Halmi, M.I.E.; Bin Abd Samad, M.Y.; Uddin, M.K.; Mahmud, K.; Abd Shukor, M.Y.; Sheikh Abdullah, S.R.; Shamsuzzaman, S.M. Design, Operation and Optimization of Constructed Wetland for Removal of Pollutant. Int. J. Env. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DB32/3462-2020; Discharge Standard of Water Pollutants for Rural Domestic Sewage Treatment Facilities. Jiangsu Provincial Department of Ecology and Environment/Jiangsu Provincial Administration for Market Regulation: Nanjing, China, 2020.
- GB/T 5750.2-2023; Standard Examination Methods for Drinking Water—Part 2: Sampling and Preservation of Water Samples. General Administration of Market Regulation of the People’s Republic of China/National Standardization Administration: Beijing, China, 2023.
- GB/T 6920-1986; Water Quality—Determination of pH Value—Glass Electrode Method. State Environmental Protection Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 1986.
- HJ 536-2009; Water Quality—Determination of Ammonia Nitrogen—Salicylate Spectrophotometric Method. Ministry of Ecology and Environment the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2009.
- HJ 636-2012; Water Quality—Determination of Total Nitrogen—Alkaline Persulfate Digestion–UV Spectrophotometric Method. Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2012.
- GB/T 11893-1989; Water Quality—Determination of Total Phosphorus—Ammonium Molybdate Spectrophotometric Method. State Environmental Protection Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 1989.
- HJ 828-2017; Water Quality—Determination of Chemical Oxygen Demand—Dichromate Method. Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Hunt, C.J. Technical Considerations in the Freezing, Low-Temperature Storage and Thawing of Stem Cells for Cellular Therapies. Transfusion medicine and hemotherapy: Offizielles Organ der Deutschen Gesellschaft fur Transfusionsmedizin und Immunhamatologie. Transfus. Med. Hemother. 2019, 46, 134–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LY/T 1234-2015; Determination of Available Potassium in Forest Soil—Ammonium Acetate Extraction and Flame Photometry Method. State Forestry Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2015.
- LY/T 1269-1999; Determination of Total Nitrogen in Forest Plant and Forest Floor. State Forestry Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 1999.
- LY/T 1271-1999; Determination of Total Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium, Sodium, Calcium, Magnesium in Forest Plant and Forest Floor. State Forestry Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 1999.
- Rong, S.; Fu-Liang, Q.; Yi-Ting, C.; Fa-Ping, Z.; Wei, D.; Ya-Xian, L.; Zhi-Pang, H.; Xiao-Yan, Y.; Wen, X. Soil sampling methods for microbial study in montane regions. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2023, 47, e02679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LY/T 1239-1999; Determination of pH Value in Forest Soil. State Forestry Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 1999.
- LY/T 1228-2015; Nitrogen Determination Methods of Forest Soils. State Forestry Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2015.
- LY/T 1232-2015; Determination of Total Phosphorus in Forest Soil—Sodium Hydroxide Fusion and Colorimetry Method. State Forestry Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2015.
- LY/T 1237-1999; Determination of Organic Matter in Forest Soil and Calculation Carbon-Nitrogen Ratio. State Forestry Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 1999.
- Randall, D.G.; Naidoo, V. Urine: The liquid gold of wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 2627–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, S.S.; Liu, Y.Q. Assessing environmental impacts of large centralized wastewater treatment plants with combined or separate sewer systems in dry/wet seasons by using LCA. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 15674–15690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.; Fu, X.; Zhang, G.; Li, Y.; Qin, Y.; Wang, P.; Liu, X.; Lv, L. Study on performance and mechanism of enhanced low-concentration ammonia nitrogen removal from low-temperature wastewater by iron-loaded biological activated carbon filter. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 301, 113859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, B.; Butterly, C.; Zhang, W.; He, J.-z.; Chen, D. Adsorbent materials for ammonium and ammonia removal: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 283, 124611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateus, D.M.R.; Vaz, M.M.N.; Pinho, H.J.O. Fragmented limestone wastes as a constructed wetland substrate for phosphorus removal. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 41, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Tang, W.; Pei, Y. Constructed wetland substrates: A review on development, function mechanisms, and application in contaminants removal. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, D.; Gopal, B. Effect of hydraulic retention time on the treatment of secondary effluent in a subsurface flow constructed wetland. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 1044–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, J.; Nguyen, T.B.T.; Honeyands, T.; Monaghan, B.; O’Dea, D.; Rinklebe, J.; Vinu, A.; Hoang, S.A.; Singh, G.; Kirkham, M.B.; et al. Production, characterisation, utilisation, and beneficial soil application of steel slag: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 419, 126478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, M.; Gupta, A.K.; Ghosal, P.S.; Majumder, A. A review on performance of constructed wetlands in tropical and cold climate: Insights of mechanism, role of influencing factors, and system modification in low temperature. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldrian, P.; Voříšková, J.; Dobiášová, P.; Merhautová, V.; Lisá, L.; Valášková, V. Production of extracellular enzymes and degradation of biopolymers by saprotrophic microfungi from the upper layers of forest soil. Plant Soil 2011, 338, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Heijden, M.G.A.; Martin, F.M.; Selosse, M.A.; Sanders, I.R. Mycorrhizal ecology and evolution: The past, the present, and the future. New Phytol. 2015, 205, 1406–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N. Embracing the unknown: Disentangling the complexities of the soil microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konnerup, D.; Brix, H. Nitrogen nutrition of Canna indica: Effects of ammonium versus nitrate on growth, biomass allocation, photosynthesis, nitrate reductase activity and N uptake rates. Aquat. Bot. 2010, 92, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Elrys, A.S.; Yang, W.; Du, S.; He, M.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, J.; Müller, C. Soil recalcitrant but not labile organic nitrogen mineralization contributes to microbial nitrogen immobilization and plant nitrogen uptake. Glob. Change Biol. 2024, 30, e17290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Z.; Yang, F. Migration and transformation of soil phosphorus by organic acids: A global meta-analysis. J. Soils Sediments 2024, 24, 589–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahmanzadegan, F.; Ghaemi, A. A comprehensive review on novel zeolite-based adsorbents for environmental pollutant. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2025, 17, 100617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Tian, Q.; Chen, N.; Hu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, R.; Xu, P.; Liu, W.; Stehr, A.; Barra, R.O.; et al. Assessing ammonium pollution and mitigation measures through a modified watershed non-point source model. Water Res. 2024, 254, 121372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, L.; Ji, S.; Chang, M.; Wang, L.; Gan, Y.; Liu, J. The ecology of the plastisphere: Microbial composition, function, assembly, and network in the freshwater and seawater ecosystems. Water Res. 2021, 202, 117428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendsen, R.L.; Pieterse, C.M.J.; Bakker, P.A.H.M. The rhizosphere microbiome and plant health. Trends Plant Sci. 2012, 17, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yellezuome, D.; Zhu, X.; Liu, X.; Liu, R.; Sun, C.; Abd-Alla, M.H.; Rasmey, A.-H.M. Effects of organic loading rate on hydrogen and methane production in a novel two-stage reactor system: Performance, enzyme activity and microbial structure. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 480, 148055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Zhang, W.; Nottingham, A.T.; Xiao, D.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Xu, L.; Chen, H.; Xiao, J.; Duan, P.; Tang, T.; et al. Lithological Controls on Soil Aggregates and Minerals Regulate Microbial Carbon Use Efficiency and Necromass Stability. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 21186–21199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Liao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Dang, Z.; Zhu, X.; Ji, G. Microbial coupling mechanisms of nitrogen removal in constructed wetlands: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 314, 123759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cydzik-Kwiatkowska, A.; Nosek, D. Biological release of phosphorus is more efficient from activated than from aerobic granular sludge. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Han, I.L.; Lee, J.; Li, G.; Srinivasan, V.; McCullough, K.; Klaus, S.; Kang, D.; Wang, D.; He, P.; et al. Revisiting the role of Acinetobacter spp. in side-stream enhanced biological phosphorus removal (S2EBPR) systems. Water Res. 2024, 251, 121089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Li, M.; Whelan, M. Phosphorus activators contribute to legacy phosphorus availability in agricultural soils: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 522–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Raaijmakers, J.M.; Carrión, V.J. Importance of Bacteroidetes in host–microbe interactions and ecosystem functioning. Trends Microbiol. 2023, 31, 959–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, W.; Wang, N.; Wang, W.; Ye, X.; Cui, Z.; Wang, J.; Yao, D.; Dong, Y.; Wang, H. Community Profile and Drivers of Predatory Myxobacteria under Different Compost Manures. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harb, R.; Laçin, D.; Subaşı, I.; Erguder, T.H. Denitrifying anaerobic methane oxidation (DAMO) cultures: Factors affecting their enrichment, performance and integration with anammox bacteria. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 295, 113070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chen, H.; Hu, Z.; Tian, Y.; Wang, C.; Xie, P.; Deng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, X.; Lin, X.; et al. Carbon uptake bioenergetics of PAOs and GAOs in full-scale enhanced biological phosphorus removal systems. Water Res. 2022, 216, 118258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).